金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.191, 15 Jan. 2021(下)
2020-10-29 来源: Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文11篇,涵盖了高熵合金、纳米析出钢、纯钛、钛合金、镁铝合金等,国内科研单位包括香北京理工大学、冲击环境材料技术国家级重点实验室、东北大学、北京航空航天大学、南京理工大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 191 目录
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, 15 Jan. 2021, P126-130
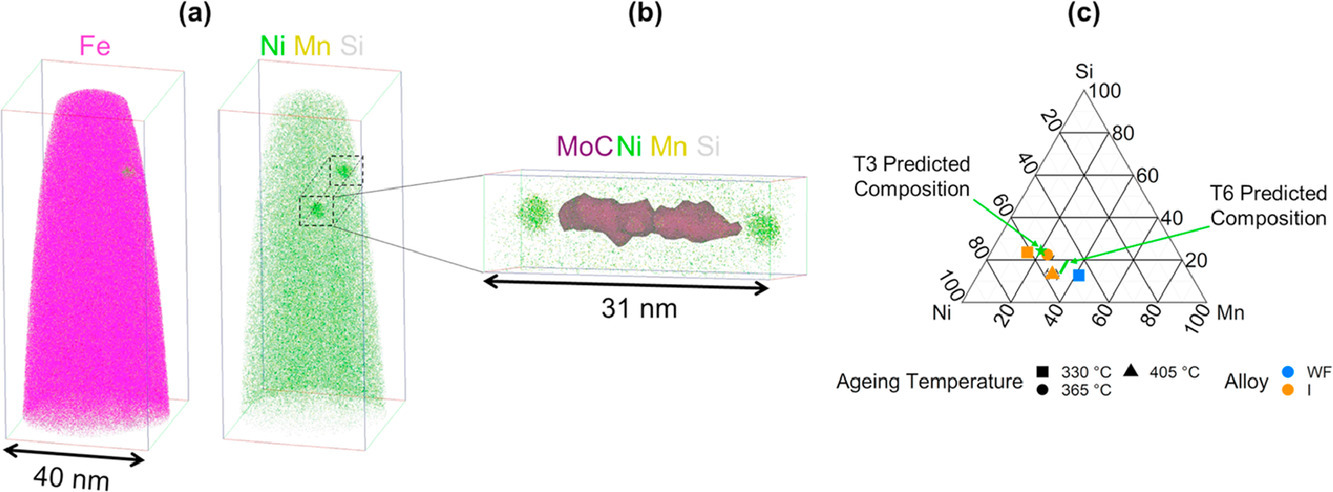
13. Observation of Mn-Ni-Si-rich features in thermally-aged model reactor pressure vessel steels
热时效模型反应堆压力容器钢中富锰-镍-硅特征的观察
B.M. Jenkins✉, P.D. Styman✉, N. Riddle, P.A.J. Bagot, M.P. Moody, G.D.W. Smith, J.M. Hyde
B.M. Jenkins: benjamin.jenkins@materials.ox.ac.uk
P.D. Styman: paul.d.styman@uknnl.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.029Get
摘要
我们用原子探针层析成像技术表征了长期热时效后的两个低铜(< 0.04 at.%)模型钢。研究发现,在短短20731小时(~2.4年)的时效后,就会形成富含锰镍硅的特征。我们将这些特征的成分与热力学模型的预测结果进行了比较,并讨论了它们的异同。
英文摘要
Atom probe tomography was used to characterise two low-Cu (< 0.04 at. %) model steels after exposure to long-term thermal ageing. Mn-Ni-Si-rich features were observed to form after as little as 20,731 h (∼ 2.4 years) of ageing. The composition of these features were compared to those predicted by thermodynamic models and the similarities and differences are discussed.
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, 15 Jan. 2021, P131-136
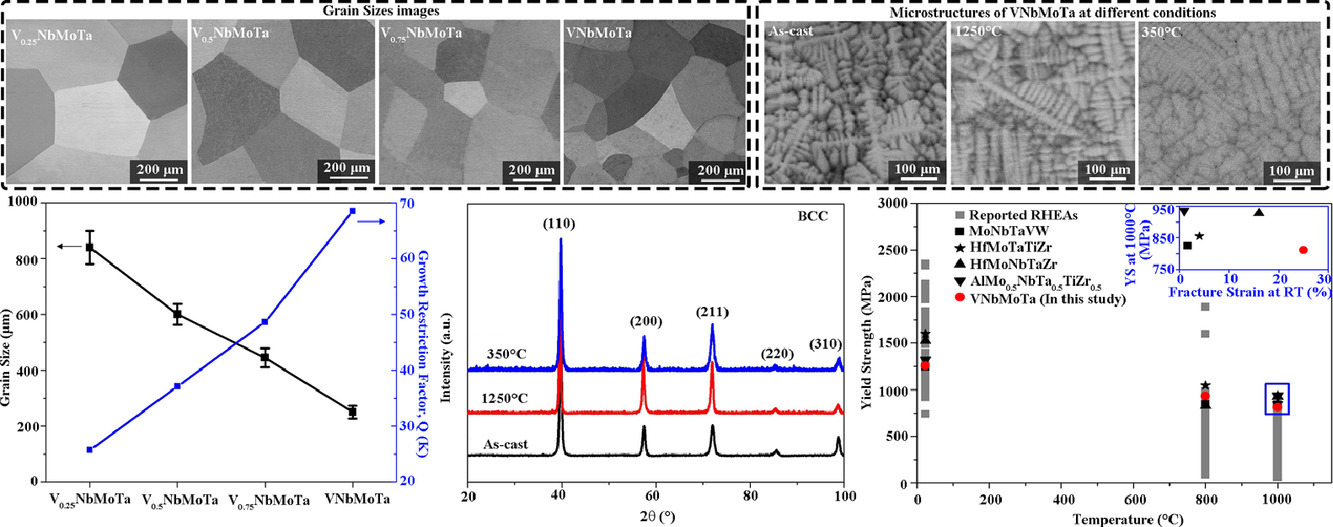
14. Designing VxNbMoTa refractory high-entropy alloys with improved properties for high-temperature applications
设计VxNbMoTa耐火高熵合金,改善高温服役性能
M. Wang, Z.L. Ma✉, Z.Q. Xu, X.W. Cheng✉
Z.L. Ma: z.l.ma@bit.edu.cn,北京理工大学,冲击环境材料技术国家级重点实验室
X.W. Cheng: chengxw@bit.edu.cn,北京理工大学,冲击环境材料技术国家级重点实验室
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.027
摘要
高/中温相稳定性差和/或室温塑性低是目前制约耐火高熵合金高温应用的瓶颈。在本工作中,我们探索了钒浓度为0-25at .%的新型VxNbMoTa耐火高熵合金。VxNbMoTa耐火高熵合金呈现出单一体心立方(BCC)结构,在固相线到350℃的宽温度范围内具有前所未有的相稳定性。随着钒浓度的增加,VxNbMoTa的晶粒结构可以得到充分细化,因为较高的钒含量会诱发更强的溶质效应,从而导致更高的生长限制因子。等摩尔比的VNbMoTa样品的屈服强度在1000℃条件下为811MPa,优于目前报道的大多数耐火高熵合金。该合金也表现出良好的室温塑性,断裂应变为> 25%,在高温下没有应变软化现象,这在众多耐火高熵合金中是少见的。VNbMoTa合金的优异性能使其成为一种非常有前途的高温应用材料。
英文摘要
Poor high/medium-temperature phase stability and/or low room-temperature ductility are currently bottlenecks of refractory high-entropy alloys (RHEAs) that restrict their high-temperature applications. Here, we explored novel VxNbMoTa RHEAs with vanadium concentrations of 0–25 at.%. VxNbMoTa RHEAs exhibit a single body-centered cubic (BCC) structure with unprecedented phase stability at a wide temperature range from solidus down to 350°C. The grain structure of VxNbMoTa can be substantially refined when increasing the V concentration since higher V contents induce stronger solutal effects which contribute to higher growth restriction factors. Equimolar VNbMoTa exhibits the yield strength of 811 MPa at 1000°C that is superior to most RHEAs reported by far, and this alloy also shows excellent room-temperature ductility with the fracture strain > 25% and no strain-softening at high temperature, which is rarely seen in many popular RHEAs. These exceptional performances of VNbMoTa enable it to be a very promising material for high-temperature applications.
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, 15 Jan. 2021, P137-142
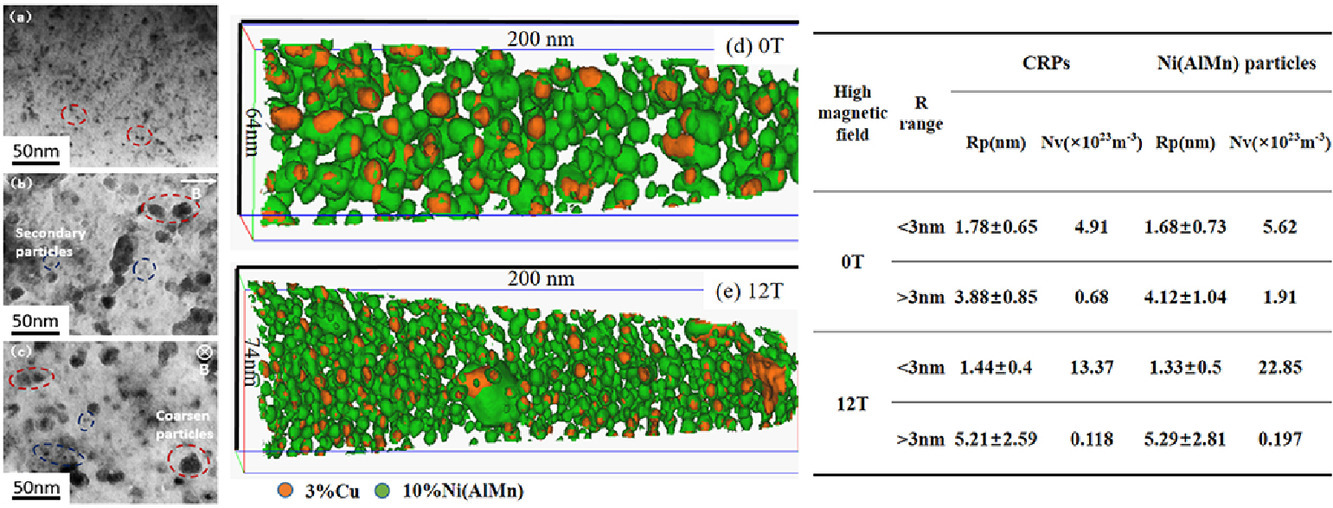
15. A novel strategy for hierarchical structure in multicomponent nano-precipitated steels by high magnetic field aging
利用高磁场时效制备多组元纳米析出钢分层结构的新策略
Nianshuang Qiu, Jiacheng Yan, Xiaowei Zuo✉
Xiaowei Zuo: zuoxw@epm.neu.edu.cn,东北大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.035
摘要
本工作研究了时效过程中强磁场(HMF)对多组元纳米钢中富铜析出和Ni(AlMn)析出的共析出行为的影响。结果表明,HMF促进了富铜和Ni(AlMn)共析出的分层结构的构建。研究认为,时效过程中,由于热力学的变化,HMF增加了二次共析出的形核速率,从而细化了二次析出。同时,在回火后的进一步时效过程中,由于Cu的扩散速率增加,HMF提高了初生颗粒的奥斯瓦尔德熟化速率,从而加速了粗化过程。
英文摘要
The influence of high magnetic field (HMF) during aging on the precipitation behavior of co-precipitates consisted of Cu-rich precipitates and Ni(AlMn) precipitates in multicomponent nano-precipitated steels was carefully investigated. It was indicated that HMF promoted the construction of hierarchical structures of Cu-rich and Ni(AlMn) co-precipitates. It was thought that HMF increased nucleation rates of secondary co-precipitates during aging because of the thermodynamics change, thus refining the secondary precipitates. Meanwhile, HMF increased the Ostwald ripening rate of primary particles during the further aging after tempering because of increasing diffusion of Cu, thus accelerating the coarsening process.
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, 15 Jan. 2021, P155-160
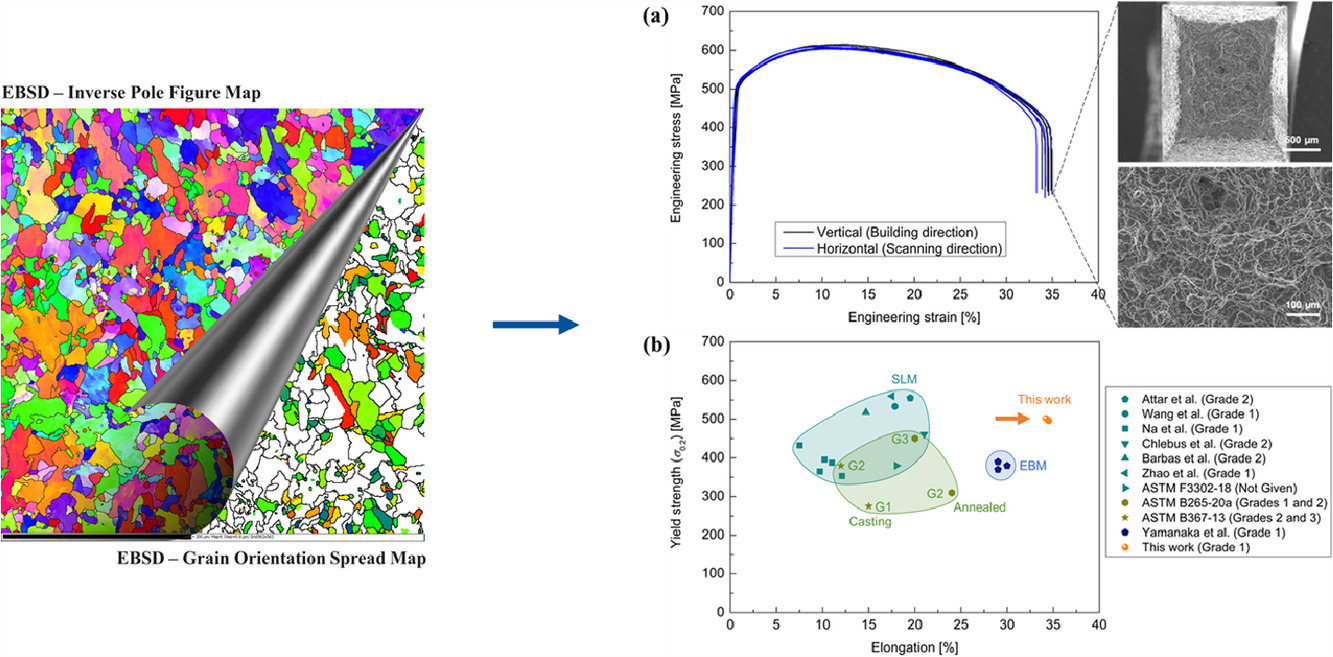
16. Achieving high ductility in a selectively laser melted commercial pure-titanium via in-situ grain refinement
通过原位晶粒细化,在选区激光熔化制备的商用纯钛中实现高延展性
Jingqi Zhang, Yingang Liu, Mohamad Bayat, Qiyang Tan, Yu Yin, Zhiqi Fan, Shiyang Liu, Jesper Henri Hattel, Matthew Dargusch, Ming-Xing Zhang✉
Ming-Xing Zhang: mingxing.zhang@uq.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.023
摘要
添加异质元素或颗粒可以促进增材制造钛和钛合金的晶粒细化,但由于脆性金属间化合物的形成会导致延展性的降低。本研究表明,通过适当控制选区激光熔化(SLM)的参数,可以实现工业纯钛(CP-Ti)的原位晶粒细化。研究发现,较高的能量输入密度有利于晶粒细化。通过详细的微观组织表征和多物理场模拟,揭示了晶粒细化的机理。这归因于SLM工艺固有的循环再加热导致的本征热处理(IHT)效应。细化的CP-Ti表现出34.3±0.5%的极高延展性,没有明显的机械各向异性。这项工作证明了在不改变化学成分的条件下,利用增材制造(AM)的热循环来细化金属晶粒的可行性。
英文摘要
Grain refinement of additively manufactured titanium and titanium alloys can be promoted via adding foreign elements or particles, but it may lead to a reduction in ductility due to the formation of brittle intermetallic compounds. The present study shows that in-situ grain refinement of commercially pure titanium (CP-Ti) can be achieved through properly controlling the selective laser melting (SLM) parameters. It was found that higher input energy density worked in favour of grain refinement. Detailed microstructural characterization coupled with multi-physics simulation were performed to reveal the grain refinement mechanism. This was attributed to the intrinsic heat treatment (IHT) effect which resulted from the cyclic reheating inherent to the SLM process. As a result, the refined CP-Ti exhibited an exceptionally high ductility of 34.3 ± 0.5% without notable mechanical anisotropy. This work demonstrates the feasibility of utilizing thermal cycling of additive manufacturing (AM) to refine grains of metals without changing the composition.
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, Jan. 2021, P29-33
17. Achieving improved workability and competitive high temperature shape memory performance by Nb addition to Ni-Ti-Hf alloys
通过在Ni-Ti-Hf合金中添加Nb来提高其可加工性和优异的高温形状记忆性能
J.N. Lemke, F. Gallino, M. Cresci, A. Coda✉
A. Coda: Alberto_Coda@saes-group.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.032
摘要
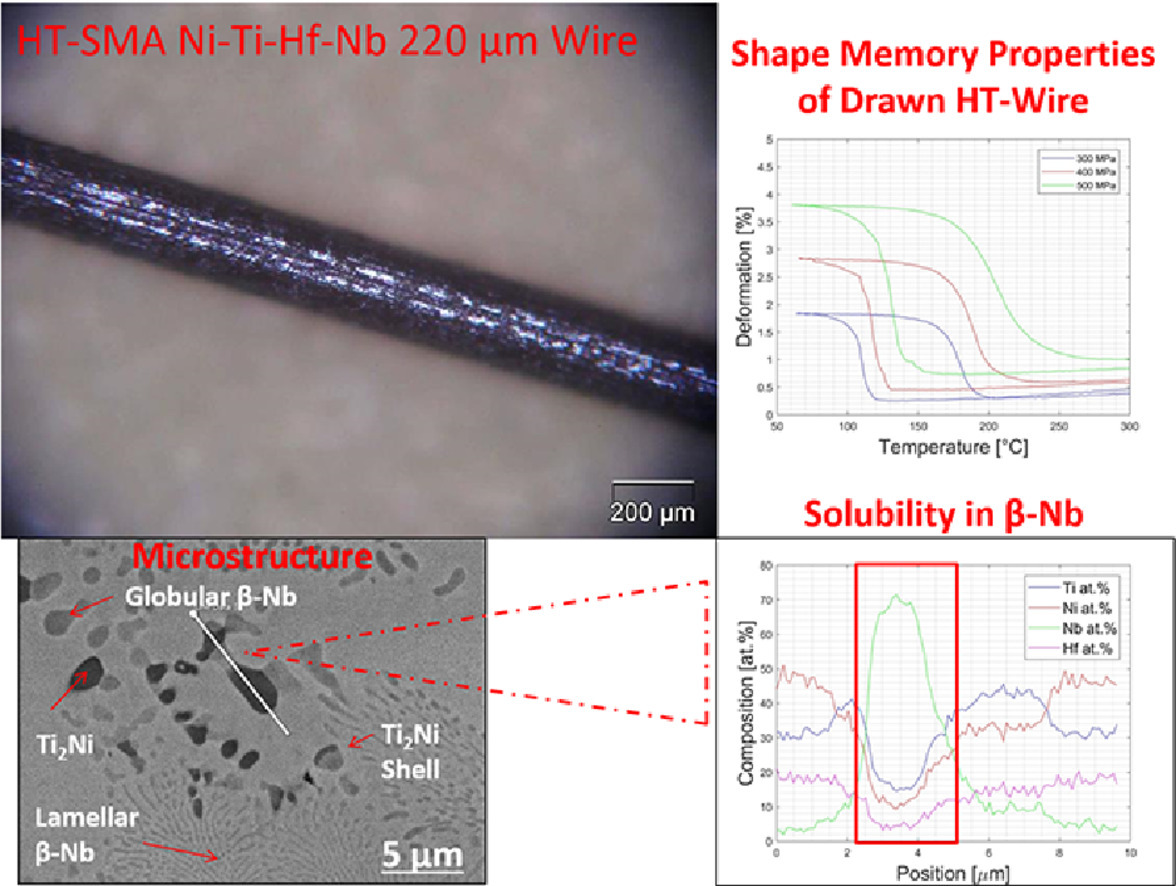
本工作描述了铌如何在不明显影响功能性的情况下提高Ni-Ti-Hf合金的延展性,这是由于由软β-Nb和B19’ Ni-Ti-Hf基体相组成的共晶组元的形成。设计高性能Ni-Ti-Hf-Nb合金的关键是考虑Nb在基体中的低溶解度以及β-Nb中元素的不同溶解度对转变温度的影响。通过对拉拔Ni-Ti-Hf-Nb丝的实例研究表明,该方法可以改善力学性能,提高转变温度,增加高温形状记忆合金拉丝的可能性。
英文摘要
This work depicts how Nb addition to Ni-Ti-Hf alloys increases their ductility without significantly deviating functional performance due to the formation of eutectic constituents composed of soft β-Nb and B19’ Ni-Ti-Hf matrix phase. Crucial for designing high performing Ni-Ti-Hf-Nb alloys is considering consequences of the low solubility of Nb in the matrix and the varying solubility of elements in β-Nb on the transformation temperatures. A case study on a drawn Ni-Ti-Hf-Nb wire demonstrates that improved mechanical properties and high transformation temperatures can be achieved by this approach, increasing the possibility for wire drawing of high temperature shape memory alloys.
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, 15 Jan. 2021, P173-178
18. Effects of annealing on hardness, yield strength and dislocation structure in single crystals of the equiatomic Cr-Mn-Fe-Co-Ni high entropy alloy
退火对等原子Cr-Mn-Fe-Co-Ni单晶高熵合金硬度、屈服强度和位错结构的影响
Dengshan Zhou✉, Zhenghao Chen, Kazuki Ehara, Kodai Nitsu, Katsushi Tanaka, Haruyuki Inui
Dengshan Zhou: zhoudengshan@mail.neu.edu.cn,京都大学,中国东北大学,德国马普所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.039
摘要
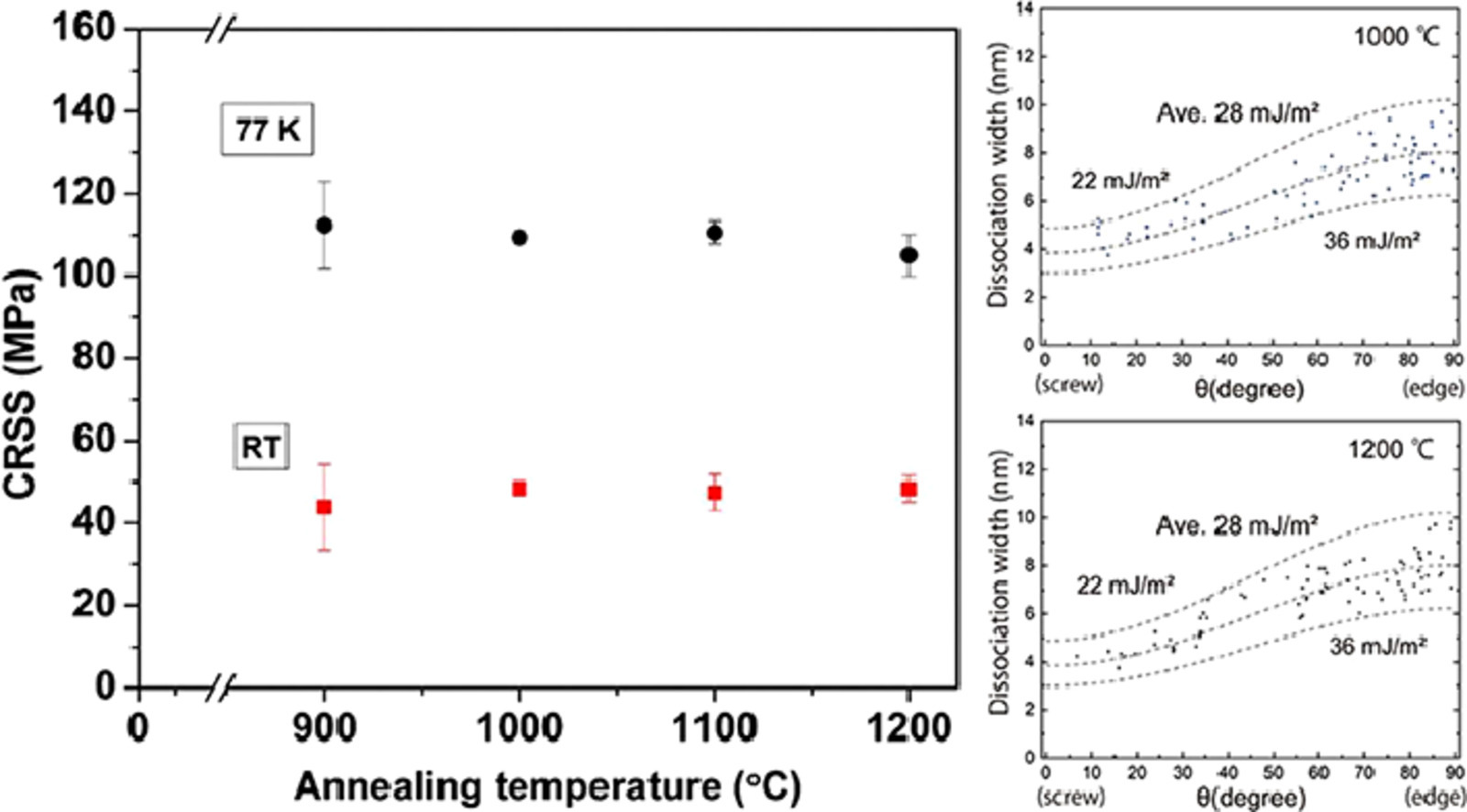
与预期相反,我们报告了面心立方单相等原子Cr-Mn-Fe-Co-Ni高熵合金的宏观力学强度不受退火的影响,在退火期间可能形成了短程有序结构。实验结果表明,室温硬度、室温和77 K下的临界分切应力以及合金的激活体积值在900-1200℃退火后不发生明显变化。在1000℃和1200℃退火后的样品,77K下变形的层错能基本相同。这些结果清晰地表明,化学短程有序的形成即使存在,对等原子Cr-Mn-Fe-Co-Ni高熵合金宏观屈服强度的影响也不明显。
英文摘要
We report that in contrast to the anticipation, the macroscopic mechanical strength of single crystals of the face-centered-cubic single-phase equiatomic Cr-Mn-Fe-Co-Ni high entropy alloy is not influenced by thermal annealing during which short-range ordering is expected to develop. Experimental evidence shows that hardness at room temperature, critical resolved shear stress at room temperature and at 77 K and activation volume values of the alloys do not significantly vary with the annealing temperature in the range from 900 to 1200°C. The stacking fault energies in the specimens deformed at 77 K following annealing at 1000 and 1200°C respectively are essentially identical to each other. These results clearly indicate that the impact of the formation of chemical short-range order on the macroscopic yield strength of the equiatomic Cr-Mn-Fe-Co-Ni high entropy alloy is insignificant, even if it exists.
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, 15 Jan. 2021, P185-190
19. Stress-driven grain refinement in a microstructurally stable nanocrystalline binary alloy
微观结构稳定的二元纳米晶合金中的应力驱动晶粒细化
K.A. Darling✉, S. Srinivasan, R.K. Koju, B.C. Hornbuckle, J. Smeltzer, Y. Mishin, K.N. Solanki✉
K.A. Darling: kristopher.a.darling.civ@mail.mil
K.N. Solanki: Kiran.solanki@asu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.041
摘要
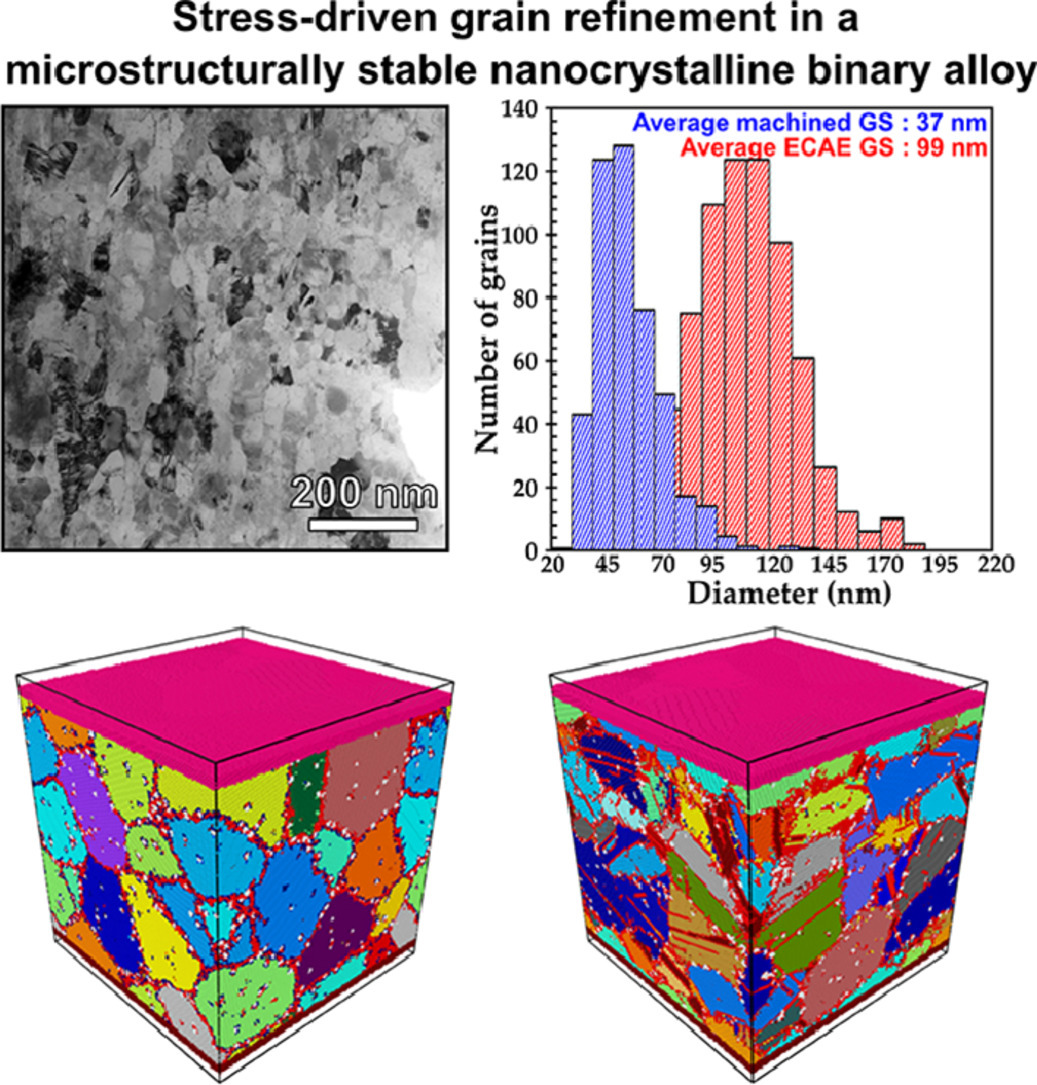
纳米晶材料中形变诱导晶粒生长是一种被广泛报道的现象,这种现象归因于晶界过程。在本文中,我们报告了与之相反的现象,即稳定的纳米晶铜-钽合金在严重塑性变形 (SPD) 过程中纳米晶粒得到进一步细化。尽管变形过程中温度升高了350℃,但当SPD达到250%时,会导致晶粒尺寸显著减小。实验和原子模拟表明,这种意想不到的晶粒细化是由于弥散分布的钽纳米团簇在整个晶粒中心和沿晶界分布的直接结果。这些钽纳米团簇充当了动力学钉扎剂,抑制了再结晶过程中的晶界过程。
英文摘要
Deformation-induced grain-growth in nanocrystalline materials is a widely-reported phenomenon that has been attributed to grain boundary (GB) processes. In this paper, we report on the opposite phenomenon, wherein a stable nanocrystalline (NC) Cu-Ta alloy undergoes a further refinement of the nano-grains during severe plastic deformation (SPD). SPD up to 250% results in a significant grain-size reduction despite the 350°C increase in temperature caused by the deformation process. Experiments and atomistic-simulations show that this unexpected grain-refinement is a direct result of well-dispersed Ta-nanoclusters throughout grain centers and along GBs acting as kinetic-pinning agents and suppressing GB processes that occur during recrystallization.
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, 15 Jan. 2021, P191-195
20. A robust algorithm to calculate parent β grain shapes and orientations from α phase electron backscatter diffraction data in α/β-titanium alloys
根据α/β-钛合金中α相电子背散射衍射数据计算母体β晶粒形状和取向的可靠算法
Alexander Zaitzeff✉, Adam Pilchak, Tracy Berman, John Allison, Selim Esedoglu
Alexander Zaitzeff: azaitzef@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.038
摘要
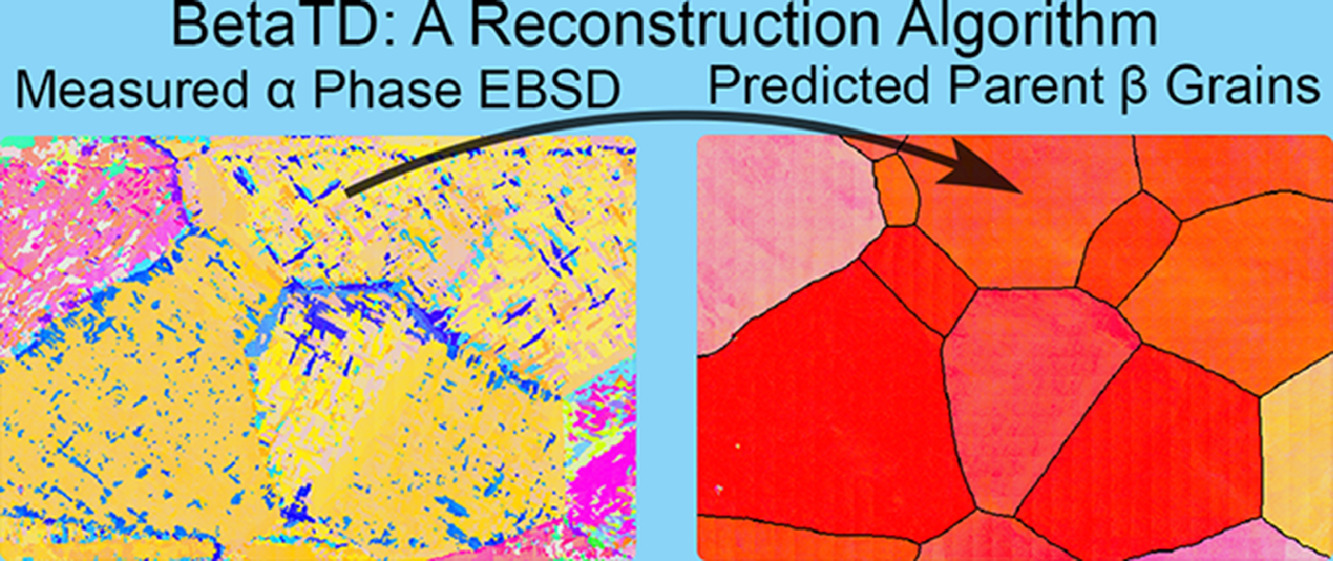
本文提出了一种新的模型和开源算法,该模型和算法可从测量的α/β钛合金中的α相电子背散射衍射数据中重建原β相的取向和晶粒形状。它基于Mumford和Shah的图像分割模型,包括一个正则化因子,用来创建平滑边界并克服了现有重建技术的缺点。此外,该新算法具有很强的抗噪性。我们的算法在模拟和真实数据上均具有有效性。
英文摘要
This paper presents a new model and open-source algorithm for reconstructing prior β phase orientation and grain shapes from measured α-phase electron backscatter diffraction data in α/β titanium alloys. It is based on the image segmentation model of Mumford and Shah, which includes a regularization term that helps create smooth boundaries and overcomes shortcomings of prior reconstruction techniques. Additionally, the new algorithm is resilient to noise. Our algorithm’s effectiveness is demonstrated on simulated and real world data.
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, 15 Jan. 2021, P196-201
21. Simultaneously enhanced strength and strain hardening capacity in FeMnCoCr high-entropy alloy via harmonic structure design
通过调和结构设计,同时提高了FeMnCoCr高熵合金的强度和应变硬化能力
Guodong Li, Maowen Liu, Shaoyuan Lyu, Masashi Nakatani, Ruixiao Zheng✉, Chaoli Ma, Qiushi Li, Kei Ameyama
Ruixiao Zheng: zhengruixiao@buaa.edu.cn,北京航空航天大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.036
摘要
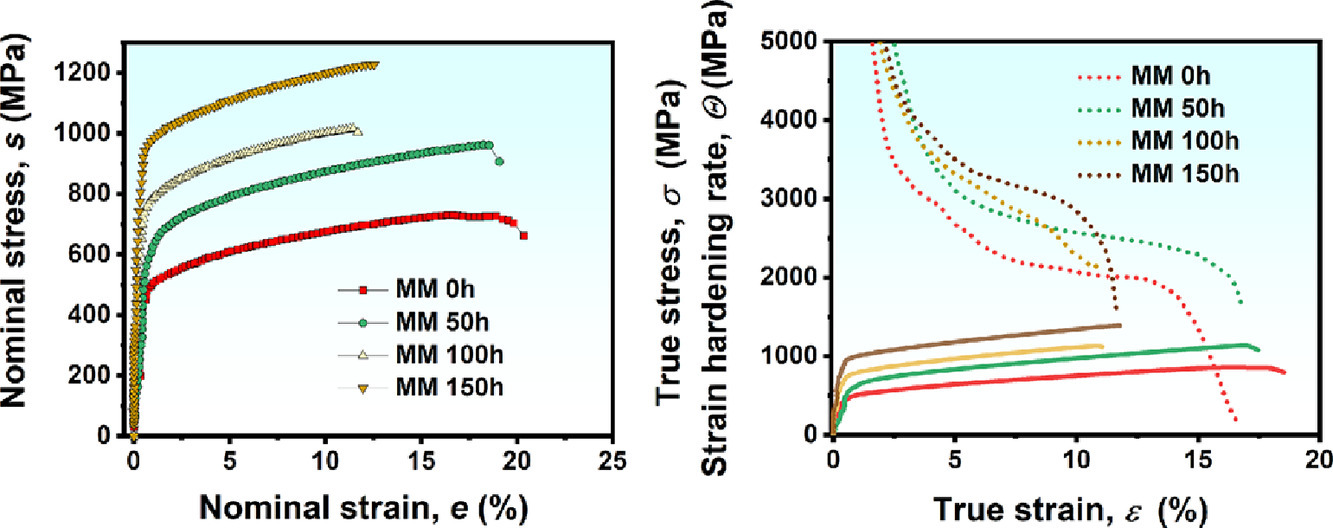
调和结构(HS)被认为是一种有效的微观组织设计策略,可以提高金属材料的强度和延展性,其结构特点为粗晶(CG)区域均匀嵌入三维连续的超细晶(UFG)区域。本研究通过可调控的机械球磨和随后的烧结过程,成功制备了具有HS特征的非等原子FeMnCoCr高熵合金样品,其中shell的体积分数可调(从~16%到~70%)。微观组织观察表明,shell区域由完全再结晶的UFG组成,平均晶粒尺寸小于1µm。拉伸试验表明,与均质结构试样相比,具有HS特征的试样的强度和应变硬化能力同时得到提高。特别是,shell体积分数约为70%的样品的抗拉强度和均匀伸长率分别为1228MPa和12.4%,表现出优异的强度-塑性协同作用。本文讨论了力学性能强化的潜在机理。
英文摘要
Harmonic structure (HS), consisting of coarse-grained (CG) areas uniformly embedded in three dimensional continuously connected ultrafine-grained (UFG) areas, is considered as an effective microstructural design strategy to achieve enhanced strength and ductility in metallic materials. In the present study, HS designed non-equiatomic FeMnCoCr high-entropy alloy samples with tunable shell fractions (ranging from ~16% to ~70%) were successfully prepared via controlled mechanical milling and subsequent sintering. Microstructure observations suggested that the shell region was composed of fully recrystallized UFGs with a mean grain size below 1 µm. Tensile test revealed that the HS designed samples exhibited simultaneously enhanced strength and strain hardening capability than those of the homogeneous structured counterpart. Particularly, the ultimate tensile strength and uniform elongation of the sample with a shell fraction of ~70% were 1228MPa and 12.4%, respectively, demonstrating superior strength-ductility synergy. The underlying mechanisms responsible for the enhanced mechanical properties were discussed.
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, 15 Jan. 2021, P215-218
22. Surface activated bonding of aluminum oxide films at room temperature
室温下氧化铝膜的表面活化键合
Jun Utsumi, Ryo Takigawa✉
Ryo Takigawa: takigawa@ed.kyushu-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.005
摘要
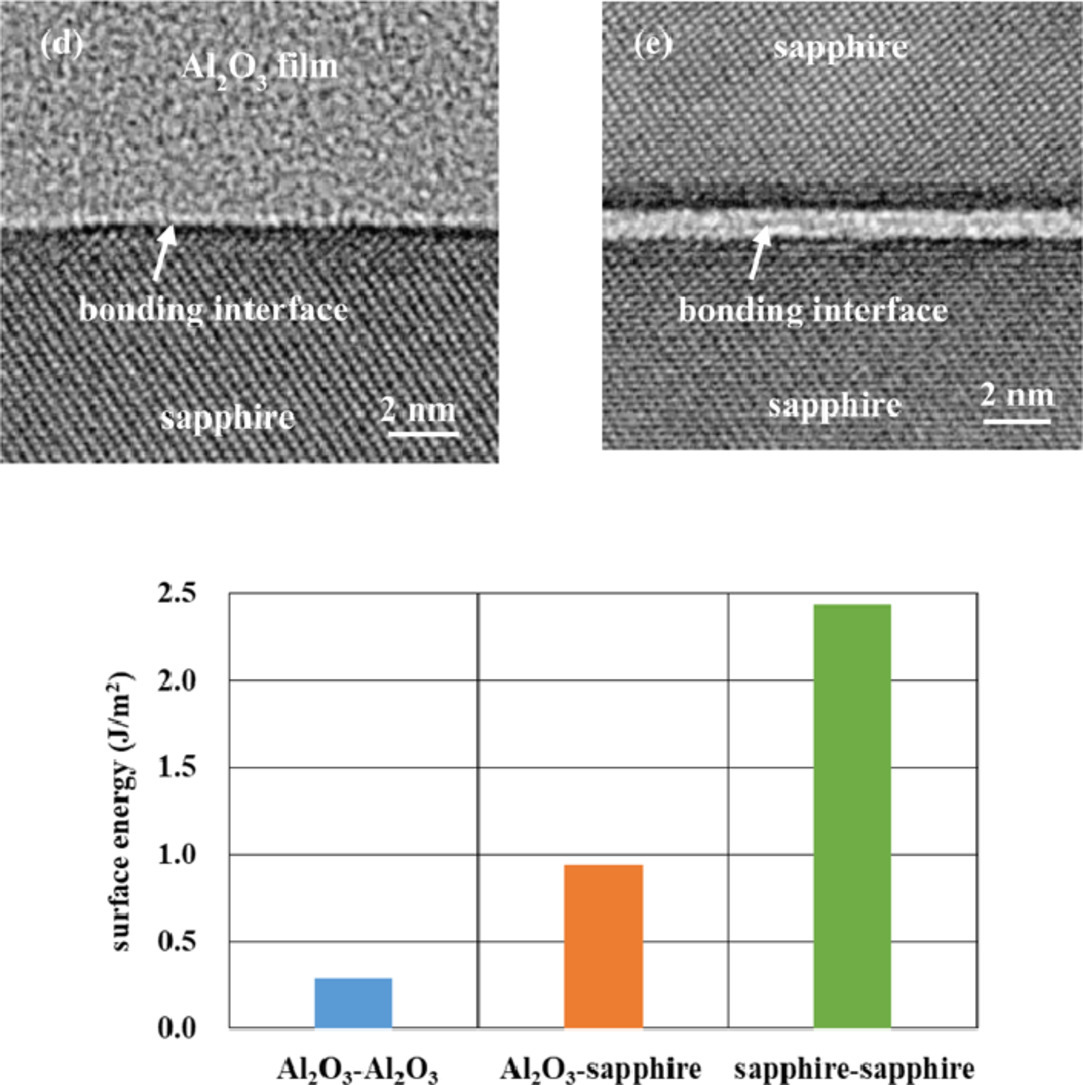
我们采用化学气相沉积的方法研究了在室温短时间活化条件下沉积氧化铝薄膜的表面活化键合行为。虽然Al2O3膜成键的表面能很低,但Al2O3膜/蓝宝石成键的表面能约为1 J m-2,蓝宝石/蓝宝石成键的表面能大于2 J m-2。透射电镜结果显示在Al2O3/Al2O3键合界面出现了约1nm厚的非晶状中间层,而在Al2O3/蓝宝石键合界面则没有观察到。此种现象表明Al2O3膜的结晶度会影响Al2O3的键合。
英文摘要
We have investigated the surface activated bonding (SAB) of deposited Al2O3 films by chemical vapor deposition under a short-time activated condition at room temperature. Although the surface energy for bonding of Al2O3 films was very low, that of Al2O3 film/sapphire bonding was approximately 1 J m-2 and more than 2 J m-2 for sapphire/sapphire bonding. Transmission electron microscopy showed an amorphous-like intermediate layer approximately 1 nm thick, observed at the bonding interface of Al2O3/Al2O3, but not in the bonding of Al2O3/sapphire, which suggests that the crystallinity of the Al2O3 film affects the bonding of Al2O3.
SCRIPTA Vol. 191, 15 Jan. 2021, P219-224
23. Effect of dislocation configuration on Ag segregation in subgrain boundary of a Mg-Ag alloy
位错构型对Mg-Ag合金中亚晶界处银偏析的影响
Lirong Xiao, Xuefei Chen, Kang Wei, Yi Liu, Dongdi Yin, Zhaohua Hu, Hao Zhou✉, Yuntian Zhu✉
Hao Zhou: hzhou511@njust.edu.cn,南京理工大学
Yuntian Zhu: ytzhu@ncsu.edu,南京理工大学,北卡罗莱纳州立大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.08.040
摘要
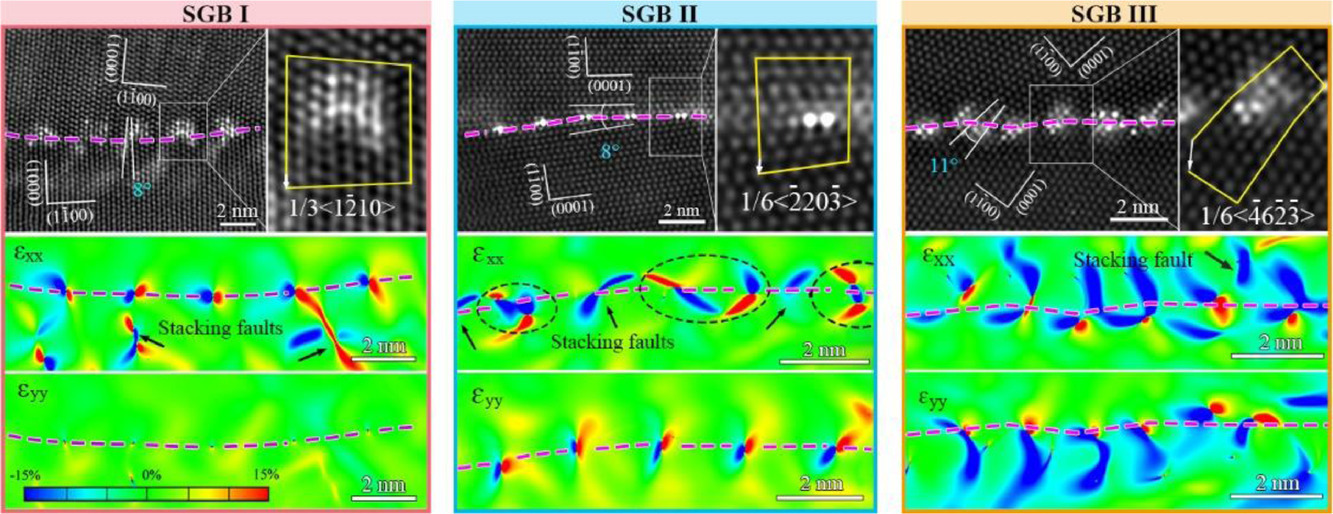
界面偏析对纳米晶镁合金的热机械稳定性起着至关重要的作用。本文报道了传统轧制过程中银偏聚辅助形成高比例亚晶界的镁银纳米晶合金。偏析结构是由位错构型、应变场和亚晶界的取向差决定的。这表明,诱导<c+a>位错的合金元素有助于提高界面的稳定性。
英文摘要
Interfacial segregation has been reported to play a critical role in the thermal-mechanical stability of nanocrystalline Mg alloys. Here we report Ag-segregation-assisted formation of nanocrystalline Mg-Ag alloy with high proportion of sub-grain boundaries during conventional rolling. The segregation structure is determined by dislocation configurations and subsequent strain field and misorientation of the sub-grain boundary. It indicates that the alloying elements, which induce <c+a> dislocations, would help to improve the stability of interfaces.
微信公众号:Goal Science
投稿邮箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
