金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.198, 1 June. 2021
2021-06-03 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文7篇,涵盖了中锰钢、高熵合金、增材制造等,国内科研单位包括清华大学、武汉理工大学、天津大学、西安交通大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 198 目录
1. Flash annealing yields a strong and ductile medium Mn steel with heterogeneous microstructure
闪速退火实现异质结构中锰钢的高强高韧
2. Achieving porous tungsten with high porosity by selective dissolution of W-Fe alloy
通过选择性溶解钨铁合金,获得孔隙率高的多孔钨
3. Formation of abnormal nodular ferrite with interphase precipitation in a vanadium microalloyed low carbon steel
钒微合金化低碳钢中具有相间析出的异常“结节状”铁素体的形成
4. The synthesis of TiC dispersed strengthened Mo alloy by freeze-drying technology and subsequent low temperature sintering
采用冷冻干燥和低温烧结技术制备TiC弥散强化的Mo合金
5. Synthesis and characterization of a new TiZrHfNbTaSn high-entropy alloy exhibiting superelastic behavior
具有超弹性的新型TiZrHfNbTaSn高熵合金的合成与表征
6. Improving creep resistance of Al-12 wt.% Ce alloy by microalloying with Sc
Sc微合金化提高Al-12 wt.% Ce合金的抗蠕变能力
7.Spherical pores as ‘microstructural informants’: Understanding compositional, thermal, and mechanical gyrations in additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V
球形孔隙作为“微观组织信息提供者”:了解增材制造Ti-6Al-4V中的成分、热和机械回旋
SCRIPTA
Vol. 198, 1 June. 2021, 113819
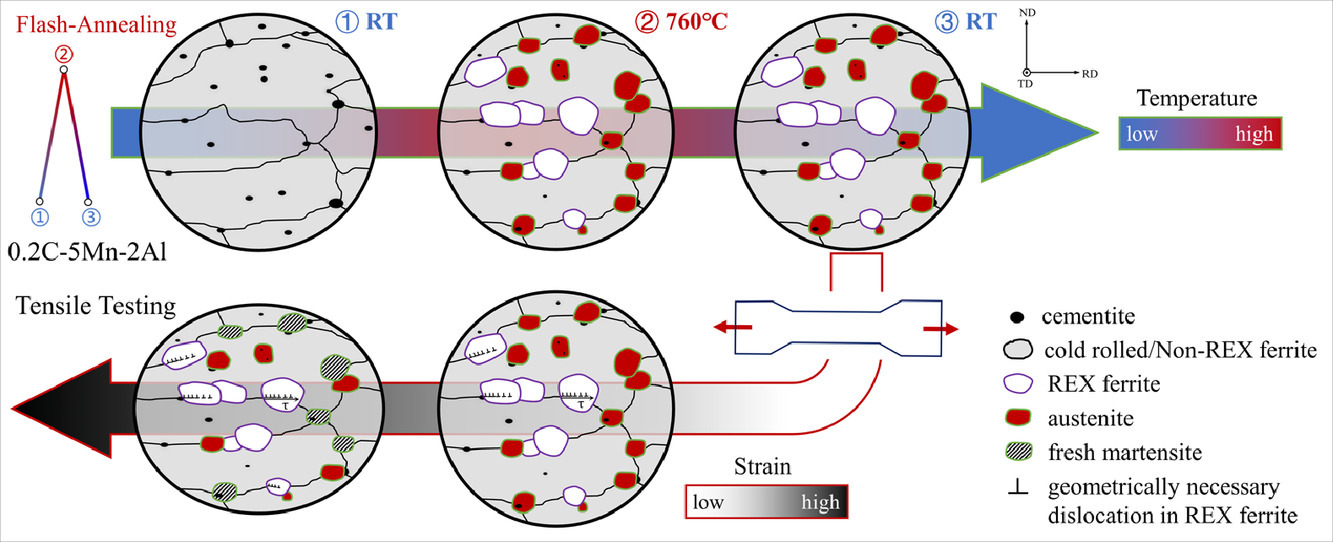
1. Flash annealing yields a strong and ductile medium Mn steel with heterogeneous microstructure
闪速退火实现异质结构中锰钢的高强高韧
Xinhao Wan, Geng Liu, Zhigang Yang, Hao Chen✉
Hao Chen: hao.chen@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn 清华大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113819
摘要
在中锰钢(MMS)中,通常利用奥氏体逆转变工艺(ART)来获取残余奥氏体(RA)。本工作中,我们提出了一种闪速退火工艺来处理中锰钢,该工艺通过奥氏体的“爆发式”形核和C元素的快速配分,在中锰钢中高效快速地获取大量的RA。此外,闪速退火还可以构建由再结晶/非再结晶铁素体晶粒组成的非均质铁素体基体,从而导致异质变形诱导硬化。和传统ART工艺处理的MMS,闪速退火工艺处理的MMS中独特的非均质组织造成了较高的屈服强度和抗拉强度,但塑性几乎无损失。闪速退火为调控微观组织和优化力学性能提供了另一种途径。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 198, 1 June. 2021, 113830
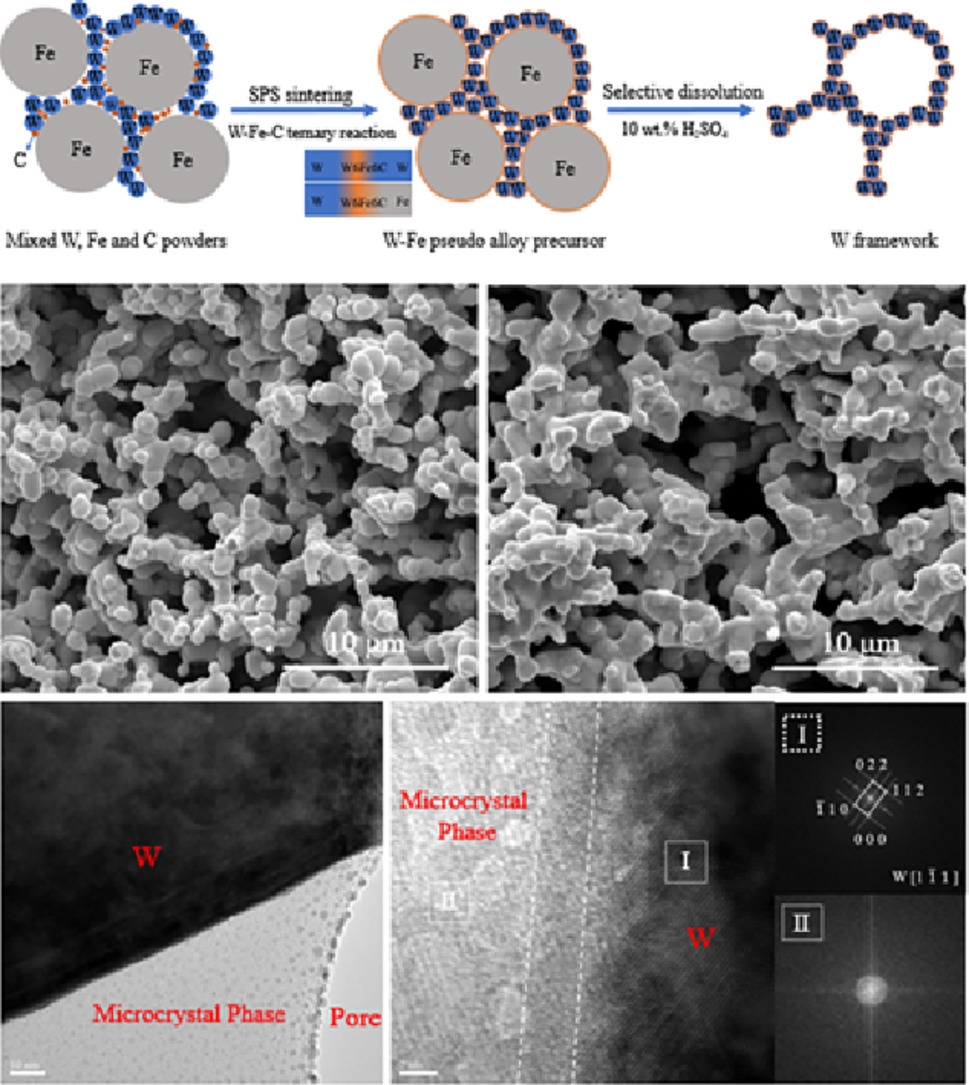
2. Achieving porous tungsten with high porosity by selective dissolution of W-Fe alloy
通过选择性溶解钨铁合金,获得孔隙率高的多孔钨
Shuai Ge, Jian Zhang✉, Zhigang Xu, Guoqiang Luo, Qiang Shen✉
Jian Zhang: zhangjian178@whut.edu.cn 武汉理工大学
Qiang Shen: sqqf@263.net 武汉理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113830
摘要
以铁为活性元素,通过选择性溶解,实现了孔隙率高达75.7%的多孔W。结果表明,在800℃下烧结W-Fe伪合金前驱体,纳米碳粉有助于原位形成W6Fe6C相,W-W和W-Fe界面均由W6Fe6C结合。它能够使前驱体继承初始致密物的形态而不变形。Fe选择性溶解后,W-W连接仍然存在,且形成W骨架。随着热处理温度的升高,孔隙率降低,抗压强度提高;由于W骨架中W6Fe6C的影响,孔径变化很小。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 198, 1 June. 2021, 113823
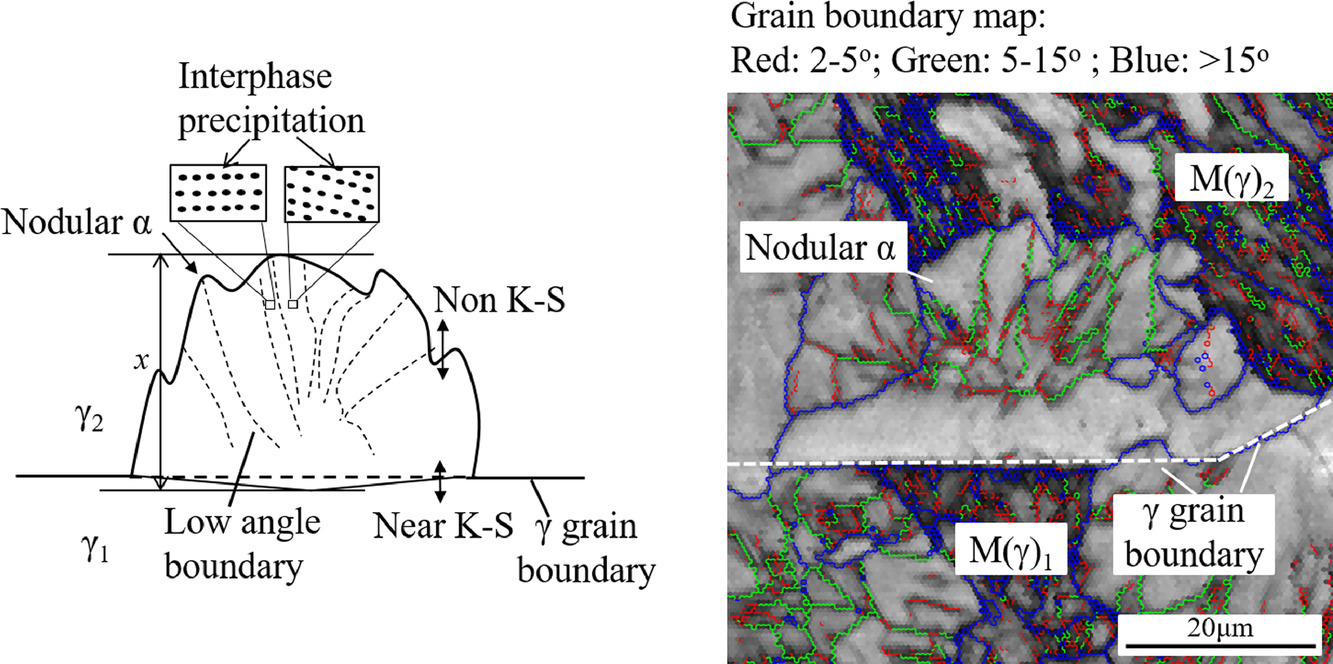
3. Formation of abnormal nodular ferrite with interphase precipitation in a vanadium microalloyed low carbon steel
钒微合金化低碳钢中具有相间析出的异常“结节状”铁素体的形成
Zhenqiang Wang, Yongjie Zhang✉, Goro Miyamoto, Tadashi Furuhara
Yongjie Zhang: yongjie@imr.tohoku.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113823
摘要
在钒微合金化低碳钢中,观察到了具有碳化钒相间析出的异常“结节状”铁素体。“结节状”铁素体的特点是具有高密度的低角度晶界,和周围奥氏体晶粒的取向与精确的Kurdjumov-Sachs取向关系偏差角度为15-30°。在同一合金中,“结节状”铁素体的生长速度明显快于正常晶界铁素体。即使在单一的“结节状”铁素体中,也确定了碳化钒相间析出多个变体的形成,且每个变体的边界都是低角度晶界。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 198, 1 June. 2021, 113831
4. The synthesis of TiC dispersed strengthened Mo alloy by freeze-drying technology and subsequent low temperature sintering
采用冷冻干燥和低温烧结技术制备TiC弥散强化的Mo合金
Weiqiang Hu, Zunfeng Du✉, Zhizhong Dong, Liming Yu, Tansir Ahamad, Zongqing Ma✉
Zunfeng Du: dzf@tju.edu.cn 天津大学
Zongqing Ma: mzq0320@163.com 天津大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113823
摘要
采用新型冷冻干燥技术和低温烧结技术合成了TiC弥散强化的Mo合金。采用冷冻干燥技术引入纳米TiC颗粒后,烧结后的Mo-TiC合金具有超细晶粒(2.38 μm)、高密度(99.3%)和高硬度(402±29 HV0.2)。冷冻干燥技术有效地抑制了Mo-TiC合金中第二相颗粒的团聚和生长。此外,我们还提出了净化和强化理论。缺少C的TiC (Ti8C5)会吸附附近的氧杂质,甚至形成TiO2来净化Mo基体。此外,TiC(002)、Ti8C5(0-24)和TiO2(111)可以与Mo(110)形成共格界面,增强相界,提高材料强度。稳定的相界面可以钉扎和限制第二相粒子的生长,从而保持其较小的尺寸(<50 nm)。
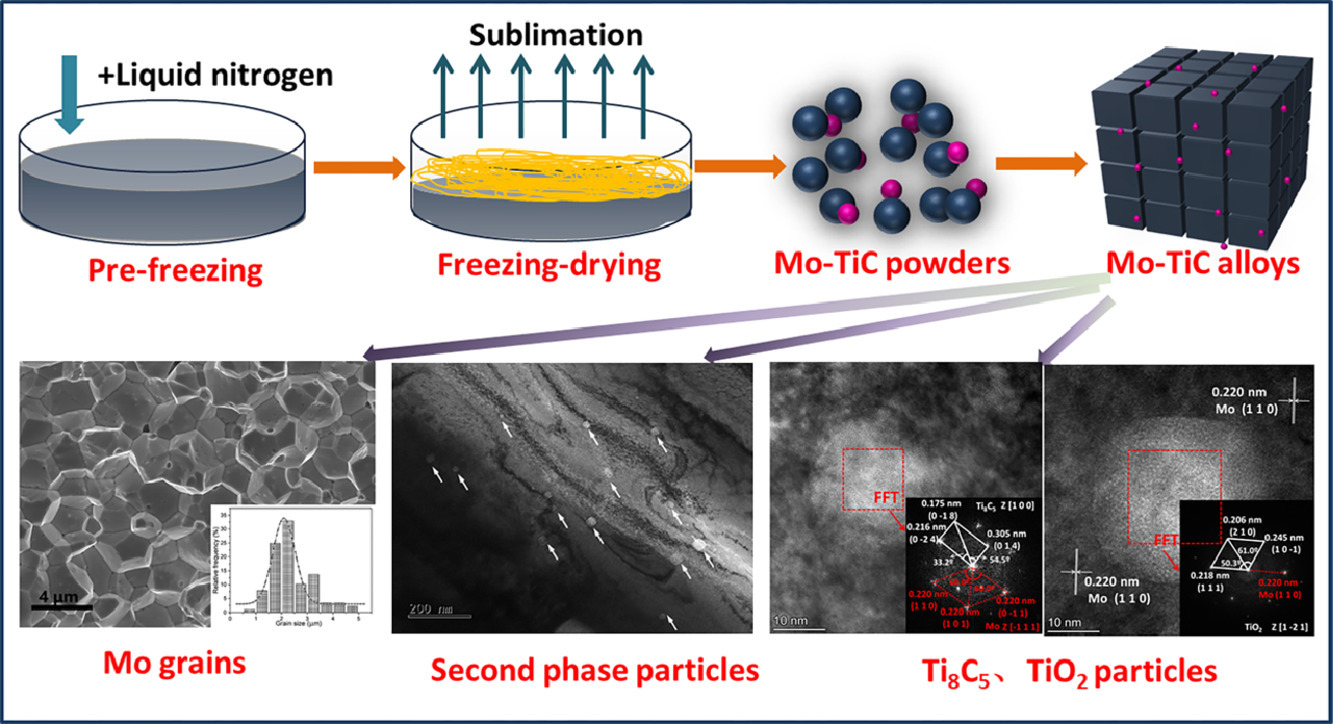
SCRIPTA
Vol. 198, 1 June. 2021, 113824
5. Synthesis and characterization of a new TiZrHfNbTaSn high-entropy alloy exhibiting superelastic behavior
具有超弹性的新型TiZrHfNbTaSn高熵合金的合成与表征
A. J. Gao, P. Castany, T. Gloriant✉
A. Gloriant: Thierry.Gloriant@insa-rennes.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113824
摘要
采用循环拉伸试验、透射电镜(TEM)、电子背散射衍射(EBSD)和原位同步X射线衍射(SXRD)等方法研究了一种新型的单相BCC结构Ti35Zr35Hf15Nb5Ta5Sn5高熵合金。该合金在β相和α''相之间发生了可逆的应力诱导马氏体相变,表现出超弹性行为。拉伸试验表明存在3.8%的高应变回复,这归因于<110>β{447}β的再结晶织构。
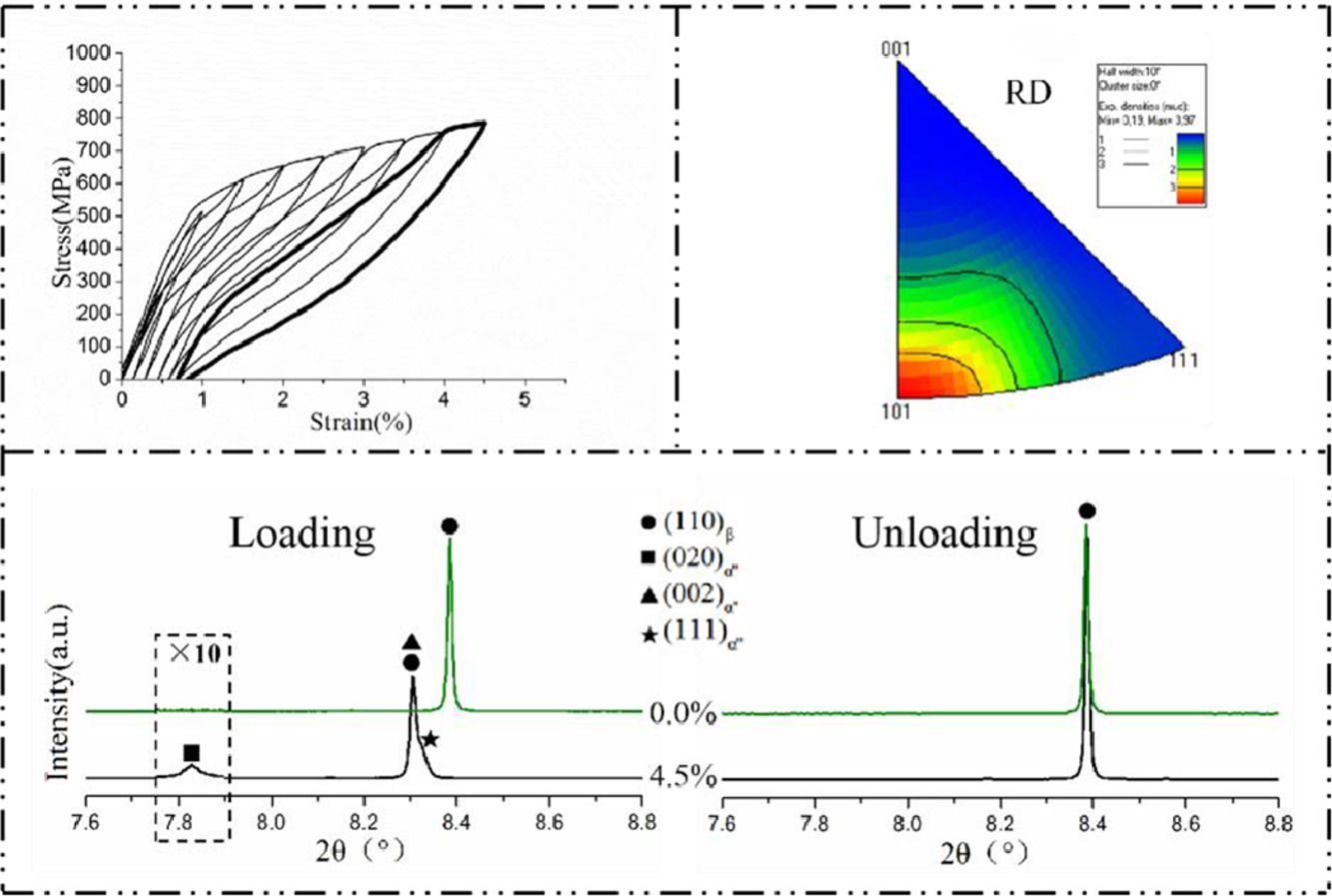
SCRIPTA
Vol. 198, 1 June. 2021, 113838
6. Improving creep resistance of Al-12 wt.% Ce alloy by microalloying with Sc
Sc微合金化提高Al-12 wt.% Ce合金的抗蠕变能力
Meng Yi, Peng Zhang✉, Chong Yang, Pengming Cheng, Shengwu Guo, Gang Liu✉, Jun Sun✉
Peng Zhang: zhangpeng.mse@xjtu.edu.cn 西安交通大学
Gang Liu: lgsammer@xjtu.edu.cn 西安交通大学
Jun Sun: junsun@xjtu.edu.cn 西安交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113838
摘要
用0.4 wt.% Sc对近共晶Al-12 wt.% Ce合金进行合金化以提高其抗蠕变性能。本文确定了Sc和Ce之间的双向影响:(i) Ce元素抑制了凝固过程中Sc在液相和固相之间的配分,降低了铸锭中Sc的显微偏析;(ii) 时效后Sc原子向Al11Ce3界面迁移,形成Al3Sc薄层或颗粒。前者促进了Al3Sc析出相在Al基体中分布的空间均匀性,后者在Al11Ce3/Alα相界面处引入了额外的晶格错配应变,抑制了基体位错攀过Al11Ce3层。这两种效应都能提高时效Al-12Ce-0.4Sc合金的蠕变抗力,其位错蠕变具有较高的拉伸应力阈值,在300℃为∼60 MPa。
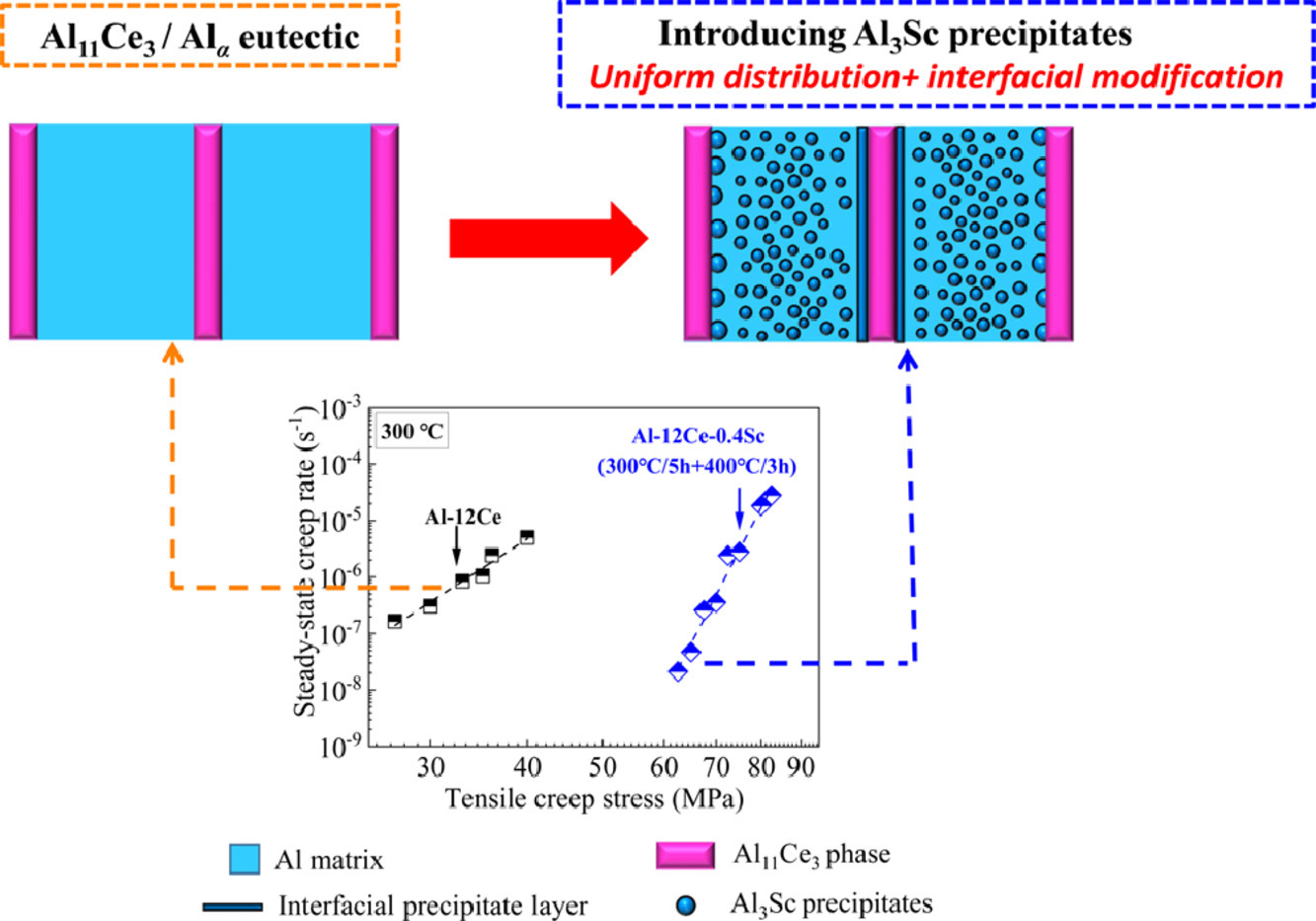
SCRIPTA
Vol. 198, 1 June. 2021, 113827
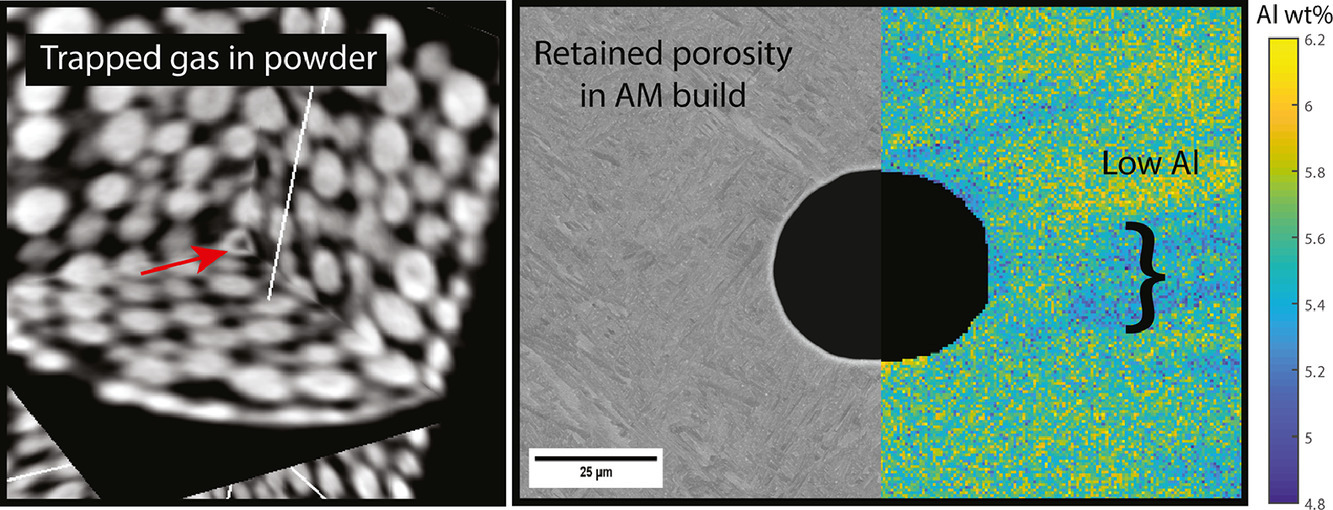
7. Spherical pores as ‘microstructural informants’: Understanding compositional, thermal, and mechanical gyrations in additively manufactured Ti-6Al-4V
球形孔隙作为“微观组织信息提供者”:了解增材制造Ti-6Al-4V中的成分、热和机械回旋
Matthew J.Kenney,KatieO'Donnell,Maria J.Quintana,Peter C.Collins✉
Peter C.Collins:pcollins@iastate.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113827
摘要
对诸如球形孔隙度等缺陷的详细分析可以充当信息提供者,提供与增材制造相关的复杂且通常被隐藏的物理特性的一些信息。这些缺陷的存在和性质的变化可以为增材制造过程提供新的见解。本文评估了电子束熔化的Ti-6Al-4V中气孔周围的化学成分,晶体学,微观组织和形貌特征,并将其与不同的扫描策略(光栅和两点熔化,Dehoff和随机扫描策略)相关联。仅在光栅扫描中存在的大球形孔(>25μm)表现出与孔垂直侧壁正交的扰动,这可能是由于化学和晶体学变化导致弹性不稳定性的结果,并且是由与循环过程相关的热应力引起的垂直压缩,实际上是微屈曲的一种形式。电子背散射衍射图支持以下理论:这些扰动在高温下以及最终的固相转变之前发生。