金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.199,15 Oct. 2020(下)
2020-10-21 来源:Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文17篇,涵盖了电工钢、中熵合金、镍合金、3D打印、高熵合金、锆合金、钛合金、316L不锈钢等,国内科研单位包括华东交通大学、东北大学、南方科技大学、上海交通大学、上海大学、中南大学、北京理工大学、北京大学、重庆大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 199 目录
ACTA Vol. 199,15 Oct. 2020, P311-325
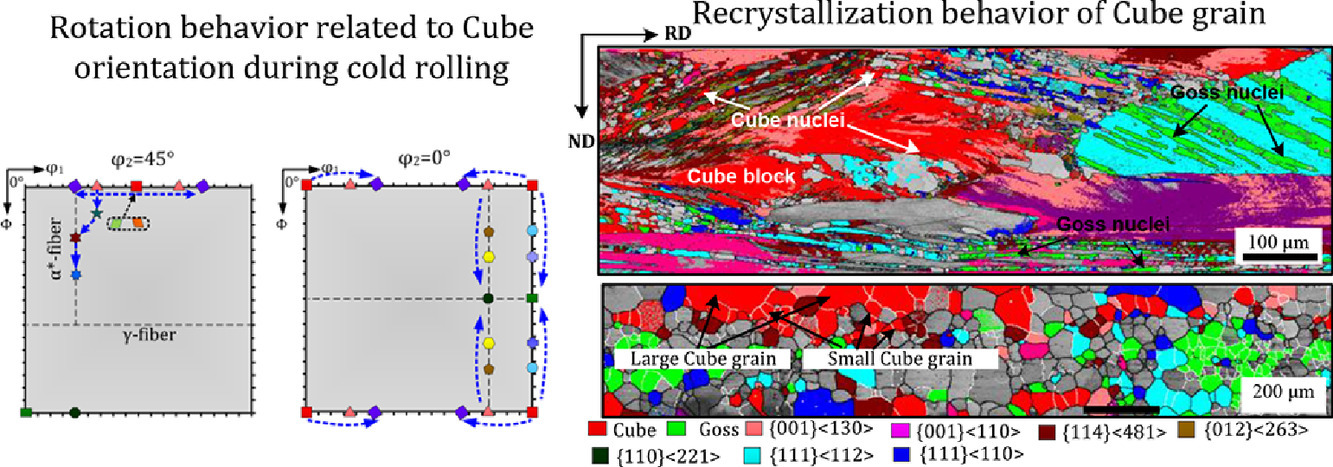
18. Texture evolution in twin-roll strip cast non-oriented electrical steel with strong Cube and Goss texture
具有强立方和高斯织构的双辊轧制无取向电工钢的织构演变
Haitao Jiao✉, Yunbo Xu✉, Longzhi Zhao✉, R.D.K. Misra, Yanchuan Tang, Dejia Liu, Yong Hu, Mingjuan Zhao, Mingxue Shen
H. Jiao:andrewjiao@163.com,华东交通大学/东北大学
Y. Xu:yunbo_xu@126.com,东北大学
L. Zhao:zhaolongzhi@163.com,华东交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.048
摘要
提高<100>//ND织构是制备高效无取向电工钢的关键。本研究通过新型双辊带钢连铸、冷轧和退火工艺成功地制备出了具有强立方织构({100}<001>)和高斯织构({110}<001>)的Fe-1.3 Si wt% 钢。我们使用光学显微镜、电子背散射衍射(EBSD)和X射线衍射(XRD)对材料的组织和织构进行了表征,从特定取向晶粒的变形和再结晶角度阐述了织构的形成机理。在冷轧过程中,晶粒除了向{001}<130>-{001}<120>方向旋转外,还向{013}<031>-{110}<110>方向旋转。此外,变形后的{115}<051>-{115}<161>晶粒中形成了新的立方变形带。重度冷轧后,保留下的立方织构部分成大块状、小条带状或微晶,立方变形结构成为新立方晶的形核位点。此外,{114}<110>、{112}<110>和{111}<112>基体中的剪切带也提供了一些立方形核位点。立方晶粒和高斯晶粒生长过程中,晶粒形貌由近棒状转变为等轴状。定向形核、定向钉扎和尺寸效应导致了再结晶织构的形成。较低的厚度和具有强{100}织构的粗大凝固组织是无取向电工钢铸带获得强立方织构和高斯织构的决定性因素。
英文摘要
Increasing magnetically favorable <100>//ND texture components is a key challenge in the preparation of high-efficiency non-oriented electrical steels. In this study, an Fe-1.3 wt% Si steel with strong Cube ({100}<001>) and Goss ({110}<001>) texture was successfully produced by novel twin-roll strip casting, cold rolling and annealing process. The microstructure and texture of the material was characterized by optical microscopy, electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The origin and formation mechanism of texture are described from the perspective of deformation and recrystallization behavior of specifically oriented grains. It was observed that initial Cube rotated toward {013}<031>-{110}<110> besides rotation toward {001}<130>-{001}<120> during cold rolling. In addition, new Cube deformation bands were developed in the deformed {115}<051>-{115}<161> grains. Cube components were partly retained as large block, small band structure and crystallite after heavy cold rolling. The Cube deformation structures served as nucleation sites of new Cube grains. The shear band within {114}<110>, {112}<110> and {111}<112> matrix also provided some Cube nuclei. Morphology change from near bar-shaped to equiaxed occurred during the growth of Cube and Goss grains. The formation of recrystallization texture is attributed to the oriented nucleation mechanism, and the orientation pinning and size effects that impacted the intensity of texture component. The low thickness of strip and coarse solidification microstructure with strong {100} texture are the decisive factors to obtain strong Cube and Goss texture in strip-cast non-oriented electrical steel.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P326-339
19. Development of a material model for predicting extreme deformation and grain refinement during cold spraying
一种关于冷喷涂过程中极端变形和晶粒细化的预测模型
Qian Wang, Ninshu Ma✉, Makoto Takahashi, Xiaotao Luo, Changjiu Li
N. Ma:ma.ninshu@jwri.osaka-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.052
摘要
基于熔体的增材制造技术,如选区激光熔化、电子束自由成形等,往往会导致晶粒粗大和高孔隙率等问题。而冷喷涂的新技术可以克服这种熔覆引起的缺陷。在本研究中,我们建立了一种位错动力学模型用于描述以下五个纳米尺度的物理现象,即应变硬化、正常范围应变速率硬化、超高应变速率硬化、热软化和晶粒尺寸的演化。Cu粒子冲击试验的结果与模型预测的微粒变形吻合良好,表明模型精度较高。我们建立相应的有限元模型,单独讨论了上述现象的影响,发现材料变形主要由超高应变率硬化控制,而喷涂主要由热软化控制。另外,模拟和实验观测到的晶粒尺寸分布表明,晶粒细化只发生在微粒-基体界面附近(主要在界面边缘)。综上所述,我们的模型可以准确地再现冲击颗粒的动态变形行为,并正确预测晶粒细化(特别是由于动态再结晶)。
英文摘要
Fusion-based additive manufacturing techniques such as selective laser melting, electron beam freeform fabrication cause solidification problems such as grain coarseness and high porosity. As a new technique, cold spraying (CS) can overcome such melting-induced drawbacks. In this study, a material model using dislocation dynamics was developed specifically for the CS process for describing the following five nanosecond-scale physical phenomena: strain hardening, normal-range strain rate hardening, ultra-high strain rate hardening, thermal softening and grain size evolution. A single Cu microparticle impact test was conducted, and a good agreement between experimental and model-predicted microparticle deformations was observed, indicating high model accuracy. The corresponding finite element model was established, and the individual effects of the above phenomena were discussed in detail to show that material deformation is mainly controlled by ultra-high strain rate hardening while jetting is controlled by thermal softening. Additionally, both simulated and actual grain size distributions indicated that grain refinement occurs only near the microparticle-substrate interface (mainly at the interface edge). Thus, the newly developed model could accurately reproduce the dynamic deformation behaviors of impacting particles and correctly predict grain refinement (particularly due to dynamic recrystallization).

ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P340-351
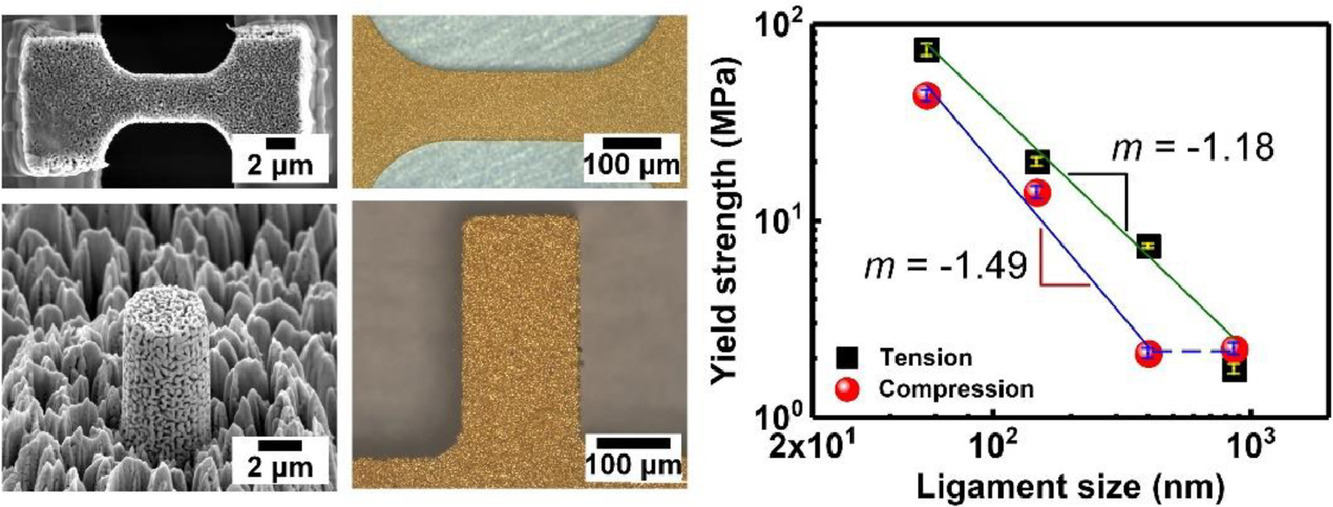
20. Tension-compression asymmetry in plasticity of nanoporous gold
纳米多孔金的拉伸-压缩塑性不对称
Hansol Jeon, Sukbin Lee✉, Ju-Young Kim✉
S. Lee:sukbinlee@unist.ac.kr
J.-Y. Kim:juyoung@unist.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.054
摘要
我们对4个纳米多孔金样品进行了拉伸和压缩试验,这些样品的韧性带尺寸分别为56、149、402和868 nm,所有样品中均没有晶界且韧性带数量相近。我们发现,当韧性带尺寸为402 nm时,拉伸屈服强度大于压缩屈服强度,而韧性带尺寸为868 nm时,拉伸和压缩屈服强度相当。尺寸效应指数-1.18可以很好地描述拉伸屈服强度与韧带尺寸之间的关系;而对于大于402 nm的韧性带结构样品,则在压缩时表现出类似块体的行为,即强度与韧性带尺寸无关。尺寸效应指数-1.49可以很好地描述韧性带尺寸52-402nm样品压缩屈服强度与韧带尺寸之间的关系。我们基于开放胞模型和位错活动,从单个韧性带的变形行为出发,对拉伸和压缩之间屈服强度和塑性的不对称性进行了讨论。
英文摘要
Tensile and compressive tests are carried out on four nanoporous gold samples with ligament sizes of 56, 149, 402, and 868 nm, all without grain boundaries and with similar number of ligaments regardless of ligament size. We find that tensile yield strengths are greater than compressive yield strengths up to ligament size of 402 nm, while yield strengths are similar in tension and compression for dL of 868 nm. The dependence of tensile yield strength on ligament size is described well using a size-effect exponent -1.18 for four samples, whereas bulk-like behavior, i.e. no ligament-size dependency, is observed for ligament size greater than 402 nm in compression; compressive yield strength depending on ligament size is described by a size-effect exponent -1.49 for ligament sizes ranging from 56 nm to 402 nm. The asymmetries in yield strength and plasticity between tension and compression are discussed in terms of the deformation behavior of individual ligaments based on a suggested open-cell model and dislocation activities in the ligaments.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P352-369
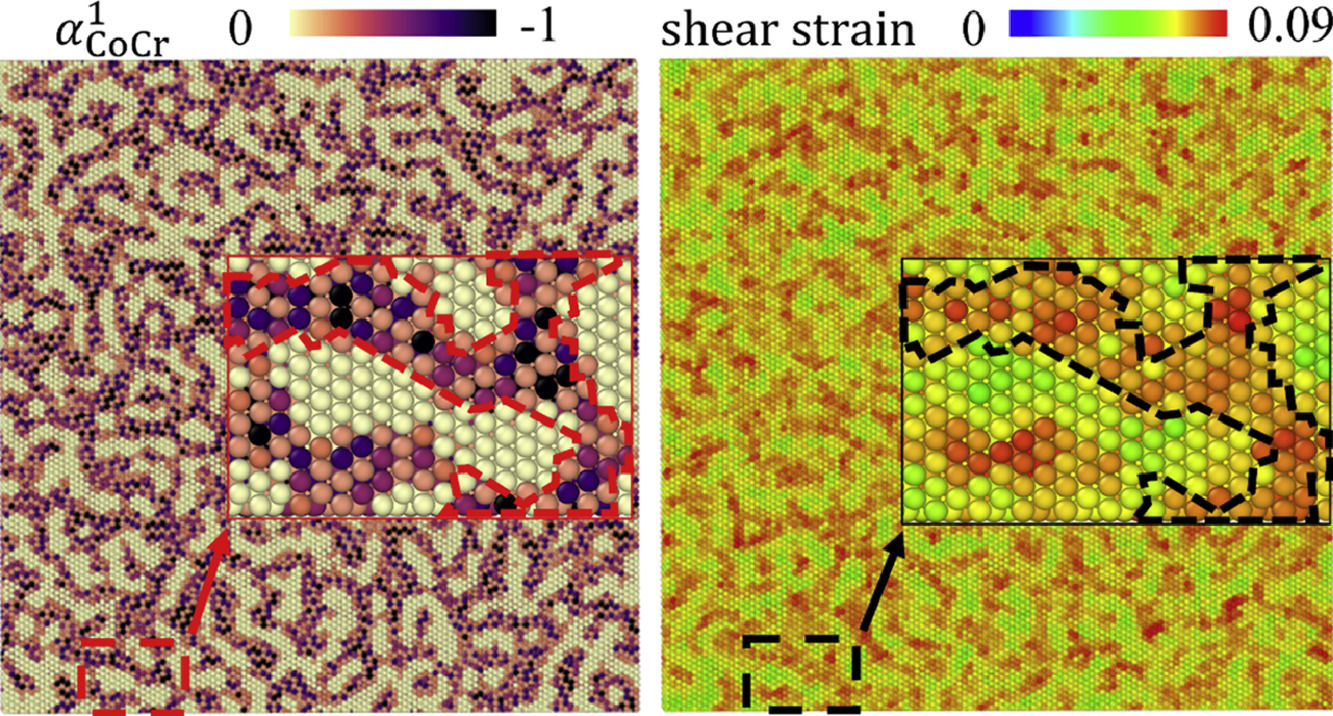
21. Effects of lattice distortion and chemical short-range order on the mechanisms of deformation in medium entropy alloy CoCrNi
晶格畸变和化学短程有序对CoCrNi中熵合金变形机理的影响
Wu-Rong Jian✉, Zhuocheng Xie, Shuozhi Xu, Yanqing Su, Xiaohu Yao✉,Irene J. Beyerlein
W.-R. Jian:wurong@ucsb.edu, yaoxh@scut.edu.cn
X. Yao:yaoxh@scut.edu.cn,南方科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.044
摘要
随着对中熵及高熵合金的研究不断深入,这类合金各种独特的性能被不断发掘。有关这些复杂合金中成分的涨落对性能的影响也越来越受到关注。在本研究中,我们结合了大规模分子动力学(MD),蒙特卡罗模拟和晶体缺陷分析等多种方法,研究了晶格畸变(LD)和化学短程有序(CSRO)对单晶和纳米晶CoCrNi中熵合金(MEA)在应变状态下,位错和孪晶形核和演化的影响。我们假设了一种与CoCrNi合金具有相同体积特征但没有LD和CSRO的纯A原子合金,通过比较两者在应变下的响应,阐明了LD和CSRO的影响。分析结果表明,材料的屈服强度是由肖克利分位错形核所需应变决定的,LD会降低该应变,而CSRO则会增加该应变。我们发现,尽管分位错倾向于在CoCr团簇附近形核,但无论其尺寸如何,随着CSRO的增加,它们都越来越难以扩展和增殖。发生屈服后,由于LD和CSRO对滑移的阻碍作用,促进了纳米孪晶通过可动肖克利分位错的形核。
英文摘要
As the numbers of medium- to high-entropy alloys being studied and impressive structural properties they exhibit increase rapidly, questions regarding the role played by their complex chemical fluctuations rise concomitantly. Here, using a combination of large-scale molecular dynamics (MD), a hybrid MD and Monte-Carlo simulation method, and crystal defect analysis, we investigate the role lattice distortion (LD) and chemical short-range order (CSRO) play in the nucleation and evolution of dislocations and nanotwins with straining in single crystal and nanocrystalline CoCrNi, a medium entropy alloy (MEA). LD and CSRO effects are elucidated by comparisons with responses from a hypothetical pure A-atom alloy, which bears the same bulk properties of the nominal MEA but no LD and no CSRO. The analysis reveals that yield strengths are determined by the strain to nucleate Shockley partial dislocations, and LD lowers this strain, while higher degrees of CSRO increase it. We show that while these partials prefer to nucleate in the CoCr clusters, regardless of their size, they find it increasingly difficult to propagate away from these sites as the level of CSRO increases. After yield, nanotwin nucleation occurs via reactions of mobile Shockley partials and is promoted in MEAs, due to the enhanced glide resistance resulting from LD and CSRO.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P370-382
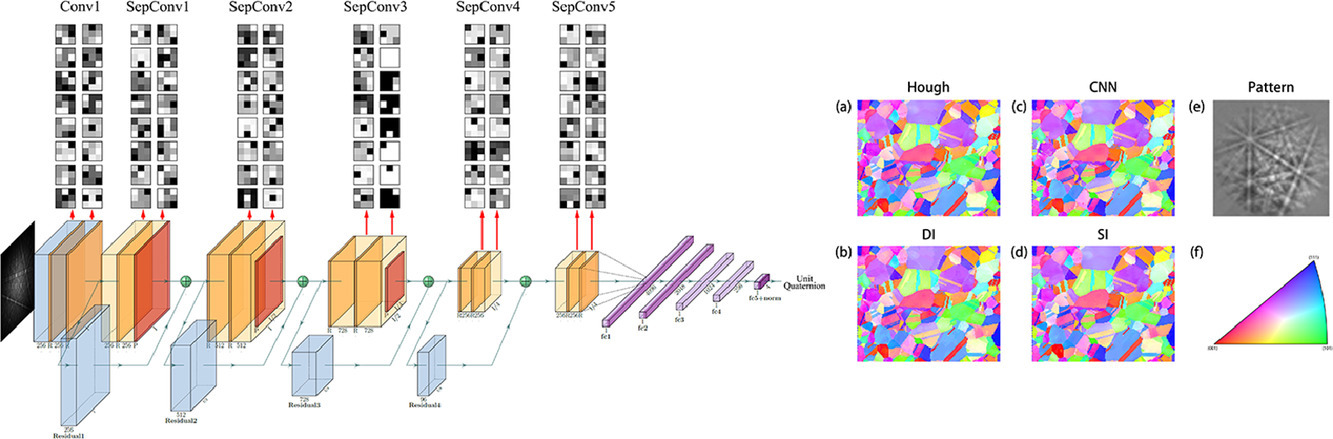
22. Indexing of electron back-scatter diffraction patterns using a convolutional neural network
利用卷积神经网络标定电子背散射衍射花样
Z. Ding✉, E. Pascal✉, M. De Graef✉
Z. Ding:zihaod@andrew.cmu.edu
E. Pascal:epascal@andrew.cmu.edu
M. De Graef:degraef@cmu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.046
摘要
EBSD图样的准确标定一直是一个材料表征过程中具有挑战性的问题。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新的卷积神经网络(EBSD- CNN)方法,对EBSD图样进行实时标定。我们通过向标准卷积神经网络中引入了一个错配损失函数实现了这一目标。我们通过模拟和实验数据对该方法的标定准确率、速度和抗噪能力进行了评估,并与其他标定方法进行了比较。结果表明,CNN与目前已经商业化的基于Hough转换的标定方法相比,准确率和速度相当,并有望实现替代。我们通过可视化所选择的过滤器来了解网络功能。此外,我们也通过对特征选择的可视化对神经网络的功能特征进行了进一步探究。
英文摘要
Accurate indexing of EBSD patterns presents a challenging problem. We propose a new convolutional neural network (EBSD-CNN) to realize real-time indexing of EBSD patterns; we implement a disorientation loss function to adapt a standard CNN model for crystallographic orientation indexing. The indexing accuracy, rate, and robustness against noise are evaluated using both simulated and experimental data, and compared with other indexing methods (Hough-based indexing, dictionary indexing, and spherical indexing). The results suggest that a CNN can provide an alternative to commercial Hough-transform-based indexing with comparative accuracy and rate. We obtain insight into the network functionality by visualization of selected filters.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P383-396
23. Control of microstructure using magnetic fields and study of the mechanical behavior of Ni-rich Ni-Mn-Ga alloys
富镍Ni-Mn-Ga合金的磁场组织控制和力学行为研究
Long Hou, Yanchao Dai, Yves Fautrelle, Zongbin Li, Zhongming Ren, Xi Li✉
X. Li:lx_net@sina.com,上海交通大学&上海大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.055
摘要
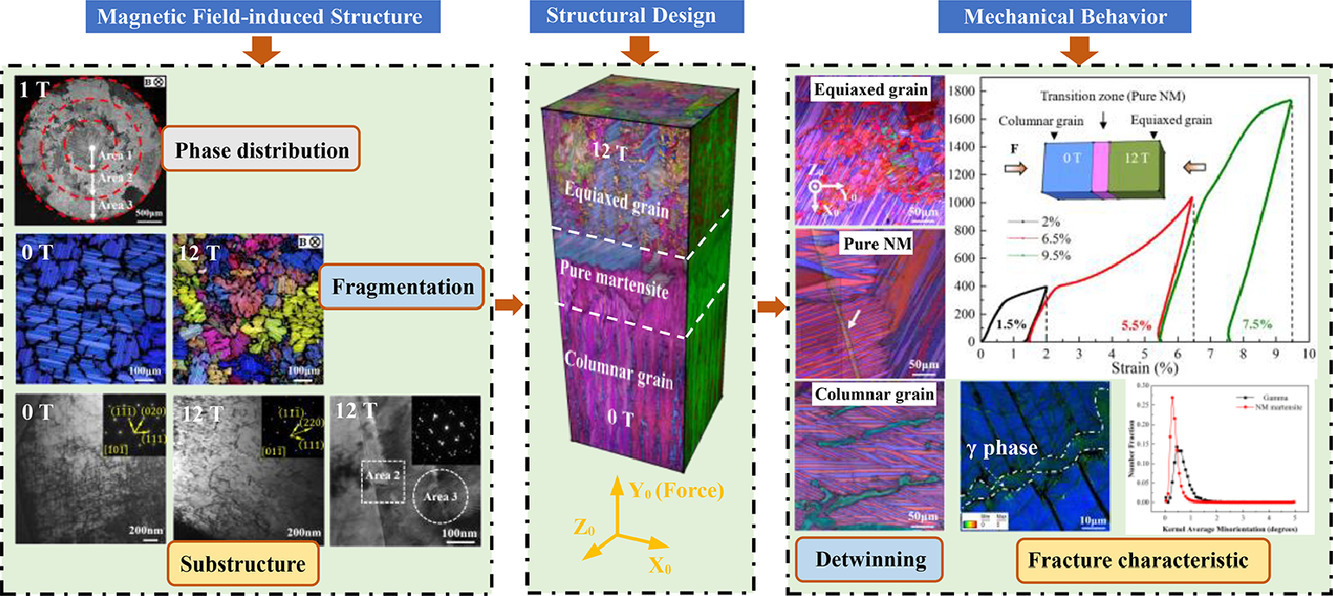
我们通过实验研究了轴向磁场对定向凝固镍锰镓合金组织的影响。研究发现,在磁场作用下,会出现γ相的径向梯度分布以及马氏体/γ相的晶粒破碎。事实上,在弱磁场(B≤2 T)下,可以观测到马氏体区、马氏体/γ相胞和共晶混合区。而在强磁场(B≥4 T)下,则会发生马氏体/γ相的晶粒破碎。此外,强磁场的应用会引起马氏体的结构畸变和γ相内部的位错重排。基与以上结果,我们利用磁场辅助定向凝固技术成功地制备了具有柱状和等轴晶的独特样品。随后,我们研究了Ni-Mn-Ga样品在压缩载荷作用下的力学行为和脱孪演变,并提出了一个基于施密德因子和变形梯度张量的通用判据来解释压缩应力诱导的脱孪演化。γ相显著提高了柱状晶和等轴晶的力学性能。特别是,γ相的随机分布更利于阻碍断裂,导致多晶Ni-Mn-Ga试样压缩应变增大。这项工作突出了磁场对材料组织的影响,并为含γ相的Ni-Mn-Ga合金的脱孪机制提供了更加深入的理解。
英文摘要
In the present work, the influence of an axial magnetic field on the structure of directionally solidified Ni-Mn-Ga alloys is investigated experimentally. It has been found that a radial graded distribution of the gamma (γ) phase and grain fragmentation of the martensite/γ phase can occur under a magnetic field. Indeed, the structures, including a single martensite zone and martensite/γ phase cellular and eutectic mixed zones, are seen under a weak magnetic field (B ≤ 2 T). Under a strong magnetic field (B ≥ 4 T), the grain fragmentation of the martensite/γ phase occurs. Moreover, the application of a strong magnetic field induces a structural distortion in the martensite and dislocation rearrangement inside the γ phase. On the basis of the above investigation, a unique sample that includes columnar and equiaxed grains was successfully prepared using magnetic-field-assisted directional solidification. Subsequently, the mechanical behavior and detwinning evolution of the Ni-Mn-Ga specimen under compressive loading were studied. A general criterion is proposed to elucidate the compressive-stress-induced detwinning evolution based on the Schmid factor and deformation gradient tensor. The γ phase significantly enhanced the mechanical behavior of both the columnar and equiaxed grain samples. In particular, the random distribution of the γ phase was more prone to hindering fracture, even resulting in a larger compression strain in the polycrystalline Ni-Mn-Ga sample. This work highlights the effect of a magnetic field on the microstructure and also provides an in-depth understanding of the detwinning mechanism in Ni-Mn-Ga alloys containing the γ phase.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P397-412
24. Additively-manufactured anisotropic and isotropic 3D plate-lattice materials for enhanced mechanical performance: Simulations & experiments
基于增材制造方法制备具有优异力学性能的各向异性和各向同性三维平板晶格材料
Shengyu Duan, Weibin Wen✉, Daining Fang✉
W. Wen:wenwbin@126.com,中南大学
D. Fang:fangdn@pku.edu.cn,北京理工大学/北京大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.063
摘要
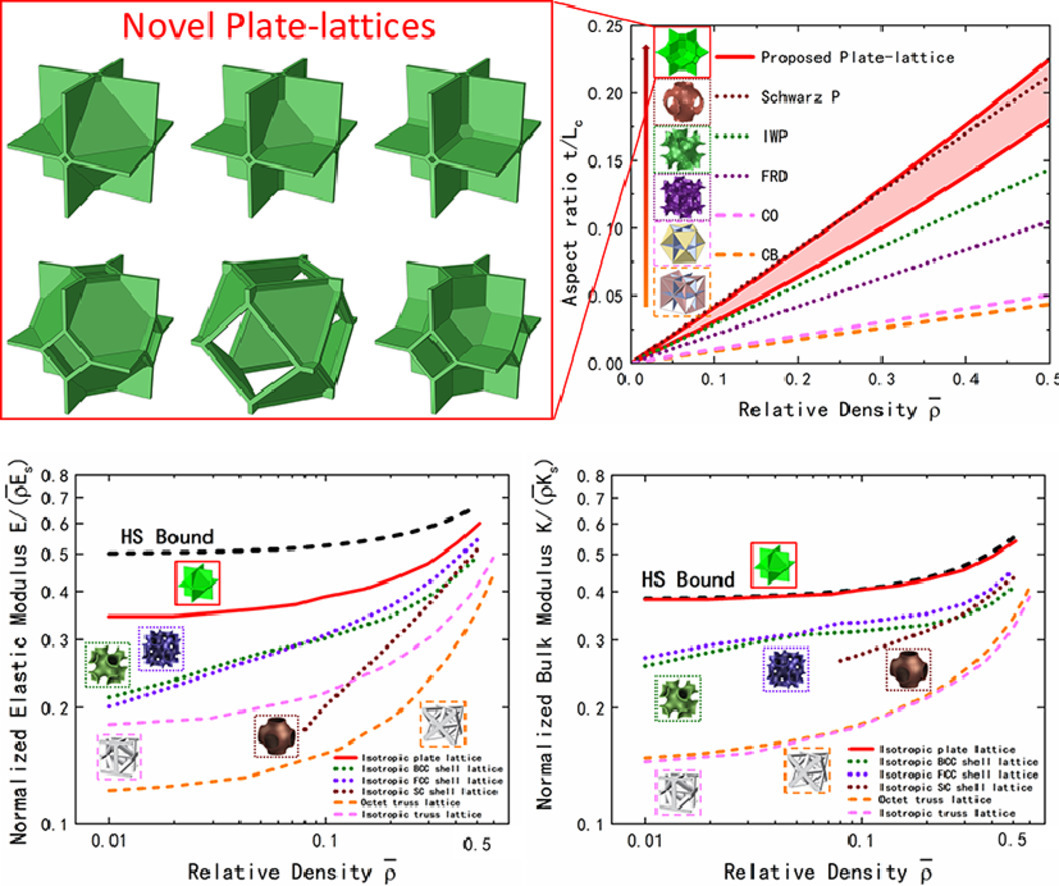
平板晶格是一类具有特殊机械性能的新兴超材料。在此,我们介绍了一种具有特殊力学性能,并且可以通过增材制造进行制备的半开放平板晶格。我们使用数值和实验方法研究了其弹塑性特性和大应变响应。通过对各向异性指数进行精细调,可以在较宽的相对密度范围内实现弹性的各向同性。数值结果表明,各向同性平板晶格的弹性特性明显高于传统拓扑结构,体模量可达到相对密度的Hashin-Shtrikman上界。大应变模拟证明了这种新型的平板晶格具有显著的能量吸收能力。我们通过对各向异性和同性的316 L不锈钢试样进行压缩实验,对数值计算结果进行了验证。综上,本研究提出了一种具有优异的机械性能和增材制造可加工性新型平板晶格,为轻量化超材料的设计提供了新的思路。
英文摘要
Plate-lattices are an emerging category of mechanical metamaterials with exceptional mechanical performance. In this paper, a family of half-open-cell plate-lattices is innovated with exceptional mechanical properties and additive manufacturability. The elastoplastic properties and large strain response of the novel plate-lattices are investigated both numerically and experimentally. Design maps for tailoring the anisotropic index reveal that elastically isotropic plate-lattices can be obtained for a wide range of relative densities. Numerical results reveal that the isotropic plate-lattices exhibit significantly higher elastic properties than other competing topologies such as conventional truss-lattices and isotropic smooth shell-lattices, and their bulk modulus can attain the Hashin-Shtrikman upper bound for all relative densities. Large strain simulations demonstrate the remarkable energy absorption capacity of the novel plate-lattices. The numerical findings are confirmed through the compression experiments on the anisotropic and isotropic stainless steel 316 L specimens manufactured by selective laser melting. This work proposes a novel type of plate-lattices with both exceptional mechanical performance and good additive manufacturability, which opens a new channel for the design of lightweight mechanical metamaterials.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P413-424
25. Effect of interstitial oxygen and nitrogen on incipient plasticity of NbTiZrHf high-entropy alloys
间隙氧和氮对NbTiZrHf高熵合金初始塑性的影响
Y.X. Ye✉, B. Ouyang, C.Z. Liu, G.J. Duscher, T.G. Nieh✉
Y.X. Ye:yye7@vols.utk.edu
T.G. Nieh:tnieh@utk.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.065
摘要
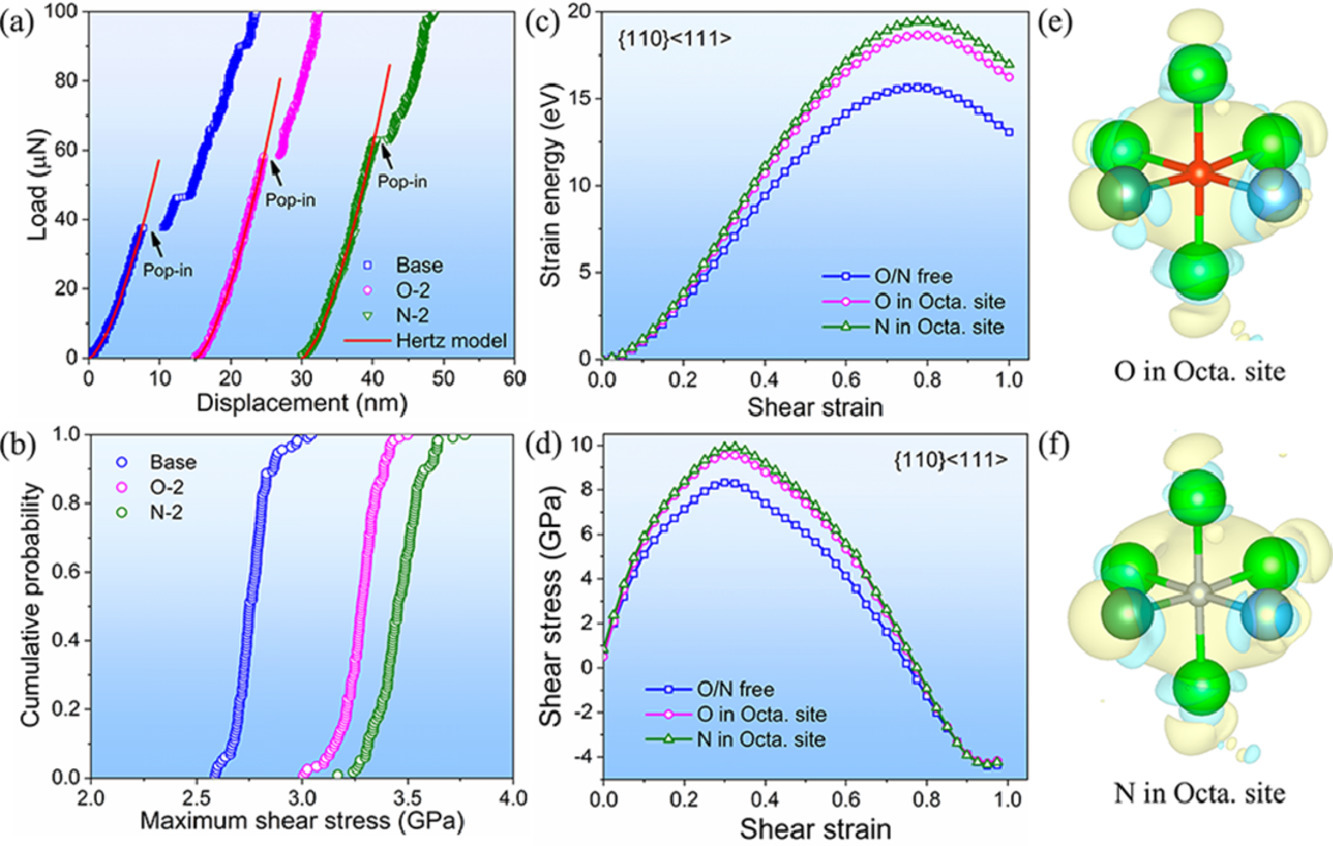
在本研究中,我们使用了纳米压痕技术研究了在10-1000µN/s载荷速率下,间隙氧元素或氮元素的添加对体心立方NbTiZrHf高熵合金(HEA)塑性和位错形核的影响。我们进行了定量统计分析和密度泛函理论(DFT)计算,以确定塑性发生初期氧/氮的作用。同步射线X射线衍射和透射电子显微实验证实了氧/氮原子以间隙溶质原子形式存在。这些间隙溶质原子会增加发生塑性形变所需的临界剪切应力,其中,氮比氧的效果更加显著。经估计,激活体积约为2-3个原子大小,这表明在位错形核过程中,发生多个原子的协同迁移。氧和氮对激活过程没有明显影响。此外,我们还进行了硬度试验。结果表明,固溶强化并不导致临界剪应力的增加。密度泛函计算表明,氧/氮间隙原子导致了局部电荷转移并提高了晶格内聚性,这可能是导致材料形变临界载荷/应力增强的原因。
英文摘要
In this work, instrumented nanoindentation was employed to investigate the effect of interstitial oxygen or nitrogen addition on the incipient plasticity and dislocation nucleation in a body-centered cubic NbTiZrHf high-entropy alloy (HEA) at loading rates of 10–1000 µN/s. We conducted quantitative statistical analysis and density functional theory (DFT) calculations to identify the role of interstitial oxygen/nitrogen during the onset of plasticity. Synchrotron X-ray diffraction and transmission electron microscopy were also performed to confirm that the oxygen/nitrogen atoms were indeed present as interstitial solutes. These interstitial solutes could increase the critical shear stress required to initiate plasticity, and nitrogen yielded a larger hardening effect than oxygen. The activation volumes were evaluated to be about 2–3 atomic volumes, indicating cooperative migration of multiple atoms during the dislocation nucleation, and neither oxygen nor nitrogen appeared to significantly affect this activation process. Hardness tests were also carried out and the result demonstrated that the enhancement of the critical shear stress for incipient plasticity was not caused by the traditional solid-solution strengthening mechanism. DFT calculations revealed that oxygen/nitrogen interstitials induced local charge transfer and improved the lattice cohesion, which was probably responsible for the enhanced pop-in load/stress in the current interstitially alloyed HEAs.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P453-468
26. Phase transformations during cooling from the βZr phase temperature domain in several hydrogen-enriched zirconium alloys studied by in situ and ex situ neutron diffraction
富氢βZr锆合金冷却过程中相变的原位和非原位中子衍射研究
Thai Le Hong, Isabelle Turque, Jean-Christophe Brachet, Jérôme Crépin, Gilles André, Quentin Barres, Raphaëlle Guillou, Caroline Toffolon-Masclet, Jean-Marc Joubert, Matthieu Le Saux✉
M. Le Saux:matthieu.le_saux@ensta-bretagne.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.061
摘要
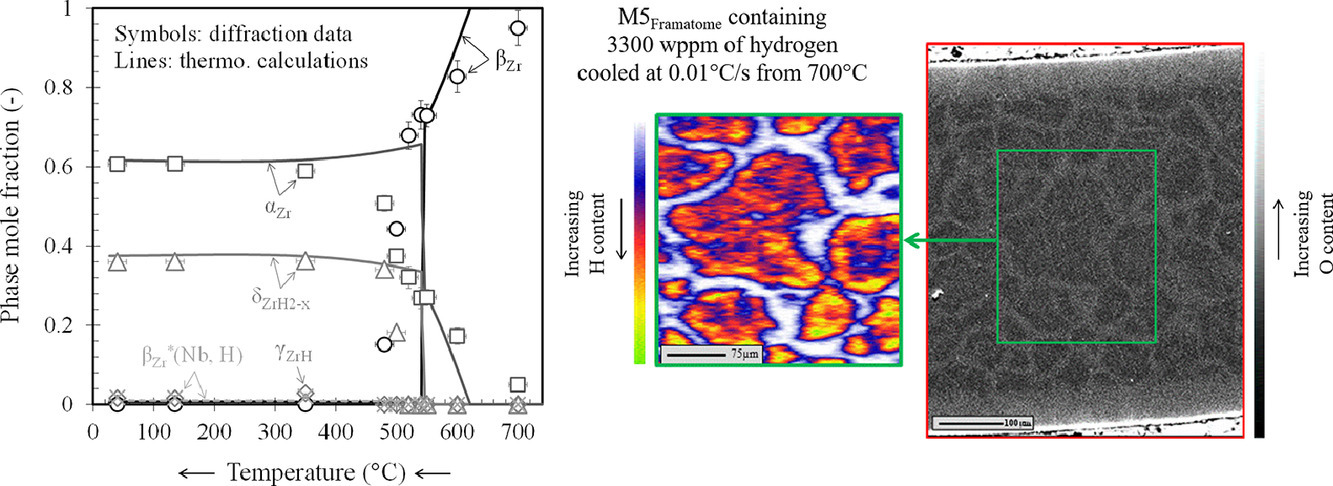
在假设发生意外时,锆基核燃料堆包层可以吸收大量的氢(高达几千wppm),并可在冷却持续前暴露在高温下(βZr相区温度)。本文深入研究了在上述条件下材料的微观组织和化学变化。我们向两种锆基合金和纯锆中预充不同含量的氢(最高达3300 wppm),随后在1000或850℃进行热处理。对样品在从700℃缓慢冷却的过程中和室温下分别进行了中子衍射分析。结果表明,预充3300wppm氢的βZr样品在冷却过程中逐渐转变为αZr,随后通过共析反应大量转变为αZr和 δZrH2-x的混合沉淀。平衡态热力学计算结果与实验一致。然而,根据冷却状态和氢含量的不同,在350℃以下,可能有亚稳γZrH混合析出,并且大量的氢可在αZr中保持固溶。电子探针和弹性冲击试验表明,βZr-αZr 相变和混合析出过程中氧和氢的配分对组织中相和晶格常数的演变具有强烈影响。
英文摘要
In hypothetical accidental conditions, zirconium-based nuclear fuel claddings can absorb high hydrogen contents (up to several thousand wppm) and be exposed to high temperatures (βZrphase temperature range) before being cooled. This paper thoroughly investigates the microstructural and microchemical evolutions that take place in such conditions. Two zirconium-based alloys and unalloyed zirconium were pre-charged with hydrogen at various contents up to 3300 wppm and heat-treated at 1000 or 850 °C. Neutron diffraction analyses were performed in situ upon slow cooling from 700 °C and at room temperature. In the materials containing 3300 wppm of hydrogen, βZr progressively transforms into αZr during slow cooling then extensively transforms into αZr and δZrH2-x hydrides precipitate via a eutectoid reaction. Thermodynamic predictions at equilibrium are in good agreement with the experimental results. However, depending on the cooling scenario and the average hydrogen content, the precipitation of γZrHhydrides, potentially metastable, is evidenced below 350 °C and a significant amount of hydrogen can remain in solid solution in αZr. These metallurgical evolutions and the evolution of the different phase lattice parameters are strongly influenced by the partitioning of oxygen and hydrogen (revealed by electron probe and elastic recoil detection microanalyses) that occurs during the βZr to αZr transformation and hydride precipitation.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P480-494
27. Microparticle impact-bonding modes for mismatched metals: From co-deformation to splatting and penetration
不同金属间微粒子的冲击结合模式: 共变形、喷溅和渗透
Mostafa Hassani✉, David Veysset✉, Yuchen Sun, Keith A. Nelson, Christopher A. Schuh
M. Hassani:hassani@cornell.edu
D. Veysset:dveysset@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.038
摘要
我们通过实验全面展现了高速运动的微粒冲击不同基材后,各种可能的变形状态。基于对撞击位置的实验观察,我们确定了三种典型的行为模式,即飞溅、共变形和穿透。我们开发一套理论框架来预测给定粒子/基体组合的行为模式,包括变形模式谱的两个极端——飞溅和穿透,以及中间的共变形。我们提出了一个基于材料性质的冲击比对以上模式谱进行量化。根据我们的理论模型,冲击比接近1时会发生共变形,而比值较大或较小时,将分别发生贯入和溅出。
英文摘要
We present a comprehensive experimental campaign of high-velocity microparticle impacts with different combinations of particle and substrate materials to identify possible deformation regimes. Based on experimental observations of the impact sites, we identify three typical modes of behavior, namely, splatting, co-deformation, and penetration. We develop a theoretical framework to predict the operative regime for a given particle/substrate combination, ranging from splatting and penetration at two extremes of a spectrum, and co-deformation in the center. We propose an impact ratio based on the materials’ properties, which can successfully quantify the spectrum. Co-deformation is expected when the ratio is around unity, while much larger or smaller ratios give rise to penetration and splatting, respectively.
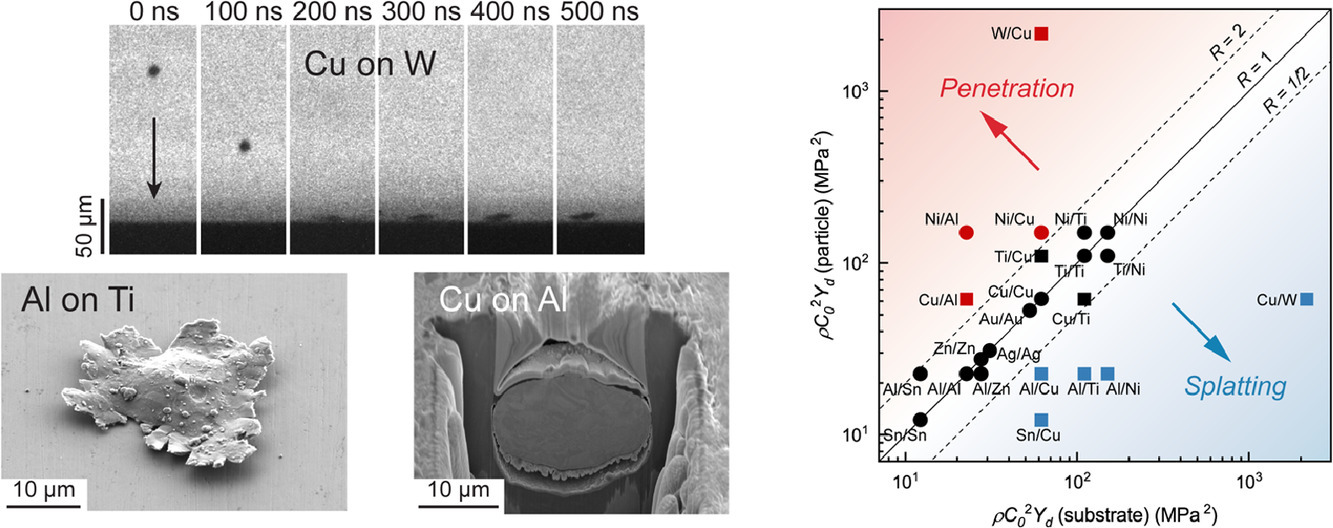
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P504-513
28. Local order in high-entropy alloys and associated deuterides – a total scattering and Reverse Monte Carlo study
关于高熵合金和相关氘化物局部有序的全散射和逆向蒙特卡洛研究
Magnus M. Nygård, Wojciech A. Sławinski, Gustav Ekc, Magnus H. Sørby✉, Martin Sahlberg, David A. Keen, Bjørn C. Hauback
M. H. Sørby:magnus.sorby@ife.no
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.045
摘要
高熵合金(HEAs)的许多特性,如硬度增加、电导热导降低以及独特的储氢特性,都被认为与合金元素尺寸差异导致的晶体局部晶格畸变有关。然而,目前文献中的直接证据非常有限,因此它仍然是一种假设。本文利用全散射测量和反向蒙特卡罗结构模拟,对3种BCC高熵合金TiVNb、TiVZrNb和TiVZrNbHf中不同原子大小差异引起的局部晶格畸变进行了详细的评估。分析表明,合金中的局部晶格畸变随元素尺寸差异的增大而增大。当BCC高熵合金中形成具有CaF2结构的二氘化物时,晶格畸变降低。对氘原子周围的局部环境的分析表明,最近邻金属的价电子浓度(VEC)与四面体间隙的稳定性相关。此外,在混合熵最小的TiVNbD5.7中,存在Ti/Nb有短程有序的趋势。而在TiVZrNbHfD10中,大约6%的氘原子从体积较小的四面体空隙被移动到八面体空隙。
英文摘要
Many of the materials properties of high-entropy alloys (HEAs), like increased hardness, reduced thermal and electrical conductivity, and interesting hydrogen storage properties, are proposed to be related to local lattice distortions of the crystal structure due to the significant size differences between the elements of the alloy. However, direct evidence of this effect is very limited in the literature, and it therefore remains a hypothesis. This work presents a detailed assessment of the local lattice distortion in three body-centered cubic (bcc) HEAs TiVNb, TiVZrNb and TiVZrNbHf with varying atomic size differences using total scattering measurements and Reverse Monte Carlo structure modelling. The analysis indicates that the amount of local lattice distortion in the alloys increases with the elemental size difference in the alloy. The amount of lattice distortion is relieved when dideuterides with CaF2-type structures () are formed from the bcc () HEAs. Analyses of the local environments around the deuterium atoms reveal an interesting correlation between the valence-electron concentration (VEC) of the nearest-neighbour metals and the stability of tetrahedral interstices with respect to deuterium occupation. Moreover, there is a tendency towards Ti/Nb short-range order in TiVNbD5.7 where the mixing entropy is lowest. In TiVZrNbHfD10, about 6% of the deuterium atoms are displaced from the tetrahedral interstices with smaller volumes to octahedral interstices.
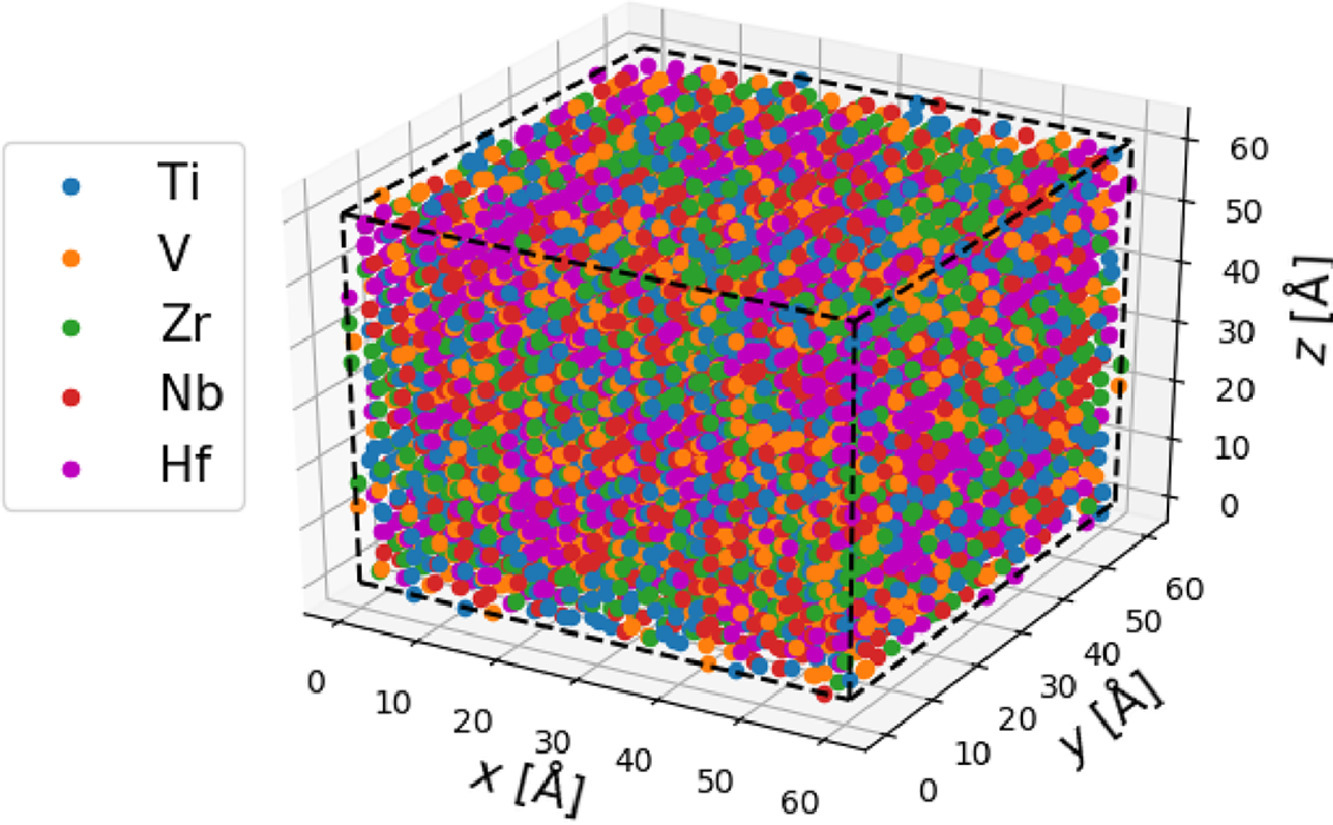
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P561-577
29. Cold creep of titanium: Analysis of stress relaxation using synchrotron diffraction and crystal plasticity simulations
基于同步衍射和晶体塑性模拟分析钛合金冷蠕变过程中的应力弛豫
Yi Xiong✉, Phani Karamched, Chi-Toan Nguyen, David M Collins, Christopher M Magazzeni, Edmund Tarletond, Angus J Wilkinson
Y. Xiong:yi.xiong@materials.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.010
摘要
钛和一些钛合金会在室温条件下发生蠕变,导致疲劳寿命因应力驻留显著降低。一些研究者认为,容易发生塑性滑移的“软”晶粒与时间有关的塑性特征导致了载荷转移,从而增加了邻近不易发生塑性滑移的“硬”晶粒应力。量化与时间相关的塑性过程是成功预测低温疲劳的关键。在此,我们使用了同步辐射XRD技术对工业纯钛(等级4)在应力松弛实验中表现出的与时间有关的塑性特征进行了研究。基于衍射峰在不同载荷取向下的偏移对晶格应变进行了测量。我们通过晶体塑性有限元模型对晶格应变弛豫响应的模拟,确定了合金柱面和基面滑移的临界剪切应力、激活能和激活体积。柱面滑移拥有较低的临界剪切应力和(τcbasal= 252 MPa,τcprism= 154 MPa)和活化能(ΔFbasal = 10.5×10−20 J = 0.65 eV,ΔFprism = 9.0×10−20 J = 0.56 eV),因此更容易发生。与基面滑移相比,棱柱滑移参数对应变率更加敏感。这种与应变速率有关的滑移模式对低温疲劳过程中应力向“硬”晶粒的重新分布有显著影响。
英文摘要
It is well known that titanium and some titanium alloys creep at ambient temperature, resulting in a significant fatigue life reduction when a stress dwell is included in the fatigue cycle. It is thought that localised time dependent plasticity in ‘soft’ grains oriented for easy plastic slip leads to load shedding and an increase in stress within a neighbouring ‘hard’ grain that is poorly oriented for easy slip. Quantifying this time dependent plasticity process is key to successfully predicting the complex cold dwell fatigue problem. In this work, synchrotron X-ray diffraction during stress relaxation experiments was performed to characterise the time dependent plastic behaviour of commercially pure titanium (grade 4). Lattice strains were measured by tracking the diffraction peak shifts from multiple plane families (21 diffraction rings) as a function of their orientation with respect to the loading direction. The critical resolved shear stress, activation energy and activation volume were established for both prismatic and basal slip modes by fitting a crystal plasticity finite element model to the lattice strain relaxation responses measured along the loading axis for three strong reflections. Prismatic slip was the easier mode having both a lower critical resolved shear stress (τcbasal =252MPa and τcprism =154MPa) and activation energy (ΔFbasal = 10.5×10−20 J = 0.65 eV and ΔFprism = 9.0×10−20 J = 0.56 eV). The prism slip parameters correspond to a stronger strain rate sensitivity compared to basal slip. This slip system dependence on strain rate has a significant effect on stress redistribution to ‘hard’ grain orientations during cold dwell fatigue.
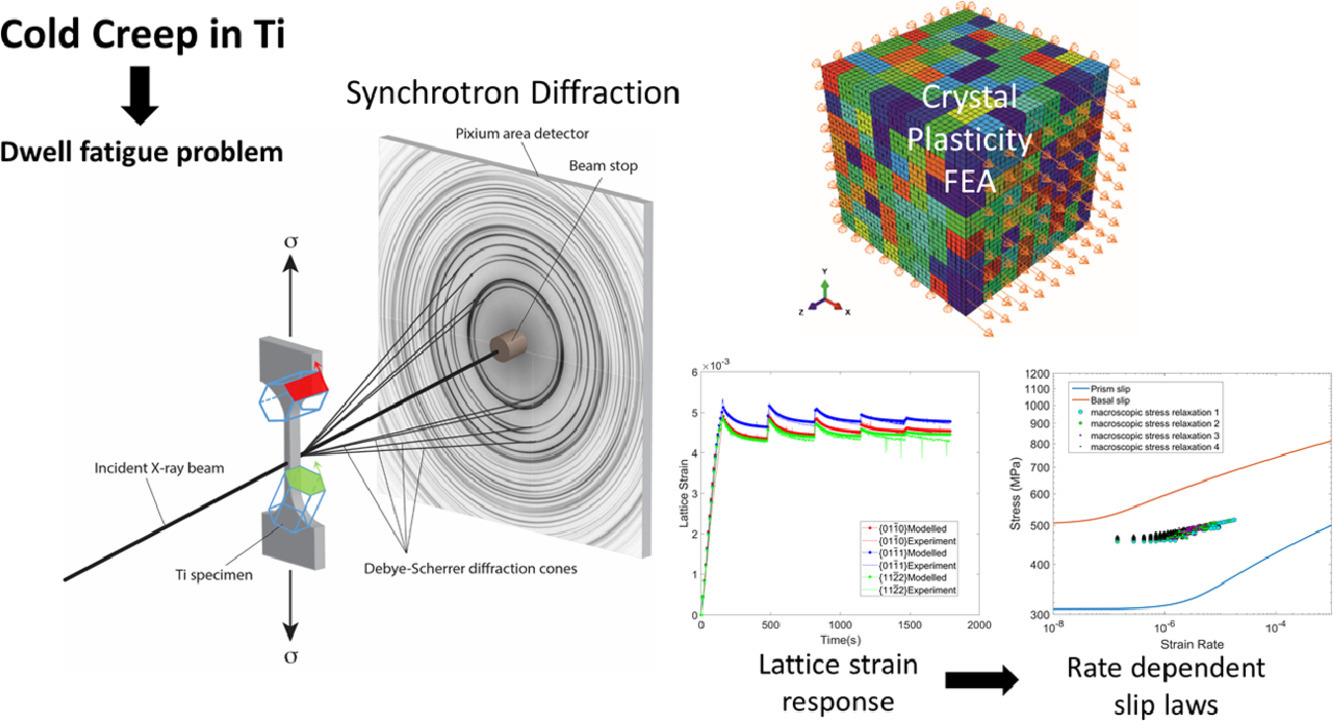
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P578-592
30. Multiaxial plasticity and fracture behavior of stainless steel 316L by laser powder bed fusion: Experiments and computational modeling
激光粉末床熔化制备的316L不锈钢的多轴塑性和断裂行为
Alexander E. Wilson-Heid, Shipin Qin, Allison M. Beese✉
A.M. Beese:amb961@psu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.066
摘要
我们实验测量了激光粉末床熔化(L-PBF)增材制造的奥氏体316L不锈钢的多轴大变形和韧性断裂行为。我们使用了两种取向、五种不同应力状态(剪切、剪切/拉伸复合加载、平面应变和单轴拉伸)和不同几何形状的试样实验数据对各向异性塑性和断裂模型进行了验证和探究。我们在剪应力占主导的试样中观测到了剪切软化。这种软化被认为是由于高初始位错密度和亚微米胞状结构导致材料中形成剪切带引起的,我们在各向异性塑性模型中引入剪切损伤准则对其进行了模拟。通过实验和计算相结合的方法,我们基于两种样品取向,对各向同性和异性的Hosford-Coulomb和Mohr-Coulomb断裂模型进行了修正。校正后的各向异性Hosford-Coulomb断裂模型可以很好地描述L-PBF 316L不锈钢与应力状态相关的各向异性断裂行为。
英文摘要
The multiaxial large deformation and ductile fracture behavior of laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF) additively manufactured austenitic 316L stainless steel was experimentally measured. Data from tests in two orientations, under five dissimilar stress states (shear, combined shear/tension loading states, plane strain tension, and uniaxial tension) were used to calibrate and validate anisotropic plasticity and fracture models, with different specimen geometries used to probe plasticity versus fracture. Shear softening, hypothesized to be due to shear band formation in the material due to high initial dislocation density and sub-micron cellular structures, was observed in shear dominated tests, and modeled through the adoption of a shear damage criterion in an anisotropic plasticity model. Using a combined experimental and computational approach, isotropic and anisotropic Hosford-Coulomb and modified Mohr-Coulomb ductile fracture models were calibrated for both sample orientations. The calibrated anisotropic Hosford-Coulomb fracture model best captures the stress state dependent and anisotropic failure behavior of L-PBF 316L.
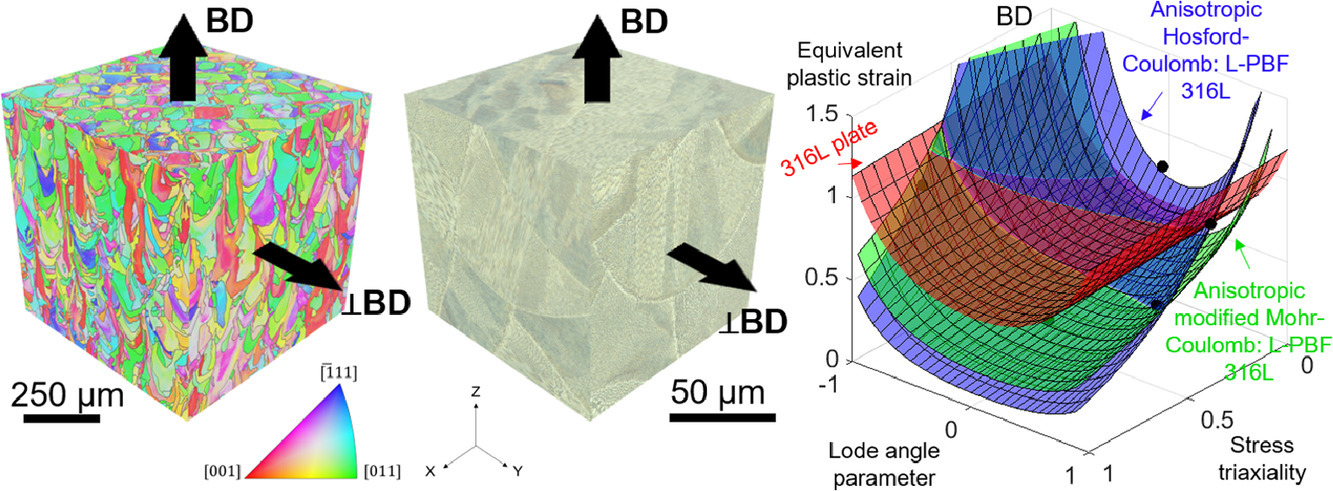
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P593-601
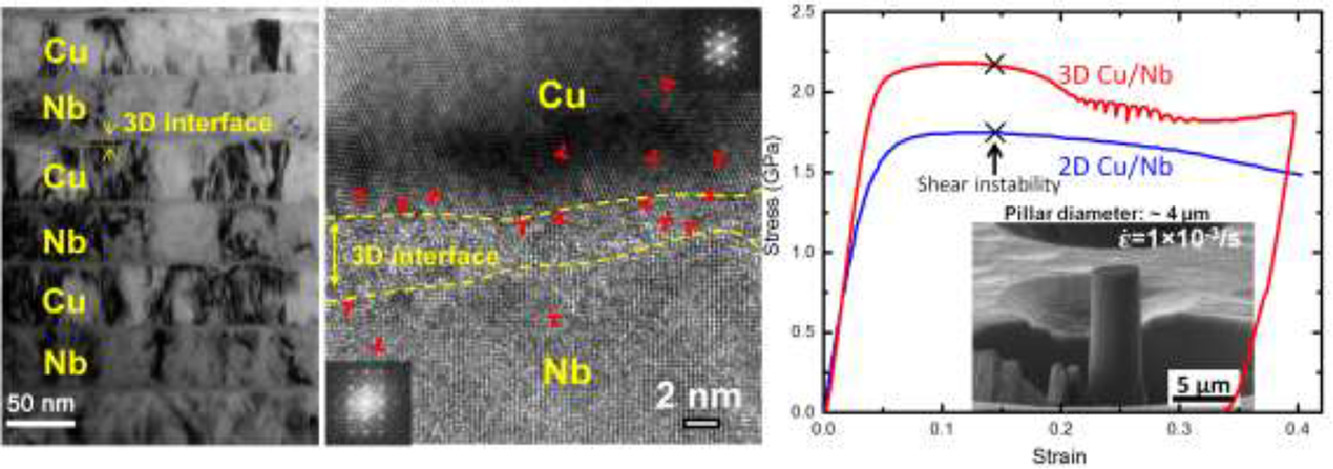
31. Effects of three-dimensional Cu/Nb interfaces on strengthening and shear banding in nanoscale metallic multilayers
三维Cu/Nb界面对纳米金属多层复合材料强化和剪切带的影响
Y. Chen✉, N. Li, R.G. Hoagland, X.-Y. Liu, J.K. Baldwin, I.J. Beyerlein, J.Y. Cheng, N.A. Mara✉
Y. Chen:ychen103@uncc.edu
N.A. Mara:mara@umn.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.019
摘要
对二维界面原子尺度的精细调控已被证实可以提高纳米复合材料的强度、变形能力和抗辐射损伤能力。在此,我们研究了一种含有三维Cu/Nb界面的纳米复合材料的力学响应。这一界面通过化学/结构梯度分离了纯Cu和纯Nb层,界面处的FCC Cu和BCC Nb存在几个纳米的晶格错配。结果表明,与二维界面层厚相当的情况下,三维界面可使复合材料屈服强度和流变强度分别提高50%和22%。在14%压缩应变后,剪切带的出现导致了剪切带内外的Cu和Nb的共变形。此外,我们还讨论了界面结构在Cu/Nb剪切带形成和长大过程中的作用。
英文摘要
Manipulation of the atomic-scale structure of two-dimensional (2D) interfaces have been shown to provide nanocomposites with enhanced strength, deformability, and radiation damage resistance. In comparison with 2D interfaces, here we investigate the mechanical response of nanocomposites containing three-dimensional (3D) Cu/Nb interfaces consisting of a chemical/structural gradient separating pure Cu and Nb layers, through which the lattice mismatch between face-centered cubic Cu and body-centered cubic Nb is accommodated over a distance of several nanometers. It is demonstrated that 3D interfaces increase the yield and flow strength by 50% and 22%, respectively, over composites containing 2D interfaces at similar layer thicknesses. After 14% compressive strain, the onset of shear banding results in co-deformation of both Cu and Nb phases within and outside of the shear band. We conclude with a discussion of the role of interface structure in shear band formation and growth in 3D Cu/Nb.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P602-612
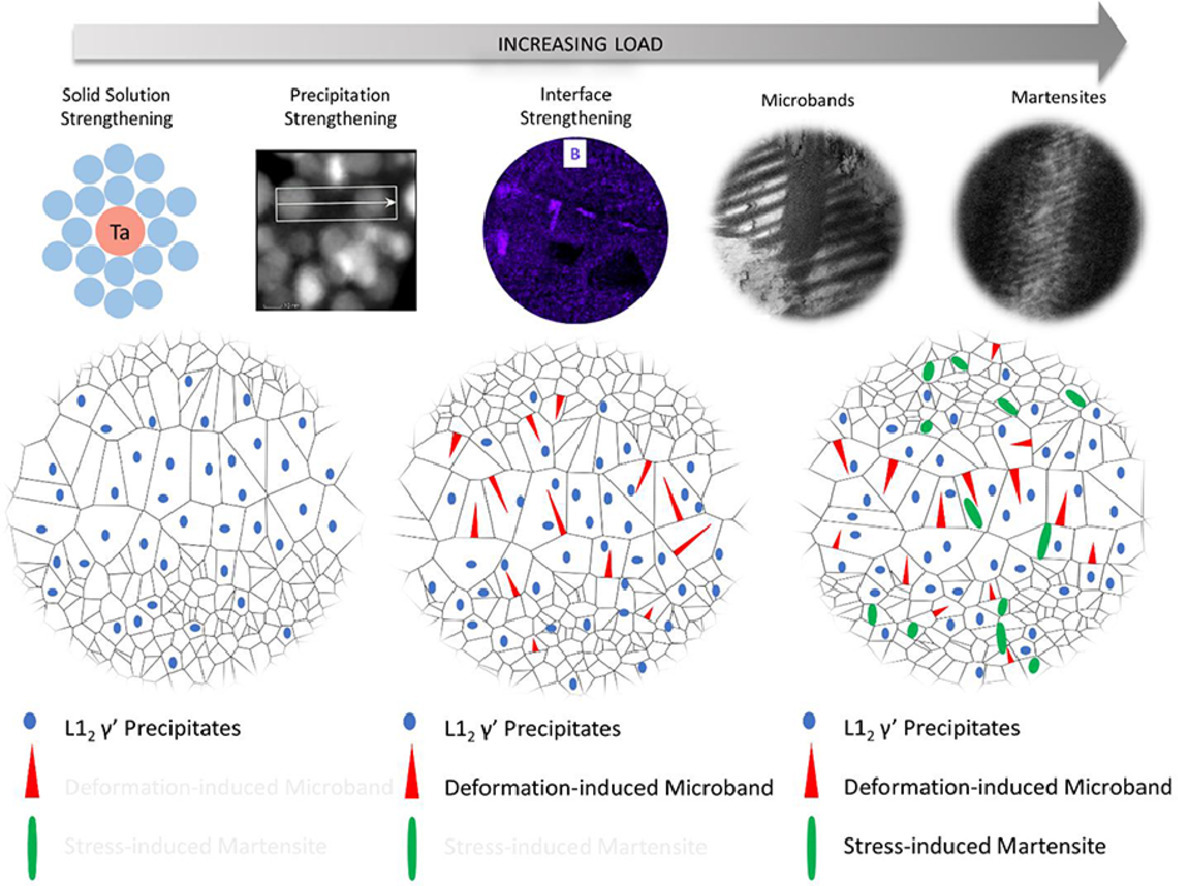
32. Aged metastable high-entropy alloys with heterogeneous lamella structure for superior strength-ductility synergy
非均匀层状结构的亚稳态时效高熵合金对强塑性耦合限制的突破
Cheng Zhang, Chaoyi Zhu, Penghui Cao, Xin Wang, Fan Ye, Kevin Kaufmann, Lee Casalena, Benjamin E. MacDonald, Xiaoqing Pan, Kenneth Vecchio✉, Enrique J. Lavernia✉
K. Vecchio:vecchio@eng.ucsd.edu
E.J. Lavernia:lavernia@uci.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.043
摘要
多组元体系高熵合金极大地扩展了合金设计的空间,并为克服合金的强韧性平衡提供了新的可能。然而,通过传统的晶粒细化和沉淀强化机制获得超高强度,必然导致塑性的急剧丧失。在此,我们设计并制备了一种具有非均匀层状结构的时效高熵合金,该合金能够达到千兆级别的抗拉强度,同时保持了优异的塑性(抗拉强度~1.4 GPa,延伸率~30%;抗拉强度~1.7 GPa,延伸率~10%)。我们的研究表明,强度和塑性的协同提高是由于各种强化机制的共同作用导致,包括固溶强化、界面强化、析出强化和马氏体相变强化。这些机制分别在不同应变水平下影响材料的硬化和变形过程。特别是,微形变带的形成和应力诱导马氏体相变导致了额外的应变硬化,提高了材料的塑性。本文所述的策略利用了异质微观结构设计的概念,为高性能结构材料的制造提供了一种实用而新颖的方法。
英文摘要
High-entropy alloys containing multi-principal-element systems significantly expand the potential alloy design space, and offer the possibility of overcoming the strength-ductility trade-off in metallurgical research. However, the gain in ultra-high strength through traditional grain refinement and precipitation-strengthening mechanisms inevitably leads to a drastic loss of ductility. Here, we report on the design and fabrication of heterogeneous-lamella structured, aged bulk high-entropy alloy, which attains gigapascal tensile strength while retaining excellent ductility (UTS ~1.4 GPa, elongation ~30%; UTS ~1.7 GPa, elongation ~10%). Our work shows that the improved strength-ductility synergy arises due to various complementary strengthening mechanisms, including solid-solution, interfaces, precipitation and martensitic transformation, which influence the hardening and deformation processes at different strain levels. In particular, the hetero-deformation that is associated with the formation of microbands as well as the stress-induced martensite promotes additional hardening and hence high ductility. The strategy described here, that is leveraging the concept of heterogeneous microstructure design, provides a practical and novel method for fabricating high-performance structural materials.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P613-632
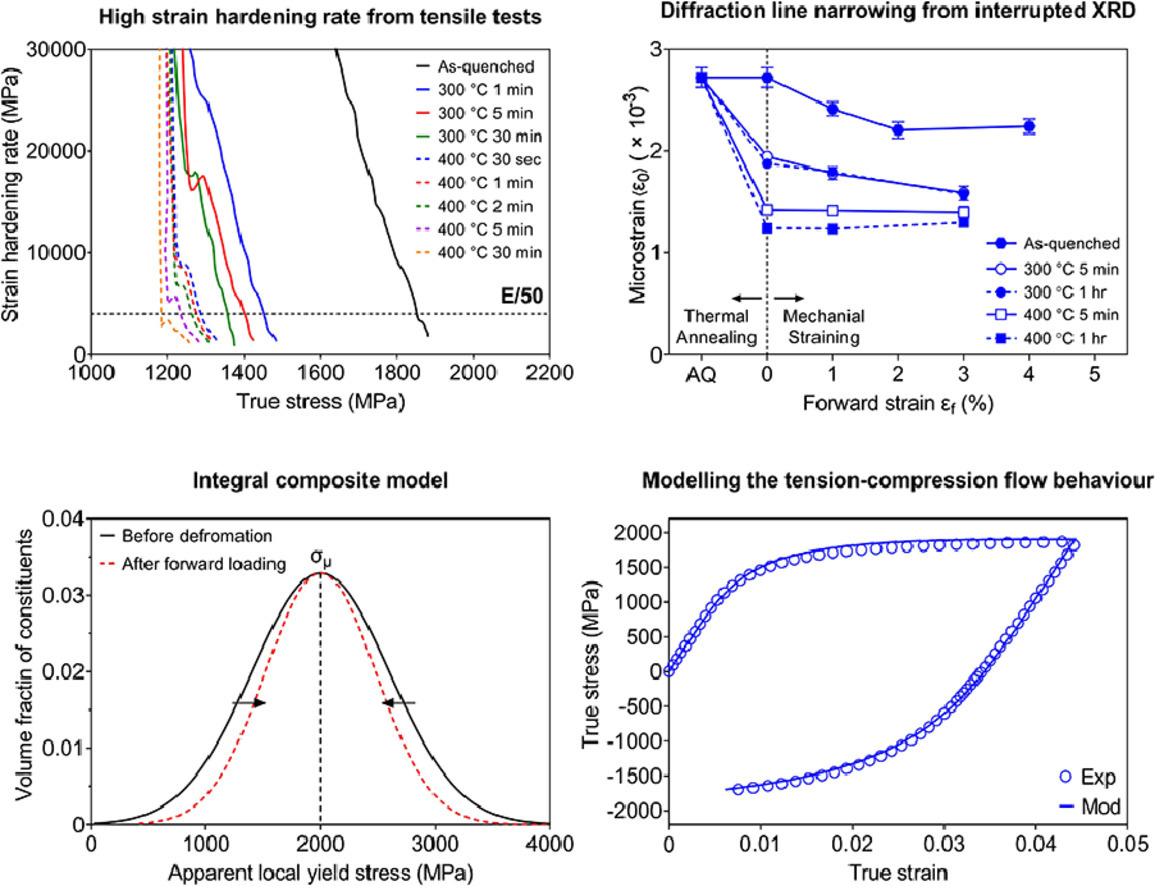
33. Strain hardening behaviour of as-quenched and tempered martensite
淬火和回火马氏体的应变硬化行为
L.Y. Wang, Y.X. Wu, W.W. Sun, Y. Bréchet, L. Brassart, A. Arlazarov, C.R. Hutchinson✉
C.R. Hutchinson:christopher.hutchinson@monash.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.067
摘要
马氏体对先进高强钢的强度起到重要作用。虽然马氏体的强度已被广泛研究,但马氏体的低弹性极限和超高应变硬化率仍是学界的一个难题。虽然最近提出的复合模型可以成功地再现和解释由于微观组织不同相具有不同屈服强度或变形引起的残余应力而导致的逐渐屈服特征,但它们都不能自洽地描述淬火马氏体拉压行为中的关键特征。将这些复合模型扩展到回火马氏体的尝试非常有限。在这篇论文中,我们采用了机械测试(例如单轴拉伸-压缩)和间断性X射线衍射对淬火和回火马氏体的应变硬化进行了系统的实验研究。结果表明,淬火马氏体在拉伸过程中表现出的高应变硬化速率、包辛格效应和衍射峰变窄等现象在回火至400℃时仍能保持。通过将马氏体理解为一种多组分复合材料,在形变时具有变化的本征屈服强度和残余应力松弛,能够较好地理解以上实验现象。
英文摘要
Martensite is a key constituent in advanced high strength steels and plays an important role in providing the high strength. While the strength of martensite has been extensively studied in the past, its low elastic limit and extremely high strain hardening rate remain a puzzle for the steel community. Composite models proposed recently can successfully reproduce these features as result of gradual yielding of microstructural constituents with either variations in intrinsic yield strengths or transformation induced residual stresses. Although these composite models can explain certain observations associated with the deformation of as-quenched martensite, neither can self-consistently describe all the key characteristics in the tension-compression behaviour of as-quenched martensite. Attempts to extend these composite models to tempered martensite have been limited. In this contribution, we conduct a systematic experimental study on the strain hardening of as-quenched and tempered martensite with mechanical testing (e.g. monotonic tension and tension-compression) and interrupted X-ray diffraction. It is shown that the high strain hardening rate, large Bauschinger effect and diffraction line narrowing found in as-quenched martensite during straining can be sustained in tempered martensite tempered up to 400 °C. These phenomena can be understood by considering martensite as a multi-constituent composite having both variations in intrinsic yield strengths and relaxation of transformation induced residual stresses during straining.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P649-668
34. Atomic scale characterization of complex stacking faults and their configurations in cold deformed Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10 high-entropy alloy
冷变形Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10高熵合金中复杂层错及其构型的原子尺度表征
L. Qi, C.Q. Liu, H.W. Chen✉, J.F. Nie✉
H.W. Chen:hwchen@cqu.edu.cn,重庆大学
J.F. Nie:jianfeng.nie@monash.edu,重庆大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.070
摘要
我们使用了原子尺度分辨率的扫描透射电子显微镜对FCC Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10 (at.%)高熵合金(HEA)冷变形样品中的层错及其构型进行了研究。结果表明,变形后的组织中包含至少四种内禀层错和两种外禀层错,包括Shockley分位错、Frank分位错和1/6<411>分位错。此外,我们还发现了17种层错构型,包括著名的Lomer-Cottrell锁、Hirth锁和层错偶极子;罕见的内-外层错弯曲;以及13种未报道过的层错构型。在这17种构型中,有15种构型是由共轭层错通过边缘连接构成,连接处的分位错为1/6<110>、1/3<110>、1/3<100>中的一种;其余2种构型由两个交叠的层错构成,且交叠处的偶极子不同。这些构型中的14中都是完全由内禀层错构成,而其余3个由内禀层错和外禀层错混合构成。此外,令人惊讶的是,有3种构型在边缘上包含一个Frank分位错,这与已有的报导,即所有构型边界处都为Shockley分位错有显著不同。我们基于伯格斯向量分析对6种层错和17种构型的形成机理进行了讨论。
英文摘要
Atomic-resolution scanning transmission electron microscopy is used to study stacking faults and their configurations formed in cold deformed samples of a face-centered cubic (FCC) Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10 (at.%) high-entropy alloy (HEA). It is found that the deformed microstructures contain at least four types of intrinsic stacking faults and two types of extrinsic stacking faults that are bounded by different partial dislocations, including Shockley, Frank and unusual 1/6<411> partials. Additionally, seventeen types of stacking fault configurations are also found, including the well-known Lomer-Cottrell lock, Hirth lock and faulted dipole, the rarely reported intrinsic-extrinsic fault bend, and thirteen hitherto unreported configurations containing different stacking faults and partial dislocations. Among these seventeen configurations, fifteen of them are constructed by conjugate stacking faults connecting at their edges, with a stair-rod partial belonging to 1/6<110>, 1/3<110> or 1/3<100> lying at every joint point of the stacking faults; and the rest two configurations have two intersecting stacking faults but contain different stair-rod dipoles at the intersection. Fourteen of these configurations are all comprised exclusively of intrinsic stacking faults, while three of them consist of a mixture of intrinsic and extrinsic stacking faults. Moreover, three out of the seventeen configurations contain surprisingly a Frank partial at one edge, in contrast to previously reported configurations that are all bounded exclusively by Shockley partials. Based on Burgers vector analysis, the formation mechanisms of the six types of stacking faults and the seventeen types of configurations are proposed and discussed.

微信公众号:Goal Science
投稿邮箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
