金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.203,15 Jan. 2021(下)
2021-03-28 来源:Goal Science

本期包含金属材料领域论文10篇,涵盖了多元合金、碳纳米管、单晶与高温合金等,国内科研单位包括东南大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 203 目录
1. Isotope study reveals atomic motion mechanism for the formation of metal whiskers in MAX phase
利用同位素方法揭示MAX相金属晶须形成的原子运动机制
2. Atomistic simulation of the generation of vacancies in rapid crystallization of metals
金属快速结晶过程中空位形成的原子尺度模拟研究
3. Design of solute clustering during thermomechanical processing of AA6016 Al–Mg–Si alloy
AA6016 Al-Mg-Si合金热机械加工过程中的溶质原子团簇设计
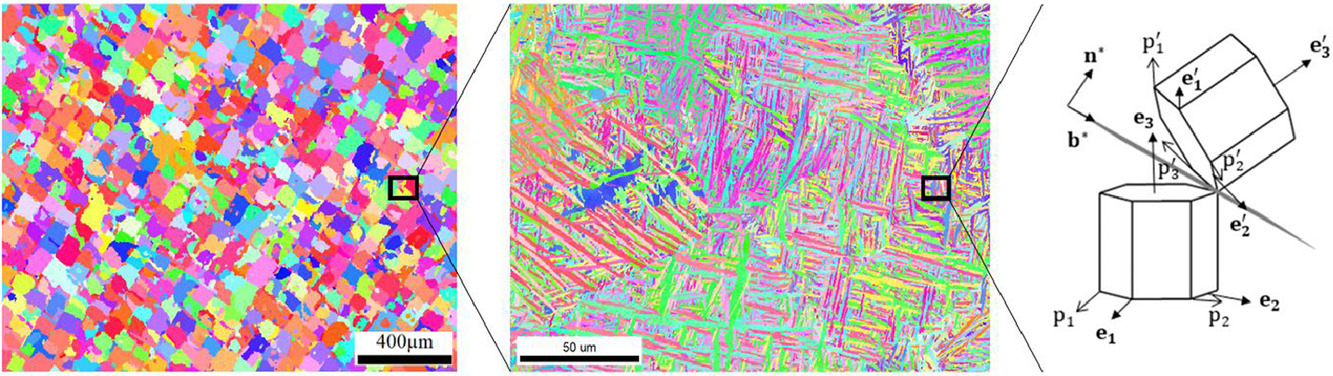
4. Uniaxial compression of [001]-oriented CaFe2As2 single crystals: the effect of microstructure and temperature on superelasticity Part II: Modeling
温度和微观组织对[001]取向CaFe2As2单晶单轴压缩超弹性影响的理论模拟研究
5. Density functional theory study of solute cluster growth processes in Mg-Y-Zn LPSO alloys
Mg-Y-Zn LPSO合金中溶质原子团簇生长过程的密度泛函理论模拟研究
6. Carbon nanotube (CNT) metal composites exhibit greatly reduced radiation damage
碳纳米管(CNT)金属复合材料的抗辐照性能研究
7. The role of carbon in the white etching crack phenomenon in bearing steels
碳在轴承钢白蚀裂纹现象中的作用
8. Developing age-hardenable Al-Zr alloy by ultra-severe plastic deformation: Significance of supersaturation, segregation and precipitation on hardening and electrical conductivity
过饱和、偏聚和析出对通过强塑性变形方法制备得到的时效硬化Al-Zr合金的硬度和电导率的影响
9. Tracer diffusion in the σ phase of the CoCrFeMnNi system
σ相CoCrFeMnNi体系中的示踪剂扩散研究
10. Modeling the role of local crystallographic correlations in microstructures of Ti-6Al-4V using a correlated structure visco-plastic self-consistent polycrystal plasticity formulation
采用关联结构粘塑性自洽多晶体模型模拟Ti-6Al-4V中局部晶体学关系对组织的影响
ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116475
1. Isotope study reveals atomic motion mechanism for the formation of metal whiskers in MAX phase
利用同位素方法揭示MAX相金属晶须形成的原子运动机制
Chengjie Lu✉, Yushuang Liu, Jian Fang, Yan Zhang, Peigen Zhang, ZhengMing Sun✉
C. Lu:chengjie.lu@seu.edu.cn(东南大学)
Z. Sun:zmsun@seu.edu.cn(东南大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.017
摘要
金属晶须的自发生长已有70年研究历史,但这一现象仍未被完全阐明。在此,我们通过实验和模拟相结合,研究了晶须从纳米层状MAX陶瓷相中的挤出形成。MAX基体中过量的A是晶须的元素来源,但在本研究中Ti2SnC/120Sn同位素实验的直接证据表明,Sn晶须中的Sn原子同时包括基体的过量Sn和晶格Sn。Ti2AC/A' (A, A' = Sn, Ga)的交叉实验表明,晶须的挤出过程中总是伴随发生过量A(或A ')原子取代晶格A原子的过程,这一过程的驱动力是化学势梯度(或焓的减少)。据此,本文提出了一种基于晶格扩散的原子运动机制,来解释MAX相中晶须形成。


ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116465
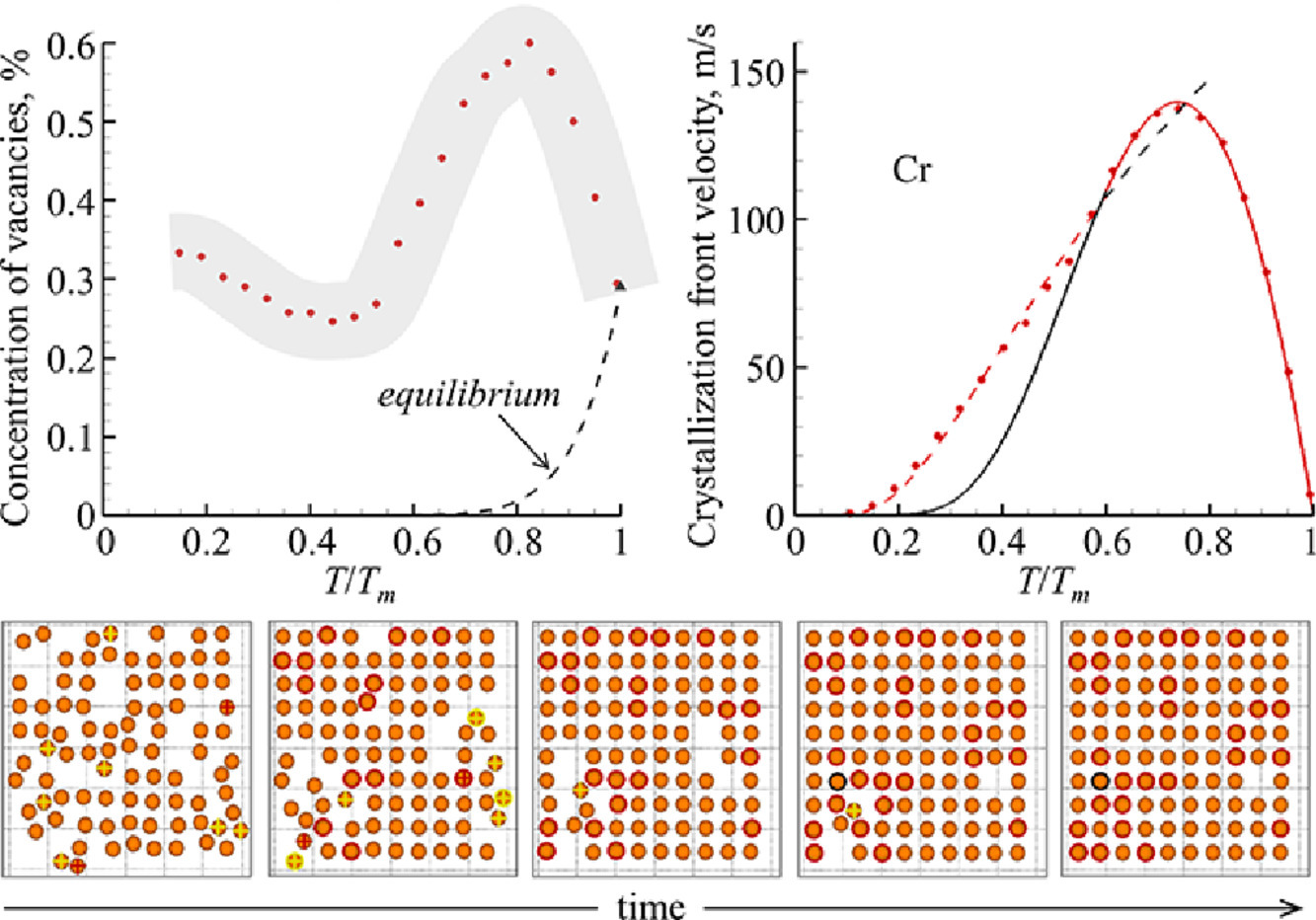
2. Atomistic simulation of the generation of vacancies in rapid crystallization of metals
金属快速结晶过程中空位形成的原子尺度模拟研究
L.V. Zhigilei:lz2n@virginia.edu
Miao He, Eaman T. Karim, Maxim V. Shugaev, Leonid V. Zhigilei
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.007
摘要
我们在严格控制温度和压力的条件下,对两种代表性金属,BCC铬和FCC镍,进行了分子动力学模拟,以研究其在低于平衡熔点的过冷条件下,固液界面前沿空位的产生过程。模拟结果表明,对于这两种金属,在结晶晶面前沿稳态推进过程中产生的空位浓度可以比相应温度下的平衡值大几个数量级。两种金属的空位浓度随温度的变化趋势不同,其中Ni的空位浓度随着过冷程度增加而增加,而Cr的空位浓度则呈非单调变化,这是由于两种金属的结晶前沿速度随温度的变化不同导致的。分子动力学预测的一般特征在不同电位和取向的Ni中得到了证实。对结晶前沿原子重排的详细分析表明,空位的过饱和程度主要是由原子在界面区域内迁移的能力和填补界面区域内为同时构建多个原子面而产生的众多空位的能力所决定的。虽然晶面构建过程中产生的大部分瞬时空位会被来自液相一侧的原子所湮灭,但仍有少部分空位滞留在结晶前沿的后方。在强烈过冷条件下,界面的快速运动和空位迁移率的降低使得结晶区的空位浓度无法达到平衡,从而形成大量的过饱和空位。通过分析结晶前沿原子重排随温度的变化可以推测,在强过冷条件下,快速推进的固液界面处和界面前沿的无序相发生不完全松弛。

ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116455
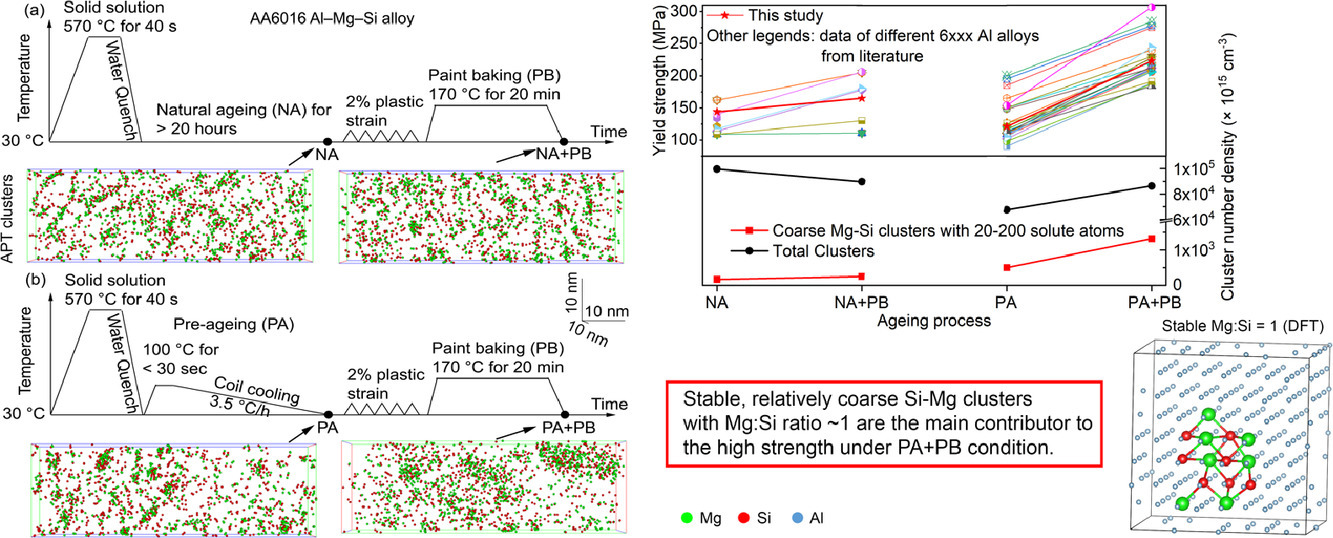
3. Design of solute clustering during thermomechanical processing of AA6016 Al–Mg–Si alloy
AA6016 Al-Mg-Si合金热机械加工过程中的溶质原子团簇设计
Suqin Zhu✉, Han-Cheng Shih, Xiangyuan Cui, Chung-Yi Yu, Simon P. Ringer✉
S. Zhu:suqin.zhu@sydney.edu.au
S.P. Ringer:simon.ringer@sydney.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.10.074
摘要
溶质团聚是铝合金制备过程中一个重要的组织演变过程。通过对这一过程进行调控,可以提高材料的合金性能,同时降低生产能耗,在汽车工业中具有重要应用价值。在本研究中,我们通过在商业化生产线固溶后的卷曲过程中插入一段预时效处理工艺,实现了对溶质团簇过程的调控。这种预时效能够有效减轻在固溶处理后、烤漆前发生的自然时效对机械性能的负面影响。我们以低铜AA6016合金为研究对象,研究了短时低温预时效的作用。通过原子探针结合第一性原理计算,我们从原子尺度揭示了这一过程中的组织演化。研究发现,20以上溶质原子的Mg-Si团簇是材料在预时效处理和烘烤后能够获得优良性能的主要原因。模拟结果表明,空位可以有效稳定单质硅团簇,使它们能够吸引更多的溶质,并形成更大的Mg-Si团簇,这对合金性能提高非常有益。此外,模拟结果还表明,最近邻原子的构型是影响团簇稳定的关键因素。

ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116462
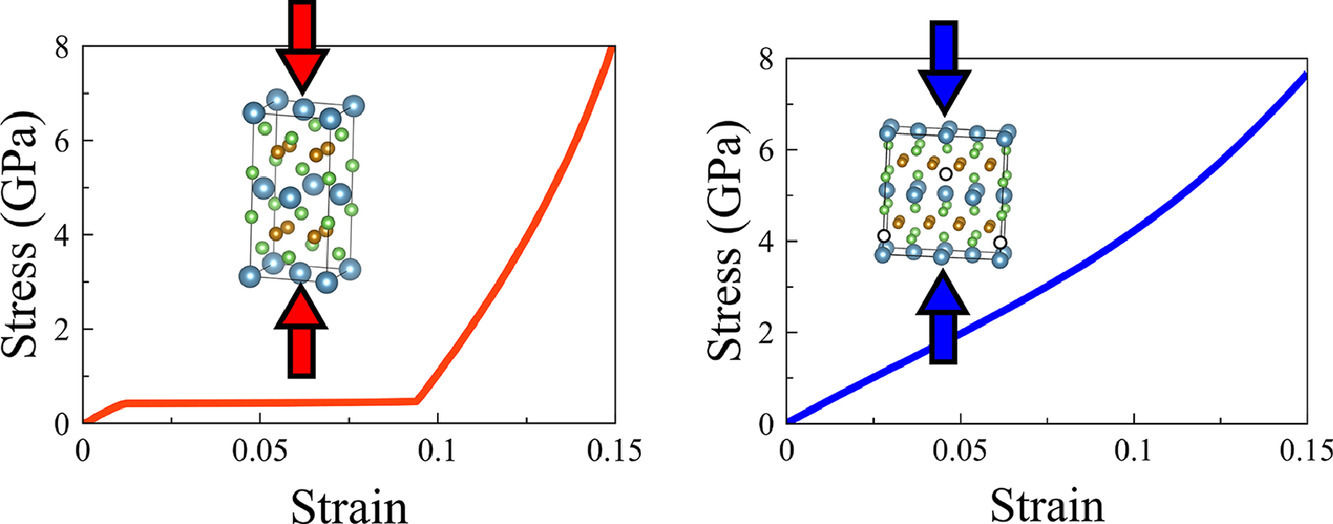
4. Uniaxial compression of [001]-oriented CaFe2As2 single crystals: the effect of microstructure and temperature on superelasticity Part II: Modeling
温度和微观组织对[001]取向CaFe2As2单晶单轴压缩超弹性影响的理论模拟研究
Ian N. Bakst, John T. Sypek, Sriram Vijayan, Shuyang Xiao, Mark Aindow, Seok-Woo Lee, Christopher R. Weinberger✉
C.R. Weinberger:Chris.Weinberger@colostate.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.004
摘要
我们通过密度泛函理论(DFT)模拟结合相关分析模型,研究了缺陷和温度对[001]取向CaFe2As2压缩性能的影响。我们已在另一篇论文中对我们的实验工作进行了描述,证明了晶体长大的溶液环境(无论是Sn还是FeAs溶液)和后续热处理都对材料的机械响应有一定影响。为了阐明这些实验现象,我们使用了DFT对Ca-Fe-As体系中的相平衡进行了模拟,并确定了在FeAs溶液中生长的CaFe2As2中的析出和缺陷结构类型。研究结果表明,CaFe2As2中会析出FeAs和Fe,并且在析出和CaFe2As2基体之间存在一个低能共格界面。此外,空位的存在将导致非化学计量比CaFe2As2的形成。对CaFe2As2机械响应的模拟表明,实验中观察到的机械刚度可能是点缺陷的结果,其最可能的来源是As空位。最后,通过使用DFT内计算自由能,我们发现,斜方和四方CaFe2As2之间的振动熵差可以部分地解释应力-应变曲线随温度的变化。

ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116491
5. Density functional theory study of solute cluster growth processes in Mg-Y-Zn LPSO alloys
Mg-Y-Zn LPSO合金中溶质原子团簇生长过程的密度泛函理论模拟研究
Mitsuhiro Itakura✉, Masatake Yamaguchi, Daisuke Egusa, Eiji Abe
M. Itakura:itakura.mitsuhiro@jaea.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116491
摘要
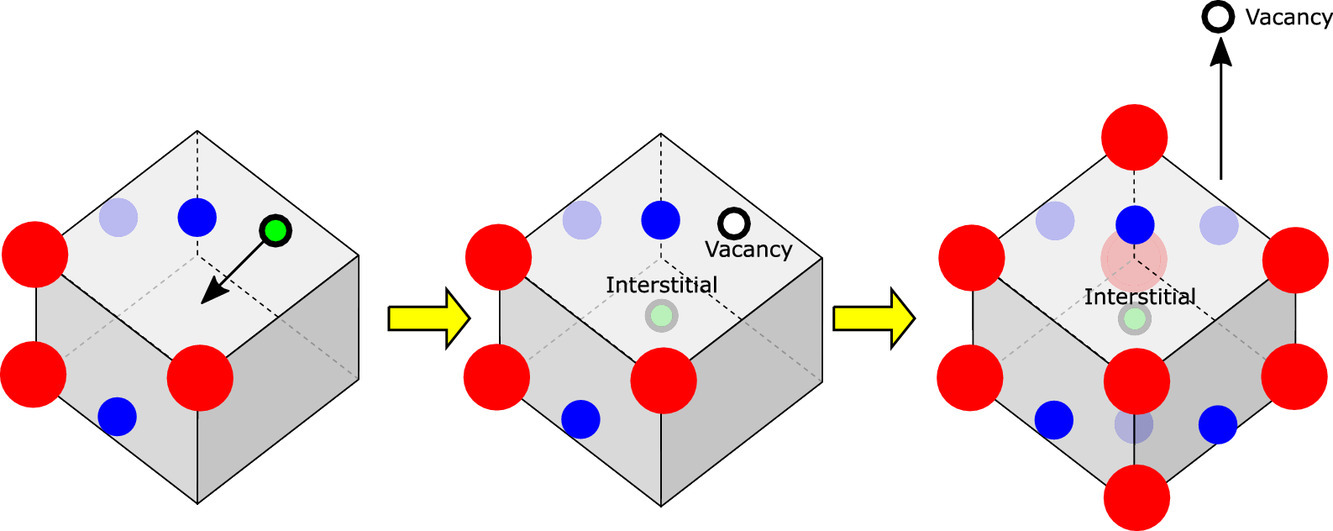
长周期堆垛(LPSO)合金中的溶质原子团簇对其特殊的塑性行为(如扭结形成和扭结强化)具有关键作用。分辨团簇结构中的原子是对LPSO合金进行原子尺度模拟的前提,同时也对材料的强塑性至关重要;然而,团簇中的间隙原子具有较强的不确定性。虽然密度泛函理论的模拟表明,在大多数LPSO合金中,间隙Mg原子的能量最低,但实验也同样观察到有其他溶质元素处于间隙位置。为了预测原子团簇中间隙原子的种类和分布,我们需要确定间隙原子形成的机制。在本研究中,我们利用密度泛函理论研究了Mg-Y-Zn LPSO合金中溶质原子团簇的生长过程,以准确确定其原子结构。研究表明,当一定数量的溶质原子被吸纳到团簇中时,会自发地产生一对间隙原子和空位,并且所有充分长大的团簇都将含有间隙原子。大部分情况下间隙原子为Mg,其余情况下为Y; 间隙原子为Zn的情况可以忽略不计。这一研究结果极大简化了Mg-Y-Zn合金中的溶质原子团簇模型。由于团簇形成导致空位产生,因此在溶质原子团簇长大的区域,空位密度达到饱和状态,这反过来进一步加速了团簇的长大。

ACTA
Vol. 203,15 Jan. 2021, 116483
6. Carbon nanotube (CNT) metal composites exhibit greatly reduced radiation damage
碳纳米管(CNT)金属复合材料的抗辐照性能研究
Penghui Cao✉, Kang Pyo So, Yang Yang, Jong Gil Park, Mingda Li, Long Yan, Jing Hu, Mark Kirk, Meimei Li, Young Hee Lee, Michael P. Short✉, Ju Li✉
P. Cao:caoph@uci.edu
M.P. Short:hereiam@mit.edu
J. Li:liju@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116483
摘要
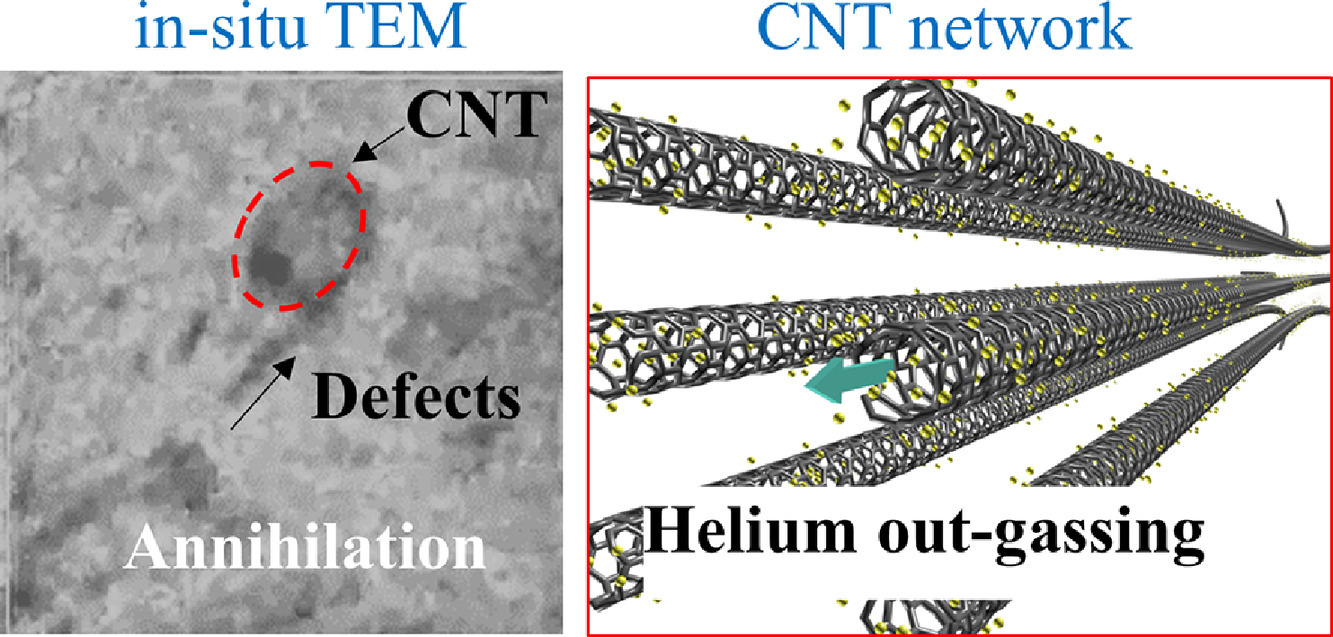
辐照会导致结构材料因机械性能退化而失效,而在材料中引入析出相或其他缺陷是提高材料抗辐射性能的常用手段。在本研究中,我们发现,通过在铝中加入一维碳纳米管(CNTs)制备而成的金属复合材料具有优异的抗辐射性能。通过原位离子辐照,结合透射电子显微镜(TEM)和原子尺度模拟,我们揭示了缺陷向CNTs快速迁移的机制,这一机制促进了缺陷复合,增强了材料的抗辐照性能。这种效应主要是由于辐照下CNT相变引起的Al基体应力梯度变化,以及碳化物的稳定性导致的。我们对于大型缺陷行为的进一步模拟表明,CNTs在减少损伤累积方面具有重要作用。以上缺陷迁移调控方法能够有效提高核材料的抗辐照性能,而无显著负面作用。

ACTA
Vol. 203, 15 Jan. 2021, 116480
7. The role of carbon in the white etching crack phenomenon in bearing steels
碳在轴承钢白蚀裂纹现象中的作用
D. Mayweg✉, L. Morsdorf, X. Wu, M. Herbig
D. Mayweg:d.mayweg@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.11.022
摘要
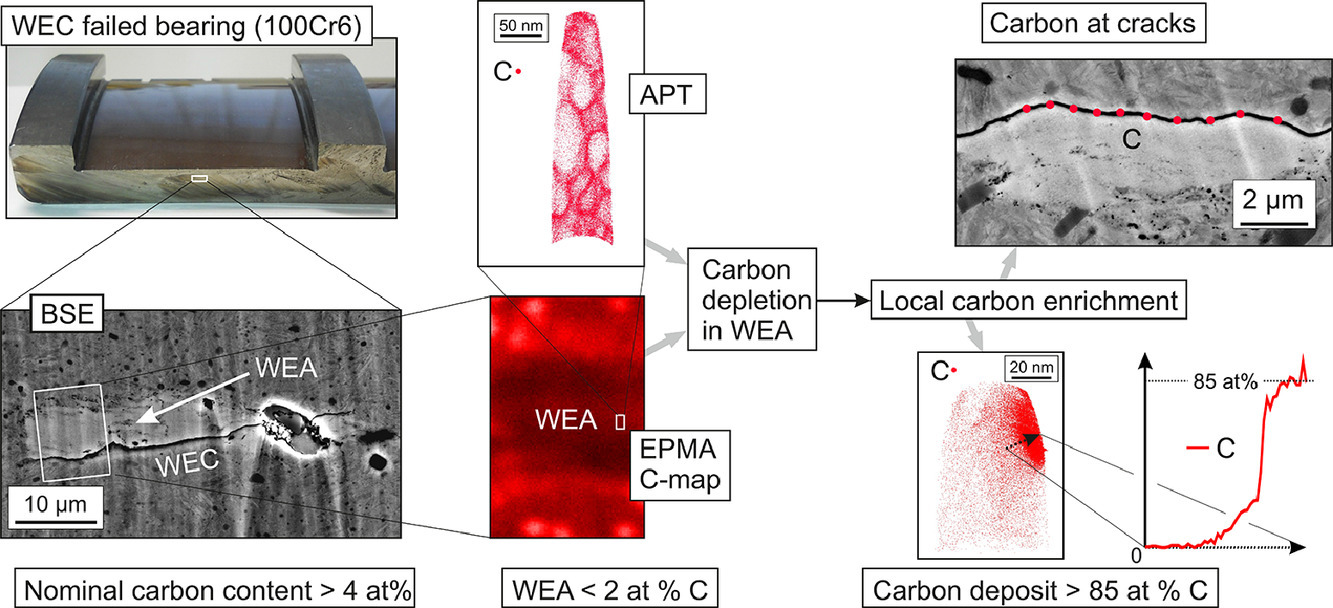
高碳钢中常常出现白色的蚀刻裂纹(WEC),在此,我们阐明了碳在这种失效机制中的作用。组成白区(WEA)的纳米晶铁素体是由于裂纹表面摩擦导致初始组织发生塑性变形而产生。我们以白区形成导致失效的100Cr6风力电机齿轮箱轴承为重点研究对象,通过电子探针、透射电子显微镜和原子探针等手段对材料中的局部碳成分在μm和nm尺度上进行了分析。结果表明,WEA中的碳含量显著降低。组织中发现了碳的沉积物,其碳含量大于85 at%,这些沉积物在WEA中分布不均。我们通过假设在裂纹表面摩擦过程中,多余的碳从WEA偏聚到开放裂纹表面对这一结果进行了解释。此外,WEC表面碳膜的“润滑”作用可能是导致WEC与经典滚动接触疲劳相比加速失效的原因。

ACTA
Vol. 203, 15 Jan. 2021, 116503
8. Developing age-hardenable Al-Zr alloy by ultra-severe plastic deformation: Significance of supersaturation, segregation and precipitation on hardening and electrical conductivity
过饱和、偏聚和析出对通过强塑性变形方法制备得到的时效硬化Al-Zr合金的硬度和电导率的影响
Abbas Mohammadi✉, Nariman A. Enikeev, Maxim Yu. Murashkin, Makoto Arita, Kaveh Edalati✉
A. Mohammadi:mohammadi.abbas.566@m.Kyushu-u.ac.jp
K. Edalati:kaveh.edalati@kyudai.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116503
摘要
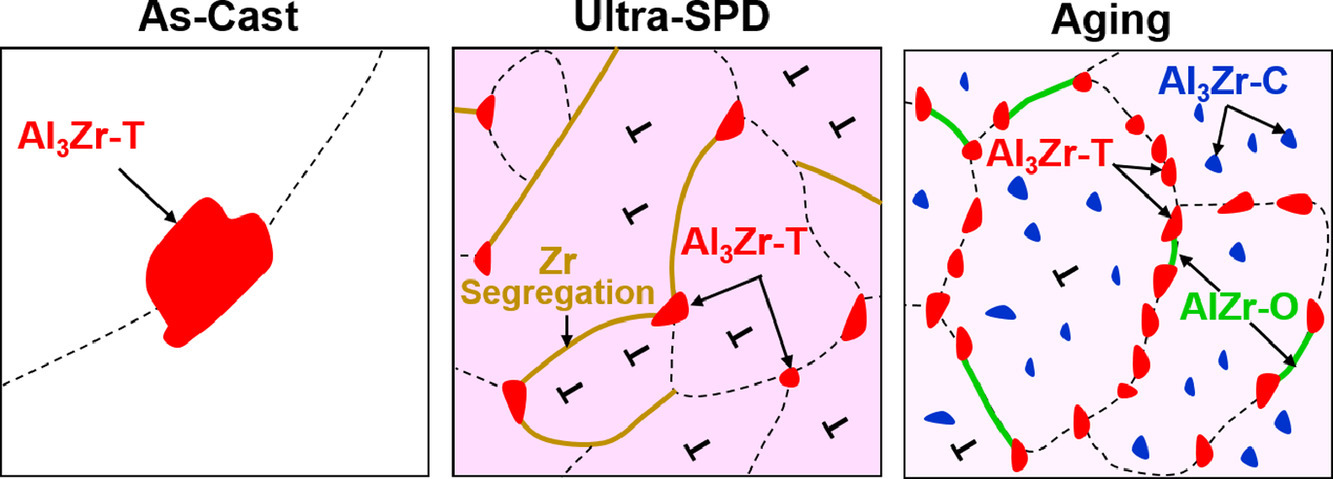
铝锆合金由于具有优越的热稳定性和电导率而收到广泛关注。而其主要缺点则是即使经过强烈塑性变形(SPD),材料的硬度仍相当低(<75Hv)。铝锆合金实际上由Al和Al3Zr金属间化合物(D023四方结构)组成,由于Zr在Al中不易固溶,因此不具备时效硬化。在本研究中,我们通过剪切应变高达40,000的高压扭转(HPT),成功制备了Al-Zr合金的过饱和固溶体。随后的时效过程中,晶界处析出Bf菱方AlZr,而晶内析出L12立方亚稳共格Al3Zr。研究发现,强烈塑性变形过程中,Zr在Al中的超饱和固溶由极快的动态扩散控制,其扩散速率与表面扩散相当;而时效时的析出形成则由晶格扩散和管道扩散控制。这些微观结构使得材料硬度显著提高(~148Hv),同时材料保持了极高的热稳定性(~523K)和不错的的导电率(~35%IACS)。进一步分析表明,约30%的硬化由析出强化引起,而其余的硬化则是由纳米晶的晶粒尺寸、晶界偏聚和位错塞积导致。综上,本研究介绍了一种有效手段,即通过及其强烈的塑性变形,成功制备出了具有高热稳定性和合理电导的新型时效硬化铝合金。

ACTA
Vol. 203, 15 Jan. 2021, 116498
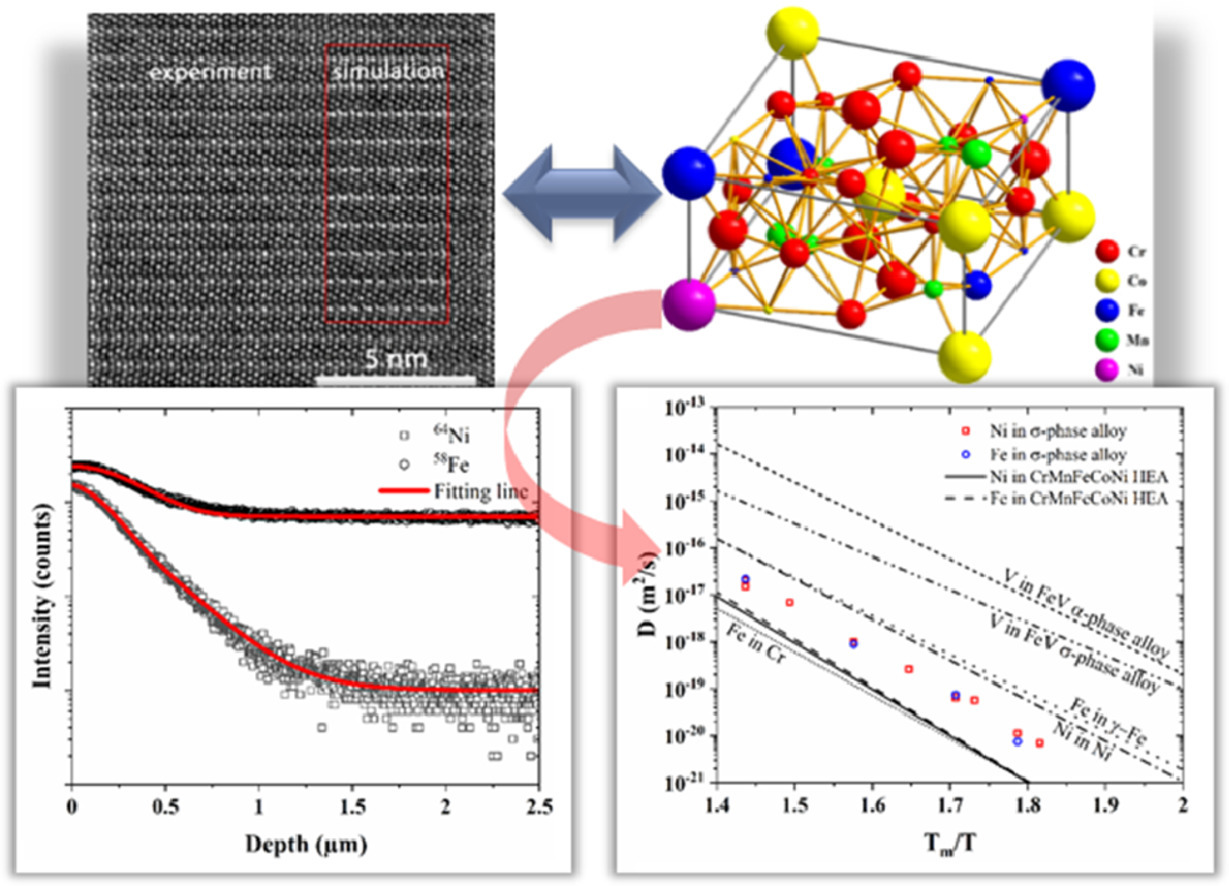
9. Tracer diffusion in the σ phase of the CoCrFeMnNi system
σ相CoCrFeMnNi体系中的示踪剂扩散研究
Jingfeng Zhang, G. Mohan Muralikrishna, Alex Asabre, Yordan Kalchev, Julian Müller, Benjamin Butz, Sven Hilke, Harald Rösner, Guillaume Laplanche, Sergiy V. Divinski✉, Gerhard Wilde
S.V. Divinski:divin@uni-muenster.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116498
摘要
我们制成了一种成分为Co17Cr46Fe16.3Mn15.2Ni5.5(at.%)的立方晶格富Cr σ相合金。我们利用了高浓度64Ni、58Fe同位素和二次离子质量谱测量了Ni和Fe的扩散系数。在类似的相对温度尺度上,与等原子比面心立方CoCrFeMnNi合金相比,Ni和Fe在σ相中的扩散速度更快。相反,在绝对温度尺度上,这些元素在两种材料中的扩散速率大致相同。我们对影响σ相中元素扩散和相稳定性的因素进行了讨论,并将其与等原子比合金进行了比较。

ACTA
Vol. 203, 15 Jan. 2021, 116502
10. Modeling the role of local crystallographic correlations in microstructures of Ti-6Al-4V using a correlated structure visco-plastic self-consistent polycrystal plasticity formulation
采用关联结构粘塑性自洽多晶体模型模拟Ti-6Al-4V中局部晶体学关系对组织的影响
Iftekhar A. Riyad, William G. Feather, Evgenii Vasilev, Ricardo A. Lebensohn, Brandon A. McWilliams, Adam L. Pilchak, Marko Knezevic✉
M. Knezevic:marko.knezevic@unh.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116502
摘要
我们提出了一种多尺度晶体塑性模拟方法,用于模拟具有α板条/层片组织的Ti-6Al-4V的力学性能和微观结构演化。该模型是关联了三个不同尺度的自洽模型:单晶代表的微观尺度、板条/层片组织代表的介观尺度和板条/层片组织集合代表的宏观尺度。模型中使用的滑移临界剪切应力是唯像的,但是根据相邻层片滑移的几何特征进行了一定调整,使之与实验证观测一致,即四面体滑移平面上的临界剪切应力不仅取决于滑移方向上的应力,还取决于两个正交剪切应力分量和三个法向应力分量。通过电子背散射衍射(EBSD)结合相关的α→β相变程序,我们对α板条/层片进行了重构,使其满足局部晶体学取向关系。程序可基于实验EBSD数据拟合单个半条/层片的体积分数,并根据负载方向生成相邻变体之间的惯析面分布。以上模拟框架可被用于解释激光粉末熔炼制备的Ti-6Al-4V沿两个样品方向的拉伸/压缩变形行为和大应变轧制过程中的织构演化。即该模型能够预测塑性各向异性和与之相应的织构演化。虽然模型揭示了惯析面与加载方向之间的夹角对屈服应力的显著影响,但数据和模型预测的比较结果表明,惯析面的随机分布与流变响应一致。因此我们推断,材料的拉压不对称性是由于非Schmid效应导致的。