金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.192, Feb. 2021
2020-11-09 来源: Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文12篇,涵盖了低碳马氏体钢、热成型钢、形状记忆合金、镍基高温合金、高熵合金、钛铝合金、铜、中锰奥氏体钢、马氏体不锈钢、奥氏体不锈钢等,国内科研单位包括中国香港大学、哈尔滨工业大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 192 目录
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P1-6
1. Tailoring the formation of twins in Al by introducing epitaxial layer interfaces
通过引入外延层界面调整Al中孪晶的形成
S.C. Xue✉, Y.F. Zhang, Qiang Li, Jie Ding, H.Wang, X. Zhang✉
S.C. Xue: xue97@purdue.edu
X. Zhang: xzhang98@purdue.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.043
摘要
孪晶界使金属材料具有独特的机械和物理性能。然而,由于铝具有高的层错能,很少在铝中观察到生长孪晶。本研究中,我们报道了在溅射Al/Mg多层膜中合成高密度生长孪晶的方法。本文讨论了非共格和共格孪晶界的形成机理,并确定了与非共格孪晶界相关的结构——9R相。本研究强调了一种有效的方法,来提高具有高层错能金属中孪晶/9R相的密度。
英文摘要
Twin boundaries have enabled unique mechanical and physical properties in metallic materials. However, growth twins are rarely observed in Al due to its high stacking fault energy. In this study, we report on the synthesis of high-density growth twins in sputtered Al/Mg multilayer films. The formation mechanisms of incoherent and coherent twin boundaries are discussed. Besides, the incoherent twin boundary related structure, 9R phase, was also identified. This study highlights an effective method to elevate the twin /9R phase density in metals with high stacking fault energy.
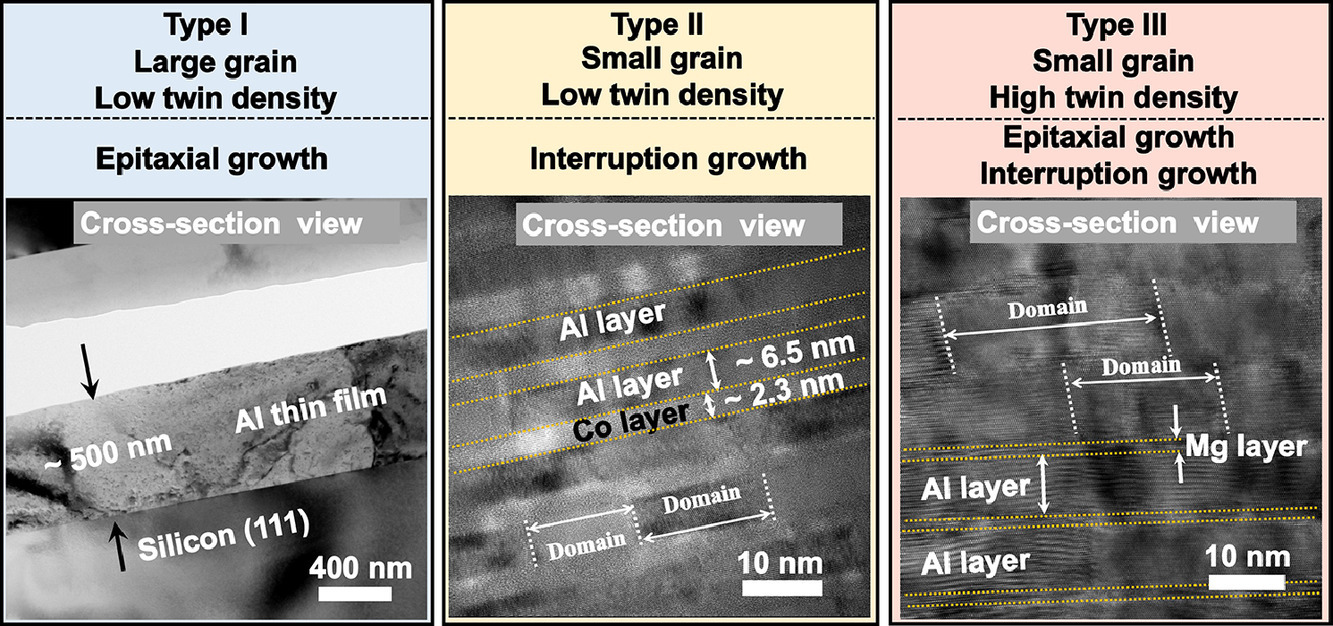
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P13-18
2. Enhancing damage-resistance in low carbon martensitic steels upon dual-pass laser treatment
通过双道激光处理提高低碳马氏体钢的抗损伤性能
Hyun Seok Oh, Jiyun Kang, C. Cem Tasan✉
C. Cem Tasan: tasan@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.047
摘要
各种增材制造工艺的快速发展推动了激光辅助处理过程中微观组织优化的研究,以便在空间上改变工程部件的材料性能。本工作表明,将双道激光处理应用于低碳板条马氏体钢中,可以同时修复凝固或疲劳裂纹,降低表面粗糙度,最重要的是,触发相变获得包含层间奥氏体的微观组织,其具有更高的抗损伤性能。我们使用扫描电子显微镜、透射高能X射线衍射分析以及力学表征测试研究了这些影响,并讨论了潜在的机制。
英文摘要
The fast development of various additive manufacturing processes is motivating research to improve microstructure control during laser assisted treatments, in order to spatially vary material properties on engineering components. In the present work, we demonstrate that a dual-pass laser treatment applied to a low carbon lath martensitic steel can simultaneously repair solidification or fatigue cracks, reduce surface roughness, and, most importantly, trigger phase transformations to create a more damage-resistant microstructure, namely, one that includes interlath austenite. We investigate these influences employing various scanning electron microscopy and transmission high energy X-ray diffraction analyses, mechanical characterization tests, and discuss the underlying mechanisms.
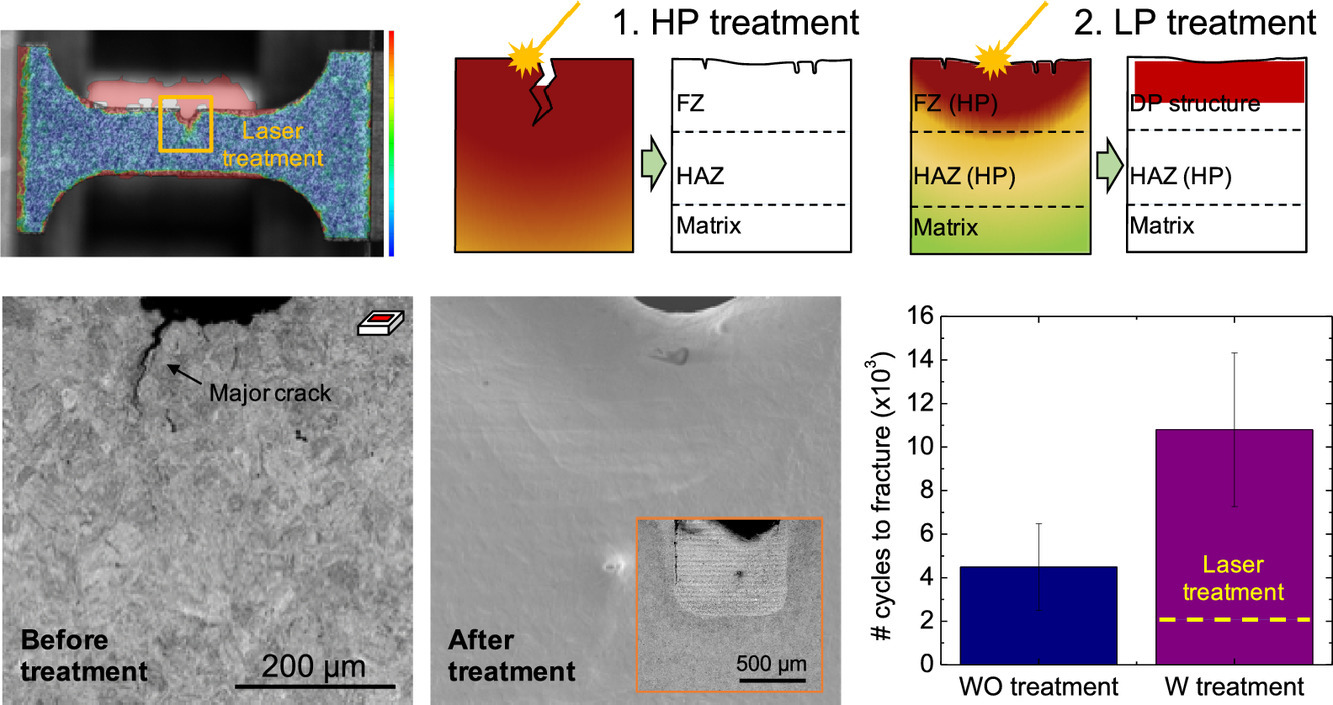
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P19-25
3. Improving the bending toughness of Al-Si coated press-hardened steel by tailoring coating thickness
通过调整涂层厚度提高铝硅涂层热成型钢的弯曲韧性
Z. Wang, Z.H. Cao, J.F. Wang, M.X. Huang✉
M.X. Huang: mxhuang@hku.hk,中国香港大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.008
摘要
在铝硅涂层热成型钢(PHS)的热冲压过程中,外层金属间化合物层和马氏体基体之间会形成铁素体层。出乎意料地是,铁素体层并不能有效地阻止脆性裂纹从金属间化合物向马氏体基体不断扩展。这导致了裂纹尖端的高应力强度因子(SIF),从而在马氏体基体中引发了高的局部剪切变形,降低了钢的可弯曲性。更薄的铝硅涂层产生更薄的脆性金属间化合物和铁素体层,因此涂层裂纹更短,裂纹尖端的SIF更小,从而改善了可弯曲性。此外,更薄的铝硅涂层降低了材料成本,同时能保持相似的可涂性和耐腐蚀性。这种薄铝硅涂层可能会改变目前铝硅涂层的操作,影响全球汽车工业。
英文摘要
A ferrite layer is formed between the outer intermetallics layers and the martensite substrate during the hot stamping process of Al-Si coated press-hardened steel (PHS). Unexpectedly, it is found here that the ferrite layer does not effectively prevent brittle cracks propagating continuously from the intermetallics to the martensite substrate. This leads to a high stress intensity factor (SIF) at the crack tip, therefore initiating highly localized shear deformation in the martensite substrate, degrading the bendability of the steel. A thinner Al-Si coating produces thinner brittle intermetallics and ferrite layers, and therefore shorter coating cracks and smaller SIF at the crack tip, thus improving the bendability. In addition, a thinner Al-Si coating also has a lower material cost while keeping similar paintability and corrosion resistance. The thin Al-Si coating could potentially change the current practice of Al-Si coating, impacting the global automotive industry.
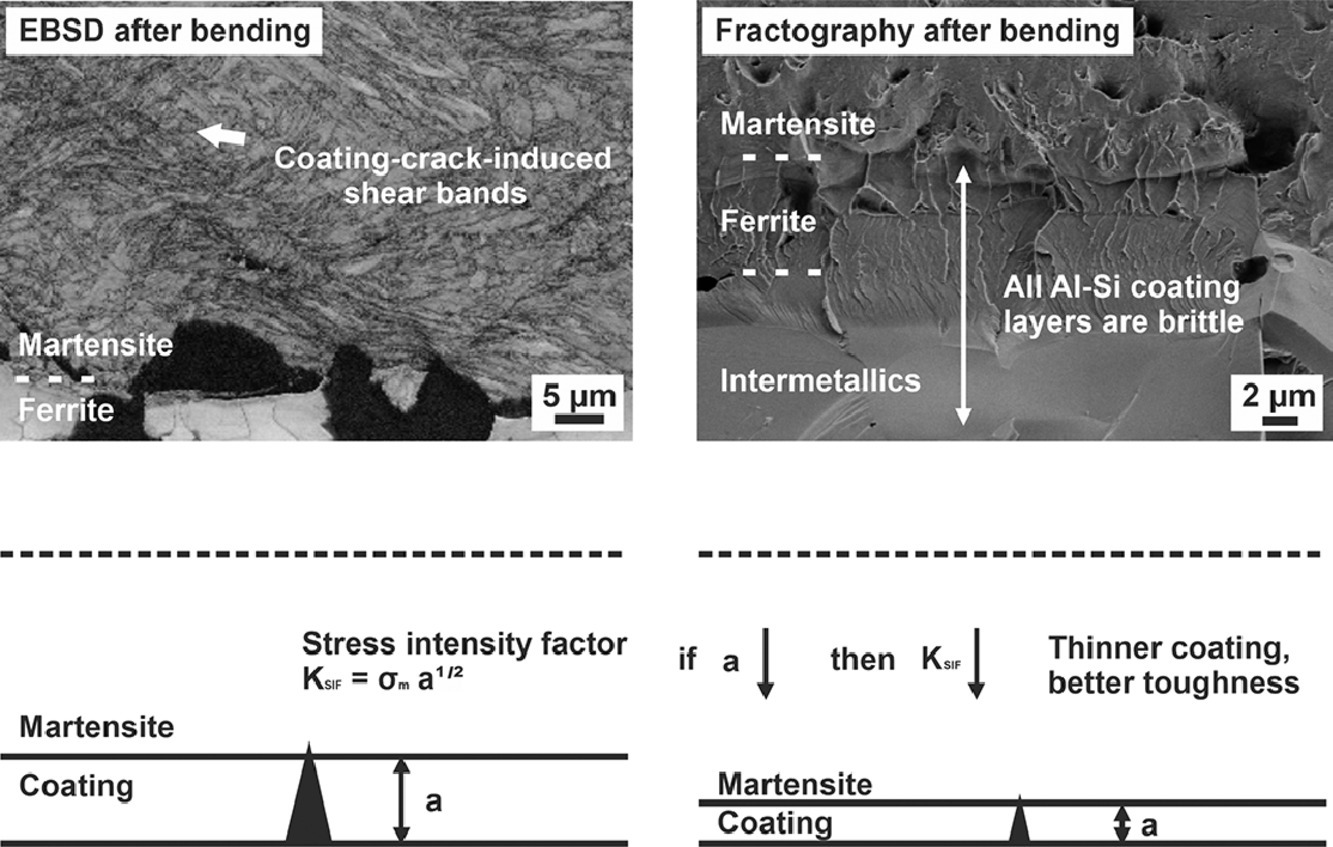
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P26-31
4. Thermodynamics of martensite formation in Fe-Mn-Al-Ni shape memory alloys
Fe-Mn-Al-Ni形状记忆合金中马氏体形成的热力学研究
Alexander Walnsch, Mario J. Kriegel✉, Mykhaylo Motylenko, Grzegorz Korpala, UlrichPrahl, Andreas Leineweber
Mario J. Kriegel: mario.kriegel@iww.tu-freiberg.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.003
摘要
Fe-Mn-Al-Ni基形状记忆合金因其相对较低的材料成本和良好的冷加工性,被认为适合于大规模应用。奥氏体态由A2结构的基体和共格的B2析出相组成,以确保热弹性的发生。马氏体态基于A1结构。对于一系列合金,马氏体相变的起始温度低于环境温度;而对于相同的合金成分,通过基于CalPhaD的计算,预测在大约1000℃的T0温度下,A2基体将转化为A1。热力学表明,1000K左右的过冷度是由于B2析出相(含一定量的铁和锰)抵抗基体马氏体转变而转变为L10结构造成的。
英文摘要
Fe-Mn-Al-Ni based shape memory alloys are regarded suitable for large scale applications due to relatively low materials costs and a good cold workability. The austenitic state consists of an A2 structured matrix with coherent B2 precipitates which are required to ensure thermoelasticity, supposedly due to a strengthening effect on the matrix. The martensitic state is based on the A1 structure. For a series of alloys, the martensite start temperatures were determined to be below ambient temperature, whereas for the same alloy compositions T0 temperatures of about 1000 °C are predicted for the transformation of the A2 matrix into A1 by means of CalPhaD-based calculations. It is shown by thermodynamic considerations that the undercooling of about 1000 K is caused by the resistance of the B2 precipitates (~NiAl with some content of Fe and Mn) to undergo the transformation to the L10 structure enforced by the martensitic transformation of the matrix.
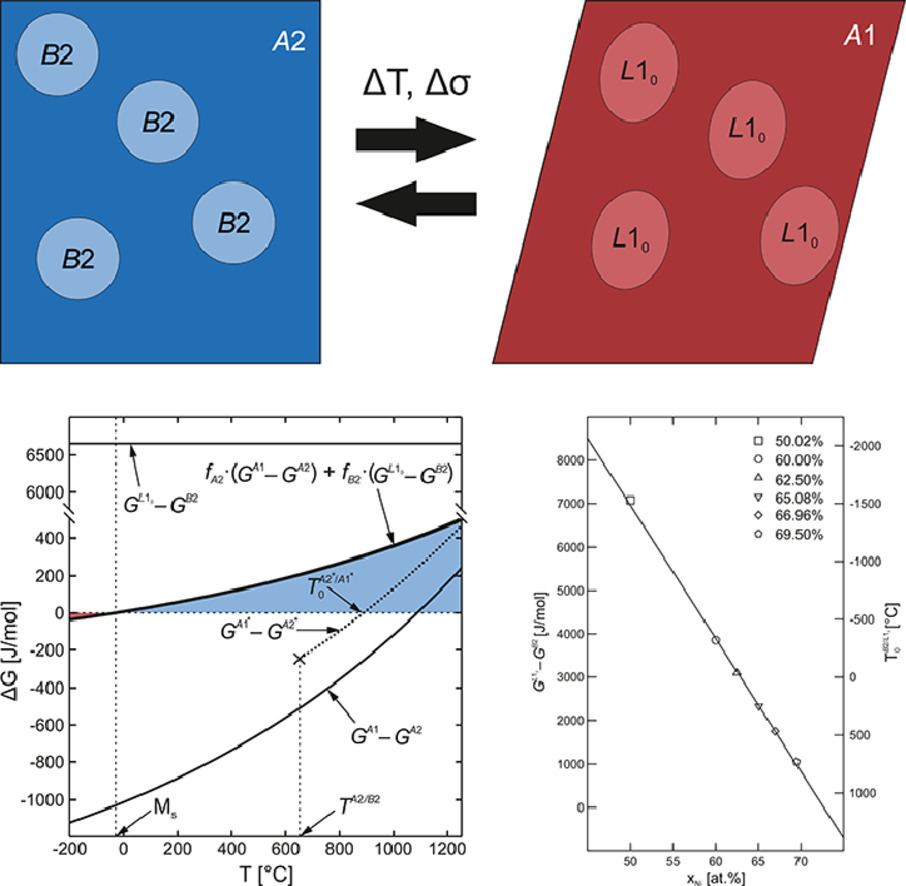
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P37-42
5. Dynamic recovery observed in distinct grains within a polycrystalline nickel-based superalloy during cyclic high temperature fatigue via high energy X-ray diffraction microscopy
利用高能X射线衍射显微镜观察在循环高温疲劳试验过程中多晶镍基高温合金不同晶粒的动态回复
Sven E. Gustafson, Darren C. Pagan, Paul A. Shade, Michael D. Sangid✉
Michael D. Sangid: msangid@purdue.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.004
摘要
利用高能X射线衍射显微镜(HEDM)对镍基高温合金多晶体的弹性微力学场进行了追踪,并通过峰展宽分析确定了在循环高温加载过程中相应的晶内变形指标。对具有252个晶粒的低固溶度、高难熔样品进行单轴拉伸并保持固定位移,同时在460℃和770℃之间进行热循环,并用HEDM进行间断性的表征,以研究晶粒对热机械变形的平均响应。研究发现,高温下样品区域内的不同晶粒表现出不均匀的回复程度,表明晶粒间的交互作用很复杂;且温度越高,恢复的程度越高。
英文摘要
Elastic micromechanical fields are tracked for a nickel-based superalloy polycrystal via high energy X-ray diffraction microscopy (HEDM) and corresponding intragranular deformation metrics are determined with peak broadening analysis during cyclic high temperature loading. A low solvus, high refractory (LSHR) sample with 252 grains was subjected to uniaxial tension and held under fixed displacement while thermally cycling between 460 °C and 770 °C with intermittent HEDM characterization to study the grain average response to thermo-mechanical deformation. Elevated temperatures were found to allow for heterogeneous amounts of recovery amongst distinct grains within the sampled region, indicating complex grain interactions; the extent of recovery was greater at higher temperatures.
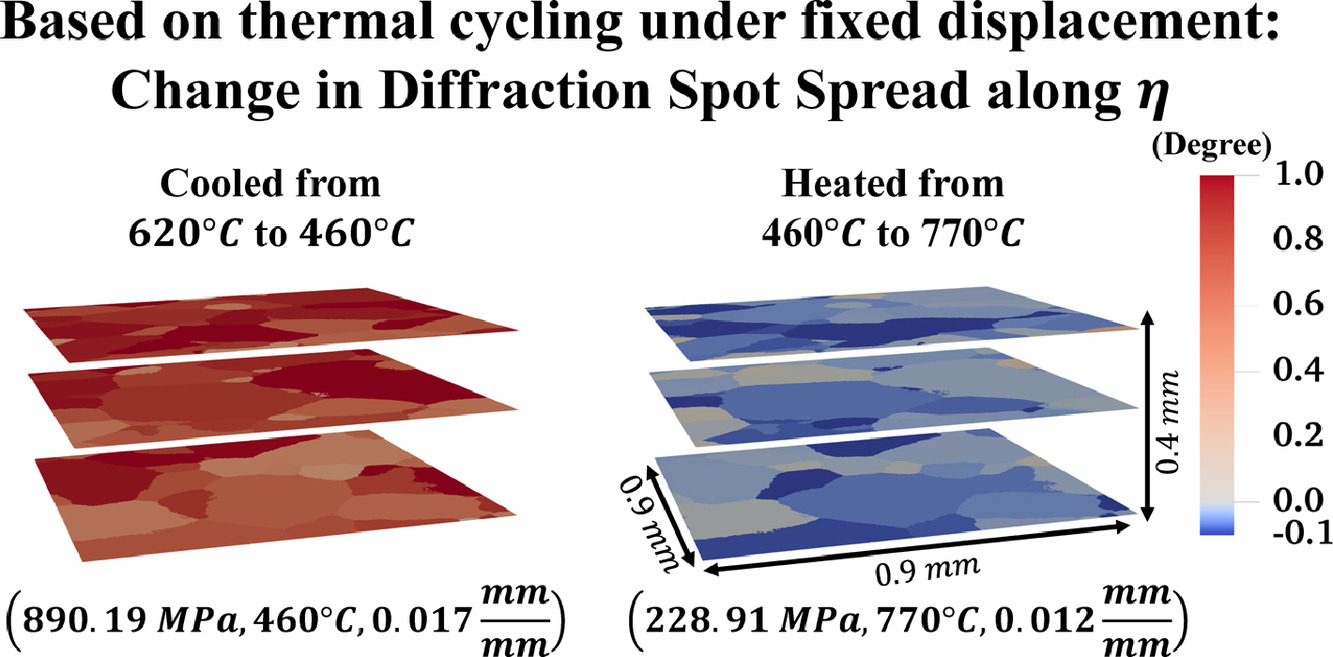
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P43-48
6. From diluted solid solutions to high entropy alloys: Saturation grain size and mechanical properties after high pressure torsion
从稀释固溶体到高熵合金:高压扭转后的饱和晶粒尺寸和力学性能
Tom Keil✉, Enrico Bruder, Mathilde Laurent-Brocq, Karsten Durst
Tom Keil: t.keil@phm.tu-darmstadt.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.046
摘要
研究了Cantor合金和x = 0.8、0.4、0.08和0的富Ni高熵合金 (CrMnFeCo)xNi1-x) 中溶质对饱和晶粒尺寸和力学性能的影响。由于较高的固溶强化和Hall-Petch贡献,粗晶粒和严重变形状态下的压痕硬度随合金含量的增加而增加。纳米压痕应变速率跳跃试验表明,变形状态具有相似的速率敏感性,但没有明显的瞬态状态。所有成分都表现出与历史相关的软化,表明其微观结构的不稳定。高压扭转变形后的饱和晶粒尺寸ds和固溶强化的贡献成负相关,即Δτ越高ds越小。
英文摘要
Effects of solutes on saturation grain size and mechanical properties are investigated for the Cantor alloy and Ni-enriched variations ((CrMnFeCo)xNi1-x) with x=0.8, 0.4, 0.08 and 0. Indentation on coarse-grained and severely deformed states shows increasing hardness with increasing alloying content due to higher solid solution strengthening and Hall-Petch contributions. Nanoindentation strain rate jump tests reveal similar rate sensitivities of the deformed states without pronounced transient regimes. All compositions exhibit a history dependent softening indicating an unstable microstructure. The saturation grain size ds after HPT deformation inversely correlates with the solid solution strengthening contribution, i.e. the higher Δτ the lower ds.
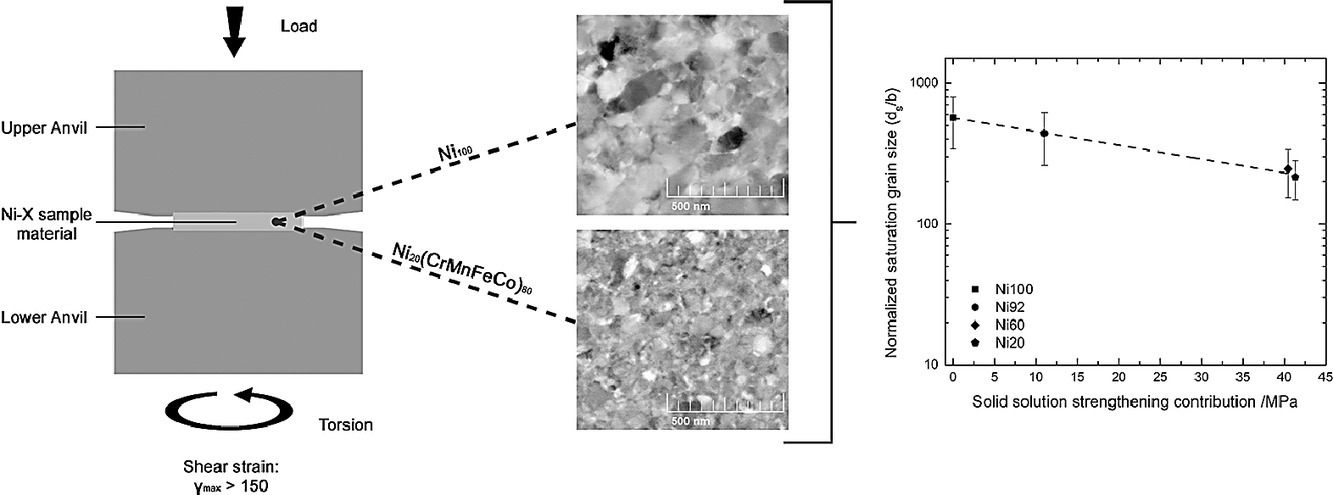
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P55-60
7. A β-solidifying TiAl alloy reinforced with ultra-fine Y-rich precipitates
一种超细富钇析出强化的β-凝固TiAl合金
Xu Gu, Sida Jiang✉, Fuyang Cao, Guoqing Zhang, Dongye Yang, ShuGuo, Heqian Song, Jianfei Sun✉
Sida Jiang: jiangsida@hit.edu.cn,哈尔滨工业大学
Jianfei Sun: jfsun@hit.edu.cn,哈尔滨工业大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.010
摘要
采用扫描电镜和透射电镜研究了一种经放电等离子烧结制备的具有精细组织和超细富钇析出物的β-凝固TiAl合金。两类富钇析出物Y2O3和YAl2在基体中均匀分布,粒径从几十纳米到几百纳米不等。通过选区电子衍射和高分辨透射电子显微镜,确定了两种析出与基体之间的晶体学关系。该放电等离子烧结制备的TiAl合金具有均匀的双相组织,在室温下展现出良好的拉伸性能。特别地,1150℃烧结样品的抗拉强度为1113.1 MPa,屈服强度为881MPa,塑性延伸率为1.41%。
英文摘要
A β-solidifying TiAl alloy with a refined microstructure and ultra-fine yttrium-rich precipitates that was consolidated by spark plasma sintering was investigated by scanning and transmission electron microscopies. Two categories of yttrium-rich precipitates, Y2O3 and YAl2, with sizes ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers were found to be dispersed within the matrix uniformly. The crystallographic relationship between the two precipitates and the γ-TiAl matrix was determined by the selected area electron diffraction and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. This spark plasma sintered TiAl alloy was characterized by a uniform duplex microstructure, and it exhibited excellent tensile properties at room temperature. Typically, specimen sintered at 1150°C has an ultimate tensile strength of 1113.1 MPa, yield strength of 881MPa, and a moderate plastic elongation of 1.41%.
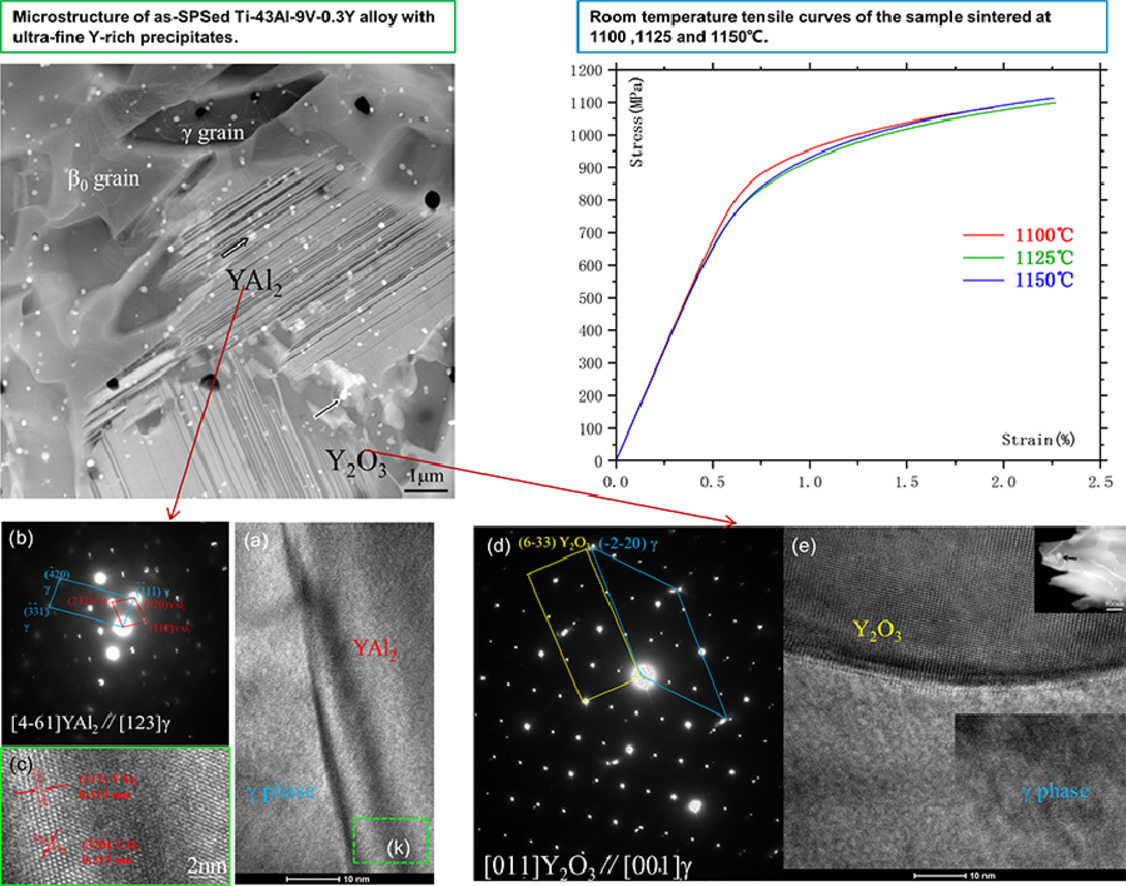
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P61-66
8. Associating GB characteristics with its sink efficiency in absorbing Frank loops in Cu
铜中晶界特征和其吸收弗兰克环效率的关联
J. Chen, K. Dang, H.T. Vo, P. Hosemann, S.J. Fensin✉
S.J. Fensin: saryuj@lanl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.006
摘要
将Cu中沿[100]倾斜轴的一组晶界(GB)作为模型系统,对晶界(GB)与间隙弗兰克环的相互作用进行了分子动力学(MD)模拟。结果表明,两者的相互作用与取向差角度直接相关。具体地,三种模式的相互作用是取向差角度的函数。GB吸收弗兰克环的能力随着取向差角度的增加而增加。上述趋势是基于包括晶界的结构单元的差异来解释的。此外,通过改变局部晶界结构可以改变不同模式之间的转换角度。
英文摘要
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations are performed to investigate the interaction of a migrating grain boundary (GB) with interstitial Frank loops, using a set of GBs along the [100] tilt axis in Cu as model systems. Our results show that the interaction is directly related to the misorientation angle. Specifically, three modes of interaction are observed as a function of misorientation angle. The sink efficiency of a GB, namely, the capability of a GB to absorb the Frank loops, increases with misorientation angle. The above trends are explained based on the differences in the structural units comprising the GB. Additionally, the transition angle between different modes can be altered by varying the local GB structure.
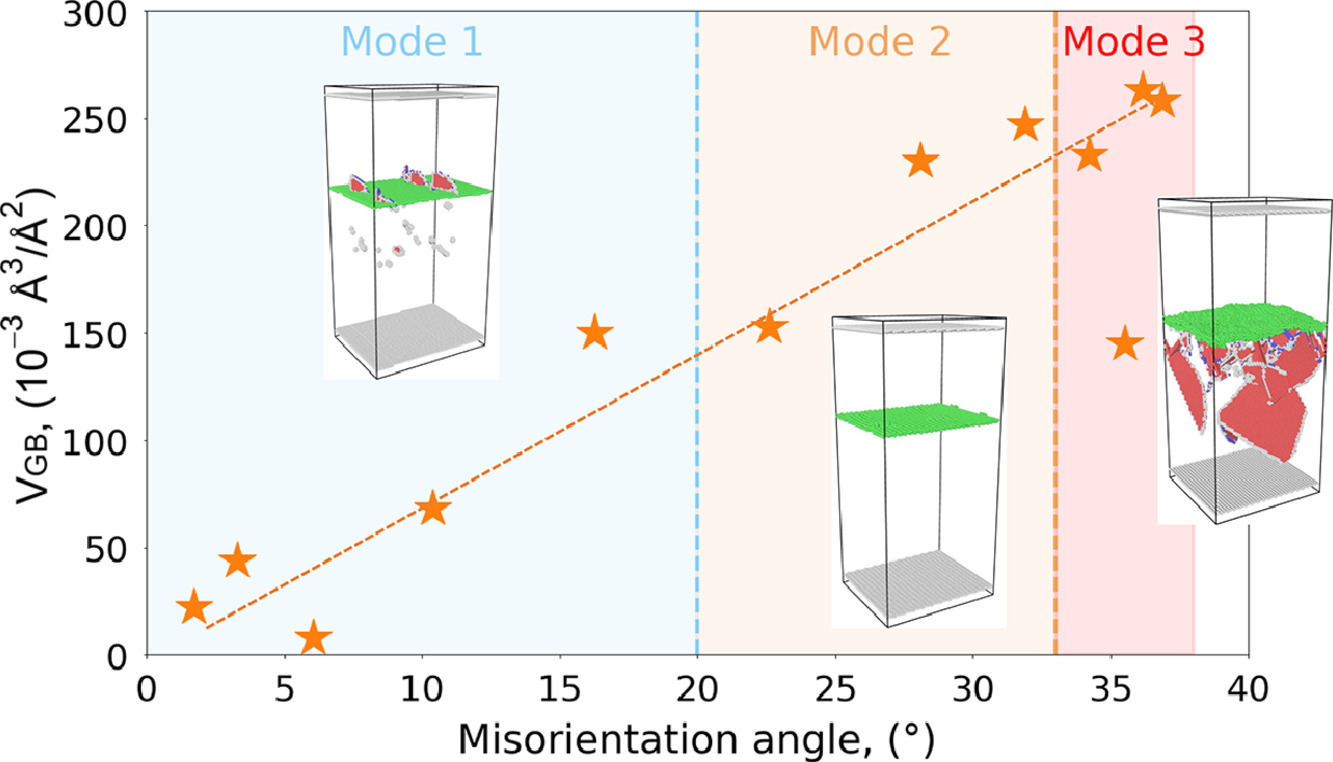
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P78-82
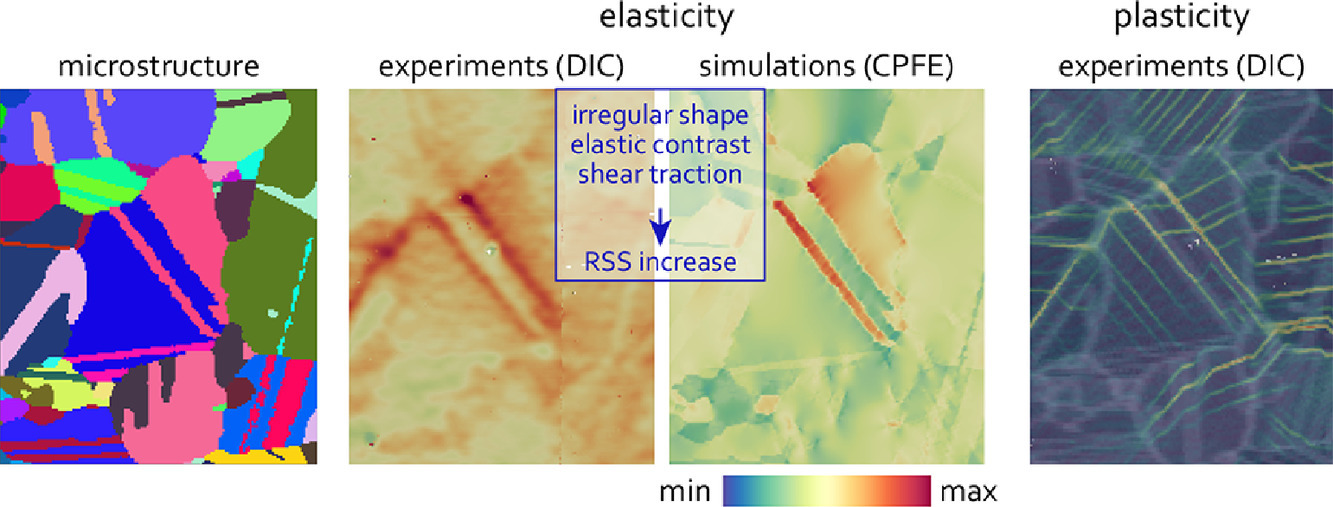
9. Insight into microstructure-sensitive elastic strain concentrations from integrated computational modeling and digital image correlation
通过集成计算模型和数字图像相关法研究对微观组织敏感的弹性应变集中
Marat I. Latypov✉, Jean-Charles Stinville, Jason R. Mayeur, Jonathan M. Hestroffer, Tresa M.Pollock, Irene J. Beyerlein✉
Marat I. Latypov: latmarat@ucsb.edu
Irene J. Beyerlein: beyerlein@ucsb.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.001
摘要
采用晶粒尺度、原位数字图像相关法和晶体塑性有限元方法研究了单调加载下多晶体微观组织中局部高弹性应变集中的微观组织根源。结果表明,微观组织中异常高的弹性应变集中的位置与晶粒特定的晶体学和形貌取向有关,而与其临近晶体的细节关系不大。在此基础上,我们讨论了多晶镍基高温合金微观组织中,退火孪晶界的拓扑和晶体学特征如何提高滑移带开动的可能性。
英文摘要
The microstructural origins of highly localized elastic strain concentrations in polycrystalline microstructures under monotonic loading are studied using grain-scale, in situ digital image correlation and crystal plasticity finite element method. It is shown that the locations of exceptionally high elastic strain concentrations in the microstructure depend on particular crystallographic and morphological orientations of grains and less so on crystalline details of their local neighborhood. Based on these results, we discuss how topological and crystallographic features of annealing twin boundaries can increase the likelihood of slip band initiation throughout the microstructure of polycrystalline Ni-base superalloys.

SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P83-88
10. Activation of a hybrid twinning mechanism in a Cr-Ni-Si-V-N medium manganese austenitic steel containing precipitates
含析出的Cr-Ni-Si-V-N中锰奥氏体钢中混合孪生激活的机理研究
S. Shyamal, M. Ghiasabadi Farahani, T. Allam, A.S. Hamada, C. Haase, J.I. Kömi, P.C. Chakraborti, P. Sahu✉
P. Sahu: psahu@phys.jdvu.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.011
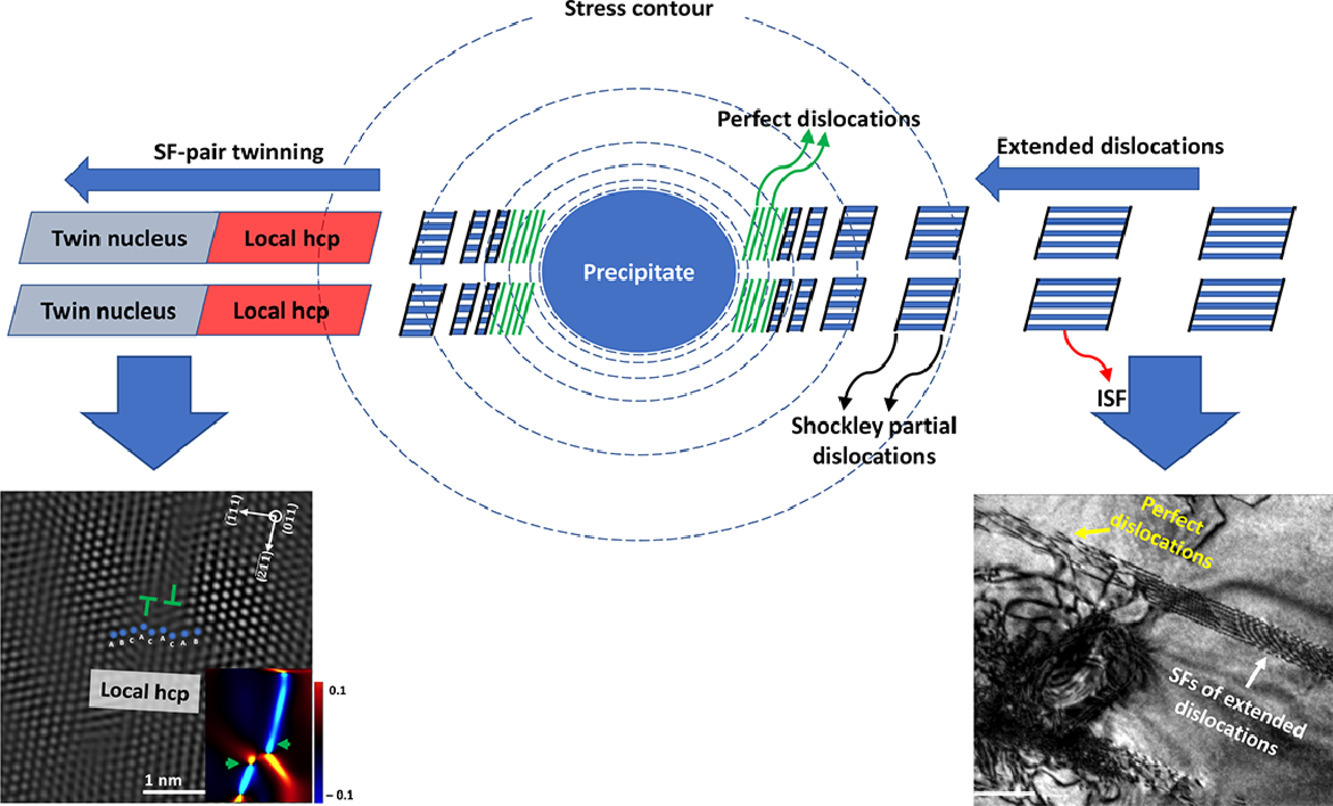
摘要
本工作用透射电镜研究了含析出的中锰奥氏体钢在低应变~ 0.02条件下的孪晶形核行为。在析出相附近,更容易发生无层错的位错反应,而在离析出相更远的地方孪晶会被激活。孪晶形核遵循一种混合机制,即通过经典位错分解产生层错,而这些层错随后又遵循非经典交替层错对机制重叠,从而形成三层孪晶核。我们从基体中能垒变化的角度对观察到的孪生行为进行了解释。
英文摘要
Twinning nucleation in a medium Mn austenitic steel containing precipitates is studied at low strain ~ 0.02, using transmission electron microscopy. In the near vicinity of the precipitates, unfaulting dislocation reaction is favored, while twinning is activated farther from the precipitates. Twin nucleation follows a hybrid mechanism, involving creation of stacking faults through classical dislocation dissociation, while those stacking faults subsequently overlapped following a non-classical alternated stacking fault pair mechanism to create a three-layer twin nucleus. The observed twinning behavior is interpreted from an energy barrier variation viewpoint within the matrix.
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P106-110
11. C clustering and partitioning by static strain aging in cold-rolled 16Cr-5Ni supermartensitic stainless steel
冷轧16Cr-5Ni超级马氏体不锈钢中静态应变时效引发C的团簇和配分
Hojun Gwon, Sung-Ho Kim, Jong Jin Jeon, Sung-Joon Kim✉
Sung-Joon Kim: sjkim1@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.016
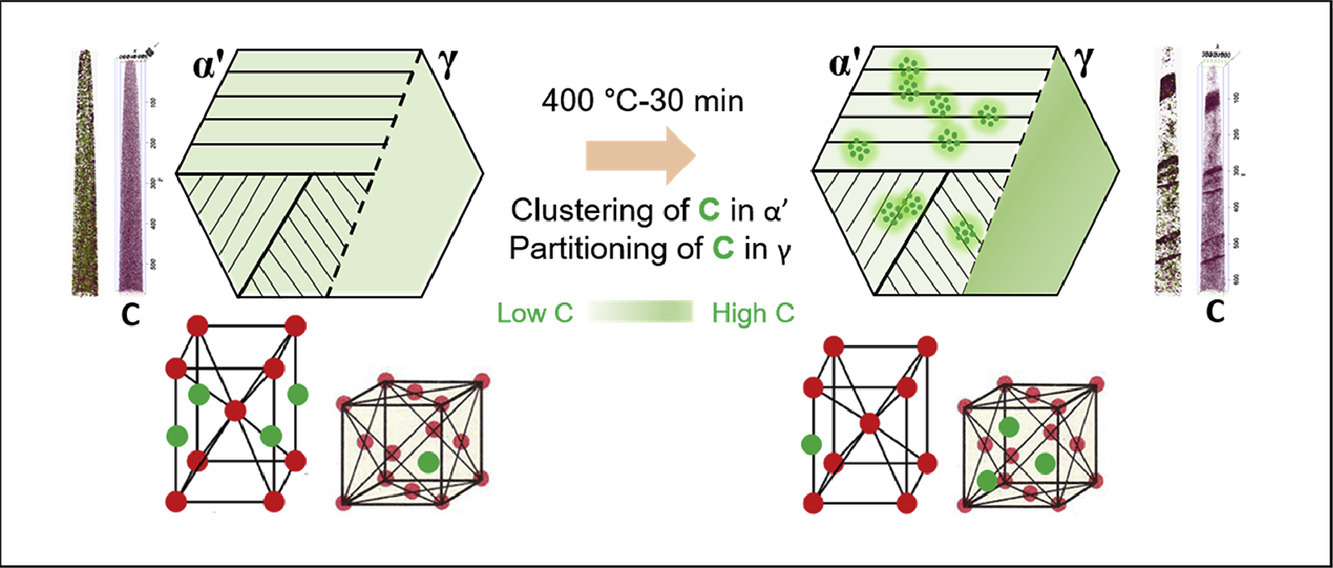
摘要
本文研究了冷轧16Cr-5Ni超级马氏体不锈钢在400℃时效30min后的静态应变时效行为。在20%冷轧试样的单轴拉伸试验中,相比于冷轧试样,时效试样的屈服强度提高了~300MPa,应变硬化率降低。在中断拉伸试验中,观察到时效试样中马氏体相变发生延迟。膨胀分析法检测到试样在400℃保温30分钟过程中发生了体积收缩,表明碳从马氏体配分到了奥氏体中。利用脉冲内摩擦技术证实了马氏体中C的团簇。三维原子探针断层扫描分析揭示了C原子向奥氏体中的配分以及C原子在马氏体中的团簇。屈服强度的显著提高是由于时效过程中C原子的重新分布所致。
英文摘要
Static strain aging behavior of cold-rolled 16Cr-5Ni supermartensitic stainless steel was investigated after it had been aged for 30 min at 400°C. In uniaxial tensile tests of 20% cold-rolled specimens, increase of yield strength to ~300 MPa and decrease of strain hardening rate were observed in the aged specimen, compared to the as-rolled specimen. In interrupted tensile tests, delayed martensitic transformation was observed in the aged specimen. Dilatometry analysis detected volume shrinkage during the 30 min holding period at 400°C indicating partitioning of carbon (C) from α’ martensite to austenite. The clustering of C in α’ martensite was confirmed by impulse internal friction technique with observation of Cottrell atmosphere formation. 3D atom probe tomography analysis revealed partitioning of C atoms into austenite and clustering of C atoms in the α’ martensite. The remarkable increase of yield strength was attributed to redistribution of C atoms during the aging treatment.
SCRIPTA Vol. 192, Feb. 2021, P115-119
12. Grain boundary character distribution in an additively manufactured austenitic stainless steel
增材制造奥氏体不锈钢中晶界的特征分布
Majid Laleh, Anthony E. Hughes, Mike Y. Tan, Gregory S. Rohrer, Sophie Primig, Nima Haghdadi✉
Nima Haghdadi: nima.haghdadi@unsw.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.018
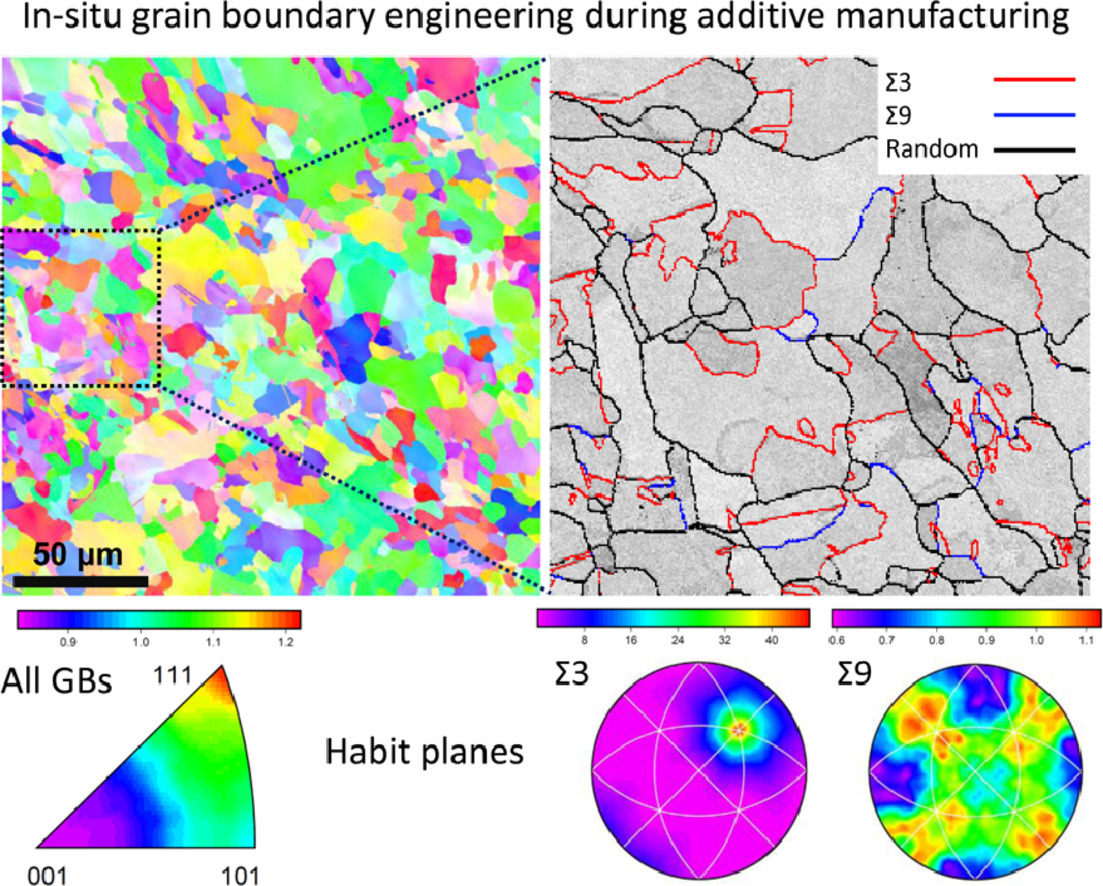
摘要
本文研究了增材制造奥氏体不锈钢在初始态和退火条件下的晶界特征分布(GBCD)。增材制造实现了相对较细的晶粒和无丝织构的组织,初始结构中展现出大量的Σ3界。一个5参数的GBCD分析表明,微观结构主要是由高度非共格的Σ3界组成。晶界网络也包含终止于具有纯扭曲特征的(111)面的大角度共格Σ3界和倾斜的Σ9界。研究结果表明,通过增材制造过程中热循环引发的应力和热,可以对材料的晶界网络进行原位设计。
英文摘要
The grain boundary character distribution (GBCD) in an austenitic stainless steel produced by additive manufacturing (AM) in both as-built and annealed conditions was studied. Relatively fine grains and a non-fibre texture was achieved by AM, and as-built structure showed a high population of Σ3 boundaries. A five-parameter GBCD analysis revealed that the microstructure is mostly dominated by highly incoherent Σ3 boundaries. The grain boundary network also consisted of random high angle, coherent Σ3s terminating on (111) planes with a pure twist character, and tilt Σ9 boundaries. The findings show prospects for the possibility of engineering the grain boundary network of materials in-situ, via the stress and heat induced by the thermal cycles during AM.
微信公众号:Goal Science
投稿邮箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
