金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.202,1 Jan. 2021(下)
2021-02-24 来源:Goal Science
Vol. 202 目录
1. In Situ Micro-Pillar Compression to Examine Radiation-Induced Hardening Mechanisms of FeCrAl Alloys
FeCrAl合金辐照诱导硬化机制的原位微柱压缩实验研究
2. 3D arrangement of atomic polyhedra in tilt grain boundaries
倾侧晶界中原子多面体的三维排布
3. An unexpected role of atomic oxygen dopants in Au evolution from clusters to a layer
氧原子掺杂剂在金团簇-层演化中的作用
4. Atomic scale understanding of the defects process in concurrent recrystallization and precipitation of Sm-Co-Fe-Cu-Zr alloys
Sm-Co-Fe-Cu-Zr合金同时发生再结晶和析出过程时缺陷演化的原子尺度研究
5. Isothermal bainite transformation in low-alloy steels: Mechanism of transformation
低合金钢的等温贝氏体相变机制研究
6. Interphase boundary layer-dominated strain mechanisms in Cu+ implanted Zr-Nb nanoscale multilayers
经Cu+注入的Zr-Nb纳米多层结构中受中间界面层控制的应变机制研究
7. Dissecting functional degradation in NiTi shape memory alloys containing amorphous regions via atomistic simulations
含非晶区NiTi形状记忆合金功能退化的原子尺度模拟研究
8. Fracture mechanism and toughness of a rolled magnesium alloy under dynamic loading
轧制镁合金在动态载荷下的韧性与断裂机理
9. Intermediate structural evolution preceding growing BCC crystal interface in deeply undercooled monatomic metallic liquids
高度过冷的单一金属液体中BCC晶体生长前沿的中间态结构演化
10. Coupled crystal plasticity finite element-phase field model with kinetics-controlled twinning mechanism for hexagonal metals
六方金属中动力学控制孪晶机制的有限元-相场耦合模型
11. Alloys-by-design: Application to new superalloys for additive manufacturing
利用增材制造方法设计制备新型高温合金
12. Recovery of cold-worked Al0.3CoCrFeNi complex concentrated alloy through twinning assisted B2 precipitation
B2析出诱导孪晶引起的冷加工Al0.3CoCrFeNi多组元合金回复过程研究
13. Dendritic needle network modeling of the Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transition. Part II: three dimensional formulation, implementation and comparison with experiments
柱状晶向等轴晶转变的枝状针形网络三维模型模拟与实验对比
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P255-265
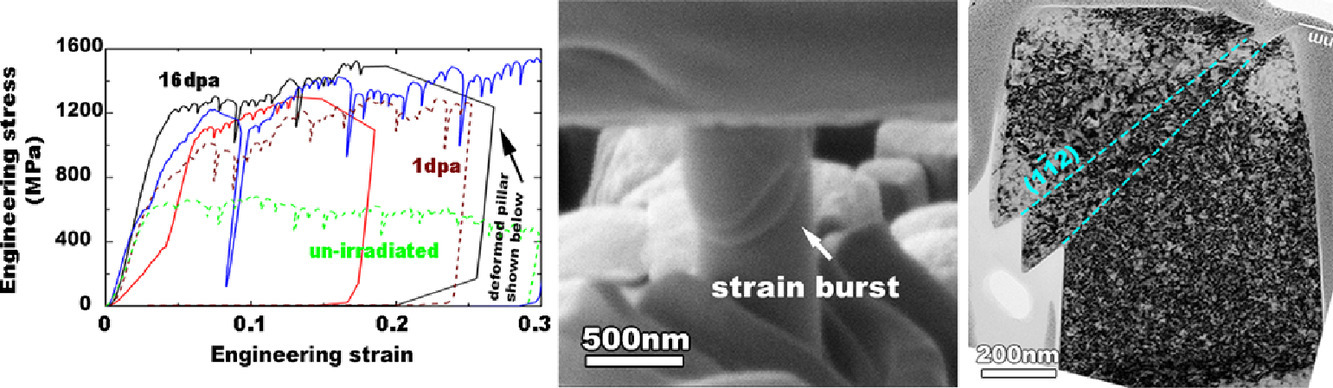
1. In Situ Micro-Pillar Compression to Examine Radiation-Induced Hardening Mechanisms of FeCrAl Alloys
FeCrAl合金辐照诱导硬化机制的原位微柱压缩实验研究
Yuchi Cui, Eda Aydogan, Jonathan G. Gigax, Yongqiang Wang, Amit Misra, Stuart A. Maloy, Nan Li✉
N. Li:nanli@lanl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.047
摘要
我们研究了300℃下5MeV Fe2+离子辐照对FeCrAl C26M合金组织演变和形变行为的影响。结果表明,当损伤剂量从1 dpa增加到16 dpa时,位错环的密度增加了一个数量级,而位错环的尺寸则逐渐饱和。我们制备了直径600 nm、高1.3μm的微柱,并对<001>、<011>和<111>取向的晶粒进行了压缩。在未辐照和经辐照的合金中,初始滑移系统均为{112}<111>。辐照后,沿<001>和<011>方向的屈服强度相比<111>方向有明显增加。Orowan势垒模型的相关分析表明,屈服强度的增加主要是由于辐射产生的缺陷环具有滑移抗力。我们通过TEM对应力升高时辐照诱导位错的分布和Burgers矢量进行了表征。结果表明,局部切变失稳是由于大量½<111>位错滑出实验柱引起的。同时,滑移带附近形成的大量<100>位错导致了合金在的应变硬化。
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P266-276
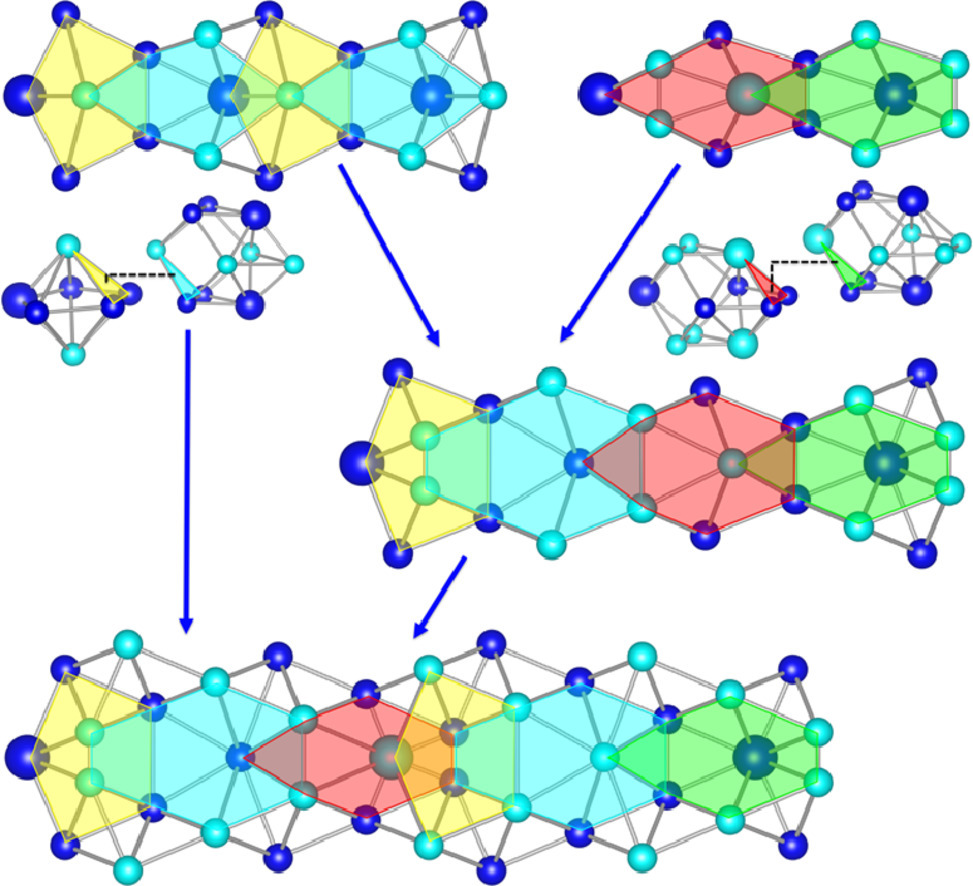
2. 3D arrangement of atomic polyhedra in tilt grain boundaries
倾侧晶界中原子多面体的三维排布
Kazutoshi Inoue✉, Kazuaki Kawahara, Mitsuhiro Saito, Motoko Kotani, Yuichi Ikuhara✉
K. Inoue:kinoue@wpi-aimr.tohoku.ac.jp
Y. Ikuhara:ikuhara@sigma.t.utokyo.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.017
摘要
多晶材料的宏观性能与其晶体结构中的缺陷密切相关。晶界的独特性质取决于其附近及纳米的空间结构,因此对于构成晶界的原子多面体的类型和结构的研究就至关重要,尤其是晶界原子排布的数学规律和结构-性能关系。在本研究中,我们对[001]、[110]和[111]对称倾侧晶界的三维结构进行了分析。我们对这些多面体结构进行了严格定义,以区别二维模型中的多边形排布。研究表明,晶界区域只能由特定类型的多面体单元构成,且这些多面体之间的差异不大。我们通过数值分析对晶界的三维原子排布进行了系统的定量描述。不仅如此,我们还发现晶界层级遵循修正后的Farey图中所呈现的有理数分布规律。我们将由不超过两种多面体单元构成的晶界定义为奇异晶界,而任何晶界均可以由组成奇异晶界的多面体单元构成。
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P277-289
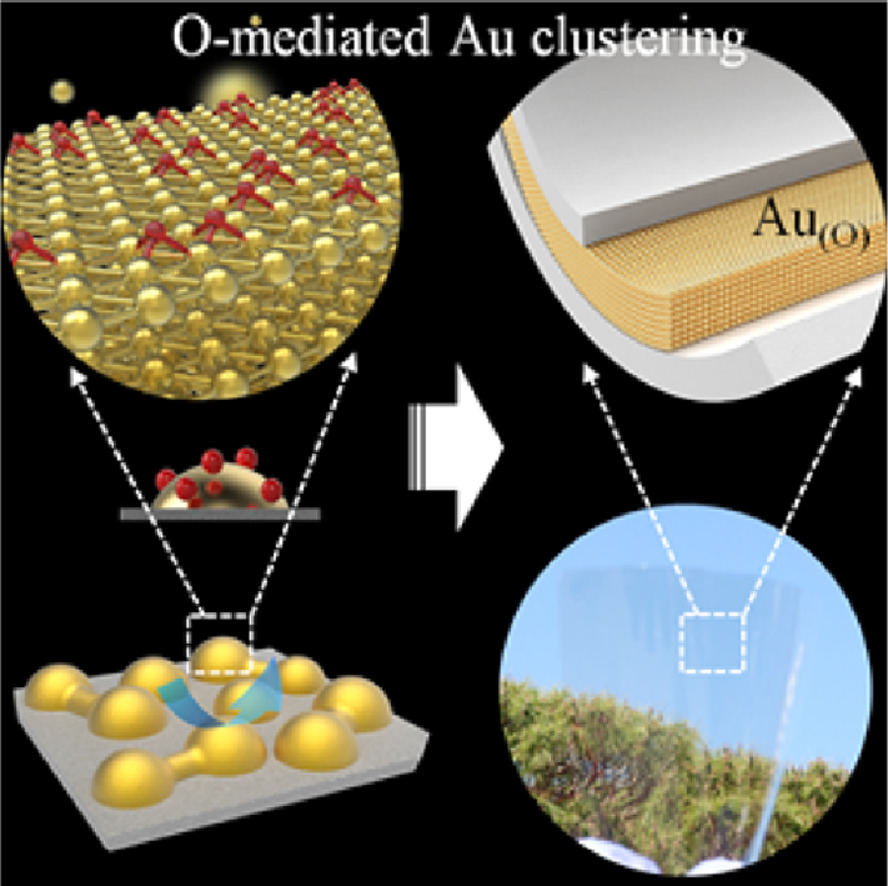
3. An unexpected role of atomic oxygen dopants in Au evolution from clusters to a layer
氧原子掺杂剂在金团簇-层演化中的作用
Eunwook Jeong, Eun-Ae Choi✉, Yoshifumi Ikoma✉, Seung Min Yu, Jong-Seong Bae,Sang-Geul Lee, Seung Zeon Han, Gun-Hwan Lee, Jungheum Yun✉
E.-A. Choi:eunae.choi@kims.re.kr
Y. Ikoma:ikoma@zaiko.kyushuu.ac.jp
J. Yun:jungheum@kims.re.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.063
摘要
结构调控是实现金的化学、电学和光学性能调控的重要手段。然而,由于缺乏有效手段避免Au在气相沉积过程(或之后)的本征结构演化,因此设计金的纳米结构一直是一个难题。在此,我们提出了一种方法:利用氧化诱导Au的聚集和分层。由于O对纳米金几何结构的最外层具有强烈的干涉效应,因此金的团簇以及和氧高度浸润的表层的演化显著加快。通过这一调控方式,我们成功制备出了4纳米厚的外延Au层结构,它比Ag具有更高的光学透明度,体电阻率接近于8×10−8Ω,并对化学腐蚀和机械变形的具有极好的抗性。这一结果为解决透明金属电极在工作环境中容易发生损坏导致性能劣化的问题提供了一个明确的解决方案。
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P290-301
4. Atomic scale understanding of the defects process in concurrent recrystallization and precipitation of Sm-Co-Fe-Cu-Zr alloys
Sm-Co-Fe-Cu-Zr合金同时发生再结晶和析出过程时缺陷演化的原子尺度研究
Xin Song, Tianyu Ma✉, Xianglong Zhou, Fan Ye, Tao Yuan, Jingdong Wang, Ming Yue, Feng Liu, Xiaobing Ren
T. Ma:matianyu@xjtu.edu.cn (西安交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.067
摘要
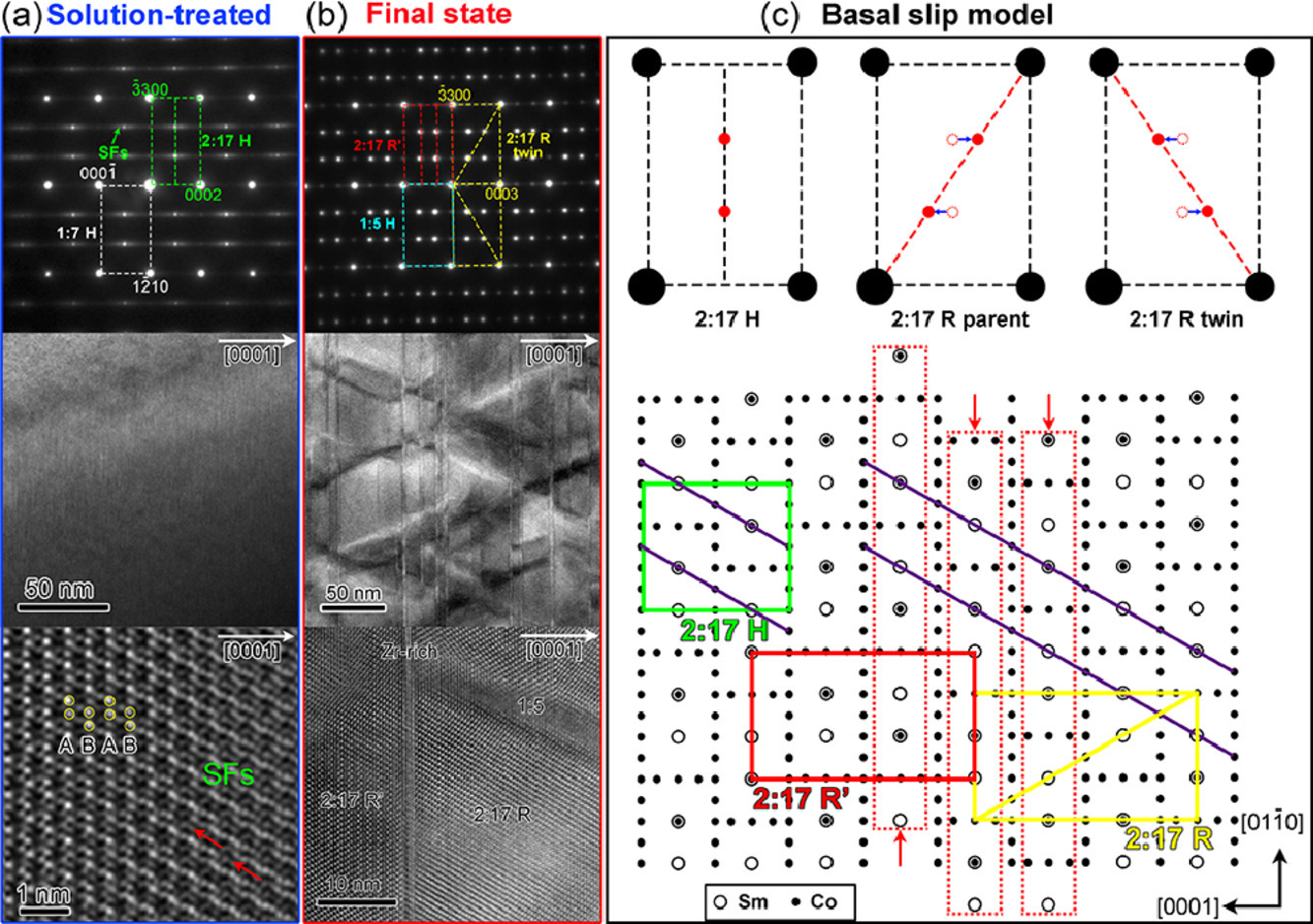
理解过饱和固溶体时效时同时发生的再结晶和析出过程中的缺陷演化,对于理解它们的相互作用机制和组织调控至关重要,但在原子尺度上的相关研究却少有报导。我们通过透射电子显微镜对过饱和六方Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)7.5合金中,由于层错、空位、间隙原子等缺陷形成/分解导致的再结晶、亚晶形成、析出过程进行了详细研究。研究表明,扩散控制的<a>型分位错滑移不仅导致了基体由六方Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)7 (1:7H) 和Sm2(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)17 (2:17H)的混合状态转变为了贫Sm的斜方Sm2(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)17 (2:17R) ,并且提供了连续的扩散通道,抑制了点缺陷形成富Sm六方 Sm(Co, Fe, Cu, Zr)5 (1:5H) 晶胞界面析出和富Zr斜方(Sm, Zr)(Co, Fe, Cu)3 (1:3R)片晶。这表明存在一种扩散控制的相变机制,可以通过2:17R’ 中间相的成分进行描述表征,而成分取决于不完全基面滑移和元素偏聚。再结晶晶胞和析出相长大的速度都与缺陷密度密切相关,时效早期阶段缺陷密度高,长大速度快;后期阶段缺陷密度低,长大速度慢。我们提出了一种基面滑移模型对缺陷的分解/形成、以及同时形成的连续原子扩散通道进行了解释。以上研究可以帮助我们加深对再结晶和析出相互作用的了解。
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P302-316
5. Isothermal bainite transformation in low-alloy steels: Mechanism of transformation
低合金钢的等温贝氏体相变机制研究
Ravi Ranjan✉, Shiv Brat Singh✉
R.Ranjan:ravi.ranjan5@tatasteel.com, ravi.ranjan.9007@gmail.com
S.B. Singh:sbs22@metal.iitkgp.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.048
摘要
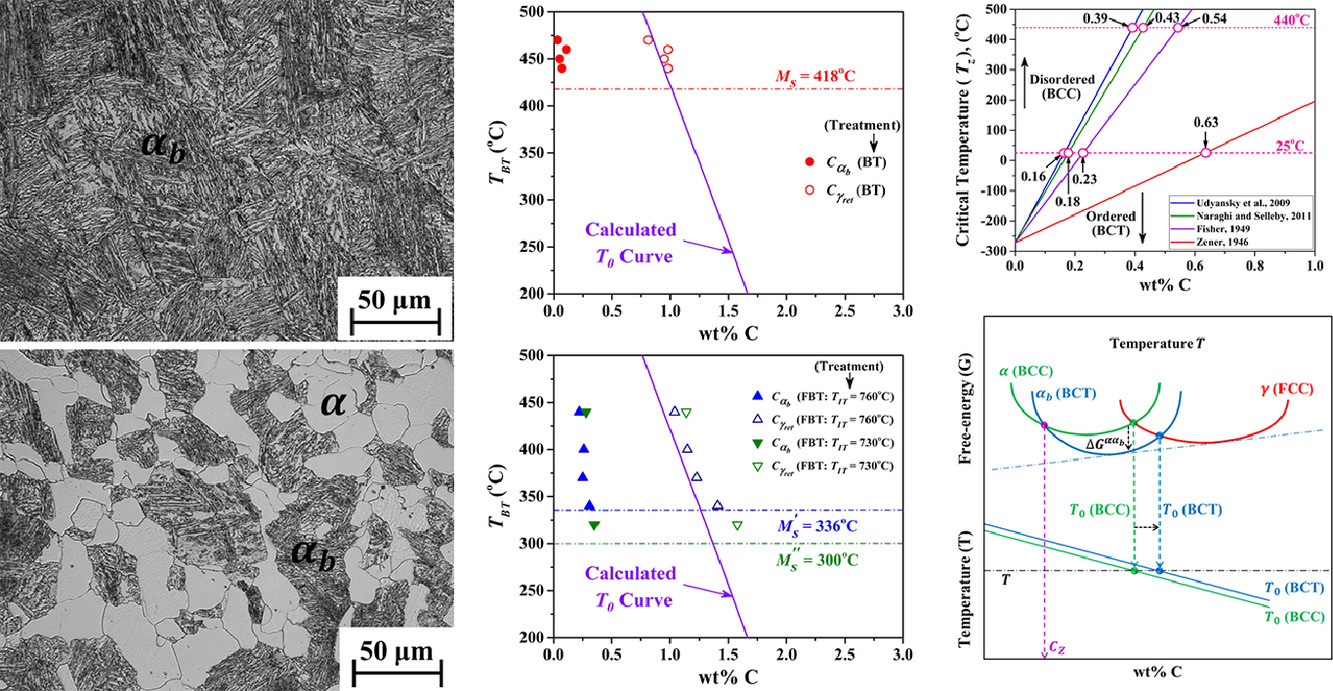
我们研究了奥氏体碳浓度对贝氏体等温相变的影响。结果表明,当奥氏体碳浓度较低且相变温度高于Zener有序温度时,贝氏体中的碳含量较低;而母奥氏体中碳含量较高且相变温度低于Zener有序温度时,贝氏体中的碳含量较高。我们基于碳原子的Zener有序会导致具有较高碳溶解度的BCT铁素体形成的相关理论,对实验结果进行了合理解释。类似地,我们发现在前一种情况中,未转变奥氏体中的碳含量接近T0线,而在后一种情况下,则高于T0线。我们基于BCT铁素体和奥氏体的平衡理论对这种碳浓度相对于T0的偏离进行了解释。最后,我们对贝氏体和奥氏体中碳含量的计算进行了修正,以便更好地计算当相变温度低于Zener有序温度时贝氏体和奥氏体的相对体积分数。
ACTA
Vol. 202,1 Jan. 2021, P317-330
6. Interphase boundary layer-dominated strain mechanisms in Cu+ implanted Zr-Nb nanoscale multilayers
经Cu+注入的Zr-Nb纳米多层结构中受中间界面层控制的应变机制研究
N. Daghbouj✉, M. Callisti✉, H.S. Sen✉, M. Karlik, J. Cech, M. Vronka, V. Havránek, J. Capek, P. Minárik, P. Bábor, T. Polcar
N. Daghbouj:Nabil.Daghbouj@fjfi.cvut.cz
M. Callisti:m.callisti@hotmail.it
H.S. Sen:senhusey@fel.cvut.cz
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.072
摘要
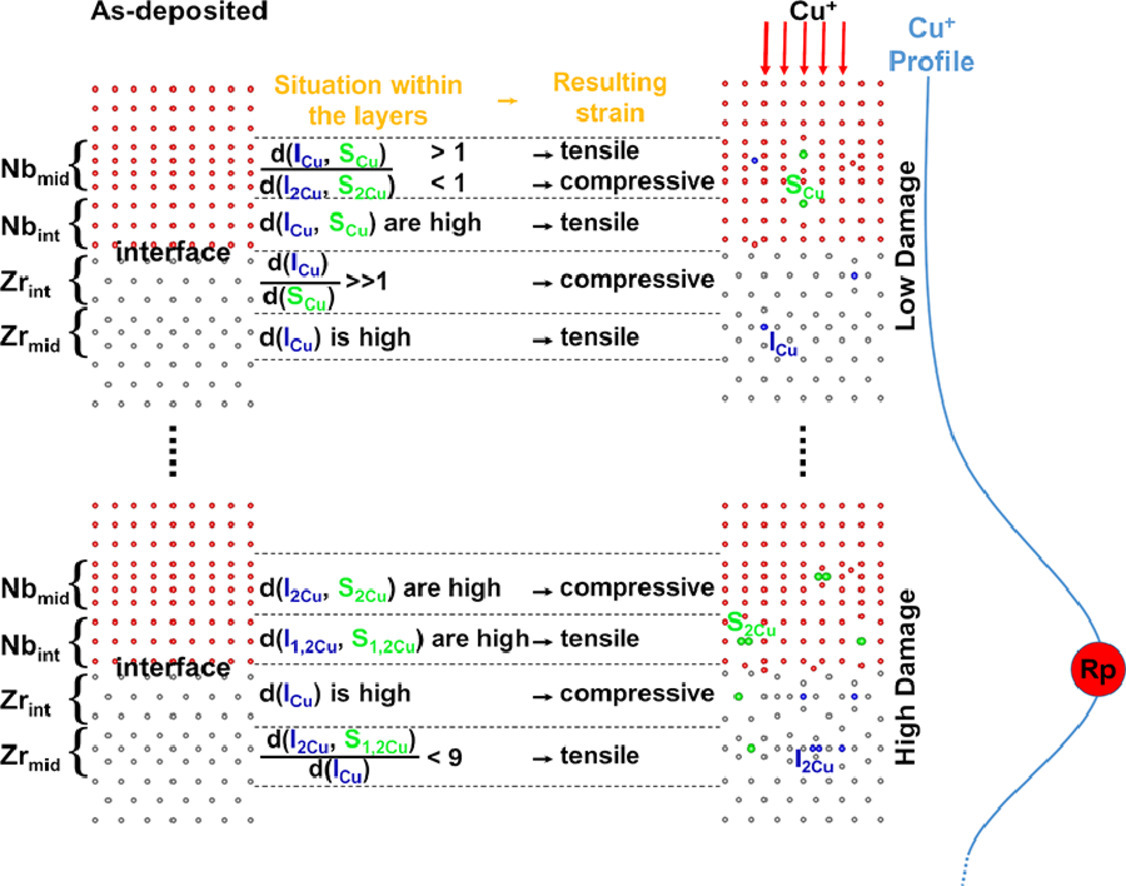
我们在高、低两种不同通量下,对溅射沉积制备的具有不同单层厚度(27nm或96nm)的Zr/Nb纳米金属多层薄膜注入了Cu+,随后采用了多种表征手段结合第一性原理计算,对其进行了研究。研究表明,注入Cu+后,薄层样品的Nb层中出现了沿c轴的拉伸应变,而Zr层中出现压缩应变,而厚层样品在Nb层和Zr层中均出现压缩应变。应变在薄层样品中较高,且随辐照通量的增加而增大。我们提出了一种数学方法来描述辐射损伤后,金属多层膜结构中的变形机制。在该模型中,单层累积的应变由界面应变和内部应变组成。模型的半解析解预测,界面应变占主导地位,并在界面周围的一定区域内扩展。这一结论得到了第一性原理计算的支持。第一性原理计算表明,空位和间隙原子在界面附近和Zr一侧比在Nb一侧具有更高的迁移率,因此具有更高的复合率,从而导致界面Zr侧的应变比Nb侧的应变小。我们将模型预测结果和第一性原理结合,得到了不同类型缺陷在不同离子损伤区的密度和分布。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P331-349
7. Dissecting functional degradation in NiTi shape memory alloys containing amorphous regions via atomistic simulations
含非晶区NiTi形状记忆合金功能退化的原子尺度模拟研究
Won-Seok Ko✉, Won Seok Choi✉, Guanglong Xu, Pyuck-Pa Choi, Yuji Ikeda, Blazej Grabowski
W.-S. Ko:wonsko@ulsan.ac.kr
P.-P. Choi:p.choi@kaist.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.070
摘要
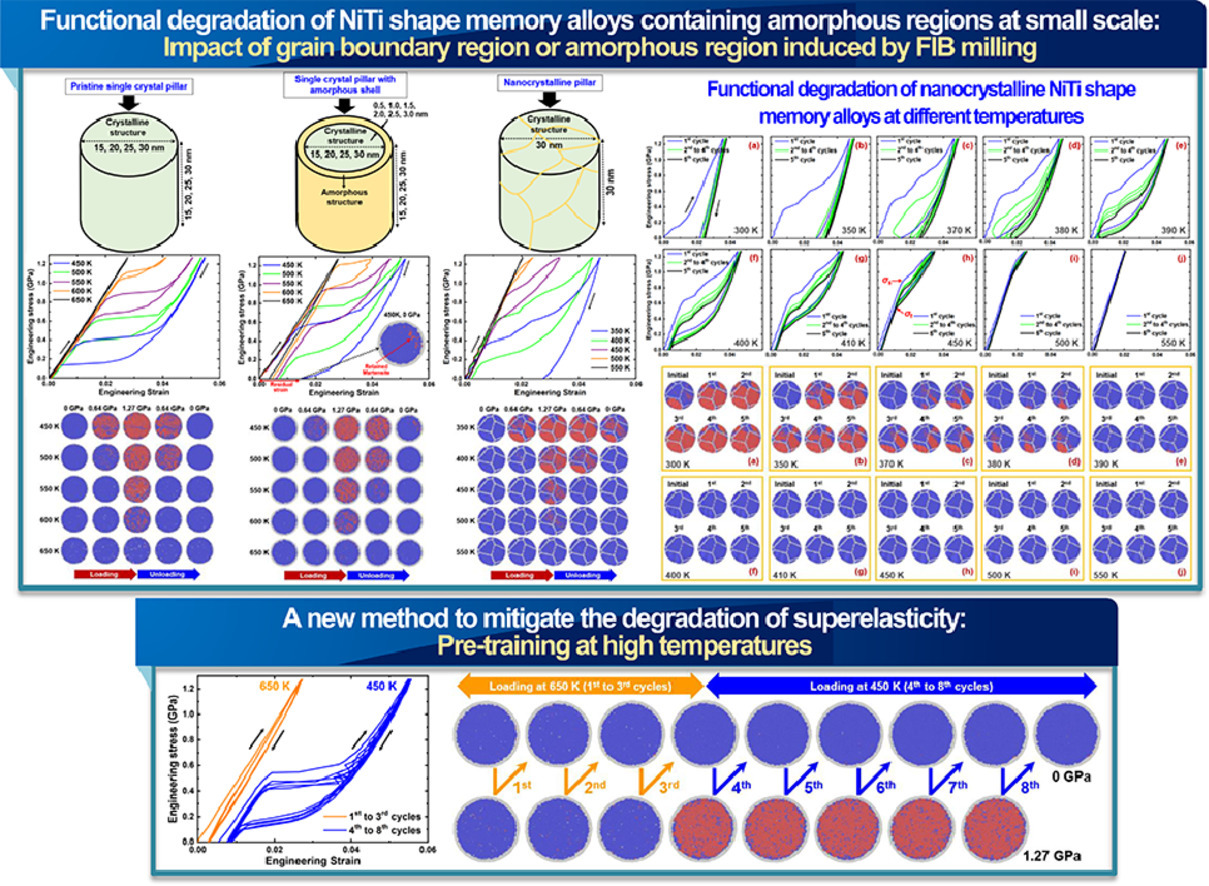
我们使用分子动力学模拟,对含非晶区的纳米NiTi形状记忆合金的性能劣化进行了详细研究。通过对相关原子过程的深入理解,我们对实验观测到的现象,即材料在循环载荷下的塑性变形积累和残余应变突然增加,进行了解释。研究表明,形状记忆合金微柱在循环压缩下的力学响应显著地受非晶晶界或表面的影响。在循环加载下超弹性退化的主要原因是塑性变形的累积和由非晶区、晶体区协同作用产生的残留马氏体。而由于非晶相的存在,增加了马氏体的稳定性,导致了循环载荷下应力平台和滞回的减小。我们基于上述的性能劣化机制,对已报导的恢复超弹性方法进行了验证,并提出了新的方法来阻止非晶和晶体区的协同作用,例如在小尺度上实现形状记忆合金功能的稳定运行。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P350-365
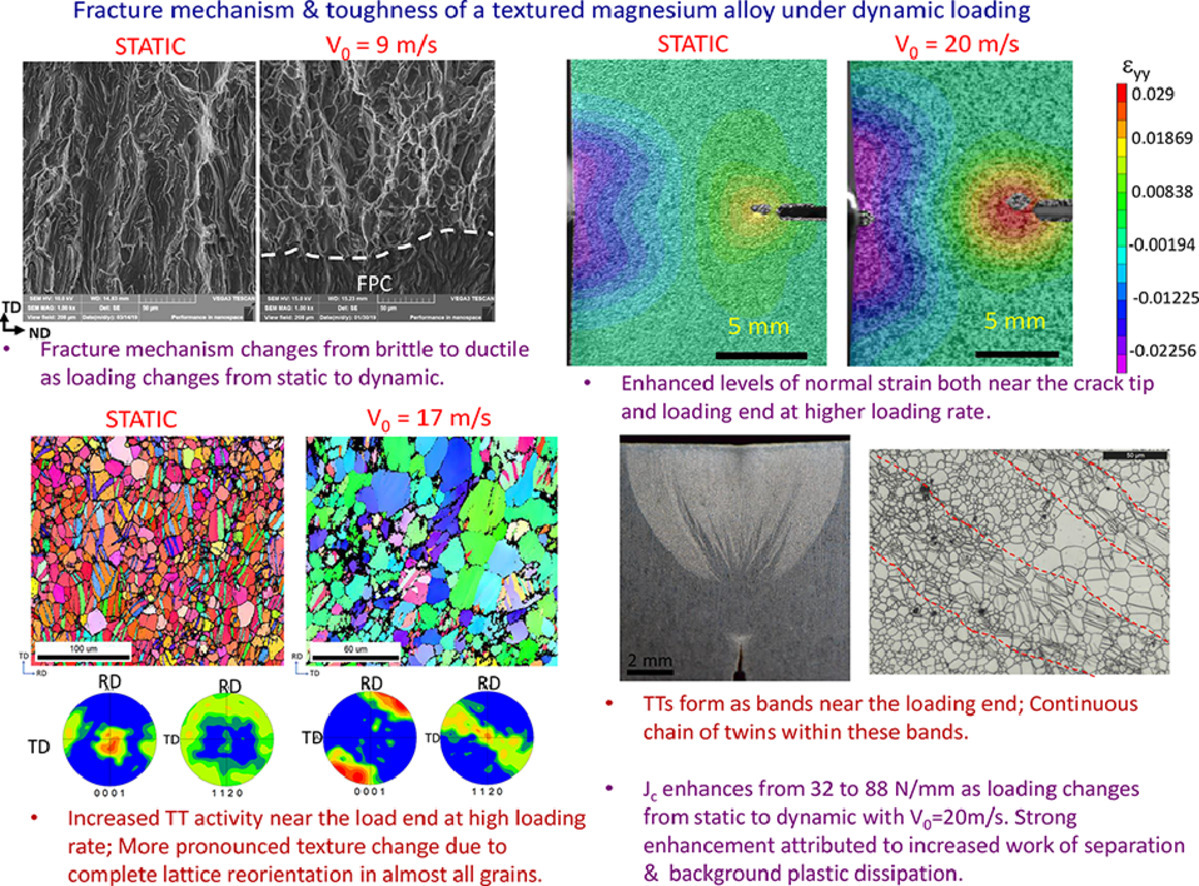
8. Fracture mechanism and toughness of a rolled magnesium alloy under dynamic loading
轧制镁合金在动态载荷下的韧性与断裂机理
Arjun Sreedhar S, Suraj Ravindran, Gyan Shankar, S. Suwas, R. Narasimhan✉
R. Narasimhan:narasi@iisc.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.059
摘要
我们使用了液压试验机和Hopkinson杆装置分别对轧态AZ31镁合金的疲劳预裂三点弯试样进行了静态和动态断裂试验,并采用原位光学成像结合数字分析对实验结果进行了解释。研究发现,试样在静态加载下的断裂机制为孪晶诱导准脆性断裂,而在动态加载下则转变为微孔洞长大聚集。且随着加载速率的增加,试样尖端附近的拉伸孪晶减少;而远端的孪晶密度和织构则显著增加。在高加载速率下,由于背景塑性区的能量耗散增加,使得材料的断裂韧性显著增强。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P387-398
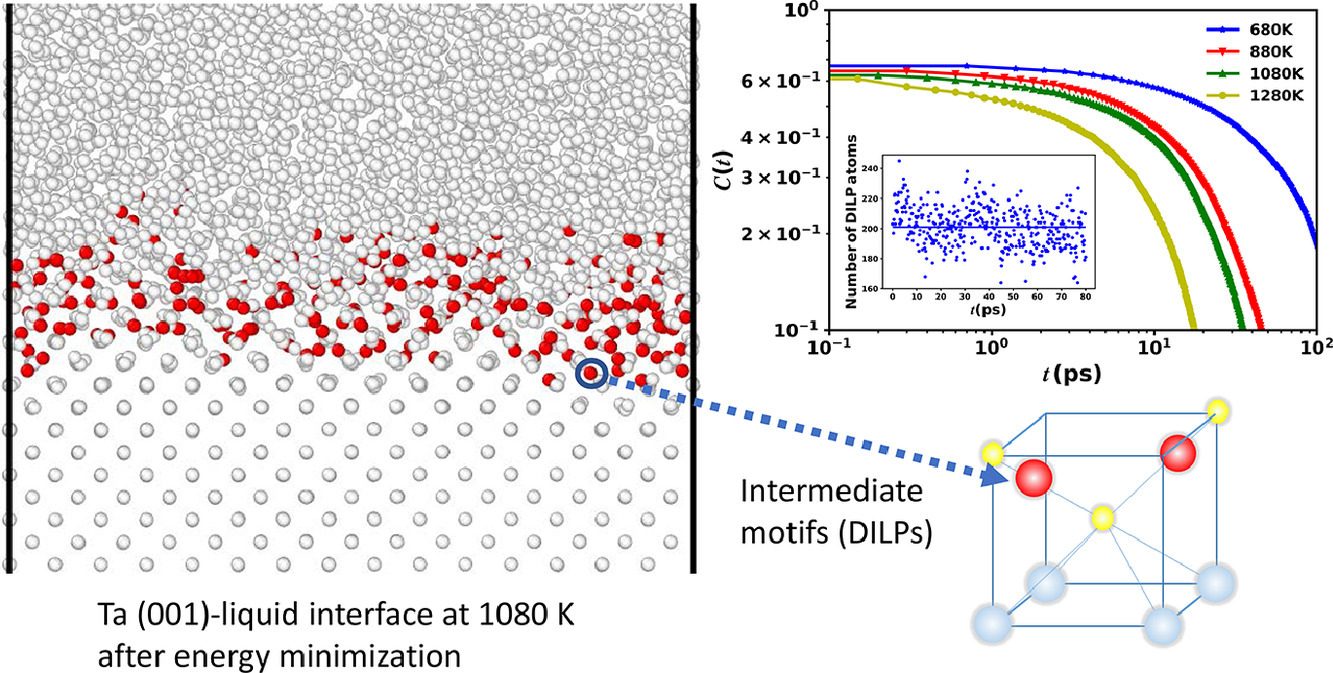
9. Intermediate structural evolution preceding growing BCC crystal interface in deeply undercooled monatomic metallic liquids
高度过冷的单一金属液体中BCC晶体生长前沿的中间态结构演化
Zhenzhen Yan, Howard Sheng, Evan Ma✉, Bin Xub, Jinfu Li, Lingti Kong✉
E. Ma:ema.matscieng@gmail.com
L.Kong:konglt@sjtu.edu.cn (上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.001
摘要
我们对高度过冷的单质金属液体凝固时,晶体/液体界面的结构演化进行了理论分析。具体来说,我们使用了分子动力学模拟了BCC晶体长大前沿哑铃状间隙原子对(DILPs)的演化过程。这种方法使我们能够详细研究DILPs在并入晶格前的分布、相互联系、能量、以及动力学状态。研究表明,在高度过冷条件下,DILP并入生长中的晶体需要大量的原子协同作用和重排,因此需要激活能垒。相比之下,对于FCC晶体的长大,这种中间态结构能以一维链的形式通过简单滑移并入晶格。以上过渡模态和活化能垒的差异,能够帮助我们从结构演化的角度,解释BCC和FCC金属在高度过冷液体中晶体生长的速度差异。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P399-416
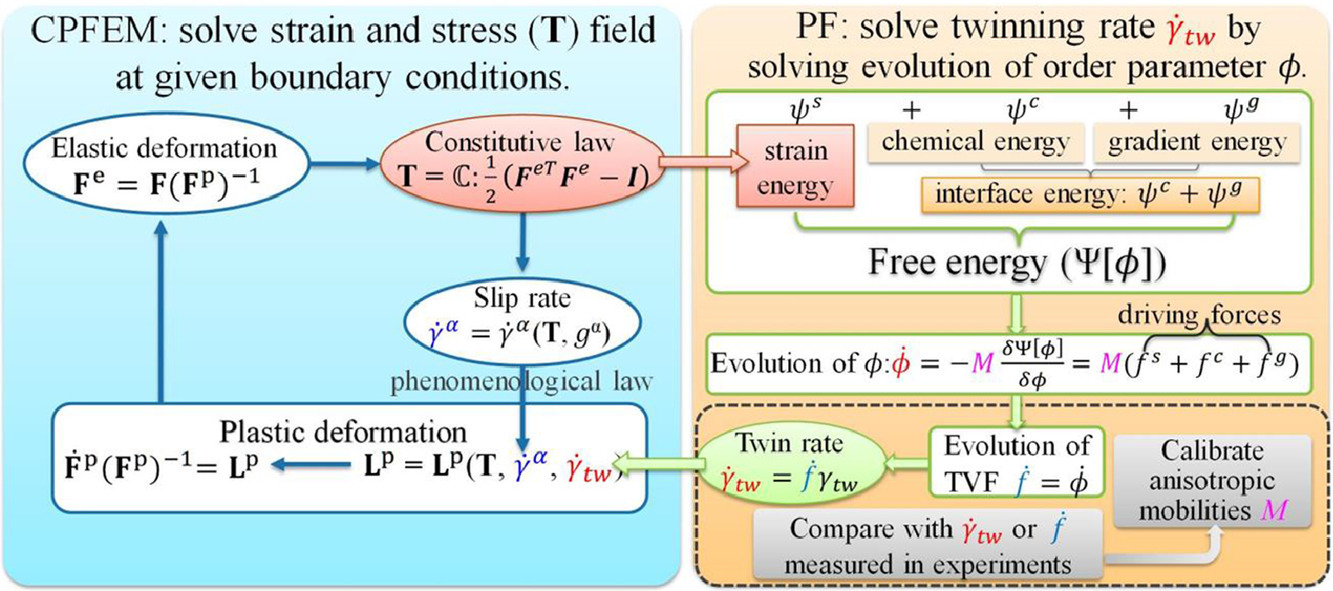
10. Coupled crystal plasticity finite element-phase field model with kinetics-controlled twinning mechanism for hexagonal metals
六方金属中动力学控制孪晶机制的有限元-相场耦合模型
Guisen Liu✉, Hanxuan Mo, Jian Wang, Yao Shen✉
G. Liu:liuguisen@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
Y. Shen:yaoshen@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.002
摘要
六方金属借助位错和孪晶的演化发生塑性变形。变形孪晶导致与晶体取向有关的孪晶畴的形成。在原子尺度上,孪晶畴通过孪晶位错/断点(TDs)的形核和运动来实现生长,而在微观/宏观尺度上,可以通过孪晶界(TBs)的迁移来对此进行描述。在本研究中,我们通过在微观尺度上耦合具有各向异性孪晶界迁移率的孪晶模型,建立了孪晶界迁移动力学的晶体塑性有限元-相场(CPFE-PF)模型。我们通过晶体塑性有限元(CPFEM)求解了位错滑移和孪生引起的弹性场和塑性变形。随后采用相场(PF)方法对孪晶畴与基体进行空间上的区分,并对孪晶界的迁移进行跟踪。孪晶界的迁移受孪晶驱动力和各向异性的晶界迁移率共同控制,其中迁移率借由实验测得的孪晶应变速率估计,而驱动力由晶体塑性有限元计算得到的应变能和由有限体积方法计算得到的界面能变化组成。值得一提的是,相场模型采用了实验测得的孪晶界面能和临界梯度准则来限制孪晶界的宽度。我们的CPFE-PF模型能够很好地预测实验观测到的孪晶长大行为,并可被进一步用于研究六方金属中与孪晶相关的组织演化和力学行为。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P417-436
11. Alloys-by-design: Application to new superalloys for additive manufacturing
利用增材制造方法设计制备新型高温合金
Yuanbo T. Tang, Chinnapat Panwisawas, Joseph N. Ghoussoub, Yilun Gong, John W.G. Clark, André A.N. Németh, D. Graham McCartney, Roger C. Reed✉
R.C. Reed:roger.reed@eng.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.09.023
摘要
我们使用了计算方法,设计出了可使用增材制造方法制备的新型γ/γ′镍基高温合金。在此过程中,我们充分考虑到了凝固和固态相变引起的裂纹和缺陷。我们使用激光粉末选区熔化方法对材料进行了试制,并将其与传统的IN939和CM247LC合金进行了比较。我们对材料进行了组织表征、热差分析和高温拉伸,结果表明设计出的新型合金具有优异的可加工性和力学性能。此外,我们对合金的设计模拟提出了一些可供改进的建议。
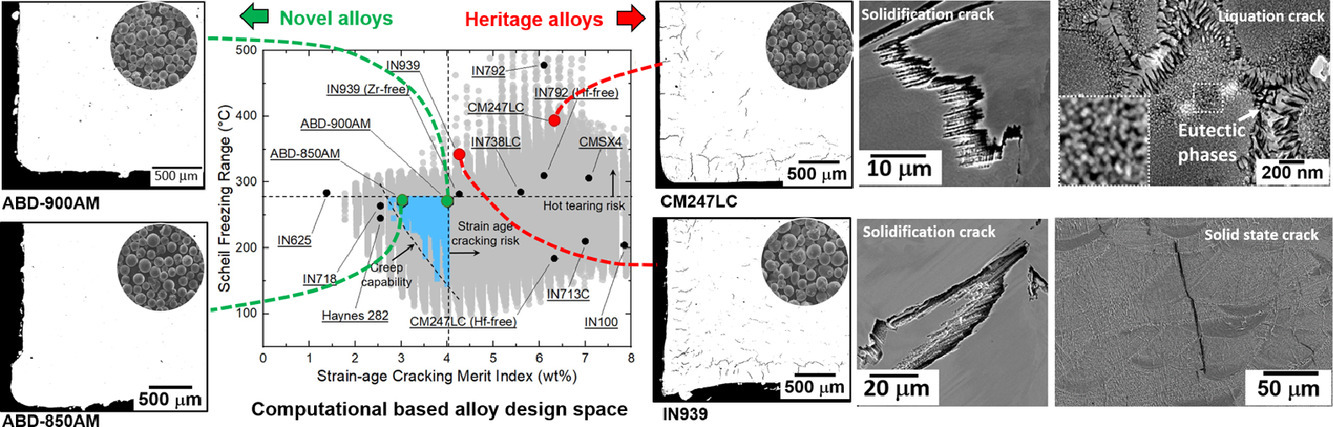

ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P448-462
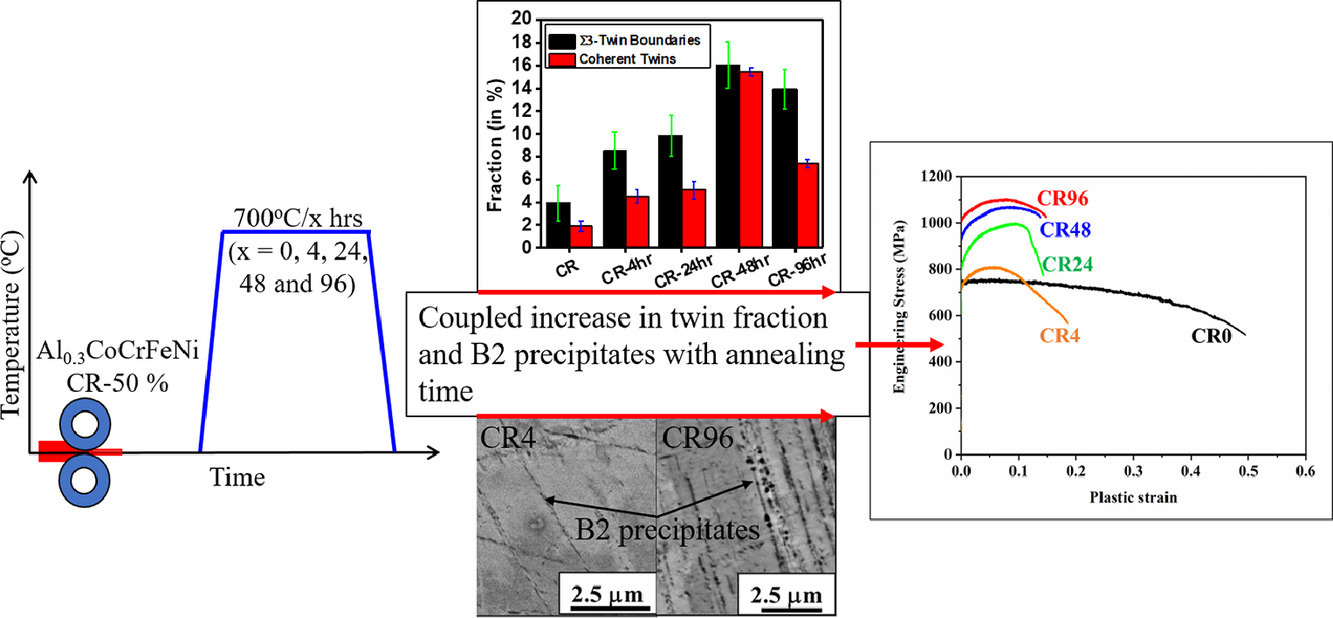
12. Recovery of cold-worked Al0.3CoCrFeNi complex concentrated alloy through twinning assisted B2 precipitation
B2析出诱导孪晶引起的冷加工Al0.3CoCrFeNi多组元合金回复过程研究
S. Dasari, A. Sarkar, A. Sharma✉, B. Gwalani, D. Choudhuri, V. Soni, S. Manda, I. Samajdar✉, R. Banerjee✉
A. Sharma:abhishek.sharma@unt.edu
I. Samajdar:indra@iitb.ac.in
R. Banerjee:raj.banerjee@unt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.071
摘要
虽然对纯金属和简单合金退火过程中的回复再结晶理论研究已经较为完善,但在高熵合金或多组元合金中(HEA/CCAs),对这一过程的系统研究却相当有限。本文研究了经冷加工的Al0.3CoCrFeNi合金在等温退火回复过程中,位错湮没、孪晶形成和析出相形成之间的复杂相互作用。冷加工后,合金中含有高密的形变孪晶;等温退火后 Σ3孪晶界的比例进一步增加,并成为B2有序相的非均匀形核位点。等温退火后的非均匀组织由为粗大的非再结晶FCC晶粒和均匀分布在晶界、变形带和孪晶处的B2析出相组成。拉伸屈服强度随退火时间的延长而增加,我们认为这是由于Σ3孪晶界增加和晶界处的B2相修饰共同导致的。在700°C长时间退火后,合金屈服强度约为1010MPa,延伸率约为15%,同时伴随应变硬化的大幅恢复。
ACTA
Vol. 202, 1 Jan. 2021, P463-477
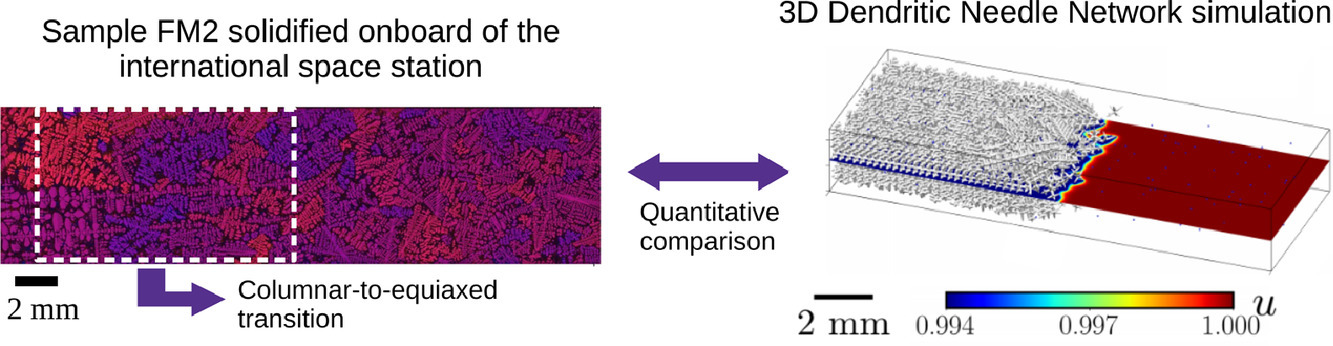
13. Dendritic needle network modeling of the Columnar-to-Equiaxed Transition. Part II: three dimensional formulation, implementation and comparison with experiments
柱状晶向等轴晶转变的枝状针形网络三维模型模拟与实验对比
Chih-Hung Chen✉, Amirhossein Molavi Tabrizi, Pierre-Antoine Geslin, Alain Karma✉
C.-H. Chen:chchen@iam.ntu.edu.tw (国立台湾大学)
A. Karma:a.karma@northeastern.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.012
摘要
枝状针形网络(DNN)模型通过追踪枝晶网络层级结构中枝晶前沿的扩散控制长大,可以很好地将不同尺度上的相场模型和粗晶模型联系起来。特别是,DNN模型放宽了粗晶模型中,对枝晶生长动力学和晶粒结构的假设。在本文的第一部分,我们提出了DNN模型的二维形式,并将其应用到了柱状晶-等轴晶转变(CET)的研究,阐明了这些假设对CET预测的影响。为了克服二维模型固有的局限性,在本文的第二部分,我们介绍了DNN模型的三维形式及其在CET中的应用。在验证了三维模型的有效性后,我们对Al-7wt.% Si合金的凝固过程进行了模拟,并将其与在国际空间站上进行的凝固项目实验结果进行了比较。结果表明,现有的三维DNN模型能够在实验的时间和长度尺度上定量地CET的位置和类型,而不需要任何可调参数。