金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.201,Dec. 2021(下)
2021-02-02 来源:Goal Science
Vol. 201 目录
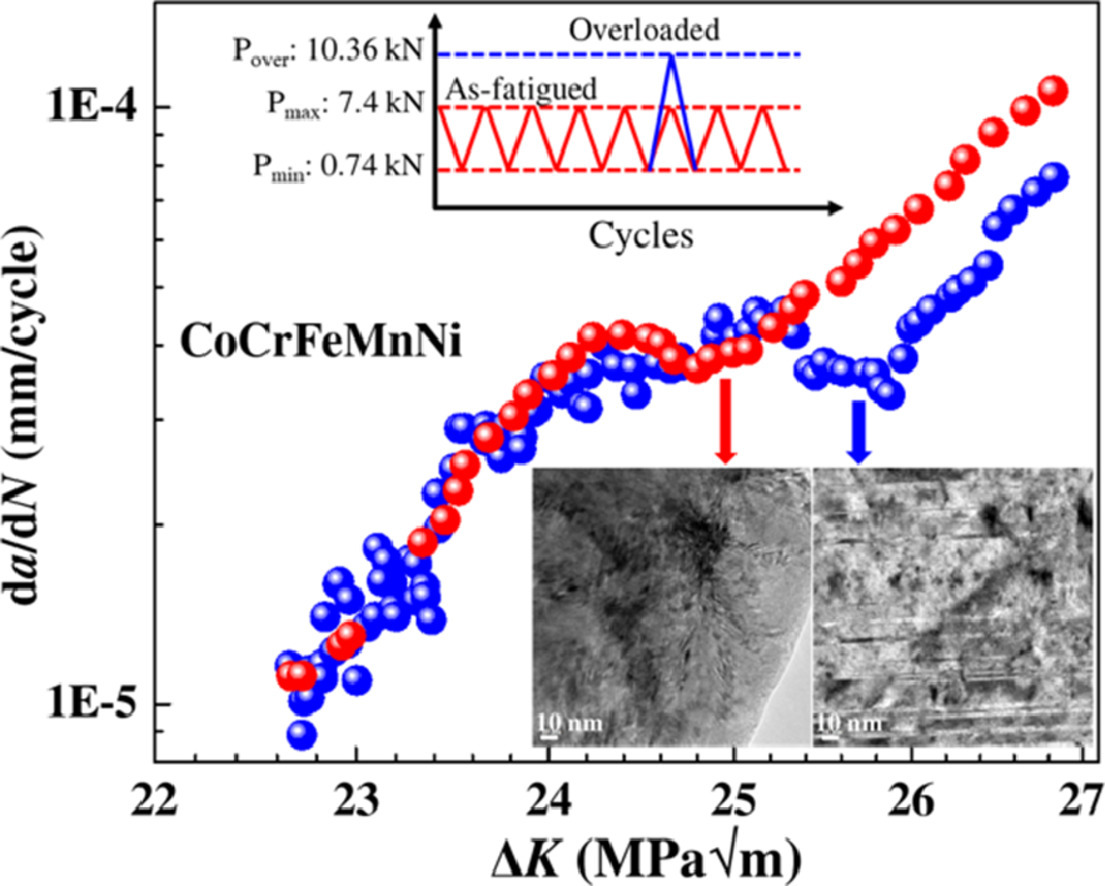
1. Enhancement of fatigue resistance by overload-induced deformation twinning in a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy
通过过载诱导形变孪晶增强CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金的抗疲劳性能
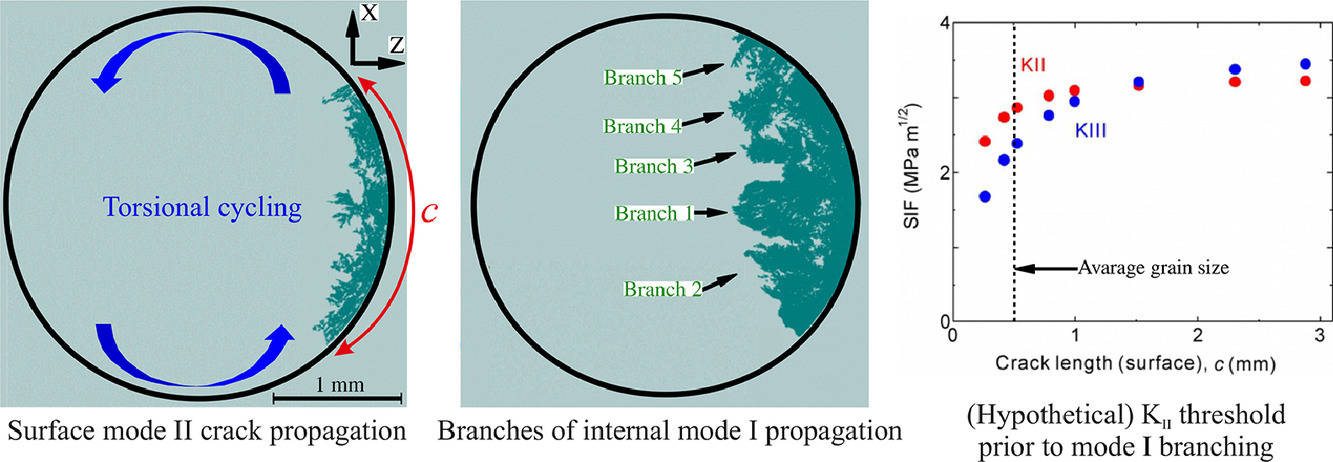
2. Torsional fatigue mechanisms of an A357-T6 cast aluminium alloy
A357-T6铸造铝合金的扭转疲劳机制
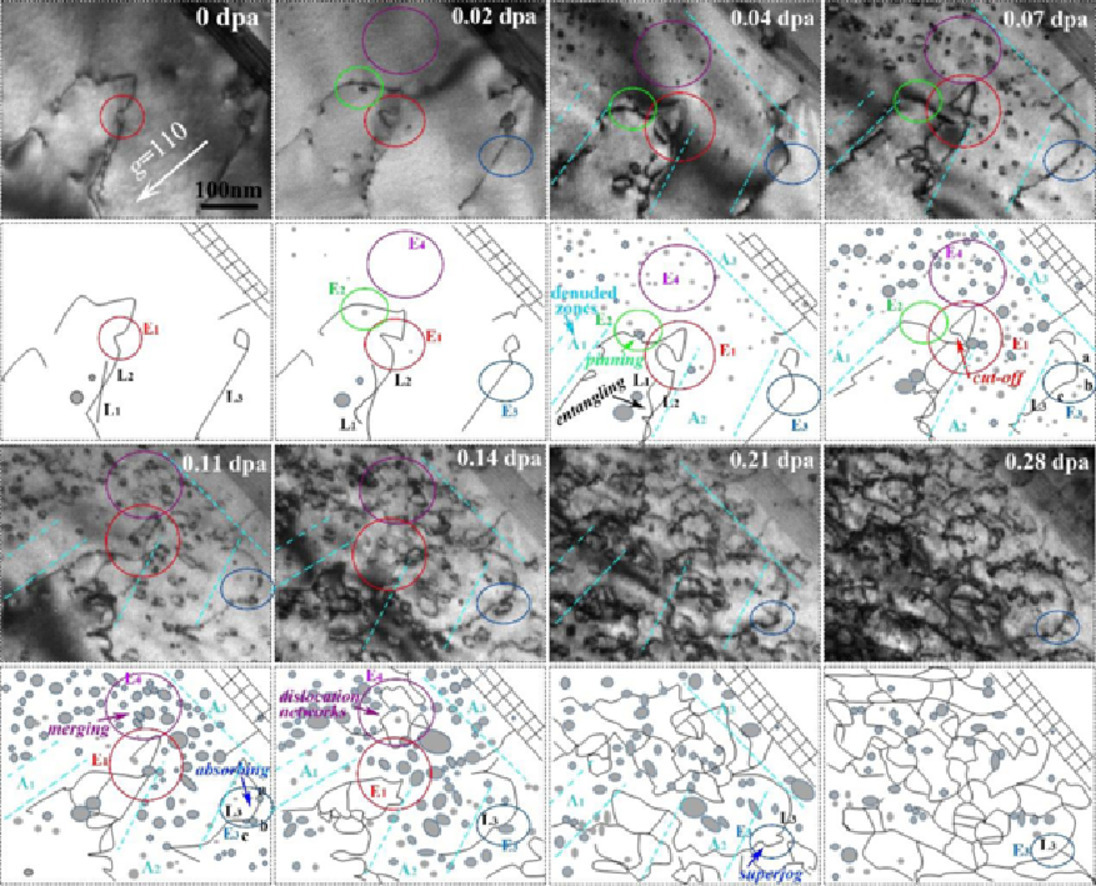
3. The evolution of dislocation loop and its interaction with pre-existing dislocation in He+-irradiated molybdenum: in-situ TEM observation and molecular dynamics simulation
He+辐照条件下钼中位错环的演化及其与位错相互作用的原位TEM观察和分子动力学模拟
4. Lithium Cluster Segregation in Coherent Contraction Twin Boundaries of Magnesium Alloys
镁合金共格收缩孪晶界处的锂团簇偏析研究
高温辐照诱导Cu中孔洞球化、收缩和迁移的原位研究
低温下TiZrHfNbTa高熵合金的力学不稳定性和拉伸性能研究
离子辐照后FeCr合金的硬度、热导和晶格应变表征
8. Microstructure evolution of thin nickel films with embedded chromium oxide nanoparticles
嵌氧化铬纳米粒子镍薄膜的微观组织演变研究
多晶形状记忆合金中形状记忆效应、伪弹性和热形变训练的非对称弹塑性相场模型
Al-Mg合金中晶界偏析和扩散的原子尺度研究
10M Ni-Mn-Ga中的II型形变孪晶拓扑模型
ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P412-424
1. Enhancement of fatigue resistance by overload-induced deformation twinning in a CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy
通过过载诱导形变孪晶增强CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金的抗疲劳性能
Tu-Ngoc Lam, Soo Yeol Lee✉, Nien-Ti Tsou, Hung-Sheng Chou, Bo-Hong Lai, Yao-Jen Chang, Rui Feng, Takuro Kawasaki, Stefanus Harjo, Peter K. Liaw, An-Chou Yeh,Ming-Jun Li, Ren-Fong Cai, Sheng-Chuan Lo h, E-Wen Huang✉
S.Y. Lee:sylee2012@cnu.ac.kr
E.-W. Huang:EwenHUANG@nctu.edu.tw(台湾国立交通大学/国立清华大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.016
摘要
我们利用中子衍射技术,研究了CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金(HEAs)在疲劳和拉伸过载条件下的疲劳裂纹扩展行为。我们采用高分辨率透射电子显微技术(HRTEM)和中子衍射应变图谱对组织进行了表征。与疲劳状态相比,由于单次拉伸过载后疲劳抗力增加,因此裂纹扩展被推迟。过载引起的大塑性变形、残余压应力和塑性区增大,以及裂纹尖端钝化和变形孪晶等机制共同导致了这一行为。拉伸过载后,沿裂纹扩展方向出现明显的锯齿形断口。此外,在室温过载条件下,塑性区的塑性变形机制由平面位错滑移为主变为孪晶为主,这与有限元模拟结果一致。以上大晶粒尺寸CoCrFeMnNi合金的拉伸过载诱发效应为提高高强度材料的疲劳性能提供了理论依据。

ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P435-447
2. Torsional fatigue mechanisms of an A357-T6 cast aluminium alloy
A357-T6铸造铝合金的扭转疲劳机制
I. Serrano-Munoz✉, D. Shiozawa, S. Dancette, C. Verdu, J.-Y. Buffiere✉
I. Serrano-Munoz:itziar.serrano.munoz@gmail.com
J.-Y. Buffiere:jeanyves.buffiere@insa-lyon.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.046
摘要
我们研究了A357-T6铸造铝合金在循环扭转载荷下的疲劳响应机制。我们采用表面裂纹监测与背散电子衍射(EBSD)研究了裂纹的萌生;基于S-N曲线结合原位疲劳同步层析成像研究传了裂纹的扩展。结果表明,断口形貌取决于应力水平。在中-低应力水平(τmax < 100 MPa)下,晶粒组织决定了裂纹萌生和扩展周期。裂纹通常在接近或垂直于试样轴的滑移面以模式II形核。裂纹扩展的早期以II型裂纹扩展为主,III型裂纹的向内扩展显著减缓。这种行为导致了浅表面裂纹的形成。随着裂纹逐渐变长,模式III的驱动力超过了模式II,裂纹就会形成~ 45°的模式I分支。

ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P462-476
3. The evolution of dislocation loop and its interaction with pre-existing dislocation in He+-irradiated molybdenum: in-situ TEM observation and molecular dynamics simulation
He+辐照条件下钼中位错环的演化及其与位错相互作用的原位TEM观察和分子动力学模拟
Yipeng Li, Guang Ran✉, Yijia Guo, Zhipeng Sun✉, Xinyi Liu, Yuanming Li, Xi Qiu, Yong Xin
G. Ran:gran@xmu.edu.cn (厦门大学/福建省核工程研究中心)
Z. Sun:superszp@163.com (中国核电研究院,成都)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.022
摘要
我们采用了原位TEM和分子动力学模拟,对673 K、30kev He+辐照条件下Mo中位错环的演化及其与位错线的相互作用进行了研究。我们详细研究了位错环的形核、湮没、合并、尺寸变化和类型,并分析了位错环导致的硬化效应。研究表明,随着氦离子注入量的增加,位错环的体积数密度先迅速增大,随后缓慢减小,到达一平台值;同时,位错环的平均尺寸不断增大,直至达到上限。在3.95×1015 He+辐照下(对应0.07dpa), 组织中形成了1/2<111>和<100>位错环,占比分别为60.2% 和39.8%。组织中预先存在的位错线会抑制位错环的形核和长大,而辐照诱导的位错环对位错线有较强的钉扎作用,阻碍其运动。通过分子动力学模拟,我们阐明了位错线与位错环相互作用的原子尺度机制,模拟结果与原位实验的观测结果基本一致。不同的相互作用过程主要取决于位错环所在平面和伯氏矢量、位错的运动、位错反应动力学和外加载荷。

ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P477-487
4. Lithium Cluster Segregation in Coherent Contraction Twin Boundaries of Magnesium Alloys
镁合金共格收缩孪晶界处的锂团簇偏析研究
Bingcheng Ge, Meng Yang, Qun Zu, Jianxin Guo, Yongjun Tian, Qiuming Peng✉
Q. Peng:pengqiuming@ysu.edu.cn(燕山大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.041
摘要
孪晶界调控被认为是许多工程合金实现高强度、高延性的潜在策略。在本文中,我们报导了Mg合金中一种独特的共格收缩孪晶界处Li团簇偏析现象。我们通过透射电子显微镜对原子尺度的组织结构进行了表征。同时,通过第一性原理计算和分子动力学模拟分别阐明了偏析驱动力和强化机制。实验结果表明,具有六边形密排结构的偏聚Li原子团簇与收缩孪晶共格。理论计算表明,Li团簇倾向于占据收缩孪晶界的空位,并沿孪晶界优先生长。最后,动力学模拟和实验观察都表明,收缩孪晶界处Li原子团簇的形成不仅能钉扎位错,达到类似析出强化的作用,而且能提高收缩孪晶界的临界剪切应变,抑制其形变或宽化。这种孪晶边界处的团簇偏聚现象在其他体系中也有发现,这为通过孪晶界调控金属和陶瓷的力学性能开辟了一条重要途径。
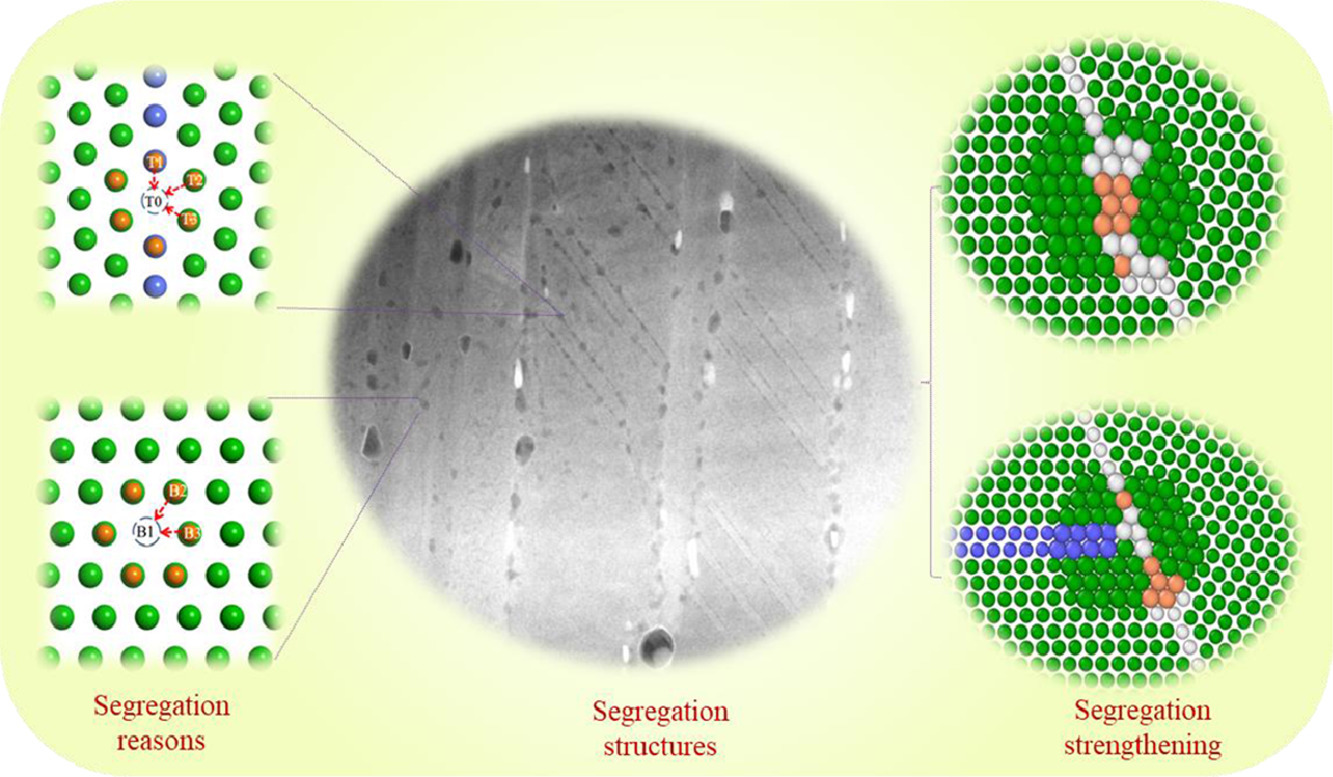

ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P504-516
5. Irradiation induced void spheroidization, shrinkage and migration in Cu at elevated temperatures: An in situ study
高温辐照诱导Cu中孔洞球化、收缩和迁移的原位研究
Cuncai Fan✉, Rayaprolu Goutham Sreekar Annadanam, Zhongxia Shang, Jin Li, Meimei Li, Haiyan Wang, Anter El-Azab, Xinghang Zhang✉
C. Fan:cuncaifan@gmail.com
X.Zhang:xzhang98@purdue.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.008
摘要
辐照诱发的孔洞形成通常会导致材料发生明显的体积膨胀和力学性能退化,因此了解辐照环境下的孔洞演化具有重要意义。然而,关于纳米孔洞在高温辐照下的原位研究目前仍然非常有限。在本研究中,我们对铜中的纳米孔洞演化进行了系统的TEM原位辐照实验,辐照粒子为1 MeV Kr++,辐照温度最高达350°C。原位研究揭示了孔洞的球化、收缩和迁移。此外,研究表明,纳米孔洞的形貌和迁移极大地受辐照温度和初始孔洞尺影响。通过对辐照样品的分析,我们发现缺陷团簇通常以四面体层错和较大的多面体孔洞形式存在。我们基于相场模型对辐照导致的孔洞球化和收缩机理进行了讨论。
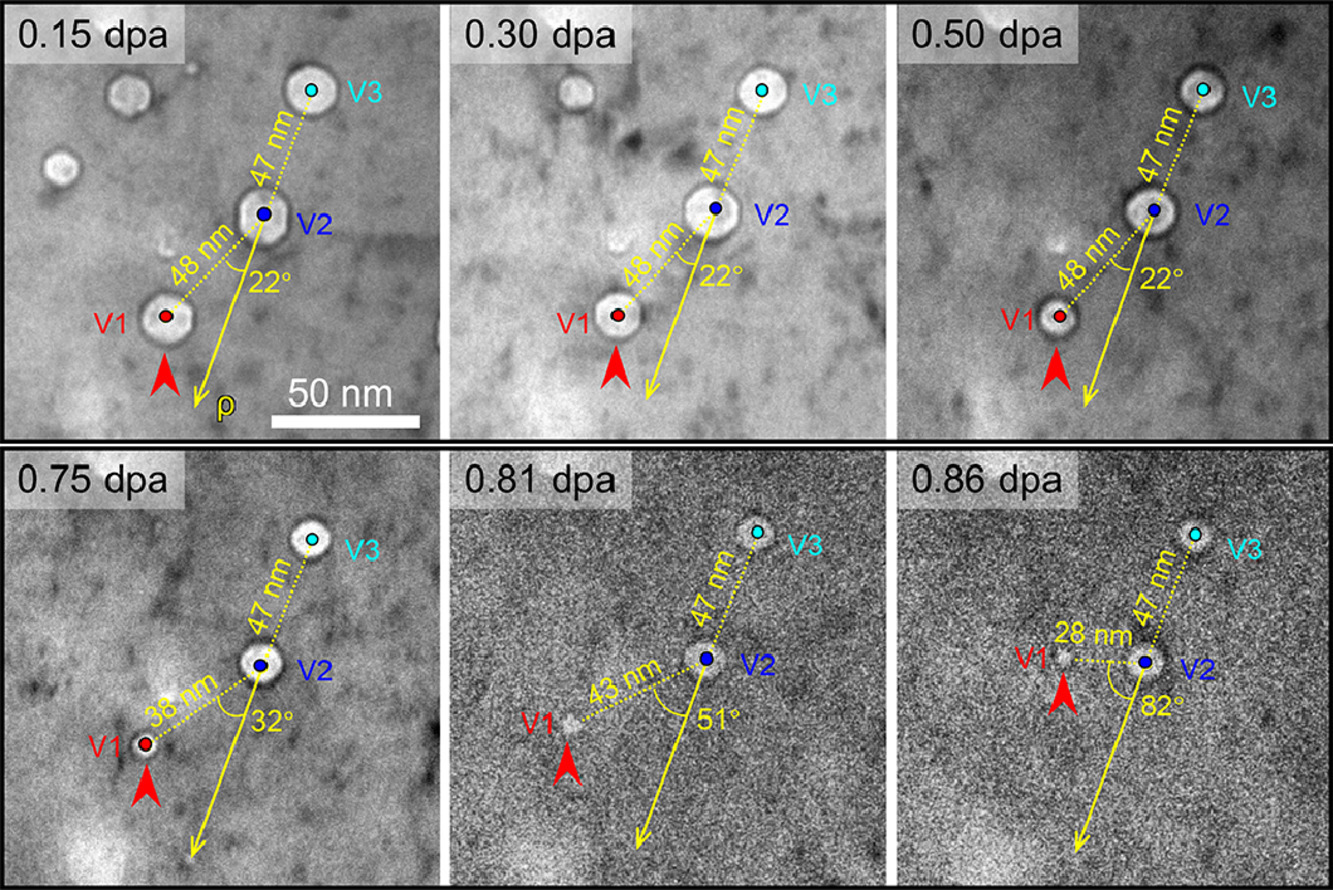

ACTA
Vol. 201,Dec. 2021, P517-527
6.Mechanical instability and tensile properties of TiZrHfNbTa high entropy alloy at cryogenic temperatures
低温下TiZrHfNbTa高熵合金的力学不稳定性和拉伸性能研究
Shubin Wang, Mingxu Wu, Da Shu✉, Guoliang Zhu, Donghong Wang, Baode Sun✉
D. Shu:dshu@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
B. Sun:bdsun@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.044
摘要
等原子比TiZrHfNbTa合金是为数不多的在室温下具有较高拉伸塑性的高熵合金之一,其变形机制主要是位错滑移。我们在低温拉伸变形的过程中发现,随着位错的不断滑移,{112}<111>纳米孪晶被激活,同时发生BCC到非密排六方晶型的ω相变,这表明了单相BCC TiZrHfNbTa合金具有内在力学不稳定性。当温度从277 K降低到77 K时,合金的屈服强度显著提高,达到1549 MPa,且没有发生明显的韧脆转变,保持了较高的伸长率20.8%。通过考虑螺位错滑移、{112}<111>机械孪晶和BCC→ω相变的协同效应,我们对合金在低温下表现出的高强高塑特性进行了解释。这些结果加深了我们对高熔点TiZrHfNbTa合金的理解,并且表明TiZrHfNbTa合金不仅在高温应用方面很有前景,在航空航天、海洋船舶和天然气等行业要求的极端低温环境下也有很大的应用潜力。
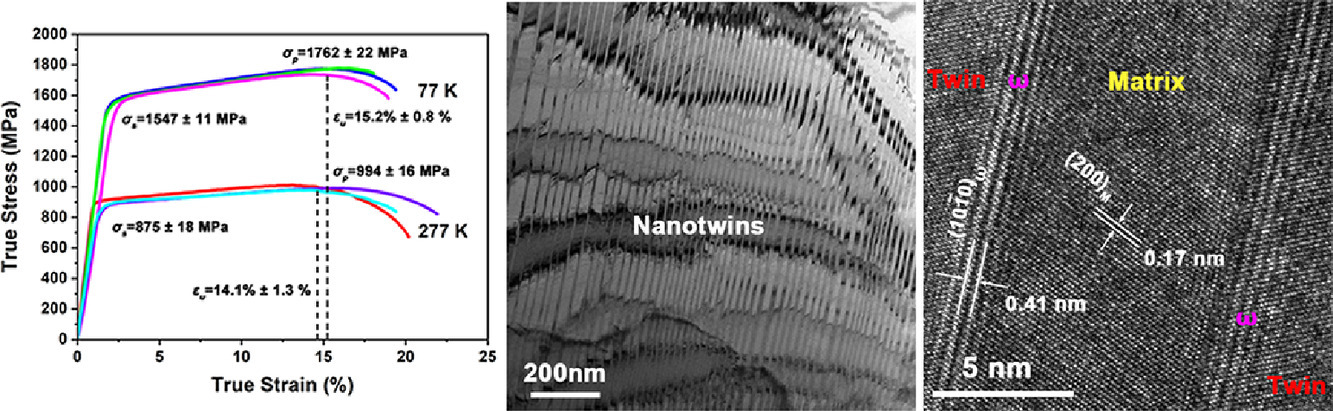

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P535-546
7.Characterising Ion-Irradiated FeCr: Hardness, Thermal Diffusivity and Lattice Strain
离子辐照后FeCr合金的硬度、热导和晶格应变表征
Kay Song✉, Suchandrima Das, Abdallah Reza, Nicholas W. Phillips, Ruqing Xu, Hongbing Yu, Kenichiro Mizohata, David E.J. Armstrong✉, Felix Hofmann✉
K. Song:kay.song@eng.ox.ac.uk
D.E.J. Armstrong:david.armstrong@materials.ox.ac.uk
F. Hofmann:felix.hofmann@eng.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.015
摘要
对FeCr合金进行的离子辐照实验有助于我们理解和预测未来核反应堆结构钢的中子损伤。以往的研究主要集中在辐照缺陷的TEM表征和力学性能变化方面。在这些研究中,研究人员对具有不同加工历史的样品进行了各种条件下的辐照实验,这使得对于缺陷和材料性能之间关系的分析变得十分复杂、困难。此外,对于材料的某些关键性质,如热导和晶格应变,几乎没有探讨。
鉴于以上原因,我们对Fe3Cr、Fe5Cr和Fe10Cr二元合金进行了系统的室温辐照实验研究,辐照粒子为20MeV Fe3+, 损伤剂量分别为0.01 dpa和0.1 dpa。我们采用纳米压痕、瞬态光栅光谱(TGS)和X射线衍射法研究了材料硬度、热扩散系数和应变随损伤程度和Cr含量的变化规律。结果表明,Cr的增加将导致辐照缺陷增加,从而导致硬度和晶格应变发生显著变化。而材料的热扩散系数随损伤程度的增加变化不大,但随Cr含量的增加显著降低。此外,我们发现即使在名义损伤量为0.01 dpa的样品中,也存在显著的晶格应变。基于晶格应变预测的缺陷密度显著高于之前研究中的TEM观测结果,这表明TEM可能不能完全地表征辐照导致的缺陷。
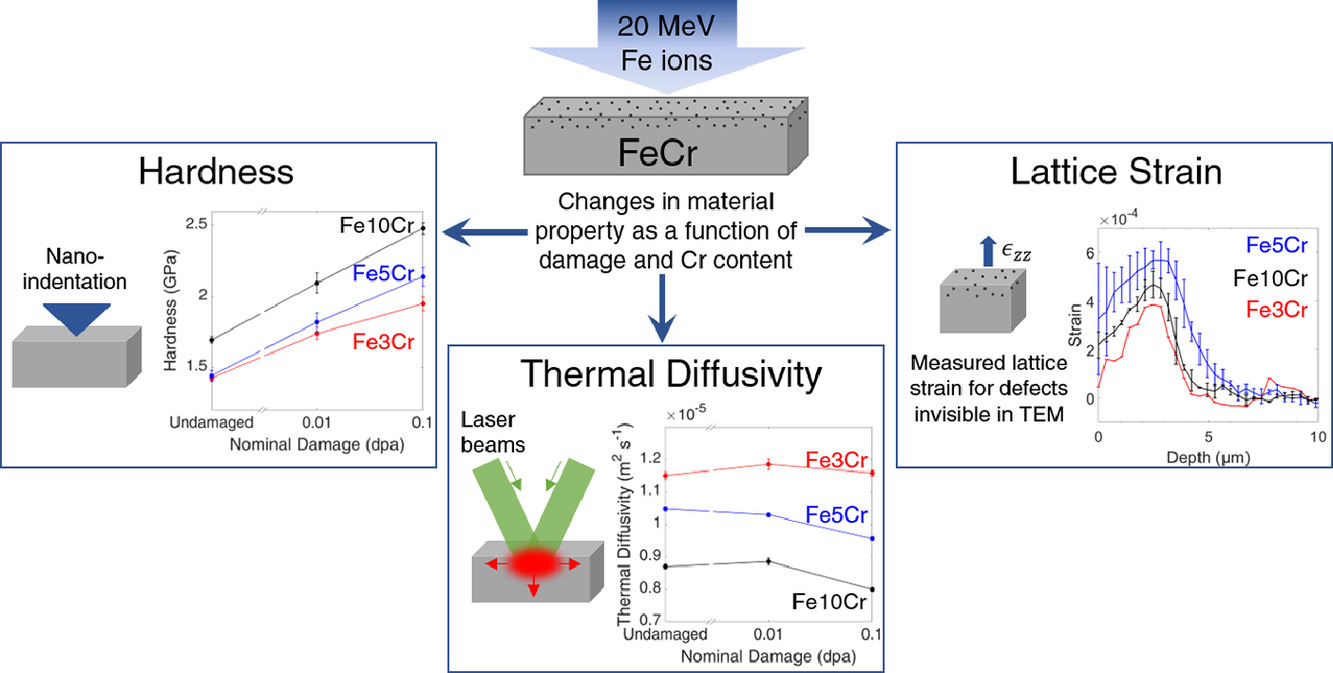

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P561-571
8.Microstructure evolution of thin nickel films with embedded chromium oxide nanoparticles
嵌氧化铬纳米粒子镍薄膜的微观组织演变研究
Hagit Barda, Leonid Klinger, Eugen Rabkin✉
E. Rabkin:erabkin@tx.technion.ac.il
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.032
摘要
在本文中,我们提出了一种纳米陶瓷颗粒增强金属基复合薄膜的制备方法。为此,我们首先在蓝宝石衬底上沉积了20 nm Ni /超薄Cr氧化物层/ 20 nm Ni的三明治结构,随后将其在700℃下退火。研究发现,退火10 min后,Cr氧化物层中形成了单晶或双晶多面体Cr2O3纳米颗粒,并与Ni基体形成了(11-1)Ni||(0006)Cr2O3和[112]Ni||[1-210]Cr2O3的取向关系。我们惊讶地发现Cr氧化物粒子的质心相对初始位置发生了垂直漂移。我们建立了颗粒形状演变和垂直漂移的动力学模型,从而对Ni-Cr2O3界面的有效扩散系数进行了估计(Di=7.4·10−19m2/s)。尽管界面扩散比Ni中的晶界扩散慢得多,但这种界面扩散能够使得超薄Cr氧化物层快速转变为嵌入Ni薄膜中的Cr2O3纳米颗粒阵列。以上研究结果对颗粒增强金属薄膜中粒子空间位置的精确调控具有重要意义。
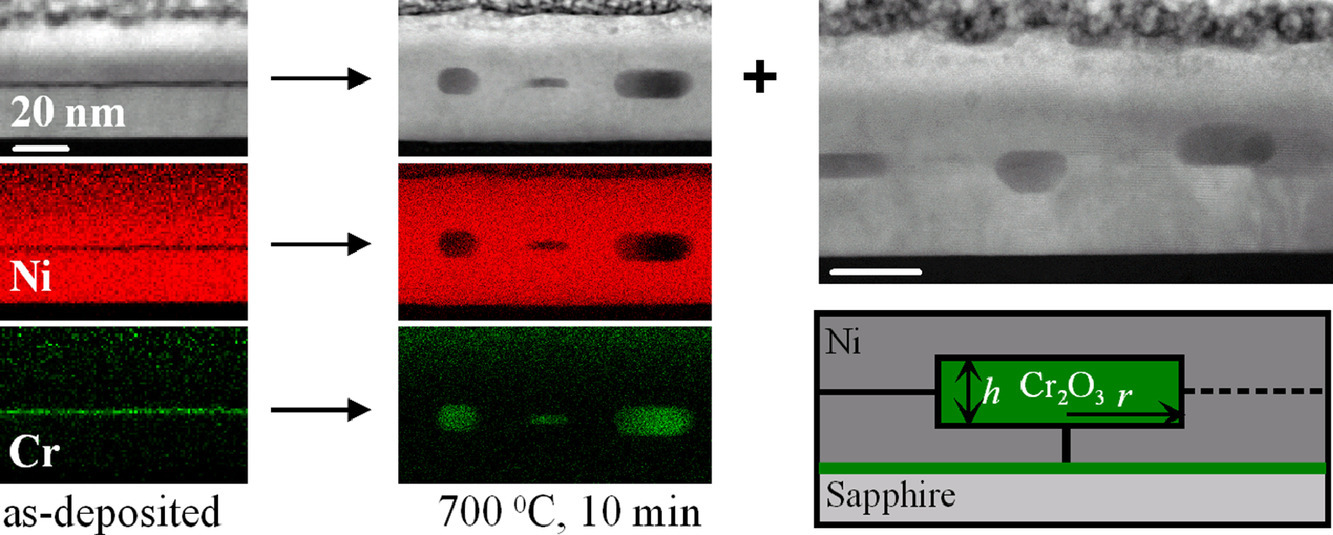

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P580-595
9. An Asymmetric Elasto-Plastic Phase-Field Model for Shape Memory Effect, Pseudoelasticity and Thermomechanical Training in Polycrystalline Shape Memory Alloys
多晶形状记忆合金中形状记忆效应、伪弹性和热形变训练的非对称弹塑性相场模型
Cheikh Cissé, Mohsen Asle Zaeem✉
M. Asle Zaeem:zaeem@mines.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.034
摘要
我们提出了一种弹塑性相场模型(PFM),首次对CuAlBe形状记忆合金(SMA)的形状记忆效应(SME)、伪弹性、应力辅助双向记忆效应(SATWME) 等特征进行了微观尺度的理论研究。这种非等温相场模型考虑了与温度对相关材料性质、潜热、晶界以及非对称相变和塑性的影响。模拟结果表明,模型能够很好地模拟形状记忆效应中的热机械和纯机械形状恢复。由于晶界的作用,晶粒细化将导致更高的相变应力、更明显的相变硬化和更小的形状记忆和伪弹性的滞回线。模拟结果还指出,采用几何晶界进行模拟时,相变应力更高。应力辅助双向记忆效应的模拟结果表明,残余马氏体随着保有应力的增大而增大,这与实验观测结果一致。模型首次实现了在几个循环内模拟材料的热力学状态,结果表明塑性应变和相关的残余应变在前4个循环逐渐增加,并在之后保持稳定。塑性的激活总是发生在相变开始之后。尽管塑性导致了更多的应力松弛,但由于它阻碍了反向相变,因此使得材料的形状记忆能力和伪弹性发生了劣化。此外,拉伸和压缩的比较表明该相场模型首次成功解释了形状记忆合金中的非对称相变和塑性响应。
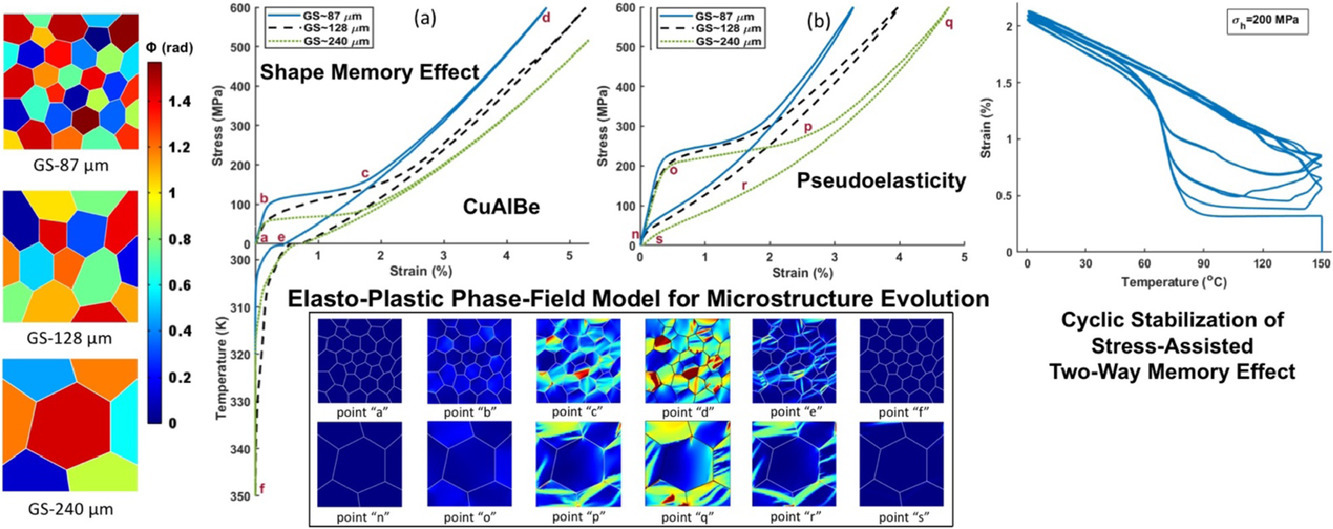

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P596-603
10. Atomistic study of grain-boundary segregation and grain-boundary diffusion in Al-Mg alloys
Al-Mg合金中晶界偏析和扩散的原子尺度研究
R.K. Koju, Y. Mishin✉
Y. Mishin:ymishin@gmu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.029
摘要
Mg在晶界处的偏聚和扩散对Al-Mg合金的加工和性能有很大影响,而目前却鲜有相关的实验测量或模拟预测被报导。在本研究中,我们采用了原子尺度的计算机模拟对Mg的晶界偏聚能量能、以及偏聚对两种合金组分晶界扩散的影响进行了预测。研究发现,低温下Mg原子趋向于在倾侧晶界偏聚,并形成高度各向异性的团簇。Mg在Al 晶界中的扩散速度比Al基体中慢,且两者都比Al的晶界自扩散慢。因此,Mg的偏析可显著降低Al-Mg合金中沿晶界的原子迁移速率,从而提高组织的高温稳定性。
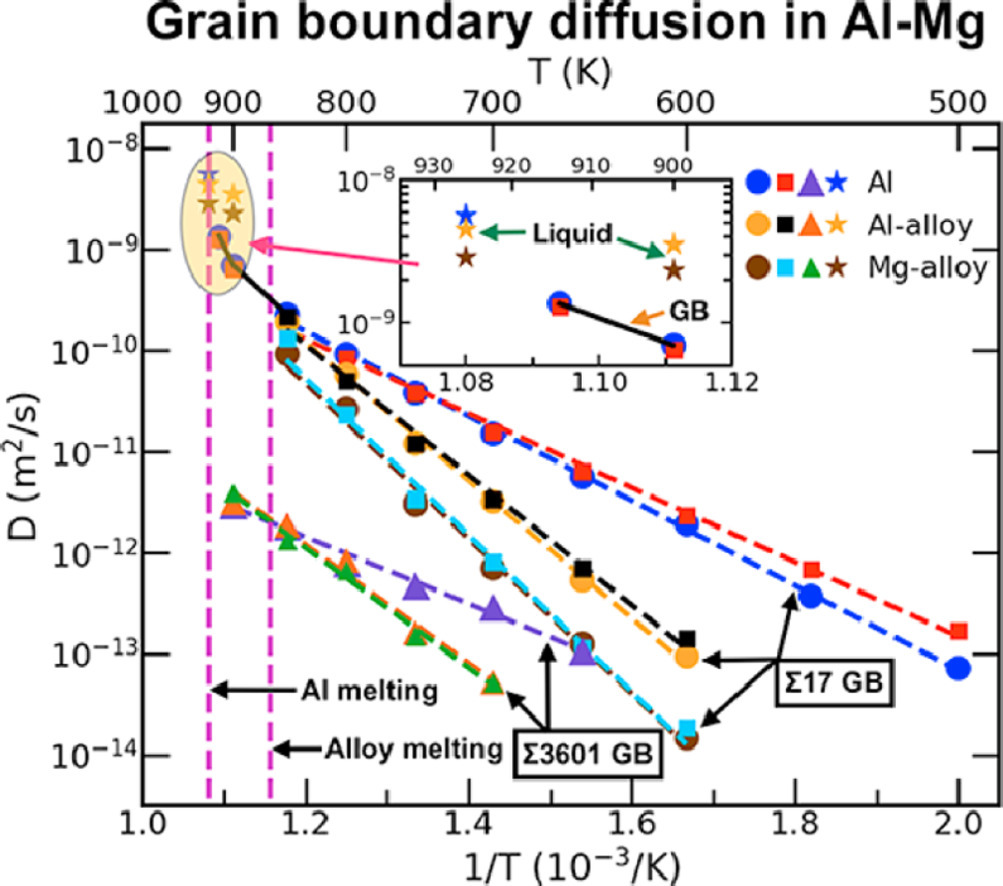

ACTA
Vol. 201, Dec. 2021, P604-616
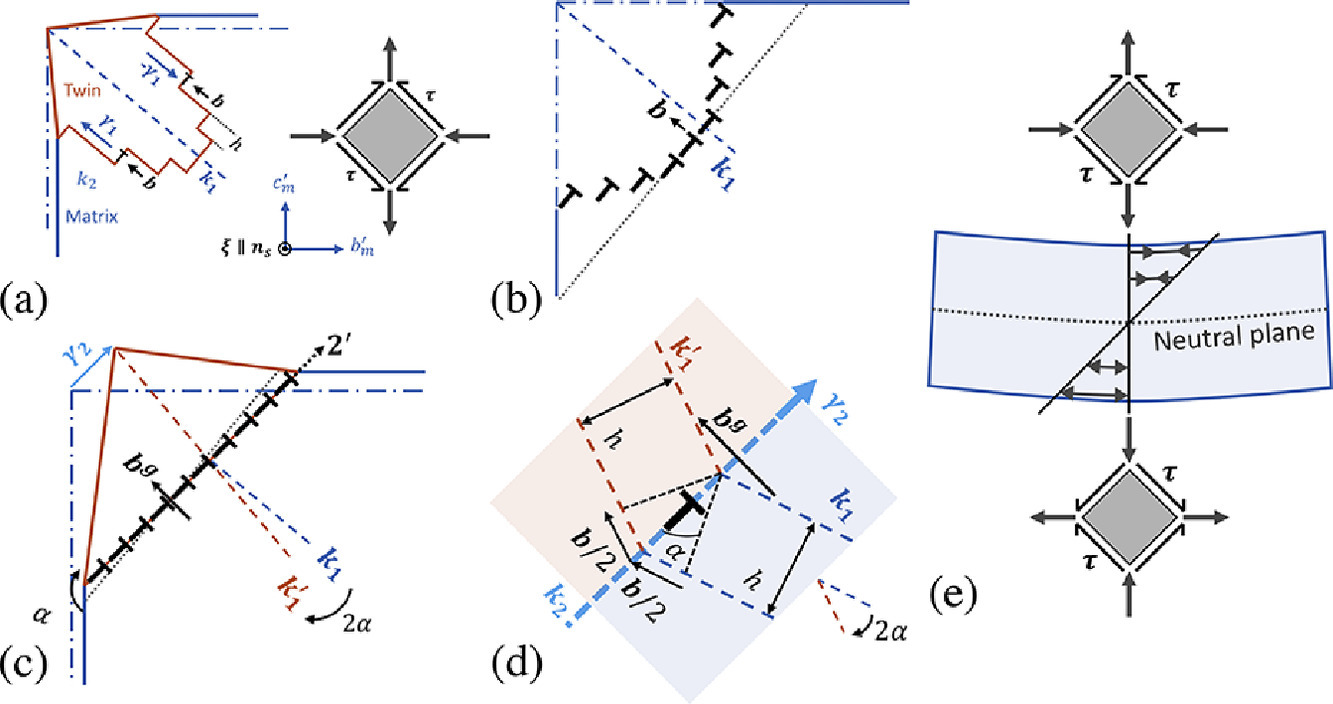
11. Topological model of type II deformation twinning in 10M Ni-Mn-Ga
10M Ni-Mn-Ga中的II型形变孪晶拓扑模型
Bibek Karki✉, Peter Müllner, Robert Pond
B. Karki:bkkarki@u.boisestate.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.020
摘要
我们使用拓扑方法模拟了10M Ni-Mn-Ga合金中的II型孪晶结构。该方法预测的孪生参数与Bevis和Crocker的动态模型相同。此外,我们借助拓扑模型得到了界面迁移速率、孪晶应力及其与温度之间的关系。我们假设II型孪晶借助前驱体(即其I型共轭)形成。前驱体k1面上的断点对齐形成倾侧壁,倾侧壁经扭转松弛后形成平行于k2平面的II型孪晶界。缺陷组元可排列成壁,或松弛形成较不规则的结构。这两种界面都能容纳额外的滑动断点,这些断点可沿界面运动导致界面迁移和切变。这些缺陷的可动性随其核心宽度的增加而增加,而核心宽度又随界面的锐度增加而降低。在其他材料中的一些实验证据表明,II型孪晶可以通过采取低指数面构型来降低其界面能,从而降低孪晶界迁移率。而拓扑模型表明,这样的协同多面体结构不太可能在10M Ni-Mn-Ga合金中出现,这与II型孪晶界的高迁移率一致。