金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.203,15 Jan. 2021(上)
2021-02-24 来源:Goal Science

本期包含金属材料领域论文10篇,涵盖了不锈钢、高熵合金、单晶与高温合金等,国内科研单位包括哈尔滨工业大学、大连理工大学、中科院金属所、南方科技大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 203 目录
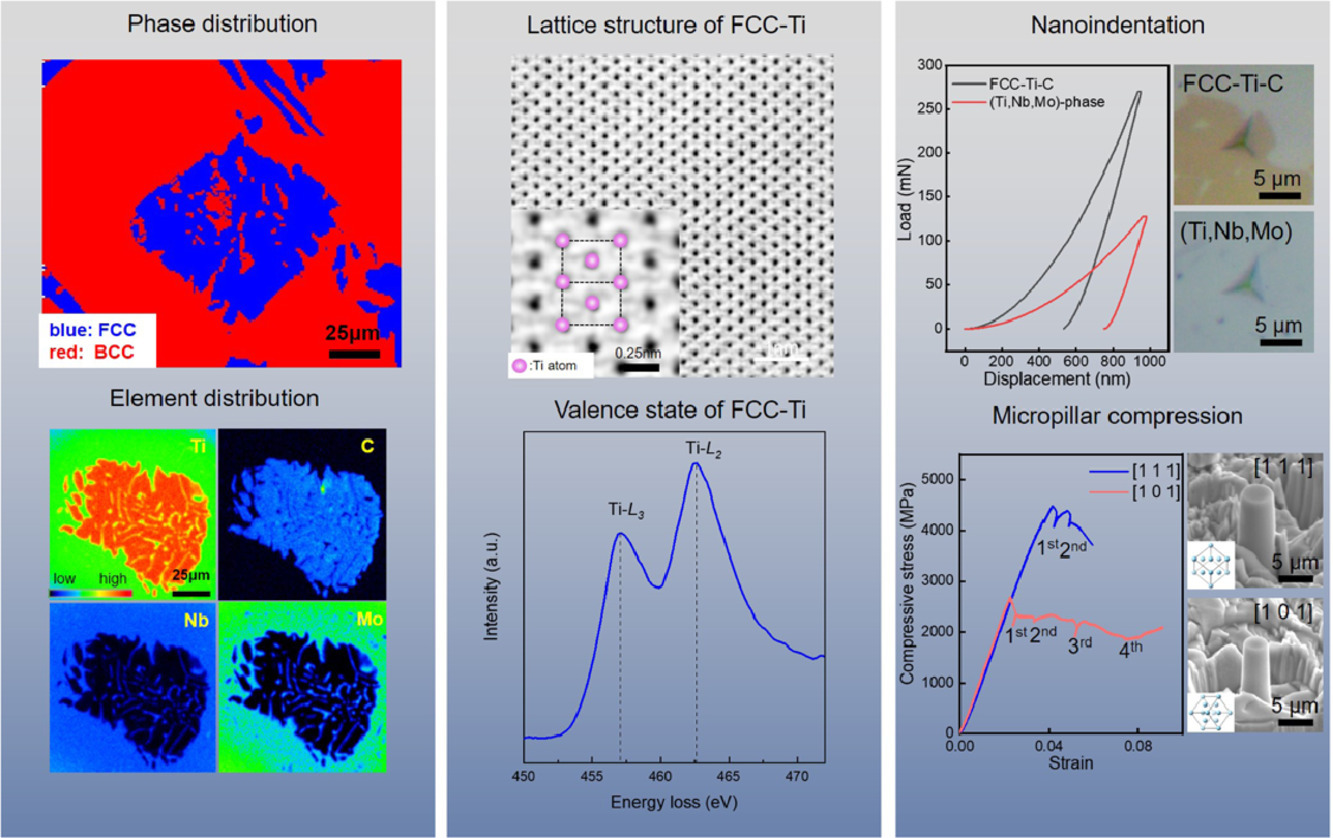
1. Interstitial carbon induced FCC-Ti exhibiting ultrahigh strength in a Ti37Nb28Mo28-C7 complex concentrated alloy
超高强度掺碳Ti37Nb28Mo28-C7多组分合金研究
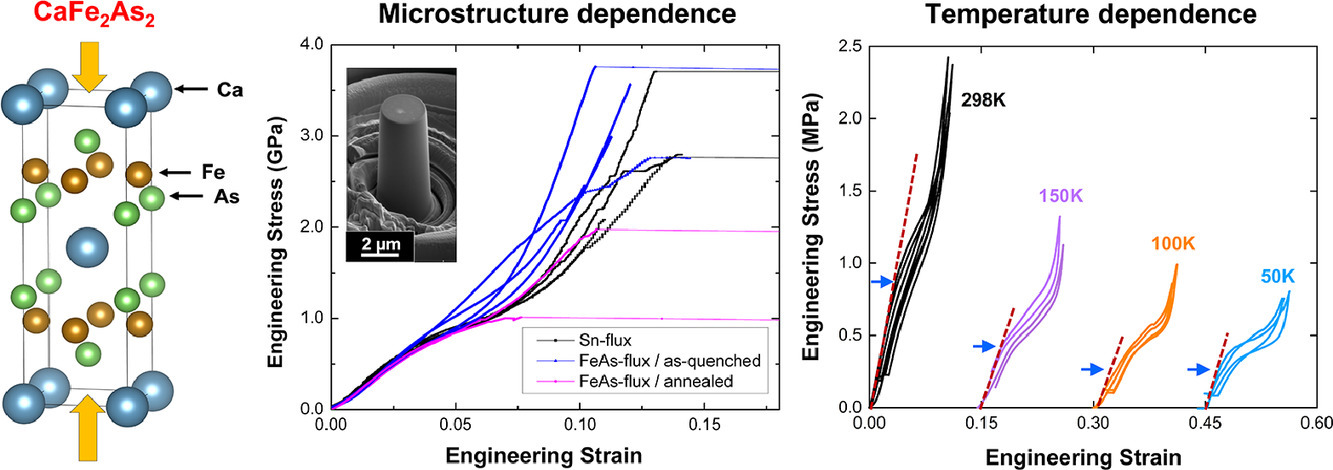
2. Uniaxial compression of [001]-oriented CaFe2As2 single crystals:the effects of microstructure and temperature on superelasticity Part I: Experimental observations
温度和微观组织对[001]取向CaFe2As2单晶单轴压缩超弹性影响的实验研究
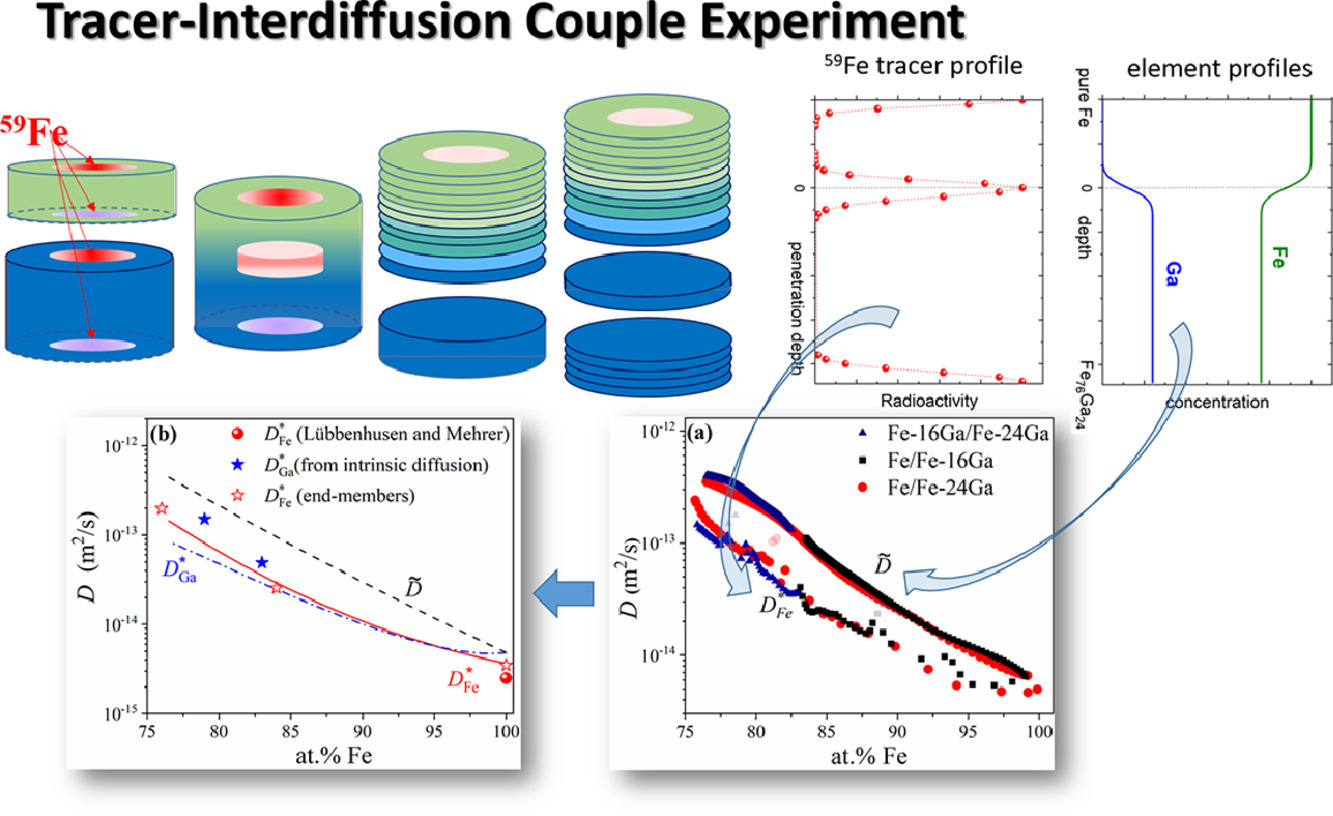
3. Composition dependence of tracer diffusion coefficients in Fe–Ga alloys: A case study by a tracer-diffusion couple method
通过示踪-扩散耦方法研究Fe-Ga合金中示踪剂扩散系数随成分的变化
4. Plastic deformation of single crystals of the equiatomic Cr−Mn−Fe−Co−Ni high-entropy alloy in tension and compression from 10 K to 1273 K
等原子比Cr−Mn−Fe−Co−Ni高熵合金单晶在10~ 1273K范围内的拉伸和压缩塑性变形行为研究
5. The Mechanical Response of Nanoporous Gold and Silver Foams with Varying Composition and Surface Segregation
具有不同成分和表面偏聚的Au-Ag纳米多孔泡沫材料的力学性能研究
6. Ultra-high temperature deformation in a single crystal superalloy: Mesoscale process simulation and micromechanisms
单晶高温合金在极高温度下形变的微观机制与介观模拟
7. New insights on cellular structures strengthening mechanisms and thermal stability of an austenitic stainless steel fabricated by laser powder-bed-fusion
激光粉末熔炼制备奥氏体不锈钢的胞状结构、强化机理和热稳定性研究
8. Cuboidal γ' phase coherent precipitation-strengthened Cu–Ni–Al alloys with high softening temperature
具有较高软化温度的共格γ′相析出强化Cu-Ni-Al合金
9. Study on the mechanism of hydrostatic pressure promoting electrochemical corrosion of pure iron in 3.5% NaCl solution
静水压力促进纯铁在3.5% NaCl溶液中电化学腐蚀的机理研究
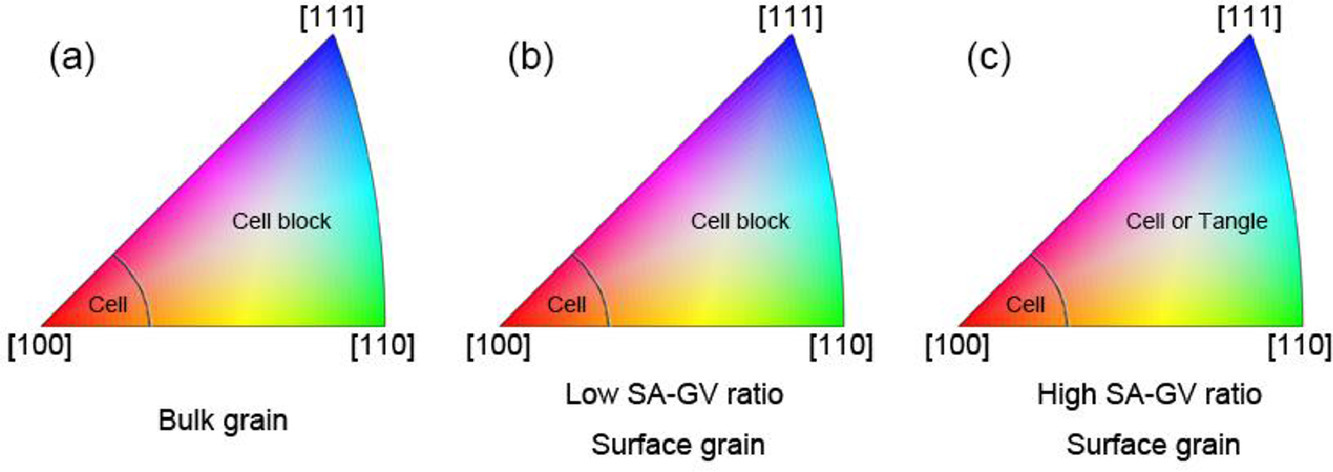
10. Orientation dependence of dislocation structure in surface grain of pure copper deformed in tension
拉伸变形过程中纯铜表面晶粒中位错结构与取向的关系
ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116456
1. Interstitial carbon induced FCC-Ti exhibiting ultrahigh strength in a Ti37Nb28Mo28-C7 complex concentrated alloy
超高强度掺碳Ti37Nb28Mo28-C7 多组分合金研究
Shan Jianga, Lujun Huang✉, Xiang Gao, Gang Liu, Rui Zhang, Yang Jiaoa, Shang Peng, Qi An, Shuai Wang, Lin Geng
L. Huang:huanglujun@hit.edu.cn(哈尔滨工业大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.075
摘要
我们在掺碳的Ti37Nb28Mo28-C7 at.%多组分合金(TNMC合金)中观察到了一种间隙碳原子诱导形成的FCC-Ti。我们使用球差校正STEM表征了FCC-Ti的晶体结构,并通过纳米压痕和微柱压缩测试了其力学性能。结果表明,FCC-Ti的纳米硬度和弹性模量都较高,分别为17.8GPa和233.1GPa。微柱压缩试验表明,间隙碳原子诱导FCC-Ti的具有极高的强度([1 1 1]方向4.48 GPa,[1 0 1]方向2.67 GPa,CRSS为1.12 ± 0.07 GPa)。通过第一性原理计算,我们发现这种FCC-Ti的性质由于间隙碳原子引起的晶格结构重排引起的。本研究加深了对FCC-Ti性质以及间隙原子在多组元合金中作用的理解,为未来的材料设计提供了无限可能。
ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116464
2. Uniaxial compression of [001]-oriented CaFe2As2 single crystals:the effects of microstructure and temperature on superelasticity Part I: Experimental observations
温度和微观组织对[001]取向CaFe2As2单晶单轴压缩超弹性影响的实验研究
John T. Sypek, Sriram Vijayan, Ian Bakst, Shuyang Xiao, Matthew J. Kramer, Paul C. Canfield, Mark Aindow, Christopher R. Weinberger, Seok-Woo Lee✉
S.-W. Lee:seok-woo.lee@uconn.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.006
摘要
微柱压缩实验表明,[001]取向的CaFe2As2单晶具有超弹性,弹性极限高达10%以上。超弹性的主要机制为:CaFe2As2的四方晶型相变是一个单轴收缩过程,在此过程中,横跨Ca平面形成As-As键。通常情况下,超弹性和相关相变容易受微观组织和温度影响。因此,在本研究中,我们通过低温原位机械测试结合透射电镜,研究了组织和温度对从液相生长的CaFe2As2单晶上切下的[001]取向微柱超弹性的影响。研究表明,CaFe2As2的组织受晶体生长条件和后续热处理的影响很大。Ca、As空位和FeAs纳米析出对材料力学行为有显著影响。此外,随着温度的降低,四方晶型相变的起始应力逐渐减小。我们对实验结果基于As-As键的形成进行了讨论,而这种As-As键是超弹性机制的基本特征。综上所述,本研究为CaFe2As2在单轴压缩下表现出的超弹性提供了更加深入的认识。
ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116446
3. Composition dependence of tracer diffusion coefficients in Fe–Ga alloys: A case study by a tracer-diffusion couple method
通过示踪-扩散耦方法研究Fe-Ga合金中示踪剂扩散系数随成分的变化
G.M. Muralikrishna, B. Tas a, N. Esakkiraja, V.A. Esin, K.C. Hari Kumar, I.S. Golovin, I.V. Belova, G.E. Murch, A. Paul, S.V. Divinski ✉
S.V. Divinski:divin@uni-muenster.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.065
摘要
我们在没有合适放射性同位素和可靠的热力学参数的条件下,利用创新性的放射性示踪-扩散偶技术,对示踪剂的扩散系数成功进行了估算。我们在扩散系数与成分具有较强关联的Fe-Ga合金体系中通过实验获取了可靠、可重复的迁移率数据,证明了这一方法的可行性。我们在1143 K同时测量了Fe/Fe-16 Ga、Fe/Fe-24 Ga和Fe-16 Ga/Fe-24 Ga三种扩散偶中的59Fe浓度和互扩散系数。对于不同扩散偶,在扩散区间内得到的结果相互之间有很好的一致性。我们评估了摩尔体积对59Fe和互扩散系数测量结果的影响,并基于热力学计算和Darken-Manning关系,对0-24 at.% Ga成分范围内Ga示踪剂的扩散系数和空位系数进行了估计。本研究的结果证明了放射性示踪-扩散偶技术在高精度测量扩散数据方面的可靠性。进而有助于Fe-Ga BCC系统中的迁移率研究。我们通过实验测定了Kirkendall标记面处的Fe、Ga示踪剂扩散系数比值,并利用辐射示踪方法直接测量了Fe示踪剂的扩散系数,从而对Ga示踪剂的扩散系数进行了细致估算。

ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116454
4. Plastic deformation of single crystals of the equiatomic Cr−Mn−Fe−Co−Ni high-entropy alloy in tension and compression from 10 K to 1273 K
等原子比Cr−Mn−Fe−Co−Ni高熵合金单晶在10~ 1273K范围内的拉伸和压缩塑性变形行为研究
Marino Kawamura, Makoto Asakura, Norihiko L. Okamoto✉, Kyosuke Kishida, Haruyuki Inui, Easo P. George
N.L. Okamoto:nlokamoto@tohoku.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.073
摘要
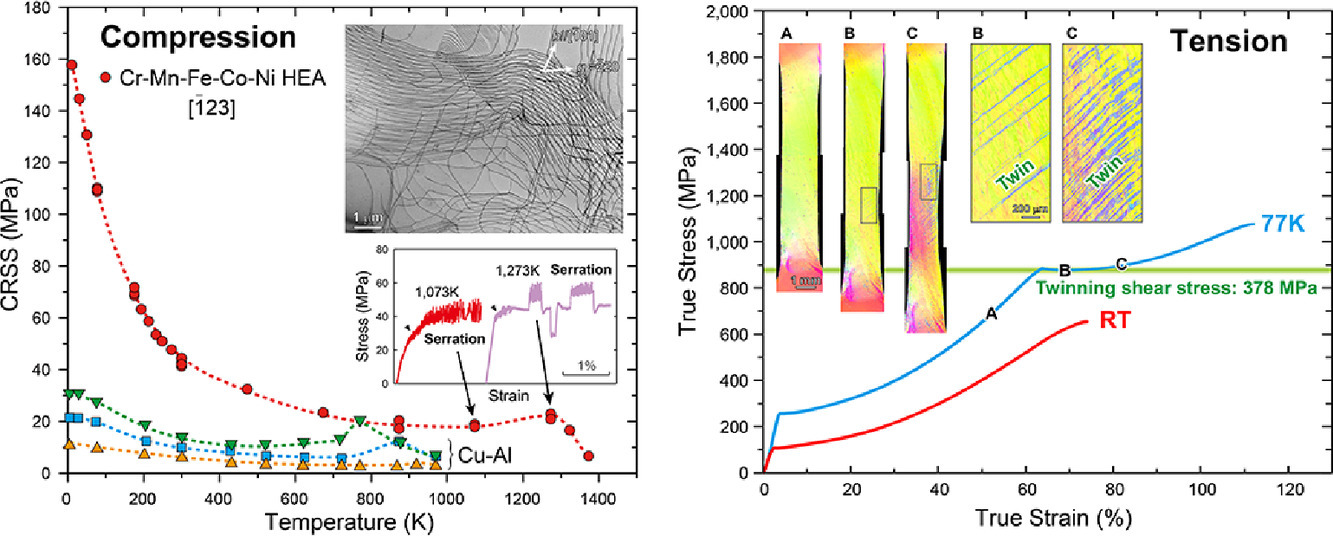
我们在10K到1373K的范围内,研究了面心立方五元等原子比Cr-Mn-Fe-Co-Ni高熵单晶合金(HEA)在拉伸和压缩条件下的塑性变形行为随晶体取向和温度的变化。室温下,{111}<110>滑移的临界剪切应力(CRSS)为42-45MPa。它与晶体取向和与载荷形式(拉伸/压缩)关系不大。该值随温度的降低而增加,基于测得的屈服应力进行外延估计,可得0K下的CRSS值为168MPa。在低温下,实验中流变应力对应变速率敏感的特点与活化体积较小是一致的。应力等效对CRSS的温度依赖性和活化体积依赖性均成立,表明固溶硬化是材料的主要强化机制。77K下材料发生孪晶,而孪晶在室温下不发生,因此77K下拉伸伸长率显著提高。77 K下,当材料通过滑移和线性加工硬化实现85%塑性形变后,共轭(-1-11)平面上的剪切应力达到378 MPa,形变孪生以吕德斯带的形式发生。
ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116445
5. The Mechanical Response of Nanoporous Gold and Silver Foams with Varying Composition and Surface Segregation
具有不同成分和表面偏聚的Au-Ag纳米多孔泡沫材料的力学性能研究
Nathan Beets✉, Diana Farkas, Karsten Albe
N. Beets:bnathan2@vt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.064
摘要
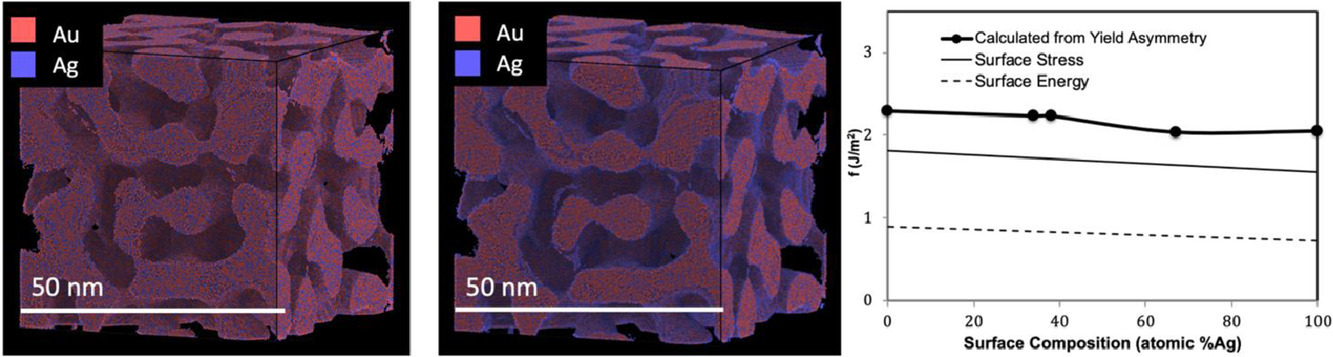
我们通过分子动力学模拟研究了Au-Ag纳米多孔泡沫的力学性能,并通过蒙特卡洛模拟了材料中的偏聚效应。研究表明,在纳米多孔Au中加入Ag可以提高材料的强度。我们对合金和纯金属中的位错演化进行了比较分析,发现屈服性能取决于表面成分和相应的毛细作用力,而弹性性能则取决于材料的体成分。我们通过考虑表面效应,成功建立了一个能够准确预测材料屈服强度随尺寸和表面成分变化的模型。
ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116468
6. Ultra-high temperature deformation in a single crystal superalloy: Mesoscale process simulation and micromechanisms
单晶高温合金在极高温度下形变的微观机制与介观模拟
Yuanbo T. Tang, Neil D’Souza, Bryan Roebuck, Phani Karamched, Chinnapat Panwisawas, David M. Collins✉
D.M. Collins:d.m.collins@bham.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.010
摘要
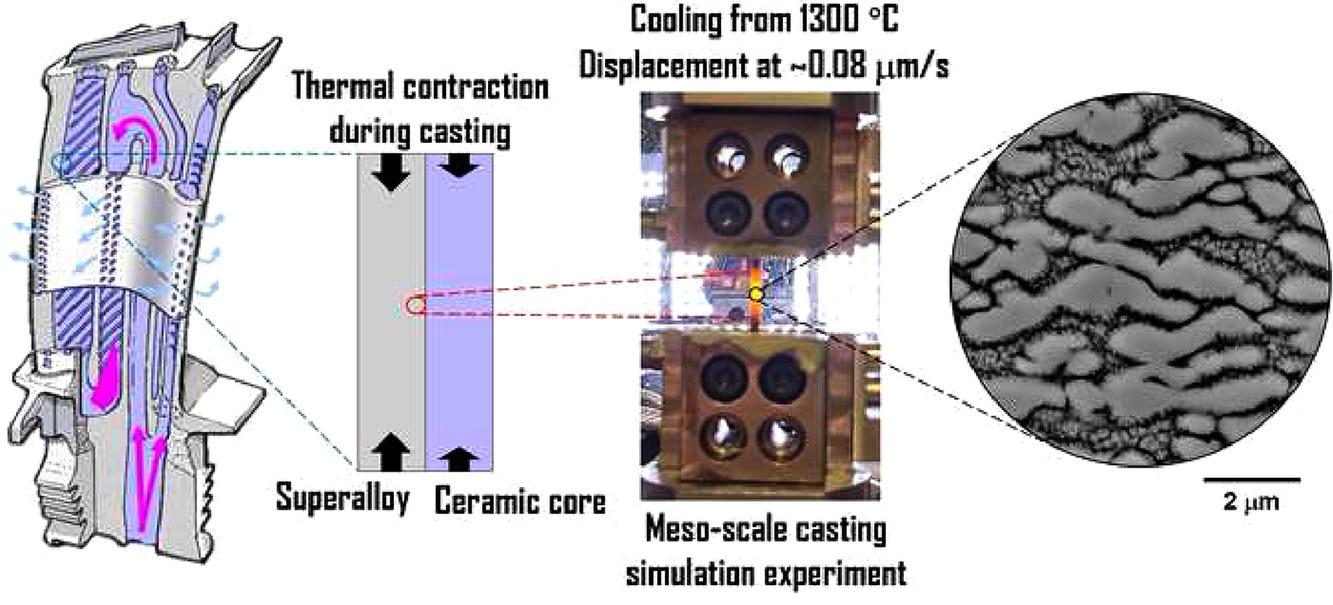
我们通过对镍基单晶高温合金的介观研究和工艺模拟,揭示了材料微观组织演化与机械性能之间的复杂相互作用。由于试样的标距段的体积小于生产它们的母体材料中芯结构,这种细微的成分差异导致了二次枝晶间距、γ′固溶温度和可逆γ/γ′组织的差异,进而导致了不同的加工硬化速率。由于八面体长大和N型漂流溶质传输机制的存在,使得γ′沉淀物呈蝴蝶状。高分辨率背散电子衍射(HR-EBSD)表征揭示了γ/γ′组织的形变模式,几何必要位错密布在γ/γ′界面,而Orowan环则作为传导塑性的机制。对残余弹性应力的表征表明,蝶形γ′析出显著增强形变不均匀性,导致γ相中的应力状态有利于滑移,并促进γ′析出的进一步生长。这种局部塑性和残余应力的共同作用是铸造后均一化热处理过程中再结晶缺陷形成的关键。
ACTA
Vol. 203, 15 Jan. 2021, 116476
7. New insights on cellular structures strengthening mechanisms and thermal stability of an austenitic stainless steel fabricated by laser powder-bed-fusion
激光粉末熔炼制备奥氏体不锈钢的胞状结构、强化机理和热稳定性研究
Thomas Voisin✉, Jean-Baptiste Forien, Aurelien Perron, Sylvie Aubry, Nicolas Bertin,
Amit Samanta, Alexander Baker, Y. Morris Wang
T. Voisin:voisin2@llnl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.018
摘要
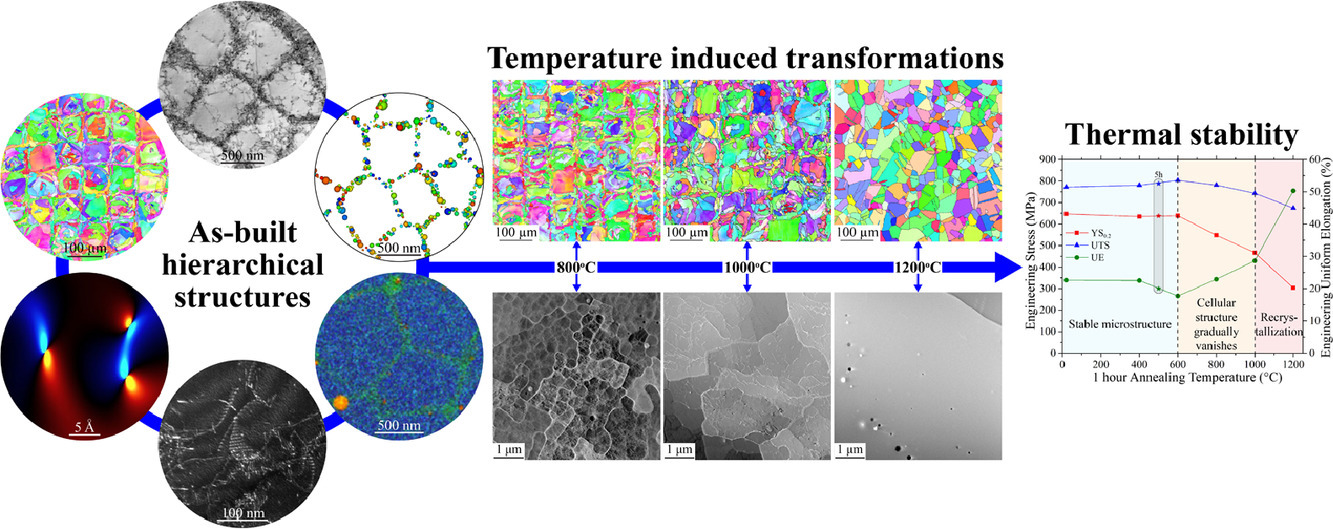
众所周知,快速凝固导致的胞状结构对激光粉末熔炼(L-PBF)制备的316L奥氏体不锈钢的高强度和高延展性具有重要作用。尽管如此,关于胞状结构的内在特征(如取向、位错、析出、元素偏聚等)及其对材料强度和热稳定性的影响仍有待研究。我们使用透射电子显微镜(TEM)对各种强化机制进行了研究,并发现胞壁遵循特定的晶体学取向。研究发现,胞壁内部的高密度位错具有较高的分解倾向,进而形成层错,而氧化物析出则被限制在胞壁内部。这些缺陷在塑性变形时能够阻碍位错运动,提高材料强度。位错动态模拟表明,聚集的颗粒能有效地在局部阻碍位错,促进位错胞形成和材料强化。为了研究L-PBF 316L SS的热稳定性,我们对材料进行了系统的400-1200℃热处理。通过背散电子衍射、TEM和同步辐射X射线衍射组织表征,结合位错动力学、CALPHAD模拟和拉伸试验,我们发现存在三个热处理区间,可对材料的组织-性能进行调控。600℃退火后,组织保持稳定,但应变硬化行为发生改变,材料仍保持高强度和高延展性。600-1000℃之间退火将激活元素扩散,胞壁逐渐消失,导致屈服强度显著下降。小角度晶界在1000℃以下保持稳定,而平均晶粒尺寸在800℃以下几近不变。1100℃以上退火可以消除所有的L-PBF特有结构,使材料组织接近传统组织。与传统制备方法相比,L-PBF 316L不锈钢在高温下具有更高的热稳定性和优异的性能。
ACTA
Vol. 203, 15 Jan. 2021, 116458
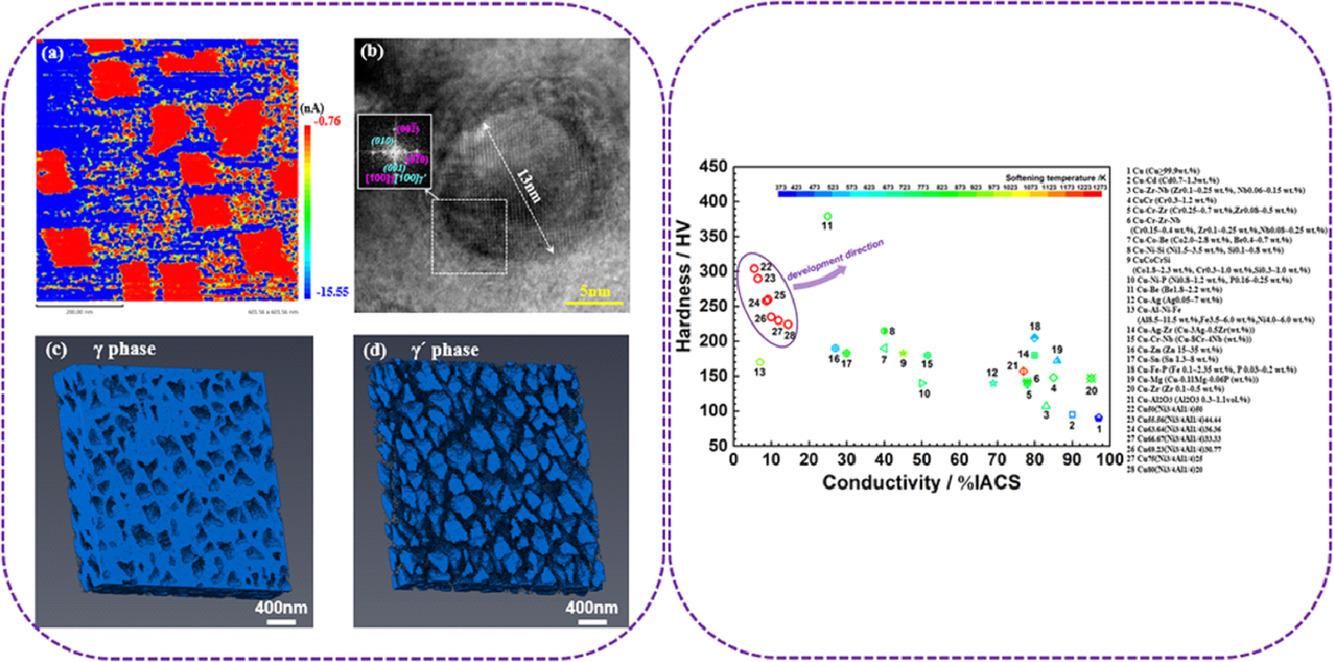
8. Cuboidal γ' phase coherent precipitation-strengthened Cu–Ni–Al alloys with high softening temperature
具有较高软化温度的共格γ′相析出强化Cu-Ni-Al合金
Z.M. Li, X.N. Li✉, Y.L. Hu, Y.H. Zheng, M. Yang, N.J. Li, L.X. Bi, R.W. Liu, Q. Wang, C. Dong, Y.X. Jiang, X.W. Zhang
X.N. Li:lixiaona@dlut.edu.cn(大连理工大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.076
摘要
γ'相立方共格析出对于提高镍基合金的高温性能具有重要作用。本工作旨在将这种强化机制引入铜合金中,以提高其高温性能。我们在(Ni+Al)含量为20~50 at. %的范围内,成功制备了一系列立方共格γ'相析出强化的Cu100-y(Ni3/4Al1/4)y合金。研究表明,这些合金具有优良的综合力学性能和高熔点,软化温度在1273K以上。由于弥散γ′相的作用,使得材料的硬度和屈服强度随温度的升高而增加。原子力显微镜表征和三维组织重建表明,Cu100-y(Ni3/4Al1/4)y合金中的γ相仍为导体。我们对材料的电阻随温度的变化进行了表征和讨论,发现由于γ'相的析出,使得材料的电阻和热稳定性有所提高。与其他商业化Cu合金相比,γ'相强化Cu合金在高温环境下具有很大的应用潜力。同时,我们计划对Cu100-y(Ni3/4Al1/4)y的合金成分进行进一步设计优化,以提高其综合性能。
ACTA
Vol. 203, 15 Jan. 2021, 116467
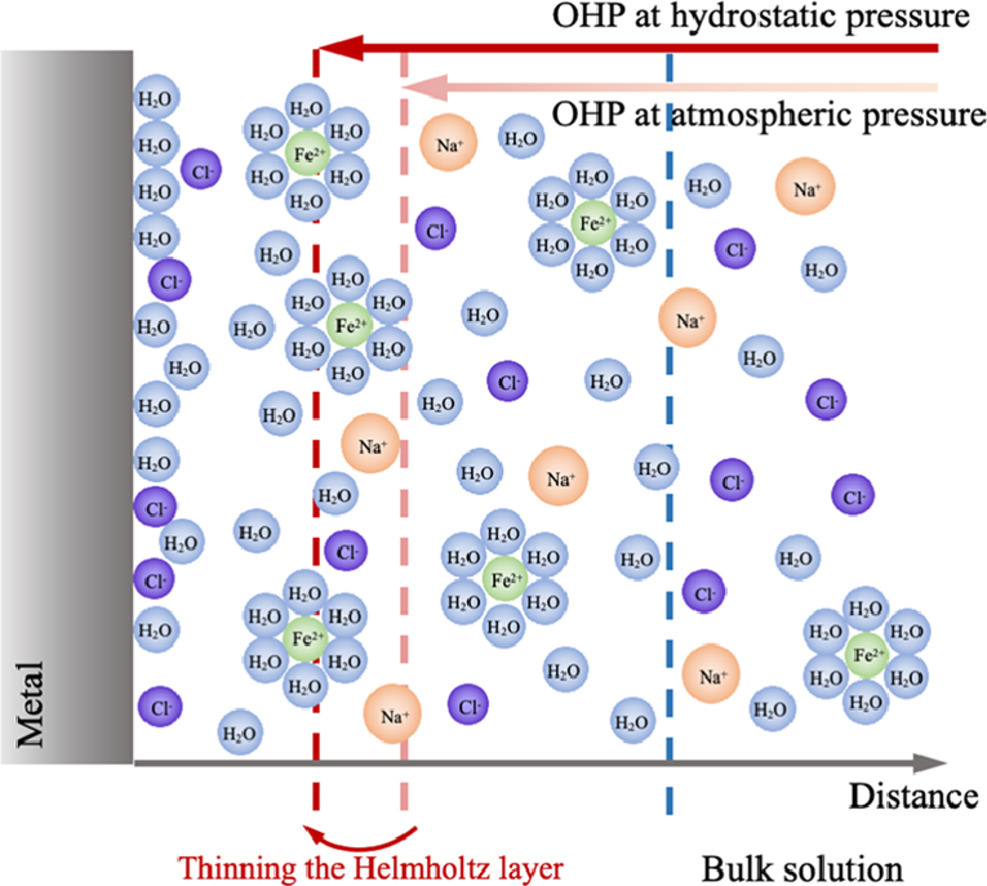
9. Study on the mechanism of hydrostatic pressure promoting electrochemical corrosion of pure iron in 3.5% NaCl solution
静水压力促进纯铁在3.5% NaCl溶液中电化学腐蚀的机理研究
Rui Liu, Yu Cui, Li Liu✉, Fuhui Wang
L. Liu:liuli@mail.neu.edu.cn(中科院金属所/中国科学技术大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.009
摘要
我们采用电化学测量和分子动力学模拟,研究了不同静水压力下,纯铁在3.5%NaCl溶液中的电化学腐蚀机制。结果表明,静水压通过改变金属/溶液界面的Fe2+浓度和降低Helmholtz层的厚度来放大了ψ1效应,这是静水压下铁溶解加快的决定因素。相反,Cl-在铁表面的吸附在静水压促进腐蚀的过程中并没有起到重要作用。
ACTA
Vol. 203, 15 Jan. 2021, 116474
10. Orientation dependence of dislocation structure in surface grain of pure copper deformed in tension
拉伸变形过程中纯铜表面晶粒中位错结构与取向的关系
Qingqing Sun✉, Yong Ni, Shuai Wang✉
Q. Sun:sunqq@sustech.edu.cn (南方科技大学/中国科技大学)
S. Wang:wangs@sustech.edu.cn(南方科技大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.016
摘要
我们研究了张力作用下纯铜表面晶粒取向对于位错结构的影响,并将其与块体内部晶粒进行了比较。给定应变下,[100]-[100]表面晶粒的位错结构以位错胞为主,与内部晶粒相同。对于[110]-[110]和[110]-[111],在一定应变范围内,块体内部晶粒中的位错结构以位错胞塞积为主,而表面晶粒中的位错结构可以根据晶粒的几何形状和应变水平演变为位错胞塞积或缠结。表面晶粒的镜像力作用将导致表面晶粒中的位错结构演化被推迟。研究结果表明,纯铜表面晶粒中的位错演化不仅与取向有关,也与晶粒的几何形状密切相关。