金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.194, 15 Mar. 2021(中)
2021-02-23 来源:Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文11篇,涵盖了增材制造、高熵合金、高强钢、多元合金等,国内科研单位包括上海交通大学等(通讯作者单位)。
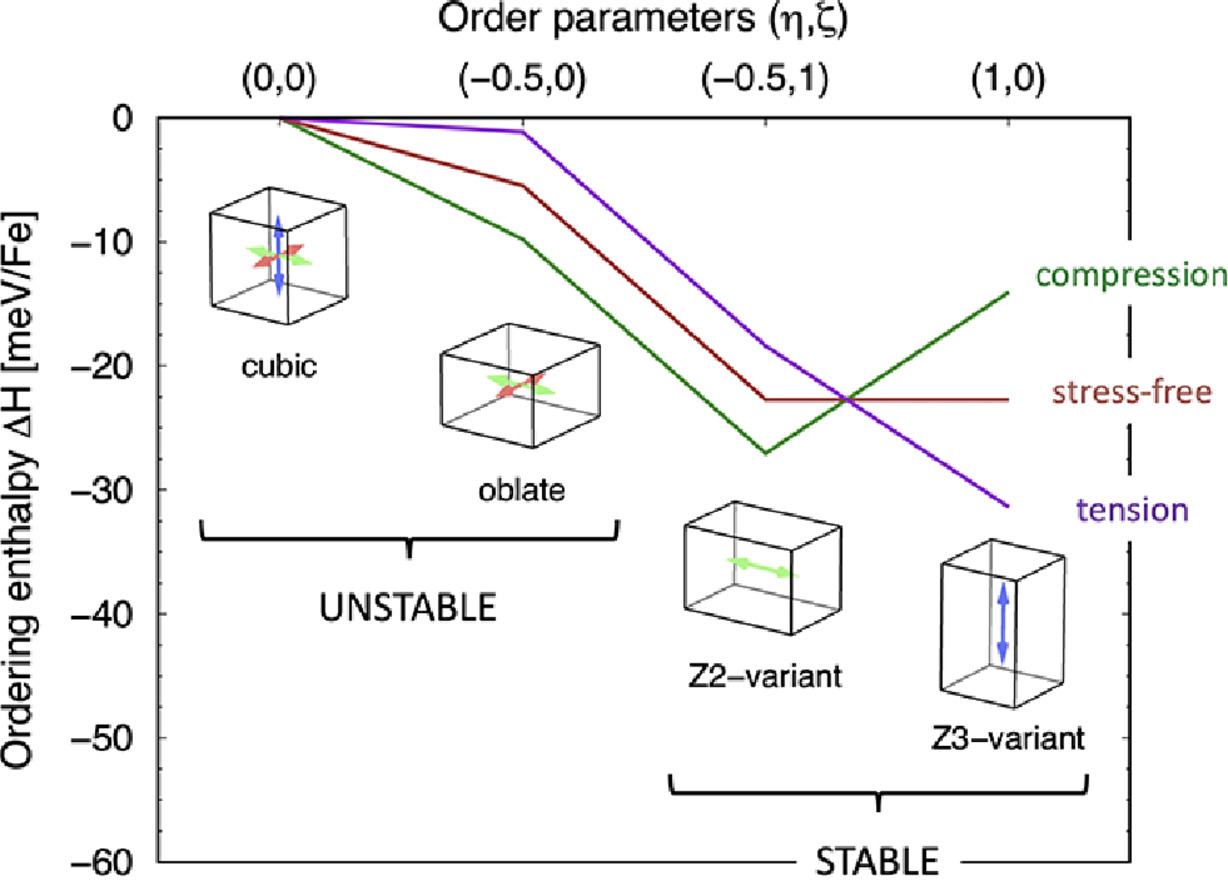
11. Stability of Zener order in martensite: an atomistic evidence
马氏体中Zener有序化的稳定性:原子层面的证据
12. Refined heterogeneous phase unit enhances ductility in quenched ultra-high strength steels
细化的异质相单元提高了淬火超高强度钢的延展性
13. Clarification of creep deformation mechanism in heat-affected zone of 9Cr steels with In Situ experiments
原位实验阐明9Cr钢热影响区的蠕变变形机理
14. TWIP-TRIP effect in single crystalline VFeCoCrNi multi-principle element alloy
单晶VFeCoCrNi多主元合金的TWIP-TRIP效应
15. Tensile creep properties of a CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy
CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金的拉伸蠕变性能
16. The effect of nitrogen alloying on hydrogen-assisted plastic deformation and fracture in FeMnNiCoCr high-entropy alloys
氮合金化对FeMnNiCoCr高熵合金氢致塑性变形和断裂的影响
17. Fine granular area linked to very high cycle fatigue in martensitic and bainitic steels: Characterization by means of EBSD-dictionary indexing
用EBSD-dictionary索引法表征马氏体和贝氏体钢中与极高循环疲劳相关的细晶区
18. Alloying induces directionally-dependent mobility and alters migration mechanisms of faceted grain boundaries
合金化引起了定向迁移,改变了多面晶界的迁移机制
19. Element redistributions during early stages of oxidation in a Ni38Cr22Fe20Mn10Co10 multi-principal element alloy
Ni38Cr22Fe20Mn10Co10多主元合金氧化早期的元素重分布
20. Enhanced cryogenic tensile properties with multi-stage strain hardening through partial recrystallization in a ferrous medium-entropy alloy
在铁基中熵合金中,通过部分再结晶的多阶段应变硬化提高低温拉伸性能
21. Experimental determination of solute redistribution behavior during solidification of additively manufactured 316L
增材制造316L凝固过程中溶质再分布行为的实验测定
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113632
11. Stability of Zener order in martensite: an atomistic evidence
马氏体中Zener有序化的稳定性:原子层面的证据
Philippe Maugis✉, Damien Connétable, Paul Eyméoud
Philippe Maugis:philippe.maugis@im2np.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113632
摘要
马氏体是一种碳在体心立方铁中的过饱和固溶体,其间隙碳原子优先占据一个八面体的亚晶格。尽管经过了一个世纪的研究,这种长期有序的机制仍然是一个有争议的话题。最近,Zener的有序化理论在实验和理论上都受到了挑战。为了解决这一争议,我们利用密度泛函理论研究了具有不同阶数的铁碳构型的基态。我们发现完全Zener有序化结构在能量上总是最稳定的,从而证实了Zener的理论。与平均场弹性和Ising型模型的比较,支持了Zener有序化的弹性起源。
Martensite is a supersaturated solid solution of carbon in body-centered iron wherein interstitial carbon atoms preferentially occupy a single octahedral sublattice. Despite a century of research, the mechanism of this long-range ordering is still a subject of debate. Recently, Zener’s theory of ordering was challenged both experimentally and theoretically. In an attempt to settle the controversy, we investigated by density functional theory the ground states of Fe-C configurations having various degrees of order. We conclude that the fully Zener-ordered configurations are always the most stable energetically, thus confirming Zener’s theory. Comparison with mean-field elasticity and Ising-type modelling supports the elastic origin of Zener ordering.
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113636
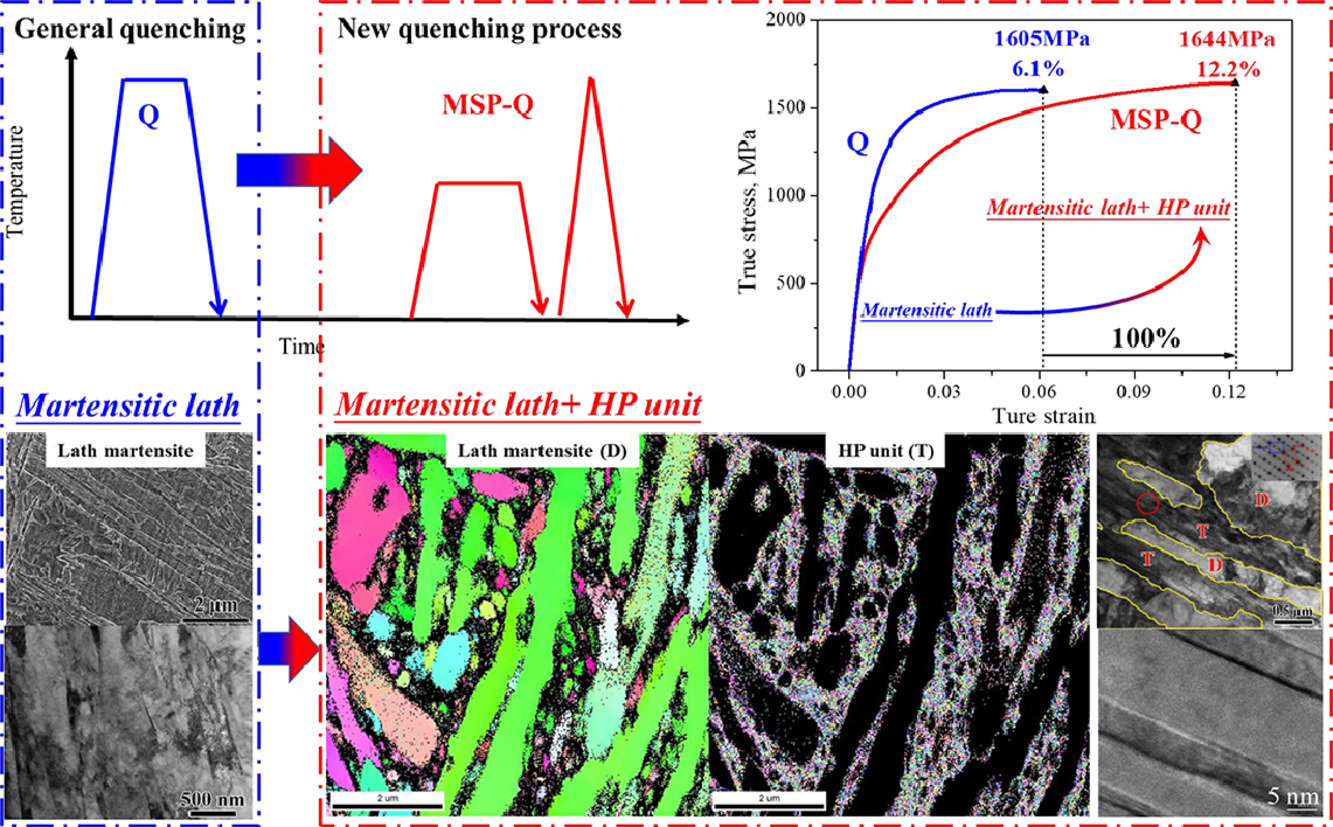
12. Refined heterogeneous phase unit enhances ductility in quenched ultra-high strength steels
细化的异质相单元提高了淬火超高强度钢的延展性
Shilong Liu✉, Bin Hu, Wei Li, R. D. K. Misra, Xuejun Jin✉
Shilong Liu: sliu6@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学
Xuejun Jin: jin@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113636
摘要
淬火后的高延展性对于超高强度钢具有明显的优势,特别是从可成型性的角度来看。在快速淬火(闪速加热)之前先进行临界退火,以获得由纳米孪晶马氏体和残留奥氏体组成的异相(HP)单元。由于纳米孪晶马氏体和残留奥氏体,均匀延伸率得到了明显提高,且不影响最终的抗拉强度。纳米孪晶马氏体和残余奥氏体的形成,是由于退火和闪速加热工艺的结合使合金元素(Mn和Al)发生微偏析造成的。热力学计算使我们能够对合金和热处理工艺进行设计。
High ductility after quenching has significant benefits for ultra-high strength steels, especially from the perspective of formability. Intercritical annealing was applied prior to rapid quenching (flash) to obtain heterogeneous phase (HP) units, consisting of nano-twinned martensite and retained austenite. The uniform elongation was significantly enhanced without compromising ultimate tensile strength because of nanoscale twinned martensite and retained austenite. The formation of nanoscale twinned martensite and retained austenite occurred because of micro-segregation of alloying elements (Mn and Al) by combining annealing and flash process. Thermodynamic calculations enabled us to design the alloy and heat treatment.
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113640
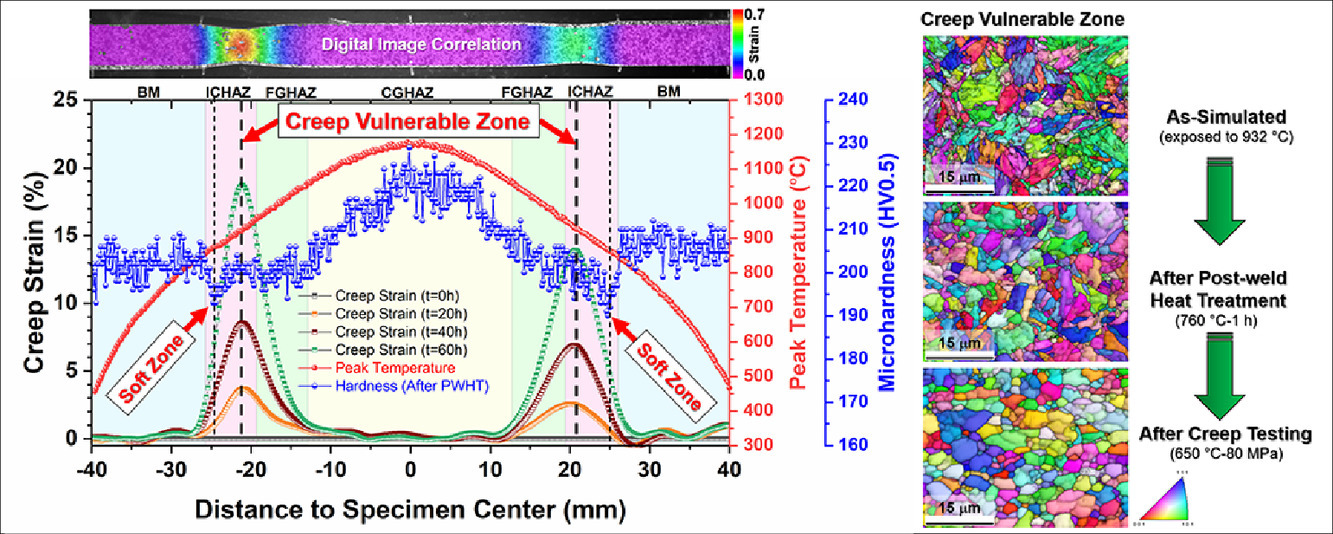
13. Clarification of creep deformation mechanism in heat-affected zone of 9Cr steels with In Situ experiments
原位实验阐明9Cr钢热影响区的蠕变变形机理
Yiyu Wang✉, Wei Zhang, Hui Huang, Yanli Wang, Weicheng Zhong, Jian Chen, Zhili Feng✉
Yiyu Wang: wangy4@ornl.gov
Zhili Feng: fengz@ornl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113640
摘要
本研究通过复杂巧妙的实验,包括电-热有限元模型辅助的Gleeble热力学模拟和原位数字图像相关(DIC)的高温蠕变测试,量化了Grade 91钢在非均质热影响区(HAZ)的非均匀蠕变变形行为。用DIC定量测量了热影响区的高温蠕变特性。利用峰值温度、硬度、局部蠕变应变和底层微观组织,进一步阐述了热影响区的蠕变变形机制。DIC测量结果显示,在蠕变发生前,临界HAZ中暴露于峰值温度为932℃(接近AC3)的蠕变脆弱区(CVZ)会经历最快的蠕变强度退化,而不是硬度最低的软区。未溶解和粗化的M23C6碳化物的错配显著降低了析出强化,导致CVZ中回火马氏体的快速再结晶。溶解的M23C6引起的局部铬富集稳定了弱的未转变回火马氏体(铁素体晶粒),也损害了CVZ的蠕变抗力。
This work quantified nonuniform creep deformation across the heterogeneous heat-affected zone (HAZ) of Grade 91 steel with sophisticated experiments, including an electric-thermal finite element model–assisted Gleeble thermomechanical simulation and a high-temperature creep testing with in situ digital image correlation (DIC). High temperature creep properties of HAZ sub-zones were quantitatively measured by the DIC. By utilizing peak temperature, hardness, local creep strain, and underlying microstructures, creep deformation mechanisms in HAZ were further understood. DIC measurements reveal a creep-vulnerable zone (CVZ) exposed to a peak temperature of 932°C (close to AC3) in the intercritical HAZ experienced the fastest creep strength degradation instead of the soft zone with the lowest hardness prior to creep. The significantly reduced precipitation strengthening from misplacement of undissolved and coarsened M23C6 carbides led to a faster recrystallization of tempered martensite in the CVZ. Weak untransformed tempered martensite (ferrite grains) stabilized by local Cr enrichment from dissolved M23C6 also harmed the CVZ's creep resistance.
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113637
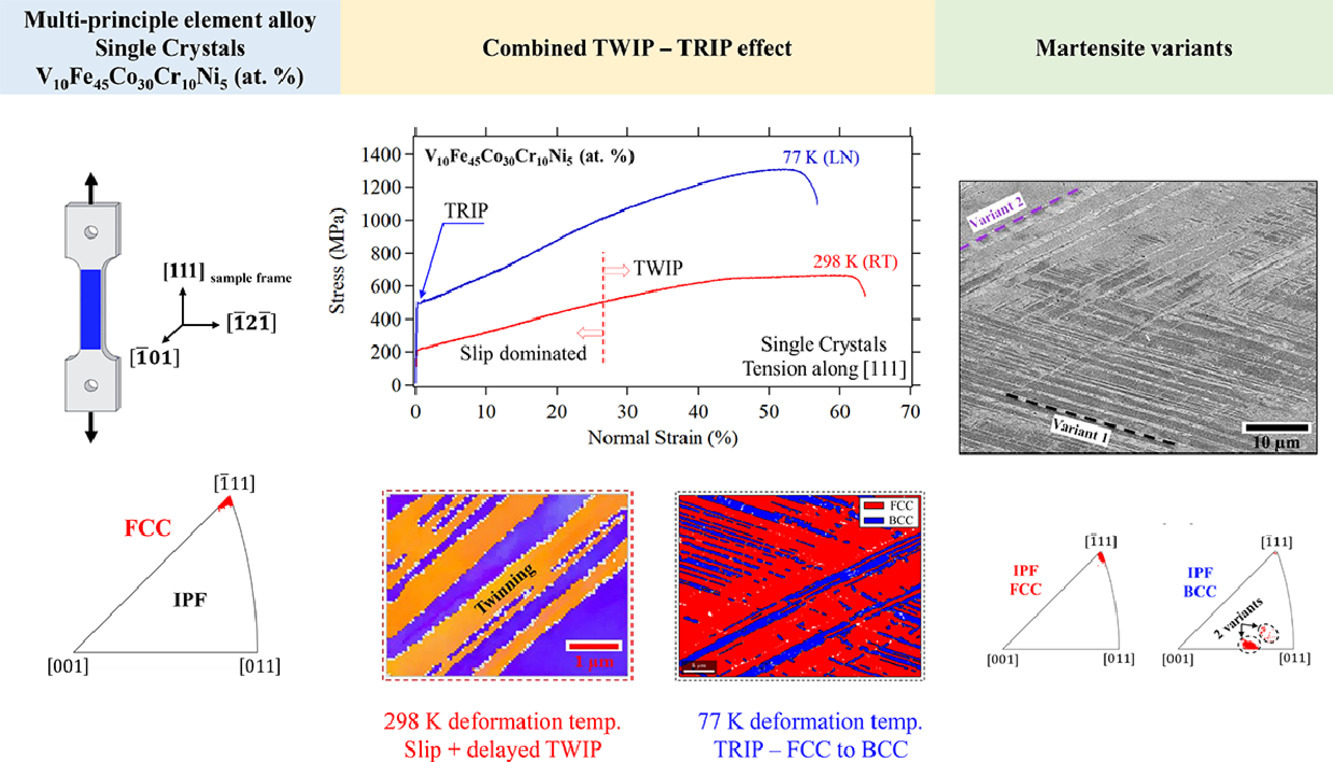
14. TWIP-TRIP effect in single crystalline VFeCoCrNi multi-principle element alloy
单晶VFeCoCrNi多主元合金的TWIP-TRIP效应
Wael Abuzaid✉, Mehmet Egilmez, Yuri I. Chumlyakov
Wael Abuzaid: wabuzaid@aus.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113637
摘要
各种多主元合金在包括低温在内的各种温度范围内都表现出优异的力学性能。在大多数体系中,其优异的性能归因于变形孪晶(孪晶诱导塑性)。最新研究表明,VFeCoCrNi多主元合金在室温下表现出孪晶诱导塑性效应,在低变形温度下表现出相变诱导塑性效应。本工作研究了沿[111]方向加载的VFeCoCrNi单晶试样。室温下,在低于22%的低塑性应变下,滑移占优势,并观察到孪晶的延迟激活。77K下,我们观察到早期的面心立方向体心立方的转变,且两者保持着{111}FCC//{110}BCC和⟨110⟩FCC//⟨111⟩BCC的位相关系。
Various multi-principle element alloys exhibit superior mechanical properties across a wide range of temperatures including cryogenic temperatures. In most systems, the remarkable properties are attributed to deformation twinning (twinning induced plasticity). The recent VFeCoCrNi multi-principle element alloy displays a combined twinning induced plasticity effect, at room-temperature, and phase transformation at low deformation temperatures (transformation induced plasticity). This work considers single crystalline specimens of VFeCoCrNi loaded along the [111] direction. At room-temperature, slip dominates at low strains, below 22% plastic strain, and a delayed activation of twinning is observed. At 77 K, early activation of transformation, face-center cubic to body-center cubic having {111}FCC//{110}BCC and ⟨110⟩FCC//⟨111⟩BCC parallel relations, was revealed.
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113633
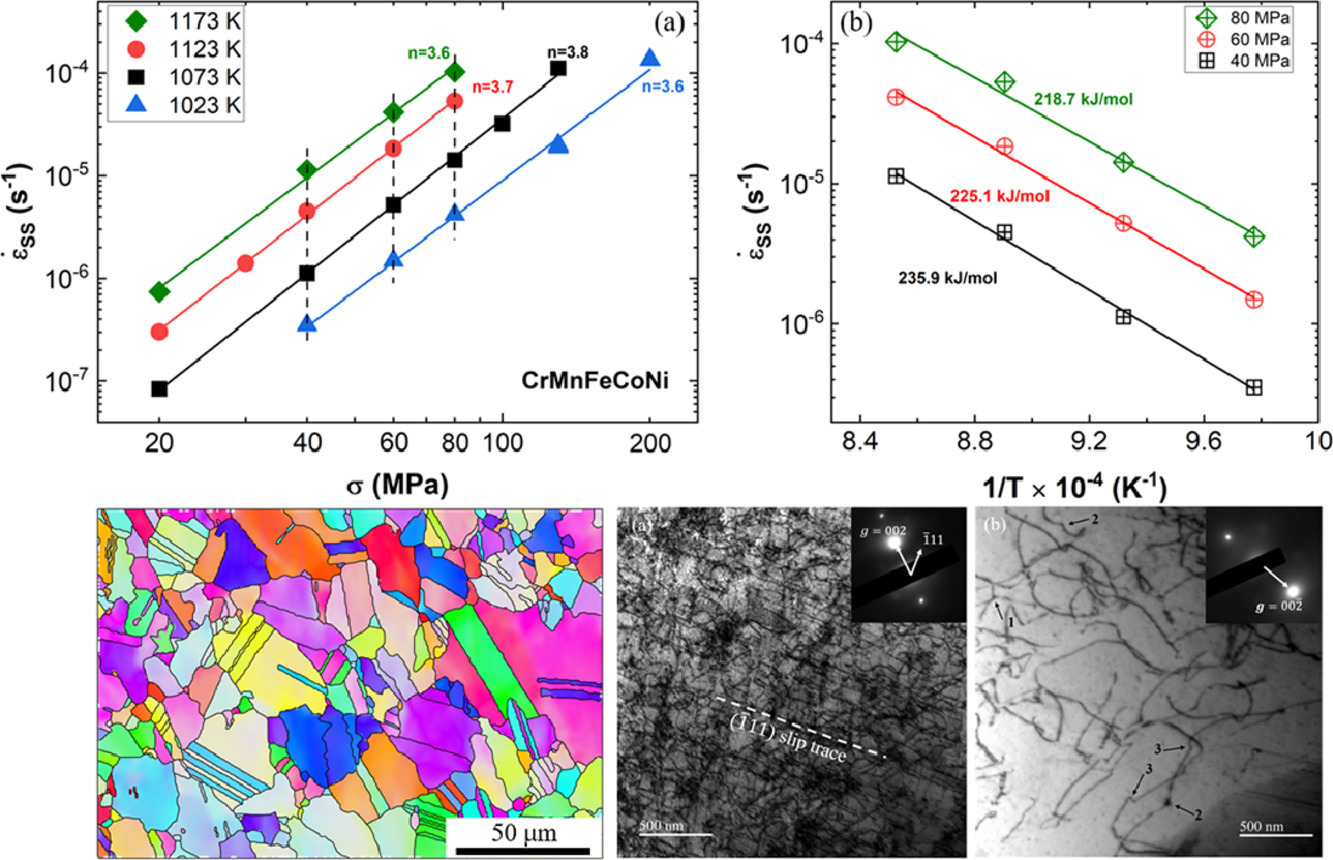
15. Tensile creep properties of a CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy
CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金的拉伸蠕变性能
A. Zhang, E.P. George, J.C. Gibeling✉
J. C. Gibeling: jcgibeling@ucdavis.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113633
摘要
我们在1023K至1173K温度下对CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金进行了拉伸蠕变测试。在所有温度下均发现了3.7±0.1的均匀应力指数。在各种外加应力下的蠕变表观活化能确定为约230 kJ/mol,并随应力的增加而降低,表明了一种有应力辅助的热激活行为。稳态蠕变微观组织的特征是没有亚晶粒的形成和晶粒内的高位错密度。根据结果,我们认为CrMnFeCoNi的蠕变速率受位错-位错相互作用和位错-晶格相互作用的共同控制。
Tensile creep tests were performed on a CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy at temperatures from 1023 K to 1173 K. A uniform stress exponent 3.7 ± 0.1 was found across all temperatures. The apparent activation energies of creep under various applied stresses were determined to be around 230 kJ/mol and decrease with increasing stress, indicating a stress-assisted, thermally activated behavior. Steady-state creep microstructures feature no subgrain formation and high dislocation density within grains. Based on our results, the creep rate of CrMnFeCoNi is believed to be controlled by both dislocation-dislocation interactions and dislocation-lattice interactions.
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113642
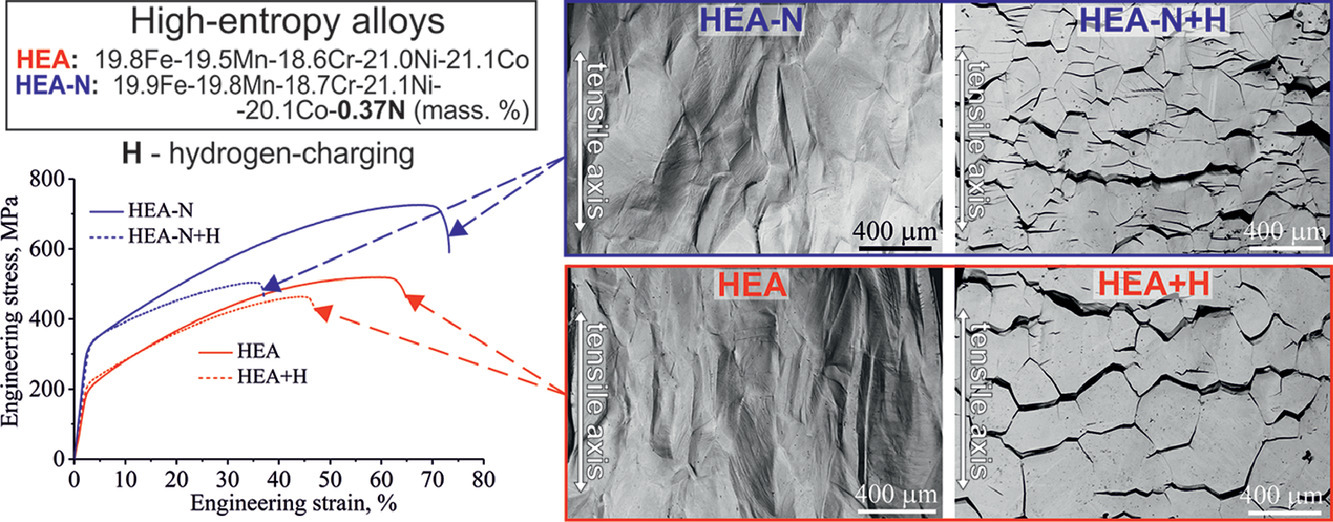
16. The effect of nitrogen alloying on hydrogen-assisted plastic deformation and fracture in FeMnNiCoCr high-entropy alloys
氮合金化对FeMnNiCoCr高熵合金氢致塑性变形和断裂的影响
A. G. Astafurova✉, M.Yu. Panchenko, K.A. Reunova, A.S. Mikhno, V.A. Moskvina, E.V. Melnikov, S.V. Astafurov, H.J. Maier
A. G. Astafurova: elena.g.astafurova@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113642
摘要
本文研究了氮的合金化对FeMnNiCoCr高熵合金氢脆的影响。在拉伸过程中,无氢的氮合金化FeMnNiCoCr高熵合金(0.37 wt.% N)的强度、应变硬化和总延伸率均高于无间隙氮的FeMnNiCoCr合金。尽管两种合金的拉伸性能不同,但断裂形式均为韧性韧窝微观机制断裂。充氢后,氮合金化材料的应变硬化率较低,对氢致脆化的敏感性高于无间隙合金。两种合金均具有稳定的奥氏体组织和相似的晶粒尺寸,但氮合金化的FeMnNiCoCr合金更容易发生氢脆。虽然整体的恶化效果是相似的,但对比高熵合金与常规奥氏体不锈钢,在力学行为和充氢时的氢输运方面有明显的差异。实验表明氮合金化提高了Cantor合金中的氢扩散率。
In the present study, the effect of nitrogen alloying on hydrogen embrittlement in FeMnNiCoCr high-entropy alloys was investigated. In tension, hydrogen-free nitrogen-alloyed FeMnNiCoCrN alloy (0.37 wt.% N) demonstrated higher strength, strain hardening, and elongation-to-failure than the interstitial-free FeMnNiCoCr Cantor alloy. Despite the different tensile properties, both alloys fractured via a ductile dimple micromechanism. After hydrogen charging, the nitrogen-alloyed material demonstrated lower strain hardening and higher sensitivity to hydrogen-assisted embrittlement than the interstitial-free alloy. Both alloys featured a stable austenitic structure and similar grain size, yet, the nitrogen-alloyed FeMnNiCoCr alloy was more susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement. Although, the overall degradation effects appear similar, there are pronounced differences in mechanical behavior and hydrogen transport upon hydrogen charging when the high-entropy alloys are compared to conventional austenitic stainless steels, and the experiments reveales that nitrogen alloying enhances hydrogen diffusivity in the Cantor alloy.
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113644
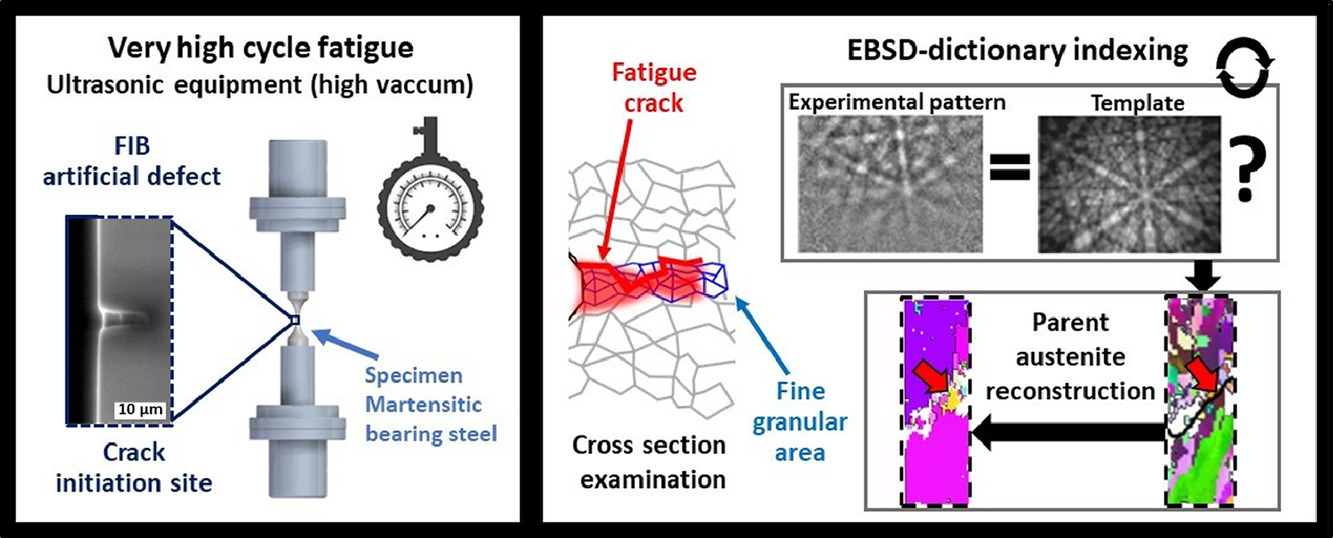
17. Fine granular area linked to very high cycle fatigue in martensitic and bainitic steels: Characterization by means of EBSD-dictionary indexing
用EBSD-dictionary索引法表征马氏体和贝氏体钢中与极高循环疲劳相关的细晶区
Lucia Morales-Rivas✉, Farangis Ram, Daniel Spriestersbach, Jan Sippel, Marc De Graef, Eberhard Kerscher
Lucia Morales-Rivas: rivas@mv.uni-kl.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113644
摘要
马氏体/贝氏体轴承钢中,在远低于耐力极限(107个循环)下,无法观察到由内部夹杂物诱发的临界裂纹,从而造成极高的循环疲劳破坏。即使这些裂纹的应力强度因子低于长时间裂纹扩展的阈值,也无法确保这些裂纹的稳定性,这严重损害了机械部件的安全性。据报道,这种裂纹的传播是先于细晶区(FGA)结构形成的。由于对表征和测试实验环境的要求很高,对FGA的晶体学了解甚少。最近的进展来自实验过程策略,该策略触发了在预测裂纹诱发位置处的FGA的形成。事实证明,新颖的EBSD-dictionary索引技术是一种功能强大的工具,FGA的形成可从该工具中获得新的价值,并为不同裂纹长度值下系统的微观组织表征打开了大门。
In martensitic/bainitic bearing steels, non-observable critical cracks can initiate at inner inclusions well below the endurance limit (at 107 cycles), leading to very high cycle fatigue failure. The stability of these cracks is not ensured even if they have a stress intensity factor lower than the threshold for long crack propagation, strongly compromising the safety of the mechanical component. Propagation of such cracks is reported to be preceded by the formation of a fine granular area (FGA) structure. Due to the high demanding characterization and testing experimental circumstances, the crystallography of FGA is far from understood. Recent advances have come hand by hand from an experimental procedure strategy which triggers the FGA formation at predicted crack initiation sites. The novel EBSD-dictionary indexing has proven to be a powerful tool from which FGA formation acquires new value and opens the door for a systematic microstructural characterization at different crack length values.
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113643
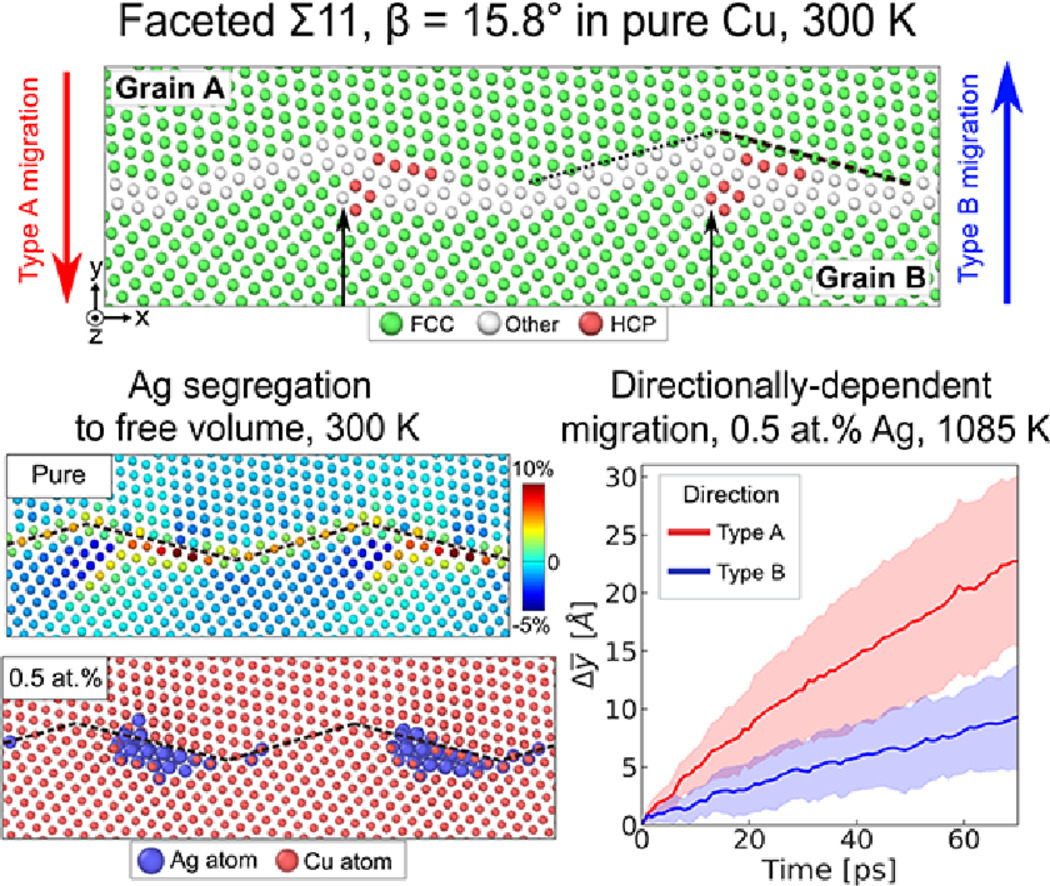
18. Alloying induces directionally-dependent mobility and alters migration mechanisms of faceted grain boundaries
合金化引起了定向迁移,改变了多面晶界的迁移机制
Megan J. McCarthy, Timothy J. Rupert✉
Timothy J. Rupert: trupert@uci.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113643
摘要
多面晶界表现出不寻常的偏析和迁移倾向。为了更深入地理解在迁移过程中溶质原子是如何与多面界面结构相互作用的,本文研究了掺杂Ag原子的铜中多面Σ11界面的迁移行为。由于存在一个方向性相关的运动机制,该机制可以逃脱溶质钉扎,从而加速迁移,因此,在一个迁移方向上,溶质会偏聚到有更多自由体积的面上,并强烈地降低界面速度。这些模拟结果揭示了化学诱导晶界迁移率各向异性的新机制。
Faceted grain boundaries exhibit unusual segregation and migration tendencies. To gain a deeper understanding of how solute atoms interact with faceted interfacial structures during migration, this study probes the migration behavior of a faceted Σ11 boundary in Cu doped with Ag atoms. The solutes are found to segregate to the facet with more free volume and strongly reduce boundary velocity in one migration direction, but not the other, due to the presence of a directionally-dependent motion mechanism that can escape solute pinning and therefore speed up migration. Hence, a new mechanism of chemically-induced anisotropy in grain boundary mobility is uncovered by these simulations.
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113609
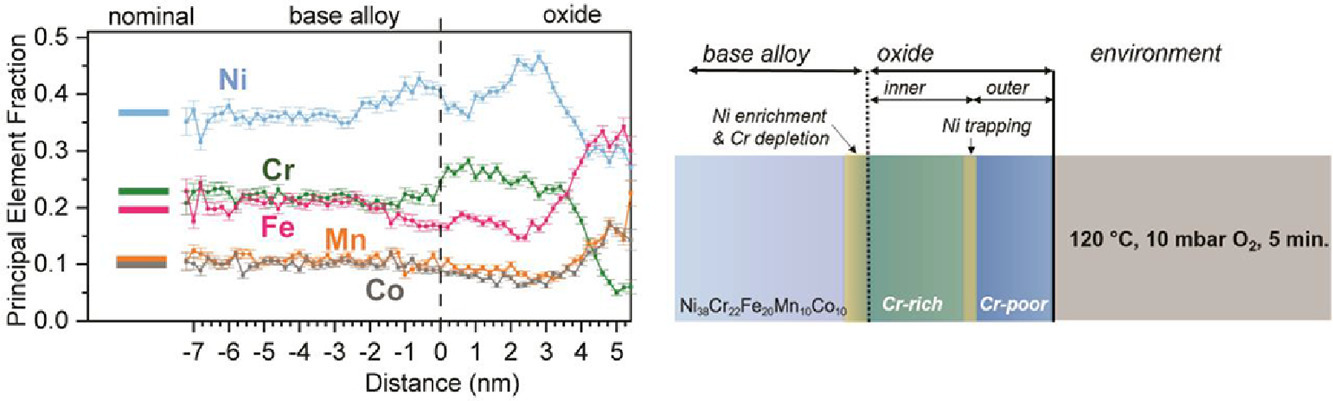
19. Element redistributions during early stages of oxidation in a Ni38Cr22Fe20Mn10Co10 multi-principal element alloy
Ni38Cr22Fe20Mn10Co10多主元合金氧化早期的元素重分布
Elizabeth J. Kautz✉, Sten V. Lambeets, Daniel E. Perea, Angela Y. Gerard, Junsoo Han, John R. Scully, James E. Saal, Daniel K. Schreiber✉
Elizabeth J. Kautz: elizabeth.kautz@pnnl.gov
Daniel K. Schreiber: daniel.schreiber@pnnl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.10.051
摘要
通过原位原子探针断层扫描技术捕获了Ni38Cr22Fe20Mn10Co10 (at.%)多主元合金在120℃和300℃初始氧化后的元素重分布。所有的阳离子在两种条件下都形成氧化物,包括一种富铬的内氧化物和一种富铁、锰、钴和镍的外氧化物。在较低的温度下,Ni倾向于富集在外/内氧化物的界面,而在较高的温度下,随着Cr金属的耗尽,Ni富集在氧化物/金属界面。这些观察结果证实,复杂合金的氧化涉及亚稳态、多层氧化膜的形成,具有明显的溶质捕获趋势。
Element redistributions after initial oxidation of a Ni38Cr22Fe20Mn10Co10 (at.%) multi-principle element alloy at 120 °C and 300 °C is captured via in situ atom probe tomography. All cations contribute to the oxide in both conditions, consisting of a Cr-rich inner oxide and a Fe, Mn, Co and Ni-rich outer oxide. At lower temperature, Ni tends to be trapped at the outer/inner oxide interface, while Ni enriches at the oxide/metal interface at higher temperature in tandem with Cr metal depletion. These observations confirm oxidation of complex alloys involves the formation of metastable, multi-layered oxide films, with a distinct tendency for solute trapping.
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113653
20. Enhanced cryogenic tensile properties with multi-stage strain hardening through partial recrystallization in a ferrous medium-entropy alloy
在铁基中熵合金中,通过部分再结晶的多阶段应变硬化提高低温拉伸性能
Jae Wung Bae, Jungwan Lee, Alireza Zargaran, Hyoung Seop Kim✉
Hyoung Seop Kim: hskim@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113653
摘要
本工作中,我们证明了将Fe60Co15Ni15Cr10(at %)铁基中熵合金进行冷轧后,进行单步热处理可形成部分再结晶的双峰微观组织,从而将屈服强度提高到~1.1 GPa,极限拉伸强度提高到1.7 GPa,且持续延展性保持为61%,避免了强度-延展性的权衡。与完全再结晶状态相比,变形亚结构的保留使屈服强度提高了约79%,且在成分不变的情况下机械稳定性得到了改善,从而在77K拉伸变形过程中产生了多阶段的应变硬化能力。
We demonstrate the formation of partially recrystallized bimodal microstructures through single-step heat treatment after cold-rolling in Fe60Co15Ni15Cr10 (at%) ferrous medium-entropy alloy that leads to the enhanced yield-strength of ~1.1 GPa and ultimate-tensile-strength of 1.7 GPa at persistent ductility of 61%, evading strength-ductility trade-off. The retention of deformation substructures allows a yield-strength increase by ~79% compared to that in a fully-recrystallized state, together with the modification of mechanical stability without compositional variation, resulting in multi-stage strain hardening capability during tensile deformation at 77 K.
Vol. 194, 15 Mar. 2021, 113663
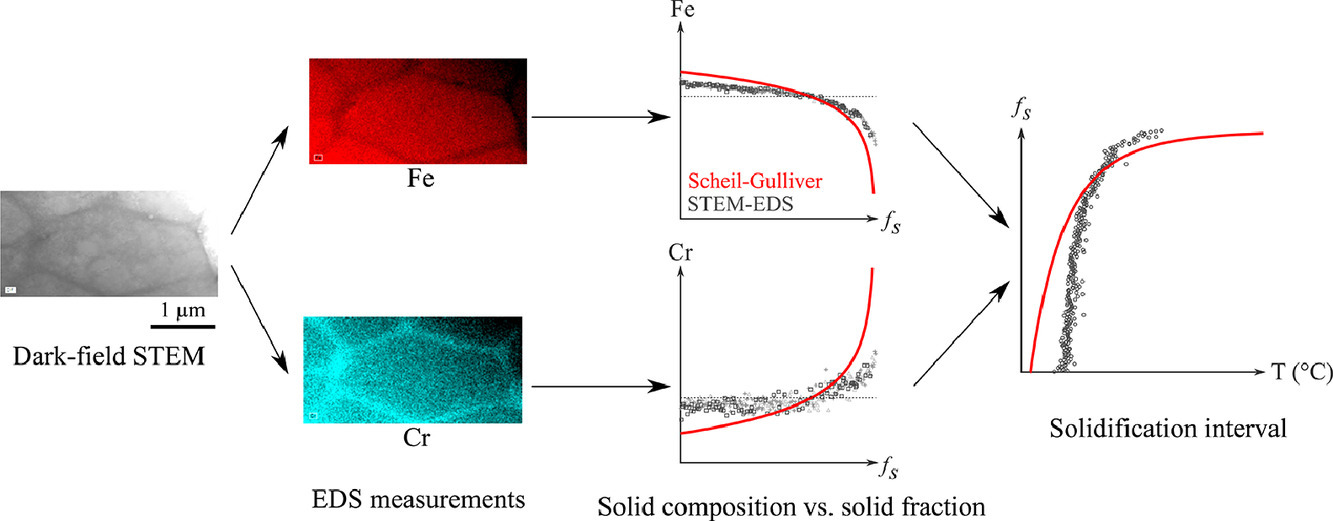
21. Experimental determination of solute redistribution behavior during solidification of additively manufactured 316L
增材制造316L凝固过程中溶质再分布行为的实验测定
Sylvain Dépinoy✉, Mohamed Sennour, Lyliat Ferhat, Christophe Colin
Sylvain Dépinoy: sylvain.depinoy@mines-paristech.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113663
摘要
采用改进的加权区间排序法(WIRS)对扫描透射电子显微镜(STEM)能谱仪(EDS)化学测点进行处理,进而研究了316L不锈钢凝固过程中溶质的再分布规律。虽然实验中的偏析程度低于理论中的偏析程度,但Schiller-Gulliver计算给出了很好的初步近似。这些差异被认为是由于快速的凝固速度。用改进的WIRS方法处理的STEM-EDS数据是表征增材制造金属偏析分布的一种强有力且可靠的技术,该方法被证明减少了与微量元素定量相关的实验不确定性。
Chemical measurement points obtained with energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) in scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) were processed by a modified weighted interval rank sort (WIRS) method in order to study the solute redistribution during solidification of an additively manufactured 316L stainless steel. Scheil-Gulliver calculations give a good first approximation, although the extent of segregation is lower experimentally than theoretically. These discrepancies are believed to be due to the fast solidification rate involved. STEM-EDS data processed by the modified WIRS method is a strong and reliable technique for characterizing the segregation profile for additively manufactured metals, and the proposed method is shown to reduce the experimental uncertainty associated with the quantification of minor elements.