金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.193, 1 Mar. 2021(全)
2021-01-27 来源:Goal Science
Vol. 193 目录
1. Machine learning based surrogate modeling approach for mapping crystal deformation in three dimensions
基于机器学习的替代建模方法,用于绘制三维晶体变形
2. Hydride formation in Ti6Al4V: An in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction study
Ti6Al4V中氢化物的形成:原位同步X射线衍射研究
3. Atomic configurations of planar defects in μ phase in Ni-based superalloys
镍基高温合金μ相中平面缺陷的原子构型
4. Race against the Machine: can deep learning recognize microstructures as well as the trained human eye?
和机器赛跑:深度学习能像训练有素的人眼那样识别微观组织吗?
5. Revisiting ω phase embrittlement in metastable β titanium alloys: Role of elemental partitioning
回顾亚稳β钛合金中的ω相脆化:元素配分的作用
6. Bimorphic microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V alloy manipulated by spark plasma sintering and in-situ press forging
火花等离子体烧结和原位锻造处理的Ti-6Al-4V合金的双晶组织
7. Deformation-induced ultrafine grains near fatigue crack tip and correlative fatigue damage in Al matrix composite
铝基复合材料疲劳裂纹尖端附近变形诱导的超细晶粒及其相关的疲劳损伤
8. Multiscale characterization of the 3D network structure of metal carbides in a Ni superalloy by synchrotron X-ray microtomography and ptychography
用同步加速X射线显微层析术和叠层成像术对镍基超合金中金属碳化物的3D网络结构进行多尺度表征
9. Ensuring the strength and ductility synergy in an austenitic stainless steel: single- or multi-phase hetero-structures design
确保奥氏体不锈钢强度和塑性的协同提升:单相或多相异质结构设计
10. High-throughput mapping method for mechanical properties, oxidation resistance, and phase stability in Ni-based superalloys using composition-graded unidirectional solidified alloys
基于成分梯度单向凝固的镍基高温合金力学性能、抗氧化性和相稳定性的高通量映射方法
11. Stable high-entropy TiZrHfNbVCrMoMnFeCoNiAl Laves phase
稳定的高熵TiZrHfNbVCrMoMnFeCoNiAl Laves相
12. Formation of core-shell type structure in Duplex Martensitic Steel
双相马氏体钢中核壳型结构的形成
13. Achieving exceptionally high strength in binary Mg-13Gd alloy by strong texture and substantial precipitates
通过强烈的织构和大量析出,在二元Mg-13Gd合金中实现极高的强度
14. Modeling the precipitation processes and the formation of hierarchical microstructures in a single crystal high entropy superalloy
模拟单晶高熵高温合金中的析出过程和分层微观组织的形成
15. Properties and influence of microstructure and crystal defects in Fe2VAl modified by laser surface remelting
激光表面重熔改性Fe2VAl的性能及其微观组织和晶体缺陷的影响
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P1-5
1. Machine learning based surrogate modeling approach for mapping crystal deformation in three dimensions
基于机器学习的替代建模方法,用于绘制三维晶体变形
Anup Pandey✉, Reeju Pokharel
Anup Pandey: anup@lanl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.025
摘要
我们提出了一种基于机器学习的替代建模方法,用于预测多晶材料在单轴拉伸载荷下空间分辨的三维晶体学取向演化。我们的方法比现有的晶体塑性方法快了一个数量级,可以用来模拟其他计算方法无法实现的大体积体系。这项工作是对现有基于机器学习模型的重大突破,现有的模型要么局限于2D结构,要么只能提供平均的,而非局部的三维全场预测结果。我们展示了替代模型方法在搜集面心立方铜试样拉伸变形实验数据的速度和准确性。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P12-16
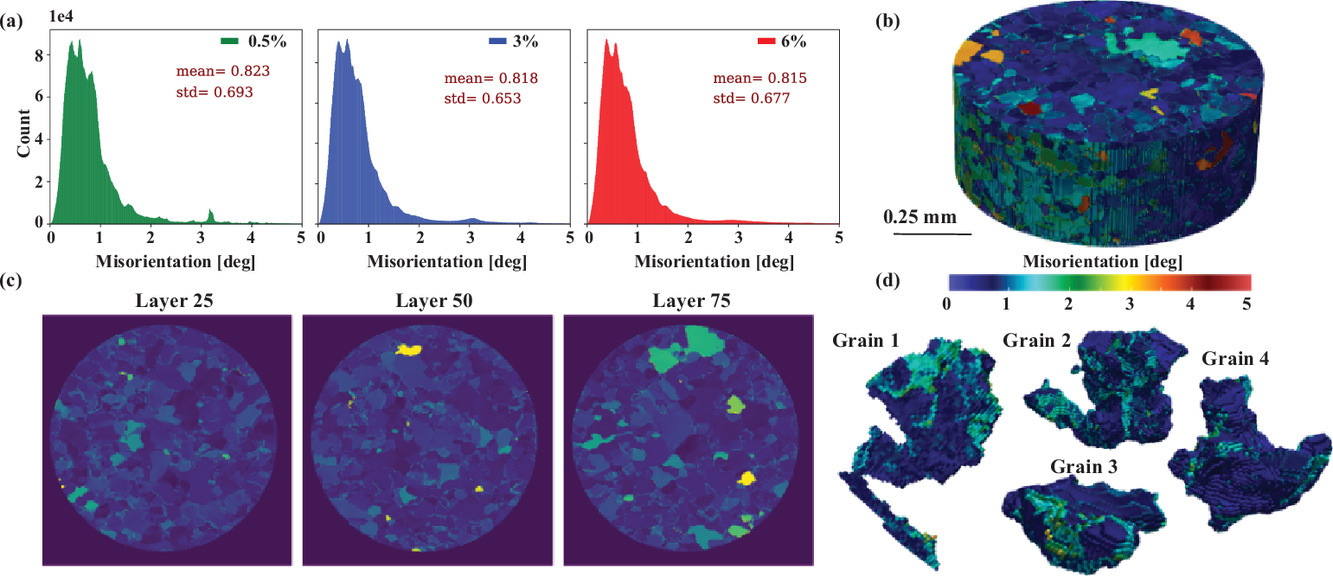
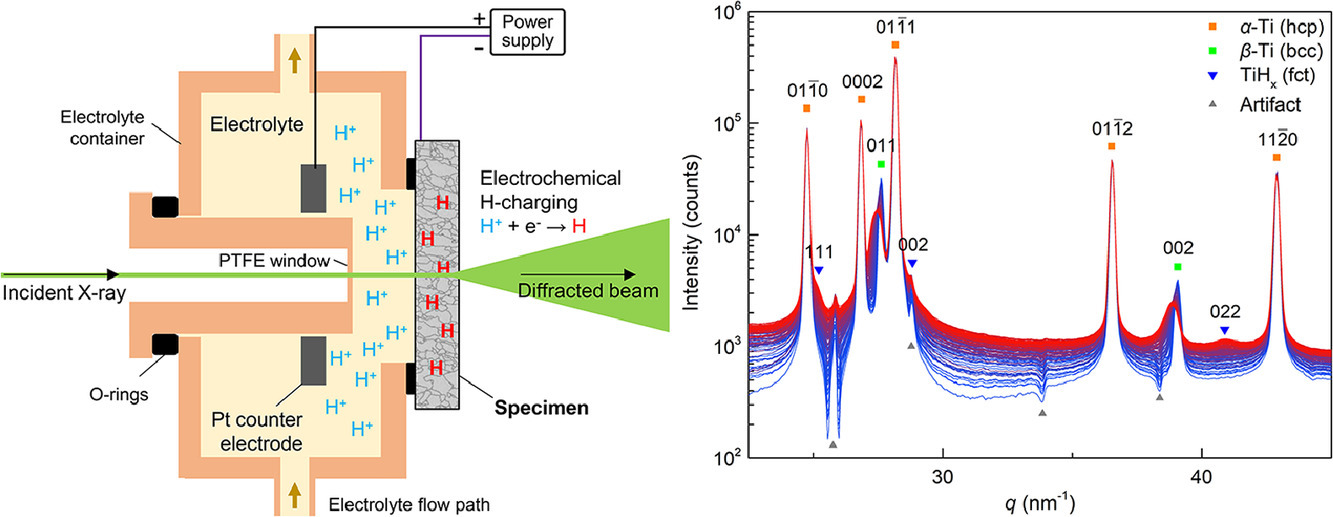
2. Hydride formation in Ti6Al4V: An in situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction study
Ti6Al4V中氢化物的形成:原位同步X射线衍射研究
Jinwoo Kim, Jiyun Kang, C. Cem Tasan✉
C. Cem Tasan: tasan@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.025
摘要
吸氢会导致Ti6Al4V中氢化物形成、晶格应变和其他晶体学变化。为了更好地监测和了解这些变化,我们开发了一种用于透射X射线衍射的原位充氢装置,并将其用于高能同步X射线源。我们观察到两相中氢进入引起的各向异性晶格膨胀以及氢化物形成导致的微应变的演化。我们利用电子背散射衍射分析,对氢化物相进行了晶体学表征,包括其与相邻相的取向关系。本文还进一步讨论了该方法在研究氢与微观结构交互作用方面的应用。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P27-32
3. Atomic configurations of planar defects in μ phase in Ni-based superalloys
镍基高温合金μ相中平面缺陷的原子构型
Yongxin Cheng, Guanglei Wang, Jide Liu, Lianlong He✉
Lianlong He: llhe@imr.ac.cn,中科院沈阳金属所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.09.045
摘要
高温合金中普遍存在μ拓扑致密相,其本征变形对其性能至关重要。通过像差校正扫描透射电镜和几何结构分析,研究了μ相平面缺陷的原子构型。研究发现,μ相基面滑移是由Laves内三层同步剪切完成的,而非基面的剪切变形则与长程扩散或局部原子重排有关。与(1-102)金字塔平面不同,(-1101)金字塔平面上的平面错位位移向量偏离滑移平面,导致错位区域收缩或膨胀。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P33-37
4. Race against the Machine: can deep learning recognize microstructures as well as the trained human eye?
和机器赛跑:深度学习能像训练有素的人眼那样识别微观组织吗?
Michiel Larmuseau✉, Michael Sluydts, Koenraad Theuwissen, Lode Duprez, TomDhaene, Stefaan Cottenier
Michiel Larmuseau: michiel.larmuseau@ugent.be
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.026
摘要
图像识别中深度学习的前景表明了材料科学中微观分析的巨大潜力。在材料研究中采用这种方法的一个主要挑战是可供训练模型使用的图像数量有限。在此,我们提出了一种方法,以创建准确的图像识别模型与小数据集。通过明确地考虑到放大率和引入适当的转换,我们在模型中结合了材料科学尽可能多的见解。这需要对复杂的深度学习模型进行高数据效率的训练。我们的结果表明,用本方法训练的模型能够超过人类专家。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P38-42
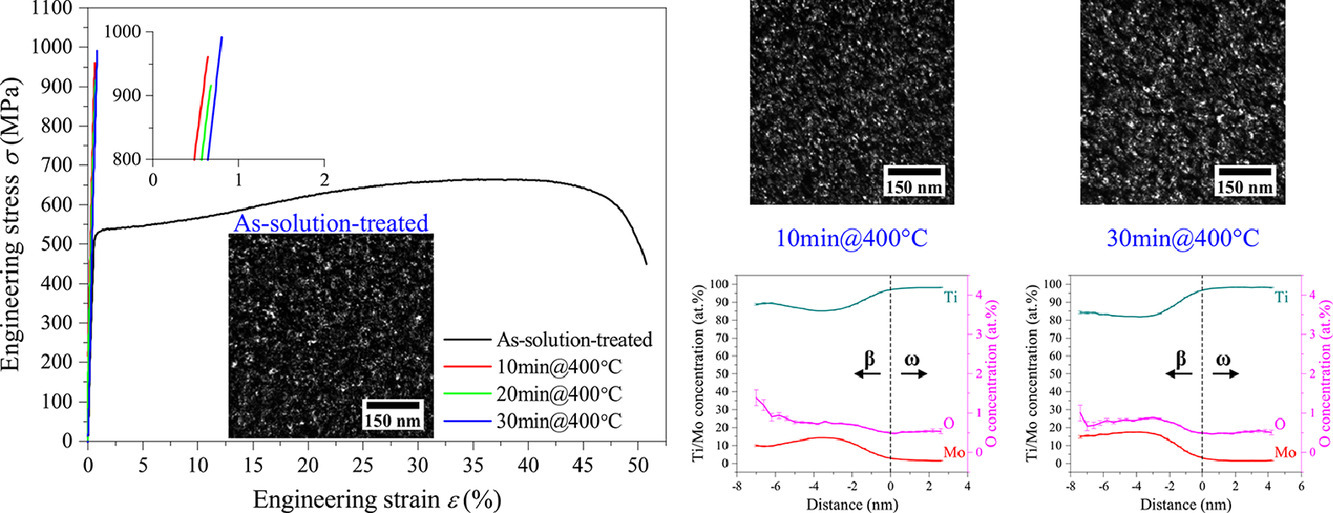
5. Revisiting ω phase embrittlement in metastable β titanium alloys: Role of elemental partitioning
回顾亚稳β钛合金中的ω相脆化:元素配分的作用
M.J. Lai✉, T. Li, F.K. Yan, J.S. Li✉, D. Raabe
M.J. Lai: lai@nwpu.edu.cn
J.S. Li: ljsh@nwpu.edu.cn,西北工业大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.031
摘要
我们用透射电镜和原子探针断层扫描技术研究了最初包含韧性ω相的Ti-12Mo (wt. %)模型合金中,β和ω相之间元素配分对合金脆化的影响。结果表明在400°C时效短短10min,合金就已经发生了脆化,而这时ω颗粒的尺寸、颗粒间距以及体积分数几乎没有发生变化。时效诱导脆化的根源是在时效过程中ω颗粒对Mo元素(>5 at.%)的强烈排斥,这会导致ω颗粒剪切模量(>30GPa)的急剧增加,使得在宏观屈服前就发生强烈的塑性流变应力集中,引起裂纹的萌生。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P43-48
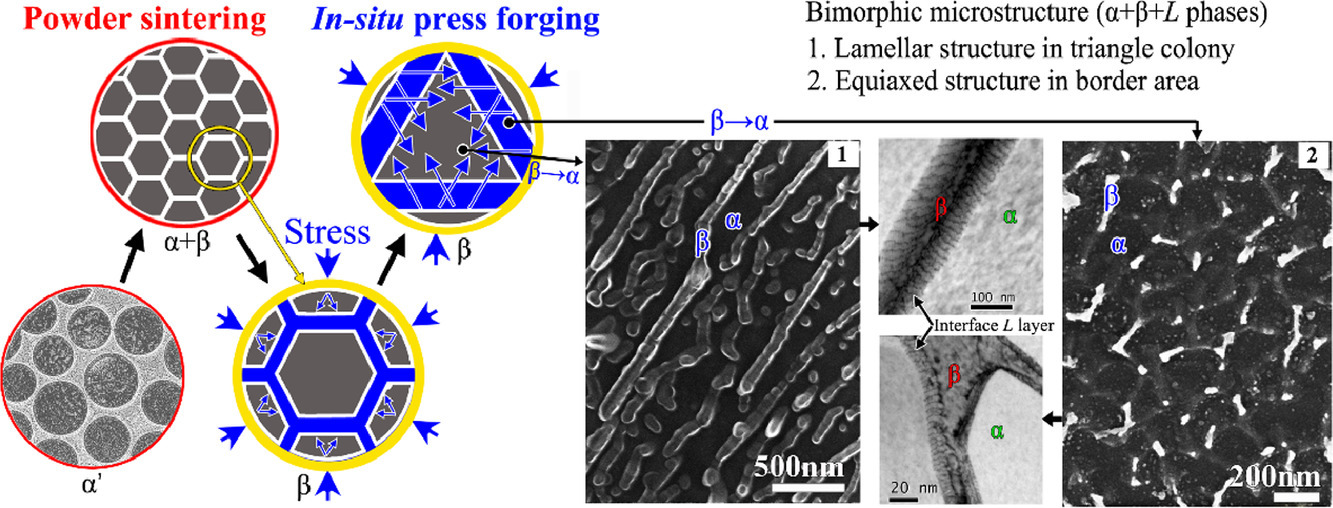
6. Bimorphic microstructure in Ti-6Al-4V alloy manipulated by spark plasma sintering and in-situ press forging
火花等离子体烧结和原位锻造处理的Ti-6Al-4V合金的双晶组织
L.M. Kang, Y.J. Cai, X.C. Luo, Z.J. Li, X.B. Liu, Z. Wang, Y.Y. Li, C. Yang✉
C. Yang: cyang@scut.edu.cn,华南理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.035
摘要
本文报道了一种粉末烧结和原位压锻的方法,用于控制Ti-6Al-4V合金中一种新的双晶组织。微观组织包括具有超细α/β层状结构的典型三角区域,具有超细等轴α晶和分散的纳米/超细β晶的边界区域以及α/β界面L层。令人惊讶的是,该双晶合金在拉伸和压缩条件下均表现出优异的力学性能,远优于目前报道的其他Ti-6Al-4V合金及其复合材料。因此,本研究为制备高性能金属合金提供了一种简单而经济的方法。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P49-54
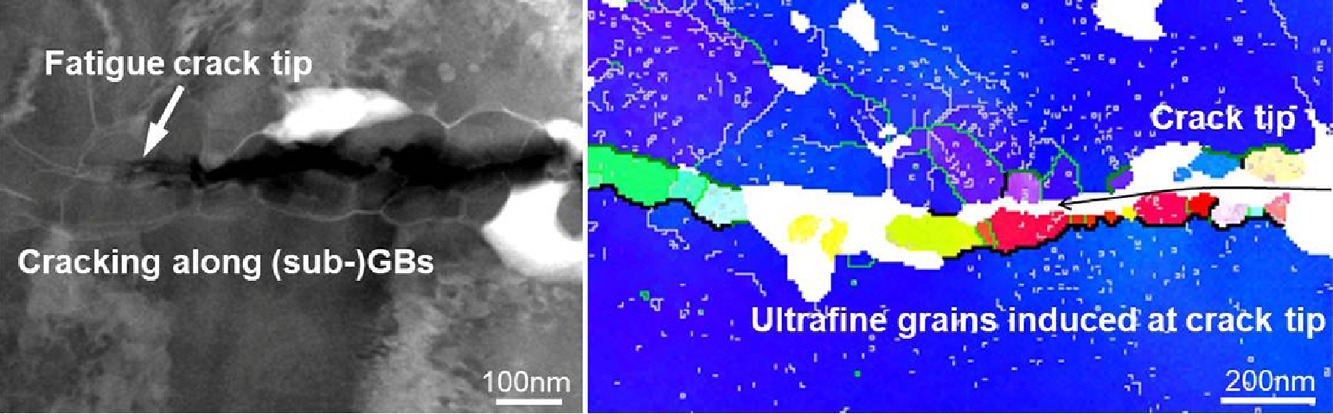
7. Deformation-induced ultrafine grains near fatigue crack tip and correlative fatigue damage in Al matrix composite
铝基复合材料疲劳裂纹尖端附近变形诱导的超细晶粒及其相关的疲劳损伤
Jiwei Geng, Yugang Li, Hongyu Xiao, Zhiping Wang, Mingliang Wang, Dong Chen✉, Haowei Wang
Dong Chen: chend@sjtu.edu.cn,上海交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.040
摘要
我们通过透射菊池衍射和透射电子显微镜对TiB2/Al复合材料疲劳裂纹尖端附近的组织演变和相关的损伤机理进行了新的认识。我们发现微形变带从裂纹尖端形成,沿着滑移面延伸。超细晶是在形变带中产生的,疲劳裂纹倾向于沿着这些形变诱导的边界扩展。此过程被首次证明是裂纹跨越母相晶粒和晶界的基本过程。在裂纹尖端前部,TiB2颗粒可通过阻止变形带的连续扩展来影响裂纹生长。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P71-76
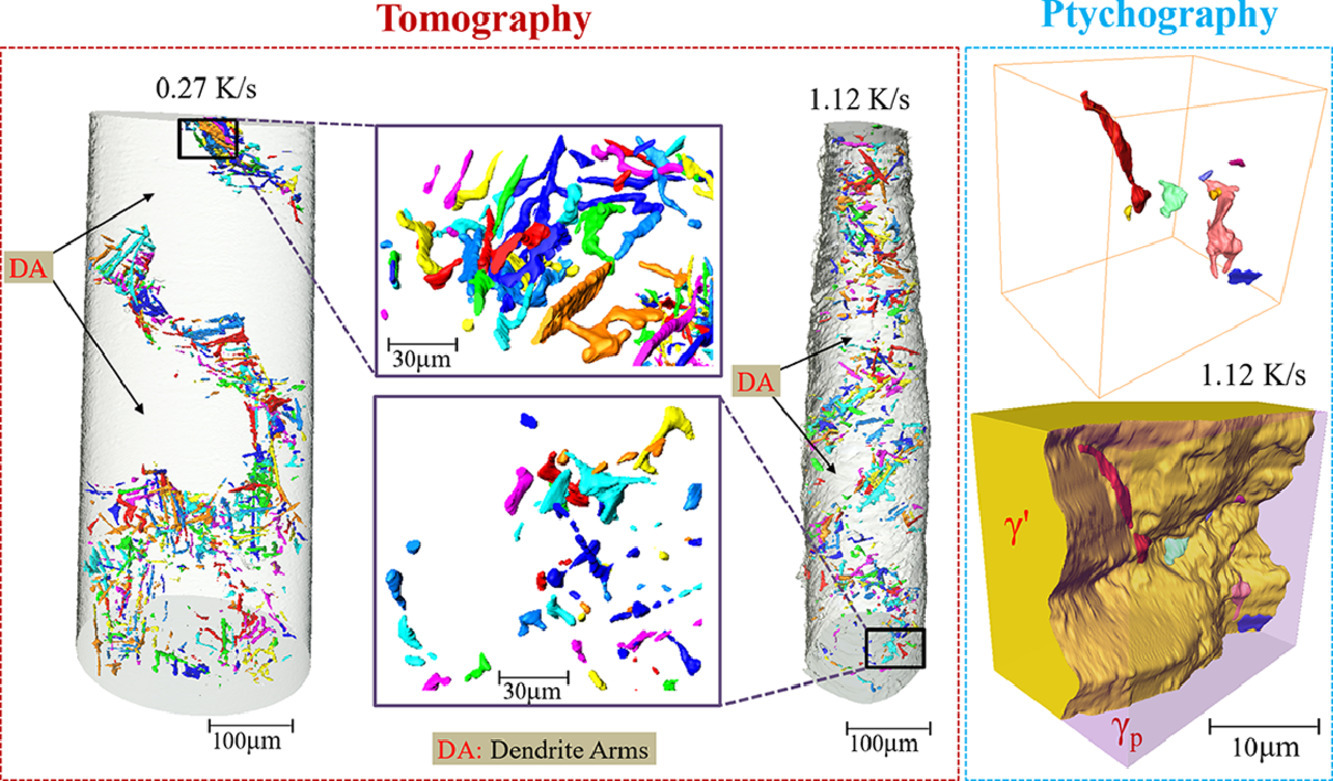
8. Multiscale characterization of the 3D network structure of metal carbides in a Ni superalloy by synchrotron X-ray microtomography and ptychography
用同步加速X射线显微层析术和叠层成像术对镍基超合金中金属碳化物的3D网络结构进行多尺度表征
Zhiguo Zhang, Jia Chuan Khong, Billy Koe, Shifeng Luo, Shi Huang, Ling Qin, Silvia Cipiccia, Darren Batey, Andrew J.Bodey, Christoph Rau, Yu Lung Chiu, Zhu Zhang, Jean-Christophe Gebelin, Nick Green, Jiawei Mi✉
Jiawei Mi: J.Mi@hull.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.032
摘要
采用同步X射线显微层析术和叠层成像术对铸态IN713LC镍基高温合金中金属碳化物的三维网络结构、形貌和分布进行了表征。MC型碳化物主要分布在基体γ和γ'相的晶界。凝固冷速的差异对MC型碳化物的体积分数影响不大,但是会强烈影响碳化物的尺寸、分布和网络形貌。根据残余液相的局部成分和几何约束,碳化物可以形成球形、条状或网状形貌。研究结果表明,两种互补层析技术协同应用于三维空间非破坏性复杂多相结构的研究具有一定的优势和技术潜力,空间分辨率可达~30 nm。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P81-85
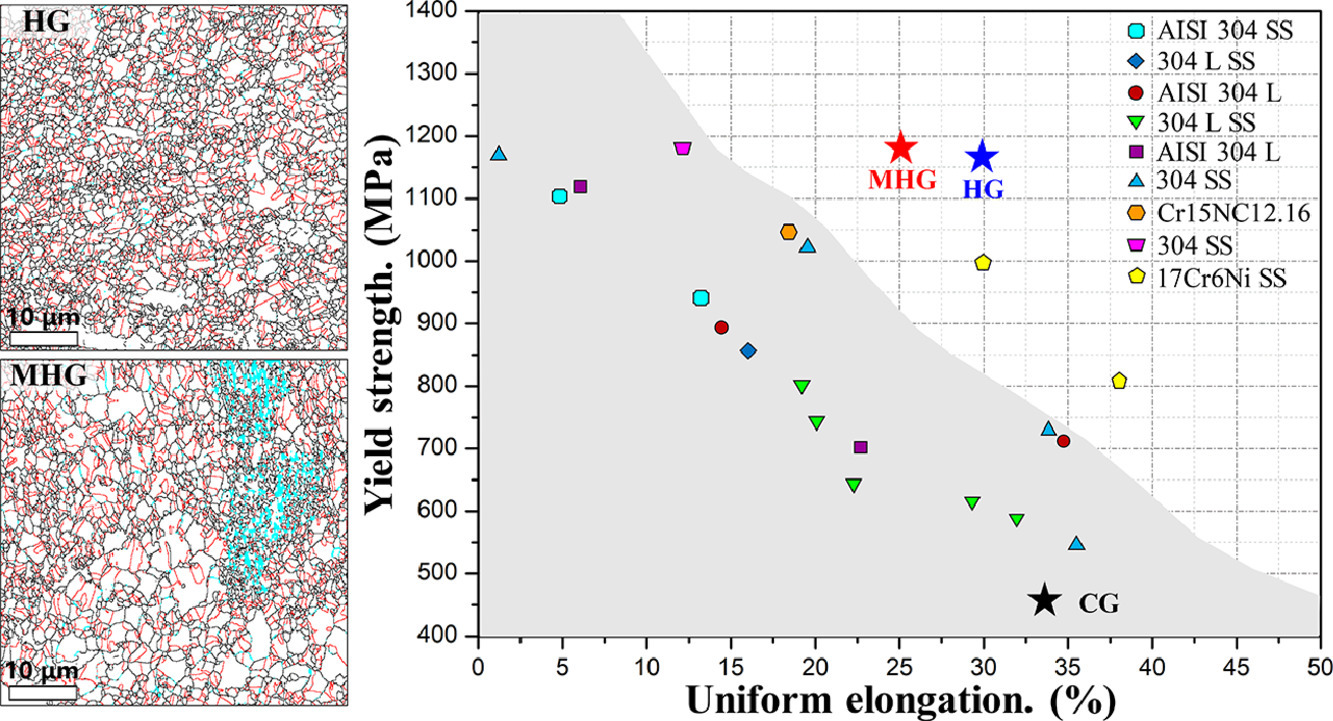
9. Ensuring the strength and ductility synergy in an austenitic stainless steel: single- or multi-phase hetero-structures design
确保奥氏体不锈钢强度和塑性的协同提升:单相或多相异质结构设计
Yong Li, Wei Li✉, Shilei Li, Na Min, Laizhu Jiang, Qinglong Zhou, Xuejun Jin
Wei Li: weilee@sjtu.edu.cn,上海交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.041
摘要
在许多合金体系中,异质微观组织被提出用来优化力学性能,以协同提高强度和塑性。本研究通过调整热机械加工参数,获得了包含细晶和粗晶的多相异质结构,其中铁素体分布在纳米晶粒周围。结果表明,多相异质结构钢的屈服强度达到1.2 GPa,是粗晶组织样品屈服强度的2倍以上,且均匀延伸率损失较小。我们用同步X射线衍射研究了这种复杂组织中的微观载荷转移。样品的持续加工硬化归功于异质变形诱导应力,以及相变诱导塑性(TRIP)效应和孪晶诱导塑性(TWIP)效应的共同激活。对比之下,单相异质结构钢的强度较低,但均匀延伸率较高。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P91-96
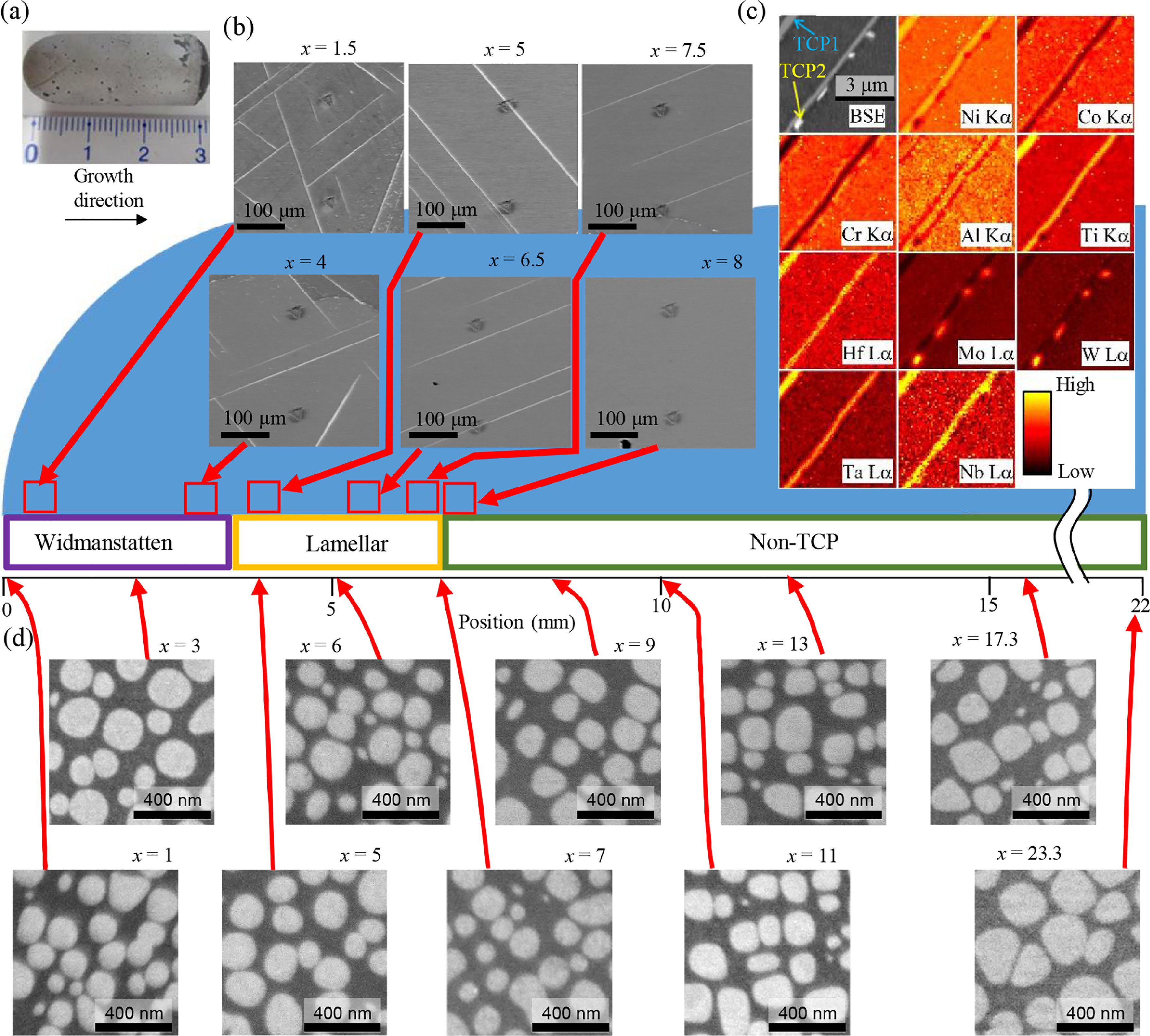
10. High-throughput mapping method for mechanical properties, oxidation resistance, and phase stability in Ni-based superalloys using composition-graded unidirectional solidified alloys
基于成分梯度单向凝固的镍基高温合金力学性能、抗氧化性和相稳定性的高通量映射方法
Ayako Ikeda✉, Kenta Goto, Toshio Osada, Ikumu Watanabe, Kyoko Kawagishi
Ayako Ikeda: IKEDA.Ayako@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.043
摘要
本文提出了一种新的高通量实验评估方法,用来评价镍基高温合金的相稳定性、力学性能和氧化性能。利用Bridgman法,研究了一个样品中9种元素在长距离内(~24 mm)的渐变特征以及η、μ和γ′相体积分数等宽范围的微观组织特征。我们利用纳米压痕法和微观组织观察提取了γ-γ′两相结构的弹性模量/硬度,并评价了氧化样品中的氧化层。我们的方法使得获得大量与高温合金成分和微观组织相关的数据集成为可能。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P108-111
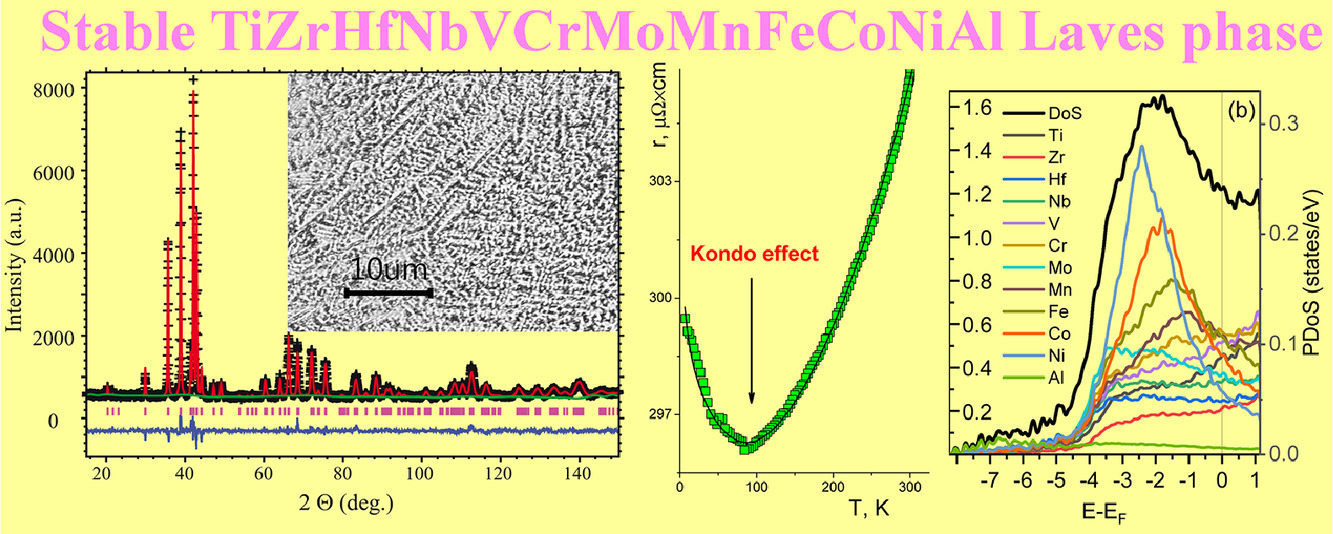
11. Stable high-entropy TiZrHfNbVCrMoMnFeCoNiAl Laves phase
稳定的高熵TiZrHfNbVCrMoMnFeCoNiAl Laves相
S.A. Uporov✉, R.E. Ryltsev, S.Kh. Estemirova, E.V. Sterkhov, N.M. Chtchelkatchev
S.A. Uporov: segga@bk.ru
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.049
摘要
近年来在高熵材料领域的研究发现了一个有趣的结果:具有不同价态和半径的化学元素组成的多组分体系可以形成具有金属间Laves相结构的单相固溶体。本文报道了在TiZrHfNbVCrMoMnFeCoNiAl合金中制备六方Laves相(C14,原型MgZn2)的过程。在973 K热处理50 h后,相很稳定。为了表征这种材料,我们验证了它的导电性和磁性能。测量结果表明,Laves相为Curie-Weiss顺磁体,在80 K时表现出金属导电性和明显的类Kondo异常。对实验数据的分析和从头计算表明,化学复杂性和成分无序性导致了强烈的s-d带散射,从而导致了导带中相当高密度的d态。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P112-116
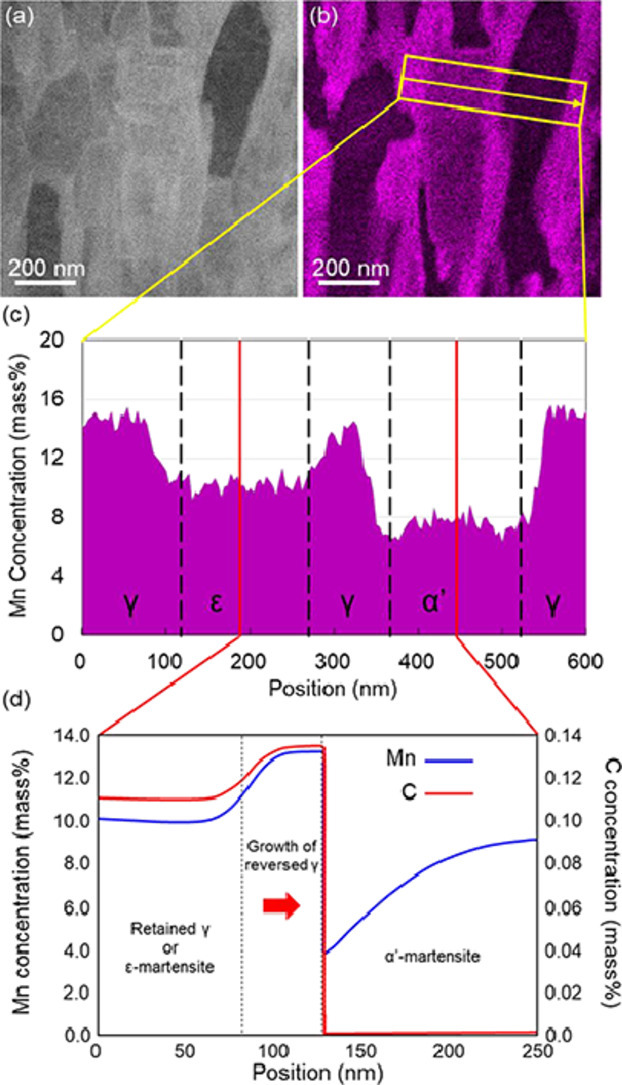
12. Formation of core-shell type structure in Duplex Martensitic Steel
双相马氏体钢中核壳型结构的形成
Kenji Kaneko✉, Takuya Maeda, Yasuhito Kawahara, Kazuhiro Ichino, Takuro Masumura, Toshihiro Tsuchiyama, Hiroyuki Shirahata, Ryuji Uemori
Kenji Kaneko: kaneko@zaiko.kyushu-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.044
摘要
通过透射电子显微镜研究了淬火和临界退火中锰钢的微观组织,以更好地理解γ-ɛ和γ-α'马氏体相变。各相之间的取向关系为(-110)α′//(0001)ε,[111]α′//[11-20]ε(淬火样品),和(-110)α′//(-111)γ//(0001)ε,[111]α′//[110]γ//[11-20]ε(临界退火样品)。另外,我们证实了具有Mn浓度梯度的核壳型微观组织的存在,其为残余奥氏体包围着ɛ-马氏体。我们发现各相的Mn浓度取决于临界退火过程中Mn扩散控制的逆转变奥氏体的长大。结果强烈表明在临界退火过程中形成的Mn浓度梯度会影响相稳定性,从而导致ε/γ核壳微观结构的形成。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P142-146
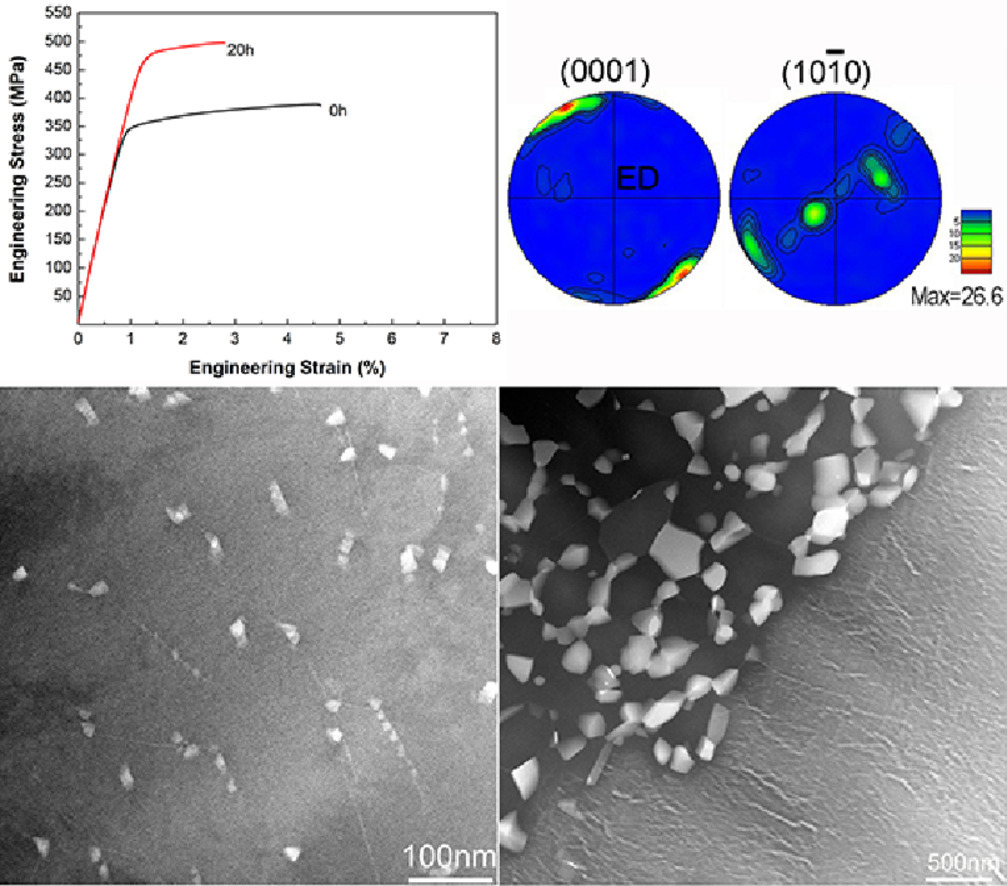
13. Achieving exceptionally high strength in binary Mg-13Gd alloy by strong texture and substantial precipitates
通过强烈的织构和大量析出,在二元Mg-13Gd合金中实现极高的强度
R.G. Li, H.R. Li, H.C. Pan✉, D.S. Xie, J.H. Zhang✉, D.Q. Fang✉, Y.Q. Dai, D.Y. Zhao, H. Zhang
H.C. Pan: panhc@atm.neu.edu.cn,中国东北大学
J.H. Zhang: jinghuaizhang@gmail.com,哈尔滨工程大学
D.Q. Fang: fangdaqing@xjtu.edu.cn,西安交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.052
摘要
在简单的二元Mg-Gd合金中,仅以很小的挤压比即可获得超高强度,其主要的强化机制与以前的报道有所不同。Mg-13Gd合金的热挤压比为4时,其拉伸屈服强度(TYS)可以达到350 MPa。占大比例的非动态再结晶区域内的强织构和内部的位错钉扎对挤压态合金的强度有很大贡献。我们首次发现了时效沉淀仅在大的未再结晶晶粒中形成,而不会在细小的再结晶晶粒中形成。挤压+峰时效合金的TYS增加到了470 MPa。超高的强度主要与织构强化和析出强化有关,和具有大塑性变形的传统Mg合金中的细晶强化和析出强化不同。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P147-152
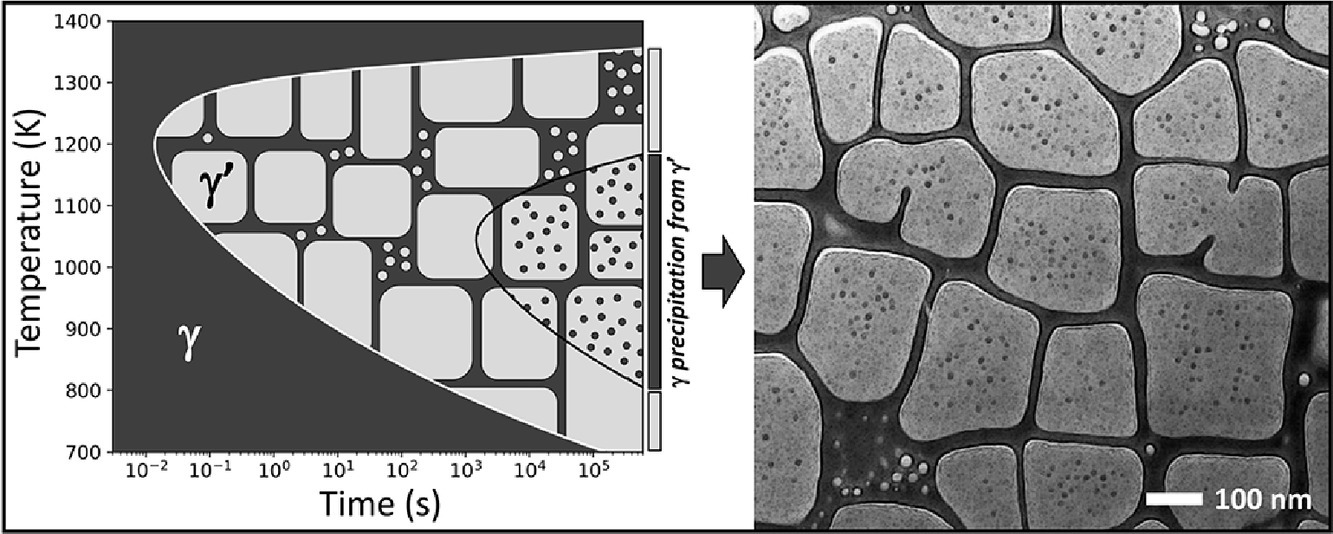
14. Modeling the precipitation processes and the formation of hierarchical microstructures in a single crystal high entropy superalloy
模拟单晶高熵高温合金中的析出过程和分层微观组织的形成
Stéphane Gorsse✉, Yung-Ta Chen, Wei-Che Hsu, Hideyuki Murakami, An-Chou Yeh✉
Stéphane Gorsse: stephane.gorsse@icmcb.cnrs.fr,国立清华大学
An-Chou Yeh: yehac@mx.nthu.edu.tw,国立清华大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.002
摘要
尽管高熵高温合金(HESAs)优异的高温拉伸屈服强度得益于其分层微观组织,但驱动其形成的析出过程仍不明确。在本研究中,我们使用常规的计算热力学和动力学工具,分析了γ'和γ析出的动力学、长大和粗化过程,以模拟热处理过程中HESA的微观组织发生和演化过程。我们评估了模拟再现实验观察到的微观组织参数的能力。我们计算了温度-时间-转变(TTT)图,为进一步优化HESA的分层微观组织提供指导。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 193, 1 Mar. 2021, P153-157
15. Properties and influence of microstructure and crystal defects in Fe2VAl modified by laser surface remelting
激光表面重熔改性Fe2VAl的性能及其微观组织和晶体缺陷的影响
Leonie Gomell✉, Moritz Roscher, Hanna Bishara, Eric A. Jägle, Christina Scheu, Baptiste Gault✉
Leonie Gomell: l.gomell@mpie.de
Baptiste Gault: b.gault@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.050
摘要
激光表面重熔可用于调控铸造材料的微观组织。本工作对激光表面重熔后的Fe2VAl进行详细分析。在熔池中,拉长的晶粒几乎沿着热影响区外延生长。这些晶粒通过取向差为1°-5°的小角度晶界分开。我们使用原子探针层析成像技术观察到钒、碳和氮在晶界和位错处的偏析,通过原位四点探针技术测量局部的电阻率。与铸造样品中的大角度晶界相比,在这些小角度晶界处观察到了较小的电阻率增加。这表明晶界工程在调控热电性能方面有很大潜力。




