金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.201,Dec. 2021(上)
2021-01-28 来源:Goal Science
Vol. 201 目录
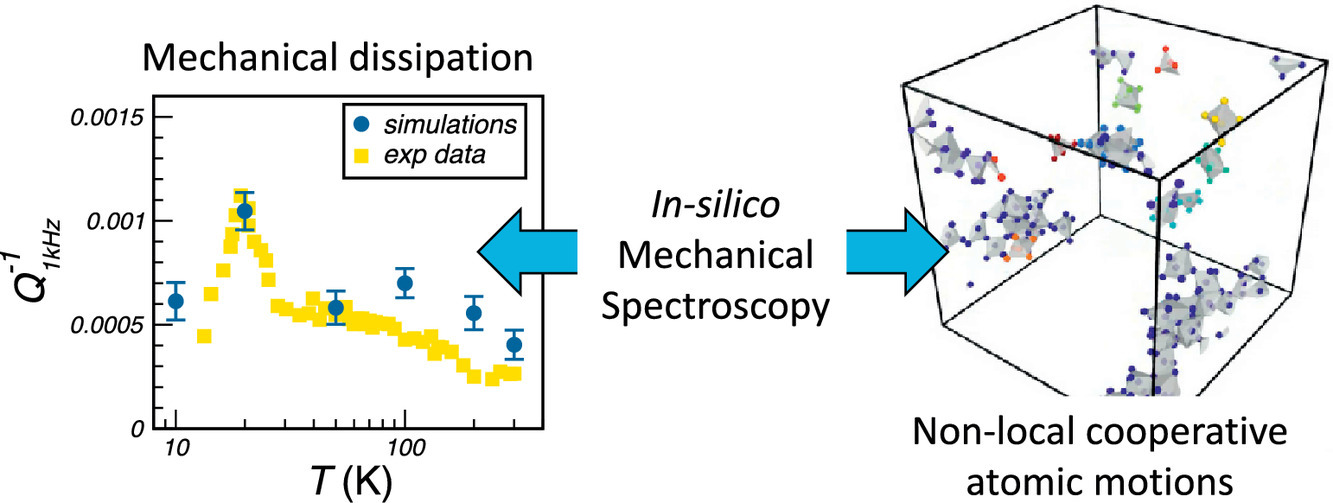
1. Non-local cooperative atomic motions that govern dissipation in amorphous tantala unveiled by dynamical mechanical spectroscopy
通过机械动力学光谱揭示非晶钽中的非局域原子协同运动耗散
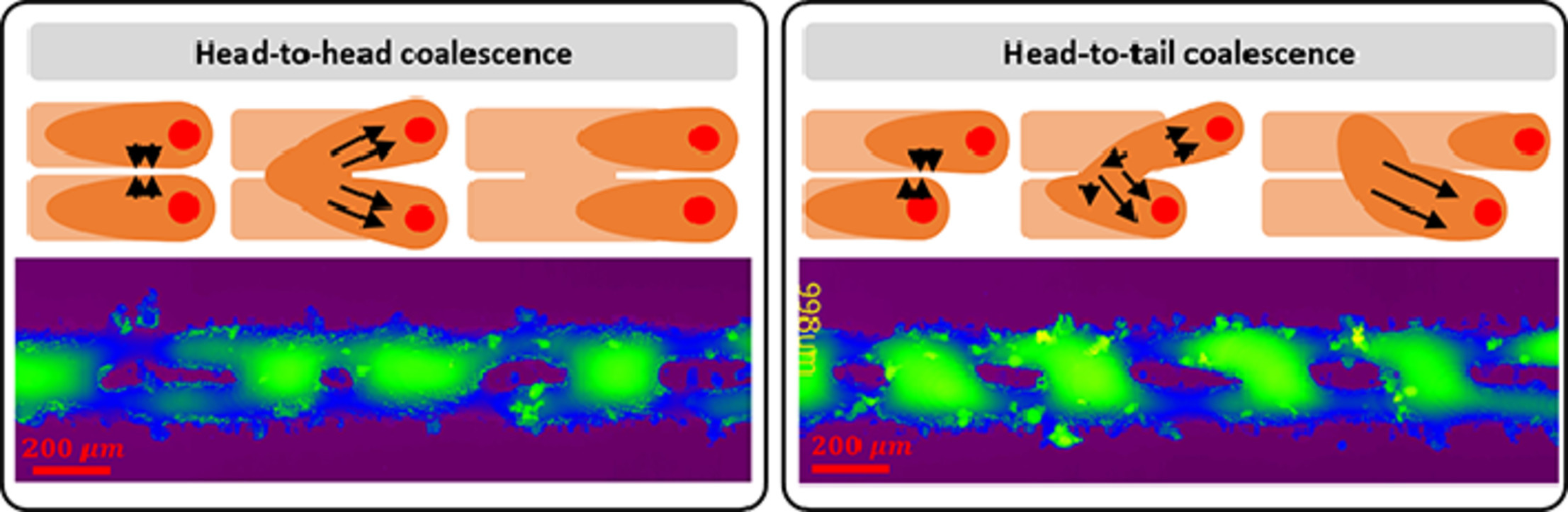
2. Using a dual-laser system to create periodic coalescence in laser powder bed fusion
利用双激光系统调控激光粉末熔炼中的周期性聚结构
100Cr6轴承钢在高压扭转过程中的渗碳体分解机理
包含23种合金元素的镁合金扩散迁移率数据库
通过原位小角中子散射研究钒微合金钢中析出相的组成演变
平台温度对激光粉末熔炼AlSi10Mg的组织、强度和延展性的影响
闪速加热退火Q&P钢中的元素不均匀对相变和力学行为的影响
Al-Ge等轴晶凝固特征的X射线衍射与DNN模型对比研究
利用纳米压痕方法分析NiTi形状记忆合金中的小尺度变形特性和应力应变行为
利用机器学习方法优化AlSi10Mg的激光熔炼工艺:新的组织描述指标和断裂机制
合金元素对晶界面结构稳定性的影响
多晶固体内部耗散随晶粒度和频率的变化
铜-镍体系中晶界偏聚、晶界张力和晶界形成能的解析性描述
ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P1-6
1. Non-local cooperative atomic motions that govern dissipation in amorphous tantala unveiled by dynamical mechanical spectroscopy
通过机械动力学光谱揭示非晶钽中的非局域原子协同运动耗散
F. Puosi✉, F. Fidecaro, S. Capaccioli, D. Pisignano, D. Leporini
F. Puosi:francesco.puosi@pi.infn.it
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.054
摘要
通过分子动力学模拟在大温度和频率范围内研究了非晶钽中机械耗散的控制机制。我们发现耗散与不可逆的原子重排有关,原子重排具有明显的协同性,涉及到在空间扩展多面体簇中排列的数十到数百个原子。值得注意的是,在低温下,我们观察到大量的氧原子发生塑性重排,这与宏观力学损失的实验峰值一致。详细的结构分析表明,不可逆重排在共边和共面位置优先发生。这些结果对于在结构力学、光学和传感应用领域中减少相关材料的机械损失的具有重要指导意义。

ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P14-22
2. Using a dual-laser system to create periodic coalescence in laser powder bed fusion
利用双激光系统调控激光粉末熔炼中的周期性聚结构
Wenxuan Zhang, Wenyuan Hou, Luc Deike, Craig B. Arnold✉
C.B. Arnold:cbarnold@princeton.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.071
摘要
传统的激光熔覆金属粉末技术(PBF-LB/M)由于制备速率和生产能力较低,导致其实用性受限。解决这个问题的一种方法是将多个激光束并行,提高工艺的灵活性。例如,最近有研究表明使用两束或更多激光束有助于提高最终产品的机械性能。然而,在熔池接近和相互作用方面仍有一些问题需要解决,特别是两个紧密平行的熔池间的相互作用。在这项研究中,我们使用两个激光器,在两个平行运行的熔池之间产生了一个小的空间偏移。实验结果表明,在不同的空间偏移量下,除了完全融合和完全分离外,还存在一个新的模式,即两个熔池产生周期性的结合。高速成像技术揭示了这种结合的两种不同机制,我们分别称之为头对头结合和头尾结合。通过改变激光功率和空间偏置等加工参数,利用这种双激光方法可以设计出不同波长的周期性材料结构。

ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P23-35
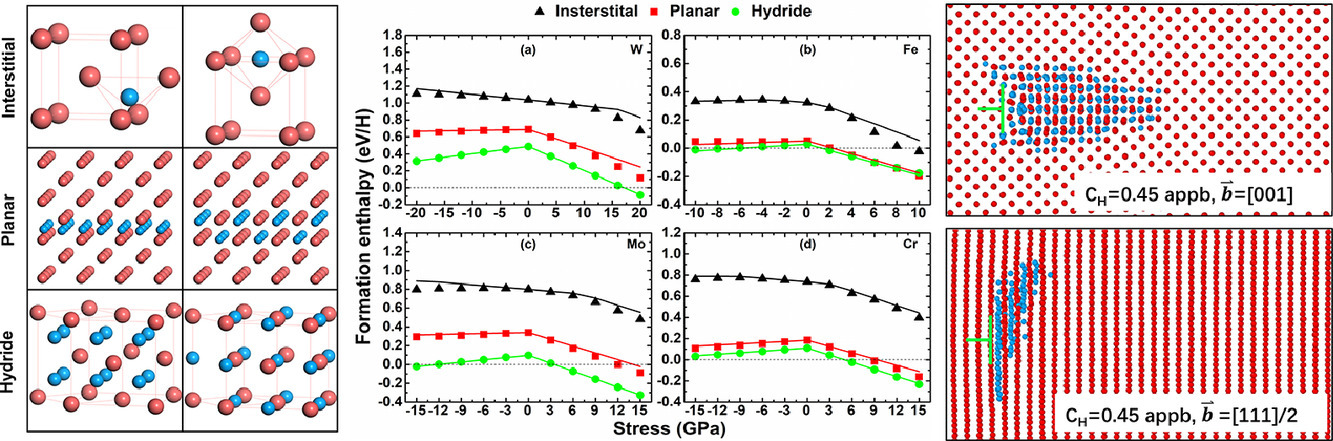
3. Hydrogen clustering in bcc metals: Atomic origin and strong stress anisotropy
BCC金属中氢团簇的原子尺度成因与显著应力各向异性
Jie Hou, Xiang-Shan Kong, C.S. Liu, Jun Song✉
J. Song:jun.song2@mcgill.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.048
摘要
氢对金属的损伤是工业界长期以来面临的一个难题。损伤的其中一种形式与氢聚集有关,目前原子尺度的起因仍有争议,特别是对非氢化物形成金属。在本研究中,我们结合第一性原理计算和蒙特卡洛模拟系统地研究了以W、Fe、Mo、Cr为代表的BCC金属中的氢聚集行为。我们发现,氢聚集与能量有关,并能被主分量沿<001>晶体方向的各向异性应力场强烈促进。基于氢形成体积张量的连续介质模型可以很好地预测应力效应。在刃位错处发生氢聚集在热力学上是可能的,极低氢浓度下的纳米氢化物形成证明了这一点。此外,纳米氢化物以薄片状结构生长,使<001>张力最大化,这很好地反映了应力的各向异性。特别是< 001 >刃位错,其<001>拉伸分量最大,因此极大了促进了氢的聚集,这与最近的实验观察结果非常一致。这项工作定量阐明了应力对氢能垒和聚集行为的各向异性性质,为理解金属中氢致损伤提供了新的见解。

ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P36-54
4. A complete grain-level assessment of the stress-strain evolution and associated deformation response in polycrystalline alloys
多晶合金应力-应变演化和相关变形响应的晶粒尺度分析
Michael D. Sangid✉, John Rotella, Diwakar Naragani, Jun-Sang Park, Peter Kenesei, Paul A. Shade
M.D. Sangid:msangid@purdue.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.051
摘要
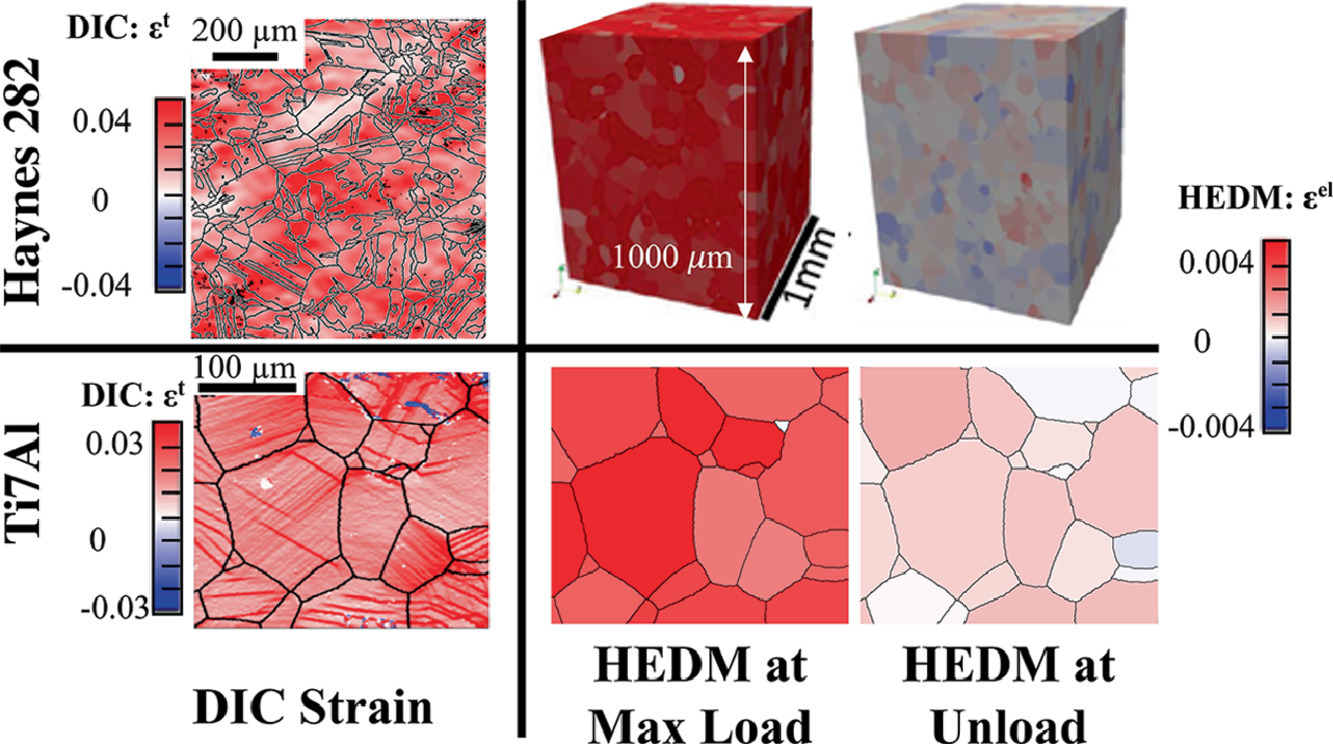
多晶合金被广泛应用于各种结构,并为此进行了大量的实验测试。由于微观组织和应变场的的不均匀性,我们必须对材料进行大量具有统计意义的测试,以知晓其性能的变化范围。为了更直接地获取相关信息,我们采用了多模态实验技术对特定区域内的每个晶粒在载荷过程中微观力学状态的完整演变进行了追踪和测量。具体来说,我们选择了Haynes 282和Ti7Al合金,对其进行了高能XRD和DIC+EBSD实验研究。结果表明,材料的不均匀程度随变形量增加而增加,并且我们将其与评估材料应力状态时代表体积单元中所必需的晶粒数量之间建立了联系。此外,我们采用高分辨成像技术对材料的滑移系统和滑移模式转变进行了研究。结果表明,相邻晶粒的应力相互作用是发生滑移模式转变的关键。

ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P55-62
5. Hydrogen atom-ion synergy in surface lattice modification at sub-threshold energy
亚阈值能量下氢原子-离子在表面晶格修饰中的协同作用
L. Gao✉, M. Wilde , A. Manhard, U. von Toussaint, W. Jacob
L. Gao:liang.gao@ipp.mpg.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.065
摘要
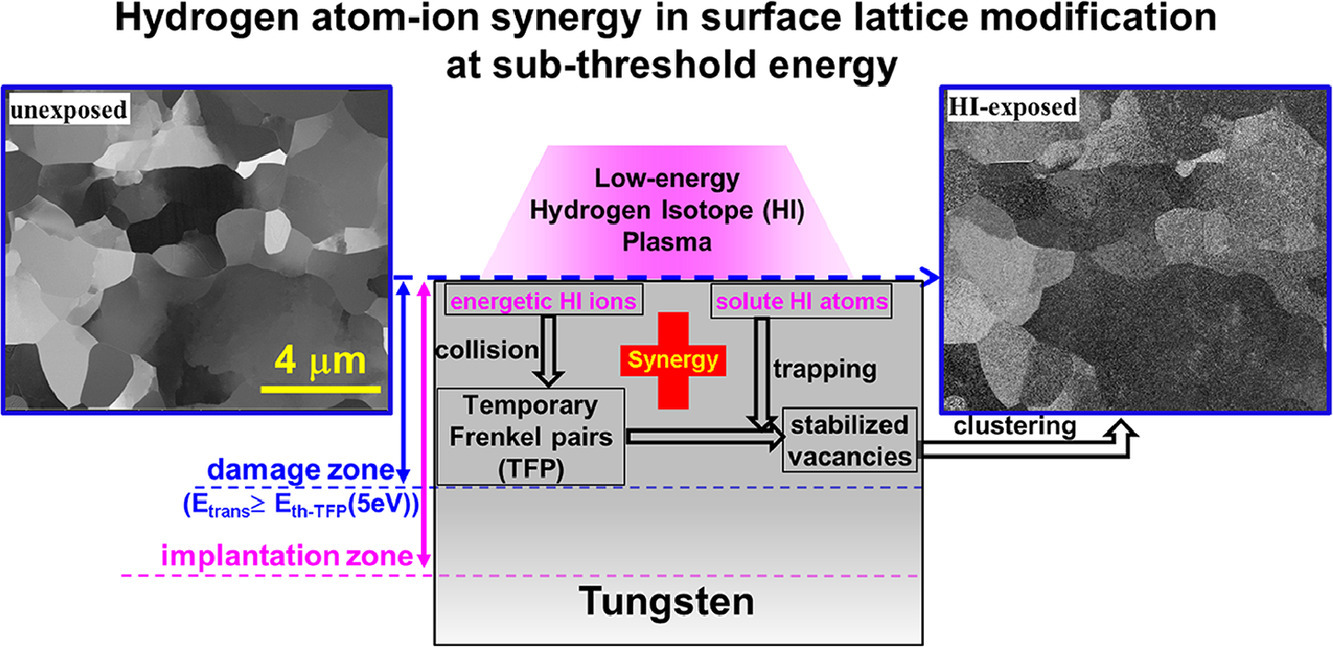
低能氢同位素(HI)等离子体被广泛应用于工业表面处理。在本研究中,我们证明了HI等离子体——即使其能量远低于稳定Frenkel缺陷对产生的阈值——也可以通过形成厚约几纳米、HI含量为几个at.%的具有严重晶格畸变的表面层来对晶体材料进行表面修饰。我们通过对亚阈值HI离子能量进行调整,在经氘和氢等离子体辐照的钨表面实验重现了相同的点阵修饰。我们提出了一种低能初级缺陷产生的物理模型,该模型涉及因HI离子碰撞产生的亚稳Frenkel对与因俘获溶质HI原子导致的空位稳定之间的协同作用。这种协同缺陷通常在高能离子(如离子、中子)注入时产生,并可能导致材料劣化。利用低能量H等离子体在材料(即使是那些氢溶解度可以忽略的材料)表面制备纳米级富氢层作为一种表面改性手段,在催化和电化学领域具有广阔的应用前景。

ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P79-93
6. Mechanism of cementite decomposition in 100Cr6 bearing steels during high pressure torsion
100Cr6轴承钢在高压扭转过程中的渗碳体分解机理
Yu Qin, David Mayweg, Po-Yen Tung, Reinhard Pippan, Michael Herbig✉
M. Herbig:m.herbig@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.069
摘要
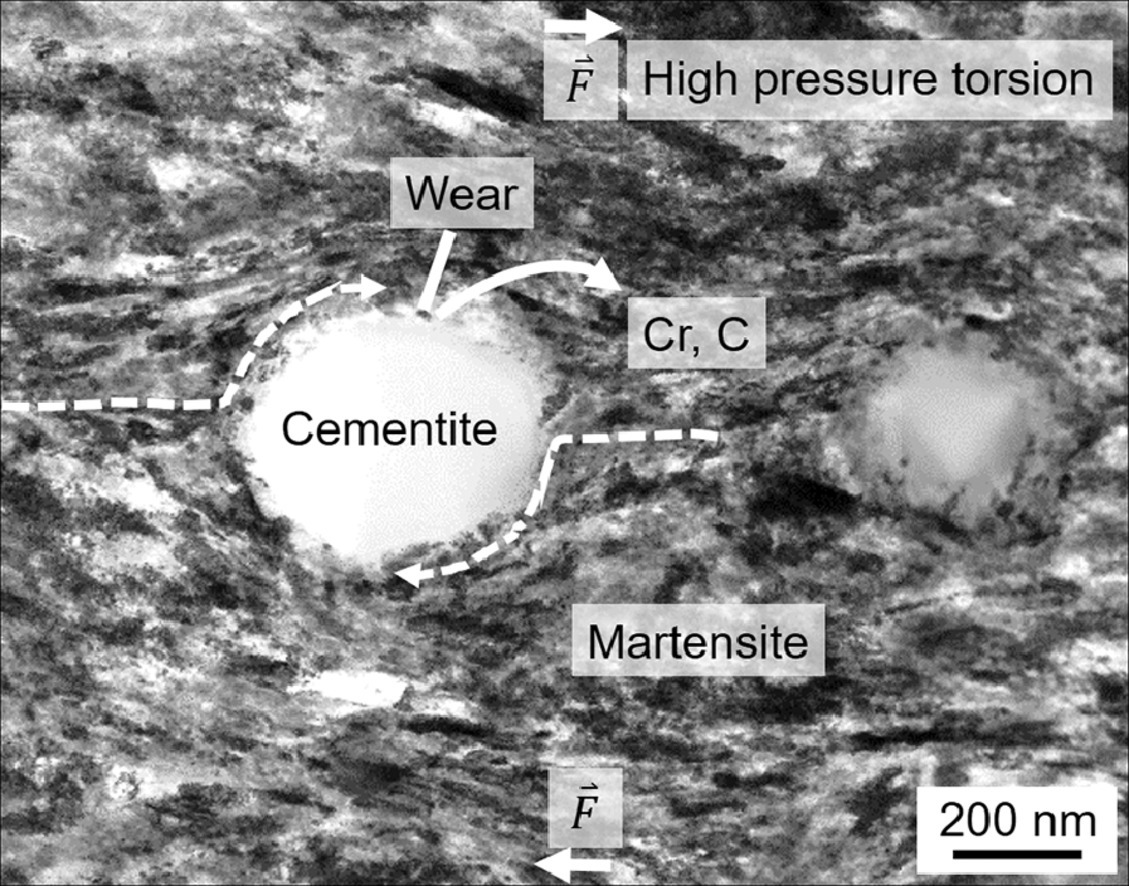
严重塑性变形可能导致珠光体和马氏体钢中的渗碳体分解,产生高强度的纳米晶铁素体。这种效应既可用于增强珠光体线材,也可能使轴承钢或轨道钢中产生白蚀裂纹(WECs),并最终导致材料失效。为此,我们对洛氏硬度62的100Cr6马氏体轴承钢在9.5 GPa高压扭转过程中的球状渗碳体分解行为进行了研究。马氏体基体和球状渗碳体析出的塑性相应非常不同。宏观塑性变形强化几乎完全由基体承担。基体在球状渗碳体周围的塑性流变导致了渗碳体的磨损,基体中铬的不断增加证明了这一点。位错滑移在基体/渗碳体界面的磨损处优先发生,渗碳体通过这种塑性变形加速了磨损。较大的球状渗碳体更容易发生塑性变形和分解。对于在高压扭转作用下具有大应变差的多相材料,这一机理通常是成立的。虽然在100Cr6轴承钢中可以通过减小球状渗碳体的尺寸来减慢白蚀裂纹的形成,但无法完全抑制这种失效机制。

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P94-101
7. Geometry and energy barrier of martensite in the initial stage martensitic transformation in B19’ TiNi shape memory alloy
B19' TiNi形状记忆合金马氏体相变初期的马氏体几何形貌及能垒研究
T. Teramoto✉, K. Nagahira, K. Tanaka
T. Teramoto:teramoto@mech.kobe-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.060
摘要
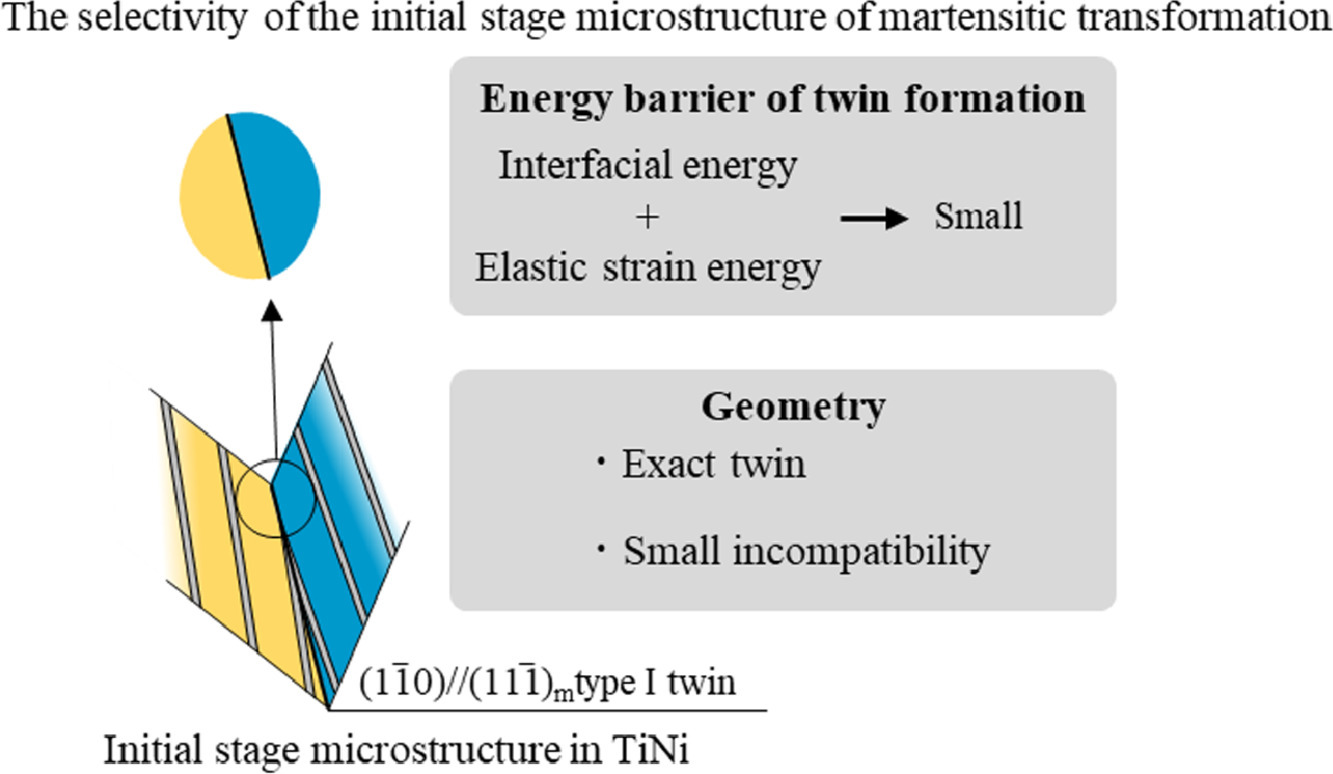
我们对B19' TiNi马氏体相变初始阶段的自适应变体选择进行了研究。已有研究表明,相变初始阶段,特定的惯析面变体(HPV)对,包括所谓的{11-1}m type I型孪晶初始微观结构(ISM),会优先形成。为了阐明ISM的选择性,我们对HPV对的几何特征和可能的孪晶平面形成能垒进行了理论分析。基于几何非线性理论,我们发现在特定的五组HPV对中可以形成具有精确取向关系的孪晶平面。第一性原理和Eshelby理论分析结果表明, {11-1}m type I型孪晶具有相对较低的能垒。因此,那些具有较低形成能垒的孪晶平面和结构所对应的变体,能有效降低弹性应变,从而优先形成ISM。

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P102-113
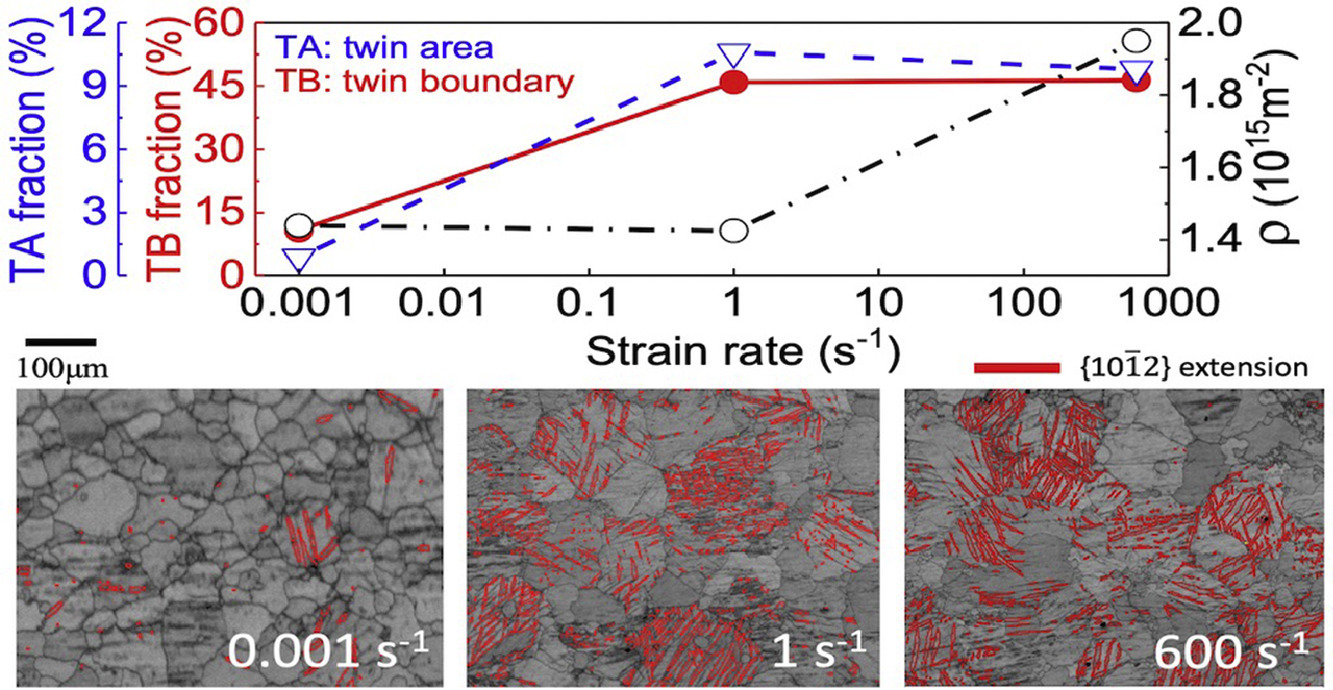
8. Evolution of dislocation and twin densities in a Mg alloy at quasi-static and high strain rates
镁合金在准静态和高应变速率下位错和孪晶密度的演化
M. Wang, X.Y. Xu, H.Y. Wang, L.H. He, M.X. Huang✉
M.X. Huang:mxhuang@hku.hk (香港大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.082
摘要
我们首次对不同应变速率下ATZ311镁合金中位错和形变孪晶的演化进行了定量研究。我们分别在0.001,1和600 s−1的应变速率下对样品进行了断拉伸试验。我们测量了样品中的孪晶体积分数,并基于中子衍射实验结果,确定了具有不同伯氏矢量的位错的平均密度和相对比例。结果表明,在较低的应变速率(0.001- 1s−1)下,孪晶体积分数迅速增加并达到饱和,而位错密度只在较高的应变速率(600 s−1)下才明显增加。此外,高应变率下的高流动应力使得当〈a〉型位错在小应变下迅速达到饱和后,较难激活的< c+a >型位错密度大幅度增加。在应变速率大于1 s –1的条件下,由于局部应力集中,具有相反极性的孪晶模式能够共存于同一晶粒中。

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P114-130
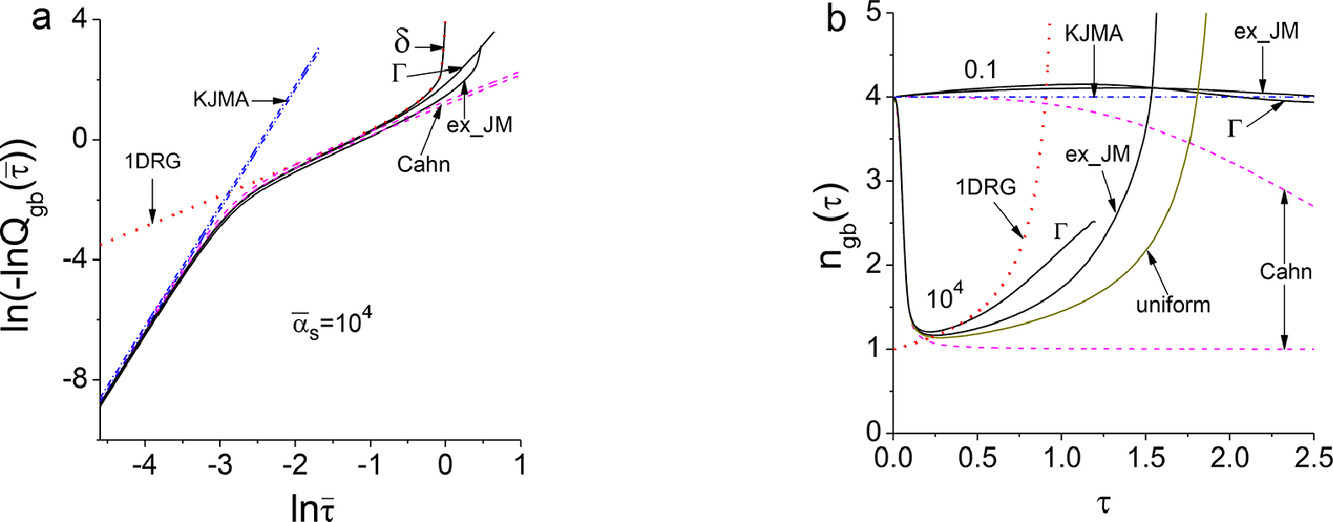
9. Kinetics of the surface-nucleated transformation of spherical particles and new model for grain-boundary nucleated transformations
球形粒子表面形核相变动力学及晶界形核相变新模型
Nikolay V. Alekseechkin✉
Nikolay V. Alekseechkin:n.alex@kipt.kharkov.ua
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.061
摘要
我们在Kolmogorov方法的框架下,推导出了等温或变温状态下,球形粒子表面形核相变的相变体积分数方程。我们在Avrami指数关系假设下,确定了控制相变动力学的特征参数。结果表明,表面形核与体形核重要的一点不同在于,相变早期表面完全相变后一维新相径向长大导致其特征参数较大。这种效应也表现在需要考虑粒子尺寸分布的晶界形核相变过程中。正态分布粒子的计算结果表明,达到相同相变体积分数和Avrami指数关系的时间增加。我们提出了一种基于给定尺寸分布的球形粒子穿过晶界形核长大可能性的晶界形核相变模型,以取代Cahn的随机平面的模型。 这种模型与Cahn模型有质的不同。尤其是方程参数较大时,双对数体积分数曲线末端将表现出特征弯曲,而这种现象可在金属玻璃结晶实验上观察到。这表明金属玻璃具有晶体结构,并且在簇间晶界发生形核。正是由于晶界封闭的几何结构和新相的一维径向生长,导致了曲线上的这种弯曲。

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P131-146
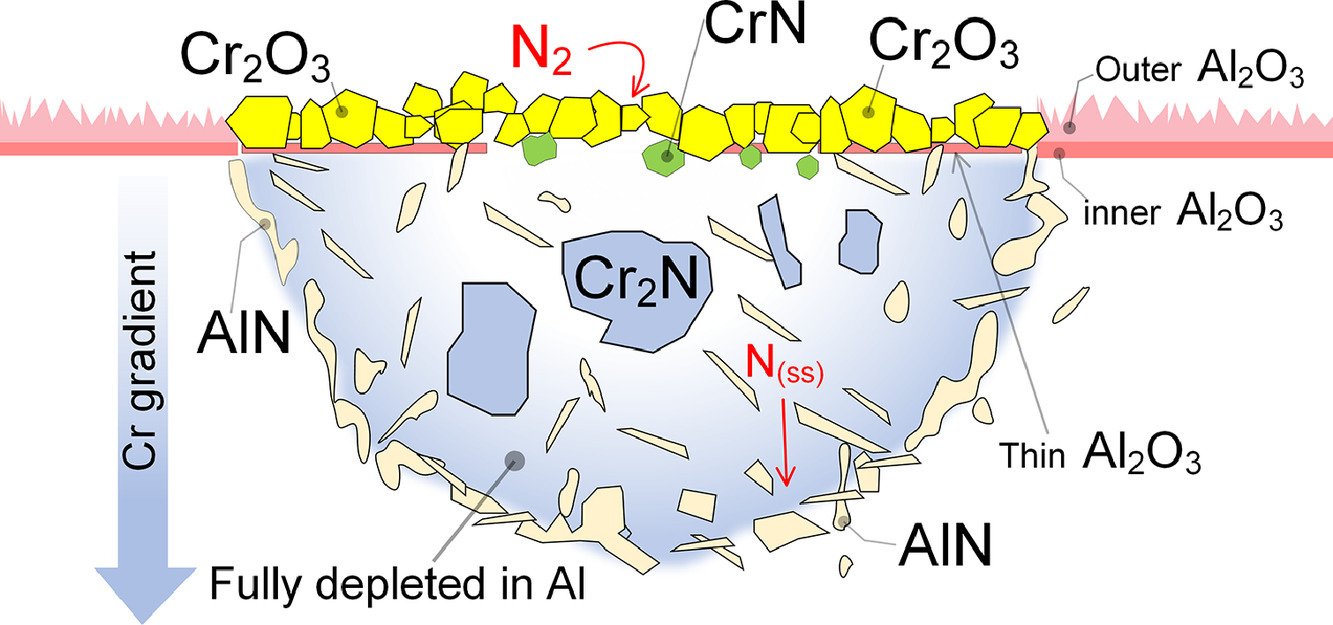
10. Exploring failure modes of alumina scales on FeCrAl and FeNiCrAl alloys in a nitriding environment
FeCrAl 和FeNiCrAl合金在氮化环境下的失效模式研究
A.N. Mortazavi✉, M. Esmaily, C. Geers, N. Birbilis, Jan-Erik Svensson, M. Halvarsson, D. Chandrasekaran, L.G. Johansson
A.N. Mortazavi:nmortazavi@seas.harvard.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.058
摘要
我们将两种高温合金FeCrAl和FeNiCrAl暴露在900℃的强氮化环境下,并对其氮化产物进行了研究。准原位实验表明,与合金组织的特定表面位置首先发生氮化,此位置氮可以穿过氧化铝。(112)取向的FeCrAl合金晶粒形成向外生长的氧化铝薄膜易发生氮化。在FeNiCrAl合金碳化铬析出物附近同样观察到了向外生长的鳞片和基体氮化。这两种合金在富活性元素的(Y和Zr)第二相大于一定临界尺寸时都发生了氮化反应。后一种类型的腐蚀是由鳞片中的裂纹和孔洞引起的。这一发现对开发性能优良的下一代高温合金具有重要意义。

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P147-157
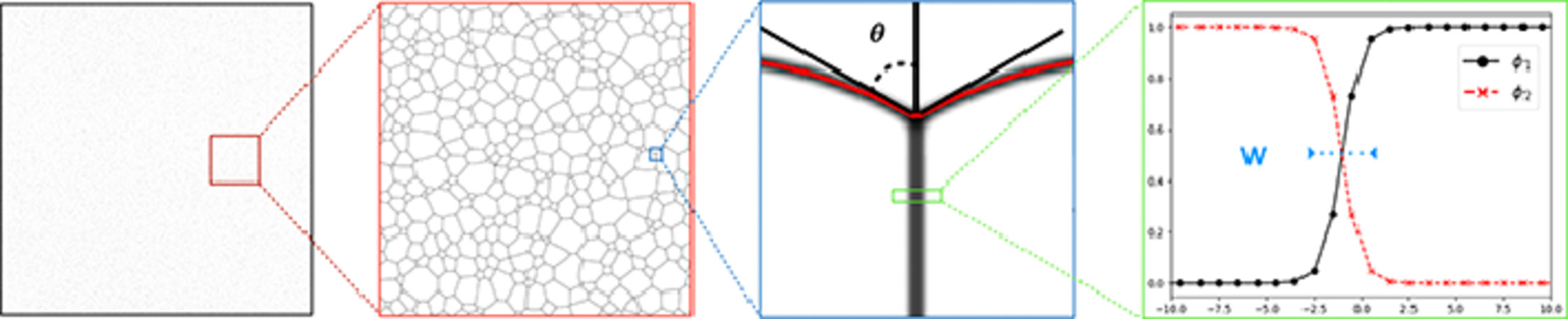
11. S-PFM model for ideal grain growth
理想晶粒长大的S-PFM模型
A. Dimokrati, Y. Le Bouar✉, M. Benyoucef, A. Finel
Y. Le Bouar:yann.lebouar@onera.fr, yann.lebouar@free.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.073
摘要
相场被广泛用于金属材料晶粒生长的研究。这种方法为研究晶粒生长过程中的组织演变提供了一个一致的热力学框架,而不需明确追踪界面位置。然而,模型的数值求解要求网格间距比界面宽度小得多。这导致当体系中存在大量晶粒时,模型的计算强度极高。最近提出的S-PFM方法提出了一种新的相场模型离散化公式,其中界面宽度和网格间距大小相当,从而大幅提高了相场的数值性能。在此,我们将该方法推广到了理想晶粒生长的多相场模型。我们通过二维模拟对晶界和三叉界面的动力学进行了详细分析。我们将我们的模型与经典相场模型进行了比较,结果表明,对于给定的精度要求,内存需求和模拟时间都减少到了4D分之一,其中D是空间维数。最后, 我们对大规模晶粒生长进行了二维模拟,证明了该方法可以揭示晶粒的尺寸分布和拓扑类别。

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P167-181
12. Generalized stability criterion for exploiting optimized mechanical properties by a general correlation between phase transformations and plastic deformations
基于相变和塑性变形间的普适联系探索最佳力学性能的广义稳定性判据
Linke Huang, Weitong Lin, Yubing Zhang, Dan Feng, Yujiao Li, Xiang Chen, Kai Niu, Feng Liu✉
F. Liu:liufeng@nwpu.edu.cn (西北工业大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.005
摘要
具有优异力学性能的结构材料设计一般侧重材料的微观组织,而微观组织通常由工艺过程中的相变决定。然而,相变和力学性能之间的直接联系目前仍未被阐明。在此,我们提出了一个新的概念——广义稳定性(generalized stability,GS),基于热力学和动力学描述相变与塑性变形之间存在的联系。具有优异强塑性耦合的结构材料, 应当具有高广义稳定性(GS)、高热力学驱动力(ΔG)和动力学活化能(Q)的相变和/或塑性形变。我们在相变调控的纳米结构Fe合金中验证了GS的概念,该合金具有2.61 GPa的超高屈服强度和3.32 GPa的抗压强度,同时通过多重强化和硬化机制实现了35%的失效应变。理论分析和组织表征表明,在相变过程的热动力学参数(例如,高GS-highΔG-high Q)在形变塑性过程中保持了下来,并最终导致了优异的力学性能。这一概念有望成为首个将相变与塑性变形联系起来的理论准则或一般规律,从而帮助相变调控,获得优异的材料力学性能。
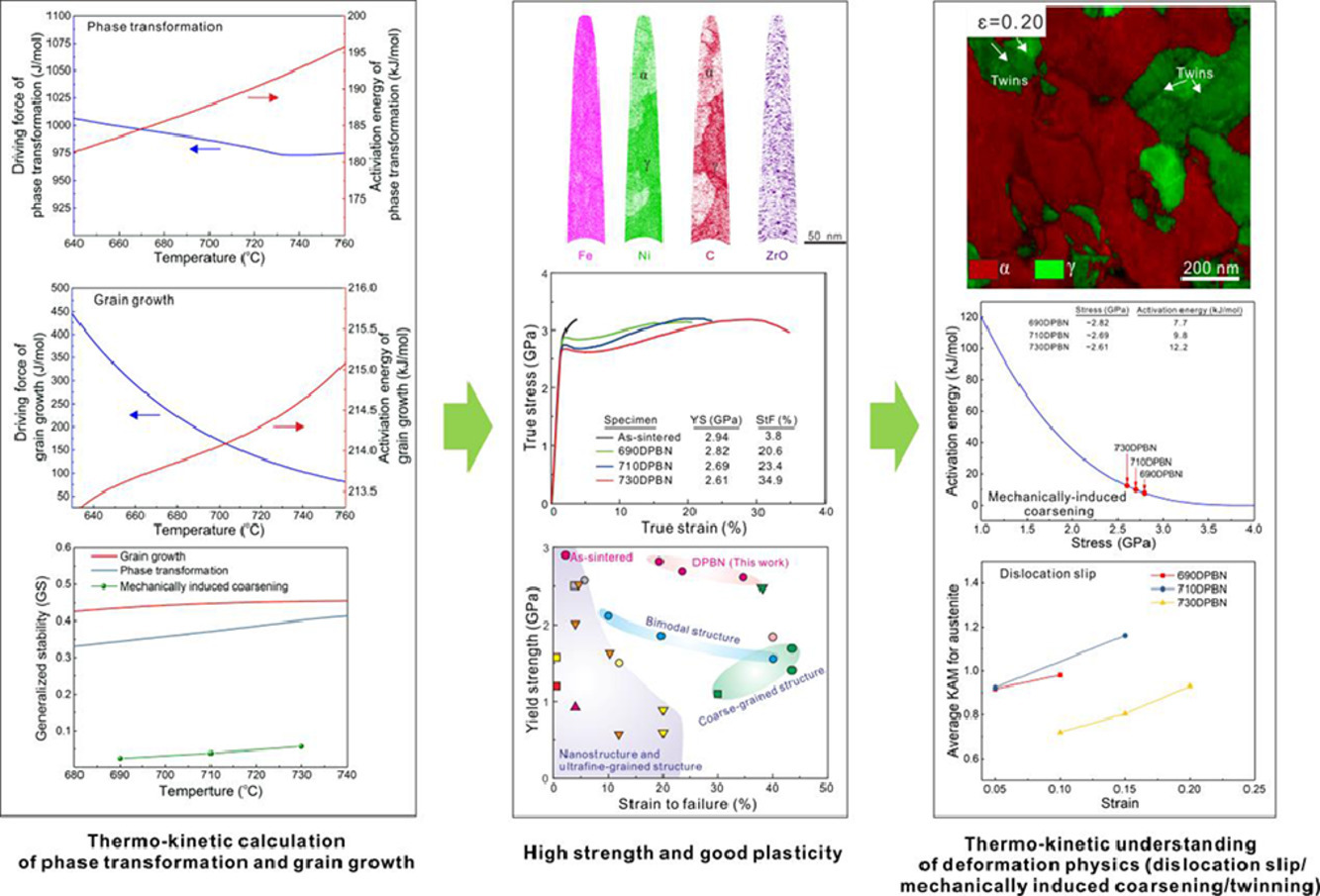

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P191-208
13. A comprehensive diffusion mobility database comprising 23 elements for magnesium alloys
包含23种合金元素的镁合金扩散迁移率数据库
Wei Zhong, Ji-Cheng Zhao✉
J.-C. Zhao:jczhao@umd.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.079
摘要
我们结合已有文献和实验数据,获得了10种重要合金元素在Mg中的扩散系数,并基于这些数据对第一性原理计算得到的扩散系数进行系统的验证。结果表明,计算得到的活化能相当准确(误差在0.2 eV以内),但相比之下,计算得到的预因子的可靠性则较差。因此,我们提出了一种具有较高实用性的策略,即当实验数据被限制在一个较窄的温度范围时,通过计算得到的活化能和拟合预因子来进行扩散速率的计算。第一性原理计算和实验数据之间较高的一致性表明我们可以基于该方法对实验无法获取的数据进行估计。我们针对HCP镁中的23种元素(Mg, Ag, Al, Be, Ca, Cd, Ce, Cu, Fe, Ga, Gd, In, La, Li, Mn, Nd, Ni, Pu, Sb, Sn, U, Y, Zn)迁移率建立了系统的数据库。这对未来先进镁合金的发展具有重要意义。此外,本研究提出的方法,也对建立其他合金系统的迁移率数据库非常有益。


ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P217-230
14. Evolution of the precipitate composition during annealing of vanadium micro-alloyed steels by in-situ SANS
通过原位小角中子散射研究钒微合金钢中析出相的组成演变
Chrysoula Ioannidou✉, Alfonso Navarro-López, Arjan Rijkenberg, Robert M. Dalgliesh, Sebastian Koelling, Catherine Pappas, Jilt Sietsma, Ad A. van Well, S. Erik Offerman
C. Ioannidou:c.ioannidou@tudelft.nl
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.083
摘要
我们使用原位小角中子散射(SANS)测量了三种不同钒(V)和碳(C)浓度的微合金钢在650℃和700℃析出物化学成分随时间的演化。我们在所有钢中测量了析出的碳-金属化学计量比。析出物最初处于富Fe的亚稳态,随后Fe在等温退火过程中逐渐被V取代。最终,析出相组成达到稳定状态。700℃时由于V的扩散较快,因此所有实验钢中的析出相化学成分变化都较快。在两个实验温度下,添加更多V和C由于提高了析出驱动力而对析出相组成演变有加速作用。此外,添加钒会使得富V析出增加,且析出中的Fe含量减少,同时碳-金属比也减小。原子探针结果表明,650℃或700℃退火10小时后,碳与金属的比值分布在0.75-1之间。以上实验结果结合ThermoCalc 计算和文献,进一步支持了小角中子散射结果。
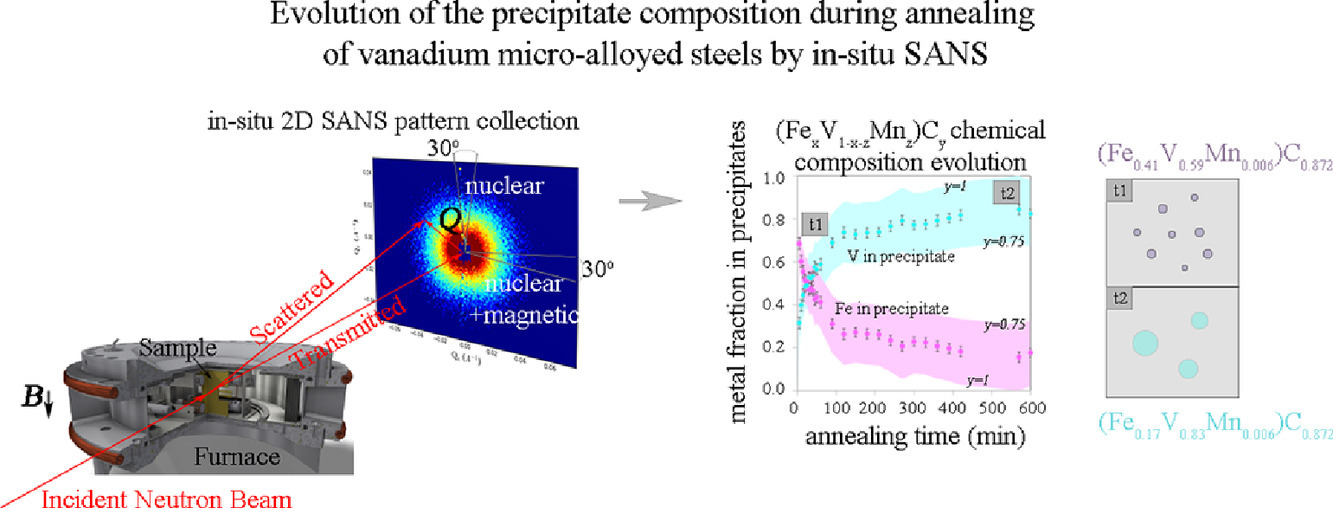

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P231-243
15. Influence on microstructure, strength and ductility of build platform temperature during laser powder bed fusion of AlSi10Mg
平台温度对激光粉末熔炼AlSi10Mg的组织、强度和延展性的影响
Juan Guillermo Santos Macías✉, Thierry Douillard, Lv Zhao, Eric Maire, Grzegorz Pyka, Aude Simar
J.G. Santos Macías:juan.santos@uclouvain.be
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.001
摘要
通过激光粉末熔炼制备的AlSi10Mg合金由于其组织很细,因此具有与铸造合金相当或更好的机械强度。而平台温度是影响制备过程中冷却速率和热梯度的重要工艺参数。当平台温度为200℃时,样品的残余应力可以忽略不计。然而,当平台温度为35℃时,尽管制备得到的材料断裂应变相当,但强度更高。我们通过聚焦离子束/扫描电子显微镜等手段对材料中的富硅共晶网络进行了详细的三维结构表征,并阐明了其与强度和断裂应变的关系。结果表明,平台温度200℃制备的材料中α-Al晶胞和富硅沉淀的尺寸较大,强化效果较低。此外,富硅共晶网络的连接也较少,厚度较大,因此更易发生损伤。我们建立了模型,基于材料的组织特征对强度进行预测。
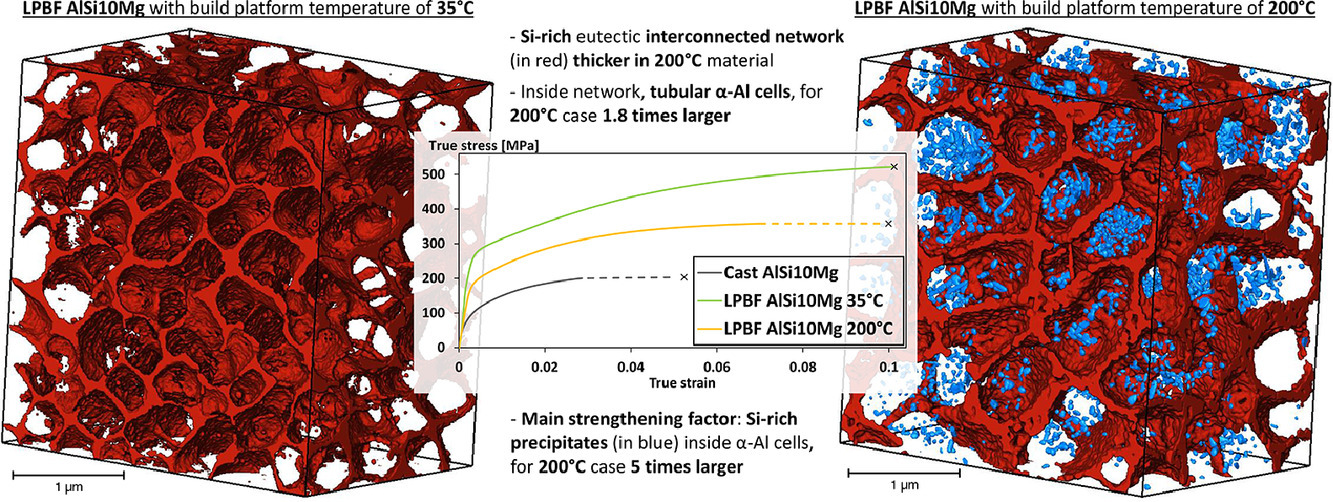

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P266-277
16. On the role of chemical heterogeneity in phase transformations and mechanical behavior of flash annealed quenching & partitioning steels
闪速加热退火Q&P钢中的元素不均匀对相变和力学行为的影响
Geng Liu, Tong Li, Zhigang Yang, Chi Zhang, Jun Li, Hao Chen✉
H. Chen:hao.chen@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn (清华大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.007
摘要
人们通常通过冷却过程中的奥氏体分解对先进高强度钢(AHSS)的组织进行调控,却较少关注升温过程中的奥氏体化过程。在本研究中,我们通过快速加热方法在Q&P钢中实现了化学成分的不均匀,并借此对Q&P钢的组织和性能进行调控。一方面,快速加热可以细化两相区退火过程中的形成的奥氏体;另一方面,由于Mn的扩散十分缓慢,使得快速加热过程中形成的奥氏体能够继承珠光体-铁素体初始组织中的合金成分不均。这种成分不均能够显著地改变冷却过程中的奥氏体分解和碳配分动力学,从而提高残余奥氏体的热稳定性。我们借助相场方法对以上过程进行了合理的模拟和解释。经过快速加热方法处理后的Q&P钢表现出了显著的性能提升,抗拉强度由980MPa提升至1180MPa。我们的研究表明,快速加热是一种实现先进高强度钢组织调控和性能提升的有效方法。
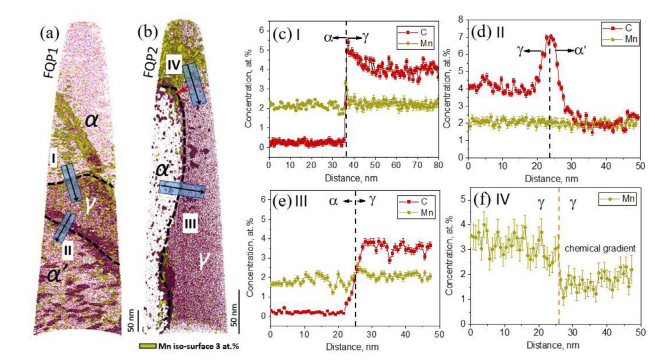

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P286-302
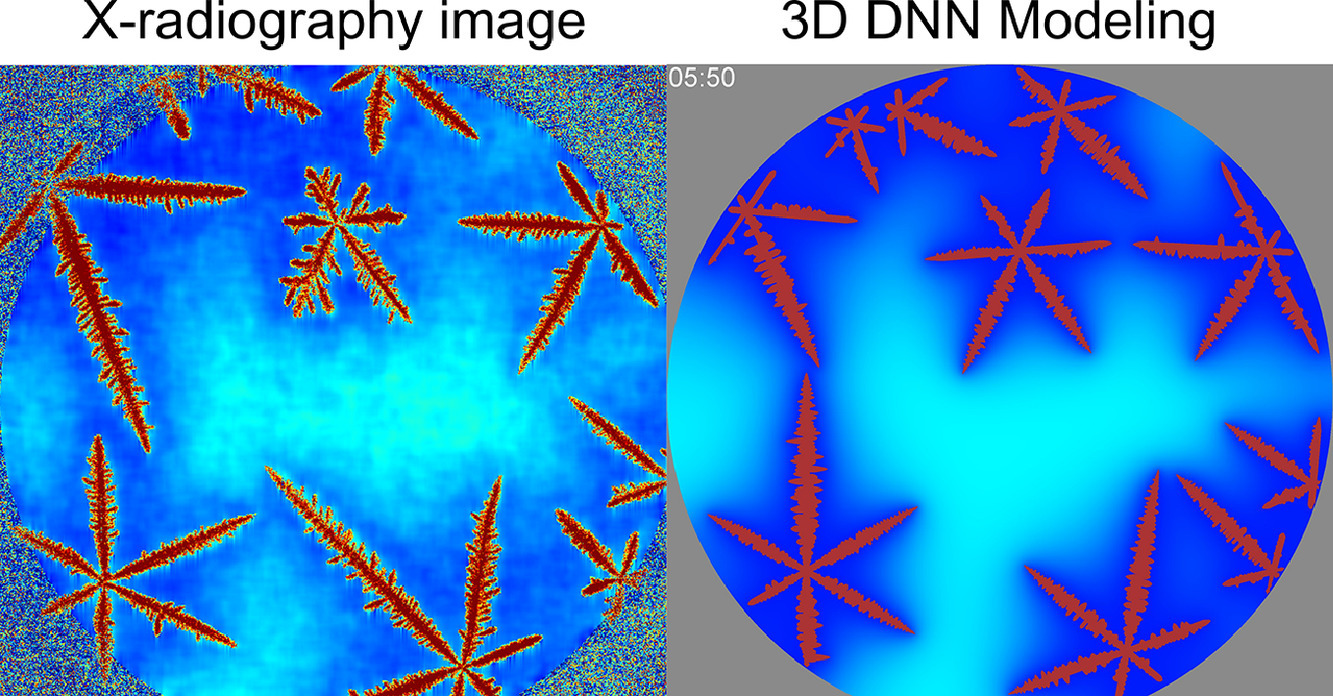
17. A comparative in situ X-radiography and DNN model study of solidification characteristics of an equiaxed dendritic Al-Ge alloy sample
Al-Ge等轴晶凝固特征的X射线衍射与DNN模型对比研究
Maike Becker✉, Laszlo Sturz✉, Dirk Bräuer, Florian Kargl
M. Becker:maike.becker@dlr.de
L. Sturz:l.sturz@access-technology.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.078
摘要
我们在200 µm厚的Al-24 at.% Ge薄膜样品等温凝固过程中,通过原位X射线衍射对样品的枝晶生长速率、液体浓度和产物固体组分进行了测量。实验可以在整个过程中很好地追踪枝晶尖端的生长速度。我们对单一枝晶尖端的浓度分布进行了测量,并分析了由于溶质积累导致的远场溶质浓度增加。通过在不同时间对12mm直径样品进行完整分析,我们推导得到了熔体全局浓度。这使我们能够对合金的初始形核过冷行进分析,而这是目前为止尚未解决的难题。我们将实验结果与三维枝晶网络模型进行了比较。模型模拟了实验条件下六边形枝晶的结构和几何形状。虽然模拟结果对过冷参数和枝晶选择常数的变化非常敏感,但我们成功找到了一个模型参数集,再现了实验测得的所有凝固特征。实验和模型的全面比较表明,实验条件下受过冷度影响导致的枝晶生长速率比非限制条件下低7倍。

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P303-315
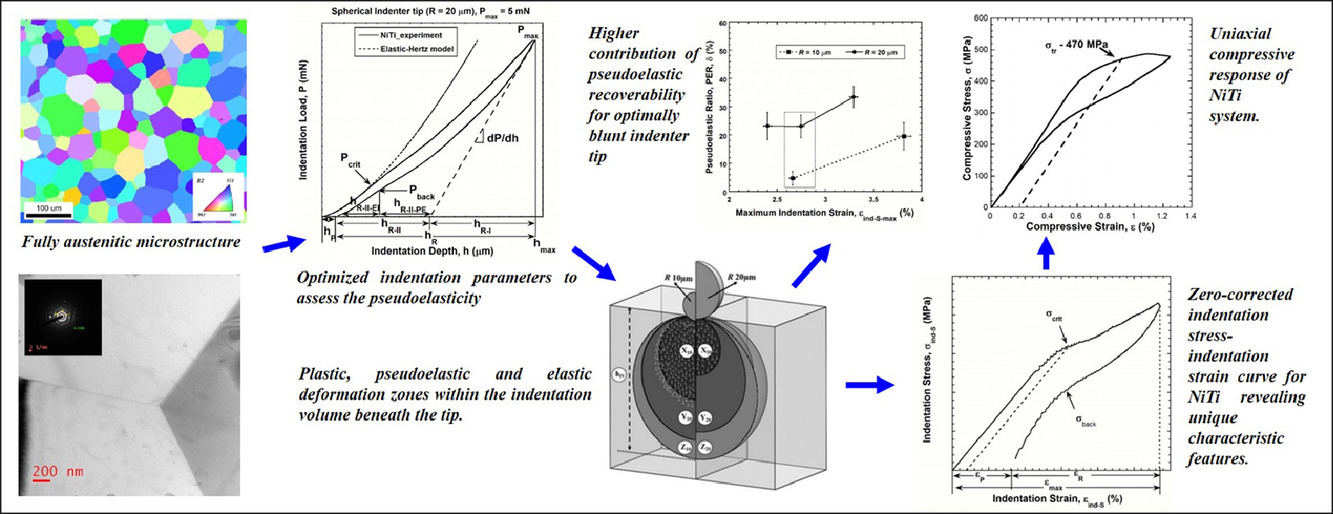
18. Assessment of small-scale deformation characteristics and stress-strain behavior of NiTi based shape memory alloy using nanoindentation
利用纳米压痕方法分析NiTi形状记忆合金中的小尺度变形特性和应力应变行为
Sujith Kumar S, I. Anand Kumar, Lakhindra Marandi, Indrani Sen✉
I. Sen:indrani.sen@metal.iitkgp.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.080
摘要
本研究的重点是探究亚微米尺度下富镍NiTi合金变形的微观机制。该合金通过可逆的应力诱导马氏体相变,表现出假弹性特点,具有显著的可恢复应变。我们使用纳米压痕作为主要的实验工具,对包括压头尖端配置、尺寸和应用负载水平在内的各种参数进行系统性地变化。结果表明,与常用且锋利的Berkovich压头相比,使用钝球形压头将使得在压痕体积内施加的应变量和应变梯度减小。这为系统性地改变NiTi合金的形变模式提供了可能。进一步分析表明,采用最佳的压头结构、尺寸和载荷水平组合是探究NiTi假弹性机理的前提。最重要的是,我们为将纳米压痕的载荷-位移响应转换为对应的压痕-应力-应变行为,制定了一套简化规则。无需特定的实验模式即可实现这些反应材料变形特征曲线。总之,本研究强调了选择合适纳米压痕参数对评估亚微米尺度下镍钛合金伪弹性的重要性,并据此对合金变形行为进行了研究。

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P316-328
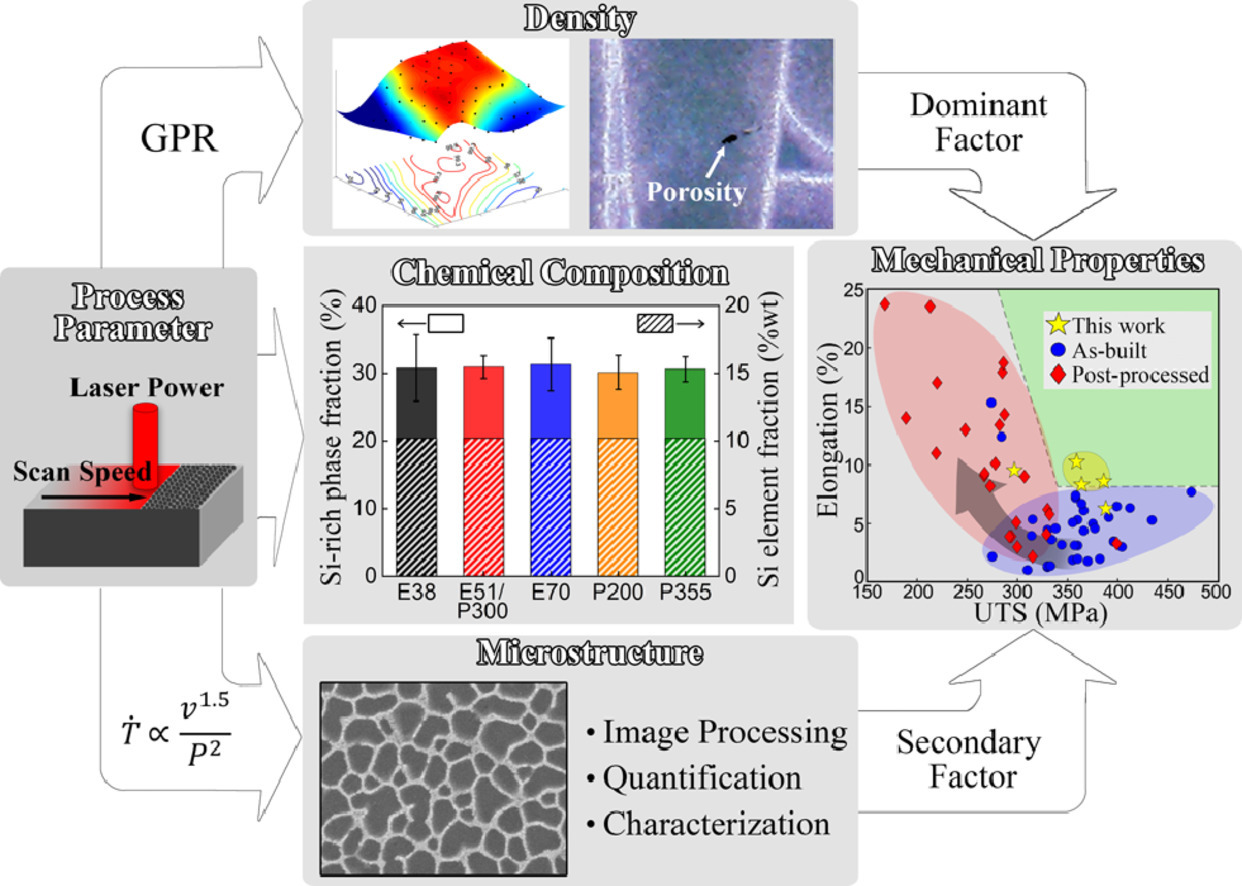
19. Machine-learning assisted laser powder bed fusion process optimization for AlSi10Mg: New microstructure description indices and fracture mechanisms
利用机器学习方法优化AlSi10Mg的激光熔炼工艺:新的组织描述指标和断裂机制
Qian Liu, Hongkun Wu, Moses J. Paul, Peidong He, Zhongxiao Peng, Bernd Gludovatz, Jamie J. Kruzic, Chun H. Wang, Xiaopeng Li✉
X. Li:xiaopeng.li@unsw.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.010
摘要
在本研究中,我们提出了一种基于高斯过程回归的机器学习方法来识别激光粉末熔炼(LPBF)的最佳工艺窗口。借此我们发现了一个新的、更大的工艺窗口,用以制备高致密度AlSi10Mg(相对密度≥99%)。优化后工艺参数(如激光功率和扫描速度)可以实现突破性的高强度和延展性的组合。结果表明,尽管AlSi10Mg样品具有与Al-Si共晶组织类似结构(例如晶粒中的胞状结构),但这两者在机械性能上具有显著区别,包括硬度(118 - 137 HV10),抗拉强度(297 - 389 MPa),延伸率(6.3 - 10.3%),断裂韧性(9.9 - 12.7 kJ/m2)等。这是由于两者组织的细微差异导致的。通过扫描电子显微镜表征,我们定义了两个新的形貌参数(尺寸参数Id和形状参数Is)对此进行进一步的解释。研究发现,除了晶粒结构外,亚晶尺寸和胞状结构界面形貌对材料的力学性能也有很大影响。值得一提的是,本研究中提出的方法同样可以应用于其他金属或合金的激光粉末熔炼工艺优化和力学性能调控。

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P329-340
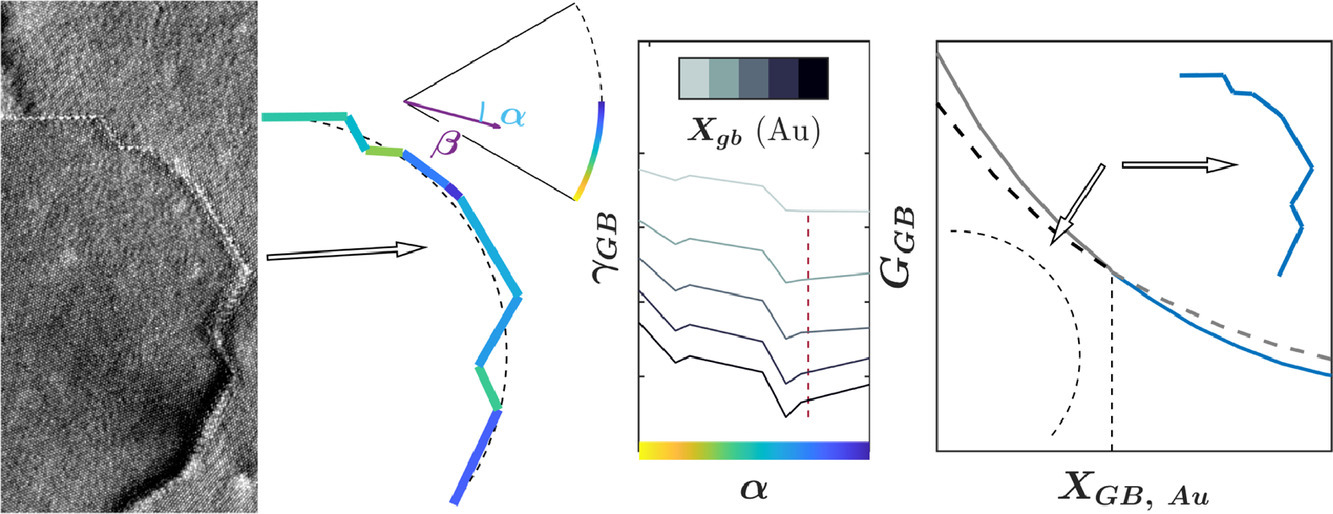
20. The influence of alloying in stabilizing a faceted grain boundary structure
合金元素对晶界面结构稳定性的影响
Jonathan L. Priedeman, Gregory B. Thompson✉
G.B. Thompson:gthompson@eng.ua.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.085
摘要
大量研究表明,晶界结构与溶质元素和温度等因素有关。本研究中,我们使用了原位原子尺度的表征技术对600℃和800℃下Pt-5Au(at. %)纳米晶的Σ21a [1 1 1]倾侧晶界进行了观测。结果表明,随着温度的增加,界面从许多小平面逐步演化为较少的大平面。这些择优平面通常是对称等效倾侧晶界。Pt双晶的模拟表明,这些择优面并非所有可能形成的倾侧晶界中的能量最小平面;而通过计算Au在这些晶界位置的偏析焓,我们发现Au更倾向于处在这些格点位置,从而降低晶界能,这为观测到的稳定晶面提供了合理解释。

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P350-363
21. Scaling of internal dissipation of polycrystalline solids on grain-size and frequency
多晶固体内部耗散随晶粒度和频率的变化
Chuangchuang Duan, Yujie Wei
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.004
摘要
在几乎所有固体中,内摩擦都是能量耗散的重要机制之一。Zener (Phys. Rev. 60 (1941) 906-908) 和 Kê (Phys. Rev. 71 (1947) 533-546)等人的工作表明,多晶固体的模量损失谱中存在由于晶界的粘性滑动引起的单一峰值。在本研究中,我们建立了晶界内弹性变形、粘性蠕变和扩散耦合的连续介质模型,揭示了由于晶界内粘性变形,导致模量损失谱存在第二峰值。当内部耗散达到局部最大值时,对应的两个频率与晶粒尺寸d有关,一个与d成反比,另一个与d−3成正比。我们研究了晶界的局部弹性和扩散对模量损失谱的影响,确定了双峰出现的条件。以上结果对研究多晶和多孔材料中的内部耗散和地质学中的地震活动具有重要价值。
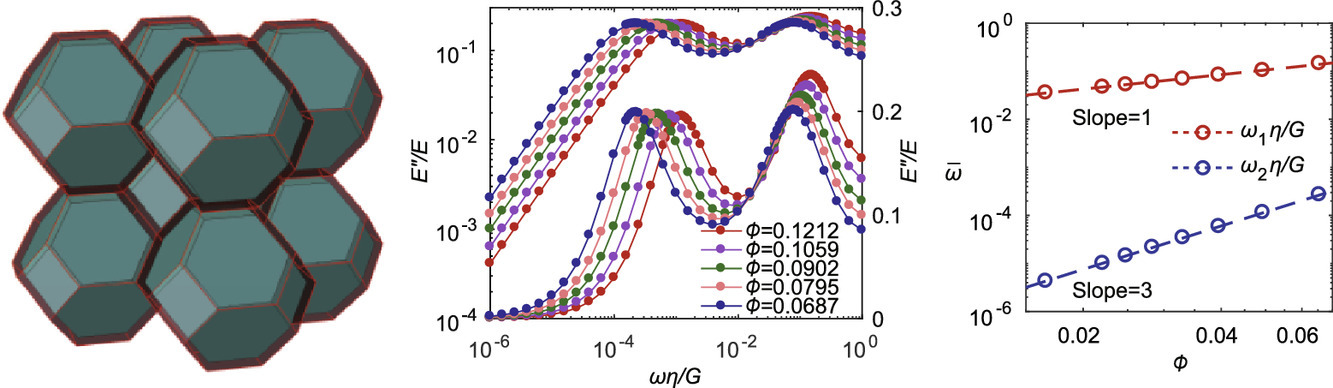

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P364-372
22. Analytic description of grain boundary segregation, tension, and formation energy in the copper–nickel system
铜-镍体系中晶界偏聚、晶界张力和晶界形成能的解析性描述
F. Fischer✉, S.M. Eich✉
F. Fischer:Felix.Fischer@mp.imw.uni-stuttgart.de
S.M. Eich:Sebastian.Eich@imw.uni-stuttgart.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.039
摘要
在本研究中,我们将最近提出的偏聚模型应用到了基于嵌入原子势的Σ5 Cu-Ni晶界偏聚计算中。为了全面探究500 K到1000 K下的完整成分范围,我们不断改变化学势,系统地研究了半巨正则系综中的偏聚。模型避免了使用界面成分,因而无需定义界面体积,而是模拟了热力学上具有明确定义的溶质过量,将其作为一个主要的热力学特征。结果表明,基于成分有关、温度无关的等效偏聚能,可以非常准确地描述大温度和成分范围内的溶质过量和界面形成能。然而,该模型最初是基于无晶格错配系统推导的,因此忽略了界面张力。鉴于Cu-Ni体系的晶格错配度约为2.7%,因此在本研究中,我们通过线性弹性理论进一步对偏聚模型进行了拓展,使其可以考虑界面张力。利用这一扩展模型,可以证明在所有温度和成分范围内,通过等效偏析能就可以得到溶质过量、晶界张力和晶界形成能。由于在原理上只需要一根的偏析等温线就足以确定等效偏析能,从而对上述界面热力学性质进行计算,因此该模型对于通过简单的实验测量估计界面参数非常有意义。
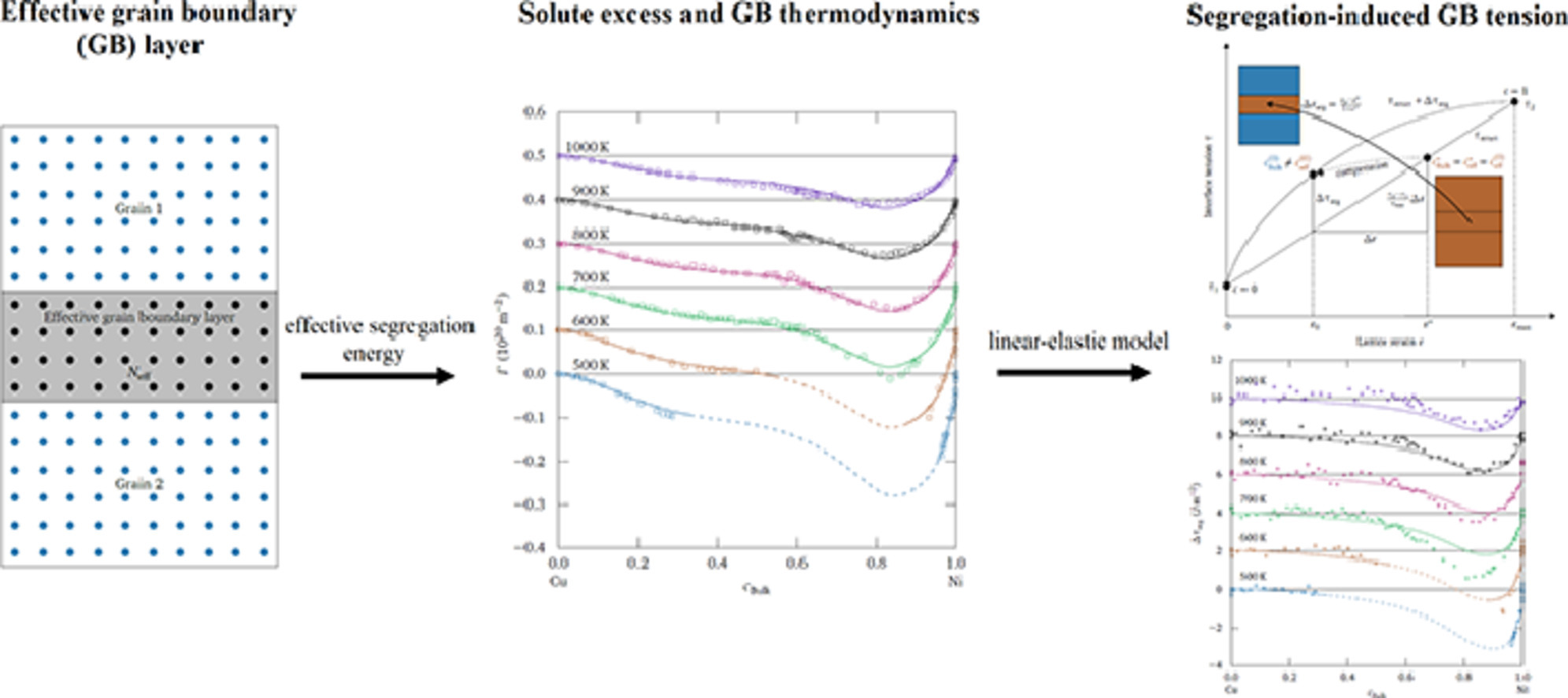

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P386-402
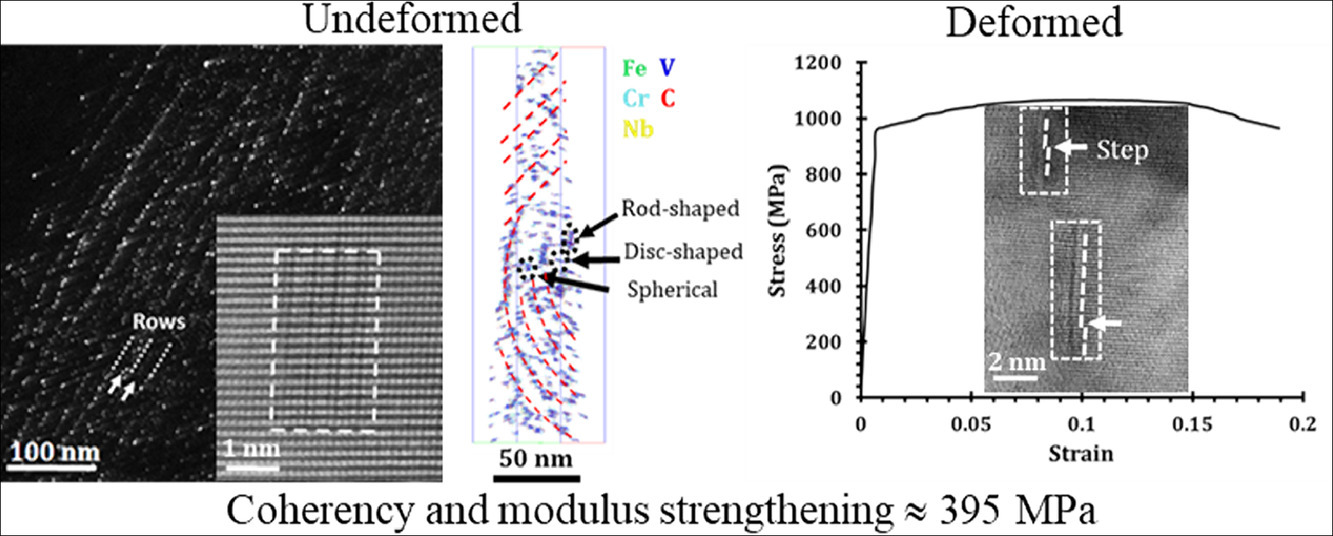
23. Application of advanced experimental techniques to elucidate the strengthening mechanisms operating in microalloyed ferritic steels with interphase precipitation
利用先进实验技术阐明微合金化铁素体钢中的相间析出强化机制
Navjeet Singh, Gilberto Casillas, David Wexler, Chris Killmore, Elena Pereloma✉
E. Pereloma:elenap@uow.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.014
摘要
我们采用扫描透射电镜、原子探针和单轴拉伸等方法对经热机械处理的Mo、Cr、V和Nb合金铁素体钢组织和拉伸性能进行了研究。结果表明,材料组织由多边形铁素体(平均晶粒尺寸~4±3µm)和高密度纳米盘状相间析出(直径~2-4 nm,厚度~1±0.4 nm)组成。V、Cr、Nb合金钢中还存在纤维状相间析出碳化物。析出间的铁素体基体中有团簇形成。我们分析了不同强化机制对屈服强度的贡献,并首次考虑了纳米相间析出的共格和模量强化机制。结果表明,强度的主要贡献来自晶界强化和纳米析出,分别约为280 MPa和395 MPa。此外,团簇的强化作用也十分显著(~150-170 MPa)。