金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.205,15 Fed. 2021
2021-06-03 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文17篇,涵盖了铝合金、不锈钢、高熵合金、复合材料等,国内科研单位包括哈尔滨工业大学、上海交通大学、东北大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 205 目录
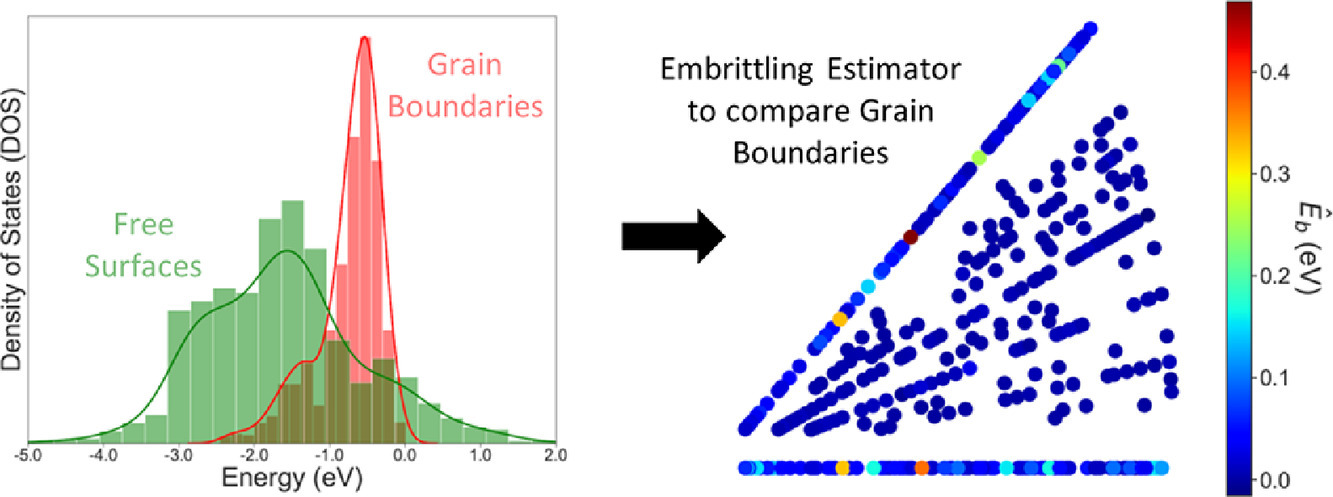
1. Spectrum of embrittling potencies and relation to properties of symmetric-tilt grain boundaries
对称倾斜晶界的脆化与晶界性质的关系研究
2. Stress relaxations during cyclic loading-unloading in precipitation hardened Mg-4.5Zn
Mg-4.5Zn在循环加载-卸载过程中的应力松弛
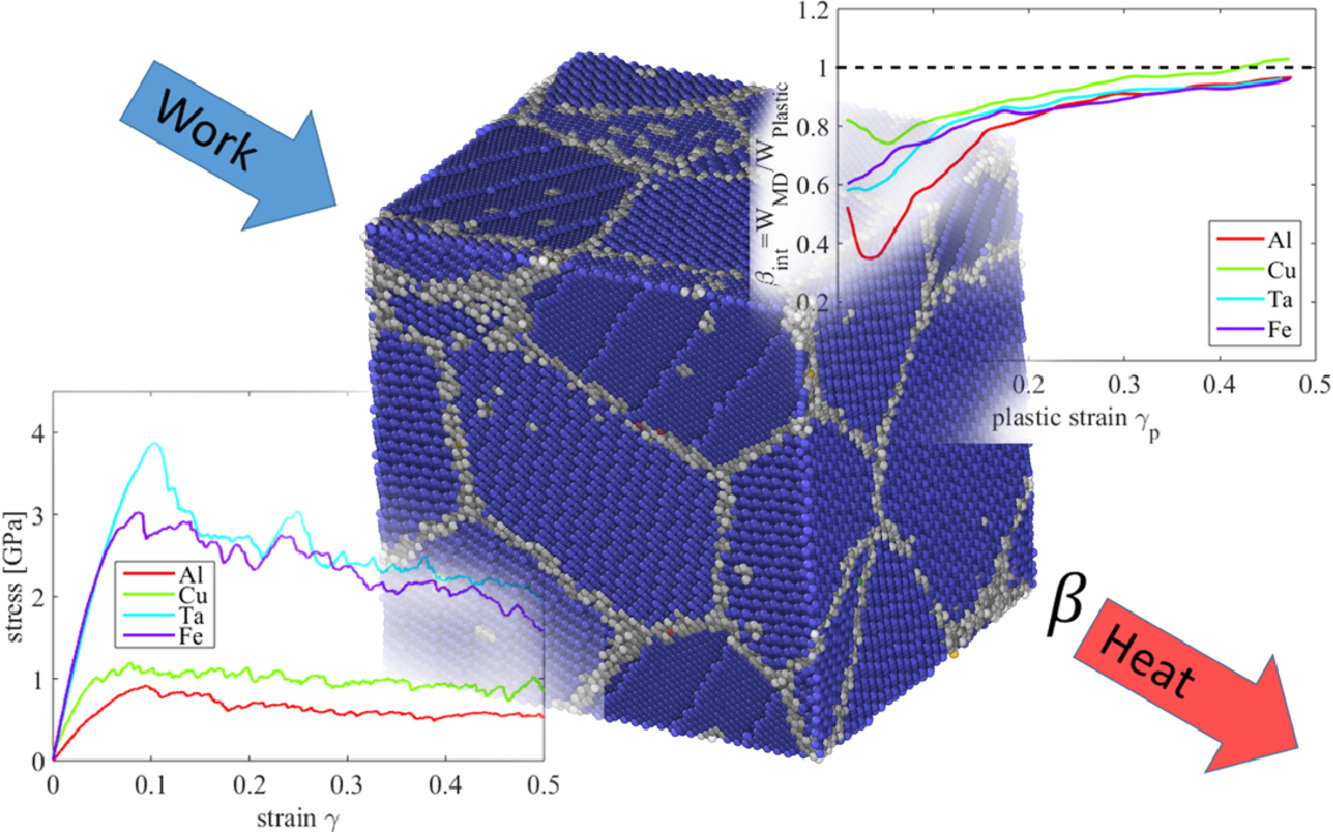
3. Employing molecular dynamics to shed light on the microstructural origins of the Taylor-Quinney coefficient
利用分子动力学阐明Taylor-Quinney系数与微观组织的联系
4. Modeling size and orientation effects on the morphology of microstructure formed in martensitic phase transformations using a novel discrete particle model
基于离散粒子模型研究尺寸和取向对马氏体相变组织形貌的影响
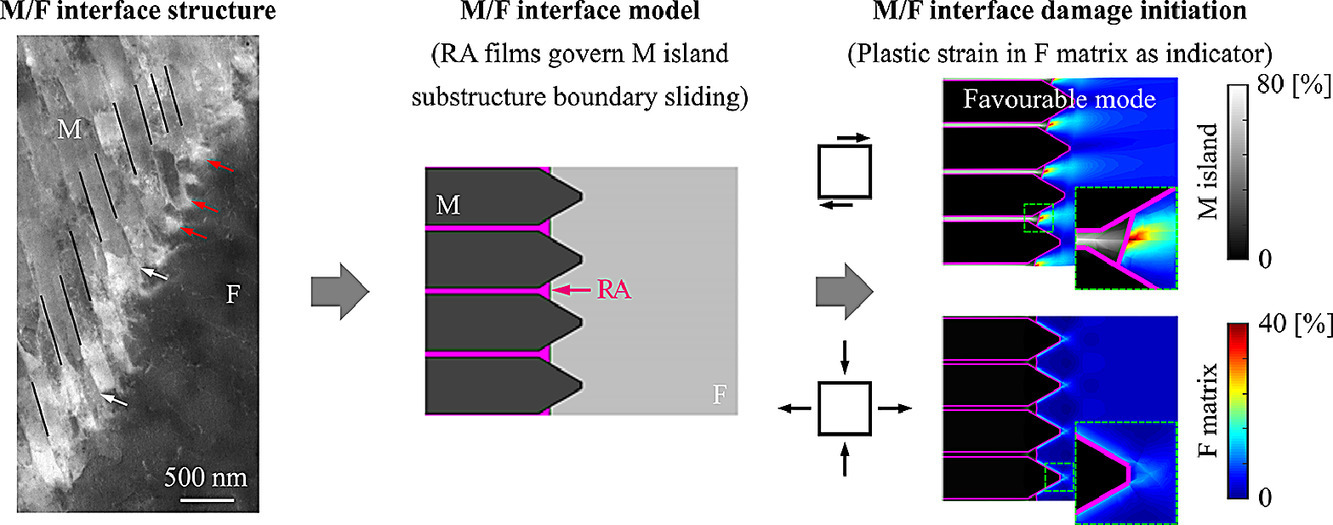
5. Revisiting the martensite/ferrite interface damage initiation mechanism: The key role of substructure boundary sliding
子结构界面滑移在马氏体/铁素体界面损伤机制中的关键作用
6. Creep Micromechanics in Meso-Length Scale Samples
中尺度试样中的微观蠕变力学研究
7. Direct observation of the dynamic evolution of precipitates in aluminium alloy 7021 at high strain rates via high energy synchrotron X-rays
7021铝合金在高应变率下析出相动态演化的高能X射线表征研究
8. Microstructural origin of ultrahigh damping capacity in Ni50.8Ti49.2 alloy containing nanodomains induced by insufficient annealing and low-temperature aging
通过不完全退火和低温时效制备含纳米畴的超高阻Ni50.8Ti49.2合金
9. The average and local structure of TiVCrNbDx (x=0, 2.2, 8) from total scattering and neutron spectroscopy
TiVCrNbDx (x= 0,2.2, 8)平均和局部结构的全散射和中子光谱分析研究
10. Precipitation behavior in G-phase strengthened ferritic stainless steels
G相强化铁素体不锈钢中的析出行为
11. Carbon redistribution in quenched and tempered lath martensite
淬火和回火板条马氏体中的碳再配分
12. Micromechanical behavior of multilayered Ti/Nb composites processed by accumulative roll bonding: An in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction investigation
叠轧多层Ti/Nb复合材料微观力学行为的原位同步辐射X射线衍射研究
13. Mesoscopic nature of serration behavior in high-Mn austenitic steel
高锰奥氏体钢锯齿行为的介观性质研究
14. On the low-cycle fatigue response of CoCrNiFeMn high entropy alloy with ultra-fine grain structure
超细晶CoCrNiFeMn高熵合金的低周疲劳响应
15. Morphological stability of spherical particles - Extension of the Mullins-Sekerka criteria to multi-component alloys under a non-stationary diffusive regime
基于对Mullins-Sekerka准则的拓展研究球形颗粒在多组分合金中非稳态扩散条件下的形貌稳定性
16. Temperature-induced wear transition in ceramic-metal composites
陶瓷-金属复合材料中的温度诱导磨损机制转变
17. A novel medium-Mn steel with superior mechanical properties and marginal oxidization after press hardening
一种具有优异力学性能和热压抗氧化性能的新型中锰钢研究
ACTA
Vol. 205,15 Fed. 2021, 116527
1. Spectrum of embrittling potencies and relation to properties of symmetric-tilt grain boundaries
对称倾斜晶界的脆化与晶界性质的关系研究
Doruk Aksoy, Rémi Dingreville, Douglas E. Spearot✉
D.E. Spearot:dspearot@ufl.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116527
摘要
金属材料中的晶界广泛存在于各种稳定/亚稳定结构中,而溶质偏聚可以改变晶界性质。在这本研究中,我们提出了一个公式,将溶质偏析脆化与占位统计建立了联系,并以Ni中S的晶界偏聚对脆化的影响说明了其应用。为了获得不同位置的偏析能,我们使用了嵌入原子势方法,对378个不同的对称倾斜晶界及其等效自由表面进行了分子静力学计算。结果表明,为了描述晶界的一般脆化性质,既需要考虑与脆化有关的能量,又需要考虑原子的占位概率。单独分析时,某些晶界表现出较大的脆化趋势;然而,当考虑多晶中S偏析到晶界的可能性时,脆化趋势就大幅减小了。为此,我们提出了一种新的物理量用于估计脆,它不仅对晶界进行了分类(脆化或强化),而且考虑了原子占位概率,从而可以对同一晶界网络内的晶界脆化行为进行比较。最后,我们对晶界脆化和晶界固有性质(如自由体积)之间的联系进行了统计研究,发现晶界脆化与过剩体积或能量之间无法简单地用线性模型解释。以上研究为亚稳合金的晶界调控提供了一项有效的理论工具。
ACTA
Vol. 205,15 Fed. 2021, 116531
2. Stress relaxations during cyclic loading-unloading in precipitation hardened Mg-4.5Zn
Mg-4.5Zn在循环加载-卸载过程中的应力松弛
Jun Wang✉, Mahmoud Reza Ghandehari Ferdowsi, Sitarama R. Kada, Peter A. Lynch, Zhiyang Wang, Justin A. Kimpton, Matthew R. Barnett
J. Wang:jun.wang2@deakin.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116531
摘要
我们研究了时效对Mg-Zn合金压缩循环载荷响应的影响。我们对样品进行了原位同步辐射X射线衍射和背散电子衍射表征,并对拉伸样品和锌含量较低的样品也进行了额外的测试。时效的影响是复杂的。在加载初期,时效显著促进了滑移孪晶的形成。但时效样品中的孪晶宽度比非孪晶样品中更短。卸载过程中,时效样品中形成额外的“向前”孪晶,随后发生脱孪。未时效样品中同样出现脱孪现象,但没有额外的“向前”孪晶形成。在之后的再加载过程中,未时效样品表现出再加载屈服效应,而时效样品则没有。时效还会导致明显的棘轮张力。为解释这些现象,需要考虑孪晶和析出周围位错活动引起的应力松弛。位错对孪晶附近高应力区的滑移松弛有阻碍作用。同时,未变形第二相周围应力区域的滑移会引起载荷的重新分布,并导致时效样品中的棘轮效应。模拟时效镁合金的循环载荷响应需要考虑这些复杂的松弛效应。

ACTA
Vol. 205,15 Fed. 2021, 116511
3. Employing molecular dynamics to shed light on the microstructural origins of the Taylor-Quinney coefficient
利用分子动力学阐明Taylor-Quinney系数与微观组织的联系
Roman Kositski✉, Dan Mordehai
R. Kositski:kositski@gmail.com, romka055@gmail.com, romanko@tx.technion.ac.il
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116511
摘要
Taylor-Quinney系数(TQC)或冷加工转换系数是指,材料在塑性变形过程中,外部功转化为热的百分数。自其在近一个世纪前被首次提出以来,其实验测量值通常介于0.1到1之间的一个较大范围,并被认为与应变和应变速率有关。然而,对于组织与TQC之间的关系,特别是位错和晶界与塑性变形过程中能量存储之间的关系,却少有研究。在此,我们利用了分子动力学模拟对铝、铜、铁、钽单晶和纳米晶样品在极高应变速率下塑性变形过程中的功-热转换进行了研究。研究发现,如果拖曳控制状态下的位错滑移是塑性变形的唯一机制,那么所有的外部功都将转化为热,就像在位错偶极单晶中的情况一样。另一方面,我们在纳米晶样品发现,依据晶界形貌和分布的演变,部分能量会被储存在晶体中,或从晶体中被释放出来。此外,我们强调了TQC的积分测量和微分测量之间的区别。如果应变增加导致微观组织缺陷退火,那么微分测量结果甚至可以大于1。基于以上原子尺度研究结果,我们认为,在实验应变速率条件下,晶界的演化对多晶材料中的能量存储有重要影响。
ACTA
Vol. 205,15 Fed. 2021, 116528
4. Modeling size and orientation effects on the morphology of microstructure formed in martensitic phase transformations using a novel discrete particle model
基于离散粒子模型研究尺寸和取向对马氏体相变组织形貌的影响
Mahendaran Uchimali, Balkrishna C. Rao, Srikanth Vedantam✉
S. Vedantam:srikanth@iitm.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116528
摘要
样品经可逆马氏体相变后的组织形貌与其尺寸及样品相对于热机械载荷的取向有关。在此,我们采用了一种新的离散粒子方法来研究这些影响。这一方法用到了从材料的自由能函数直接推导得到的离散多体粒子相互作用。为了研究奥氏体/马氏体界面,我们将样品置于温度梯度之下。孪晶马氏体自适应和界面相容性之间的竞争导致了样品具有非常独特的显微组织。我们研究了外加温度梯度与母相取向间的夹角对相界的影响。在小样品中,由于自由表面和相关组织的影响,奥氏体和单一马氏体变体间的相界呈带状。机械载荷引起的脱孪与初始组织显著相关。孪晶界传播的动力学表现为经典的粘附-滑移形式。

ACTA
Vol. 205,15 Fed. 2021, 116533
5. Revisiting the martensite/ferrite interface damage initiation mechanism: The key role of substructure boundary sliding
子结构界面滑移在马氏体/铁素体界面损伤机制中的关键作用
L. Liu, F. Maresca, J.P.M. Hoefnagels, T. Vermeij, M.G.D. Geers, V.G. Kouznetsova✉
V.G. Kouznetsova:v.g.kouznetsova@tue.nl
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116533
摘要
马氏体/铁素体(M/F)界面损伤是双相钢失效的重要控制因素,一般认为,损伤的主要原因是马氏体和铁素体之间存在较大的相差。然而,这与最近的一些实验观测结果矛盾,这些结果表明,相当部分M/F界面损伤的萌生往往伴随着明显的马氏体塑性变形和较弱的马氏体/铁素体应变分配。事实上,马氏体具有复杂的层次结构,因此其塑性响应具有强烈的非均匀性和取向依赖性。一般认为(板条)马氏体很难变形。然而,在特定取向条件下,触发半条界滑移所需的分切应力可与铁素体相当。此外,对M/F界面结构的精细表征表明,嵌入铁素体的尖锐马氏体和板条台阶边界共同构成了M/F界面的锯齿状形貌,它们对M/F界面行为有很大影响。通过考虑在文献中通常被忽视的子结构和形貌特征,我们重新研究了M/F界面损伤的萌生机制。我们对不同的加载条件、相分数、马氏体相变残余应力/应变以及可能的M/F界面形貌进行了系统研究。我们使用晶体塑性模拟了板条间的残留奥氏体(RA)薄膜对子结构边界滑移的影响。结果表明,亚结构边界滑移是板条马氏体最有利的塑性变形方式,这种滑移可以触发M/F界面损伤,从而导致DP钢的时效。以上研究有助于我们重新认识DP钢中M/F界面损伤的机制。
ACTA
Vol. 205,15 Fed. 2021, 116535
6. Creep Micromechanics in Meso-Length Scale Samples
中尺度试样中的微观蠕变力学研究
Syed Idrees Afzal Jalali✉, Vikram Jayaram✉, Praveen Kumar✉
S.I.A. Jalali:li.idrees2@gmail.com
V. Jayaram:qjayaram@iisc.ac.in
P. Kumar:praveenk@iisc.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116535
摘要
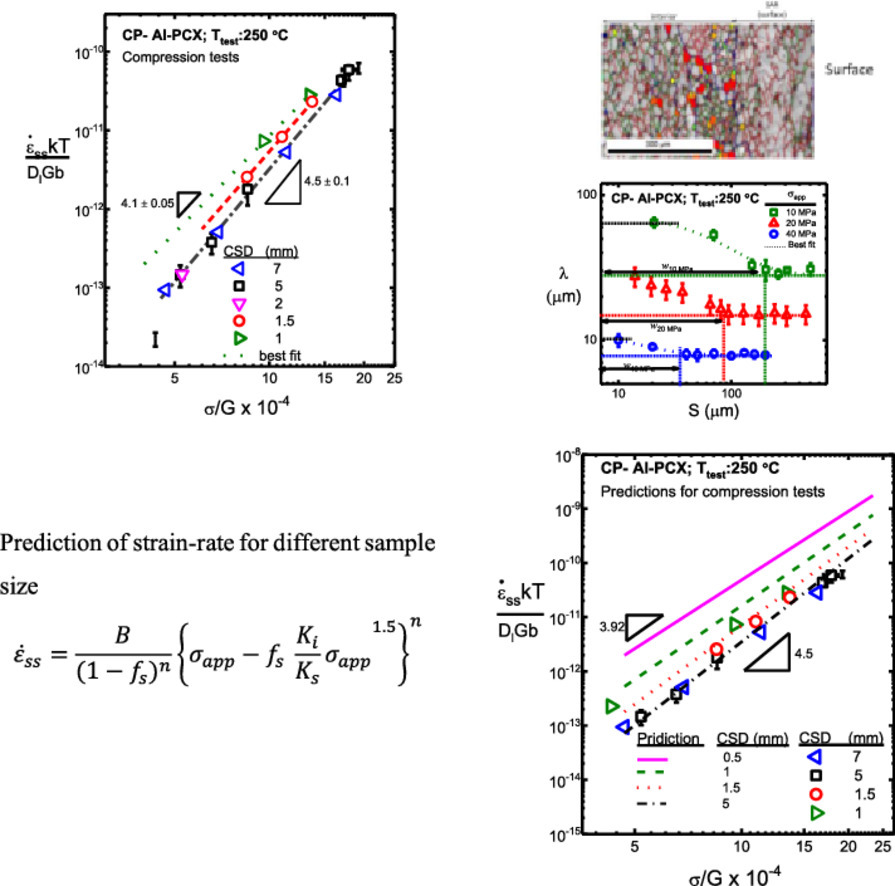
本工作主要研究中长尺度系统中的蠕变响应,最小尺寸为几百微米到几毫米。我们对商业纯铝多晶样品进行了单轴蠕变实验,样品尺寸介于500 μm至7 mm。与内部相比,近表面区域形成了蠕变位错亚结构,位错密度较低,亚晶尺寸较大。此外,表面影响区(SAR)的大小随外加应力增加而减小,并受晶粒尺寸的限制。当表面影响区大小与试样尺寸相当时,蠕变响应显著受到表面影响,使得材料整体的蠕变性能降低。这也导致应力指数随样品尺寸的降低而降低。表面和内部蠕变性能的差异导致材料表面和内部出现载荷转移。我们建立了一个组织敏感的等应变量化复合模型,对不同长度尺度下观察到的蠕变响应进行了解释。因此,本研究对蠕变微观力学提供了新的见解,并较好地统一了不同尺度下的幂律蠕变响应规律。
ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116532
7. Direct observation of the dynamic evolution of precipitates in aluminium alloy 7021 at high strain rates via high energy synchrotron X-rays
7021铝合金在高应变率下析出相动态演化的高能X射线表征研究
Priya Ravi, Diwakar Naragani, Peter Kenesei, Jun-Sang Park, Michael D. Sangid✉
M.D. Sangid:msangid@purdue.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116564
摘要
深入理解高强度铝合金中的动态析出现象对于精确模拟铝合金的工业制造具有重要意义。7系铝合金中的动态时效是应变和高温共同作用的结果。小角X射线散射(SAXS)是一种可对析出进行原位研究的先进技术,但目前只能在显著低于工业应变速率的条件下(< 10−3)进行。在本研究中,我们通过使用高能同步辐射X射线,证明了SAXS在更高的应变速率(10−2)下对合金进行原位研究的潜力。SAXS的时空间信息可被用于评估动态析出演化模型,并且表明除了应变、动力学等因素外,为了阐明应变速率对动态析出的影响,必须考虑空位湮灭的作用。

ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116541
8. Microstructural origin of ultrahigh damping capacity in Ni50.8Ti49.2 alloy containing nanodomains induced by insufficient annealing and low-temperature aging
通过不完全退火和低温时效制备含纳米畴的超高阻Ni50.8Ti49.2合金
Yuanwei Song, Mingjiang Jin✉, Xiaocang Han, Xiaodong Wang✉, Peng Chen, Xuejun Jin
M. Jin:jinmj@sjtu.edu.cn (上海交通大学)
X. Wang:xdwang77@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116541
摘要
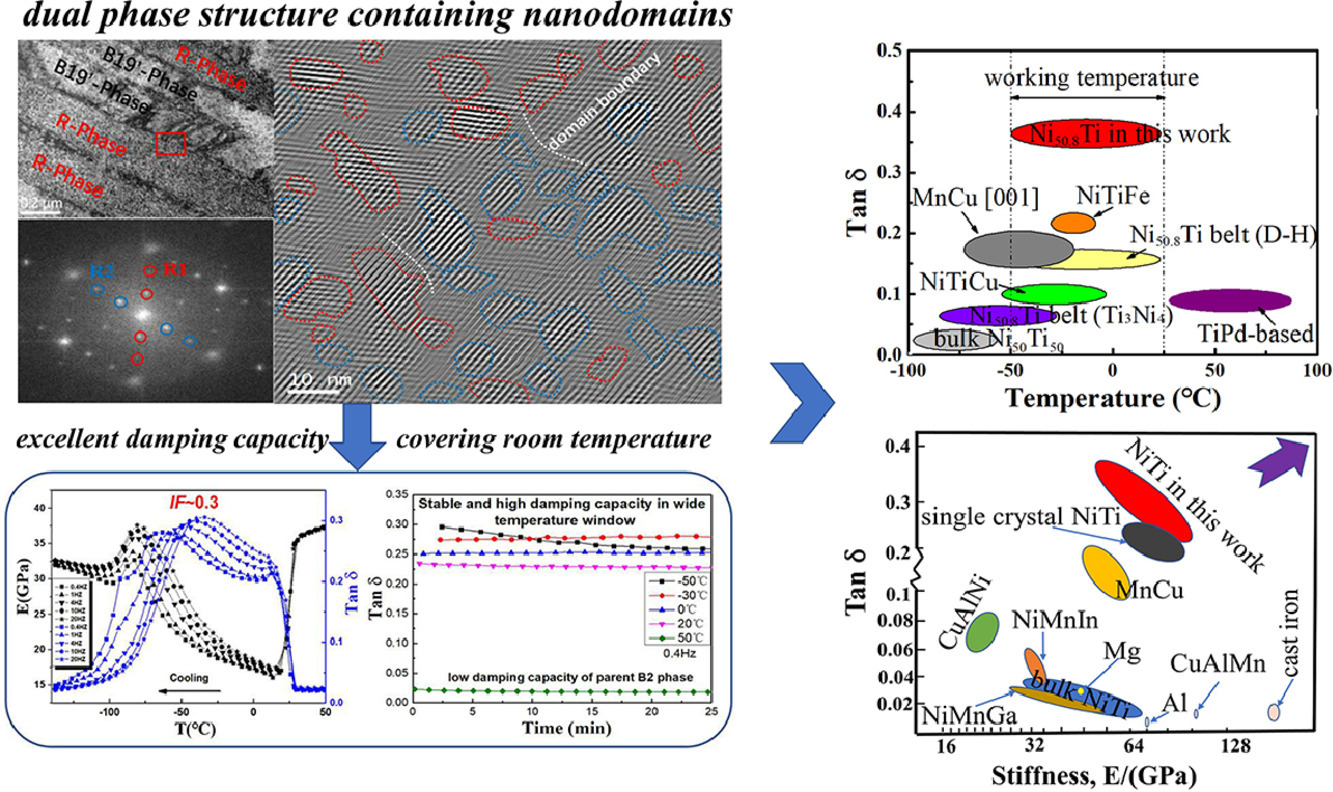
我们报道了一种具有极高阻尼特性的Ni50.8Ti49.2合金,该合金在低频和较宽温度窗口的内耗值为~ 0.35(tanδ)。该合金是通过强烈变形(~90%冷加工)后不完全退火,随后低温时效制备得到的。通过相变分析和微观结构表征,我们发现这种内耗平台的产生是由于纳米畴的存在、以及B19’相和R相能在较宽的温度范围内稳定共存。大量的相界和纳米畴间的可动界面对这一摩擦平台具有重要贡献。进一步的分析表明,低温时效引起的Ni偏聚对诱导纳米畴形成具有关键作用。我们在室温下观察到了针状B19 '马氏体的异常形成,这是由于不完全退火后的缺陷促进了低温时效过程中Ni的局部损耗或富集。以上结果表明,强烈变形后的Ni50.8Ti49.2合金中经不完全退火和低温时效两个步骤,可产生高密度纳米畴,这对于基于“畴工程”的高阻尼结构设计具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116496
9. The average and local structure of TiVCrNbDx (x=0, 2.2, 8) from total scattering and neutron spectroscopy
TiVCrNbDx (x= 0,2.2, 8)平均和局部结构的全散射和中子光谱分析研究
Magnus M. Nygård, Øystein S. Fjellvåg, Magnus H. Sørby✉, Kouji Sakaki, Kazutaka Ikeda, Jeff Armstrong, Ponniah Vajeeston, Wojciech A. Sławinski, Hyunjeong Kim, Akihiko Machida, Yumiko Nakamura, Bjørn C. Hauback
M.H. Sørby:magnus.sorby@ife.no
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116496
摘要
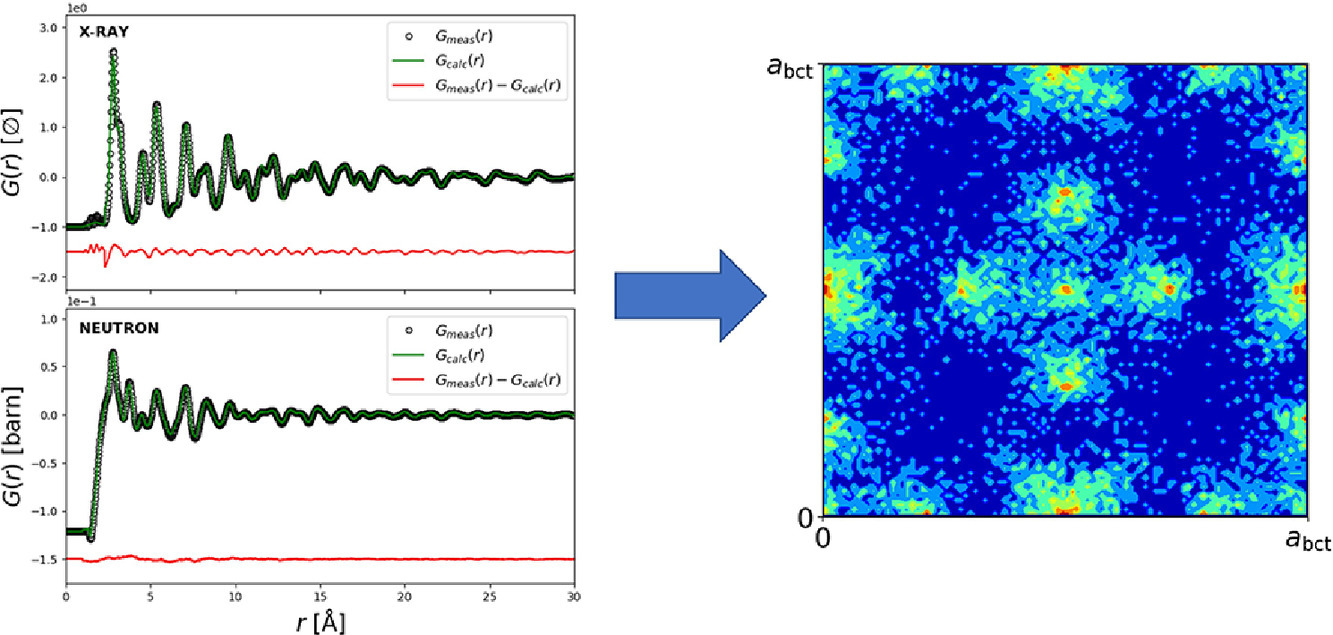
TiVCrNbH8的体氢密度最高的间隙氢化物之一,可达160 kg H/m3。但报道的室温下实际可逆H容量仅为理论容量的2/3左右。我们通过全散射测量和反向蒙特卡罗(RMC)模拟,对TiVCrNbDx(x=0, 2.2, 8 x = 0,2.2, 8)的局部结构进行了研究,以揭示氢/氘的占位是如何破坏其余位点的稳定的。研究表明,部分脱附的氘化物(x = 2.2)为I4/mmm体心四方结构,其中氘原子部分地占据四面体和八面体间隙位置。同时,具有低价电子浓度的最近邻金属占位显著增加,这可能引起氢化物的进一步失稳。非弹性中子散射(INS)和密度泛函理论计算(DFT)表明,TiVCrNbH2.4中的态振动密度差异很大,因此氢原子可在临近的间隙之间移动。
ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116542
10. Precipitation behavior in G-phase strengthened ferritic stainless steels
G相强化铁素体不锈钢中的析出行为
Mujin Yang, Daniel.J.M. King, Ivan Postugar, Yuren Wen, Junhua Luan, Bernd Kuhn, Zengbao Jiao, Cuiping Wang✉, M.R. Wenman, Xingjun Liu✉
C. Wang:wangcp@xmu.edu.cn(厦门大学)
X. Liu:xjliu@hit.edu.cn(哈尔滨工业大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116542
摘要
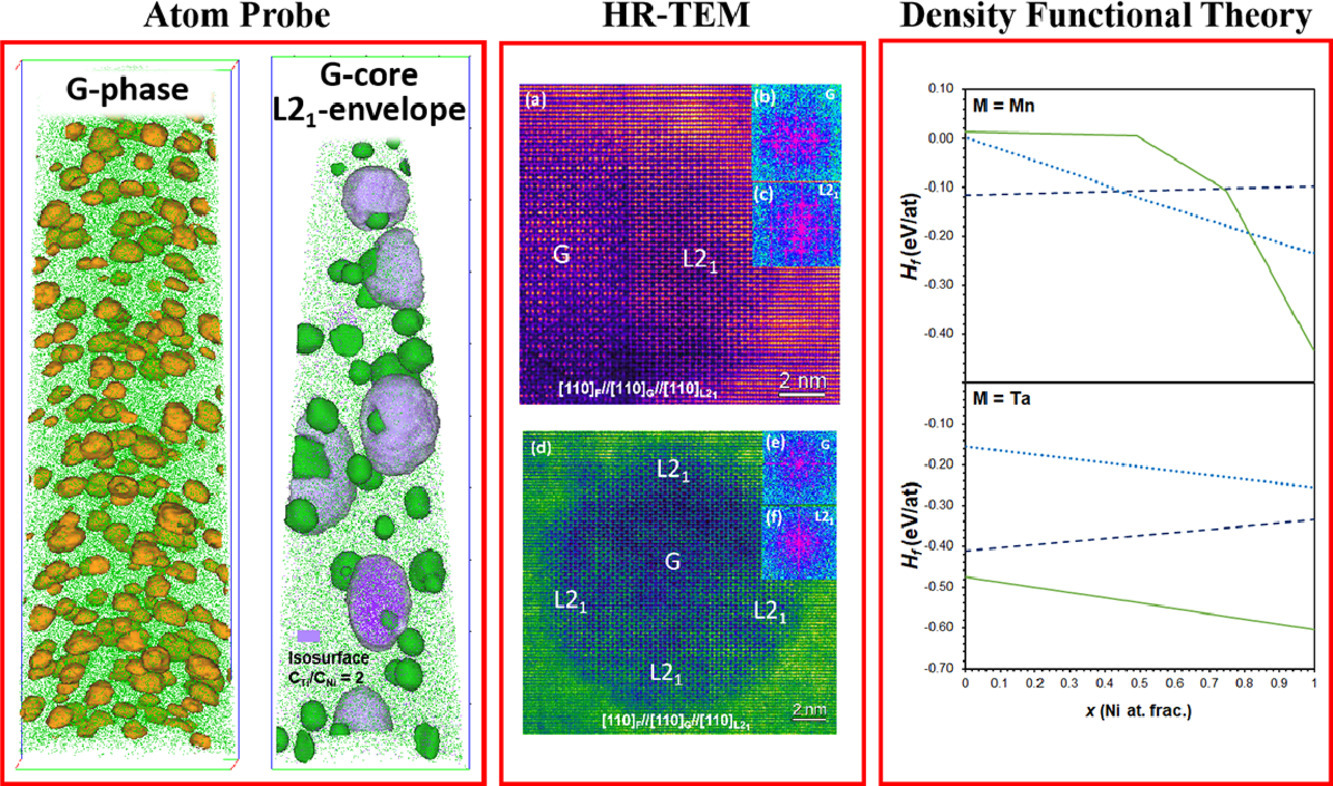
我们使用了显微硬度、透射电镜、原子探针等实验手段和第一性原理模拟对一系列经时效的G相强化铁素体不锈钢(Fe-20Cr-3Ni-3Si-X,X = 2Mn、1Mn-2Ti、1Mn-2Nb、1Mn-2Ta)进行了研究和表征。结果表明, 由于Ni16Mn6Si7G相和BCC相的生成焓相差不大,且其生成需要较高的Ni:Fe比,因此Ni16Mn6Si7 G相在时效过程的析出较为缓慢。在含Ti合金的早期时效(≤24 h)过程中,Ni16Ti6Si7 G相以核心形式析出,并被Fe2TiSi-L21 Heusler相包络。这种形貌的产生是由于时效早期铁素体中存在镍的团簇,而团簇附近的负镍浓度梯度有利于Fe2TiSi的形成。在96小时的时效过程中,G相只表现出颗粒粗化,而没有明显的化学成分演化。此外,硬度也显著提高,幅值约100 ~ 275 HV。以上研究结果对指导高强度钢中低错配硅化物的析出具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116521
11. Carbon redistribution in quenched and tempered lath martensite
淬火和回火板条马氏体中的碳再配分
L. Morsdorf ✉, E. Emelina, B. Gault, M. Herbig, C.C. Tasan
L. Morsdorf:l.morsdorf@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116521
摘要
回火引起的碳在马氏体钢中的重新配分,包括团簇、碳化物析出等,与钢铁材料的工艺和性能密切相关。在马氏体开始温度远高于室温的低碳钢中,碳在淬火过程中就已经发生重新配分。即使在同一奥氏体晶粒内,淬火组织中的局部自回火程度也会因马氏体半条的相变顺序而不相同。为了克服这种碳再分配研究中的局限性,我们通过对中断回火样品的电子隧穿对比成像和原子探针表征,结合背散电子衍射取向分析,系统地研究了单个马氏体板条内因回火导致的组织演变。结果表明,淬火态下,盘状碳团簇平行于马氏体的{100}晶面,其最大碳成分低于ε或η-碳化物中的碳含量。我们基于调幅分解理论对团簇形成的驱动力进行了讨论,这一过程类似于Fe-Ni-C合金中经低温淬火马氏体相变后的室温时效。此外,我们得到了回火过程中团簇溶解以及渗碳体在富碳位错处形核的直接证据。在这一过程中,位错网络是碳从团簇向渗碳体形核位置扩散的重要途径。

ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116546
12. Micromechanical behavior of multilayered Ti/Nb composites processed by accumulative roll bonding: An in-situ synchrotron X-ray diffraction investigation
叠轧多层Ti/Nb复合材料微观力学行为的原位同步辐射X射线衍射研究
S. Jiang, R. Lin Peng, Z. Hegedűs, T. Gnäupel-Herold, J. J. Moverare, U. Lienert, F. Fang, X. Zhao, L. Zuo, N. Jia ✉
N. Jia:jian@atm.neu.edu.cn(东北大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116546
摘要
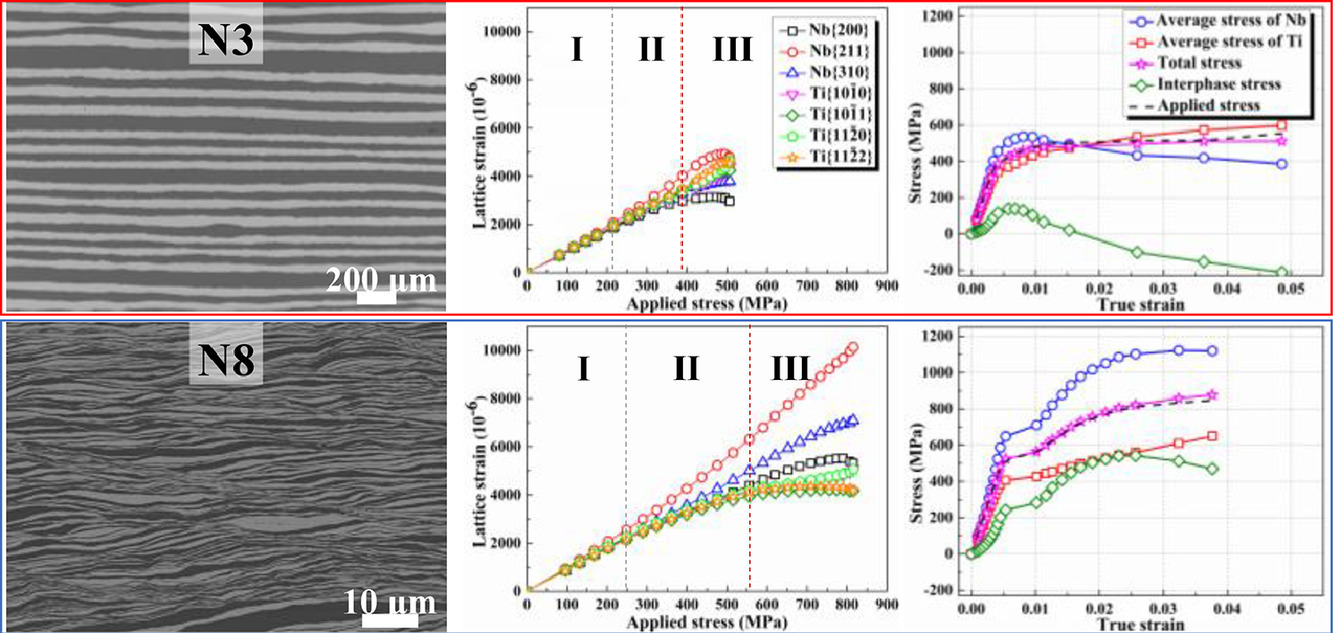
异相界面对复合材料的组织变形至关重要,从而决定了复合材料的力学性能。在此,我们通过累积叠轧方法(ARB)制备了Ti/Nb多层结构。随着轧制次数的增加,剪切带逐渐成为材料中的主要组成部分。为了探究具有不同叠层形貌的复合材料的组织与力学性能关系,我们对样品进行了原位高能X射线衍射拉伸试验。结果表明,随着ARB循环次数的增加,复合材料的快速强化主要来自Nb层中的位错、晶界和异相界面,其中{211}晶粒对材料的整体应变强化有很大贡献。较软的Ti晶粒在较大范围内表现出了应变硬化,推迟了颈缩。此外,完整的应力状态分析表明,当剪切带广泛存在时,相邻金属层间显著的载荷配分会导致各层中产生三轴应力,位错沿剪切方向滑移。这促进了位错的增殖和运动,有利于材料在保持良好延展性的同时提高强度。以上研究结果阐明了界面强约束对材料力学性能的影响,为深入理解ARB方法制备的多层结构的载荷分配和强化机制提供了基础。
ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116543
13. Mesoscopic nature of serration behavior in high-Mn austenitic steel
高锰奥氏体钢锯齿行为的介观性质研究
Sukyoung Hwang✉, Myeong-heom Park✉, Yu Bai, Akinobu Shibata✉, Wenqi Mao, Hiroki Adachi, Masugu Sato, Nobuhiro Tsuji✉
S. Hwang:hwang.sukyoung.85z@st.kyoto-u.ac.jp
M.-h. Park:park.myeongheom.8r@kyoto-u.ac.jp
Y. Bai:bai.yu.6m@kyoto-u.ac.jp
N. Tsuji:nobuhiro-tsuji@mtl.kyoto-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116543
摘要
在本文中,我们明确阐明了高锰奥氏体钢锯齿行为的本质以及与之有关的局部变形特征。我们以典型的FCC单相Fe-22Mn-0.6C (wt. %)为研究对象。材料经4个循环的冷轧和退火,得到平均晶粒尺寸为2.0 μm的完全再结晶组织。我们在室温下以8.3 × 10−4 s−1的初始应变速率对试样进行了拉伸试验,并利用数字图像关联技术(DIC)对试样的局部应变和应变速率分布进行了分析。结果表明,存在一种独特的应变集中行为,其特征是局部变形带的形成、传播和湮没,即所谓的PLC带,导致了材料应力-应变曲线的整体力学响应呈锯齿状。此外,我们利用了原位同步X射线衍射,对拉伸过程中形成的PLC带进行了详细研究。当每个PLC带穿过计量位置时,近垂直于拉伸方向的(200)面晶格应变均出现下降,这表明PLC带内部发生了应力松弛;同时,位错密度急剧增加,说明材料主要的塑性变形和加工硬化均在PLC带内发生。以上结果较好地解释了介观尺度下观测到的锯齿现象。22Mn-0.6C钢应力-应变曲线上的锯齿形行为完全由PLC带的形成、扩展和湮灭导致,即PLC带决定了材料的应变硬化特征。

ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116540
14. On the low-cycle fatigue response of CoCrNiFeMn high entropy alloy with ultra-fine grain structure
超细晶CoCrNiFeMn高熵合金的低周疲劳响应
S. Picak, T. Wegener, S.V. Sajadifar, C. Sobrero, J. Richter, H. Kime, T. Niendorf, I. Karaman✉
I. Karaman:ikaraman@tamu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116540
摘要
高熵合金是一类新型的多组分合金,具有优异的强塑性组合。然而,与其他高强度材料相比,它们的屈服强度水平仍然较低。本文采用等通道角压(ECAP)方法,通过组织细化,成功提高了 CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金的屈服强度。我们对粗晶和超细晶CoCrFeMnNi在室温下应变控制低周疲劳试验中的循环响应进行了比较研究,并对比了材料循环加载和准静态单向加载时的微观组织演变。材料经ECAP处理后屈服强度大幅提高至1 GPa左右。此外,ECAP样品在较低的应变幅值下表现出较好的疲劳寿命,而粗粒度样品则在高应变幅值下表现出较好的疲劳寿命。我们通过X射线衍射、背散电子衍射和透射电子显微镜等手段对材料的高周疲劳寿命和瞬态行为的潜在机制进行了研究。研究表明,ECAP试样中的小晶粒尺寸、高密度位错壁以及位错湮灭引起的胞结构形成是影响疲劳寿命和硬化行为的主要因素。ECAP试样在高应变幅值下的疲劳寿命较低,主要是由于高应力、以及位错湮没加速引起的循环软化所致。最后,我们基于应力对分位错的影响对位错胞结构和高密度位错壁同时形成的现象进行了合理解释。

ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116539
15. Morphological stability of spherical particles - Extension of the Mullins-Sekerka criteria to multi-component alloys under a non-stationary diffusive regime
基于对Mullins-Sekerka准则的拓展研究球形颗粒在多组分合金中非稳态扩散条件下的形貌稳定性
Gildas Guillemot✉, Charles-André Gandin
G. Guillemot:Gildas.Guillemot@mines-paristech.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116539
摘要
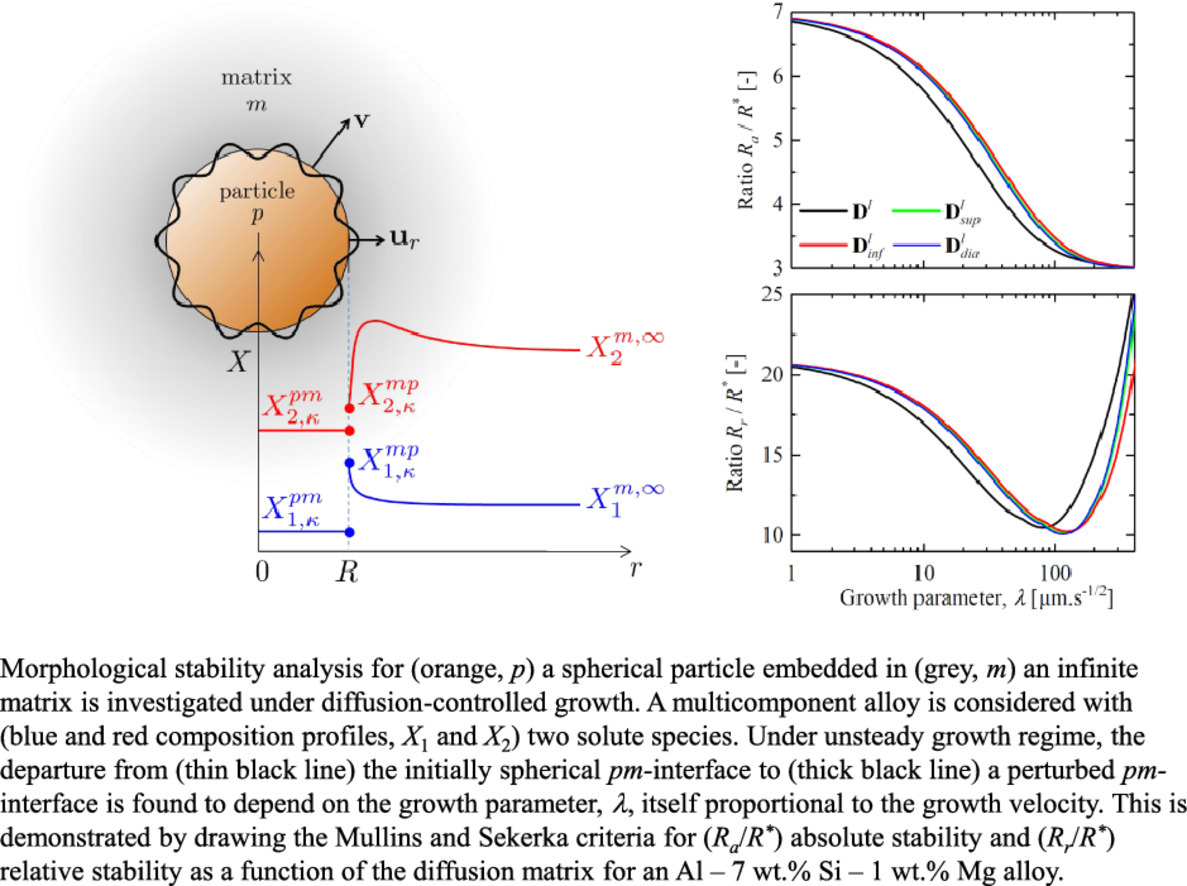
我们对Mullins和Sekerka的先驱性工作进行了拓展,分析了基体中第二相粒子球形生长的稳定条件。模型描述了多组分合金在元素互扩散非稳态生长状态下的失稳。我们基于球谐的初始扰动分解来确定它们随时间的演化。我们在绝对稳定和相对稳定条件下,推导了粒子临界半径的表达式。它于球谐函数、球的生长参数(正比于界面速度乘以时间的平方根)和扩散矩阵的特征值有关。通过考虑时变解,我们发现界面速度对稳定域有很大影响。我们将模型对文献中的其他解法进行了比较,发现它们仅在慢速条件下类似。最后,我们对模型在三元合金凝固中的应用进行了举例。
ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116545
16. Temperature-induced wear transition in ceramic-metal composites
陶瓷-金属复合材料中的温度诱导磨损机制转变
Ming Lou, Xiang Chen, Kai Xu, Zixuan Deng, Leilei Chen, Jian Lv, Keke Chang✉, Liping Wang✉
K. Chang:changkeke@nimte.ac.cn(中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所)
L. Wang:wangliping@nimte.ac.cn (中国科学院宁波材料技术与工程研究所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116545
摘要
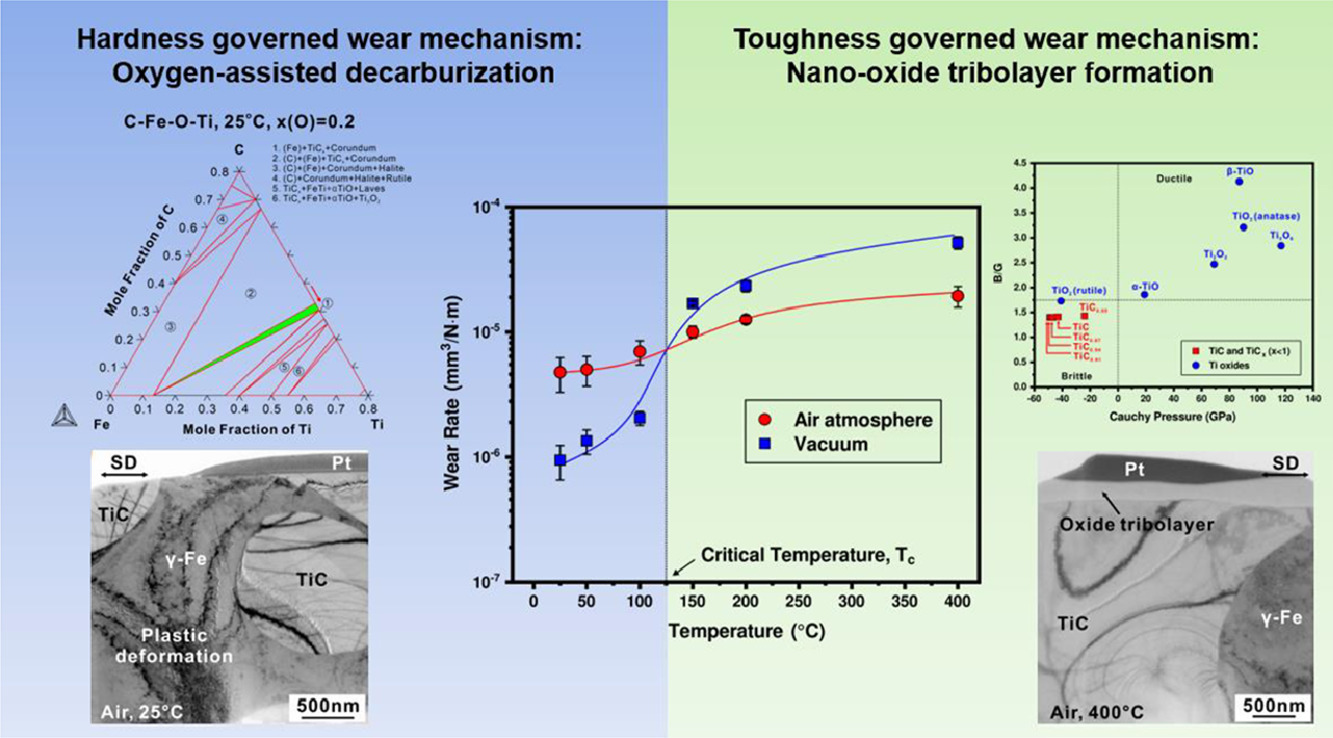
磨损劣化是工业应用中评价陶瓷-金属复合材料性能的一个重要指标。在此,我们选择了一种典型的复合材料(高锰钢+ 50 wt.% TiC)作为模型体系,对其磨损行为进行了研究。我们分析了不同温度和气氛条件下TiC陶瓷颗粒的完整性和损伤情况。我们在~125℃的临界温度下,发现材料的磨损机制发生了转变。在此温度以下,随着磨损率的增加,陶瓷颗粒表面出现氧诱导脱碳,因此硬度是磨损行为的主要控制因素。我们通过相图计算方法研究了氧诱导脱碳的热力学,并利用密度泛函计算(DFT)阐明了TiC颗粒硬度降低的过程。而当温度超过125℃时,陶瓷-金属变形不协调引起陶瓷颗粒开裂,因此韧性变为主要控制因素。DFT计算表明,纳米氧化层的形成提高了陶瓷颗粒的断裂韧性,抑制了磨损。因此,本研究揭示了陶瓷颗粒表面脱碳和增韧的微观竞争机制,可以较好地解释陶瓷-金属复合材料的磨损行为。
ACTA
Vol. 205, 15 Fed. 2021, 116567
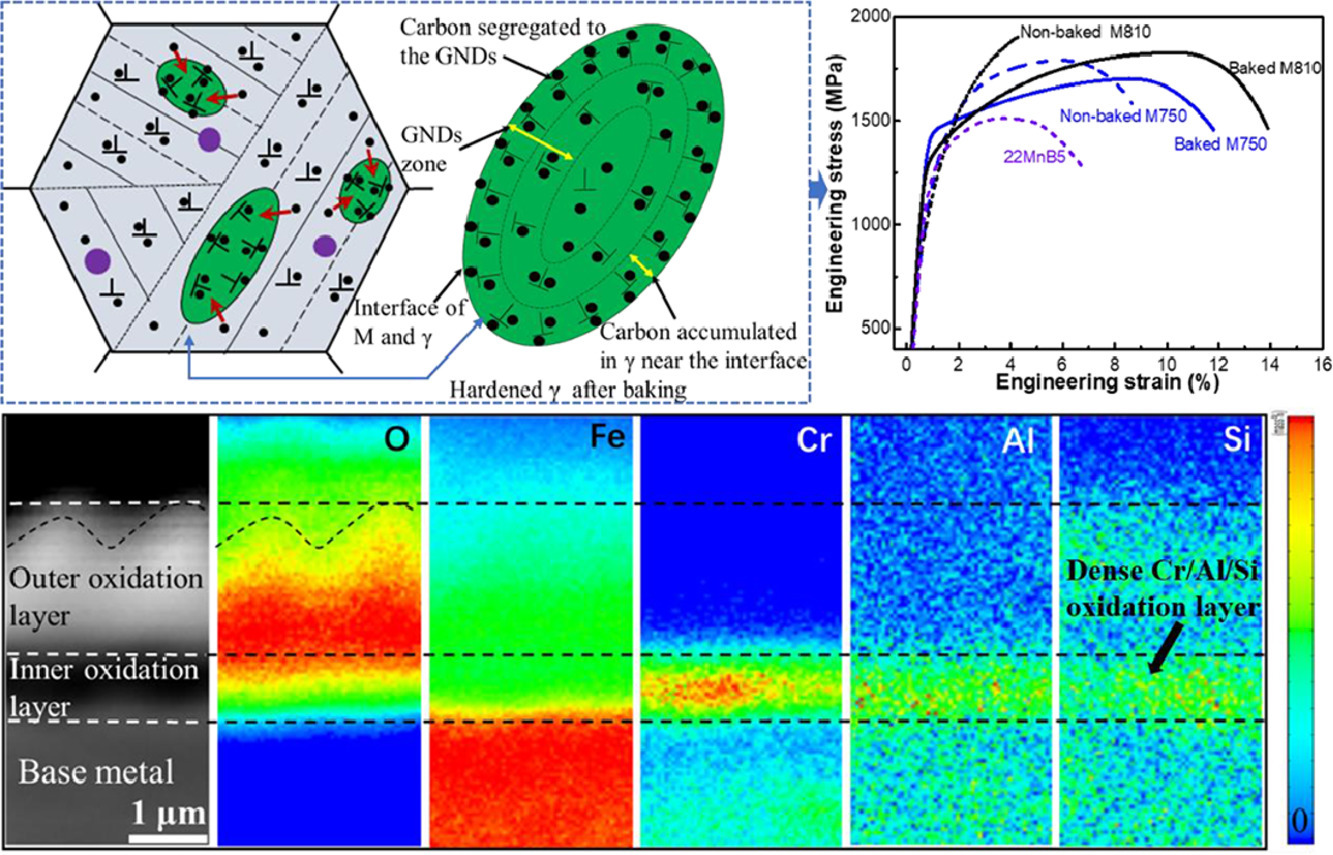
17. A novel medium-Mn steel with superior mechanical properties and marginal oxidization after press hardening
一种具有优异力学性能和热压抗氧化性能的新型中锰钢研究
Shuoshuo Li, Pengyu Wen, Shilei Li, Wenwen Song, Yandong Wang, Haiwen Luo✉
H. Luo:luohaiwen@ustb.edu.cn(北京科技大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116567
摘要
我们设计制造了一种新型的含Cr汽车用热成形中锰钢。与典型热成型钢22MnB5相比,它具有更优异的机械性能和热压抗氧化性能。同步辐射高能X射线衍射实验表明,在烘烤过程中,溶质原子C会从马氏体向奥氏体配分,随后偏聚到马氏体相变产生的几何位错上。这使得奥氏体晶粒发生强化,并在形变诱导马氏体相变过程中能够比未烘烤的奥氏体承受更多的载荷和变形,从而大大提高了材料的强度和延性。此外,这种新型中Mn钢在750 ~ 810℃热成形后,形成的氧化层厚度小于3 μm,远低于22MnB5中约100 μm的氧化层。这种抗氧化性能的大幅度提高,一方面是由于热成形的均热温度较低,另一方面是由于钢中的Cr、Al含量比22MnB5高得多,因此在氧化层底部能够形成致密的Cr/Al/Si氧化带。