金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.202,1 Jan. 2021(上)
2021-02-24 来源:Goal Science
Vol. 202 目录
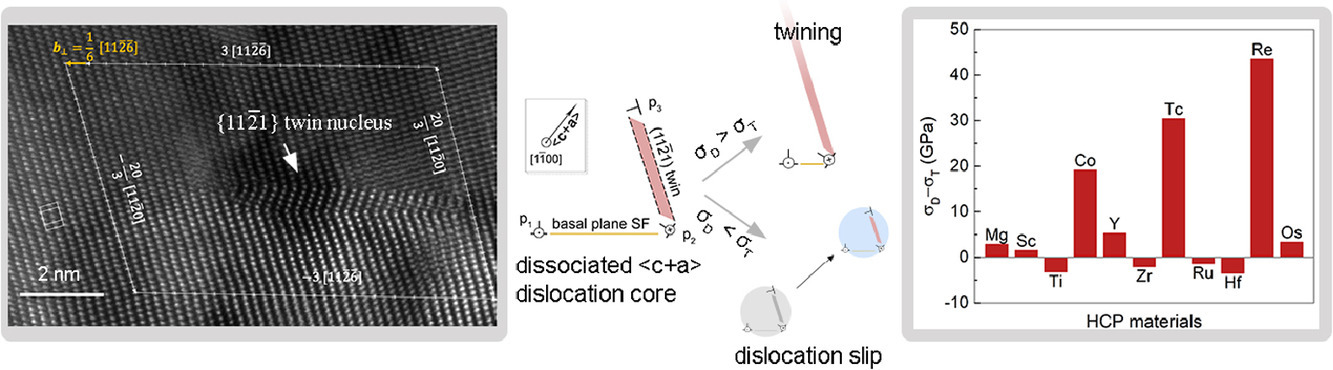
1.Twin nucleation from a single
六方密排晶体中单一位错处的孪晶形核研究
2. Local slip resistances in equal-molar MoNbTi multi-principal element alloy
等摩尔比MoNbTi多主元合金中的局部滑移阻力研究
3. Numerical analysis of twin-precipitate interactions in magnesium alloys
镁合金中孪生析出相之间相互作用的数值分析
4. Dislocation–grain boundary interaction-based discrete dislocation dynamics modeling and its application to bicrystals with different misorientations
基于位错-晶界相互作用的离散位错动力学模型及其在不同取向双晶中的应用
当马氏体相变具有两种可能的相变取向关系时应变路径的确定方法
面心立方高熵合金塑性变形初期的强度双峰特性
近等原子比NiTi合金中织构对形状记忆效应的原位中子衍射研究
8. In-situ synchrotron X-ray micro-diffraction investigation of ultra-low-strain deformation microstructure in laminated Ti-Al composites
Ti-Al层状复合材料超低应变下形变组织的原位同步X射线微衍射研究
高速金属微粒冲击过程中特定位置的喷射、粘结和局部变形研究
高强度7系 Al合金晶界组织的多尺度分析
通过数据挖掘结合机器学习探索高强度高延展性钛合金
氢-应变协同作用对锆中氢化物形成和相变的第一原理研究
通过原子尺度的层错相变提高多晶高温合金的蠕变性能
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P35-41
1. Twin nucleation from a single
六方密排晶体中单一位错处的孪晶形核研究
Lu Jiang, Velimir R. Radmilovic, Julian E.C. Sabisch, Liang Qi, Andrew M. Minor, Daryl C. Chrzan✉, Mark Asta✉
D.C. Chrzan:dcchrzan@berkeley.edu
M. Asta:mdasta@berkeley.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.038
摘要
孪晶对于调控HCP金属的强塑性平衡至关重要。我们对HCP晶体中孪晶在
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P68-79
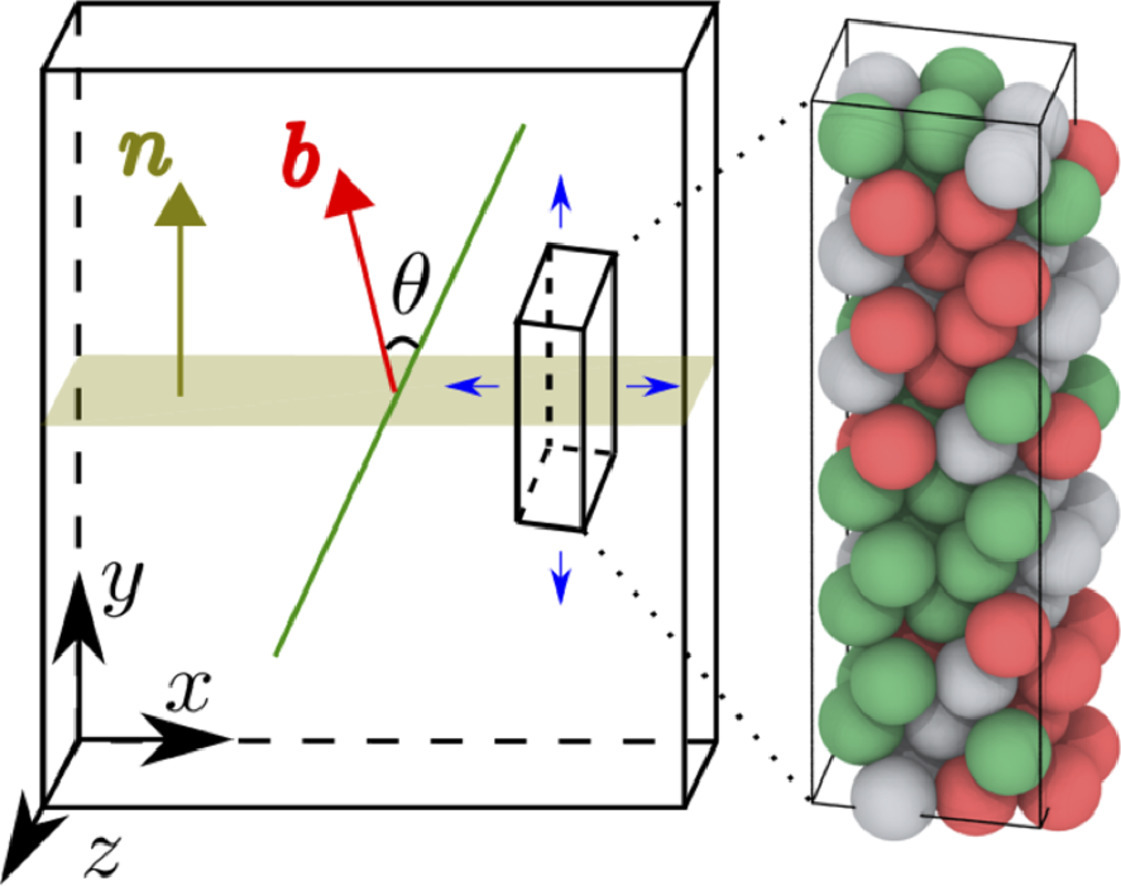
2. Local slip resistances in equal-molar MoNbTi multi-principal element alloy
等摩尔比MoNbTi多主元合金中的局部滑移阻力研究
Shuozhi Xu✉, Yanqing Su, Wu-Rong Jian, Irene J. Beyerlein
S. Xu:shuozhixu@ucsb.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.042
摘要
我们通过分子静态模拟计算了等摩尔比MoNbTi多主元合金的局部滑移阻力(LSRs)。我们考虑了螺型和刃型位错在{110}、{112}、{123}和{134}滑移面上沿111方向向前或向后的滑移。作为参考,我们计算了Mo、Nb和MoNbTi合金中对于相同位错的Peierls力,并进一步比较了局部滑移阻力与不考虑位错核引起的晶格畸变情况下的理想剪切强度。结果表明,与Mo和Nb相比,对于任何位错类型,MoNbTi合金的在{110}面上的局部滑移阻力上均非最小。{134}面上刃位错滑移最容易,而螺位错滑移最困难;相对的,{112}面上螺位错滑移最容易,而刃位错滑移最困难。我们还发现,与作为参考的纯金属相比,对同一类型的滑移面而言,MoNbTi中螺位错与刃位错的滑移阻力比降低了一个数量级。这些结果表明,与纯体心立方(BCC)金属相比,由于BCC多主元合金具有较低的螺-刃位错滑移阻力比,且刃位错在高指数面上具有较低局部滑移阻力,因此可以通过多种滑移模式进行形变。
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P80-87
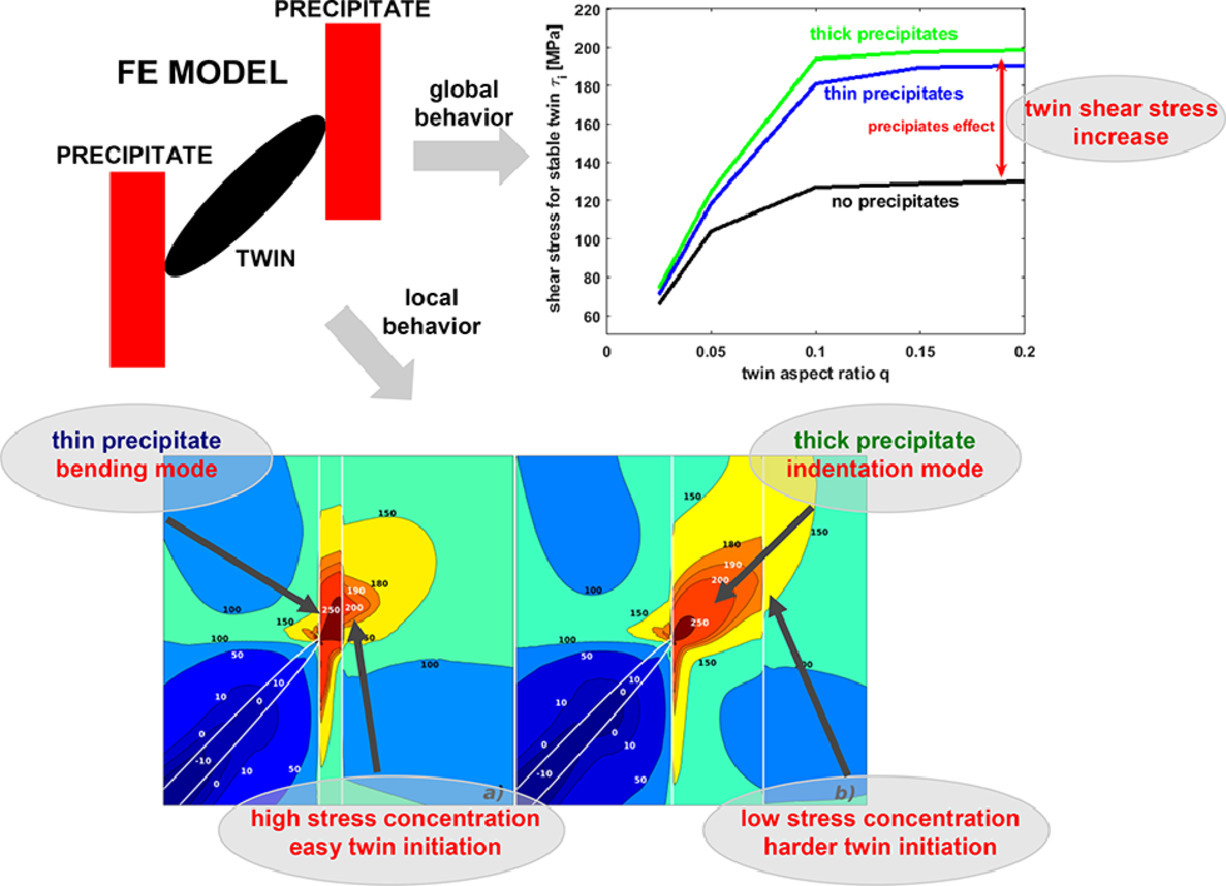
3. Numerical analysis of twin-precipitate interactions in magnesium alloys
镁合金中孪生析出相之间相互作用的数值分析
Filip Siska✉, Ludek Stratil, Jan Cizek, Tingting Guo, Matthew Barnett
F. Siska:siska@ipm.cz
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.053
摘要
本文对镁合金中{1012}拉伸孪晶与沿基面排列析出相之间的相互作用进行了二维数值模拟。模型假设在两个矩形析出相之间存在一椭圆形孪晶,基于各向异性的弹性和晶体塑性对材料行为进行模拟。模型描述了孪晶起始阶段,孪晶较小且位于析出相之间的情况。研究结果表明,沉淀相通过阻碍界面和缺陷运动和改变滑移临界剪切应力(CRSS)两种方式影响孪晶所需的剪应力。其中长宽比<0.05的孪晶同时受这两种效应的影响,而长宽比>0.1的孪晶则主要受CRSS变化的影响。此外,我们发现析出相厚度对孪晶的增厚和扩展起关键作用。增加析出相厚度会增加孪晶所需的剪应力,同时降低析出相外部应力,从而阻碍孪晶的有序扩展。
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P88-98
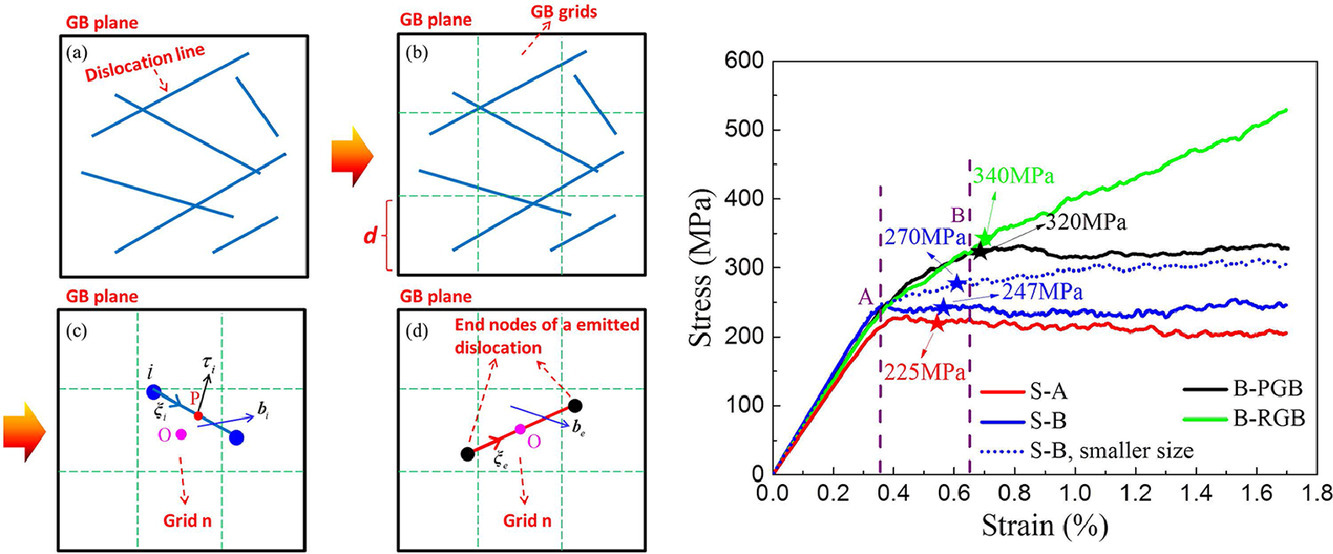
4. Dislocation–grain boundary interaction-based discrete dislocation dynamics modeling and its application to bicrystals with different misorientations
基于位错-晶界相互作用的离散位错动力学模型及其在不同取向双晶中的应用
Xu Zhang, Songjiang Lu, Bo Zhang, Xiaobao Tian, Qianhua Kan, Guozheng Kang✉
G. Kang:guozhengkang@home.swjtu.edu.cn(西南交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.052
摘要
晶界(GBs)对金属材料的力学性能有重要影响。描述位错与各种晶界的相互作用一直以来都是一个巨大的挑战。本研究中,我们建立了一种广义位错-晶界相互作用模型,并将其纳入了三维多尺度离散位错动力学的(DDD)框架之下。该模型考虑了位错与晶界相互作用的两种机制,即位错在晶界处的吸收和发射。为使模型适用于各种类型的晶界,我们采用了“粗晶化”方法对位错的吸收和发射过程进行了处理。为对模型进行验证和应用,我们研究了含有大角晶界的纳米微柱在单轴压缩下的响应。模拟结果表明,与单晶微柱相比,双晶微柱具有更高的屈服强度和流变应力,以及更小的应力降尺寸,这与文献中前期实验观测结果一致。随后,我们采用了离散位错动力学,模拟了取向差对含大角度对称倾侧晶界的双晶力学响应的影响。结果表明,双晶的力学响应受到晶界结构、位错-晶界相互作用和位错-位错相互作用的影响。相反,位错的吸收和发射、以及分切应力和位错密度的演变,与晶界取向差、晶界强度或晶界能量无关。
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P112-123
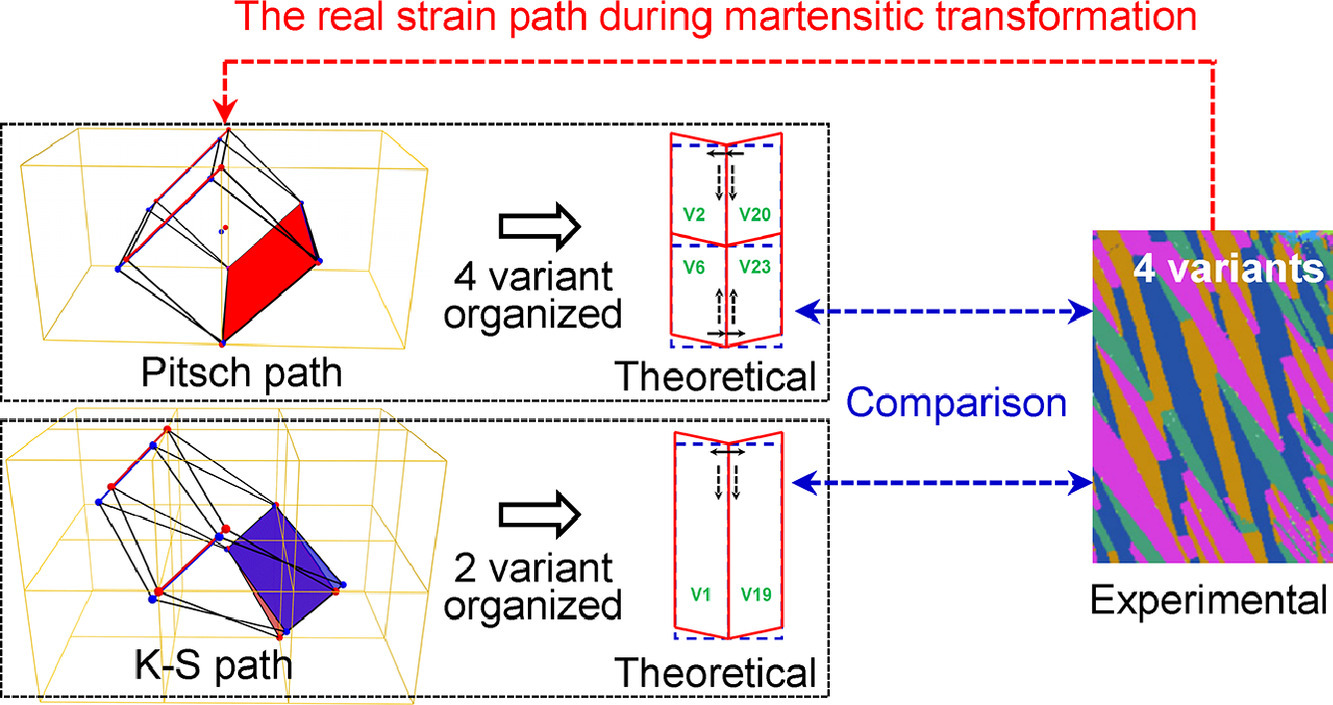
5. Determination of strain path during martensitic transformation in materials with two possible transformation orientation relationships from variant self-organization
当马氏体相变具有两种可能的相变取向关系时应变路径的确定方法
Hai-Le Yan✉, Yudong Zhang✉, Claude Esling, Xiang Zhao✉, Liang Zuo
H.-L. Yan:yanhaile@mail.neu.edu.cn(东北大学)
Y. Zhang:yudong.zhang@univlorraine.fr
X. Zhao:zhaox@mail.neu.edu.cn (东北大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.054
摘要
由于表征技术手段的局限,当马氏体相变具有两种可能的取向关系时,确定应变路径是较为困难的。在本研究中,我们以Ni-Mn基合金为例,通过考虑不同相变体系的对称性将导致不同的马氏体变体组态,提出了一种确定相变路径的分析策略。对于本研究中的合金,K-S和Pitch取向都得到了遵循。基于应力应变协调条件和最小能量准的进一步分析表明,理论上,K−S相变路径将产生2个自适应变体群,而Pitsch路径则将产生4个自适应变体群。与实验结果的比较发现,Ni - Mn基合金的Pitsch路径能量更低,并在无应力奥氏体中更容易实际发生。这项工作的意义是多方面的。它一方面解决了长期困扰学界的Ni-Mn基合金相变应变路径的问题。另一方面,这一分析框架也可被推广至其它具有多种可能的马氏体相变取向关系的体系。
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P124-134
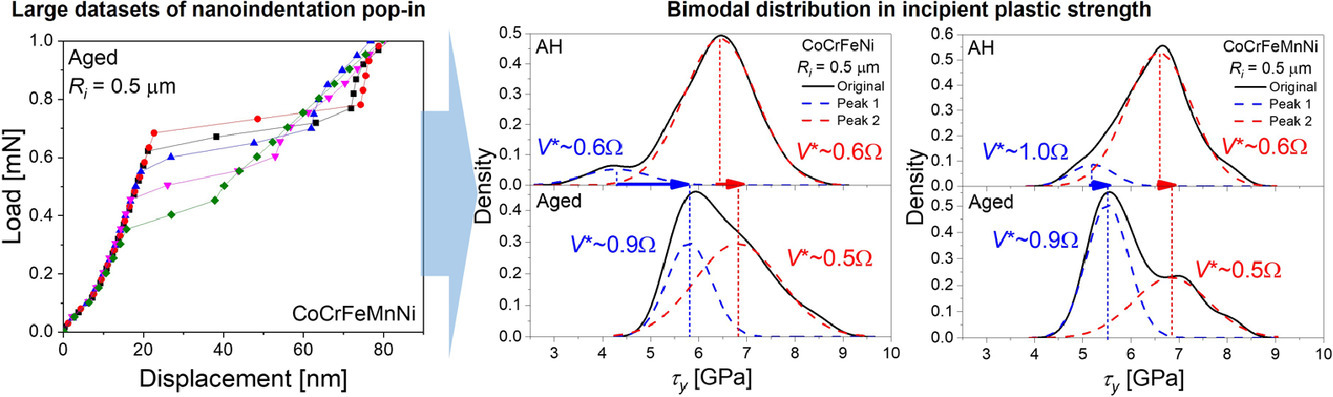
6.Bimodality of incipient plastic strength in face-centered cubic high-entropy alloys
面心立方高熵合金塑性变形初期的强度双峰特性
Yakai Zhao, Jeong-Min Park, Jae-il Jang✉, Upadrasta Ramamurty✉
J.-i. Jang:jijang@hanyang.ac.kr
U. Ramamurty:uram@ntu.edu.sg
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.066
摘要
我们采用了2种不同尺寸的球形压头,对两种典型FCC高熵合金(CoCrFeNi和CoCrFeMnNi)的固溶态和时效态进行了纳米压痕实验。我们借此获得了一个压头嵌入处强度的大型数据集,通过对其进行统计分析,加深了对单相高熵合金中塑性微观机制的理解。在所有研究的案例中,概率密度呈双峰分布。我们基于反弯曲分布假设对形变的激活体积进行了估计。研究表明,当样品体积较小时,在较低的压痕应力下,材料中就会出现空位诱导的非均位错形核; 随着载荷提高,位错发生均匀形核,并使得材料强度提高至与理论值相近。而当样品体积较大时,使用较大的压头进行加载,此时低应力下预先存在的位错或是高应力下的空位团簇/晶界诱导的非均匀位错形核成为主要强化机制。通过高温时效,提高合金中的化学短期有序程度,能够提高位错均匀形核所需的应力,从而强化合金。我们对提高材料强塑性的多种机制的贡献进行了讨论。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P135-148
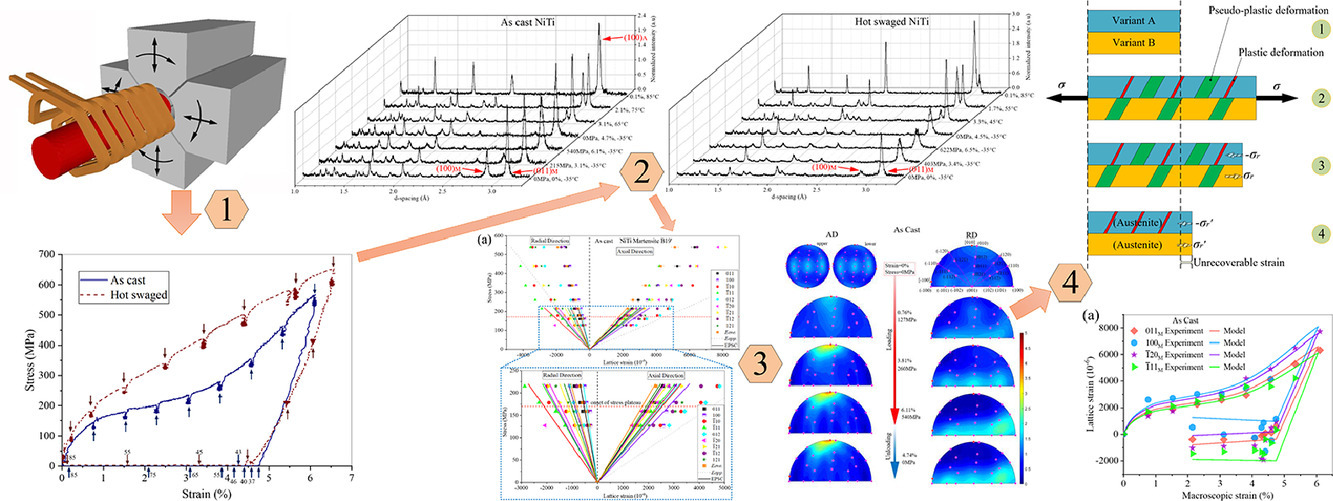
7.In situ neutron diffraction investigation of texture-dependent Shape Memory Effect in a near equiatomic NiTi alloy
近等原子比NiTi合金中织构对形状记忆效应的原位中子衍射研究
Zifan Wang, Jingwei Chen, Cyril Besnard, Lenka Kuncická, Radim Kocich, Alexander M. Korsunsky✉
A.M. Korsunsky:alexander.korsunsky@eng.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.049
摘要
为了探索通过织构对NiTi形状记忆合金的功能行为进行调控的可能性,我们分别制备了铸态和热锻态的Ni55Ti45 (wt.%)合金,并对比了它们的初始织构和宏观性能。我们使用原位中子衍射技术研究了形状记忆效应(SME)过程中织构对微观组织演变的影响,并对材料的一系列性能进行了评估。结果表明: (1)热锻使晶粒形貌发生改变,组织中的微观应变增大; (2)马氏体和奥氏体变体的热膨胀系数受织构和相变的影响较小; (3)弹塑性自洽(EPSC)模拟方法可以较好地量化织构对材料宏观和微观弹性性能的影响,各向异性的弹性模量值处于单晶和孪晶之间; (4) SME过程中的织构演变与初始组织的关系较弱; (5)马氏体取向发生了改变,<010>方向平行于加载方向,卸载时保持,这揭示了织构演化与脱孪之间的内在关系。我们基于实验结果,提出了一种用于量化形状记忆效应过程中晶格应变演化的多变量模型,并对其有效性进行了验证。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P149-158
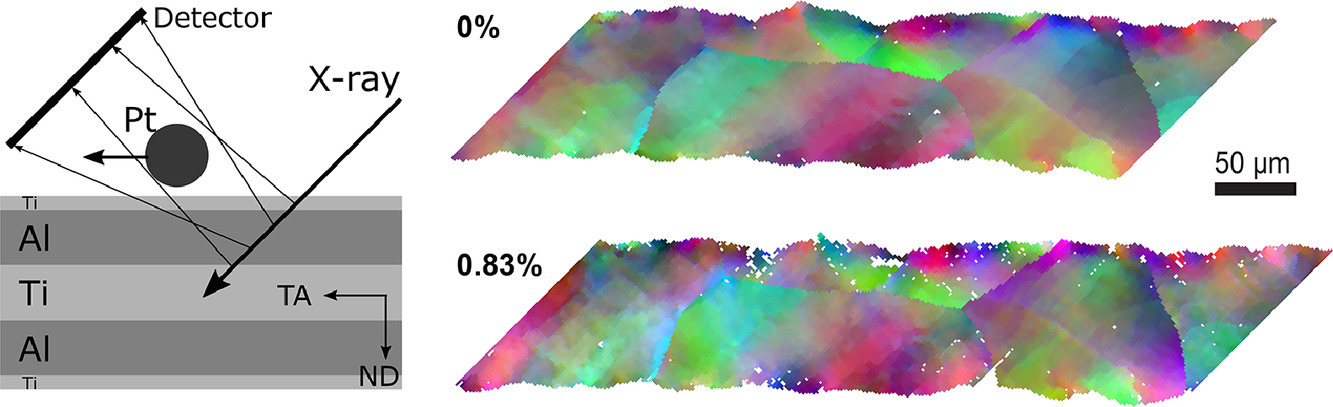
8. In-situ synchrotron X-ray micro-diffraction investigation of ultra-low-strain deformation microstructure in laminated Ti-Al composites
Ti-Al层状复合材料超低应变下形变组织的原位同步X射线微衍射研究
Tianbo Yu✉, Yan Du, Guohua Fan✉, Ruqing Xu, Rozaliya Barabash, Niels Hansen, Xiaoxu Huang, Yubin Zhang
T. Yu:tiyu@mek.dtu.dk
G. Fan:ghfan@njtech.edu.cn(南京科技大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.050
摘要
我们采用了无损的高能X射线显微衍射技术(DAXM),首次揭示了退火叠层Ti-Al复合材料内部“完全再结晶”Al层中的一种超低应变变形结构,其中DAXM的空间角分辨率达到了0.01°。这种超低应变变形组织是由于Ti、Al两种材料在退火冷却过程中热膨胀系数不同而导致的热应力引起。我们将退火后的样品进行了拉伸变形(应变量1.66%),随后基于原位DAXM和多种方法对材料的取向差进行了分析表征。结果表明,初始组织、界面约束、晶粒尺寸、晶体取向都对材料的塑性变形有重要影响。退火样品的Al层存在从层界面到层中心的位错密度梯度,且这种梯度在拉伸变形过程中略有增加。我们通过考虑形变过程中不同尺寸和取向晶粒中的位错激活和位错相互作用,对位错密度的变化规律进行了讨论。以上研究结果对于新型复合材料设计和理解叠层金属复合材料的约束效应具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P159-169
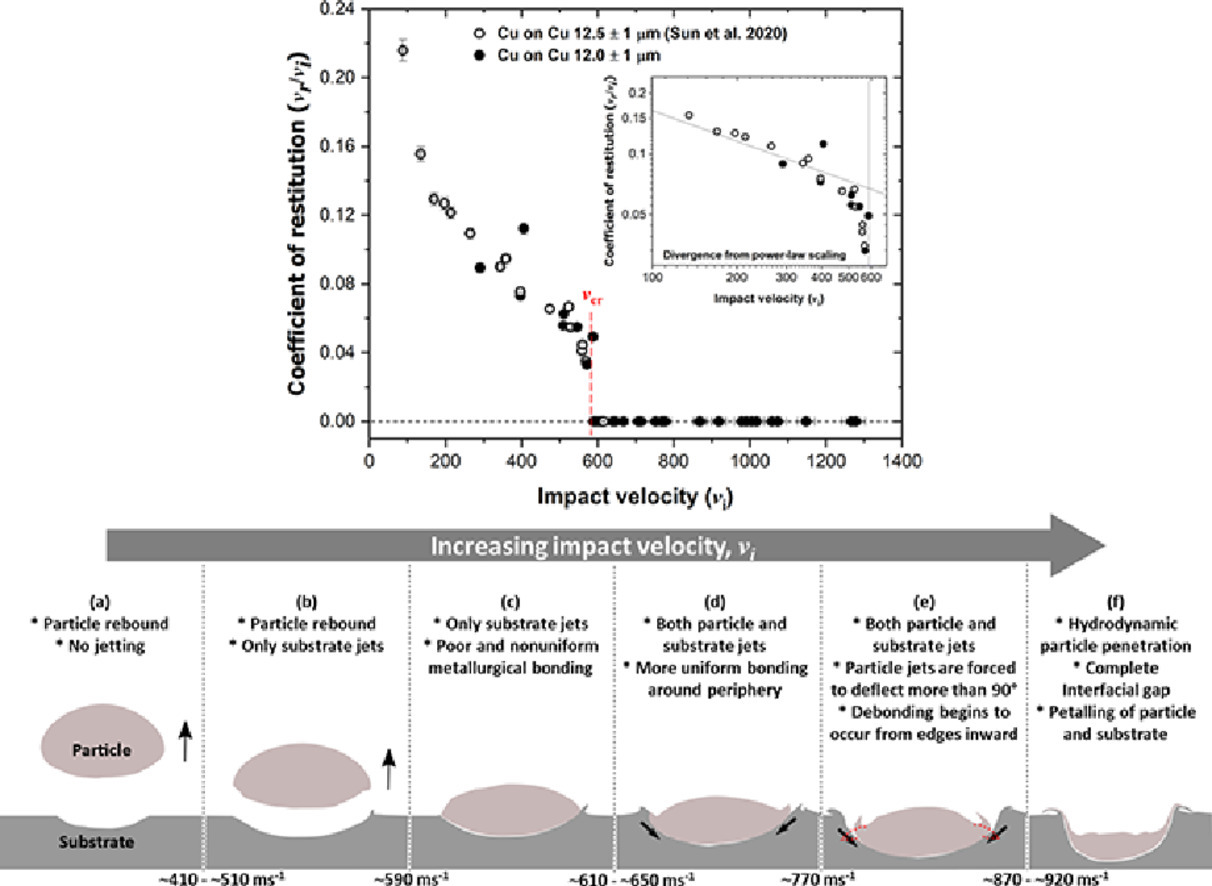
9. Site-specific study of jetting, bonding, and local deformation during high-velocity metallic microparticle impact
高速金属微粒冲击过程中特定位置的喷射、粘结和局部变形研究
Ahmed A. Tiamiyu, Yuchen Sun, Keith A. Nelson, Christopher A. Schuh✉
C.A. Schuh:schuh@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.057
摘要
在冷喷涂过程中,喷射现象通常被认为是颗粒-基体粘结的前兆,但这一现象的发生条件尚不明晰。本文系统地研究了单个Cu粒子在不同速度下撞击Cu基体的行为。通过对粒子的速度进行精准的控制,我们能够很好地辨识粒子在不同速度范围内的不同行为。在低速下,我们观测到入射粒子发生反弹,且在基体上形成一个完全塑性冲击区。随着速度的增加,即使颗粒仍被反弹,基体喷射现象也会出现。在临界粘附速度vcr下,喷射只发生在基体上,因此结合并不紧密。随着速度继续增加,结合力增强,颗粒也开始喷射,当在粒子速度约为1.3 vcr时,结合力达到最大值,之后结合强度下降。当粒子速度达到1.6 vcr以上时,我们观察了基体的剥落和颗粒嵌入基体撞击面以下的现象,即颗粒可能会部分穿透基体并造成侵蚀。以上经特定速度粒子冲击后基体结构变化的研究,可以为选择合适的冷喷涂加工窗口提供有效指导。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P190-210
10. Multiscale analysis of grain boundary microstructure in high strength 7xxx Al alloys
高强度7系 Al合金晶界组织的多尺度分析
Alistair Garner, Ryan Euesden, Yichao Yao, Yasser Aboura, Huan Zhao, Jack Donoghue, Michele Curioni, Baptiste Gault, Pratheek Shanthraj, Zak Barrett, Christian Engel, Tim L. Burnett, Phil B. Prangnell
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.021
摘要
我们采用了一系列高分辨表征手段(包括3DAP),对厚板(140 mm) 7系铝合金中的偏聚和晶界析出η相(GBPs)的尺寸、分布、化学组分进行了多尺度定量研究。我们在T7651回火条件下,对新一代高锌铝合金(AA7085)与较为成熟的AA7050进行了比较。结果表明,两种合金的大角度晶界上分布着大量的淬火诱导晶界析出η相,其中AA7050的晶界覆盖率高达40%。脆性沿晶断裂表面的三维观测表明,这些析出比之前报导的要大得多,并表现出复杂的枝状形貌。AA7050中析出相的Cu(29%)和Al(37%)含量显著高于AA7085, 而Zn(33%)含量则较低。经典模型表明,这些差异是由于不同的相变路径导致的。AA7050的淬火敏感性较高,析出相在较高的温度下形核,这使得合金化学成分的影响更加显著。在这两种合金中,晶界偏聚都十分有限,晶界处的Zn含量比基体中低,但AA7050中晶界处的Mg含量较高,Cu含量较低。因此,我们认为两种材料晶界化学成分的主要区别在于,AA7050析出相中的Cu、Al含量较高,而Zn含量较低。这也是AA7050晶界化学活性较低的主要原因。此外,我们简要讨论了材料的相对敏感性对服役环境诱导起裂的影响。

ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P211-221
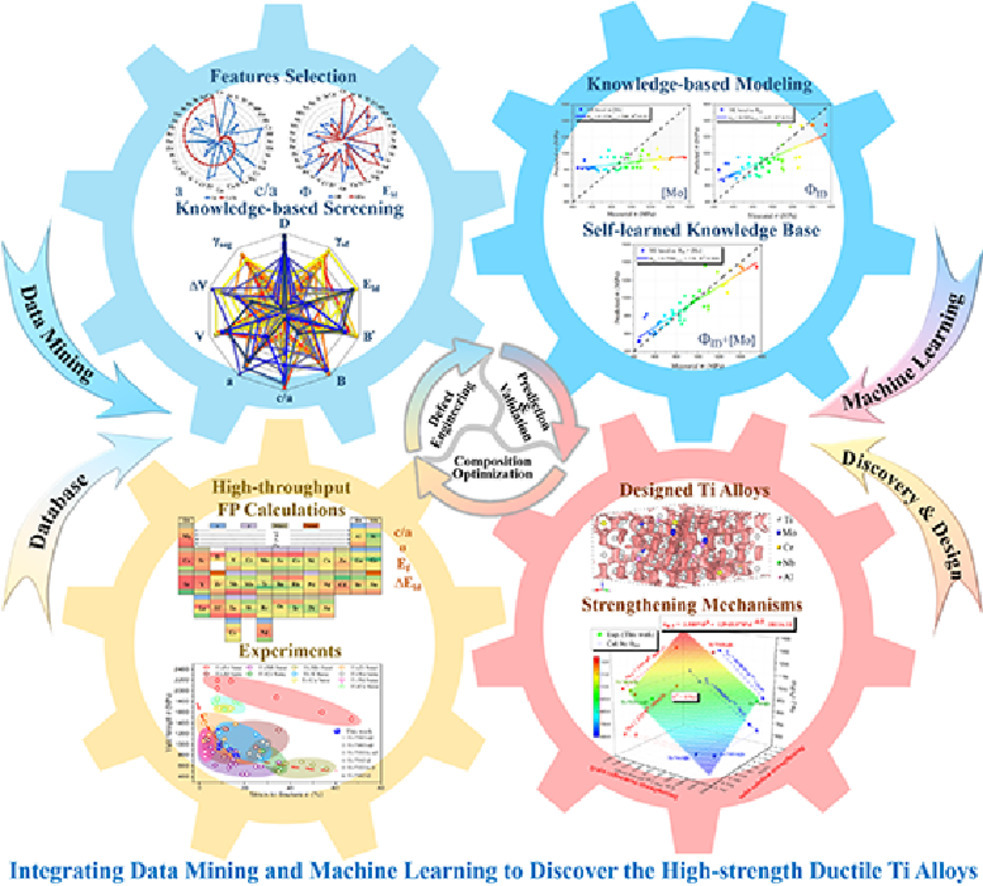
11. Integrating data mining and machine learning to discover high-strength ductile titanium alloys
通过数据挖掘结合机器学习探索高强度高延展性钛合金
Chengxiong Zou, Jinshan Li✉, William Yi Wang✉, Ying Zhang, Deye Lin, Ruihao Yuan, Xiaodan Wanga, Bin Tang, Jun Wang, Xingyu Gao, Hongchao Kou, Xidong Hui, Xiaoqin Zeng, Ma Qian, Haifeng Song✉, Zi-Kui Liu, Dongsheng Xu
J. Li:ljsh@nwpu.edu.cn (西北工业大学)
W.Y. Wang:wywang@nwpu.edu.cn (西北工业大学)
H. Song:song_haifeng@iapcm.ac.cn(北京应用物理与计算数学研究所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.056
摘要
随着计算机和算法的不断发展,在数据驱动和高通量计算的帮助下,一种加速材料发现、设计和优化的新范式正在出现。在此,我们以钛合金为例,通过材料集成计算工程,提高其强度和延展性。我们通过高通量第一性原理计算构建了电子性质的元素周期表,其中包括了电子的功函数(Ф),费米能级(EF),键合电荷密度(ρ)和晶格畸变能。我们通过数据挖掘方法揭示了从原子和电子角度揭示了材料组成-结构-性质之间的关系,找到了先进合金设计策略的关键特征和原则。在缺陷工程的指导下,我们将断层能和位错宽度作为提高塑性的主要依据,利用提出的屈服强度模型定量地计算了固溶强化和晶粒细化的贡献。基于机器学习与基础知识的协同使用,我们通过反馈优化,得到一个新的训练模型,其结果显著经验性的等效模型。因此,数据挖掘和机器学习的集成不仅能帮助我们解释现象、验证假设,还能以更加经济有效的方式对高强高韧钛合金进行设计。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P222-231
12. A first principles investigation of the hydrogen-strain synergy on the formation and phase transition of hydrides in zirconium
氢-应变协同作用对锆中氢化物形成和相变的第一原理研究
I. Cheik Njifon, E. Torres✉
E. Torres:edmanuel.torres@cnl.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.030
摘要
氢化物的析出被认为是引起锆及其合金脆化的原因之一。在本研究中,我们利用密度泛函理论(DFT)研究了氢(H)对锆(Zr)体系中的影响。我们建立模型,模拟了hcp-Zr(α-Zr)中间隙氢原子形成氢化物所需的热力学和应变条件。研究发现,Zr2H的多种共格hcp结构具有相似的形成能和结构性质,相对容易形成。部分hcp结构的Zr2H氢化物动态不稳定,因此会促进fcc相变的发生。这种六方相向立方相的转变与氢的分布、取向关系和应变条件有关。研究表明,相变需要大量的原子重排。与纯α-Zr相比,Zr2H的相变势垒更低,因此Zr2H可以诱导基体晶格发生相变,从而导致了脆性δ相的形成。以上关于机理研究对深入理解实验观测到的氢化物析出过程具有重要意义。

ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P232-242
13. Enhanced creep performance in a polycrystalline superalloy driven by atomic-scale phase transformation along planar faults
通过原子尺度的层错相变提高多晶高温合金的蠕变性能
Lola Lilensten✉, Stoichko Antonov, Baptiste Gault, Sammy Tin, Paraskevas Kontis✉
L. Lilensten:lola.lilensten@chimieparistech.psl.eu
P. Kontis:p.kontis@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.062
摘要
预测材料服役过程中的失效需要对其变形行为,以及相关的近原子尺度动态组织演化有充分了解。研究表明,溶质原子会与塑性变形导致的缺陷相互作用,影响缺陷在组织中的运动,进而影响材料的机械性能。我们对两种不同Nb含量的多晶镍基高温合金进行了研究,发现Nb含量会显著影响蠕变。750℃、600 MPa的蠕变试验表明,高Nb合金在蠕变速率更低。考虑到两种实验材料的初始组织相似,力学行为的显著区别应是由与层错类型和合金成分有关的相变导致。电子隧穿成像表明,两种合金中均存在层错。而微孪晶只在低Nb合金被观测到,这在一定程度上解释了其高蠕变速率。原子探针研究发现,在高铌合金中,根据层错偏聚行为的不同,可将层错分为两种类型。其中超晶格的内禀层错富Nb、Co、Cr、Mo;而外禀层错仅有Nb和Co的偏聚。根据成分的不同,高铌合金沿层错发生局部相变,使得蠕变速率降低。与此相对,低Nb合金中的层错则基本为富Co、Cr、Nb、Mo的内禀层错。基于以上结果,结合文献中的相关报导,我们从原子尺度提出了一种合金设计方法,通过调控材料在750°C层错的局部相变,提高高温合金的抗蠕变能力。



