金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.190, Jan. 2021(全)
2020-09-23 来源:Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文17篇,涵盖了中锰钢、纳米孪晶铜合金、高熵合金、3D打印、TWIP钢、镁铝合金、高温合金等,国内科研单位包括香清华大学、香港大学、大连理工大学、北京理工大学、北京航空航天大学、北京科技大学、华南理工大学、西南交通大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 190 目录
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P7-11
1. A molecular dynamics-informed probabilistic cross-slip model in discrete dislocation dynamics
离散位错动力学中分子动力学的概率交滑移模型
Alon Malka-Markovitz✉, Benoit Devincre, Dan Mordehai
Alon Malka-Markovitz: alonma@campus.technion.ac.il
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.008
摘要
本工作对离散位错动力学(DDD)模拟中的位错交滑移进行了定量研究,这是金属变形中必不可少的热激活过程。我们在DDD模拟中实现了应力相关的线张力模型,而从分子动力学(MD)模拟获得的信息很少。该模型在DDD模拟中再现了用MD模拟的Cu在大范围应力和温度下的概率交滑移率。原子尺度精确的交滑移模型的实现允许用DDD更准确地模拟诸如变形软化,位错-析出相互作用和位错图案等现象。
英文摘要
We present here a quantitative study of dislocation cross-slip, an essential thermally activated process in deformation of metals, in discrete dislocation dynamics (DDD) simulations. We implemented a stress-dependent line-tension model in DDD simulations, with minimal information from molecular dynamics (MD) simulations. This model allows reproducing in DDD simulations the probabilistic cross-slip rate calculated in MD simulations for Cu in a large range of stresses and temperatures. The implementation of an atomically-scale accurate cross-slip model allows simulating more accurately phenomena such as deformation softening, dislocation-precipitate interaction and dislocation patterning in DDD simulations.

SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P16-21
2. Recovering the ductility of medium-Mn steel by restoring the original microstructure
通过还原初始组织恢复中锰钢的延展性
Mun Sik Jeong, Tak Min Park, Seunggyu Choi, Seok-Jae Lee, Jeongho Han✉
Jeongho Han: jeonghohan@hanyang.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.022
摘要
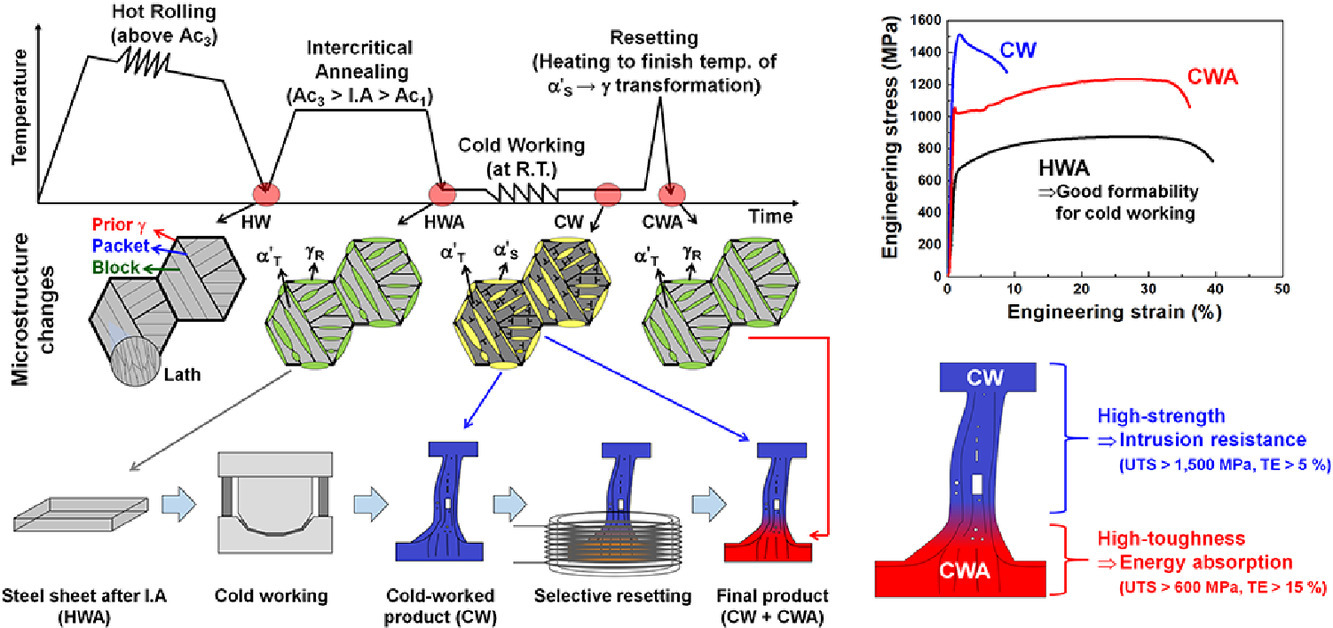
为了恢复冷加工中锰钢降低的延展性,本研究提出了一种新的复位工艺。通过简单的热处理使应变诱导的富锰马氏体发生逆转变,可以还原钢的原始组织。本工艺处理后的钢成功恢复到了冷加工之前钢的延展性,并提高了强度。此简单的热处理工艺可在单一金属板中实现最初需要两个不同部件以达到其所需相反属性的汽车零部件(例如,顶部需要较高强度而底部需要较高韧性的B柱)。
英文摘要
To recover the reduced ductility of cold-worked medium-Mn steels, a novel resetting process is proposed in this study. Through a simple heat treatment, the original microstructure of the steel is restored by the re-reversion of the Mn-enriched strain-induced martensite. The ductility of the reset steel is successfully recovered, and its strength is improved, relative to the steel prior to cold working. The present technique facilitates the use of a single sheet metal and a simple heat treatment process for an automotive component which originally comprised two different parts to compensate for the opposing attributes that it requires (e.g., having a high strength at the upper part and high toughness at the bottom part of a center pillar).
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P27-31
3. Grain boundary evolution of highly nanotwinned alloys: Effect of initial twinned microstructure
高纳米孪晶合金的晶界演化: 初始孪晶组织的影响
Joel A. Bahena, Theresa Juarez, Leonardo Velasco, Andrea M. Hodge✉
Andrea M. Hodge: ahodge@usc.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.024
摘要
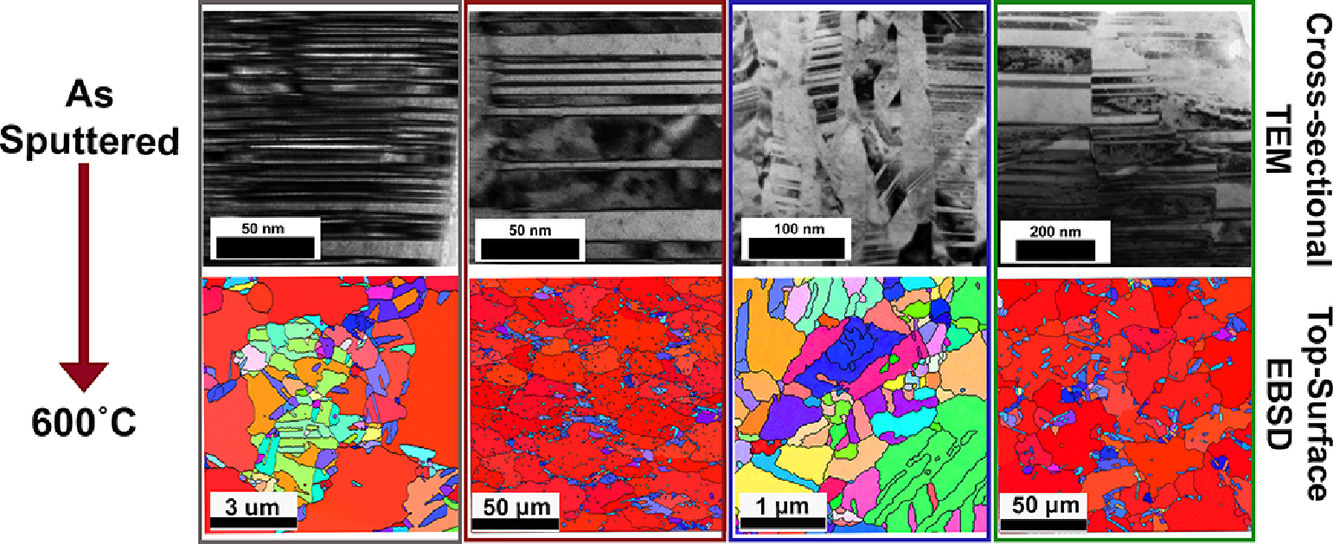
本研究比较了初始孪晶微观组织对四种溅射纳米孪晶铜合金晶粒生长行为的影响。我们用透射电子显微镜对沉积的薄膜进行了表征,并通过电子背散射衍射研究了退火样品的微观组织演变。织构显示出了明显的影响,其中具有强{111}织构的薄膜显示出了异常的晶粒生长,而在随机织构的薄膜中未观察到。此外,孪晶界诱发的稳定性似乎受到限制,这是由于高孪晶密度产生的过量能量可能会导致异常晶粒长大和再结晶的过早发生。
英文摘要
The effects of initial twinned microstructure on the grain growth behavior of four sputtered nanotwinned copper alloys were compared. As-deposited films were characterized by transmission electron microscopy and the microstructural evolution of the annealed samples was investigated through electron backscatter diffraction. Texture showed a pronounced effect, where films with strong {111} textures exhibited abnormal grain growth that was not observed in a randomly textured film. Additionally, the stability induced by twin boundaries appears to be limited, as the excess energy generated by a large twin density could drive the early onset of abnormal grain growth and recrystallization.
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P32-37
4. Critical role of Lüders banding in hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of medium Mn steels
吕德斯带在中锰钢氢脆敏感性中的关键作用
Jun Zhang, Mingxin Huang✉, Binhan Sun, Boning Zhang, Ran Ding, Cheng Luo, Wu Zeng, Chi Zhang, Zhigang Yang, Sybrand van der Zwaag, Hao Chen✉
Hao Chen: hao.chen@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn,清华大学
Mingxin Huang: mxhuang@hku.hk,香港大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.025
摘要
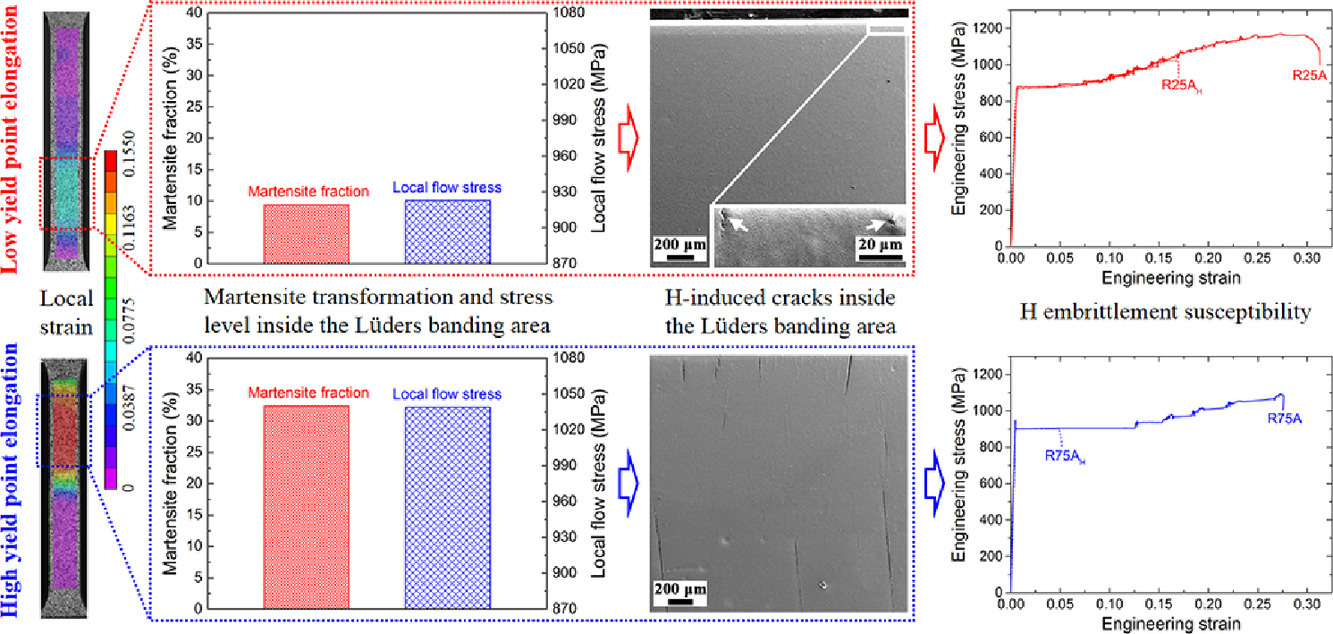
本工作通过调节拉伸过程中屈服点伸长率(YPE),研究了吕德斯带对中锰钢氢脆(HE)敏感性的影响。研究人员发现具有较大YPE的钢对氢脆更加敏感。较大的YPE导致较高的局部流变应力和较高的应变诱导马氏体体积分数,进而导致吕德斯带扩展区域中产生更多的氢致裂纹,引起灾难性破坏。本研究表明,吕德斯带及其相应的局部变形在影响中锰钢整体氢脆敏感性方面起着关键作用。
英文摘要
The effect of Lüders banding on hydrogen embrittlement (HE) susceptibility of medium Mn steels was investigated by tuning the degree of yield point elongation (YPE). It was found that the steel with a larger YPE was more susceptible to HE. A larger YPE led to a higher local flow stress and a higher fraction of strain-induced martensite, which in turns resulted in more H-induced cracks in the Lüders banding area and the consequent catastrophic failure. It thus suggests that Lüders banding and the associated localized deformation play a key role in influencing the overall HE susceptibility of medium Mn steels.
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P40-45
5. Coherent precipitation and stability of cuboidal nanoparticles in body-centered-cubic Al0.4Nb0.5Ta0.5TiZr0.8 refractory high entropy alloy
体心立方Al0.4Nb0.5Ta0.5TiZr0.8难熔高熵合金中立方纳米粒子的共格析出和稳定性
Qing Wang✉, Jincan Han, Yufeng Liu, Zhongwei Zhang✉, Chuang Dong, Peter K. Liaw
Qing Wang: wangq@dlut.edu.cn,大连理工大学
Zhongwei Zhang: zhangzhongw@163.com,北京理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.029
摘要
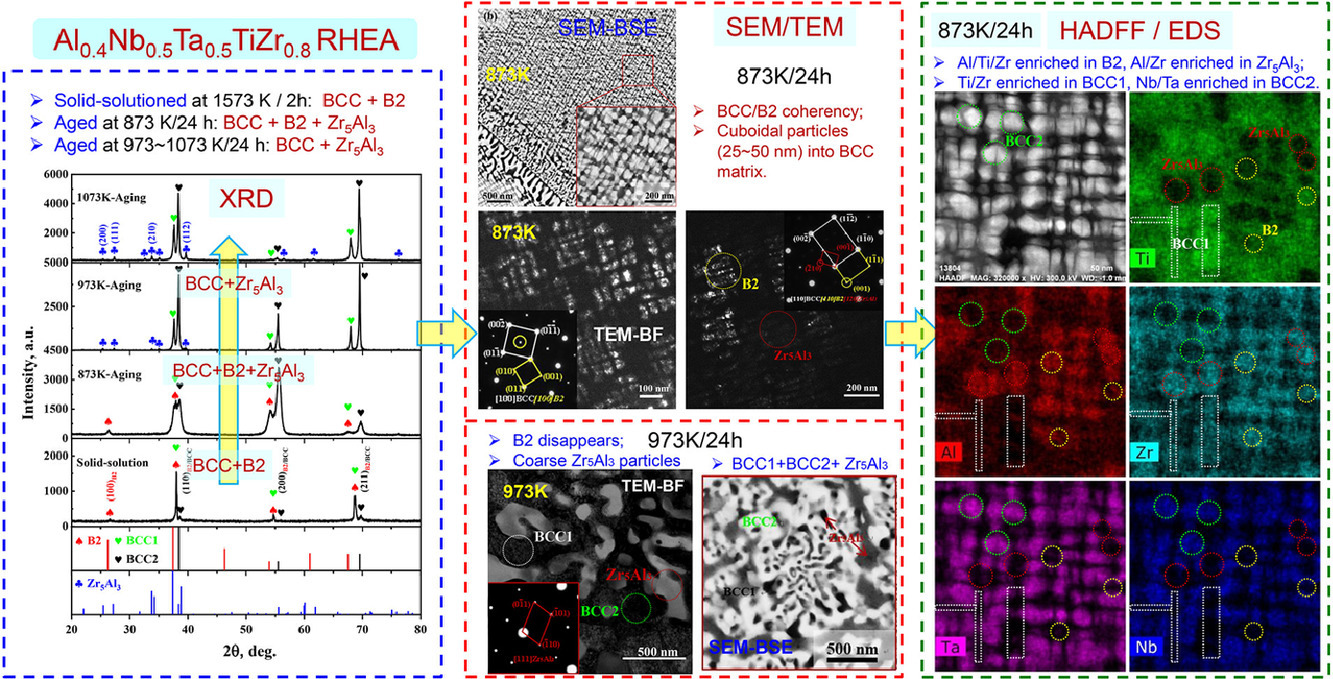
本研究开发了一种具有共格析出的体心立方(BCC)基Al0.4Nb0.5Ta0.5TiZr0.8新型难熔高熵合金。由于中等晶格失配,在873K时效时合金中会形成尺寸为25-50 nm的立方纳米析出。由于相似的化学组成,Zr5Al3相也以相同的颗粒形状与B2共存,其中B2相中富集Ti而Zr5Al3相中没有Ti的富集。随着时效温度的升高,BCC/B2的共格性将会变差,仅留下粗大的Zr5Al3。此外,由于Nb/Ta和Ti/Zr的偏聚,合金中存在两种BCC相。
英文摘要
The present work developed a new body-centered-cubic (BCC)-based Al0.4Nb0.5Ta0.5TiZr0.8refractory high entropy alloy with coherent precipitation. The formation of cuboidal nanoprecipitates with a size of 25~50 nm in an 873 K-aged alloy is ascribed to a moderate lattice misfit. A Zr5Al3 phase also coexists with B2 in a same particle shape due to similar chemical compositions, in which Ti is enriched in B2 but not in Zr5Al3. The BCC/B2 coherency would be deteriorated with increasing the aging temperature, leaving coarse Zr5Al3 alone. Besides, there exist two kinds of BCC phases due to the segregations of Nb/Ta and Ti/Zr.
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P46-51
6. Additive manufacturing of three-dimensional (3D)-architected CoCrFeNiMn high- entropy alloy with great energy absorption
高吸能三维构造CoCrFeNiMn高熵合金的增材制造过程
Siyuan Peng, Shahryar Mooraj, Rui Feng, Liang Liu, Jie Ren, Yanfang Liu, Fanyue Kong, Zhiyu Xiao, Cheng Zhu, Peter K.Liaw, Wen Chen✉
Wen Chen: wenchen@umass.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.028
摘要
在本研究中,我们开发了一种通过墨水直书写工艺与热烧结相结合的方法,对CoCrFeNiMn高熵合金进行三维(3D)构造的增材制造。三维构造的CoCrFeNiMn晶格展示了杰出的能量吸收能力,达到了现有构架材料的极限。这种高能量吸收能力来源于三维结构中弯曲为主的变形方式以及等轴晶的完全退火均匀组织,这些共同导致了变形过程中显著的应变硬化。我们的研究为用于各种结构应用的高吸能3D打印先进结构材料提供了一种新的途径。
英文摘要
In this study, we developed an approach to additive manufacturing of three-dimensional (3D)-architected CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloys by direct ink writing combined with thermal sintering. The 3D-architected CoCrFeNiMn lattices exhibit the outstanding energy absorption capacity that expands the envelope of existing architected materials. Such a high-energy absorption ability originates from the bend-dominated deformation mode of the 3D-architecture as well as the fully-annealed homogeneous microstructure of equiaxed grains, which collectively lead to remarkable strain hardening upon deformation. Our study provides a new avenue for 3D-printing advanced architected materials with extreme mechanical energy absorption for a myriad of structural applications.
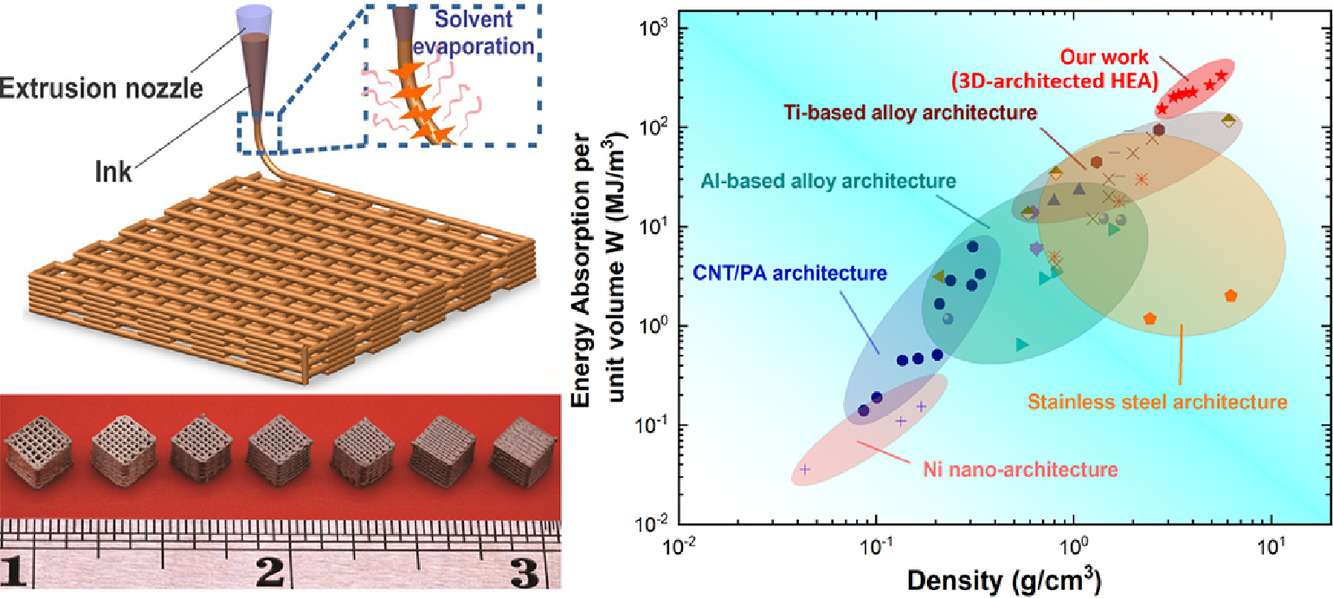
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P63-68
7. Effects of hydrogen clusters on interface facilitated plasticity at semi-coherent bimetal interfaces
氢团簇对半共格双金属界面处界面促进可塑性的影响
C.J. Wang, Z.R. Liu, B.N. Yao, X.F. Kong, D. Legut, R.F. Zhang✉, Y. Deng✉
R.F. Zhang: zrf@buaa.edu.cn,北京航空航天大学
Y. Deng: dengyuan@buaa.edu.cn,北京航空航天大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.031
摘要
位错形核和界面滑动是控制金属纳米复合材料力学塑性的两个主要行为。最近的工作表明,这两个行为可能与原子界面的几何特征密切相关,但是成分因素(比如,偏聚的氢团簇)对于这两个行为的影响尚不明确。本工作表明,错配位错节附近的氢团簇可以强烈抑制位错形核和界面滑动,而其他位置的氢团簇对位错形核的影响较弱但有助于界面滑动。这些发现为氢团簇对界面促进可塑性的影响提供了合理的原子层面的机理解释。
英文摘要
Dislocation nucleation and interface sliding are two dominant plasticity events governing the mechanical behavior of metallic nanocomposites. Recent works have shown that both events can be closely related to atomistic interface geometries, however, how compositional factors, e.g., segregated hydrogen clusters, contribute both events are nearly unknown. Herein, we demonstrate that hydrogen clusters near misfit dislocation nodes can strongly suppress dislocation nucleation and interface sliding, while clusters at other positions will contribute somehow weaker effect on dislocation nucleation but facilitate interface sliding. These findings offer a rational atomistic mechanism for the effect of hydrogen clusters on interface facilitated plasticity.
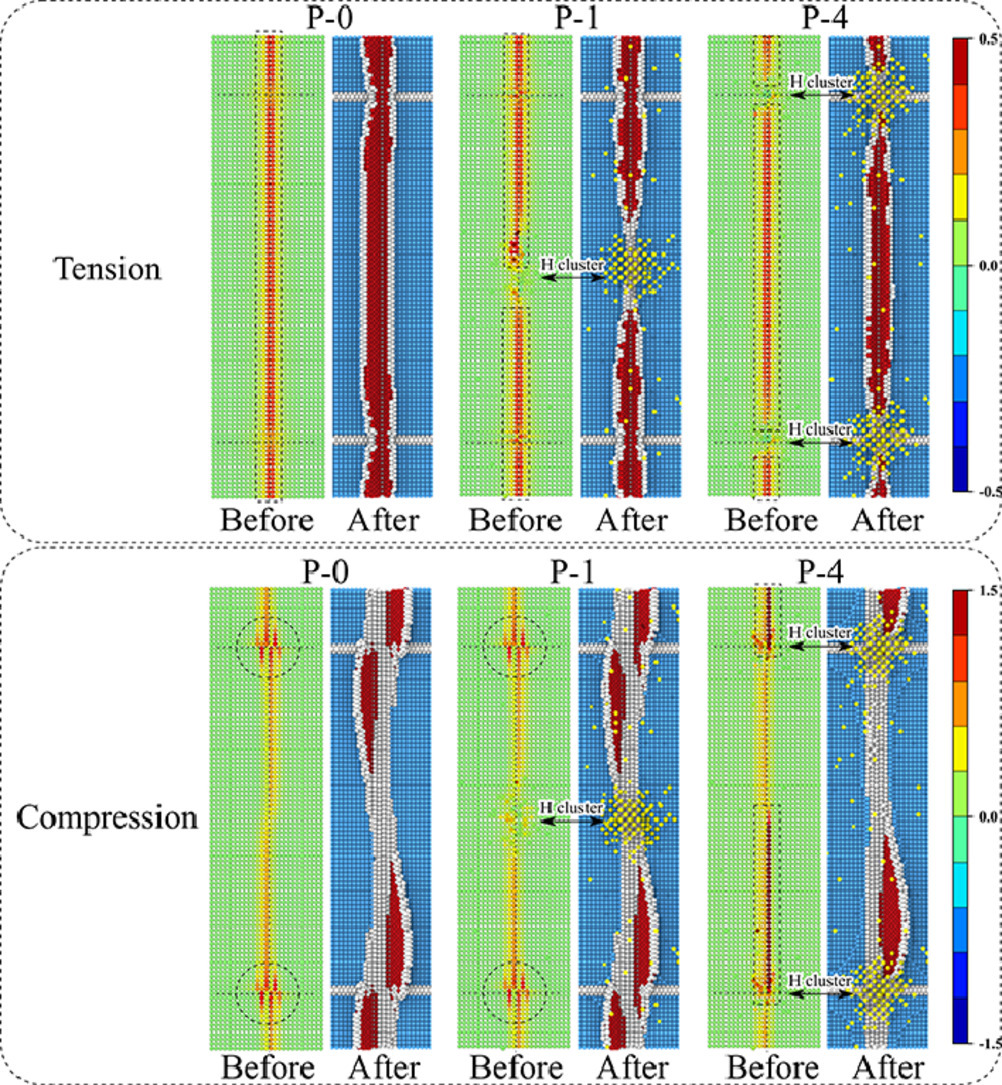
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P69-74
8. A powder-metallurgy-based fabrication route towards achieving high tensile strength with ultra-high ductility in high-entropy alloy
一种以粉末冶金为基础的高抗拉强度高塑性高熵合金的制备方法
Peyman Asghari-Rad, Praveen Sathiyamoorthi, Nhung Thi-Cam Nguyen, Alireza Zargaran, Taek SooKim, Hyoung Seop Kim✉
Hyoung Seop Kim: hskim@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.038
摘要
在材料科学界,强度与塑性之间的权衡一直是一个难题。特别地,研究人员致力于在通过粉末冶金制造的合金中,获得高抗拉强度和高的延伸率。本工作展示了一种基于粉末冶金的制造方法,该方法通过使用高压扭转对CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金粉末进行冷固成型,然后对其进行退火,从而实现高拉伸强度和延展性的协同提升。这种方法产生了754MPa的高屈服强度和58%的超高延伸率的出色协同作用,这在粉末冶金制造的合金中从未实现过。此外,可以通过退火处理来调整微结构,以实现一系列强度和延展性,这在工业上是针对特定应用的高度追求。本制备方法可应用于使用合金,金属和陶瓷粉末制备高熵合金-基体复合材料,以实现可控的微观组织和卓越的拉伸性能。
英文摘要
The strength-ductility trade-off dilemma is perennially problematic in the materials science community. In particular, the attainability of high tensile strength and large elongation is ambitious in alloys fabricated by powder metallurgy. Here, we demonstrate a powder-metallurgy-based fabrication route to achieve a high synergy of tensile strength and ductility through cold-consolidation of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy powder using high-pressure torsion followed by annealing. This approach has resulted in an exceptional synergy of high yield strength of 754 MPa with an ultra-high tensile elongation of 58% which has never been achieved in alloys fabricated by powder metallurgy routes. Additionally, the microstructure can be tuned by annealing treatment to achieve a range of strength and ductility that are highly sought after in industries for a specific application. The present fabrication route can be applied for fabrication of high-entropy alloy-matrix composites using alloys, metals, and ceramic powders to achieve controllable microstructure and eminent tensile properties.
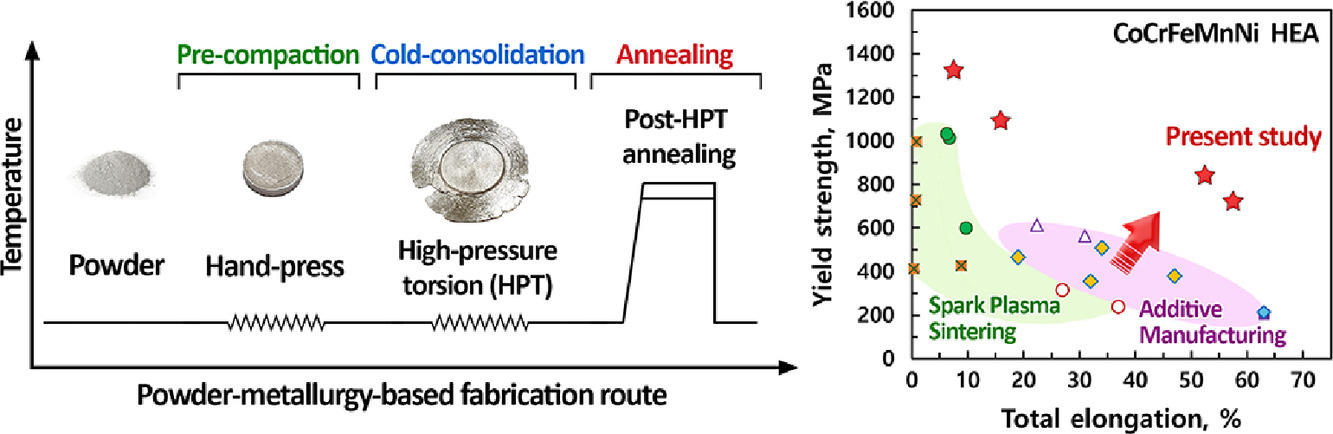
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P80-85
9. Effects of elemental segregation on microstructural evolution and local mechanical properties in a dynamically deformed CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy
元素偏析对动态变形CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金组织演变和局部力学性能的影响
M.N. Hasan, J. Gu, S. Jiang, H.J. Wang, M. Cabral, S. Ni, X.H. An✉, M. Song, L.M. Shen, X.Z. Liao✉
X.H. An: xianghai.an@sydney.edu.au
X.Z. Liao: xiaozhou.liao@sydney.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.048
摘要
本工作研究了CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金中元素偏析对高应变率变形引起的局部硬度和微观组织演变的影响。在凝固过程中,Mn和Ni元素会偏聚到枝晶间的边界上,且偏聚程度由于动态变形而加剧。Mn和Ni富集区域的局部硬度降低,这可能是由于局部层错能的增加改变了变形机制。这导致了软硬区域的交替分布,且该结构有效地阻止了韧化材料的绝热剪切带的传播。
英文摘要
The effect of elemental segregation on local hardness and microstructural evolution introduced by high strain-rate deformation in a CrMnFeCoNi high entropy alloy was investigated. Mn and Ni elemental segregation to interdendritic boundaries occurs during the solidification process and is intensified by dynamic deformation. Local hardness is reduced in the Mn and Ni enriched areas, which may be due to the increase of local stacking fault energy that changes the deformation mechanisms. This leads to the alternation of soft and hard regions and the structure is effective in hindering the propagation of adiabatic shear bands that would toughen the material.
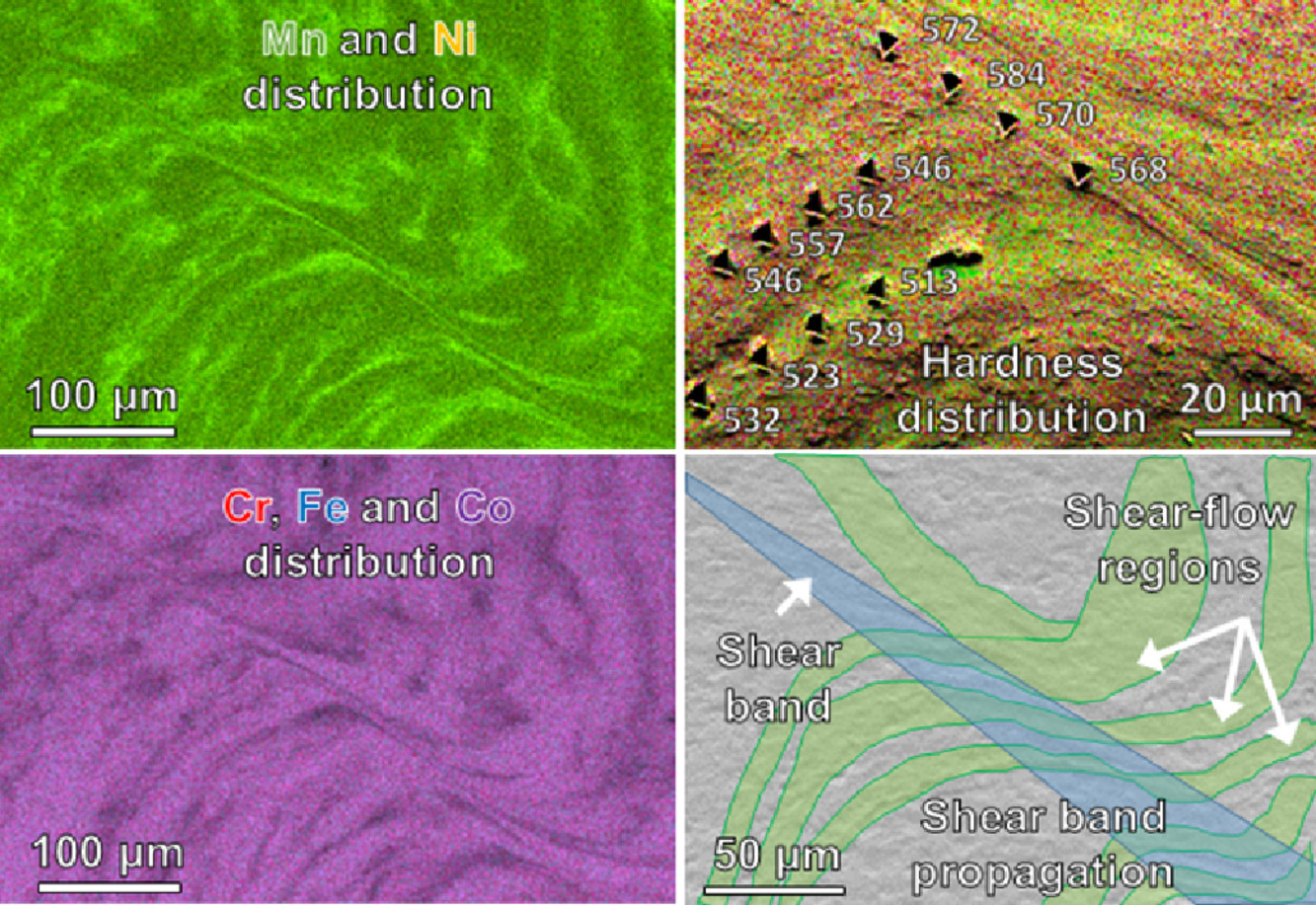
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P97-102
10. Distribution of transition metal elements in an Al-Si-Cu-based alloy
Al-Si-Cu基合金中过渡金属元素的分布
Qianying Shi✉, Yang Huo, Tracy Berman, Bita Ghaffari, Mei Li, John Allison
Qianying Shi: shiqiany@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.034
摘要
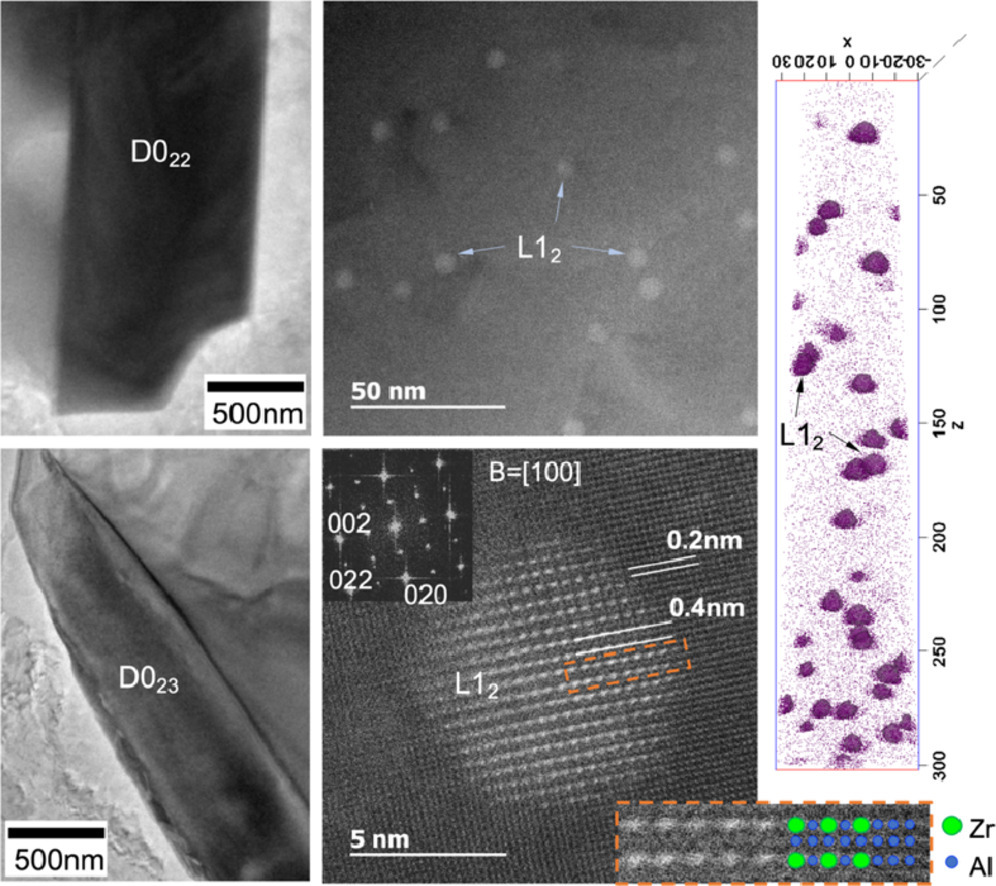
本工作用过渡金属元素Zr,V和Ti对Al-Si-Cu基铸造合金进行了改性,以提高其高温机械性能。我们运用多种微观组织表征技术研究了这些过渡金属元素的凝固偏析行为以及它们在初生金属间化合物相和次生析出中的配分。结果表明三种过渡金属元素以不同程度偏析到枝晶中心。富含不同量过渡金属元素的两个初生金属间化合物相被确定为D022和D023相。我们观察到Zr在纳米尺寸的次生L12析出相中的富集程度远高于V和Ti,次生L12析出相是在凝固后热处理过程中形成的。
英文摘要
An Al-Si-Cu-based cast alloy was modified with transition metal elements Zr, V and Ti to achieve enhanced mechanical performance at elevated temperatures. Multiple microstructural characterization techniques were used to investigate the solidification segregation behavior of these transition metal elements and their partitioning to the primary intermetallic phases and secondary precipitates. Three transition metal elements were shown to segregate into the dendrite center to varying degrees. Two primary intermetallic phases enriched with different amounts of transition metal elements were identified as D022 and D023 phases. Zr was observed to concentrate much more than V and Ti in the nano-size secondary L12 precipitates, which formed in the matrix during post-solidification heat treatment.
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P108-112
11. Hydrogen-enhanced densified twinning (HEDT) in a twinning-induced plasticity (TWIP) steel
孪晶诱导塑性(TWIP)钢中氢增密孪晶(HEDT)
Cheng Zhang, Huihui Zhi, Stoichko Antonov, Lin Chen, Yanjing Su✉
Yanjing Su: yjsu@ustb.edu.cn,北京科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.047
摘要
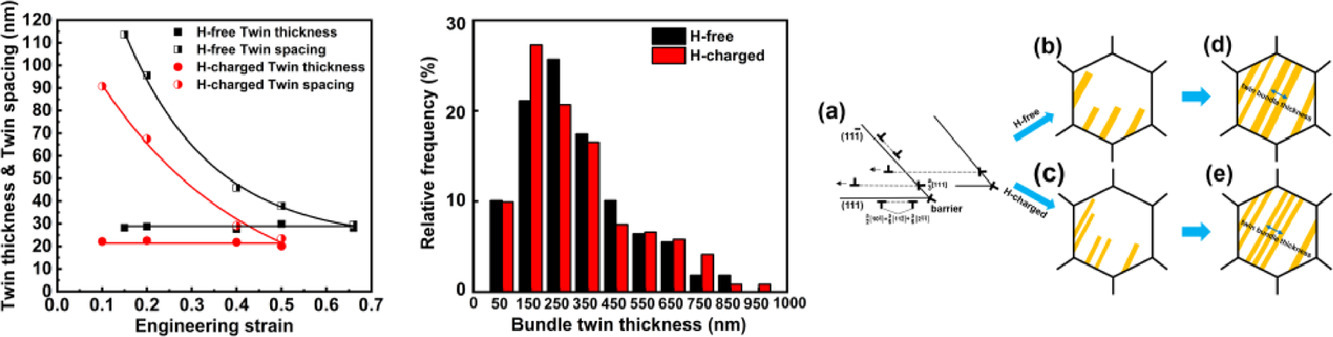
本工作研究了不同应变水平下氢对孪晶诱导塑性(TWIP)奥氏体钢孪晶演化的影响。与无氢条件相比,氢的存在降低了孪晶束的厚度,增加了单个孪晶束的密度。这一机理首次被报道,称为氢增密孪晶(HEDT)。基于实验观察,从成核、生长和稳定性三个阶段分析了氢对孪晶的影响。HEDT可以提高局部应力,从而显著影响TWIP钢的氢脆。
英文摘要
The effect of hydrogen on the twinning evolution in a twinning-induced plasticity (TWIP) austenitic steel was investigated at different strain levels. The presence of hydrogen decreased the twin thickness and increased the twin density in individual twin bundles, in comparison with the hydrogen-free condition. This mechanism, reported for the first time, was termed hydrogen-enhanced densified twinning (HEDT). Based on these experimental observations, the effect of hydrogen on twinning was analyzed from the three stages of nucleation, growth and stability. HEDT may elevate the local stress, and thus significantly affect the hydrogen embrittlement (HE) of TWIP steels.
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P113-117
12. Onset of detwinning in Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy: A synchrotron-based X-ray diffraction study
Mg-3Al-1Zn合金去孪晶的发生:基于同步辐射的X射线衍射研究
N.B. Zhang, Y.Y. Zhang, S. Chen, B.B. Zhang, Z.L. Li, H.L. Xie, L. Lu✉, X.H. Yao✉, S.N. Luo
X.H. Yao: yaoxh@scut.edu.cn,华南理工大学
L. Lu: llu@swjtu.edu.cn,西南交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.044
摘要
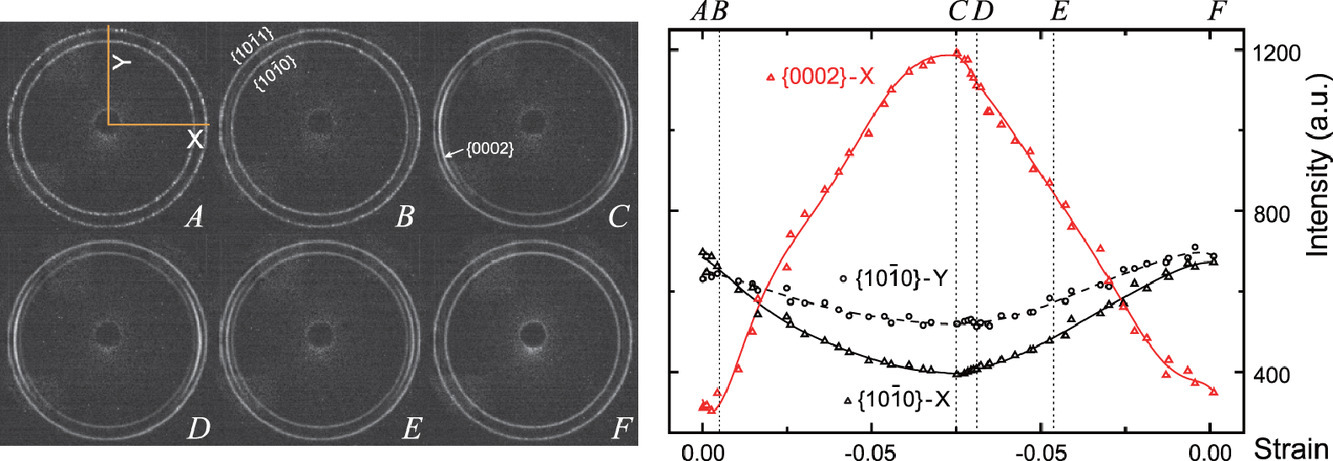
我们采用原位同步辐射X射线衍射技术研究了连续加载条件下镁合金Mg-3Al-1Zn的去孪晶的发生过程。我们研究了平行于c轴纤维的拉伸和垂直于c轴纤维的压缩所诱发的{101-2}扩展孪晶的去孪晶过程。实验结果表明,无论平行于c轴纤维的拉伸还是垂直于c轴纤维的压缩,均会使{101-2}扩展孪晶在卸载后立即发生去孪晶。
英文摘要
We investigate the onset of detwinning in magnesium alloy Mg-3Al-1Zn under continuous loading with real-time in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction. Detwinning of the {101-2} extension twins activated both by tension parallel to and compression perpendicular to the c-axis fibers is explored. The experimental results reveal that detwinning of the {101-2} extension twins occurs immediately upon unloading, regardless of whether the twins are activated by tension parallel to or compression perpendicular to the c-axis fibers.
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P121-125
13. Dislocation networks in gamma/gamma’-microstructures formed during selective laser melting of a Ni-base superalloy
镍基高温合金选择性激光熔化过程中形成的γ/γ′微观组织中的位错网络
L. Heep✉, C. Schwalbe, C. Heinze, A. Dlouhy, C.M.F. Rae, G. Eggeler
L. Heep: larissa.heep@rub.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.019
摘要
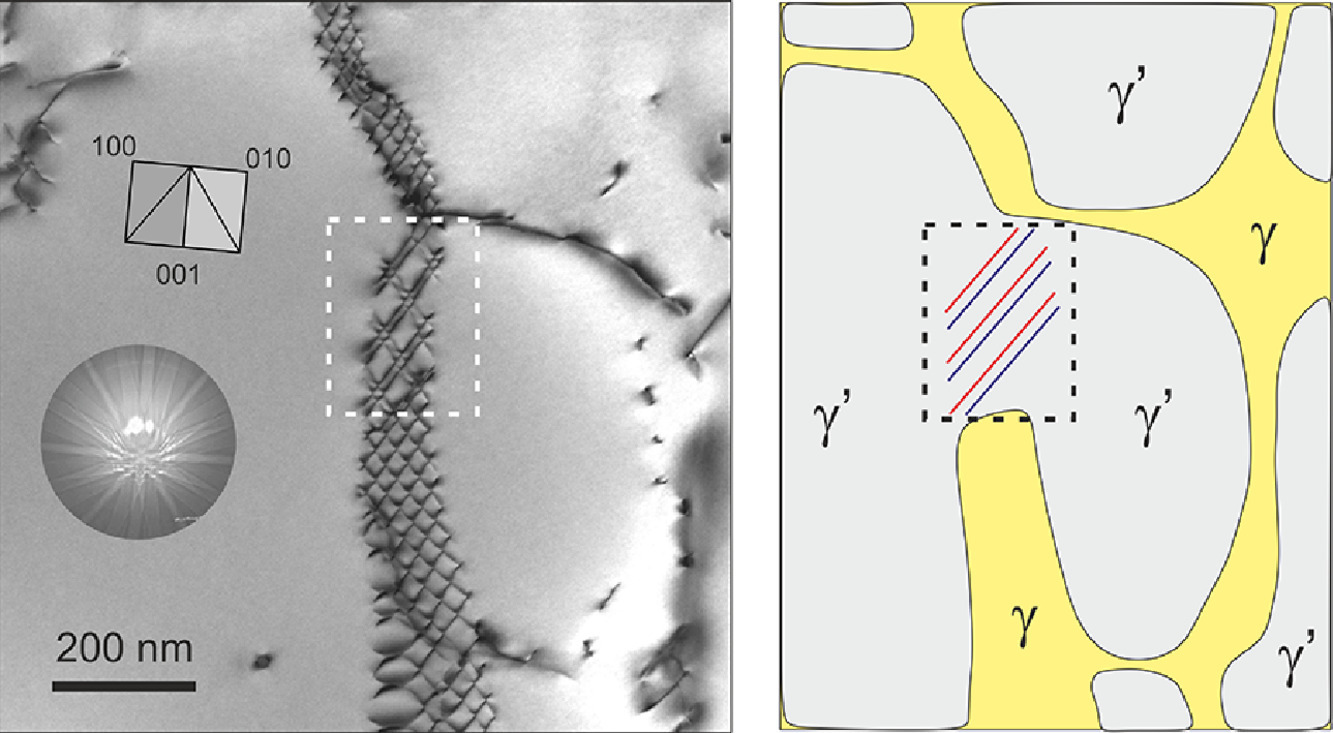
我们使用扫描透射电子显微镜(STEM)分析了镍基高温合金在选择性激光熔化(SLM)过程中形成的位错网络。该网络横贯两个相邻的γ固溶体区域之间的有序γ′相域。当两个γ相粒子开始聚结时就形成了γ′相区,将位错网络捕获在该有序区域中,从而形成了两个具有耦合超级不全位错的反相界(APB)对的位错族。本工作介绍了位错网络的特征,并讨论了以前未报告的反常特征(扭转特性和低的反相界能)。
英文摘要
A dislocation network which formed during selective laser melting (SLM) of a Ni-base superalloy was analyzed using scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). This network traverses an ordered Gamma'-phase domain, in between two adjacent Gamma-solid solution regions. The Gamma’-phase region has formed when two Gamma’-phase particles have started to coalesce, trapping the dislocation network in this ordered region so that it formed two dislocation families with pairs of anti-phase boundary (APB) coupled super partial dislocations. The network features are presented and unusual features (twist character and low APB energies), not previously reported, are discussed.
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P131-135
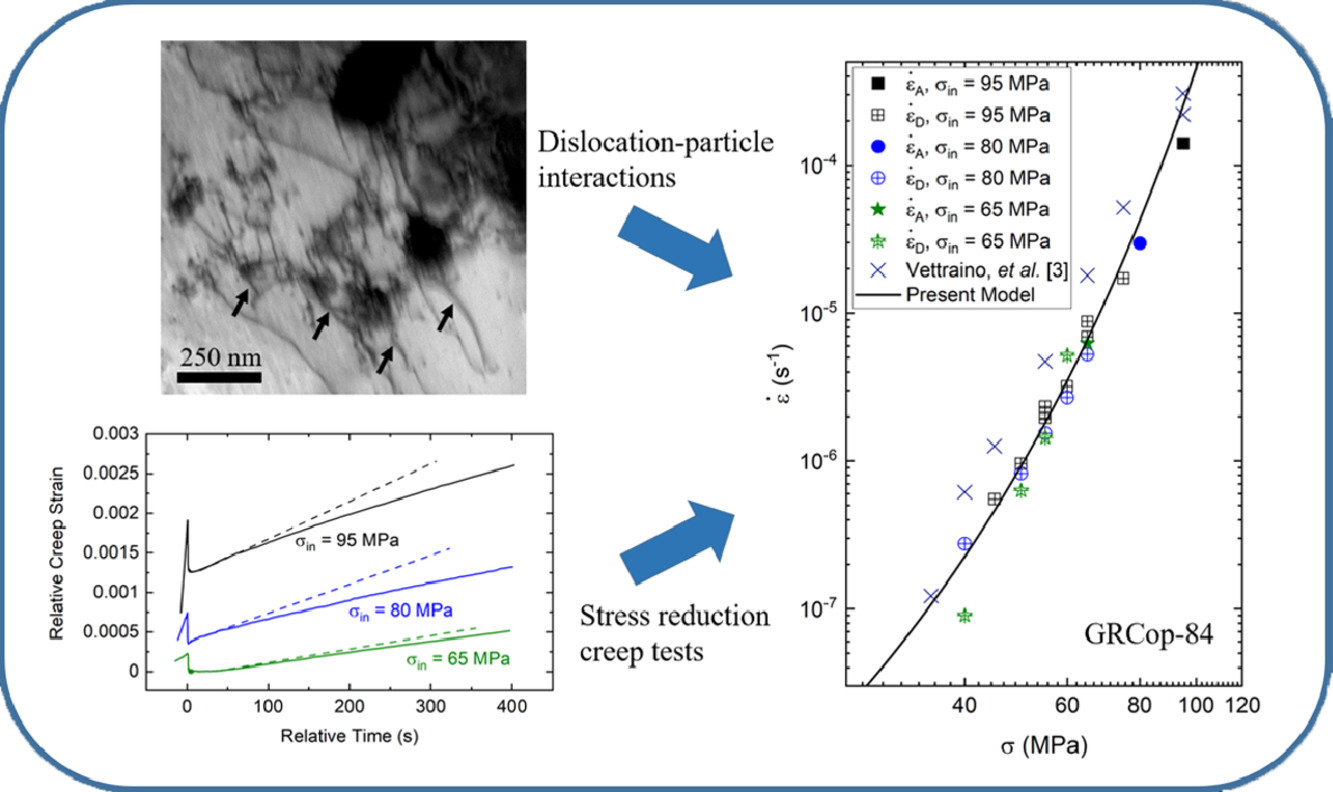
14. Understanding creep mechanisms of a Cu-Cr-Nb alloy by testing under constant structure conditions
在恒定结构条件试验下,理解Cu-Cr-Nb合金的蠕变机理
M. Zhang, J.C. Gibeling✉
J.C. Gibeling: jcgibeling@ucdavis.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.036
摘要
Cu-Cr-Nb合金(GRCop-84)在923 K下进行的应力降低蠕变测试表明,局部位错攀移是速率控制的变形机制。经测量,蠕变的激活能与铜基体自扩散的激活能一致。实验确定了大约-9 MPa的内部背应力可作用于速率控制的位错,而这是位错-颗粒交互作用的背应力与位错-位错交互作用的正应力之和。然而,这种背应力在热激活位错运动的机制内,不会导致真正的阈值。
英文摘要
Stress reduction creep tests conducted on a Cu-Cr-Nb alloy (GRCop-84) at 923 K have confirmed local dislocation climb to be the rate-controlling deformation mechanism. The activation energy of creep was measured to be consistent with that of self-diffusion in Cu matrix. An internal back stress of approximately -9 MPa was identified to act on the rate-controlling dislocations, which is believed to be the sum of the back stress for dislocation-particle interaction and the forward stress for dislocation-dislocation interaction. This back stress, however, does not lead to a true threshold in the framework of thermally activated dislocation motion.
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P141-146
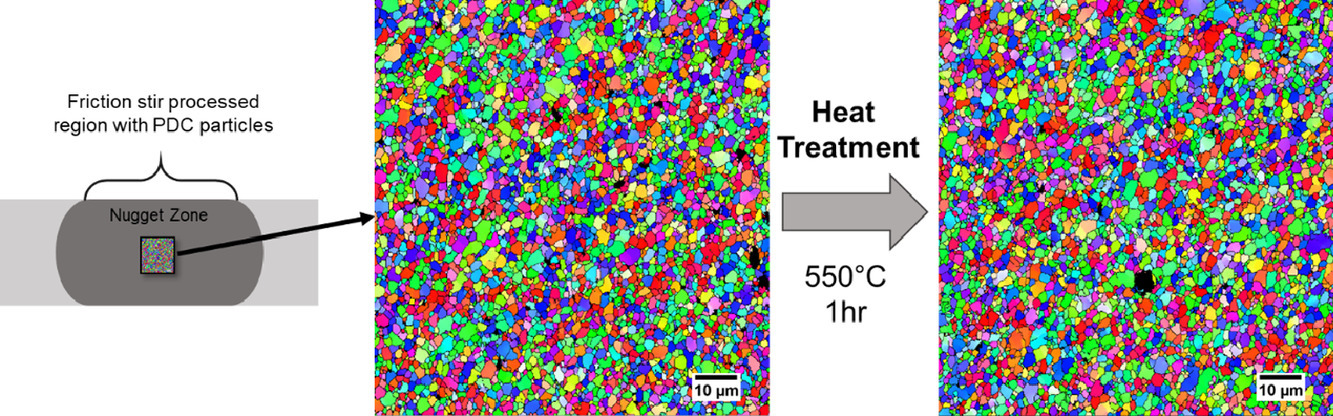
15. Imparting high-temperature grain stability to an Al-Mg alloy
铝镁合金的高温晶粒稳定性
Abhishek Pariyar✉, Laszlo S. Toth, Satish V. Kailas, Laurent Peltier
Abhishek Pariyar: abhishekp@iisc.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.035
摘要
铝合金尽管具有优异的强度重量比,但由于晶粒长大和析出相粗化导致的微观组织不稳定性,导致高温下其强度急剧下降,因而不能在高温下使用。本工作中,我们试图通过在铝镁合金中引入原位形成的聚合物衍生陶瓷来解决晶粒长大的问题。由于Zener机理下颗粒对晶界的钉扎作用,铝合金在450℃和550℃下暴露1小时,得到了硬度损失最小的晶粒稳定结构。
英文摘要
Al alloys, despite their excellent strength-to-weight ratio, cannot be used at elevated temperatures because of microstructural instability owing to grain growth and precipitate coarsening, thus, leading to a drastic loss in their strength. In this work, we have attempted to address the issue of grain growth by introducing in-situ formed polymer derived ceramics in an Al-Mg alloy. A stable grain structure with minimal loss in hardness when exposed to 450°C and 550°C for 1 hour was obtained due to the particle pinning of the grain boundaries by the Zener mechanism.
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P158-162
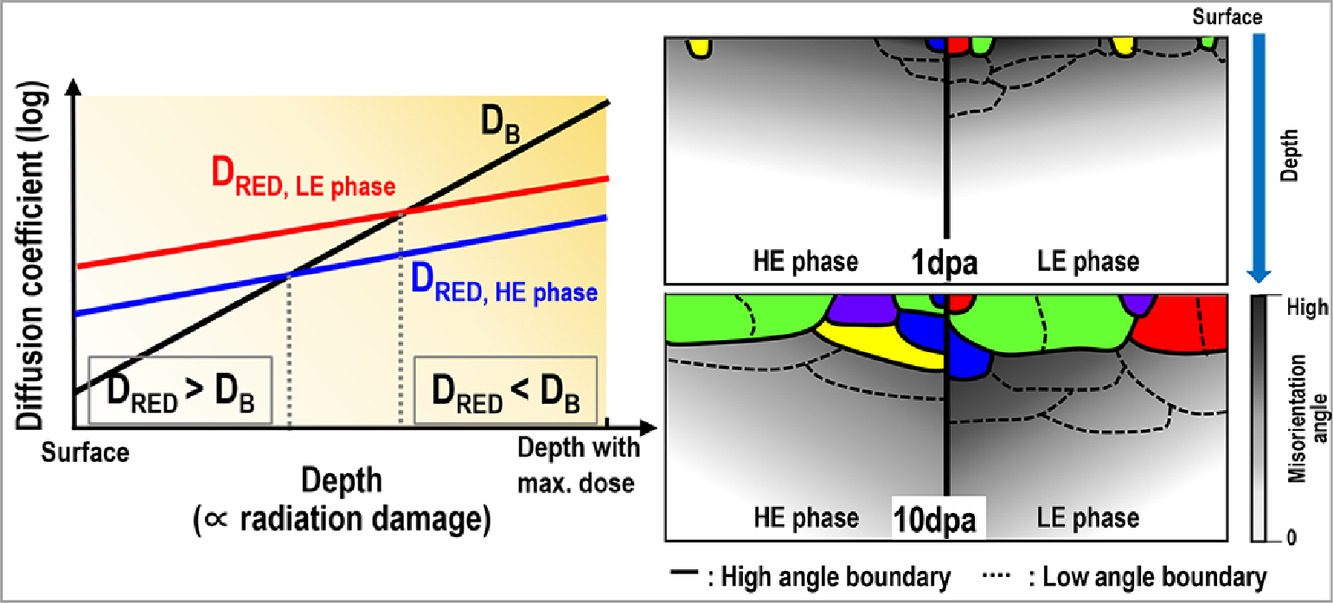
16. Suppressed radiation-induced dynamic recrystallization in CrFeCoNiCu high-entropy alloy
在CrFeCoNiCu高熵合金中抑制辐射诱导动态再结晶
Jinyeon Kim, Jong Wook Lim, Joon Kon Kim, Do Hyang Kim, Eun SooPark✉, Hye Jung Chang✉
Eun SooPark: espark@snu.ac.kr
Hye Jung Chang: almacore@kist.re.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.045
摘要
本工作在CrFeCoNiCu高熵合金中通过进动电子衍射技术获得了辐照诱导再结晶和多边形化的图案。该取向图使可视化深度依赖的再结晶现象一目了然,并揭示了辐照剂量和材料熵的影响。不连续的动态再结晶优先发生在辐照剂量低的表面附近,但是主要发生辐射增强的扩散,造成了室温下的位错攀移。有趣的是,在具有相对较低的层错能的高熵相中,由于和低熵相比具有较低的储能和晶界扩散率,不连续动态再结晶得到抑制。
英文摘要
We report a map of irradiation-induced recrystallization and polygonization in a CrFeCoNiCu high-entropy alloy obtained by a precession electron diffraction technique. This orientation map enables the visualization of depth-dependent recrystallization at a glance and reveals the effects of irradiation dose and material entropy. Discontinuous dynamic recrystallization preferentially occurs near the surface, where the irradiation dose is low, but radiation-enhanced diffusion dominantly occurs leading to dislocation climb even at room temperature. Interestingly, in the high-entropy phase with a relatively low stacking fault energy, discontinuous dynamic recrystallizastion is suppressed due to the lower stored energy and grain boundary diffusivity compared low-entropy one.
SCRIPTA Vol. 190, Jan. 2021, P179-182
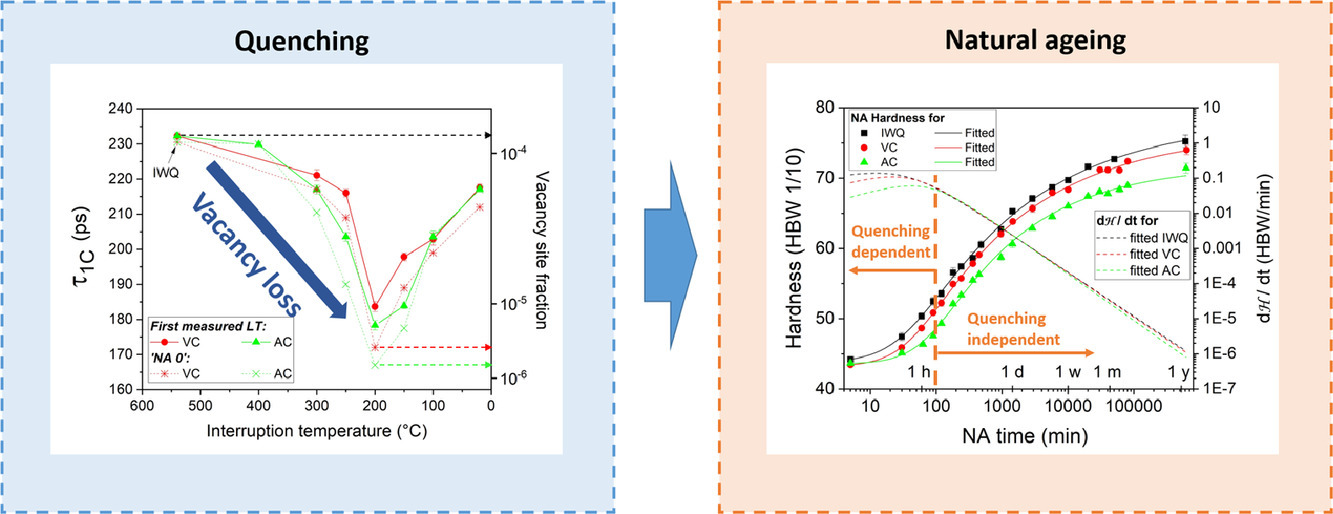
17. Natural ageing clustering under different quenching conditions in an Al-Mg-Si alloy
Al-Mg-Si合金在不同淬火条件下的自然时效团簇
Zi Yang✉, Xiaohe Jiang, Xingpu Zhang, Meng Liu, Zeqin Liang, David Leyvraz, John Banhart
Zi Yang: zi.yang@helmholtz-berlin.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.046
摘要
在铝合金从固溶温度淬火的过程中,空位部分保留为多余的空位,部分丢失至空位“渊”,确切的分数取决于冷却速率。中断淬火实验中样品的正电子寿命测量结果表明,冷却至200℃时空位会消失,此后至20℃溶质原子开始形成团簇。慢速冷却导致的多余空位比快速冷却低1-2个数量级。由于淬火空位对于Al-Mg-Si合金的自然时效(NA)至关重要,我们惊奇地发现,不同淬火条件下自然时效硬化动力学之间只存在很小的差异。具体而言,硬化速率仅在初始阶段(<100分钟)不同,此后在长达1年时间的自然时效内,硬化速率几乎相同。这表明空位和早期溶质团簇之间的相互作用有助于均衡不同淬火样品中的自由空位分数。
英文摘要
During quenching of aluminium alloys from the solutionising temperature vacancies are partially conserved as excess vacancies, partially lost to vacancy sinks, the exact fractions depending on the cooling rate. Positron lifetime measurements in samples from interrupted quenching experiments reveal that vacancies are lost during cooling down to 200 °C, after which solute atoms start to form clusters down to 20 °C. Slow cooling leads to 1 to 2 orders of magnitude lower excess vacancies than fast cooling. Since quenched-in vacancies are crucial for natural ageing (NA) in Al-Mg-Si alloys it is surprising to find just small differences between the NA hardening kinetics after different quenches. Specifically, hardening rates differ only in the initial stage (<100 min), after which they are almost identical for NA up to ~1 year. This suggests that interactions between vacancies and early-stage solute clusters help equalising the free vacancy fractions in differently quenched samples.
微信公众号:Goal Science
投稿邮箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
