金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.195(续1)
2020-06-30 来源: Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文22篇,涵盖了铝合金、高温合金、记忆合金、钛合金、铜合金、镁合金以及高熵合金等领域,国内科研单位包括东北大学、武汉大学、香港科技大学、中国科学院金属研究所、天津大学、南京工业大学、南京大学、重庆大学、北京科技大学、上海大学等(通讯作者单位)。
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P109-122
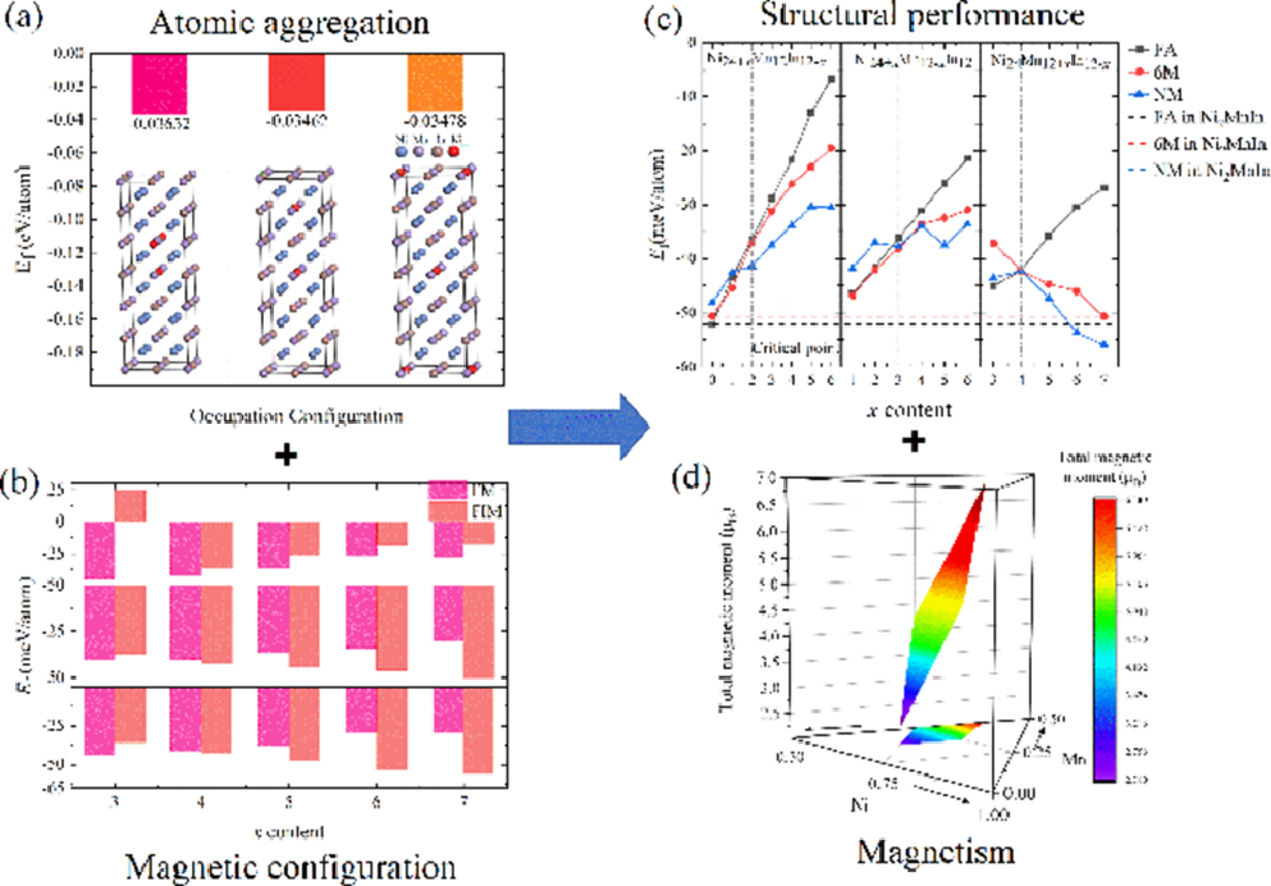
Ab initio-based investigation of phase transition path and magnetism of Ni–Mn–In alloys with excess Ni or Mn
含过量Ni或Mn的Ni-Mn-In合金相变路径及磁性的从头算研究
Xinzeng Liang, Jing Bai✉, Jianglong Gu, Jinlong Wang, Haile Yan, Yudong Zhang, Claude Esling, Xiang Zhao✉, Liang Zuo
Jing Bai:baijing@neuq.edu.cn,东北大学
Xiang Zhao:zhaox@mail.neu.edu.cn,东北大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.049
摘要
本文通过使用从头算方法揭示了含过量Ni或Mn(Ni24+xMn12In12-x、Ni24+xMn12-xIn12和Ni24Mn12+xIn12-x)的Ni-Mn-In合金相变路径和磁性。结果表明,Ni24+xMn12In12-x合金中过量Ni原子倾向于相互靠近,而Ni24+xMn12-xIn12和Ni24Mn12+xIn12-x合金中过量Ni(Mn)原子倾向于相互远离。三种合金体系的晶格常数随原子半径的变化基本相同。过量的Ni降低了铁磁奥氏体(FA)以及6M和NM马氏体的稳定性。同时,过量Ni的存在降低了居里温度(TC),但提高了马氏体相变温度(TM)。相比之下,过量Mn致使FA相不稳定,但6M和NM相更加稳定。过量Mn对TM的影响与过量Ni相似,并且影响更大,但对TC的影响较弱。实验确定了马氏体相变的临界成分和马氏体相变路径。FA相的最大总磁矩出现在Mn过量组分中,而最小总磁矩出现在Ni过量组分中。6M和NM相的总磁矩变化趋势与FA相相反。上述结果有望为Ni-Mn-In合金的相图和磁性能的预测提供参考。
英文摘要
Herein, we have revealed the phase transition path and magnetic properties of Ni–Mn–In alloys with excess Ni or Mn (Ni24+xMn12In12-x, Ni24+xMn12-xIn12 and Ni24Mn12+xIn12-x) by using ab initio calculations. It is demonstrated that excess Ni atoms prefer to be adjacent to each other for the Ni24+xMn12In12-x alloys, whereas excess Ni (Mn) atoms tend to keep away from each other for the Ni24+xMn12-xIn12 and Ni24Mn12+xIn12-x alloys. The variation of the lattice constants, which are dominated by the atomic radius, are basically the same for the three alloy systems. Excess-Ni decreases the stability of the ferromagnetic austenite (FA) as well as the 6M and NM martensites. Meanwhile, the Curie temperature (TC) is reduced but the martensitic transformation temperature (TM) is increased due to the presence of excess-Ni. In comparison, excess-Mn destabilizes the FA phase, but stabilizes the 6M and NM phases. Excess-Mn has a similar impact on the increase of TM as that of excess-Ni, but has a weak effect on TC, but increases TM. The critical composition of the martensitic transformation and martensitic transition path are determined. The highest total magnetic moment of the FA phase appears with Mn-excess compositions whilst the smallest total magnetic moment is found with Ni-excess compositions. The changes of the total magnetic moments for the 6M and NM phases demonstrate an opposite trend to that of FA phase. The above results are expected to provide information for the prediction of phase diagram and magnetic properties of Ni–Mn–In alloys.
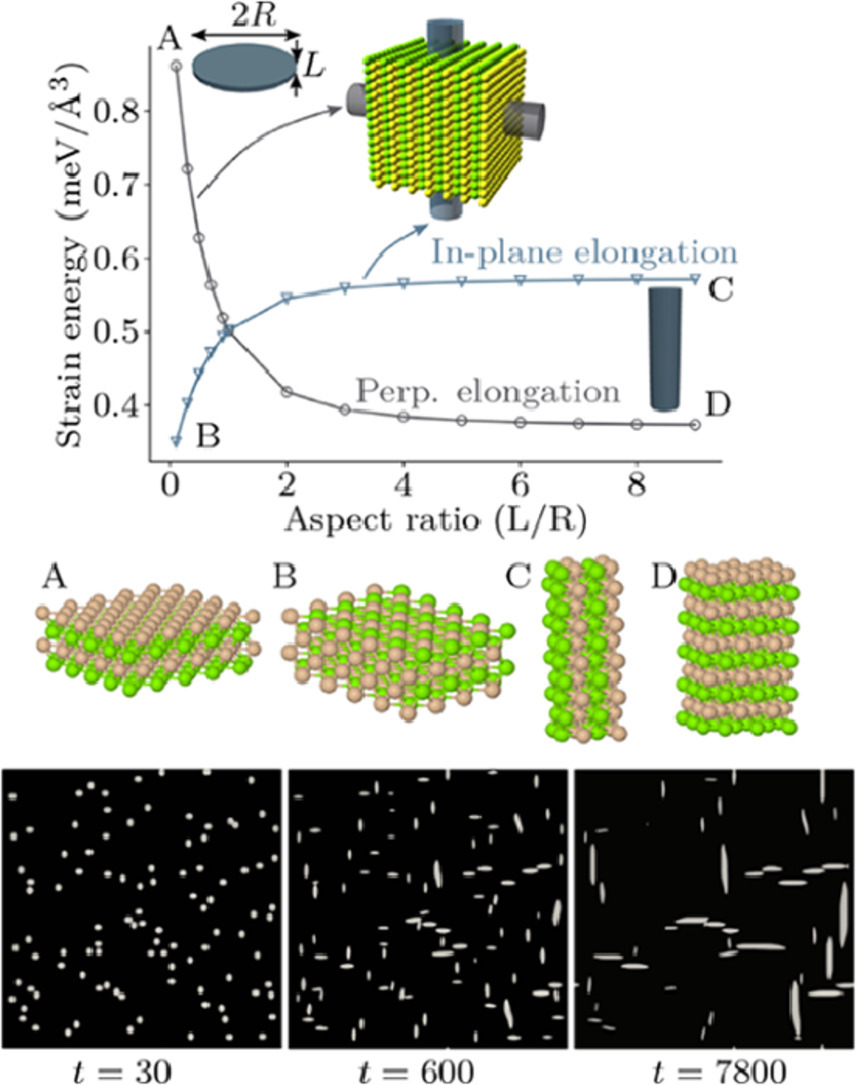
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P123-131
Precipitate formation in aluminium alloys Multi-scale modelling approach
铝合金中析出相的多尺度模拟方法
David Kleiven, Jaakko Akola✉
Jaakko Akola:jaakko.akola@ntnu.no
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.050
摘要
在跨原子和中尺度模型的多尺度方法的基础上,利用理论参数构建了三元Al-Mg-Si合金模型。首先,基于电子结构密度泛函模拟的数据,建立了原子结构(FCC晶格)总能量的团簇扩展模型。将此参数化方法与原动力学蒙特卡罗方法相结合,得到了自由能随溶质(Mg,Si)浓度和无序度的变化曲线。此外,利用线弹性理论集成自由能、表面张力和应变能,建立了中尺度相场模型。该方法的应用结果表明,具有(100)晶面的片层状MgSi相是Al基体中一个非常稳定的溶质偏聚结构。此外,相场模型表明,MgSi沉淀首先析出为针状(FCC),并于之后转变为的β〃型沉淀,而β〃型沉淀是由Mg柱平移1/2晶格矢量而形成的。结果表明,即使在没有空位的情况下,溶质也会偏聚形成针状MgSi(沉淀物),这是Al-Mg-Si合金的一个固有性质,而空位是最终转变形成β〃沉淀物的基础。
英文摘要
Ternary Al–Mg–Si alloys have been modelled based on a multi-scale approach that spans across atomistic and mesoscale models and uses theoretically determined parameters. First, a cluster expansion model for total energy has been trained for atomistic configurations (FCC lattice) based on the data from density functional simulations of electronic structure. Free energy curves as a function of solute (Mg, Si) concentrations and disorder have been obtained by using this parameterisation together with meta-dynamics Monte Carlo sampling. In addition, free energy data, surface tensions as well as strain energy using the linear elasticity theory have been collected to be combined for a mesoscale phase-field model. The application of this approach shows that the formation of a layered MgSi phase, with (100) planes, is a particularly stable solute aggregation motif within the Al host matrix. Moreover, the phase-field model demonstrates that the preferred shape of the MgSi precipitates is needle-like (in FCC), and they can act as precursors for the important and well-known β″-type precipitates which are formed by translating one Mg column by a 1/2 lattice vector. The results provide theoretical evidence that the solute aggregation into needle-like MgSi domains (precipitates) is an inherent property of Al-Mg-Si alloys, and that it takes place even without the presence of vacancies which is a precondition for the eventual formation β″ precipitates.
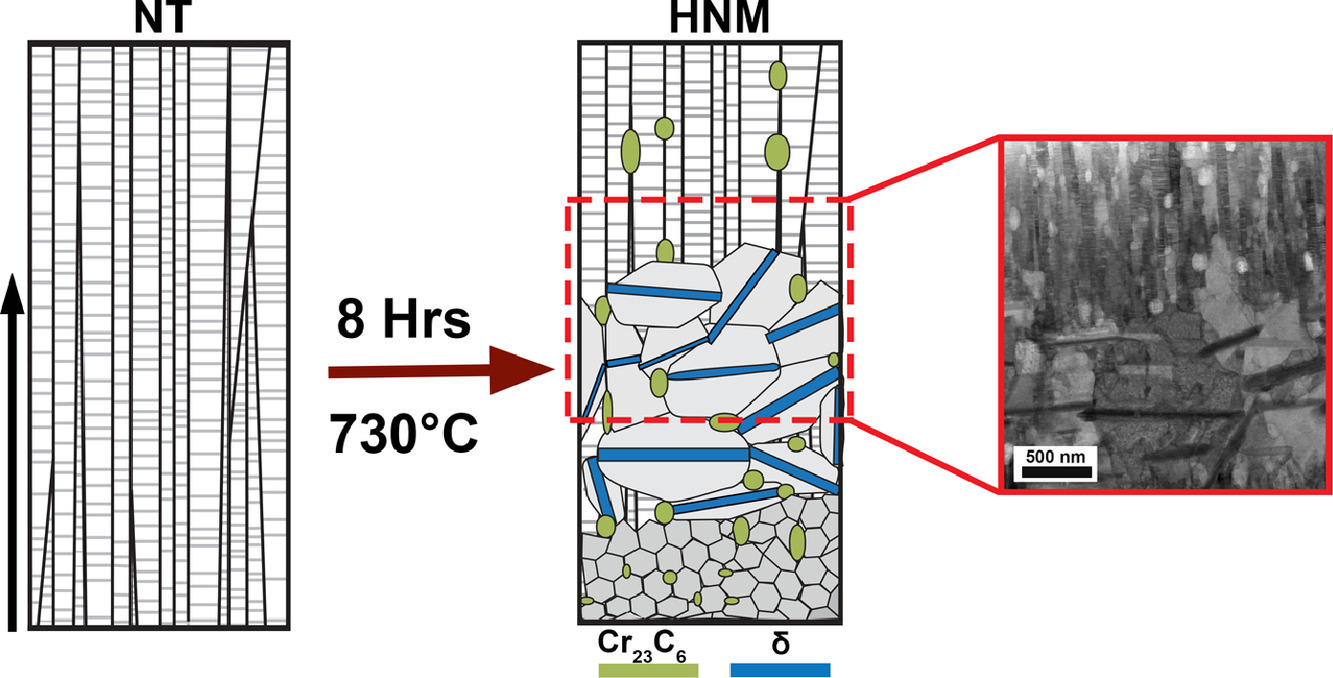
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P132-140
Development of a heterogeneous nanostructure through abnormal recrystallization of a nanotwinned Ni superalloy
纳米孪晶镍基高温合金异常再结晶导致的纳米结构非均匀化
Joel A. Bahena, Nathan M. Heckman, Christopher M. Barr, Khalid Hattar, Brad L.Boyce, Andrea M. Hodge✉
Andrea M. Hodge:ahodge@usc.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.057
摘要
本文通过粗晶镍基高温合金中的异常再结晶现象发现了非均匀纳米结构的形成。通过储能不均匀分布溅射制备Inconel 725合金薄膜,并在730℃进行时效处理,在材料厚度上观察到晶粒尺寸和形貌的独特组合。在转变后的显微组织中形成了三个不同的区域,异常粗大的晶粒位于纳米晶和纳米孪晶区域之间。为了研究向非均匀结构转变,晶体学取向和时效8h组织演变过程中元素的分布以及沉淀行为。通过实验观察和本研究的详细分析,可以利用现有的方法进一步拓展当前非均匀纳米结构材料的设计空间。
英文摘要
This work explores the development of a heterogeneous nanostructured material through leveraging abnormal recrystallization, which is a prominent phenomenon in coarse-grained Ni-based superalloys. Through synthesis of a sputtered Inconel 725 film with a heterogeneous distribution of stored energy and subsequent aging treatments at 730°C, a unique combination of grain sizes and morphologies was observed throughout the thickness of the material. Three distinct domains are formed in the aged microstructure, where abnormally large grains are observed in-between a nanocrystalline and a nanotwinned region. In order to investigate the transitions towards a heterogeneous structure, crystallographic orientation and elemental mapping at interval aging times up to 8 h revealed the microstructural evolution and precipitation behavior. From the experimental observations and the detailed analysis of this study, the current methodology can be utilized to further expand the design space of current heterogeneous nanostructured materials.
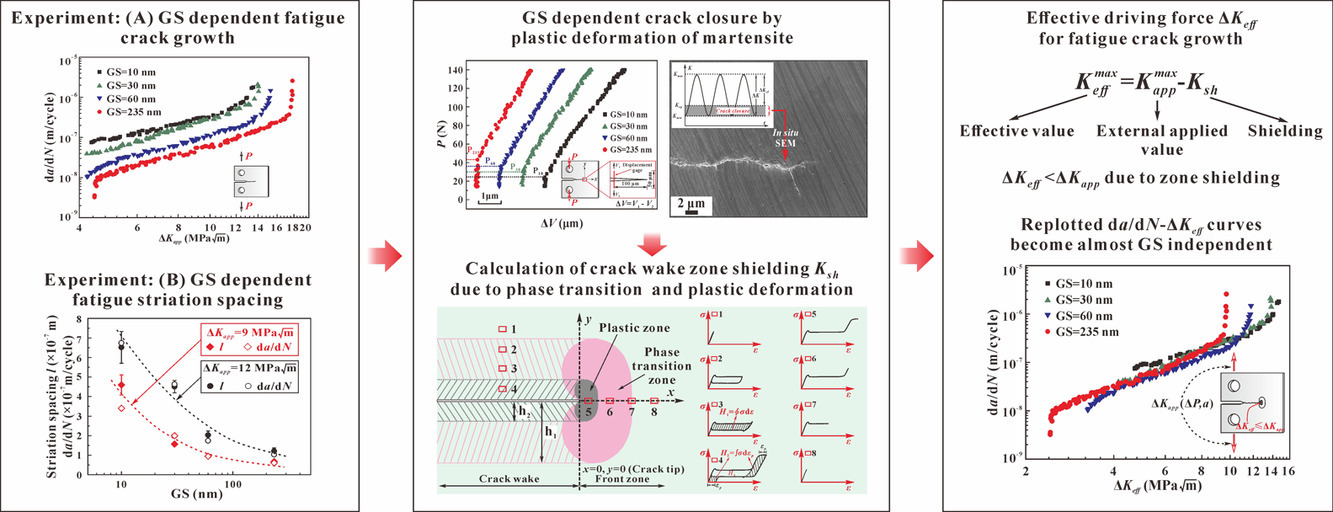
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P141-150
Effects of grain size on fatigue crack growth behaviors of nanocrystalline superelastic NiTi shape memory alloys
晶粒尺寸对纳米晶超弹性NiTi形状记忆合金疲劳裂纹扩展行为的影响
Junyu Chen, Hao Yin✉, Qingping Sun✉
Hao Yin:yinhao@whu.edu.cn,武汉大学
Qingping Sun:meqpsun@ust.hk,香港科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.008
摘要
本文研究了平均晶粒尺寸为10、30、60和235nm的纳米晶超弹性NiTi形状记忆合金疲劳裂纹扩展与晶粒尺寸的关系。试样拉伸过程中同时测量了疲劳裂纹扩展、载荷位移响应和温度场。结果表明,当晶粒尺寸从10增加到235nm时,疲劳裂纹扩展速率(da/dN)下降了10倍。通过对断后断口疲劳条纹间距的直接观察,证实了晶粒尺寸对疲劳裂纹扩展的显著影响。结果表明,晶粒尺寸的增加显著地提高了材料的相变和塑性,从而增强了裂纹尖端屏蔽(Ksh),进而降低了疲劳裂纹扩展的有效驱动力(ΔKeff)。从外加Kapp中减去相变和塑性变形引起的Ksh,即得到有效的裂纹尖端疲劳驱动力ΔKeff。在没有屏蔽效应的情况下,不同晶粒尺寸试样的da/dN-ΔKeff曲线几乎成一条曲线,该曲线可能代表NiTi的固有疲劳特性。由于屏蔽了晶粒尺寸与相变和塑性变形的影响,因此,可明显观察到的超弹性NiTi-SMAs中疲劳裂纹扩展抗力与晶粒尺寸的相关关系。
英文摘要
The grain size (GS) dependence of fatigue crack growth in nanocrystalline superelastic NiTi shape memory alloys (SMAs) with the average GS of 10, 30, 60 and 235 nm is investigated. Synchronized measurements of the fatigue crack growth, load-displacement response and temperature field of the compact tension specimens are performed. It is found that the fatigue crack growth rate (da/dN) is monotonically decreased by 10 times when the GS is increased from 10 to 235 nm. The significant GS effect on the fatigue crack growth is also confirmed by the direct observation of fatigue striation spacing on the postmortem fracture surface. It is shown that the increase of the GS significantly enhances the phase transition and plasticity of the material and therefore enhances the crack-tip shielding (Ksh) which reduces the effective driving force (ΔKeff) of the fatigue crack growth. Subtracting Ksh due to phase transition and plastic deformation from the external applied Kapp, the effective crack-tip fatigue driving force ΔKeff is obtained. The da/dN-ΔKeff curves for different GS specimens then almost collapse onto a single curve which may represent an intrinsic fatigue property of the NiTi in the absence of the shielding effects. Therefore the observed apparent GS dependence of the fatigue crack growth resistance in the superelastic NiTi SMAs is mainly caused by the shielding effect from the GS dependent phase transition and plastic deformation.
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P151-162
Diffusional-displacive transformation in a metastable β titanium alloy and its strengthening effect
亚稳β钛合金的扩散-切变型相变及其强化效应
Lu Qi, Suyun He, Chunjin Chen, Binbin Jiang, Yulin Hao, Hengqiang Ye, Rui Yang, Kui Du✉
Kui Du:kuidu@imr.ac.cn,中国科学院金属研究所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.058
摘要
扩散-切变型相变通常与材料的力学性能相关,例如高强度。因此,从物理和应用的角度来研究相变的结构演化具有重要意义。通过结合原子分辨电子显微镜、EDS和第一性原理计算,在原子水平上定量表征了亚稳态β-Ti合金时效过程中β→αʺ→α连续相转变过程。这种连续相变的机理是在结构和成分向平衡态连续转变过程中,β相成分一直处于波动状态。此外,产生的新相导致析出物晶格错位,从而在析出相周围产生相干应变场。而共格应变场显著提高了时效后合金硬度,研究结果对优化热处理工艺和提高材料力学性能具有重要作用。
英文摘要
Diffusional-displacive transformations are generally associated with mechanical properties of materials such as high strength. Understanding structure evolution of these transformations is of great interests from both physics and application perspectives. By combining atomic resolution electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectroscopy and first principles calculations, a continuous β→αʺ→α transformation process has been quantitatively characterized at the atomic level in a metastable β-Ti alloy during aging treatment. The transformation is revealed to develop by a novel mechanism involving continuous structural and compositional changes towards the equilibrium assisted by compositional fluctuation in the β matrix. Moreover, the product phase induces a precipitate-matrix lattice mismatch, thus produces a coherency strain field surrounding the precipitates. The coherent strain field contributes significantly to the increasing hardness of the alloy after aging. These results have great potential for tailoring thermomechanical treatment routes and improving mechanical properties of materials.
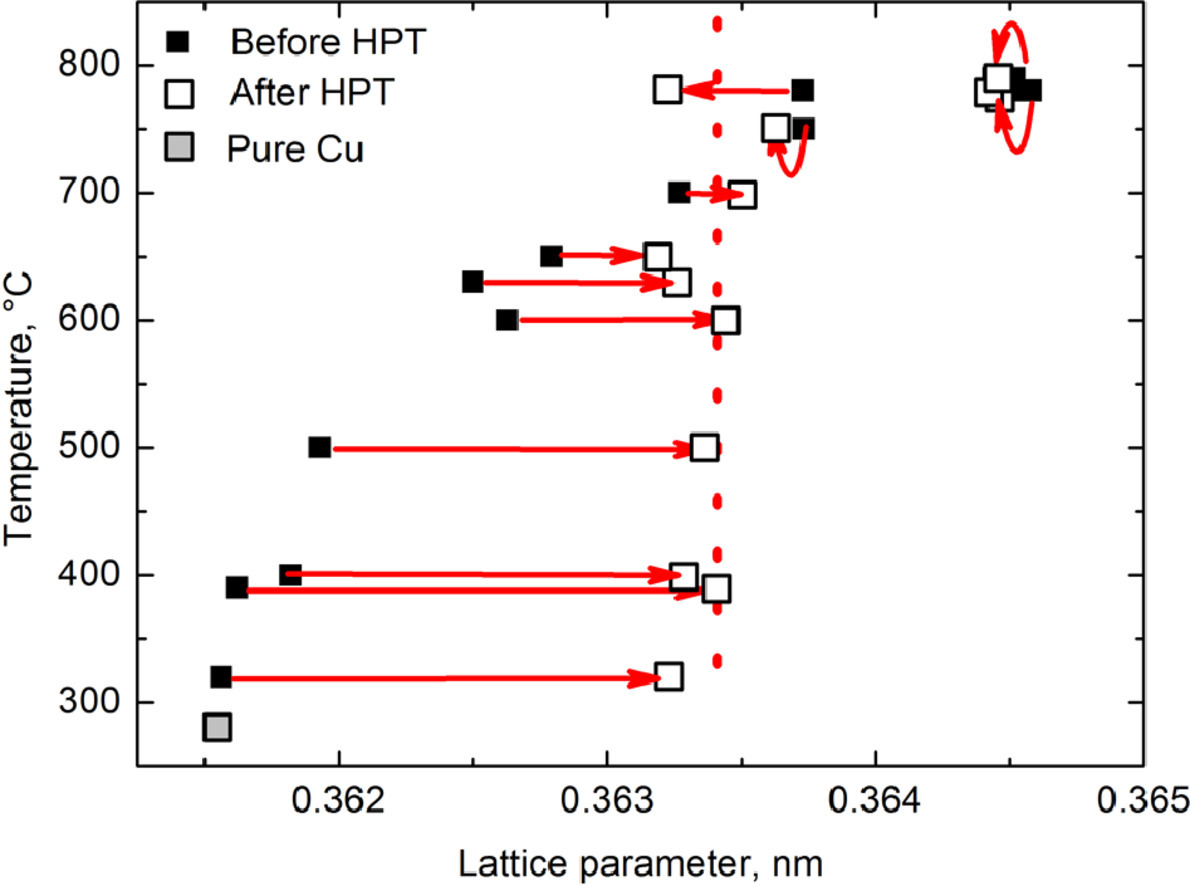
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P109-122
High pressure torsion of Cu–Ag and Cu–Sn alloys Limits for solubility and dissolution
Cu-Ag和Cu-Sn合金的高压扭转溶解和分解极限
B. B. Straumal✉, A. R. Kilmametov, B. Baretzky, O. A. Kogtenkova, P. B. Straumal, L. Lityńska-Dobrzyńska, R. Chulist, A. Korneva, P.Zięba
B. B. Straumal:straumal@issp.ac.ru
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.055
摘要
本文研究了含3,5,8,10%Ag和14%Sn的二元铜合金在室温下的高压扭转(HPT)行为。首先,Cu-Ag合金在320-800℃的12个不同温度下进行退火,Cu-14wt.%Sn在310-500℃的9个不同温度下进行退火。在HPT之前,0-8wt.%银含量的Cu-Ag合金由Cu基体和Ag析出粒子组成。Cu-14wt.%Sn合金由铜基体和含锡量为0~14wt.%Sn的ε或δ Hume-Rothery金属间化合物析出相组成。在柱塞旋转约1.5次后,合金元素的css在基体中的浓度趋于稳定,测定的css值分别为5.5±0.1wt.%Ag和13.1±0.1wt.%Sn。当Cu基体中的初始浓度cinit低于css(cinit
英文摘要
The high-pressure torsion (HPT) of binary copper alloys with 3, 5, 8, 10 wt. % Ag and 14 wt. % Sn has been studied at room temperature THPT. Before HPT, the Cu–Ag alloys have been annealed at 12 different temperatures between 320 and 800 °C and Cu–14 wt. % Sn has been annealed at 9 different temperatures between 310 and 500 °C. Thus, before HPT the Cu–Ag alloys consisted of Ag-particles in the Cu-based matrix with silver content cinit from almost zero to 8 wt.%. The Cu–14 wt. % Sn samples had Cu-based matrix with tin concentration cinit from almost zero to 14 wt.% Sn and precipitates of ε or δ Hume-Rothery intermetallic phases. After about 1.5 plunger rotations a certain steady-state concentration css of the alloying element is reached in the matrix. The measured css values were 5.5±0.1 wt. % Ag and 13.1±0.1 wt. % Sn. If the initial concentration cinit in Cu matrix was below css (cinit < css), it increased towards css during HPT. If cinit > css it decreased towards css. We observed that css did not depend on cinit in broad interval of cinit and was, therefore, equifinal. The equifinal css values corresponded to the certain equilibrium solubilities of silver and tin in Cu matrix and allowed to estimate the (elevated) effective temperature as Teff (Ag) = 700±10 °C and Teff (Sn) = 400±10 °C, respectively. The observed phenomena are discussed using the ideas of non-equilibrium thermodynamics of open systems. During HPT the decomposition of a solid solution competed with dissolution of precipitates. As a result, a dynamic equilibrium established between precipitation and dissolution at steady-state deformation stage. In this dynamic equilibrium a certain steady-state concentration css of the alloying element is reached in the matrix. In Cu-based alloys, the obtained Teff is always higher than THPT and correlates with activation enthalpy of dopant diffusion in Cu. Other HPT-driven phenomena such as accelerated mass transfer, intermetallic phase formation, grain boundary faceting and grain boundary segregation are taken into account to evaluate the effective temperature Teff.
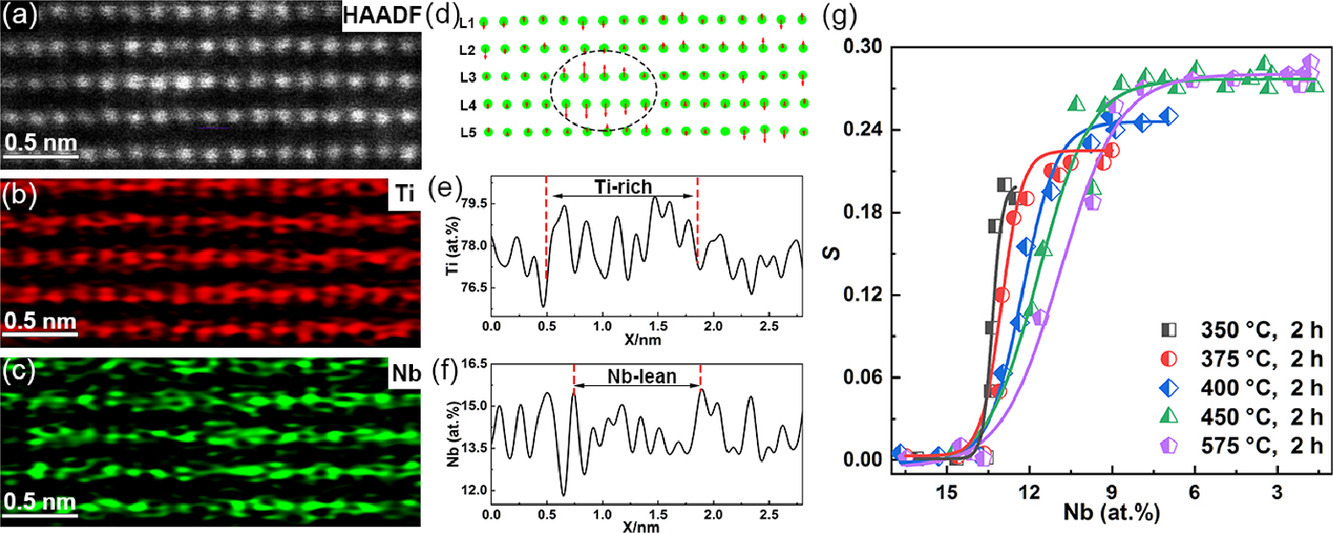
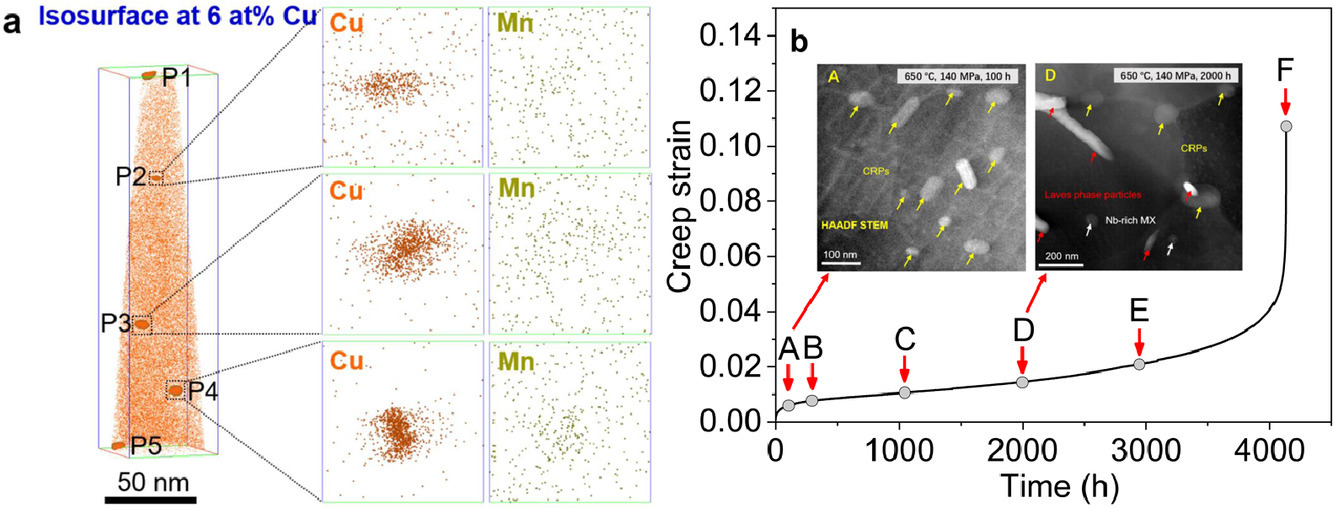
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P199-208
Solute-dislocation interactions and creep-enhanced Cu precipitation in a novel ferritic-martensitic steel
新型铁素体-马氏体钢中的溶质-位错相互作用导致铜沉淀析出的蠕变强化
BoXiao, Lianyong Xu✉, Cyril Cayron, Jing Xue, Gang Sha, Roland Logé
Lianyong Xu:xulianyong@tju.edu.cn,天津大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.054
摘要
近年来,G115钢因其在下一代超临界电厂的应用而受到越来越多的关注。G115钢在蠕变过程中,由于其高位错密度和板条马氏体界面,溶质与位错的相互作用导致了独特的组织演变,形成了致密的富铜析出相(CRPs)和M23C6碳化物。通过原子探针层析显示,发现Mn优先与CRPs结合,这可能是由于Mn原子降低了成核的临界能量。溶质拖曳和沉淀钉扎效应促进了蠕变早期位错网络的形成。与时效G115钢相比,长期蠕变变形加速了CRPs的粗化。溶质沿位错、位错网络和板条边界的快速扩散显著增加了CRP粗化动力学。颗粒粗化降低了钉扎强度,并导致长蠕变阶段位错密度降低及位错网络消失。本研究结果加深了对G115钢蠕变过程中CRP演变的认识,为设计具有优良蠕变强度的新型耐热钢提供了指导。
英文摘要
G115 steel has gained a growing interesting recently for its use in next-generation ultra-supercritical power plant applications. Due to the high densities of dislocations and lath martensite boundaries in G115 steel, interactions between solutes and dislocations result in unique microstructural evolution during creep with the formation of dense Cu-rich precipitates (CRPs) and M23C6 carbides. Atom-probe tomography reveals that Mn is preferentially associated with CRPs, probably because the Mn atoms reduce the critical energy of nucleation. Solute-dragging and precipitate-pinning effects enhance the formation of dislocation network during earlier creep deformation. Compared with aged G115 steel, long-term creep deformation accelerates the coarsening of CRPs. The fast diffusion of solutes along dislocations, dislocation network walls, and lath boundaries significantly increases the CRP coarsening kinetics. Particle coarsening reduces the pinning strength, causing the dislocation density to decrease and the dislocation network to disappear during long creep stages. Our results enhance our understanding of CRP evolution in G115 steel during creep and provide a guide for the design of novel heat-resistant steels with excellent creep strength.
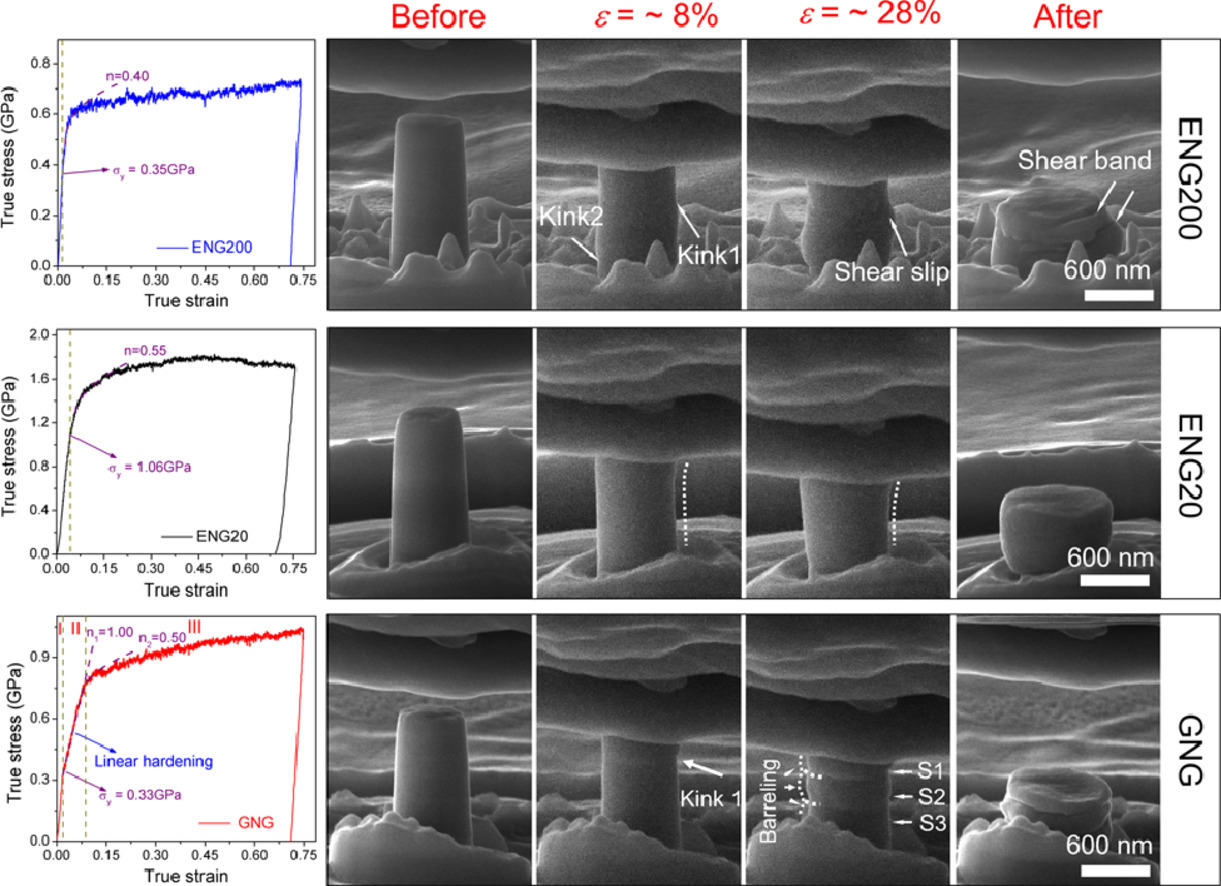
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P240-251
Strong and plastic metallic composites with nanolayered architectures
兼具强韧的人工构筑层状纳米结构金属复合材料
Z. H. Cao✉, W. Sun, Y. J. Ma, Q. Li, Z. Fan, Y. P. Cai, Z. J. Zhang, H. Wang, X. Zhang, X. K. Meng✉
Z. H. Cao:zhenhuacao@njtech.edu.cn,南京工业大学
X. K. Meng:mengxk@nju.edu.cn,南京大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.04.061
摘要
纳米结构的金属和合金通常具有很高的强度,但是由于晶界扩散和滑移的增强,应变硬化能力很差。本文通过引入坚硬且稳定的“人造”相间析出区(IBZ),构造出了均匀纳米晶Cu/Ta层状结构(ENG)和梯度纳米晶Cu/Ta层状结构(GNG)。得益于强韧IBZ对位错滑移的限制作用以及共同变形,ENG样品均匀延伸率达到了70%,屈服强度超过了1GPa。由于软硬层间强烈的应变配分,GNG样品展现出了显著的线性应变硬化现象,硬化指数为1。基于实验和分子动力学模拟结果分析,随着应变的增加,GNG纳米复合材料的变形机制由不全位错的发射演变为位错在界面的塞积。本文的研究表明,具有“人造”IBZ的异质结构为强韧材料的设计提供了新的可能。
英文摘要
Nanostructured metals and alloys are generally strong but lack strain hardening due to enhanced grain boundary diffusion and sliding. Here, equal nanograined (ENG) and gradient nanograined (GNG) layered Cu/Ta architectures were acquired by introducing a hard and stable “artificial” interphase boundary zone (IBZ). The ENG architecture produced uniform plastic strain reaching 70% and high yield strength exceeding 1 GPa, which is attributed to the constraint effect of the tough IBZ on dislocation slip mediated co-deformation. The GNG architecture exhibited a remarkable linear strain hardening with hardening exponent of 1 due to the strong strain partitioning between soft and hard layers. The dominant deformation mechanism of the GNG nanocomposite evolves from partial dislocation emission to dislocation accumulation at interface with increasing strain based on the results from experiments and molecular dynamics simulations. This finding demonstrates that heterostructure with “artificial” IBZ may offer an alternative approach to design strong and tough materials.
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P263-273
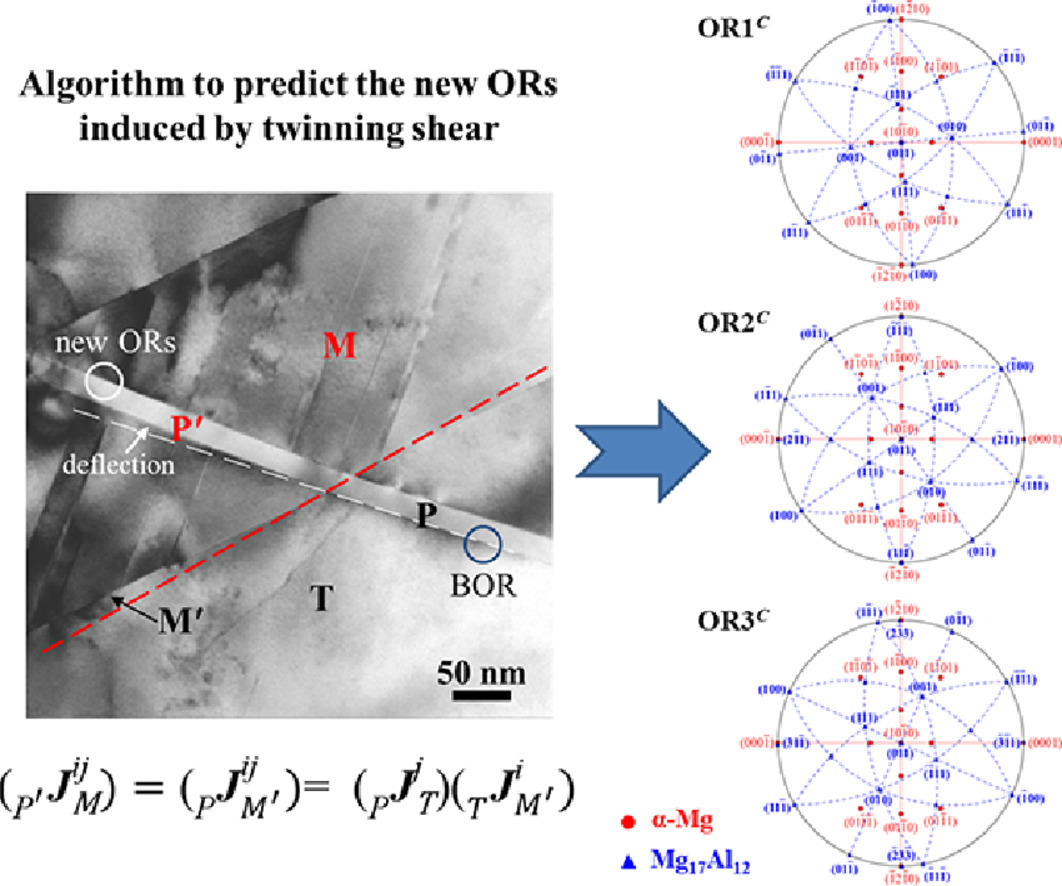
Evaluating the orientation relationship of prismatic precipitates generated by detwinning in Mg alloys
Mg合金中去孪晶过程产生的棱柱形析出的位相关系评估
Feiya Liu, Renlong Xin✉, Ming-Xing Zhang, María Teresa Pérez-Prado, Qing Liu
Renlong Xin:rlxin@cqu.edu.cn,重庆大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.031
摘要
目前普遍认为Mg合金中的棱柱形析出比在基面上形成的析出相具有更强的强化效果。然而,在大部分无稀土元素添加的Mg合金中,析出一般发生在基面上。最近的研究表明,{10-12}孪晶化、时效和去孪晶的耦合过程(TAD)会促进Mg-Al合金中的棱柱形析出,具体机理目前还不清楚。本工作旨在从理论和实验方面评估TAD样品中棱柱形析出和去孪晶基体之间可能的晶体学位相关系,以阐明析出形成的机理。本文提出了一个以晶体学为基础的算法,用来预测此种位相关系,随后用TEM实验结果对预测结果进行验证。实验中确定了Mg17Al12析出和α-Mg-Al基体的三种新的位相关系,在考虑了析出在孪晶界3.69°的旋转后,算法的预测结果与实验结果十分吻合。同时,提出的算法也在其他TAD处理的无稀土元素添加的Mg合金中得到了验证,包括Mg-Sn-Zn, Mg-Al-Ca, Mg-Zn和Mg-Ca-Zn体系。此工作为Mg合金中棱柱形析出和基体间的位向关系提供了更清晰的证据,对于充分研究棱柱形析出的强化效果具有重要意义。
英文摘要
It is commonly accepted that prismatic precipitates in Mg alloys are more potent strengtheners than the ones formed on basal planes. However, in most rare-earth (RE) free Mg alloys, precipitation commonly occurs on basal planes. Recent results showed that coupling {10-12} twinning, aging and detwinning (a process termed TAD) promotes prismatic precipitation in Mg-Al alloys by a mechanism that remains unclear. The present work aims to theoretically and experimentally evaluate possible crystallographic orientation relationships (ORs) between the prismatic precipitates and the detwinned matrix in TAD processed samples in order to understand their formation mechanism. A crystallography-based algorithm is proposed to predict such ORs and the predictions are subsequently validated through experimental observation in a transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Three new ORs between Mg17Al12 precipitates and the α-Mg-Al matrix are experimentally determined, which agree well with the predictions of the proposed algorithm after considering the 3.69° rotation of precipitates at twin boundaries. Additionally, the proposed algorithm is validated in other RE free Mg alloys produced via the TAD process, including Mg-Sn-Zn, Mg-Al-Ca, Mg-Zn and Mg-Ca-Zn systems. This work provides a clearer understanding of the ORs between prismatic precipitates and the matrices of Mg alloys that is deemed critical to fully exploit their potential for precipitation hardening.
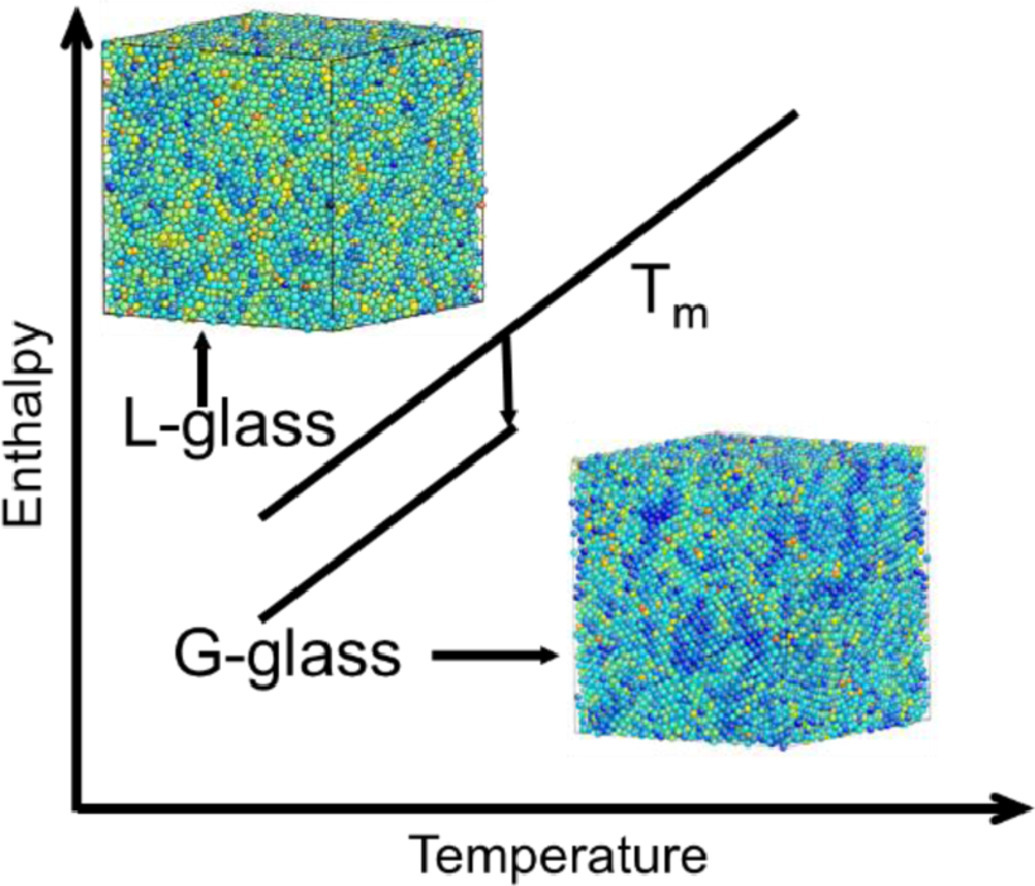
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P274-281
Formation of two glass phases in binary Cu-Ag liquid
二元Cu-Ag液相中两种玻璃相的形成
Qi An✉, William L.Johnson✉, Konrad Samwer, Sydney L.Corona, William A.GoddardIII✉
Qi An:qia@unr.edu
William L.Johnson:wlj@caltech.edu
William A.GoddardIII:wag@caltech.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.060
摘要
玻璃化转变既可以被称作是动力学转变(因为存在动力学的急剧下降),也可以描述为热力学相变。为了研究Cu-Ag液体中玻璃化转变的物理根源,本文对3200到2048000个原子的体系进行分子动力学模拟。出人意料的是,研究人员确定了从液态向亚稳异质类固态相的一级冻结转变(G-glass),这种转变是当过冷液体在熔点温度以下很大过冷度条件下等温演化的结果。相反,当液体以~1011 K/sec的冷却速度快速连续冷却至室温时,会形成更加均匀的类液态玻璃(L-glass)。本文报道了L-G转变的热力学描述,并对G-glass中异质结构的相关长度进行了表征。G-glass的剪切模量远远高于L-glass,表明一级G-G转变与G-glass中涉及元素构型激发的长程弹性密切相关。
英文摘要
The glass transition is alternatively described as either a dynamic transition in which there is a dramatic slowing down of the kinetics, or as a thermodynamic phase transition. To examine the physical origin of the glass transition in fragile Cu-Ag liquids, we employed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations on systems in the range of 32,000 to 2,048,000 atoms. Surprisingly, we identified a 1st order freezing transition from liquid (L) to metastable heterogenous solid-like phase, denoted as the G-glass, when a supercooled liquid evolves isothermally below its melting temperature at deep undercooling. In contrast, a more homogenous liquid-like glass, denoted as the L-glass, is achieved when the liquid is quenched continuously to room temperature with a fast cooling rate of ~1011 K/sec. We report a thermodynamic description of the L-G transition and characterize the correlation length of the heterogenous structure in the G-glass. The shear modulus of the G-glass is significantly higher than the L-glass, suggesting that the first order G-G transition is linked fundamentally to long-range elasticity involving elementary configurational excitations in the G-glass.
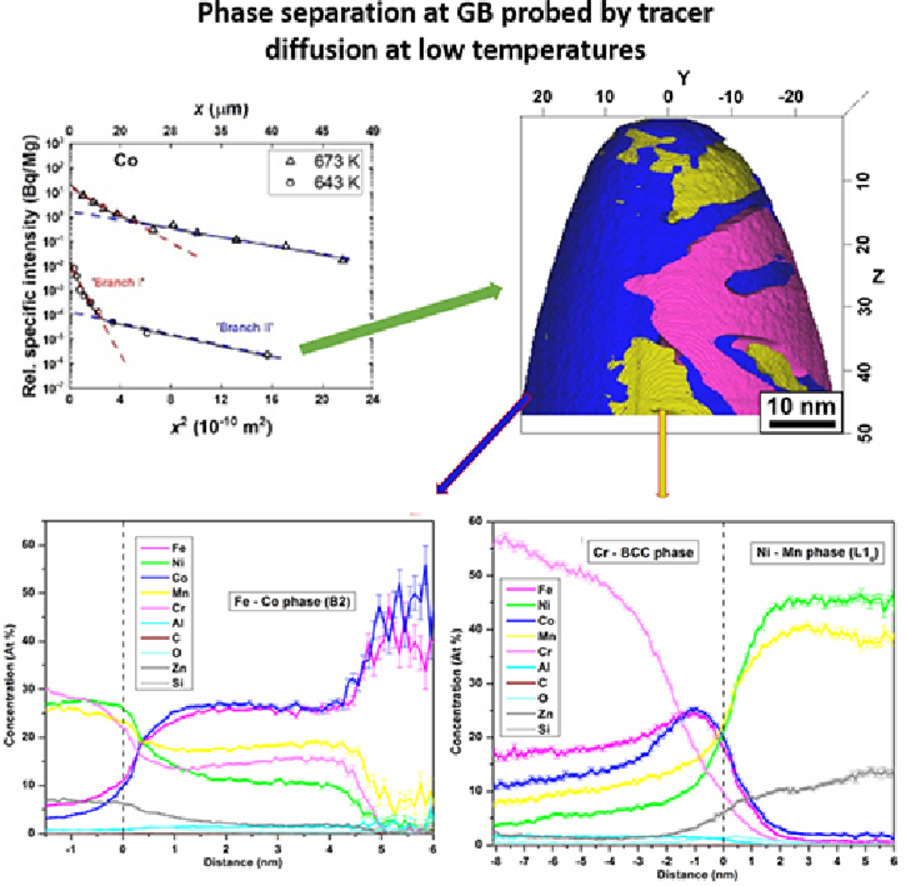
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P304-316
Grain boundary diffusion in CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy: Kinetic hints towards a phase decomposition
CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金晶界扩散:动力学揭示相分解
Marcel Glienke, Mayur Vaidya✉, K. Gururaj, Lydia Daum, Bengü Tas, Lukasz Rogal, K. G. Pradeep, Sergiy V. Divinski, Gerhard Wilde
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.009
摘要
本文研究了在643~1273 K温度范围内,粗晶等原子比CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金中主元素57Co, 51Cr, 59Fe和54Mn在Harrison分类下C型和B型动力学区的晶界扩散。结果表明,当温度高于800K时,对于所有元素,相关偏聚系数s和晶界宽度δ的乘积大约为0.5。在此温度区间,观察到了“短路”扩散的贡献。同时,C型动力学区(643-703K)的渗透曲线揭示了两个显著的贡献,暗示了在大角度晶界处的相分解以及结构多样性的存在。结合透射式菊池衍射(TKD)和三维原子探针显微技术,表征了在大角度晶界处富Ni-Mn和富Cu析出相的产生。透射电镜结果表明了在此类界面附近位错密度的增加,这可能是在低温下出现“短路”高速率扩散的原因。
英文摘要
Grain boundary diffusion of the principal elements 57Co, 51Cr, 59Fe and 54Mn in a coarse-grained equiatomic CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy is measured in a wide temperature range of 643 to 1273 K in both C- and B-type kinetic regimes after Harrison’s classification. The results suggest that the product of the pertinent segregation factors, s, and the grain boundary width, δ, is about 0.5 nm for all elements at temperatures T > 800 K. Whereas one short-circuit contribution is observed at higher temperatures above 800 K, the penetration profiles in the C-type kinetic regime (643 – 703 K) reveal two distinct contributions that hint towards a phase decomposition at a fraction of high-angle grain boundaries at these temperatures and the existence of a structural multiplicity of high-angle grain boundaries. A correlative microscopy combining transmission Kikuchi diffraction and atom probe tomography manifests formation of neighboring Ni-Mn-rich and Cr-rich precipitates at high angle grain boundaries. Transmission electron microscopy revealed an increased dislocation density in the vicinity of such interfaces which is suggested to be a reason of the enhanced diffusion rates at low temperatures for such short circuits.
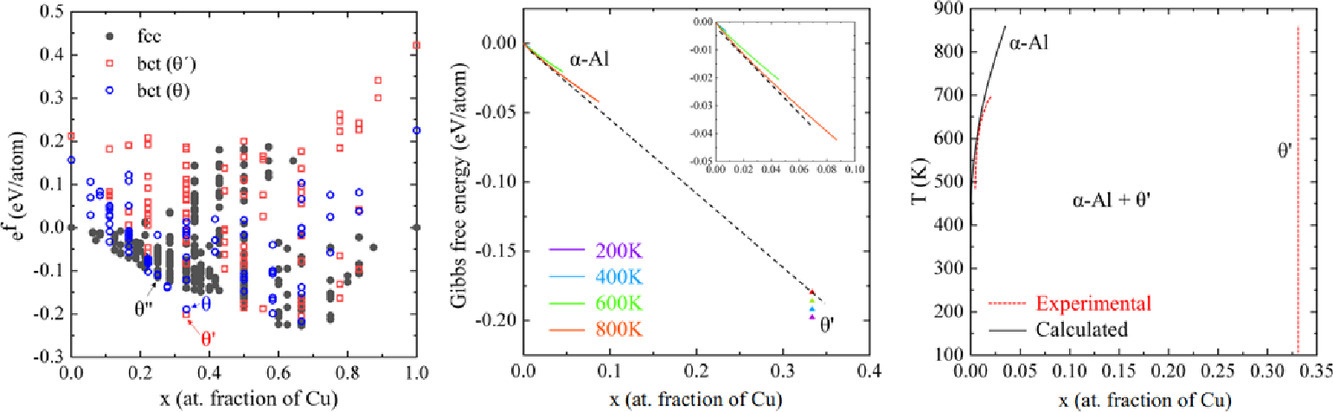
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P317-326
Prediction of the Al-rich part of the Al-Cu phase diagram using cluster expansion and statistical mechanics
集团展开和统计力学预测Al-Cu相图中的富Al部分
S. Liu, E. Martínez, J. LLorca✉
J. LLorca:javier.llorca@imdea.org
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.018
摘要
本研究通过集团展开结合统计力学成功获取了Al-Cu体系富Al部分α-Al和其他相(GP区,θ,θ’, θ’’)的热力学特征。这些信息被用来建立Al-Cu相图的富铝部分,其中考虑了振动熵对θ’的贡献,而其他相在本模拟中忽略不计。模拟预测的α-Al与θ,θ’或 θ’’相相边界随温度的变化规律与实验数据吻合良好,并且可扩展到较宽的温度范围。第一性原理计算表明在低温下部分亚稳态的G-P区结构可以和α-Al及 θ’’ 共存。同时,计算结果还表明,在550K以下,θ’是稳定相;而在此温度之上,由于振动熵对吉布斯自由能的贡献,导致θ’被θ替代。这项研究工作展示了如何结合团簇展开和统计力学来增进人们对金属合金相图的知识,抑或是通过这种方法获取不同相的吉布斯自由能作为介观尺度析出模拟的输入参数。
英文摘要
The thermodynamic properties of α-Al and other phases (GP zones, θ'', θ' and θ) in the Al-rich part of the Al-Cu system have been obtained by means of the cluster expansion formalism in combination with statistical mechanics. This information was used to build the Al-rich part of the Al-Cu phase-diagram taking into account vibrational entropic contributions for θ', as those of the other phases were negligible. The simulation predictions of the phase boundaries between α-Al and either θ'', θ' or θ phases as a function of temperature are in good agreement with experimental data and extend the phase boundaries to a wider temperature range. The DFT calculations reveal the presence of a number of metastable Guinier-Preston-zone type configurations that may coexist with α-Al and θ'' at low temperatures. They also demonstrate that θ' is the stable phase below 550K but it is replaced by θ above this temperature due to the vibrational entropic contribution to the Gibbs energy of θ'. This work shows how the combination of cluster expansion and statistical mechanics can be used to expand our knowledge of the phase diagram of metallic alloys and to provide Gibbs free energies of different phases that can be used as input in mesoscale simulations of precipitation.
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P327-340
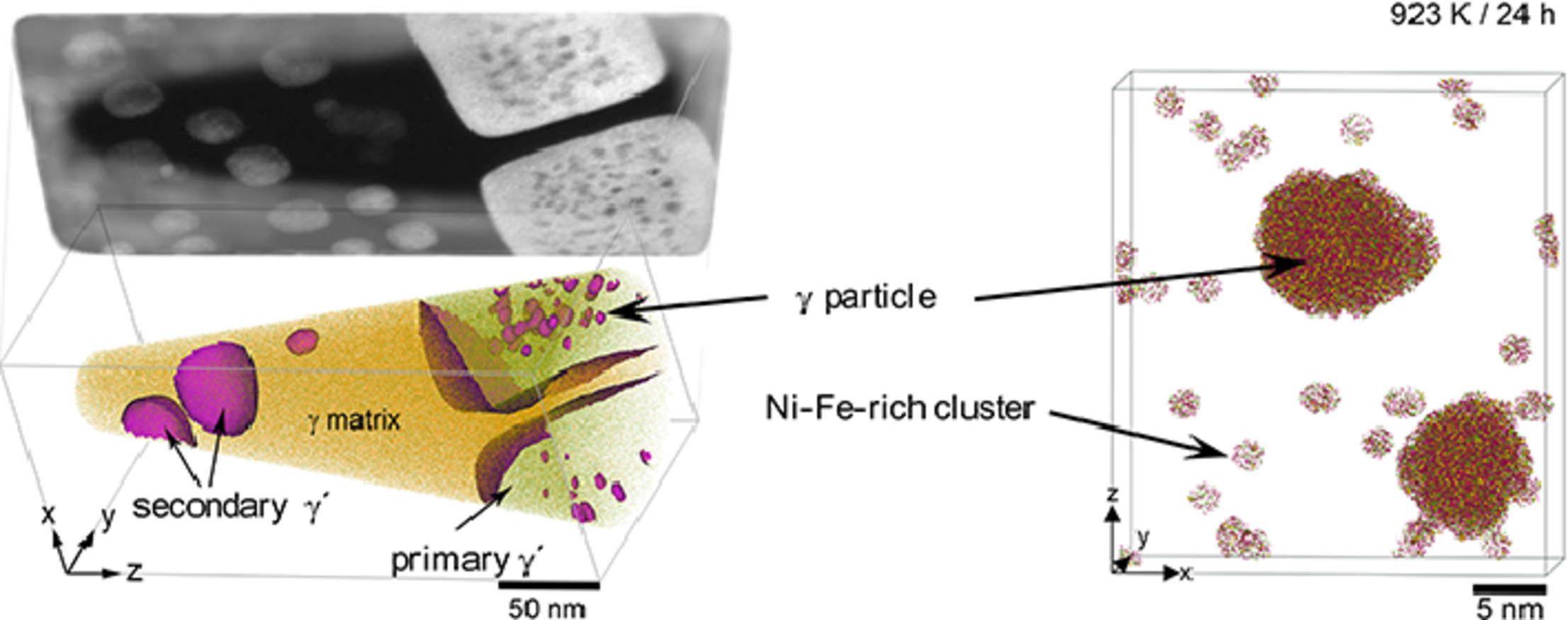
Hierarchical phase separation behavior in a Ni-Si-Fe alloy
Ni-Si-Fe合金中的分级相分离行为
E. Zaiser,X.Y. Zhou, A.M. Manzoni,S. Haas, U. Glatzel, X.P. Zhang, G.B. Thompson,W. Li, F. Vogela✉
F. Vogela:florian.vogel@helmholtz-berlin.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.023
摘要
提高耐高温合金的性能需要建立在对材料微观结构和三维纳米化学之间的联系具有足够认识的基础之上。在本研究中,我们利用透射电子显微镜和原子探针断层扫描互补的方法在三元单晶模型合金Ni83.9Si13Fe3.1 (at.%)中建立了微观组织结构和三维纳米化学间的联系。实验观测到了γ/γ’组织的形成,其中包含了一次和二次的γ’析出,类似镍基高温合金。随后,一次γ’沉淀内部γ粒子的形成创建了微观组织层次。一次γ’析出中γ相形成元素Ni、 Fe的过饱和为γ相的形成提供了驱动力。我们研究了时效对于材料力学性能的影响并发现材料在923K时效24小时后达到峰值硬度。基于TTNi8数据库的Thermo-Calc软件计算得到的平衡相成分相比于TCNi8数据库更加接近由原子探针测得的实验值。研究指出,通过调控各相的化学成分和晶格错配能够成功提高γ析出的稳定性。
英文摘要
Improving the properties of durable high-temperature alloys is based on the fundamental understanding of the link between microstructure and three-dimensional (3D) nanochemistry. Here we utilize a complementary approach of transmission electron microscopy and atom probe tomography to link microstructure and 3D nanochemistry of a ternary single crystal Ni83.9Si13Fe3.1 (at.%) model alloy. The formation of a γ/γ' microstructure is revealed, containing primary and secondary γ' precipitates analogous to Ni-based superalloys. Subsequently, microstructural hierarchy is created by the formation of γ particles inside primary γ' precipitates. The correlated supersaturation with γ forming elements (Ni, Fe) of primary γ' precipitates was identified as driving force for the formation of γ particles. The influence of aging on the mechanical properties is reported and peak hardness is achieved after 24 h of aging at 923 K. Thermo-Calc equilibrium phase concentrations based on the TTNi8 database where found to be closer to the APT data than the TCNi8 based values. Our results suggest that improved stability of γ particles can be achieved by tailoring the phase chemistry and the lattice misfit.
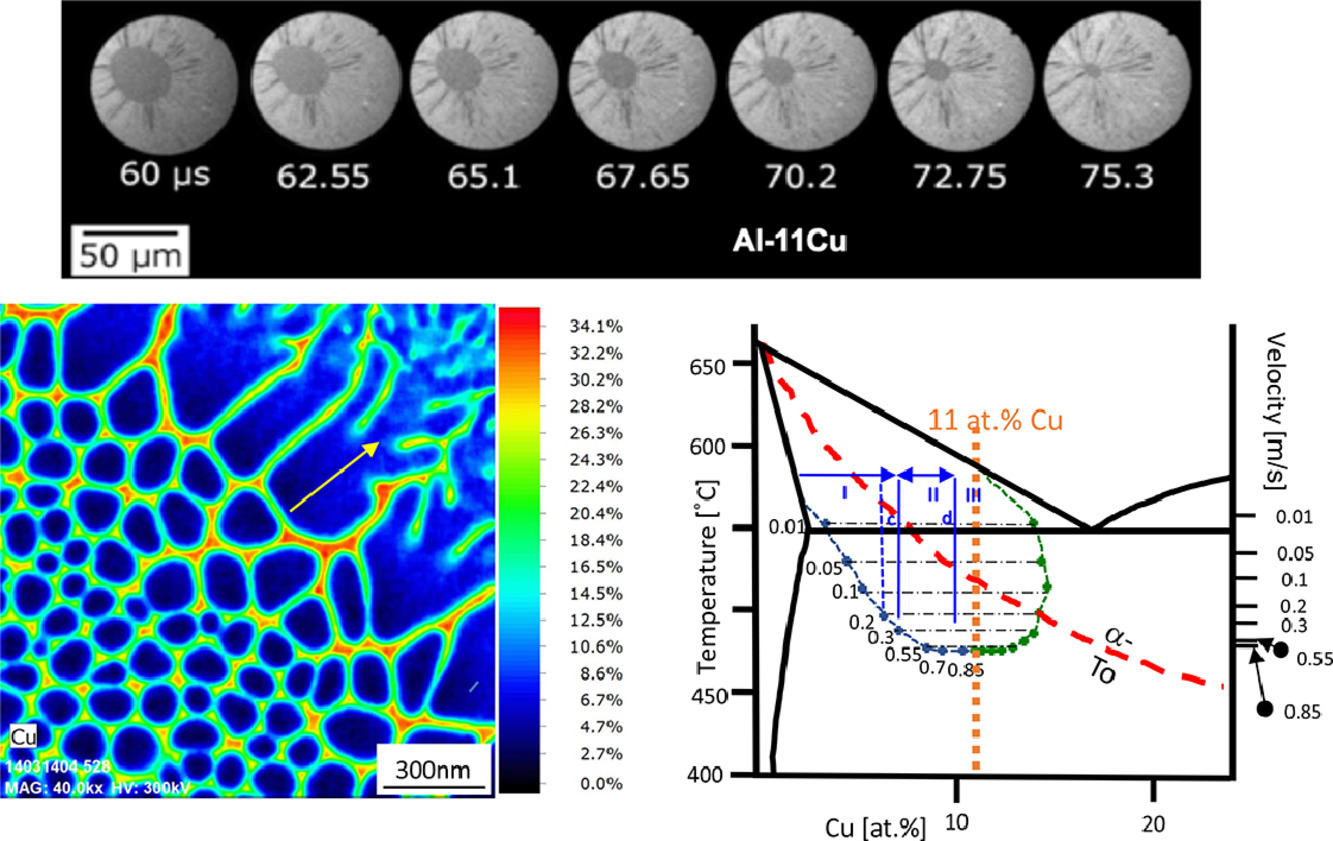
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P341-357
Interface velocity dependent solute trapping and phase selection during rapid solidification of laser melted hypo-eutectic Al-11at.%Cu alloy
激光熔凝亚共晶Al-11at%Cu合金快速凝固过程中界面速度对溶质捕获和相选择的影响
Vishwanadh Bathula, Can Liu, Kai Zweiacker, Joseph McKeown, Jorg M.K. Wiezorek✉
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.04.006
摘要
使用透射电镜(TEM)研究了亚共晶Al-11Cu(at.%)合金在激光熔化后凝固过程中的组织形成过程。通过原位透射电镜的直接观测,确定了凝固过程中固液界面速度VSL的变化过程。这使得我们能够建立固液界面速度与四个不同组织区域之间的联系。实验观测到了固液界面处多种晶体生长方式的转变,包括从平面状到胞状、胞状到树枝状、树枝状到胞状和胞状到平面状。当固液界面速度达到VSL=Va = (0.80±0.05) m/s时,发生从双相耦合生长到单相生长的转变。其中Va为带状晶粒开始形成时的完全稳态速度。原位和事后的TEM观测准确确定了快速凝固Al-11Cu合金的非平衡固相线。实验观测到了单相带状晶粒中,在小于5nm范围内发生溶质聚集和有序化的证据。单相带以在生长晶体附近液体边界层中的“冻结”结构作为其特征,其宽度约为3nm。本研究中分辨率达纳米尺度的TEM实验提供了重要的量化数据,如由凝固界面速度决定的α-Al溶质浓度,以及单相带中的原子尺度结构特征等。这些观测结果非常适合与多组分合金在激光熔化后的组织凝固理论模型进行比较。
英文摘要
Microstructure formation of a hypo-eutectic Al-11Cu (atom percent) alloy during solidification after laser melting has been studied by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). The evolution of the solid-liquid-interface velocity, VSL, during the solidification process has been determined from direct observation by in-situ TEM. This enabled correlating VSL with development of four distinct microstructure zones. Crystal growth mode transitions from planar to cellular, cellular to dendritic, dendritic to cellular, and cellular to planar, have been observed for the accelerating solid-liquid-interface. The transition from coupled two-phase growth to the single-phase growth occurred for VSL = Va = (0.80±0.05) m/s, where Va is the velocity of absolute stability, at the onset of banded morphology grain formation. The in-situ and post-mortem TEM uniquely permitted determination of the non-equilibrium solidus for the rapidly solidifying Al-11Cu alloy. Experimental evidence for solute clustering and chemical ordering tendencies at length scales on the order of ≤ 5nm has been detected in the single-phase regions of the banded grains. The structural features of the single-phase bands have been interpreted as signatures of ‘frozen in’ configurations present in the liquid boundary layer adjacent to the growing crystal, which has a width of about 3nm. The nano-scale spatiotemporal resolution experimental TEM studies performed here provided quantitative metrics, e.g. the solidification interface velocity dependent solute concentration of the α-Al phase and the near-atomic scale structure in the single-phase bands, that are uniquely suitable for comparison with theory and model predictions for solidification microstructure development in multicomponent alloys after laser melting.
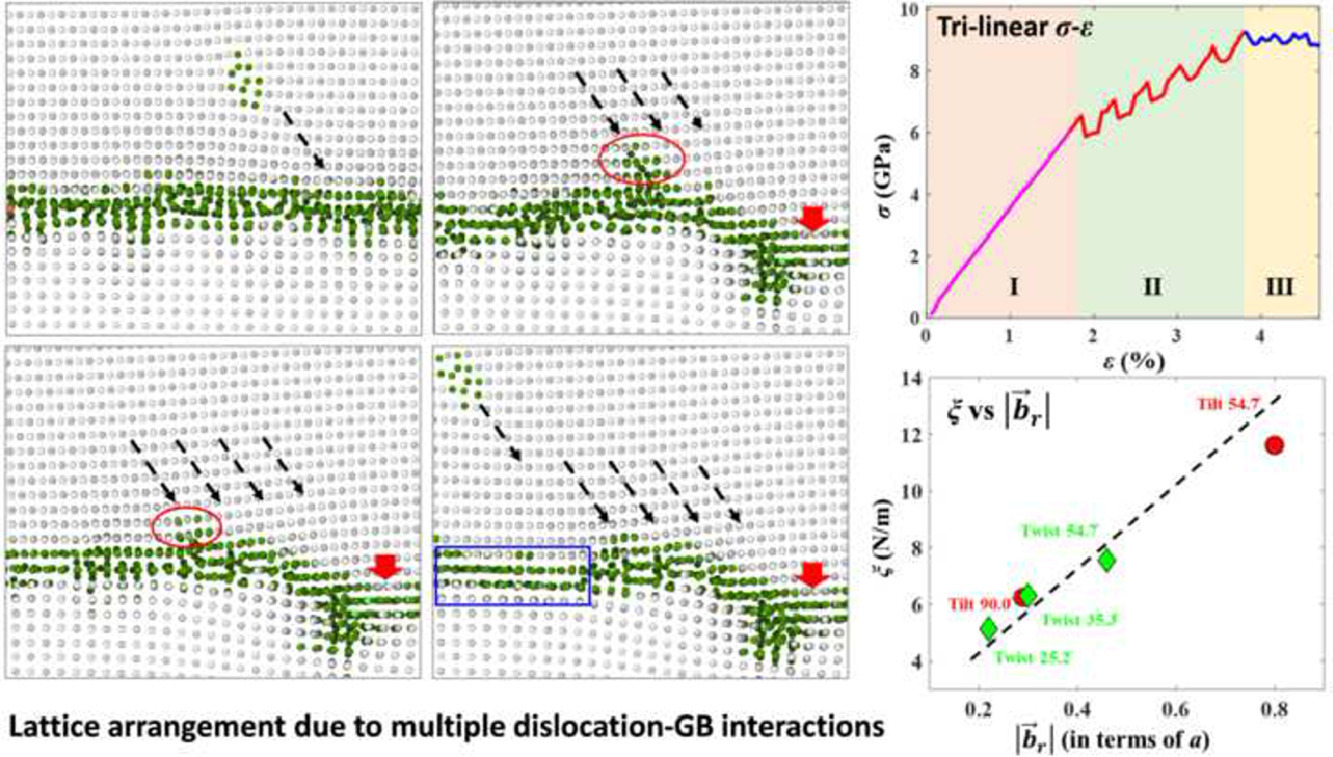
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P358-370
Using molecular dynamics to determine mechanical grain boundary energies and capture their dependence on residual Burgers vector, segregation and grain size
利用分子动力学方法确定机械晶界能并探究残余柏氏矢量、偏析和晶粒尺寸对其影响
Fei Shuang, Katerina E. Aifantis✉
Katerina E. Aifantis:kaifantis@ufl.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.014
摘要
本文致力于阐明力学界面的能量/参数,这一能量/参数是在梯度塑性中引入的,可以用于描述晶界的塑性变形能力。利用分子动力学对具有倾侧和扭曲晶界的体心立方Fe双晶的压缩过程进行了模拟。模拟过程中允许位错堆积的形成,这会导致塑性应变梯度。可以利用界面的梯度塑性解释应力-应变曲线,从而导出界面力学参数的数值。模拟结果显示,在吸收位错的过程中,晶界处的原子结构发生了变化。这说明初始晶界的静态能量参数不能表征塑性变形开始后的晶界。研究发现,界面参数的值 (1)依赖于晶界类型和晶界-位错的相互作用,它们与跨晶界的滑移传导密切相关 (2)与残余柏氏矢量的大小呈正相关,说明界面参数增加,晶界强度也增加。通过在晶界处加入氢原子重复模拟,发现元素偏聚增加了机械界面能。通过改变样品大小可以发现,这些机械能项与尺寸有关。但它们与内部长度的比例与尺寸无关,仅与晶界类型有关。对这些力学晶界能的深入理解,可能为亚微尺度工程材料的研究开辟一条新的路径。
英文摘要
The present article focuses on interpreting mechanical interface energies/parameters which have been introduced within gradient plasticity and can capture the ability of grain boundaries to deform plastically. Molecular dynamics simulation compression tests were performed on body-centered cubic Fe bicrystals with tilt and twist grain boundaries of different misorientations. The simulations allowed for the formation of dislocation pile-ups, which give rise to gradients in the plastic strain, and therefore it was possible to employ interfacial gradient plasticity to interpret the stress-strain curves and obtain values for the mechanical interface parameter. The simulations showed that the atomic structure at the grain boundary changed during dislocation absorption, illustrating that the initial grain boundary static energy cannot characterize boundaries after the onset of plastic deformation. It was found that the value of the mechanical interface parameter (i) depended on the GB type and GB-dislocation interactions that led to slip transmission across the GB, and (ii) was positively related to the magnitude of residual Burgers vector, indicating that as the mechanical interface parameter increased the GB strength increased. Repeating the simulations by adding hydrogen atoms at the grain boundaries, showed that segregation increased the mechanical interface energy. Changing the sample size indicated that such mechanical energy terms are size-dependent, however their ratio with the internal length was size independent and depended only on the GB type. A detailed understanding of these mechanical grain boundary energies may pave a new way to engineering materials in the sub-micron scales.
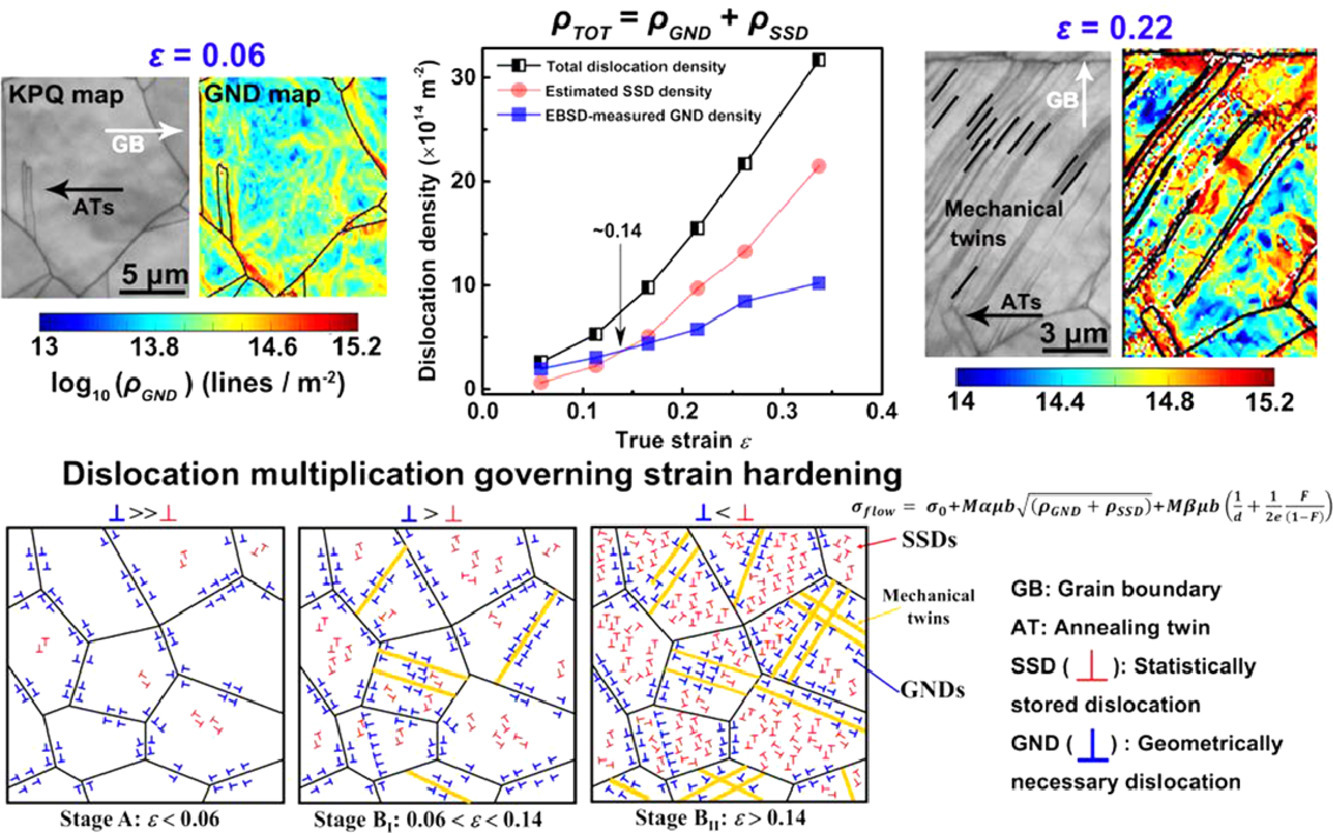
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P371-382
Investigations of dislocation-type evolution and strain hardening during mechanical twinning in Fe-22Mn-0.6C twinning-induced plasticity steel
Fe-22Mn-0.6C TWIP钢孪晶过程中的位错类型演化及应变硬化研究
Huihui Zhi, Cheng Zhang, Stoichko Antonova, Haiyang Yu, Tao Guo, Yanjing Su✉
Yanjing Su:yjsu@ustb.edu.cn,北京科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.062
摘要
我们首次在拉伸变形的Fe-22Mn-0.6C TWIP钢中实验研究了几何必要位错(GND)和统计存储位错(SSD)密度的变化及其在孪晶应变硬化中的作用。基于EBSD取向数据和改进后的应变硬化模型对GND和SSD密度进行了估计。分析表明,孪晶过程中GND密度呈非线性增加;另外,SSD的密度增加比GND快得多,说明SSD的增殖很大程度上取决于施加的应变水平。在应变早期(真应变小于0.14),GND密度较高,主导了位错硬化,而在此之后则SSD作用更大。研究还发现,这种TWIP钢中的GND密度比仅通过位错滑移机制变形的金属或合金高出几倍。我们认为这种差异是由于位错的平面滑移和孪晶的发生导致了在晶界或晶界附近大量的GND堆积。在0 ~ 0.34的真应变范围内,孪晶对流变应力增量的直接贡献小于100MPa。因此, 不同类型位错的增殖在整个变形范围内的不同阶段决定了应变硬化。本研究揭示了TWIP钢中GND和SSD的演化行为,对于进一步理解动态Hall-Petch效应和TWIP的合金设计具有重要意义。
英文摘要
In this study, for the first time, the evolution of geometrically necessary dislocation (GND) and statistically stored dislocation (SSD) densities, as well as their roles in strain hardening during mechanical twinning, was experimentally investigated in a tensile-deformed Fe-22Mn-0.6C twinning-induced plasticity (TWIP) steel. GND and SSD densities were estimated via EBSD-acquired orientation data and a modified strain hardening model, respectively. The analysis demonstrates that the GND density increases non-linearly due to mechanical twinning. The SSD density increases much faster than the GND density, which shows that multiplication of the SSDs is heavily dependent on the imposed strain level. It is revealed that the GND density is higher at early strain stages (below 0.14 true strain), dominating dislocation hardening, but thereafter the SSD density contributes more. It is also found that the GND density is several times higher in this TWIP steel than in metals or alloys, which deform through dislocation slip only. We attribute this difference to the planar slip of dislocations and the occurrence of mechanical twinning, which leads to much more pile-ups of the GNDs at/near boundaries. Mechanical twinning directly contributes less than 100 MPa to flow stress increment in the studied true strain range of 0 to 0.34. Consequently, depending on dislocation types, dislocation multiplication governs strain hardening at all deformation ranges. The findings provide insight into the evolution behaviors of GNDs and SSDs in TWIP steels, which are particularly important for further understanding of the dynamic Hall-Petch effect and useful for TWIP alloy design efforts.
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P416-424
Aluminium self-diffusion in high-purity α-Al2O3: Comparison of Ti-doped and undoped single crystals
高纯α-Al2O3中铝的自扩散:掺钛与未掺钛单晶的比较
Peter Fielitz✉, Steffen Ganschow , Klemens Kelm , Gunter Borchardt
Peter Fielitz:peter.fielitz@tu-clausthal.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.030
摘要
由于Al在α-Al2O3中可靠自扩散系数的缺失,导致我们难以给出关于异价掺杂的定量结论。本文选用掺杂Ti的高纯度单晶体作为研究对象。实验测得26Al示踪剂的扩散系数随着Ti含量增加而增加,证实了Ti占据了Al的晶格点阵位置形成Ti•Al。体系为保持电荷守恒,将伴随产生Al空位VAl’’’。这两种点缺陷的浓度随着Ti浓度和温度的变化关系可以通过考虑可能的Ti•Al:VAl’’’团簇进行定量模拟。利用已发表的计算模拟得到的结合能初值进行拟合,可以得到团簇的结合能。未掺杂样品中极高的Al扩散系数可能是固液界面处由于晶体生长过程中较低的氧化学势而产生Al间隙原子导致的。
英文摘要
Reliable data on self-diffusion of aluminium in α-Al2O3 are scarce and do not yet enable deriving quantitative conclusions about the impact of deliberate aliovalent doping. Therefore, the present study (1280 ≤ T/ °C ≤ 1500, pO2 = 200 mbar) was based on carefully grown high-purity single crystals doped with Ti. The experimentally determined 26Al tracer diffusivity increased with the Ti concentration and confirmed the incorporation of Ti on Al sites, TiAl•, with aluminium vacancies, VAl″′, formed for charge compensation. The observed relation between these two point defect concentrations as a function of the Ti concentration and the temperature can be quantitatively modelled by taking into account probable TiAl•:VAl″′ clusters. Using binding energy starting values from published computer simulations for the fit procedure cluster binding energies are obtained. The surprisingly high Al diffusivity in undoped samples can be tentatively rationalised by injection of Al interstitials at the liquid/solid interface because of the low oxygen potential during the crystal growth process.
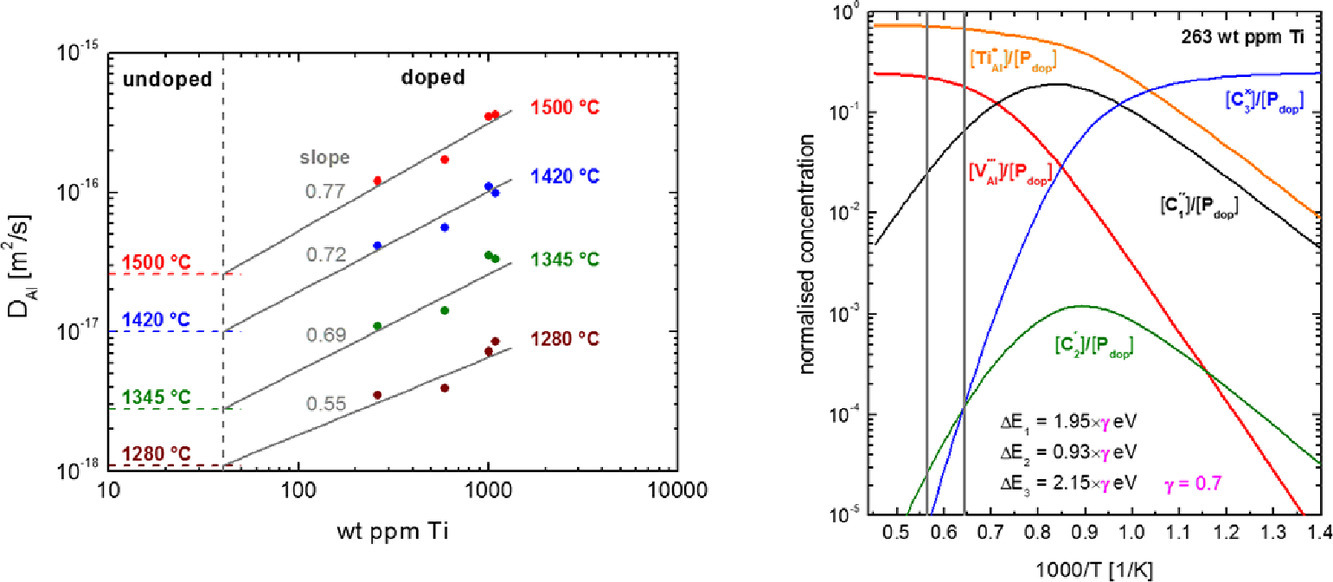
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P433-445
The correlation between microstructure and nanoindentation property of neutron-irradiated austenitic alloy D9
经中子辐照后奥氏体合金D9显微组织与纳米压痕性能的关系
Tianyi Chen✉, Lingfeng He, Mack H. Cullison , Charles Hay , Jatuporn Burns, Yaqiao Wu, Lizhen Tan✉
Tianyi Chen:Tianyi.chen@oregonstate.edu
Lizhen Tan:tanl@ornl.gov,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.020
摘要
本研究对三种改性不锈钢(即D9合金)在加速器中经过中子辐照后的微观组织和纳米力学性能进行了系统表征。样品分别在448、430和683℃下辐照至5.0、8.2和9.2 dpa。定量研究了位错环、孔洞和辐照诱导析出的演化过程,以揭示它们和辐照剂量以及温度之间的关系。对辐照后的样品在室温下进行了纳米硬度和纳米压痕蠕变试验。在高温辐照后的试样中观测了出乎意料的辐照硬化,初步认为这是由于一种未知的富镍和富硅析出物形成导致的。关于这种析出对合金抗辐照性能和力学性能的影响,本文对进行了讨论。本研究为D9合金的辐照-微观组织-性能关系提供了新的见解,对未来核电用的先进奥氏体合金的研发和优化具有重要意义。
英文摘要
The microstructure and nanomechanical properties of three samples of the modified stainless steel (referred as the alloy D9) were systematically characterized after neutron irradiation in the Advanced Test Reactor. The samples were irradiated to 5.0, 8.2, and 9.2 displacements per atom at 448, 430, and 683°C, respectively. The evolutions of dislocation loops, cavities, and radiation-induced precipitates were quantitatively studied to reveal their dose and temperature dependencies. Nanohardness and nanoindentation creep tests were conducted at room temperature on the irradiated samples. Unexpected radiation hardening was observed in the highest-temperature-irradiated sample due to the formation of an unknown type of Ni- and Si-rich precipitates whose contributions to the radiation and mechanical performances of the alloy were discussed. We provide the radiation-microstructure-property correlations of alloy D9 with new insights, which can benefit the development and optimization of advanced austenitic alloys for future nuclear applications.
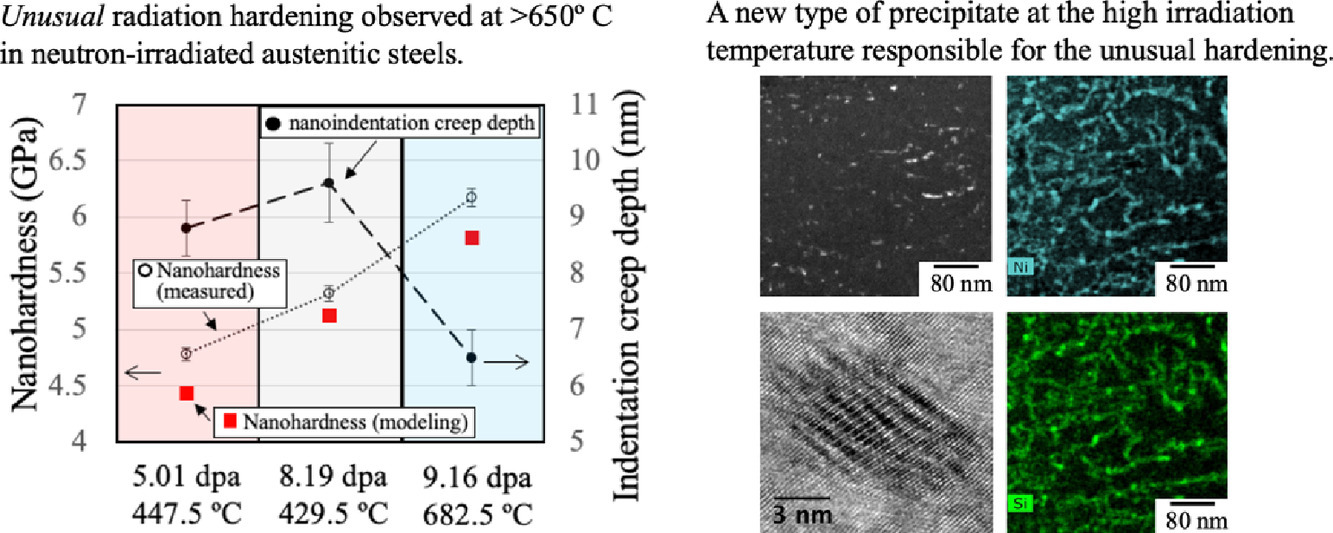
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P454-467
Predicting creep rupture life of Ni-based single crystal superalloys using divide-and-conquer approach based machine learning
基于分治学习的镍基单晶高温合金蠕变断裂寿命预测
Yue Liu , Junming Wu , Zhichao Wang , Xiao-Gang Lu , Maxim Avdeev, , Siqi Shi✉, Chongyu Wang , Tao Yu
Siqi Shi:sqshi@shu.edu.cn,上海大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.001
摘要
蠕变断裂寿命是衡量镍基单晶高温合金使用寿命和力学性能的关键参数。因此,准确有效地预测蠕变寿命具有重要的现实意义。在此,我们开发了一种包含多种材料描述符的分治自适应(DCSA)学习方法来合理和快速地预测蠕变断裂寿命。我们使用了一个包含266个合金试样的高质量蠕变数据集,该数据集包含合金成分、试验温度、试验应力和热处理工艺等特征。此外,我们基于相图计算(即CALPHAD)和材料结构-性能关系引入了五个参数,分别是堆垛层错能,晶格参数,γ'相的摩尔分数,扩散系数和剪切模量,用以揭示材料组织对蠕变性能的影响。在数据集上的机器学习结果表明,与五种目前较为先进的机器学习算法相比,该方法具备实现更高预测精度的潜力,其RMSE、MAPE和R2值分别为0.3839、0.0003和0.9176。对于新采集的8个合金试样,蠕变寿命的预测值与实验值误差均在可接受范围内(6.4486 h-40.7159 h),进一步验证了DCSA模型的有效性。综上所述,本研究中的方法能够以比实验更快速、更便宜的方式建立精确的结构-性能关系映射,对于合金的逆向设计具有重要指导意义。
英文摘要
Creep rupture life is a key material parameter for service life and mechanical properties of Ni-based single crystal superalloy materials. Therefore, it is of much practical significance to accurately and efficiently predict creep life. Here, we develop a divide-and-conquer self-adaptive (DCSA) learning method incorporating multiple material descriptors for rational and accelerated prediction of the creep rupture life. We characterize a high-quality creep dataset of 266 alloy samples with such features as alloy composition, test temperature, test stress, and heat treatment process. In addition, five microstructural parameters related to creep process, including stacking fault energy, lattice parameter, mole fraction of the γ' phase, diffusion coefficient and shear modulus, are calculated and introduced by the CALPHAD (CALculation of PHAse Diagrams) method and basic materials structure-property relationships, that enables us to reveal the effect of microstructure on creep properties. The machine learning explorations conducted on the creep dataset demonstrate the potential of the approach to achieve higher prediction accuracy with RMSE, MAPE and R2 of 0.3839, 0.0003 and 0.9176 than five alternative state-of-the-art machine learning models. On the newly collected 8 alloy samples, the error between the predicted creep life value and the experimental measured value is within the acceptable range (6.4486 h–40.7159 h), further confirming the validity of our DCSA model. Essentially, our method can establish accurate structure-property relationship mapping for the creep rupture life in a faster and cheaper manner than experiments and is expected to serve for inverse design of alloys.
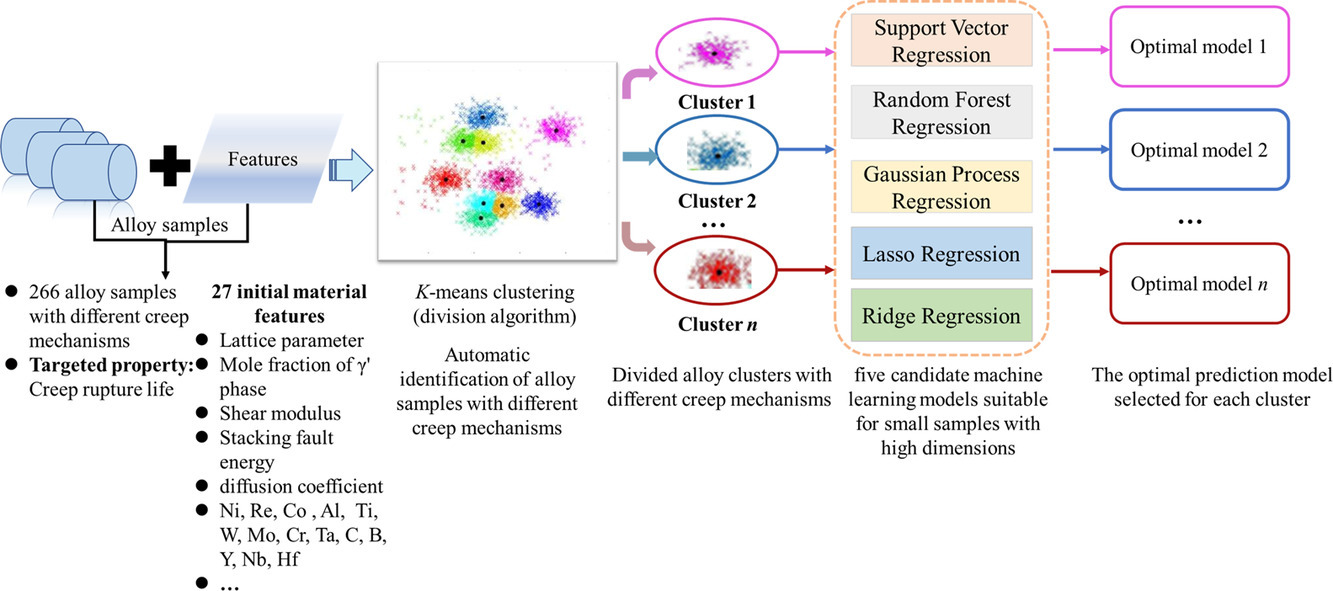
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P468-481
Toughening magnesium with gradient twin meshes
梯度孪晶网络增韧镁
Xin Wang, Lin Jiang, Chase Cooper, Kehang Yu, Dalong Zhang, Timothy J. Rupert, Subhash Mahajan, Irene J. Beyerlein, Enrique J. Lavernia, Julie M. Schoenung✉
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.021
摘要
在本研究中,我们结合了全面的特定位置的组织和性能表征对通过使用表面球磨技术在商业纯镁中引入的增韧效果进行了评估。通过表面球磨在样品中施加高频的多方向应变,可以使得样品沿垂直表面方向产生晶粒尺寸和取向的梯度。更重要的是,它同样导致了沿着样品厚度方向的孪晶网络密度的梯度。所谓孪晶网络,即指两个以上相交的孪晶阵列。室温下的拉伸试验表明,经过表面球磨后,样品的抗拉强度显著提高,并且塑性与未处理的样品相比翻了一番。通过背散电子衍射对样品初始织构和球磨参数对样品的组织演变和织构随机化的影响进行了分析。此外,为了建立微观结构的变化与该区域力学响应之间的联系,在样品表面不同距离处进行了TEM观察和SEM原位微柱压缩测试。结果表明,孪晶网络可能导致了更多滑移体系的开动和更高的加工硬化,从而提高了材料的均匀塑性应变。
英文摘要
In the present study, we combine comprehensive site-specific microstructural and mechanical characterization studies to evaluate the toughening effect induced by applying a surface SPEX milling (SSM) approach to commercially-pure Mg. Our results show that the high frequency, multi-directional deformation strain induced by SSM generated gradients in the grain size and orientation with depth from the surface. More importantly, it also resulted in a gradient in the density of twin meshes, which are defined as two or more intersecting arrays of twins, along the sample thickness direction. Tensile tests at room temperature indicate that after SSM, the samples have higher ultimate tensile strengths and two-fold increases in ductility as compared to those of the untreated samples. The effect of the initial texture and SSM parameters on the microstructural evolution and texture randomization were analyzed by electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD). Furthermore, in order to correlate the variation in microstructure with the site-specific mechanical response, TEM and in-situ micropillar compression testing in SEM were performed at various distances from the SSM-treated surface. The results show that twin meshes may be responsible for the activation of more slip systems and higher strain hardening, which result in higher uniform plastic strain.
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P501-518
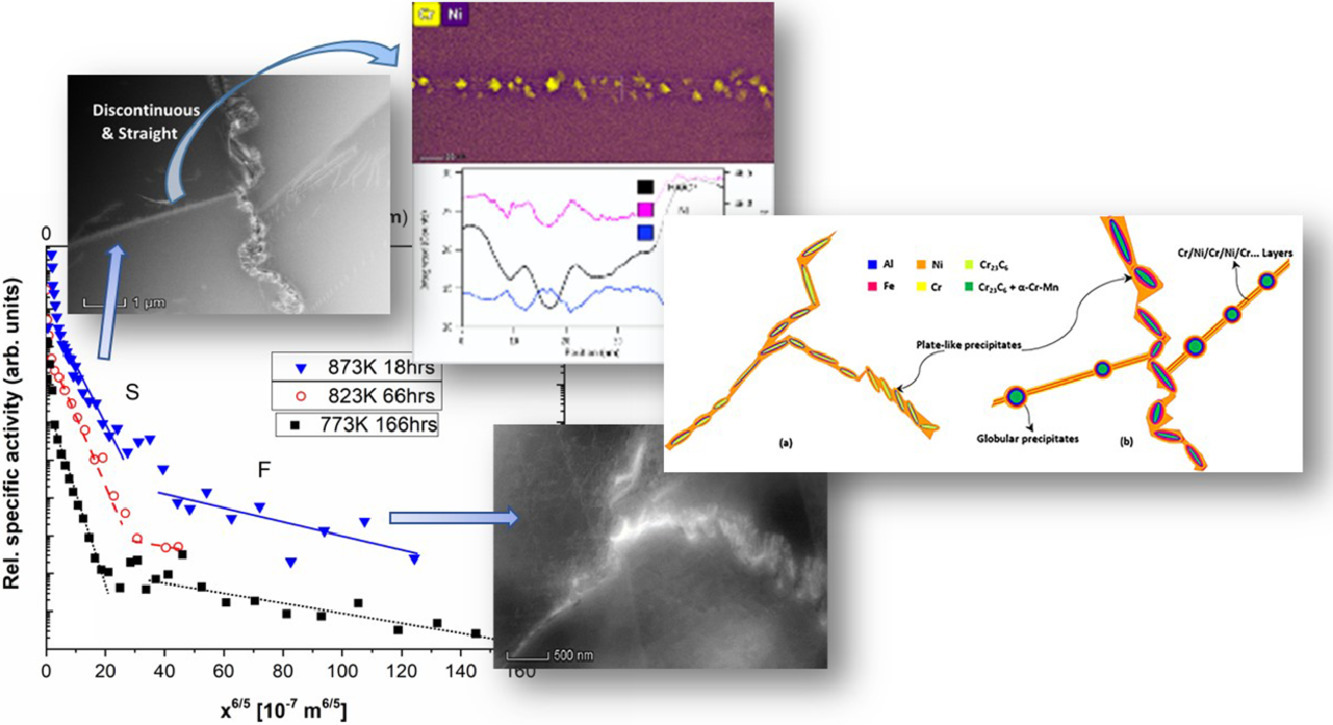
Grain boundary diffusion and grain boundary structures of a Ni-Cr-Fe- alloy: Evidences for grain boundary phase transitions
Ni-Cr-Fe合金中的晶界扩散和晶界结构:晶界相变的证据
Sai Rajeshwari K,S. Sankaran, K.C. Hari Kumar, Harald Rösner, Martin Peterlechner, Vladimir A. Esin, Sergiy Divinski✉, Gerhard Wilde
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.051
摘要
采用一种新型的示踪扩散分析显微技术研究了镍基粗晶602CA合金中的晶界结构-性能关系。在高温下,可以观察到多种失踪剂的多种短路扩散机制共同作用。这些机制与各种各样存在不同程度析出和偏聚的大角度晶界有关,我们使用高角选区衍射结合EDX,以及详尽的原子探针分析对其进行了表征。在高温退火条件下,富铬锰的α相与Cr23C6碳化物共存,Al, Ni, Fe依次在周围偏析。弯曲和锯齿状晶界处存在高密度的盘状碳化物析出;相比之下,平直晶界上则分布着化学成分相似的球状碳化物,碳化物之间存在Cr和Ni的交错层,类似于调幅分解组织。在较低的温度下,组织中主要是含Cr偏聚和富Cr碳化物析出的锯齿状界面。403K退火的合金中含有大量盘状Cr23C6析出,并且析出相周围有一层富镍层。在相对较低的温度下,Ni的晶界扩散速率呈现出几乎与温度无关的异常特征。这种特定的扩散行为与亚稳态的晶界转变有关,可以通过与晶界扩散过程相比,更长时间尺度上发生的相变诱导弹性应变所伴随的弛豫,对这一现象进行解释。本研究从热力学角度提供了晶界分解的可能机理,为镍基多组分合金中的晶界相变提供了有力证据,并且强调了动力学与组织结构联合表征在这类研究发挥的重要作用。
英文摘要
Grain boundary structure-property relationship was studied in a Ni-base 602CA coarse-grained alloy using a novel correlative tracer diffusion-analytical microscopy approach. Co-existence of several short-circuit contributions to tracer diffusion was distinguished at higher temperatures. These contributions were related to different families of high-angle grain boundaries with distinct coverages by precipitates and segregation levels as revealed by HAADF-STEM combined with EDX measurements and a detailed atom probe tomography analysis. Annealing at such conditions resulted in Cr23C6-type carbides co-existing with an α-Cr-Mn-enriched phase in addition to sequential segregation layers of Al, Ni, and Fe around them. Curved and hackly grain boundaries showed a high density of plate-like carbides. In contrast, straight grain boundaries were composed of globular carbides with similar chemical composition variations and additionally with alternating layers of Cr and Ni in-between the carbides, similar to spinodal microstructures. At lower temperatures, hackly interfaces with Cr and Cr-carbide enrichment dominated and the alloy annealed at 403 K contained plate-like Cr23C6-type carbides surrounded by a Ni-rich layer around them. The Ni grain boundary diffusion rates at these relatively low temperatures showed an anomalous character being almost temperature independent. This specific diffusion behaviour corresponds to a metastable grain boundary transition which is explained by a concomitant relaxation of transformation-induced elastic strains occurring on a longer time scale in comparison to those for grain boundary diffusion. Thermodynamic insights into the probable mechanism of decomposition at grain boundaries are provided. The paper provides solid evidences towards the existence of grain boundary phase transitions in the Ni-base multi-component alloy. It underlines the capabilities of the correlated kinetic-structure measurements as a tool to probe such changes.
ACTA Vol. 195, 15 Aug. 2020, P541-554
Age-hardening response of AlMgZn alloys with Cu and Ag additions
添加Cu和Ag的AlMgZn合金的时效硬化响应
Lukas Stemper✉, Matheus A. Tunes, Paul Oberhauser, Peter J. Uggowitzer, Stefan Pogatscher✉
Lukas Stemper:lukas.stemper@unileoben.ac.at
Stefan Pogatscher:stefan.pogatscher@unileoben.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.05.066
摘要
机械强度和成形性之间的权衡是铝合金长期以来面临的难题。解决思路之一是发展单合金铝合金,而最近,可回收性方面的要求给单合金这一概念的发展带来了进一步压力。本研究提出了一种基于AlMg体系的合金材料,通过添加某些其他元素促进时效硬化,同时保留较高的Mg含量保证其固有的应变硬化能力,使其成为高强度高成型性铝合金的一种备选材料。通过在商业化的EN AW-5182合金中添加3.5 wt.% Zn,使基体中析出T相实现时效硬化。添加少量铜和银可以增强和加速这一过程。本研究还比较了单步和双步人为时效的影响。通过硬度测试,拉伸测试和扫描透射电子显微镜方法对材料的组织和机械性能进行了表征。结果表明,添加了Zn、Cu、Ag的合金在软态下表现出更强的应变硬化能力,且锯齿状流变减少。材料的时效硬化强度高达326 MPa,使其在峰值时效条件下的极限抗拉强度达到了550 MPa。研究了少量添加Zn、Cu、Ag的合金在人工时效过程的微观结构组织演化,以及合金元素添加对析出的影响。
英文摘要
A recurrent challenge with aluminum alloys is their longstanding trade-off between mechanical strength and formability. Recently recyclability has put further pressure on the development of single-alloy concepts for solving this challenge. This study addresses an AlMg-based system featuring additional elements to facilitate age-hardening but retaining a high Mg content for inherent pronounced strain hardening as a potential candidate. Age-hardening was enabled by T-phase based precipitation in the commercial alloy EN AW-5182 via the addition of 3.5 wt.% of Zn. The investigation shows that minor additions of Cu and Ag enhance and accelerate it. The study also compares single-step and double-step artificial aging. Hardness and tensile testing and scanning transmission electron microscopy methods were deployed to characterize the alloys investigated, mechanically and microstructurally. An alloy with added Zn, Cu and Ag showed improved strain hardening and reduced serrated flow in the soft state, while exhibiting an age-hardening response of up to 326 MPa in yield strength leading to an ultimate tensile strength of 550 MPa in peak-aged condition. The study discusses the evolution of the microstructure during artificial aging in the light of Zn, Cu and Ag additions and their effect on the precipitation process.

微信公众号:Goal Science
投稿邮箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
