金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.194, 15 Mar. 2021(上)
2021-02-01 来源:Goal Science
Vol. 194 目录
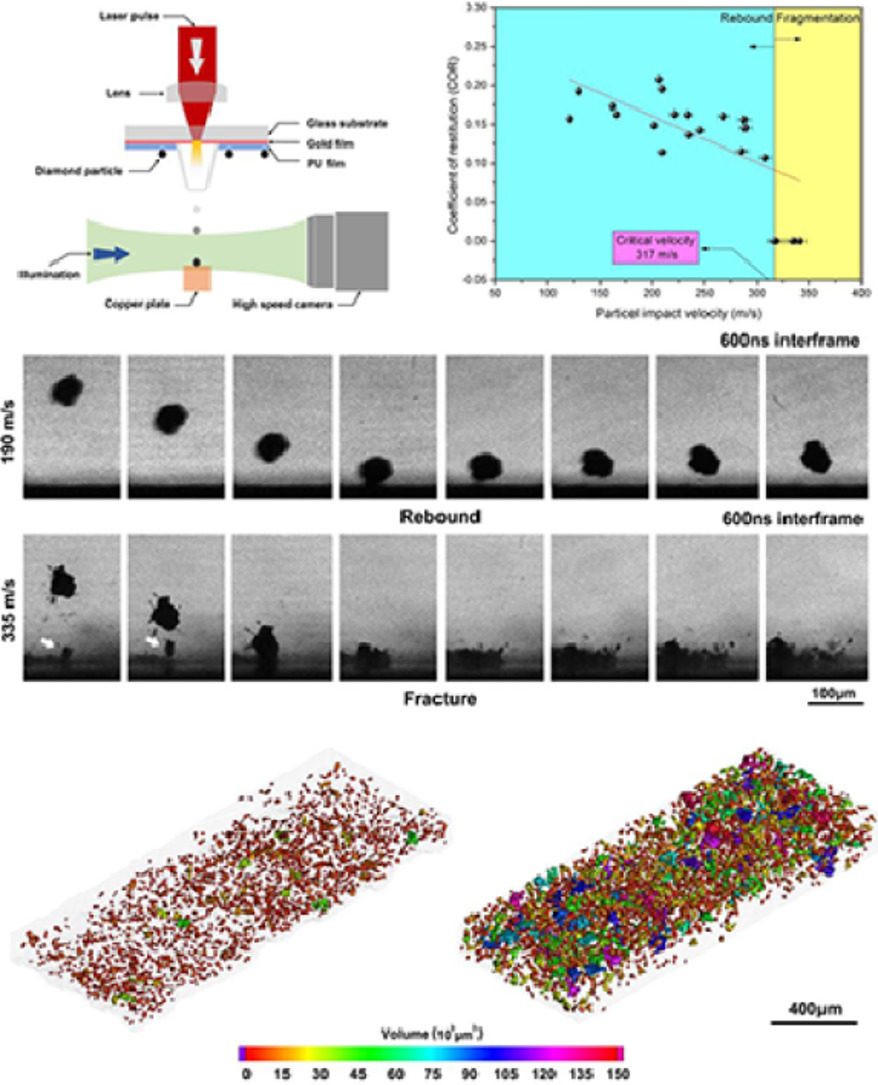
1. Unravelling the deposition mechanism of brittle particles in metal matrix composites fabricated via cold spray additive manufacturing
揭示通过冷喷涂增材制造法制备的金属基复合材料中脆性颗粒的沉积机理
2. Temperature dependence of martensite variant reorientation in stress-induced martensite aged Ni49Fe18Ga27Co6 single crystals
应力诱导马氏体时效Ni49Fe18Ga27Co6单晶中马氏体变体重取向的温度依赖性
3. Effects of grain size on body-centered-cubic martensitic transformation in metastable Fe46Co30Cr10Mn5Si7V2 high-entropy alloy
晶粒尺寸对亚稳态Fe46Co30Cr10Mn5Si7V2高熵合金体心立方马氏体相变的影响
4. Functionally graded structures realized based on Fe-Mn-Al-Ni shape memory alloys
基于Fe-Mn-Al-Ni形状记忆合金的功能梯度结构
5. Subsurface faceted cracking behavior of selective laser melting Ni-based superalloy under very high cycle fatigue
选择性激光熔化镍基高温合金在高周疲劳下的亚表面裂纹行为
6. Diffraction artefacts from twins and stacking faults, and the mirage of hexagonal, polytypes or other superstructures
孪晶和层错的衍射伪像,以及六方、多型体或其他超结构的幻象
7. Heterogenous columnar-grained high-entropy alloys produce exceptional resistance to intermediate-temperature intergranular embrittlement
异质柱状晶高熵合金对中温晶间脆化展现出优异的抵抗能力
8. Interactions of solutes with crystal defects: A new dynamic design parameter for advanced alloys
溶质与晶体缺陷的相互作用:一种新的先进合金动态设计参数
9. Nanograin formation in dimple ridges due to local severe-plastic-deformation during ductile fracture
韧性断裂过程中由于局部严重塑性变形在韧窝脊中形成纳米晶
10. Grain-boundary plane orientation dependence of faceting-roughening transition in Au grain boundaries under electron-beam irradiation
电子束辐照下金晶界切面化-粗化转变的晶界面取向依赖性
SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113614
1. Unravelling the deposition mechanism of brittle particles in metal matrix composites fabricated via cold spray additive manufacturing
揭示通过冷喷涂增材制造法制备的金属基复合材料中脆性颗粒的沉积机理
Shuo Yin✉, Mostafa Hassani, Qingge Xie, Rocco Lupoi
Shuo Yin: yins@tcd.ie
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.055
摘要
近年来,冷喷涂沉积(CSD)已发展为一种增材制造工艺。在所有金属增材制造工艺中,它具有最高的效率。本工作研究了金属基复合材料(MMCs)的CSD过程中脆性增强颗粒的沉积机理。通过原位观察以微米级的分辨率,在纳秒尺度对脆性颗粒的回弹和破碎进行了研究。我们首次确定了从粒子回弹到粒子破碎过渡的速度。在此,我们将该速度定义为“破碎速度”。在CSD沉积台上进行的X射线计算断层扫描显示,沉积台上的大多数钻石都是原始颗粒的碎片,其体积分数主要取决于其相对于破碎速度的撞击速度。基于这些发现以及微观组织特征,我们提出了MMCs在CSD过程中脆性增强颗粒的沉积机理。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113618
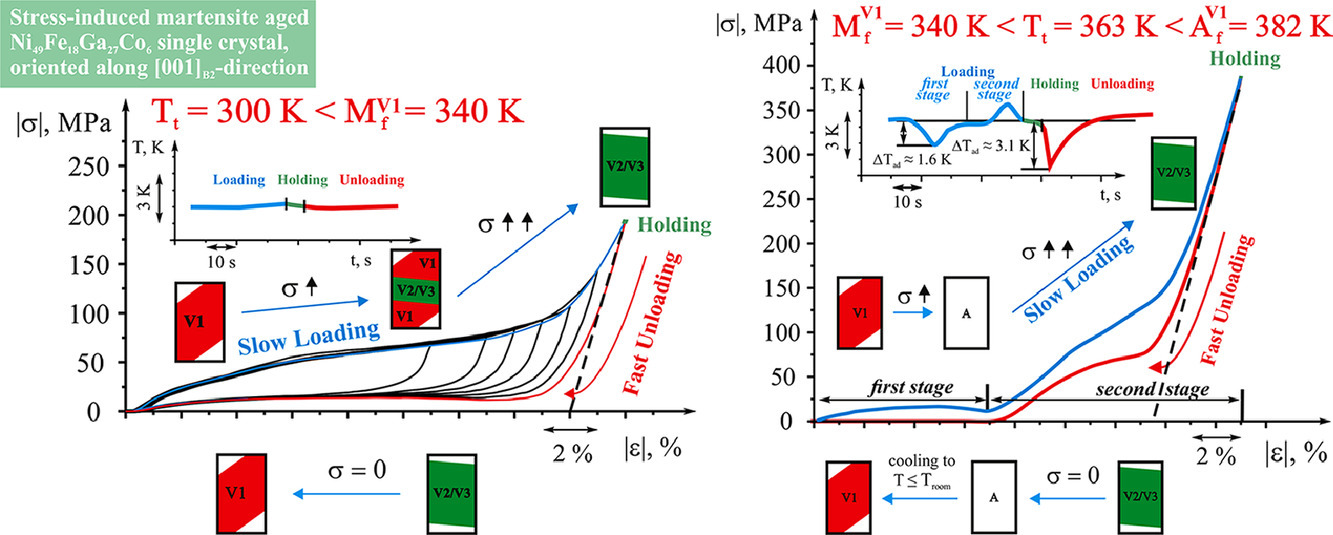
2. Temperature dependence of martensite variant reorientation in stress-induced martensite aged Ni49Fe18Ga27Co6 single crystals
应力诱导马氏体时效Ni49Fe18Ga27Co6单晶中马氏体变体重取向的温度依赖性
E. Panchenko✉, A. Tokhmetova, N. Surikov, A. Eftifeeva, A. Tagiltsev, E. Timofeeva, Y. Chumlyakov, G. Gerstein, H.J. Maier
E. Panchenko: panchenko@mail.tsu.ru
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.056
摘要
本工作研究了Ni49Fe18Ga27Co6单晶在压缩过程中,应力诱发的马氏体沿[110]B2||[100]L10方向马氏体变体重取向的温度依赖性。这种马氏体时效引起了类似橡胶的行为,在248K至344K的温度范围内,沿[001]B2方向可逆应变高达-16.0%,这是由L10-马氏体变体重取向引起的。在从344K到382K的正向和反向转变之间的较高温度下,应力诱发马氏体时效晶体表现出两阶段应力应变的响应,可逆应变高达-13.5%。第一阶段的特点是低的临界应力σcr1≈1-15MPa,且在加载下具有逆弹性效应(吸热)。在第二阶段观察到超弹性,σcr2≥100MPa。在此温度范围内,马氏体变体的重取向是通过反向然后正向的马氏体相变发生的。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113620
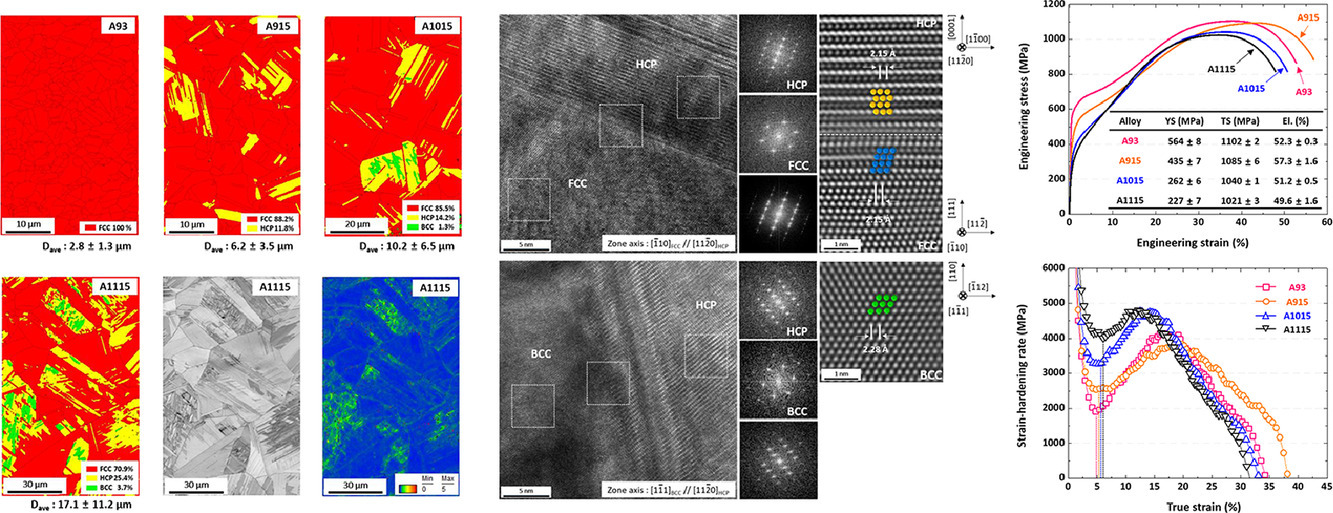
3. Effects of grain size on body-centered-cubic martensitic transformation in metastable Fe46Co30Cr10Mn5Si7V2 high-entropy alloy
晶粒尺寸对亚稳态Fe46Co30Cr10Mn5Si7V2高熵合金体心立方马氏体相变的影响
Yong Hee Jo, Dae Woong Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim, Sunghak Lee✉
Sunghak Lee: shlee@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.005
摘要
本工作系统地研究了晶粒尺寸对亚稳态Fe46Co30Cr10Mn5Si7V2高熵合金(HEA)的微观组织和力学性能的影响。晶粒粗化导致面心立方(FCC)相的稳定性降低,形成了层状六方密堆积(HCP)和蝶形体心立方(BCC)结构的马氏体。在拉伸试验中,通过中间HCP相过渡的FCC到BCC相的转变,发生了相变诱导塑性(TRIP),且BCC相的加速转变速率提高了应变硬化率。结果表明,与热诱导马氏体相变和应变硬化机制相关的微观组织演变可以通过理解从FCC到HCP到BCC相的马氏体相变来很好地解释。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113619
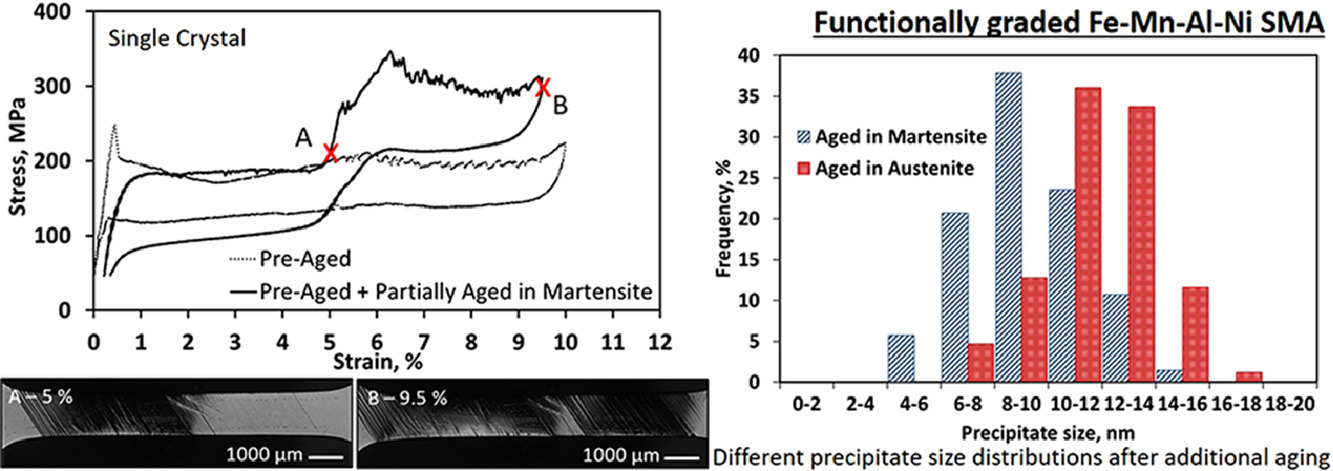
4. Functionally graded structures realized based on Fe-Mn-Al-Ni shape memory alloys
基于Fe-Mn-Al-Ni形状记忆合金的功能梯度结构
M. Vollmer✉, A. Bauer, M.J. Kriegel, M. Motylenko, T. Niendorf
M. Vollmer: vollmer@uni-kassel.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.057
摘要
本工作介绍了一种在Fe-Mn-Al-Ni形状记忆合金中获得功能梯度性能的新方法。表现出超弹性的单晶样品在部分马氏体状态下进行时效处理。结果表明奥氏体时效区的特征是超弹性滞后会发生改变,且具有不同的正/反向相变临界应力;而马氏体时效区的性能几乎保持不变。透射电子显微镜研究表明,纳米β析出,作为严重影响相变温度并最终影响相变应力的物相,在马氏体时效区的平均尺寸约为9 nm,在奥氏体时效区的平均尺寸约为12nm。基于这些结果,以某种方式调整Fe-Mn-Al-Ni的成分,使其局部表现不同的功能特性似乎是可行的。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113613
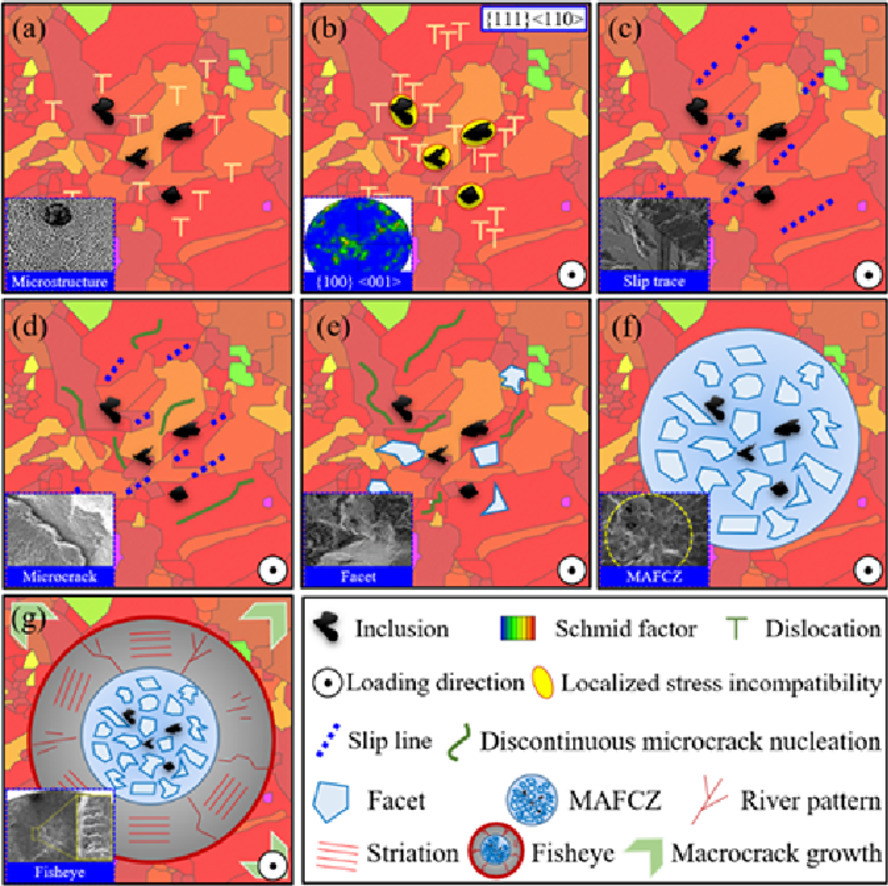
5. Machine learning based surrogate modeling approach for mapping crystal deformation in three dimensions
选择性激光熔化镍基高温合金在高周疲劳下的亚表面裂纹行为
Wei Li✉, Rui Sun, Ping Wang✉, XiaoLong Li, Yucheng Zhang, Tianyi Hu, Cheng Li, Tatsuo Sakai
Wei Li: lliw@bit.edu.cn,北京理工大学
Ping Wang: ping_wf@163.com,齐鲁工业大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.001
摘要
本文研究了在极高的循环疲劳(VHCF)下通过选择性激光熔化(SLM)制备的镍基高温合金的结构-性能,带有鱼眼图案的亚表面裂纹成为一种显著的破坏模式。由于存在亚表面破坏,出现了S-N曲线的下降特性。基于二维和三维的显微观察,鱼眼内存在一个粗糙的区域,该区域有多个小平面和夹杂物,被称为“多夹杂物辅助平面裂纹区(MAFCZ)”。结合电子背散射衍射分析,亚表面破坏与晶粒尺寸和取向,微观织构以及晶体缺陷有关。在夹杂物的帮助下,裂纹从具有最高施密特因子的大晶粒内形核。具有裂纹挠度的粗糙表面形貌揭示了MAFCZ中超慢的裂纹扩展行为。结合失效建模和断裂力学分析,阐明了VHCF条件下SLM镍基高温合金的亚表面破坏机理。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113629
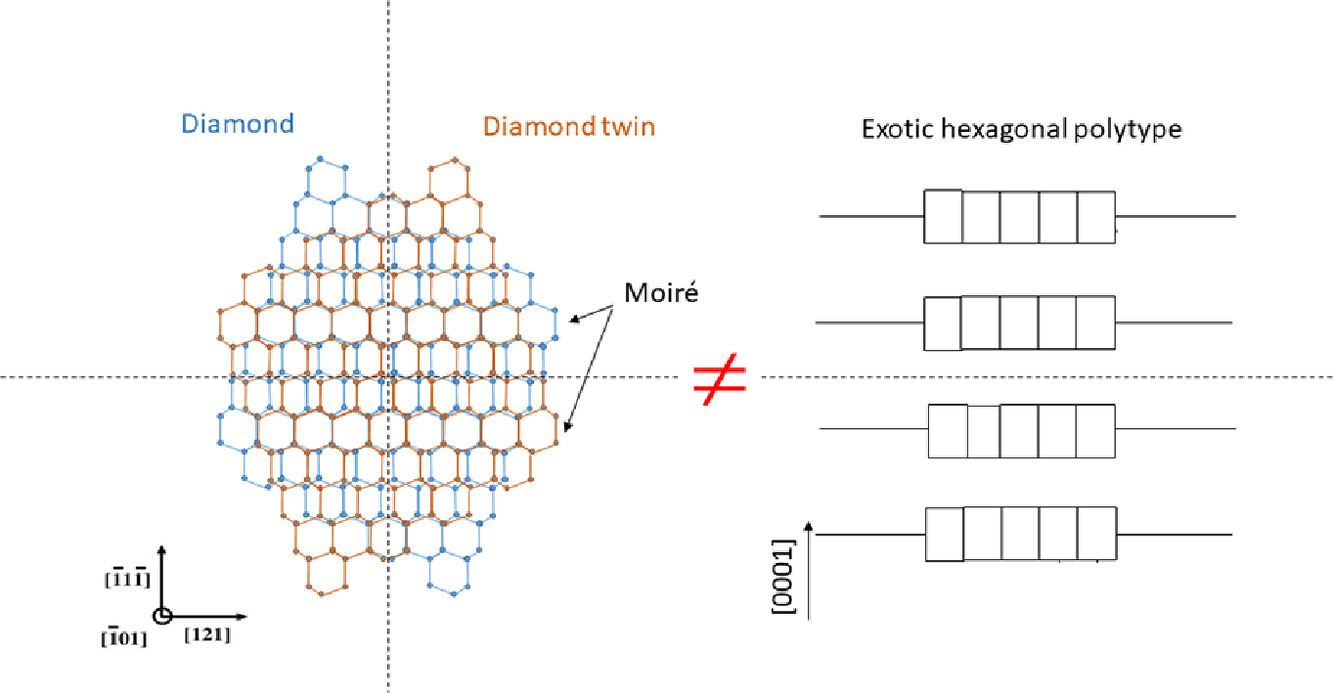
6. Diffraction artefacts from twins and stacking faults, and the mirage of hexagonal, polytypes or other superstructures
孪晶和层错的衍射伪像,以及六方、多型体或其他超结构的幻象
Cyril Cayron✉
Cyril Cayron: cyril.cayron@epfl.ch
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.014
摘要
最近,在多项研究中已报道了高碳钢中的六方相。本工作表明这些研究错误地解释了使用的电子显微镜结果。衍射花样中的额外斑点和高分辨率图像中的异常衬度不是超结构,而是由于孪晶和层错的存在引起的双重衍射和条纹效应所致。我们在报道铝或铜中存在9R结构或钻石中存在奇异形式的碳的论文中指出了类似令人遗憾的误解。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113622
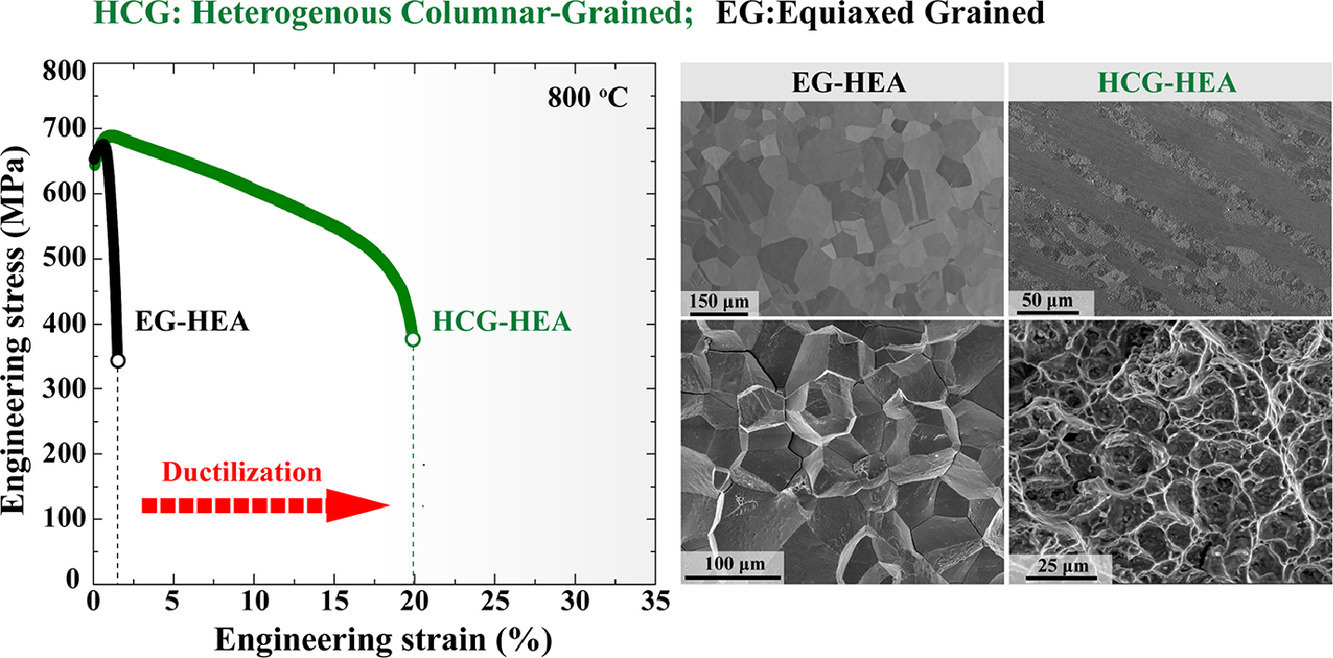
7. Heterogenous columnar-grained high-entropy alloys produce exceptional resistance to intermediate-temperature intergranular embrittlement
异质柱状晶高熵合金对中温晶间脆化展现出优异的抵抗能力
B.X. Cao, H.J. Kong, L. Fan, J.H. Luan, Z.B. Jiao, J.J. Kai, T. Yang✉, C.T. Liu✉
T. Yang: taoyang6-c@my.cityu.edu.hk,香港城市大学
C.T. Liu: chainliu@cityu.edu.hk,香港城市大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.007
摘要
由共格纳米颗粒增强的高熵合金(HEA)在高温结构应用中显示出巨大潜力,但是,在中温下进行测试时,通常会出现严重的晶间脆化。本研究中,我们展示了一种新颖的“异质柱状晶”(HCG)的方法,有效克服了这一棘手的问题。与等轴晶合金在800°C时沿晶界表现出极大的脆性不同,由于独特的晶界特征和分布,新开发的HCG-HEA展现出对晶间断裂极高的抵抗力。异质柱状晶结构的存在极大地抑制了裂纹形核和沿界面的扩展,从而在800°C下获得了~18.4%的异常拉伸塑性以及~652 MPa的高屈服强度。这一发现为具有优异机械性能的高温材料的创新设计提供了新的见解。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113626
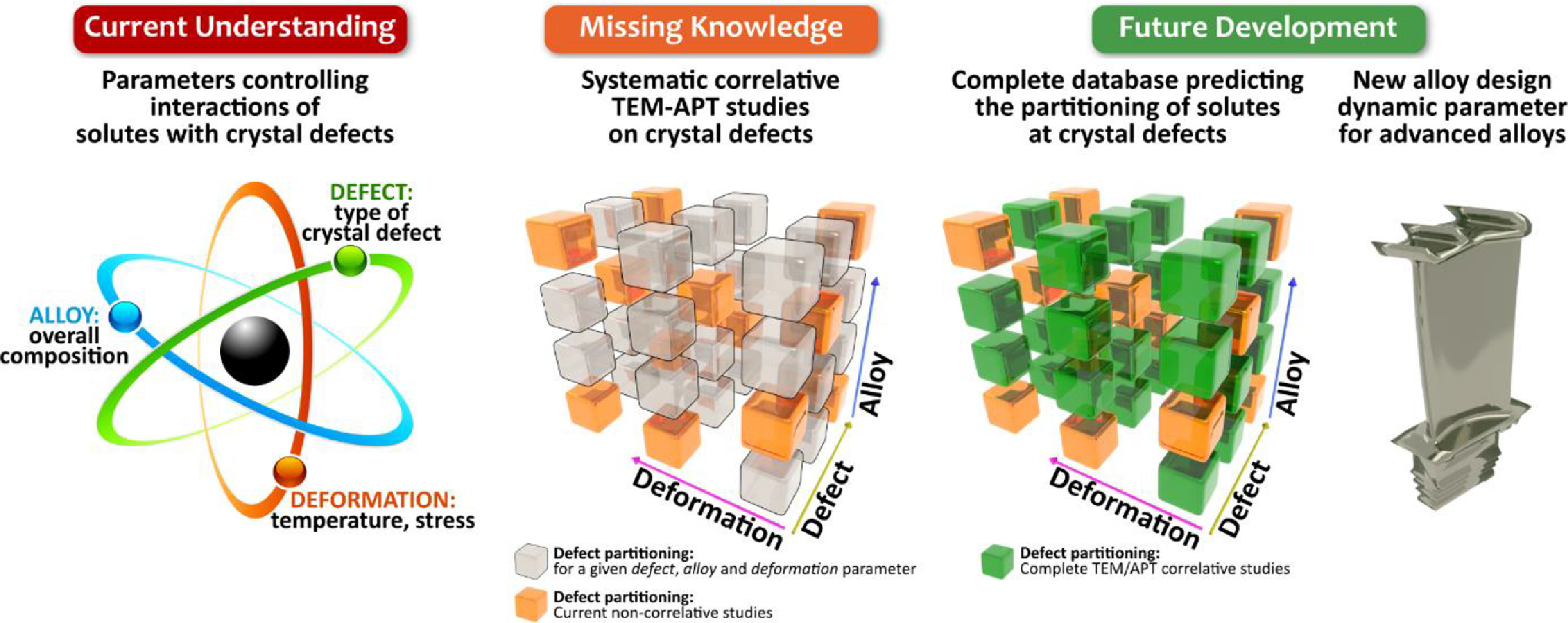
8. Interactions of solutes with crystal defects: A new dynamic design parameter for advanced alloys
溶质与晶体缺陷的相互作用:一种新的先进合金动态设计参数
Paraskevas Kontis✉
Paraskevas Kontis: p.kontis@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.011
摘要
为了实现可持续发展的未来,提高工程系统的效率和减少排放需要新材料来突破其性能极限。当前的合金设计策略将合金视为静态系统,但其微观组织和成分在操作中不断发生演化。本文关注一种新的合金设计动力学参数,该参数来源于溶质与近原子尺度获得的晶体缺陷的相互作用相关的信息。最近高分辨表征的技术突破使近原子尺度的结构和成分成像成为可能,从而为此类相互作用提供了新的见解。本文讨论了这些相互作用对决定高温合金(例如镍基,钴基合金和钛合金)失效的组织和成分不断演变的影响。开发一种能够考虑这些相互作用的溶质-缺陷数据库,旨在更准确地预测当前合金和新合金的机械性能,对于更具动态性的合金设计策略是非常必要的。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113631
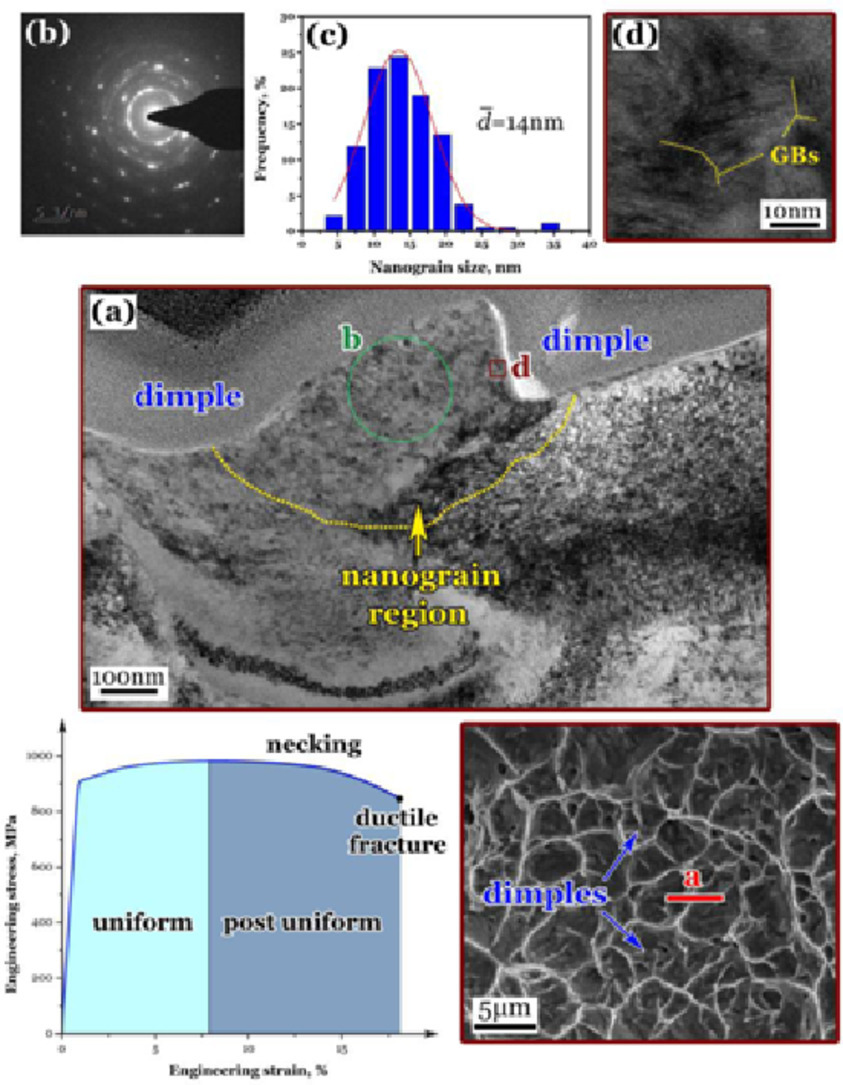
9. Nanograin formation in dimple ridges due to local severe-plastic-deformation during ductile fracture
韧性断裂过程中由于局部严重塑性变形在韧窝脊中形成纳米晶
Xiangnan Pan, Guian Qian, Youshi Hong✉
Youshi Hong: hongys@imech.ac.cn,中国科学院大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113631
摘要
纳米晶材料在力学,物理和化学方面具有卓越的性能。本研究中,我们发现了一种新现象,即钛合金在韧性断裂过程中会自发地形成纳米晶粒,其主要机制是局部严重的塑性变形(LSPD)。我们揭示了在单调拉伸的整个过程中的微观组织演变,以进一步了解从塑性变形到颈缩以及最终破坏的韧性断裂行为,尤其是在断后延伸阶段,在该阶段,孔洞形核、生长并联合。LSPD过程可以为高延展性材料的设计和生产提供新的概念和方法,其中纳米晶的形成将消耗大量的应变能,从而使试样在颈缩后的断后延伸阶段获得较大的伸长率。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113630
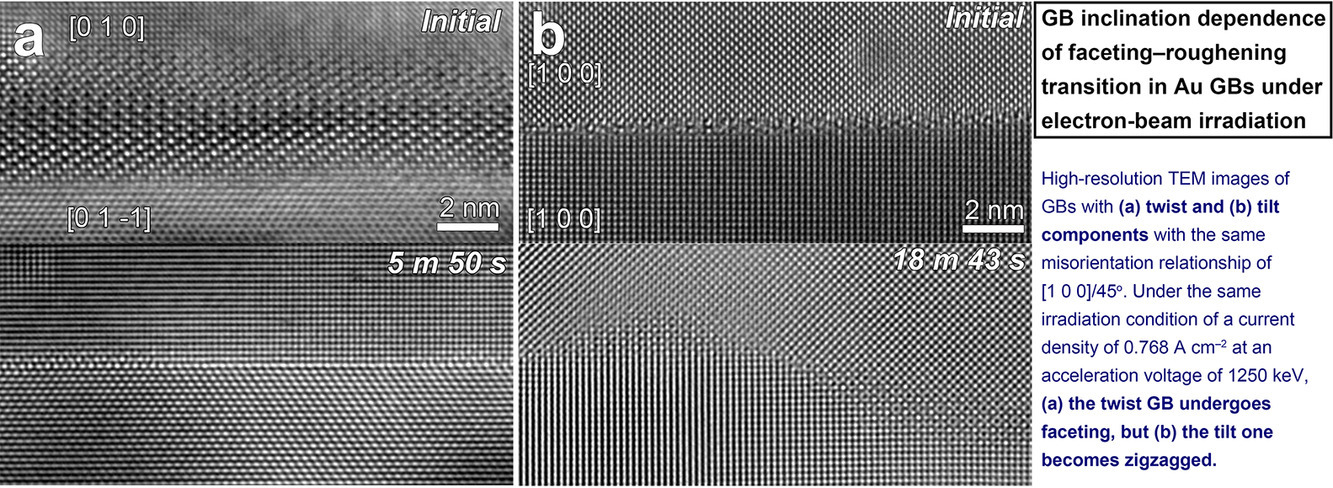
10. Grain-boundary plane orientation dependence of faceting-roughening transition in Au grain boundaries under electron-beam irradiation
电子束辐照下金晶界切面化-粗化转变的晶界面取向依赖性
Sung Bo Lee✉, Seung Jo Yoo, Jinwook Jung, Heung Nam Han
Sung Bo Lee: bolee@snu.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.11.015
摘要
晶界作用是吸收和湮灭多晶核材料中高能粒子产生的点缺陷。因此,了解高能粒子辐照对晶界结构变化的影响是发展具有理想性能核材料的先决条件。可以预料,对于不同的晶界特征,此种影响是不同的。为了探究这种可能性,我们在加速电压为1250 keV的高压透射电子显微镜下,以金为模型体系,研究了具有相同[1 0 0]/ 45°错配关系的扭曲和倾斜分量的晶界。我们观察到,在相同的辐照条件下,倾斜的晶界发生粗化,而扭曲的晶界则发生切面化。