金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.196, 15 Apr. 2021
2021-03-21 来源:Goal Science
Vol. 196 目录
1. On the oxygen-induced hot cracking in a direct laser deposited Ni-based superalloy
直接激光沉积镍基高温合金中氧致热裂的研究
2. On short-range order strengthening and its role in high-entropy alloys
高熵合金中短程有序强化及其作用
3. Roles of reinforcements in twin nucleation and nano-α precipitation in the hybrid TiB/TiC-reinforced titanium matrix composites during high-temperature fatigue
TiB/TiC增强钛基复合材料在高温疲劳过程中增强体对孪晶形核和纳米α析出的影响
4. Tantalum and molybdenum barriers to prevent carbon diffusion in spark plasma sintered tungsten
放电等离子烧结钨中钽和钼对碳的扩散的阻碍作用
5. The evolution of Σ3 grain boundaries in the strip-cast Hi-B grain orientated Fe-6.5% Si alloy
带铸Hi-B晶粒取向的Fe-6.5%Si合金中Σ3晶界的演变
6. Temperature driven texture and grain boundary engineering of electrodeposited β-Sn coatings and its effect on the coating corrosion behaviour: Five-parameter grain boundary character distribution analysis study
电沉积β-Sn涂层的温度驱动织构和晶界工程及其对涂层腐蚀行为的影响:五参数晶界特征分布分析
7. A strategy to introduce gradient equiaxed grains into Zr sheet by combining laser surface treatment, rolling and annealing
采用激光表面处理、轧制和退火相结合的方法在Zr板材中引入梯度等轴晶粒
8. Heterostructured bulk aluminum with controllable gradient structure: Fabrication strategy and deformation mechanisms
可控梯度结构的异质结构块状铝:制备策略和变形机理
9. Fine scale alpha precipitation in Ti-19at.%V in the absence of influence from omega precipitates
在不受ω析出影响的情况下,Ti-19at.%V中精细尺度的α析出
10. Suppression of abnormal grain growth in friction-stir welded Al-Cu-Mg alloy by lowering of welding temperature
降低焊接温度抑制搅拌摩擦焊Al-Cu-Mg合金中晶粒的异常生长
SCRIPTA
Vol. 196, 1 Apr. 2021, 113751
1. On the oxygen-induced hot cracking in a direct laser deposited Ni-based superalloy
直接激光沉积镍基高温合金中氧致热裂的研究
KenHee Ryou, Boryung Yoo, Pyuck-Pa Choi✉
Pyuck-Pa Choi: p.choi@kaist.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113751
我们利用联合电子、X射线和原子显微镜等技术,报道了在直接激光沉积镍基高温合金中观察到的一种新型热裂机制。所观察到的裂纹主要与在晶内和晶界上形成的Ni和Mo氧化物有关。使用原子探针层析成像技术,我们在氧化物颗粒和基体合金之间检测到了中间区域,在中间区域中氧存在于固溶体中,化学成分因氧化物的形成而变化。成分的变化降低了基体的熔点,而氧化物的存在促进了应力集中和裂纹的形核,从而在再加热过程中产生了熔融开裂。


SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113754
2. On short-range order strengthening and its role in high-entropy alloys
高熵合金中短程有序强化及其作用
Cláudio Geraldo Schön ✉
Cláudio Geraldo Schön: schoen@usp.br
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113754
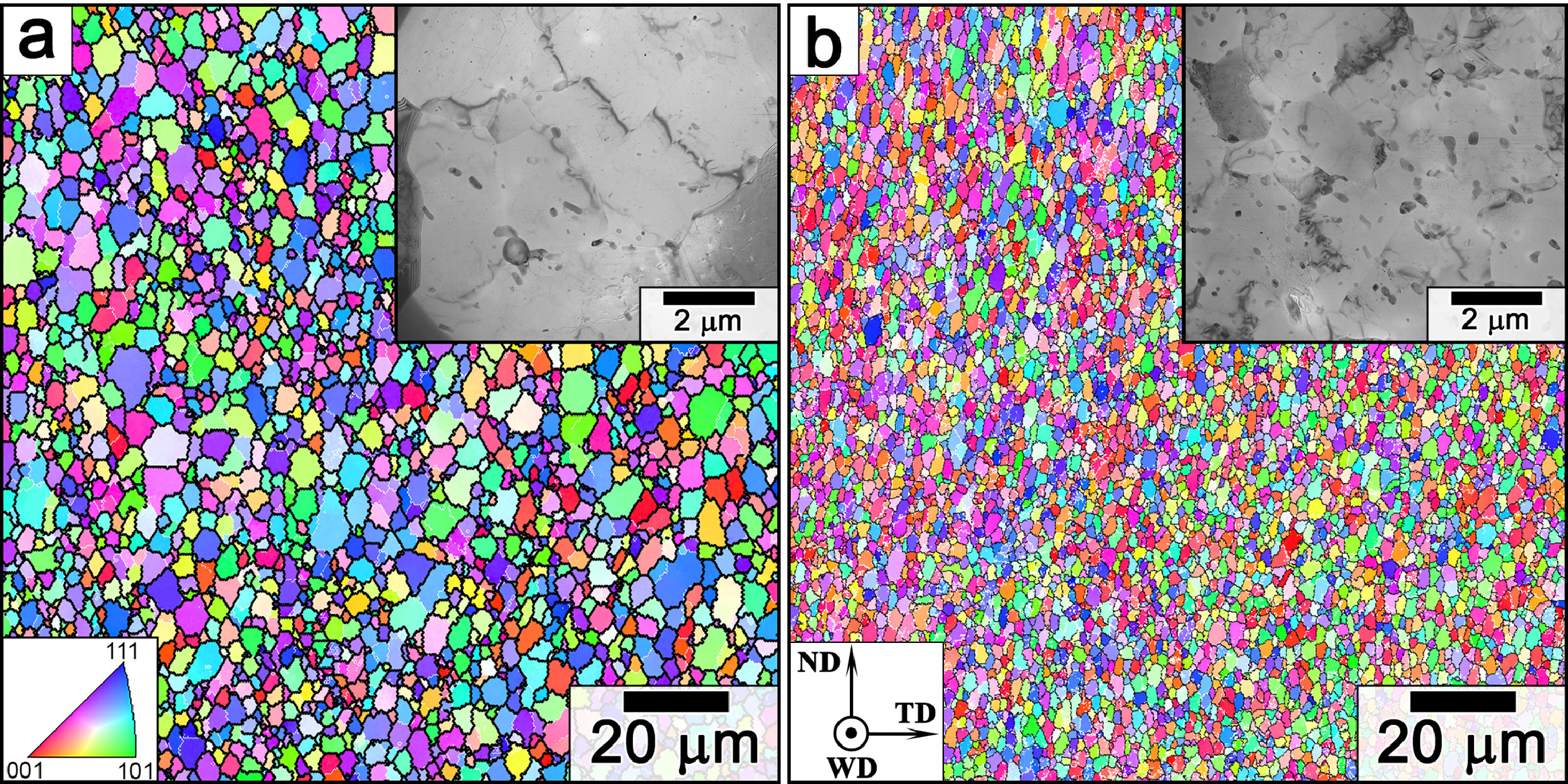
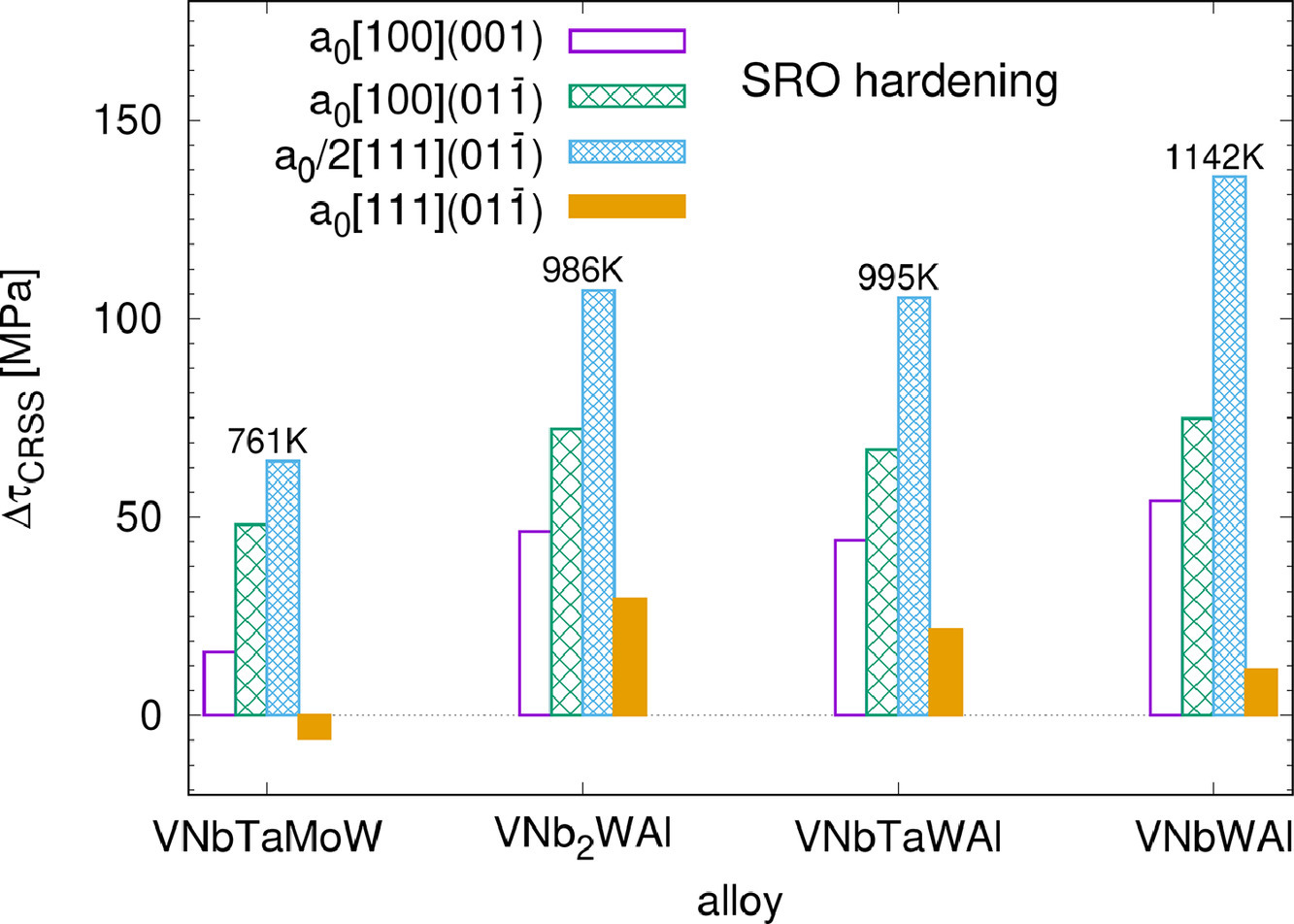
短程有序 (SRO) 强化是合金的主要强化机制之一。这主要是由于破坏有利的键增加了位错滑移的阻力。对于在滑移面上第一根位错的滑移,这种贡献可能是强烈的,但对于接下来的位错滑移肯定不太强烈。本文讨论了在不同条件下的SRO强化,重点讨论了反相畴界 (APB) 的形成引起的能量耗散。从这个意义上说,SRO强化对于定义滑移位错的摩擦应力变得很重要。采用APB能量的簇变法评估BCC合金的强化效果。我们用第一性原理导出量在VNbTaMoW和VNbTaWAl高熵合金对结果进行了说明。结果表明,在浓缩固溶体中,这种强化作用非常强烈,并且强化效果有很强的成分依赖性。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113758
3. Roles of reinforcements in twin nucleation and nano-α precipitation in the hybrid TiB/TiC-reinforced titanium matrix composites during high-temperature fatigue
TiB/TiC增强钛基复合材料在高温疲劳过程中增强体对孪晶形核和纳米α析出的影响
Xiaoyan Wang, Shaopeng Li, Yuanfei Han✉, Guangfa Huang, Jianwei Mao, Weijie Lu✉
Yuanfei Han: hyuf1@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学+上海市先进高温材料及其精密成形重点实验室
Weijie Lu: luweijie@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学+上海市先进高温材料及其精密成形重点实验室https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113758
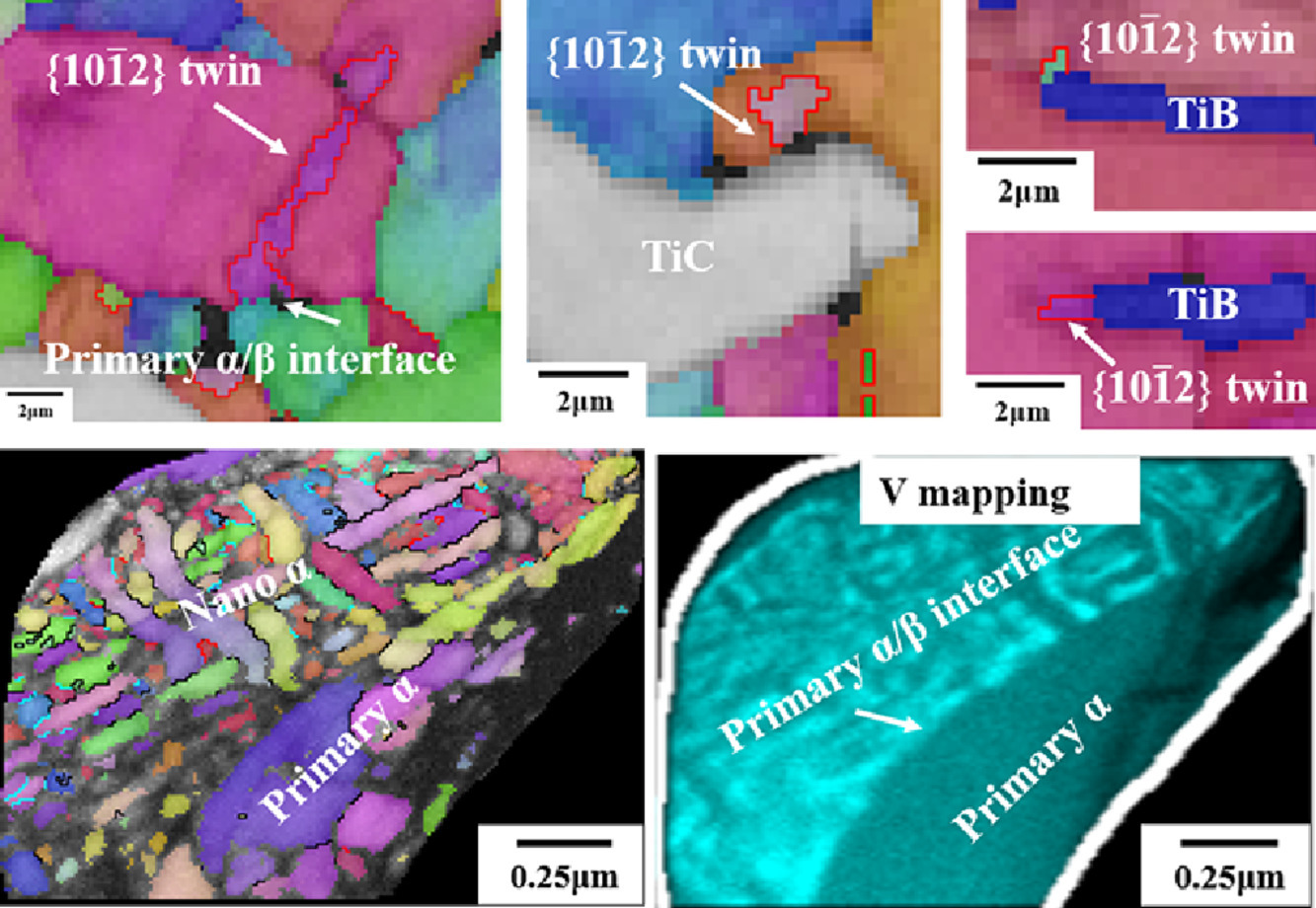
关于高温疲劳过程中增强体对钛基复合材料 (TMCs) 微观结构演变的影响,目前尚无相关研究。本研究中,短TiB纤维和TiC颗粒提高了初生α相和β相中的位错堆积,我们发现了一个新现象:{10-12}变形孪晶在α/β界面和增强体/基体界面两个界面上形核。由于局部的应力集中,位错会分解为孪晶位错,导致孪晶形核。在热激活下,位错作为V、Al和O等元素快速扩散的通道,导致β相中析出大量纳米α相,增加了初生α/β界面的局部应力集中,有利于孪晶形核。我们的工作有助于进一步阐明增强体的作用,补充高温疲劳过程中TMC失效的机理。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113759
4. Tantalum and molybdenum barriers to prevent carbon diffusion in spark plasma sintered tungsten
放电等离子烧结钨中钽和钼对碳的扩散的阻碍作用
Nojun Kwak, Guensik Min, Yeonju Oh, Dong-Woo Suh, Hyoung Chan Kim, Sung-gyu Kang✉, Heung Nam Han✉
Sung-gyu Kang: guitarpaul@snu.ac.kr
Heung Nam Han: hnhan@snu.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113759
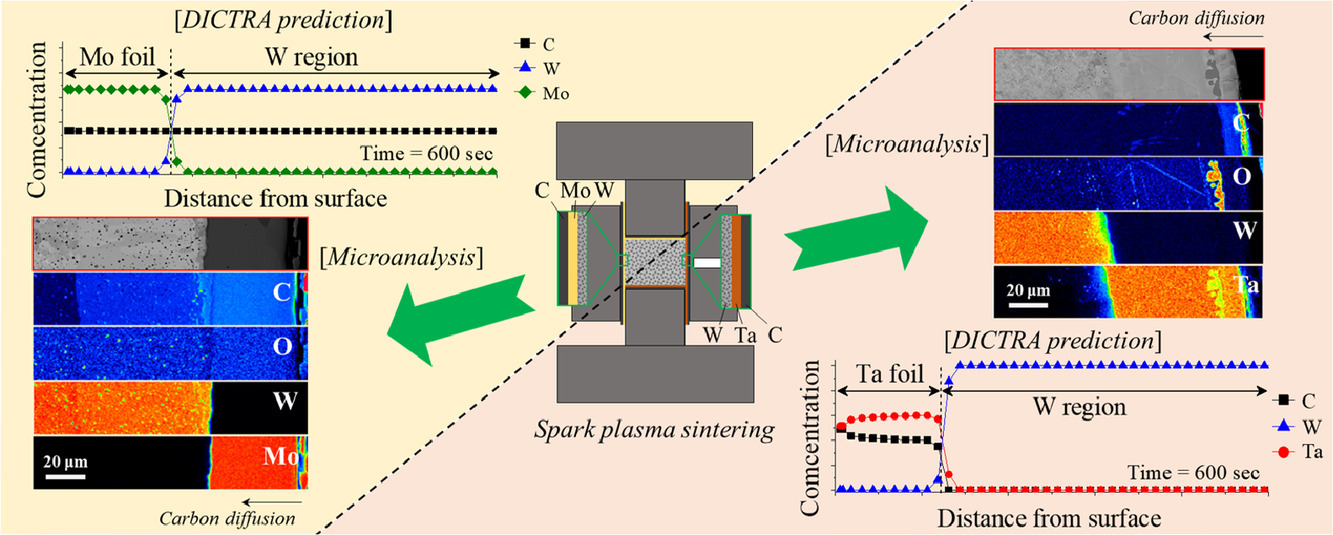
碳化物会降低钨的塑性,导致沿晶脆性断裂。这些裂纹是在放电等离子烧结过程中,由于石墨模具的作用,碳在钨中扩散形成的。本研究中,我们引入由两种不同的碳化物形成元素,钼和钽组成的保护膜,以减少碳化物的形成。横截面元素面扫结果表明,钽箔抑制了碳向钨中的扩散,而钼箔则不是有效的扩散屏障。热-动力学模拟表明,碳在钽中扩散被抑制的原因是钽的高溶解度和低扩散率。此外,热力学稳定的碳化钽阻止了碳在钽/钨界面的进一步扩散。相反,碳不仅在钼中扩散得更快,而且在钼/钨界面处也扩散得更快。这项研究为减少碳在放电等离子烧结过程中的扩散提供了方法,也有助于开发在极端碳质环境下服役的结构材料。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113768
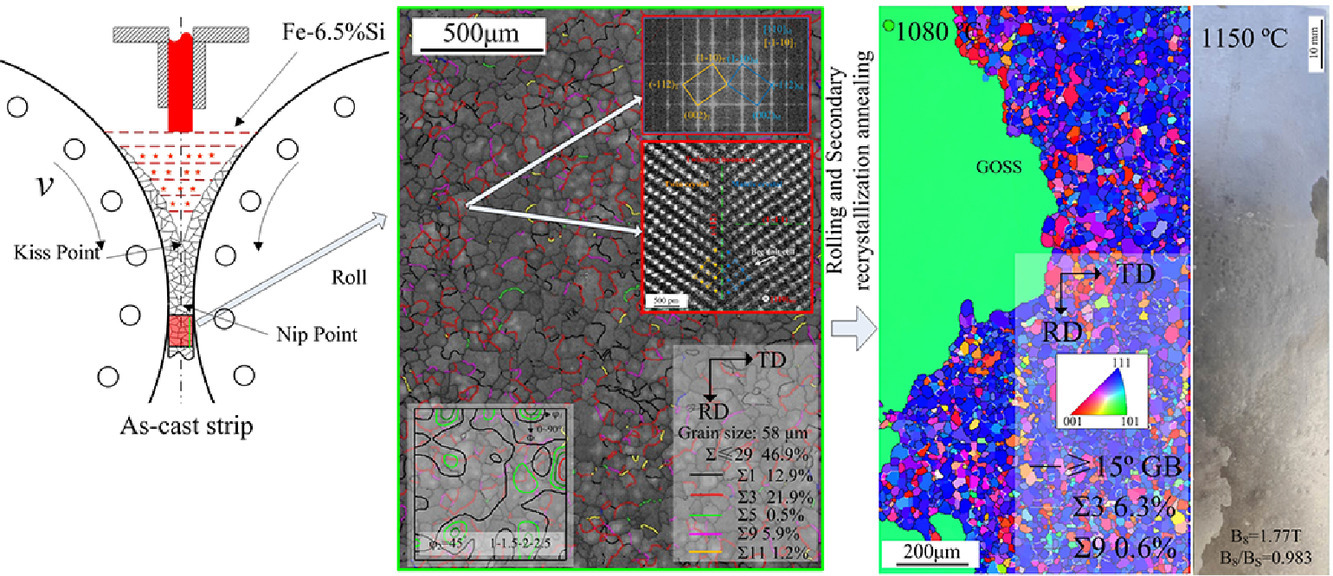
5. The evolution of Σ3 grain boundaries in the strip-cast Hi-B grain orientated Fe-6.5% Si alloy
带铸Hi-B晶粒取向的Fe-6.5%Si合金中Σ3晶界的演变
Yuanxiang Zhang, Guo Yuan✉, Yang Wang, Feng Fang, WeinaZhang, Xiaoming Zhang, Guodong Wang
Guo Yuan: yuanguoral@sina.com 东北大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113768
采用双辊带铸造制备了一种新型高磁感应Fe-6.5%Si合金,其B800可达1.77特斯拉。电子背散射衍射(EBSD)研究表明,Σ3晶界形成于无相变的体心立方(BCC)金属凝固组织中,晶界比大于20%。透射电镜结果显示,Σ3晶界部分为BCC结构的孪晶。在温轧、冷轧和退火过程中继承的一定数量的Σ3晶界,起到稳定基体晶界的作用,形成具有优良磁性能的完美Goss微观组织。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113763
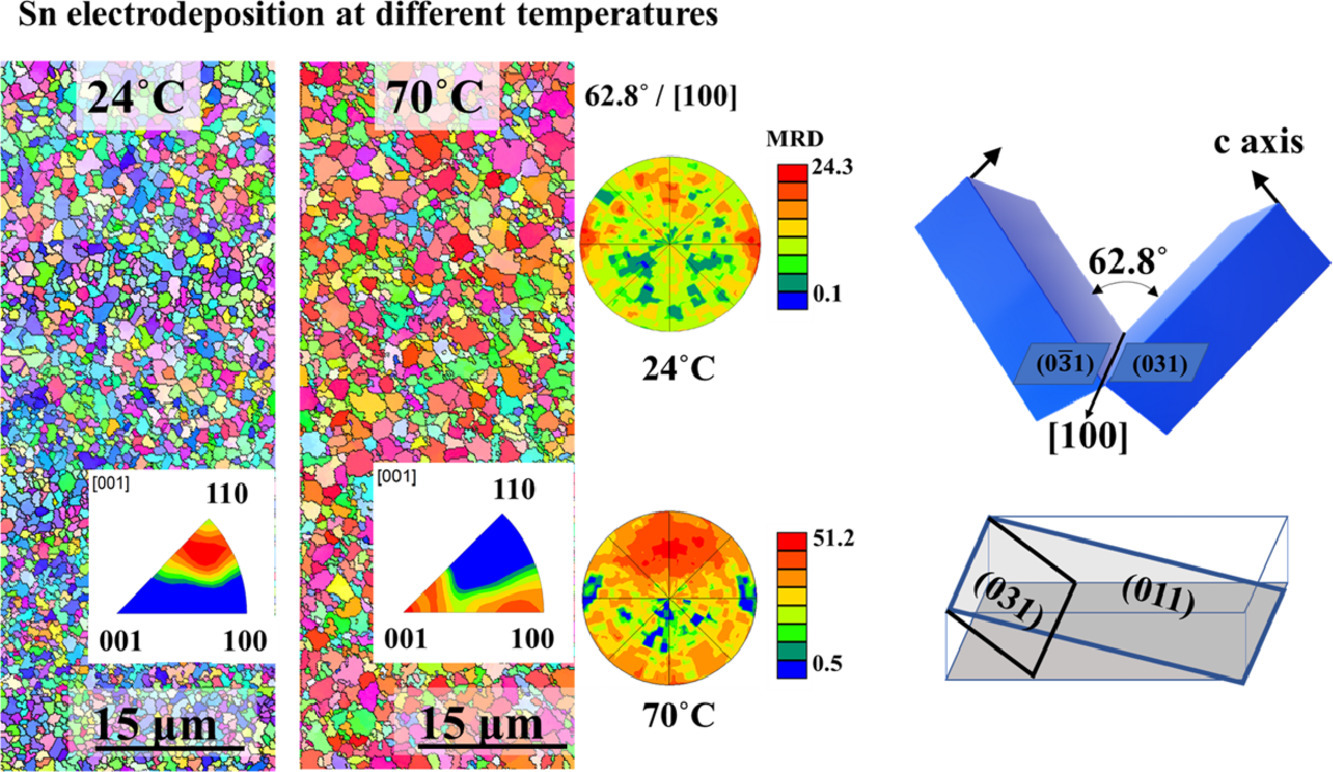
6. Temperature driven texture and grain boundary engineering of electrodeposited β-Sn coatings and its effect on the coating corrosion behaviour: Five-parameter grain boundary character distribution analysis study
电沉积β-Sn涂层的温度驱动织构和晶界工程及其对涂层腐蚀行为的影响:五参数晶界特征分布分析
Abhay Gupta, Chandan Srivastava✉
Chandan Srivastava: csrivastava@iisc.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113763
在4种不同温度(24˚C、47˚C、70˚C和80˚C)下,在软钢上电沉积Sn镀层。电化学阻抗谱显示,在70˚C (Sn3涂层)和80˚C制备的Sn涂层的耐蚀性分别是最高和最低。利用电子背散射衍射技术研究了涂层结构与电化学性能的关系。随着电沉积温度的升高,低角晶界分数明显增加。五参数晶界特征的分布分析表明,62.8˚/[100]取向差的(031)[01-3]孪晶界的最高比例和暴露的低能{100}面取向的较高比例导致了Sn3涂层最好的耐蚀性。然而,低比例的(031)[01-3]孪晶界和高比例的高能“近(110)”面取向导致了80℃制备的Sn涂层的耐蚀性较差。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113761
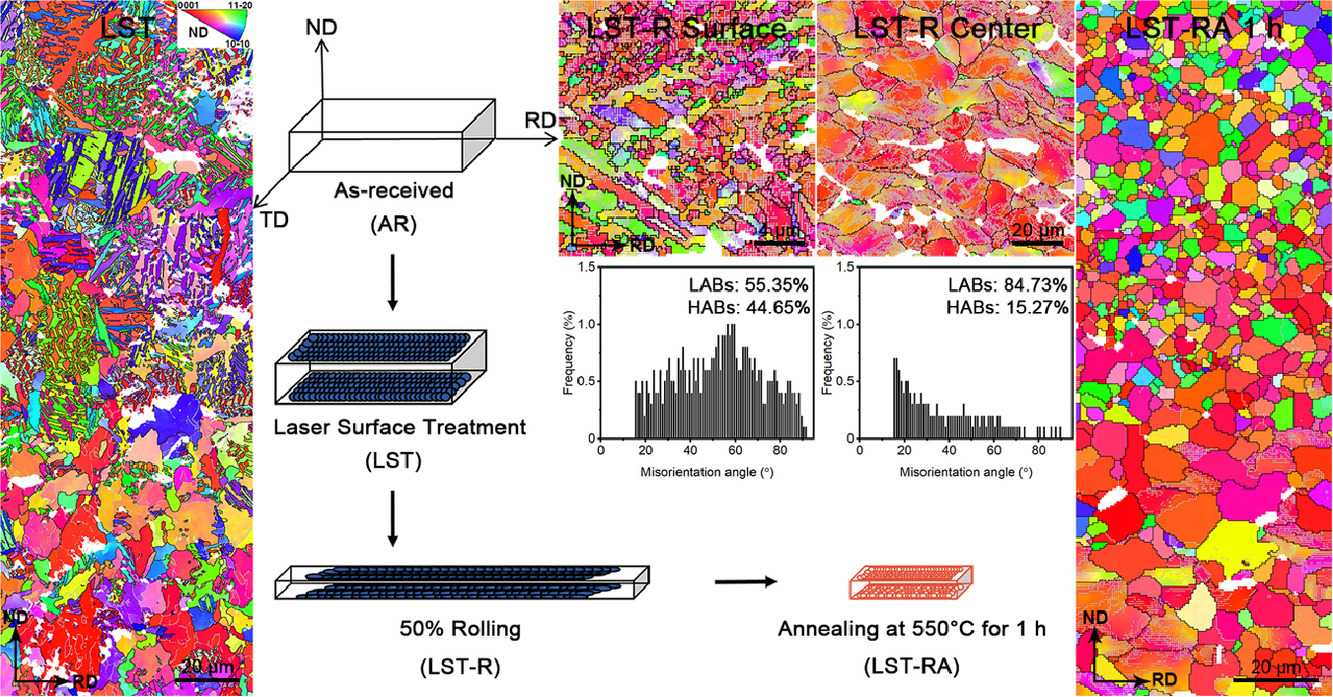
7. A strategy to introduce gradient equiaxed grains into Zr sheet by combining laser surface treatment, rolling and annealing
采用激光表面处理、轧制和退火相结合的方法在Zr板材中引入梯度等轴晶粒
Linjiang Chai✉, Yufan Zhu, Xing Hu, Korukonda L. Murty, Ning Guo, Liang-Yu Chen, Yanlong Ma, Lai-Chang Zhang
Linjiang Chai: chailinjiang@cqut.edu.cn 重庆理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113761
本文提出了一种激光表面处理、轧制和退火(LST-RA)相结合制备梯度等轴晶的新策略,并在纯Zr板材上进行了验证。在纯Zr表面,激光诱导β→α的快速相变产生了致密的高角度晶界(HABs),随后50%轧制引入了大量的储能。在随后的退火过程中,预先存在的密度较大的HABs通过应变诱导晶界迁移机制在表层产生了比基体更多的再结晶核心,最终在纯Zr板材制备出了从表面到内部的梯度等轴晶结构。此外,与粗晶基体相比,细晶表层具有较弱的织构。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113762
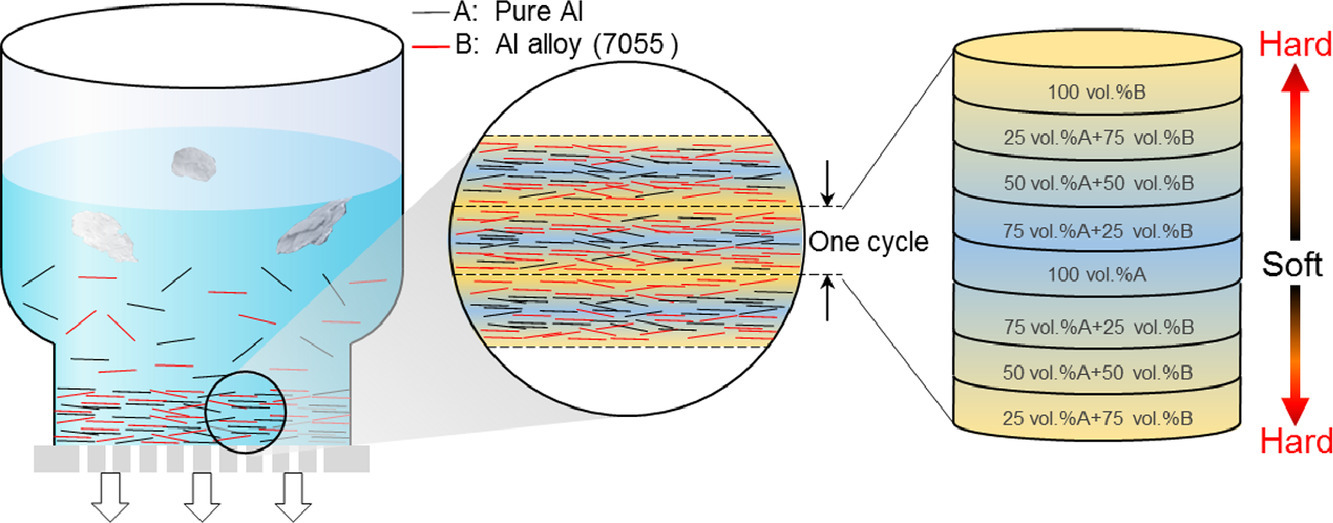
8. Heterostructured bulk aluminum with controllable gradient structure: Fabrication strategy and deformation mechanisms
可控梯度结构的异质结构块状铝:制备策略和变形机理
Ge Wang, Heng Ouyang, Yishi Su, Qiang Guo, Ding-Bang Xiong, Qianduo Zhuang, Zhenming Yue, Zan Li✉, Di Zhang✉
Zan Li: njulizan@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学
Di Zhang: zhangdi@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113762
本文探讨了块体梯度铝的变形特征和变形机理。采用粉末组装的方法,首次制备出具有微调梯度循环的块体铝。我们发现单个构件的变形行为受梯度结构的影响,这归因于异质变形引起的内应力。实验和模拟结果进一步表明,每个部件的硬化是梯度大小相关的,并受几何必须位错分布的控制。我们的工作为理解和发展具有优良性能的梯度金属材料提供了新的视角。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113766
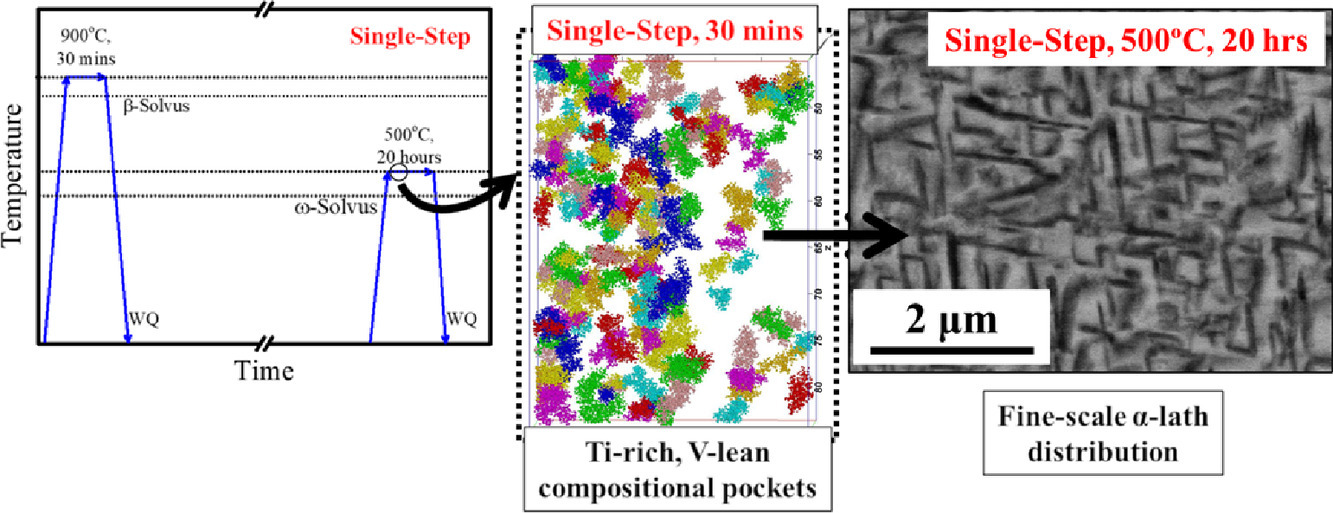
9. Fine scale alpha precipitation in Ti-19at.%V in the absence of influence from omega precipitates
在不受ω析出影响的情况下,Ti-19at.%V中精细尺度的α析出
A. Sharma, V. Soni, S. Dasari, S.A. Mantri, Y. Zheng, H. Fraser✉, R. Banerjee✉
A. Fraser: fraser.3@osu.edu
A. Banerjee: Raj.Banerjee@unt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113766
均匀分布的精细尺度α析出的等温ω辅助机制已经在几种钛合金中得到了充分的证明,包括Ti-19at%V (Ti-20wt%V)。本文报告了在没有任何直接或间接ω析出相的影响下,也可能发生类似的α析出。原子探针层析成像结果表明,将ω相固溶处理+淬火后的Ti-19at%V合金快速加热到500℃会导致非热ω析出相失稳,随后在等温保温过程中以富Ti或贫V区域的形式产生成分波动。这些区域可能是β相分离产生的,随后可能成为均匀分布的α相的形核位点。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113765
10. Suppression of abnormal grain growth in friction-stir welded Al-Cu-Mg alloy by lowering of welding temperature
降低焊接温度抑制搅拌摩擦焊Al-Cu-Mg合金中晶粒的异常生长
Ivan S. Zuiko✉, Sergey Mironov, Sergey Betsofen, Rustam Kaibyshev
Ivan S. Zuiko: zuiko_ivan@bsu.edu.ru
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113765
本文研究了焊接温度对搅拌摩擦焊 (FSWed) 2519铝合金热稳定性的影响。将焊接温度降低到颗粒溶解阈值以下是抑制焊后固溶过程中晶粒异常生长的有效方法。这一效应归因于阻止焊接材料在后续退火过程中细小弥散体的析出,从而导致相对较低的齐纳压力,最终激活了明显正常的晶粒生长机制。这一现象首次被证实,并可作为一种工艺策略来提高FSWed可热处理合金的热稳定性。