金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.206,1 Mar. 2021(上)
2021-06-03 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文13篇,涵盖了增材制造、马氏体、高温合金、复合材料等,国内科研单位包括南京理工大学、重庆大学、上海交通大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 206 目录
1. Examining material constitutive response under dynamic compression and large plastic strains using in situ imaging of hole closure
利用孔洞闭合原位成像技术检测材料在大塑性应变动态压缩下的本构响应
2. Initiation of fatigue damage in ultrafine grained metal films
超细晶金属薄膜中疲劳损伤的萌生
3. Microstructure formation and mechanical properties of ODS steels built by laser additive manufacturing of nanoparticle coated iron-chromium powders
使用纳米颗粒包覆Fe-Cr粉末和激光增材制造技术制备ODS钢的组织及力学性能研究
4. Growth of faceted, monolayer-coated nanovoids in aluminium
铝中多面体单层涂覆纳米孔洞的长大研究
5. Nucleation and growth of gas bubbles in AlSi8Mg4 foam investigated by X-ray tomoscopy
AlSi8Mg4泡沫材料中气泡形核长大的X射线断层扫描研究
6. Grain size effect on tensile properties and slip systems of pure magnesium
纯镁中晶粒尺寸对拉伸性能和滑移体系的影响
7. The mechanism of dynamic strain aging for type A serrations in tensile curves of a medium-Mn steel
中锰钢A型锯齿形拉伸曲线的动态应变时效机理研究
8. Effect of Alloying Elements on the High-Temperature Tempering of Fe-0.3N Martensite
合金元素对Fe-0.3N马氏体高温回火的影响
9. Slip-twinning interdependent activation across phase boundaries: An in-situ investigation of a Ti-Al-V-Fe (α+β) alloy
α+β双相Ti-Al-V-Fe合金中滑移-孪生相互激活的原位研究
10. Segregation and precipitation stabilizing an ultrafine lamellar-structured Al-0.3%Cu alloy
偏聚和析出对Al-0.3%Cu超细层状组织的稳定性影响研究
11. Ultrahigh tribocorrosion resistance of metals enabled by nano-layering
金属多层纳米结构的耐磨损腐蚀性能研究
12. Thermal-solutal-fluid flow of channel segregation during directional solidification of single-crystal nickel-based superalloys
镍基单晶高温合金定向凝固过程中通道偏析的热流-溶质-流体流动
13. Strength and plasticity of lamellar vs. fibrous eutectic Mg-Al nanocomposites: An in-situ microcompression study
层状与纤维状共晶Mg-Al纳米复合材料强度和塑性的原位微柱压缩比较研究
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116584
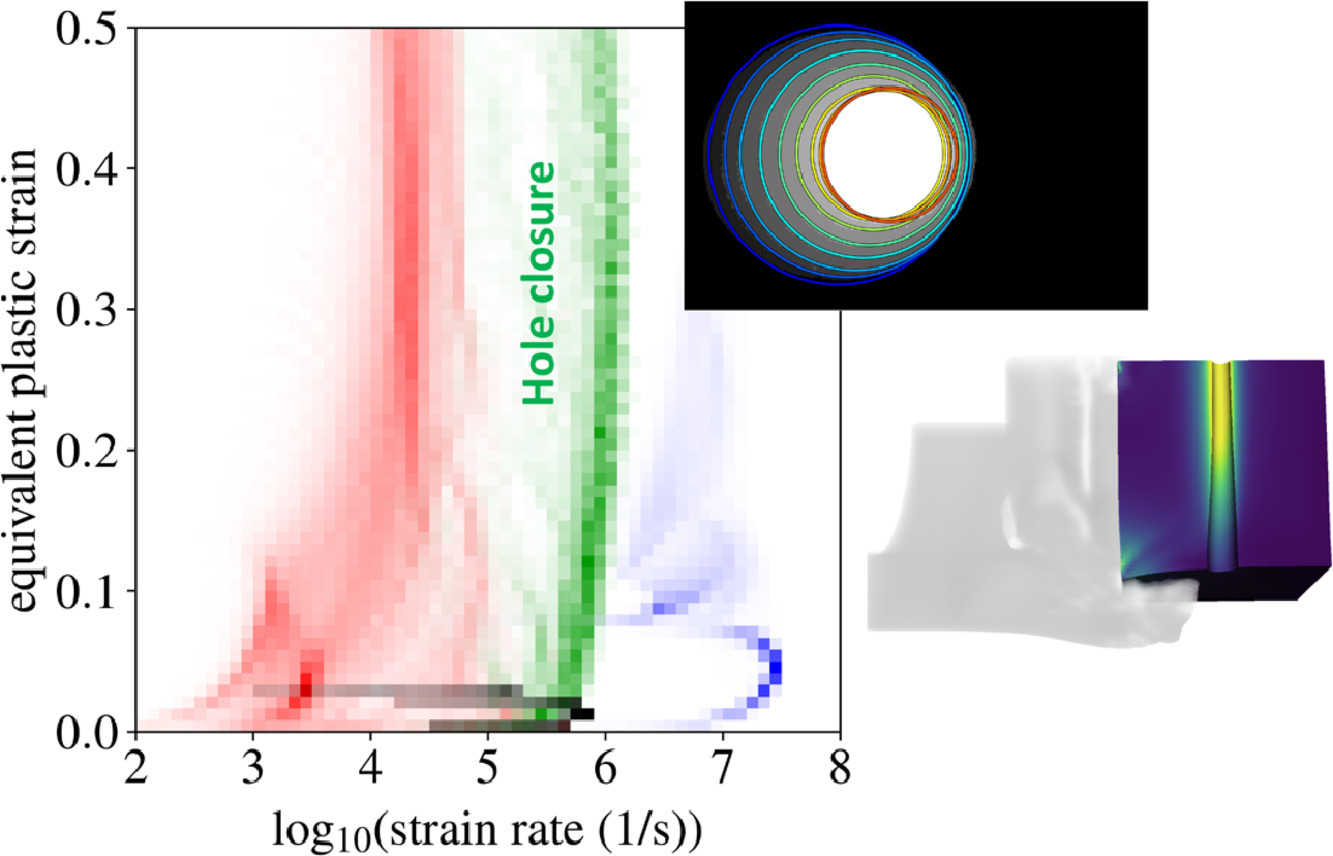
1. Examining material constitutive response under dynamic compression and large plastic strains using in situ imaging of hole closure
利用孔洞闭合原位成像技术检测材料在大塑性应变动态压缩下的本构响应
Jonathan Lind✉, Matthew D. Nelms, Andrew K. Robinson, Mukul Kumar, Nathan R. Barton
J. Lind:lind9@llnl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116584
摘要
为了了解材料在动态加载下的性能,需要研究应变速率以及材料初始状态对动态响应的影响。研究者通往往基于形状变化来推断材料在高应变率(>103/s)下的流变强度。考虑到应力和应变的非均质性,通过模拟的比较,可以更好地从实验观测结果推断出流动强度。我们介绍了一种新的平板冲击实验测试方法,该方法采用原位X射线成像技术来观察圆孔在可控幅度和持续时间的压力脉冲下的闭合情况。我们采用多帧成像技术测量圆孔闭合情况随时间的变化,从而获取材料在高应变率下塑性响应数据。我们将实验结果与PTW(Preston-Tonks-Wallace)数值模拟和MTS(Mechanical Threshold Stress)流变强度模型的预测结果进行了比较。定量分析结果提供了高速率硬化行为的MTS模型参数,这些参数难以通过准静态实验获得。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116599
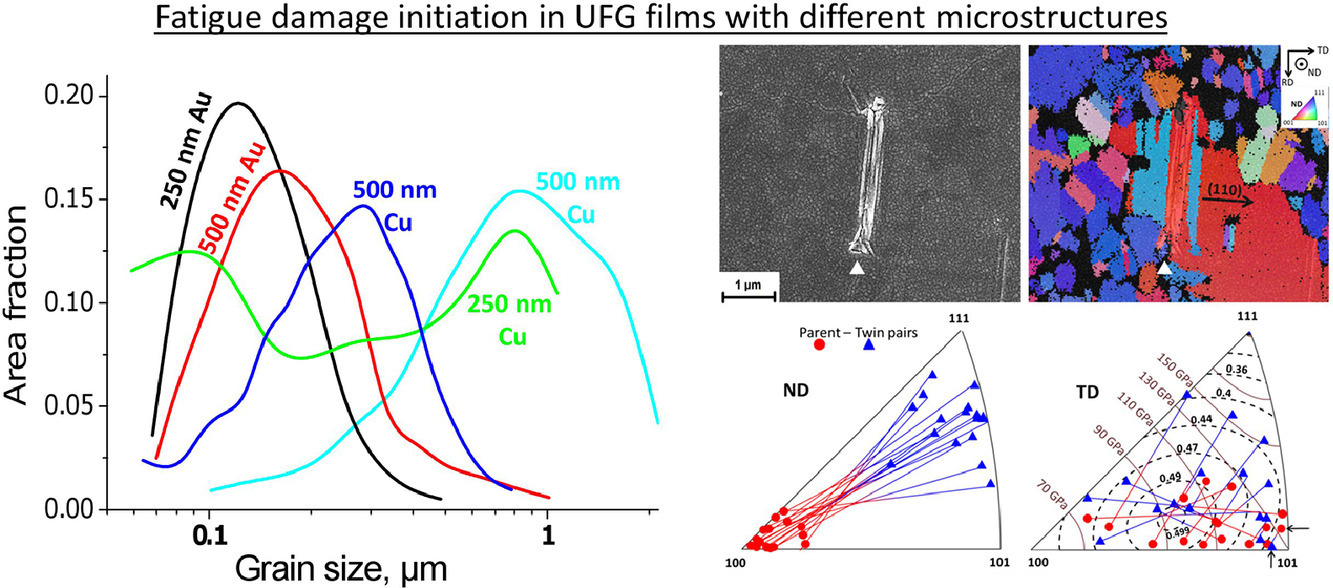
2. Initiation of fatigue damage in ultrafine grained metal films
超细晶金属薄膜中疲劳损伤的萌生
O. Glushko✉, D. Kiener
O. Glushko:oleksandr.glushko@unileoben.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116599
摘要
本研究的目的深入理解局部组织特征(如晶粒尺寸、晶粒取向、晶界特征等)和整体特征(如织构、晶粒尺寸分布、孪晶界分数等)对薄膜材料疲劳损伤萌生的影响。我们对于聚合物支撑的超细晶金和铜薄膜进行了振幅1%的循环应变,从而在单一宏观样品中观测材料的局部塑性响应。我们对发生塑性响应区域的微观组织进行了详细的背散电子衍射表征和统计分析。从微观组织上看,损伤发生在大晶粒(>1µm)附近特定取向的共格孪晶界附近。当初始组织中不存在满足条件的大晶粒时,机械诱导的晶粒粗化将促进疲劳损伤的发生。如果初始组织中没有满足取向条件的共格孪晶界,则动态粗化后的局部晶粒尺寸是控制塑性滑移集中的唯一参数。从宏观尺度上看,影响疲劳损伤萌生的组织参数主要是孪晶界比例、织构和晶粒尺寸分布的宽度。基于以上结果,我们对提高薄膜疲劳寿命的策略进行了讨论。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116566
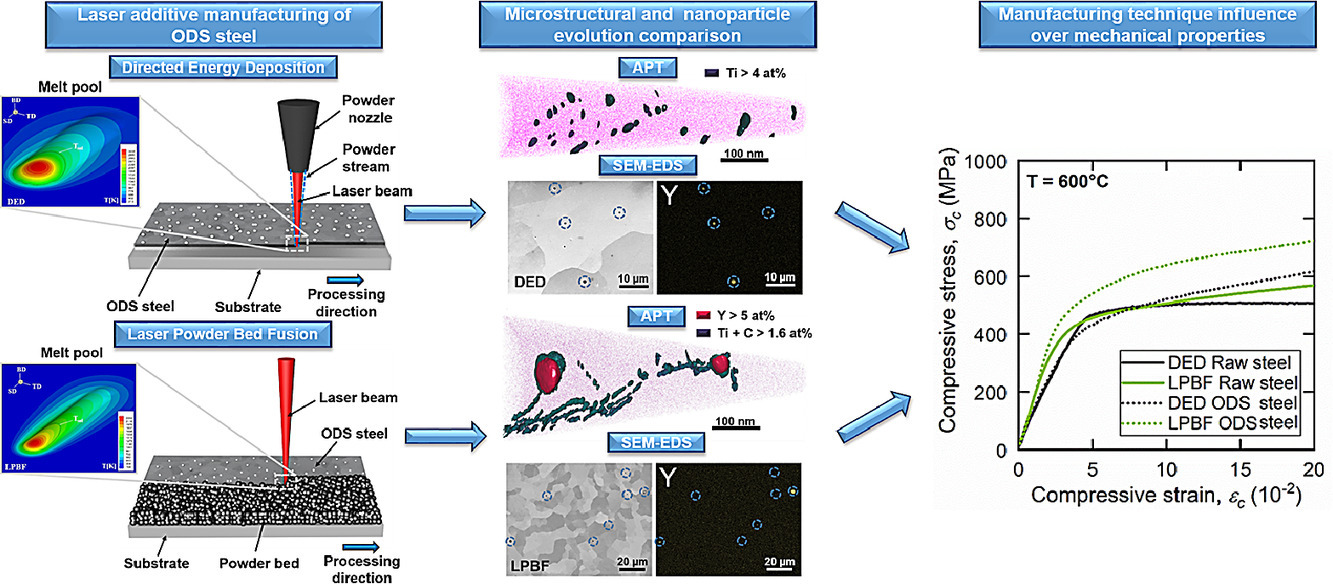
3. Microstructure formation and mechanical properties of ODS steels built by laser additive manufacturing of nanoparticle coated iron-chromium powders
使用纳米颗粒包覆Fe-Cr粉末和激光增材制造技术制备ODS钢的组织及力学性能研究
C. Doñate-Buendia, P. Kürnsteiner, F. Stern, M.B. Wilms, R. Streubel, I.M. Kusoglu, J. Tenkamp, E. Bruder, N. Pirch, S. Barcikowski, K. Durst, J.H. Schleifenbaum, F. Walther, B. Gault, B. Gökce✉
B. Gökce:bilal.goekce@uni-due.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116566
摘要
氧化物弥散强化(ODS)钢因其在高温或辐照条件下优异的机械性能而受到广泛关注。它们的组织与工艺密切相关,包括将纳米粒子加入基体钢粉,以及粉末的加工。对于ODS钢的增材制造而言,工艺的优化和控制仍是一个挑战。在此,我们通过介电控制吸附激光打印制备了含0.08 wt% Y2O3的PM2000 ODS钢,并对其组织、纳米粒子的演化和力学性能进行了表征和分析,研究了定向沉积(DED)和激光粉末熔化(LPBF)两种增材制造技术对ODS钢制备工艺的影响。与未添加Y2O3的DED和LPBF钢相比,ODS钢在600℃时的抗压强度分别提高了21%和29%。LPBF ODS钢的马氏硬度提高了9%,而DED ODS钢则没有明显变化。我们采用了背散电子衍射、扫描电子显微镜-X射线能谱和原子探针等方法,对DED和LPBF样品的围观组织和纳米粒子的组成、分布进行了研究。在600℃时,LPBF样品中Y-O纳米粒子的尺寸更小、分布更均匀,从而使得样品力学性能提高。通过限元方法模拟熔池,我们发现,LPBF的冷却速率比DED快约两个数量级,因此LPBF试样的粒子弥散程度和力学性能更佳。综上所述,本研究提出并验证了一种完全基于激光的ODS钢加工制备方法,并证明了该方法制备材料的组织和力学性能的优越性。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116594
4. Growth of faceted, monolayer-coated nanovoids in aluminium
铝中多面体单层涂覆纳米孔洞的长大研究
Xiaofen Tan✉, Matthew Weyland, Yu Chen, Timothy Williams, Philip N.H. Nakashima✉, Laure Bourgeois✉
X. Tan:xiaofen.tan1@monash.edu
P.N.H. Nakashima:philip.nakashima@monash.edu
L. Bourgeois:laure.bourgeois@monash.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116594
摘要
孔洞虽然可能导致材料的结构或电磁性能失效,但同时在等离子体和光学方面具有重要的应用前景。了解孔洞机械、光电和热学性质的关键是准确表征其结构演化,特别是孔洞的表面。在此,我们报导了在两种铝合金中形成、且表面被单层锡涂覆的孔洞。在特定的热处理条件下,部分具有高纵横比的孔洞(“管状孔洞”)可以生长至几百纳米。通过原子尺度分辨率的扫描透射电子显微镜(STEM)和光谱技术,我们发现孔洞表面被单原子层锡壳连续覆盖,并且锡壳与铝基体具有相同的原子结构。管状孔洞通常附着在与Al基体具有特定取向关系的Sn粒子上,而等轴孔洞则不附着在这类Sn粒子上。管状孔洞的长径比强烈地受到Sn粒子与孔洞壳层Sn原子排列共格性的影响。这些管状孔洞可以看作是嵌入铝基体的单壁纳米管。它们具有重要的研究价值,因为它们比相同体积的等轴孔洞更容易引起机械或电磁故障。被涂层包覆的孔洞易制备、可调控、无污染,是未来局部表面等离子体共振(LSPRs)研究的理想材料。
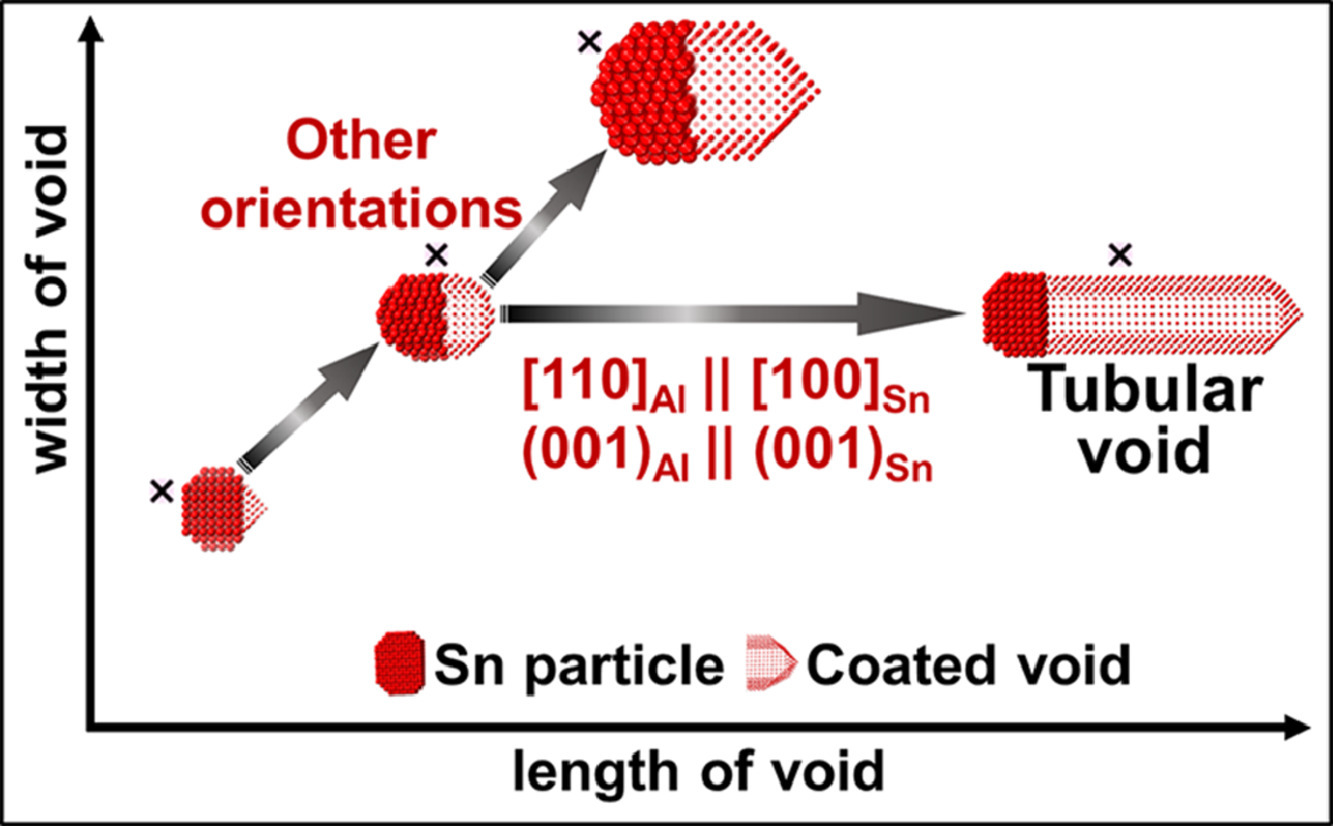
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116583
5. Nucleation and growth of gas bubbles in AlSi8Mg4 foam investigated by X-ray tomoscopy
AlSi8Mg4泡沫材料中气泡形核长大的X射线断层扫描研究
Paul Hans Kamm✉, Tillmann Robert Neu, Francisco García-Moreno, John Banhart
P.H. Kamm:paul.kamm@helmholtz-berlin.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116583
摘要
泡沫金属的萌生和生长是一个复杂的动态过程,本质上具有三维空间和时间依赖性。时分辨断层扫描技术能够实时跟踪AlSi8Mg4合金在发泡过程中气泡的形核和生长,包括单个气泡的位置、大小和形状,时间步长为1s,空间分辨率为几µm。此外,我们还基于一系列三维图像成功识别出了气泡的组成,即Al-Mg相和TiH2颗粒。通过图像对气泡和气生相,以及它们之间的关系进行定量分析,我们把发泡的过程分为了两个阶段:(1)由吸附气体和组织中先发生熔融组分驱动的均一化;(2)合金熔化和TiH2粒子释放氢引起泡沫增长。研究表明,通过调控Al-Mg粉的性能,可以改善AlSi8Mg4泡沫金属的性能。
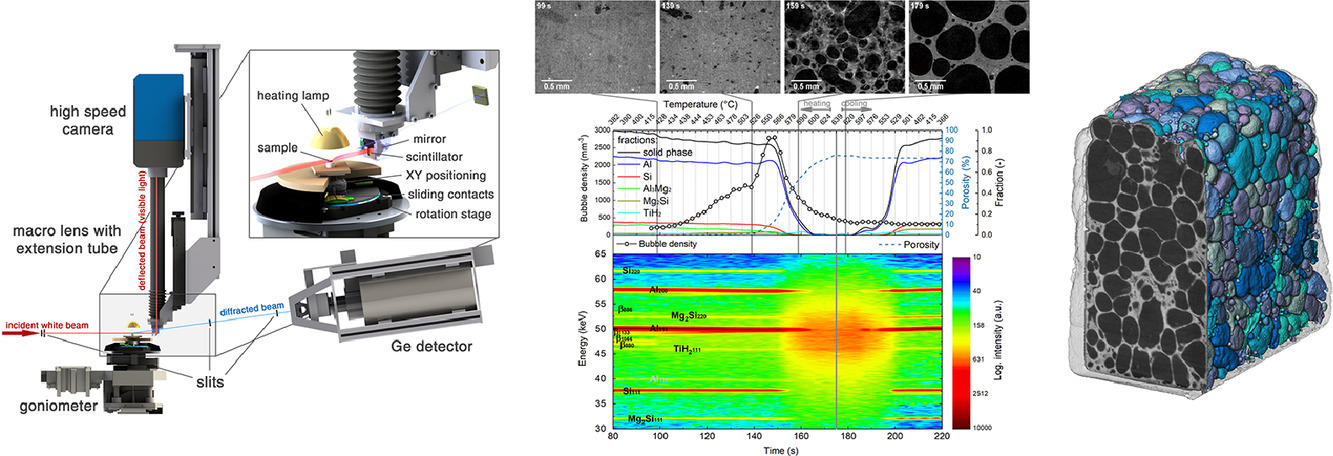
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116604
6. Grain size effect on tensile properties and slip systems of pure magnesium
纯镁中晶粒尺寸对拉伸性能和滑移体系的影响
Kang Wei, Rong Hu, Dongdi Yin, Lirong Xiao, Song Pang, Yang Cao, Hao Zhou✉, Yonghao Zhao✉, Yuntian Zhu✉
H. Zhou:hzhou511@njust.edu.cn(南京理工大学)
Y. Zhao:yhzhao@njust.edu.cn(南京理工大学)
Y. Zhu:y.zhu@cityu.edu.hk(南京理工大学/香港城市大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116604
摘要
晶粒细化可以显著提高金属材料的强度,但往往会降低材料塑性。我们发现,通过晶粒细化不仅可以提高镁合金的强度,而且由于激活了更多的滑移体系,同时也提高了延性。结果表明,由于基滑体系的限制,大晶粒尺寸(d=125 μm)纯Mg的塑性和均匀延伸率都较低(5.3%)。相比之下,细晶Mg (d=5.5 μm)的加工硬化能力、塑性以及均匀延伸率(18.3%)都得到了显著提高。双束条件的TEM分析表明,<c> 和 <c + a> 位错的激活是晶粒尺寸的减小后,合金性能提高的主要原因。此外,我们还发现,<c + a>位错不稳定,可能分解<c> 位错和<a>位错或I1层错。我们对纳米层错在提高镁合金强度和塑性方面的贡献及其形成机制进行了讨论。
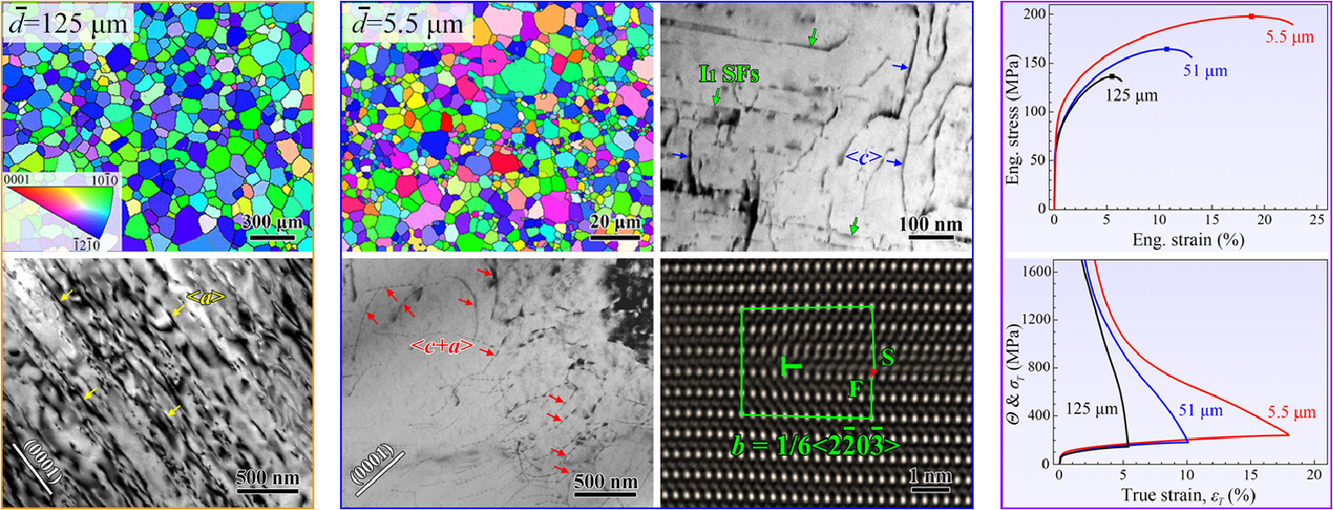
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116613
7. The mechanism of dynamic strain aging for type A serrations in tensile curves of a medium-Mn steel
中锰钢A型锯齿形拉伸曲线的动态应变时效机理研究
Jae-Hoon Nam, Seon-Keun Oh, Myeong-heom Park, Young-Kook Lee✉
Y.-K. Lee:yklee@yonsei.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116613
摘要
本文旨在阐明动态应变时效(DSA)对Fe-5.15Mn-0.15C-0.37Si-0.0039N (wt%)中Mn钢锯齿形拉伸流变的影响机理。该试样为残留奥氏体(γR)、铁素体(α)和回火马氏体(α’T)三相。为此,我们在温度273 - 333K、初始应变率5 × 10−4 - 1 × 10−2 s−1的各种条件下对试样进行了拉伸。拉伸曲线显示,试样在Lüders带扩展后表现出A型锯齿状流变。锯齿与α和α’T均无关;它们并非由应变诱导马氏体相变引起的,而是由γR中的DSA引起。由于驻留时间和二次取向时间之间没有交叠,因此基于分位错和C-Mn配合物相互作用的短程扩散模型无法解释DSA。基于考虑长程扩散的位错阻滞模型,测量了锯齿形流变的γR临界应变 (ecγ) 。他们表现出正常的PLC行为,即ecγ值随着温度的增加和初始应变率的降低而降低。基于ecγ 测得的活化能与碳原子的位错管道扩散活化能接近。以上结果表明,中锰钢中的DSA可以用基于C原子的长程管道扩散的位错阻滞模型解释,而不能用基于C- Mn配合物的二次取向的短程扩散模型解释。
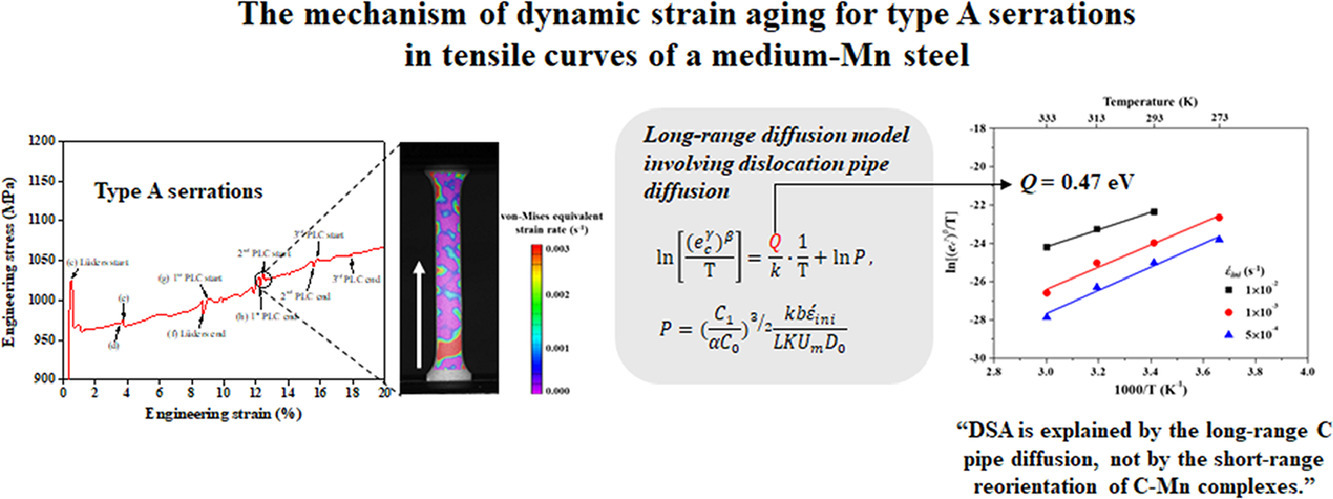
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116612
8. Effect of Alloying Elements on the High-Temperature Tempering of Fe-0.3N Martensite
合金元素对Fe-0.3N马氏体高温回火的影响
Shao-Wen Young, Mitsutaka Sato✉, Kazuhiro Yamamitsu, Yusuke Shimada, Yongjie Zhang, Goro Miyamoto, Tadashi Furuhara
M. Sato:m-sato@imr.tohoku.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116612
摘要
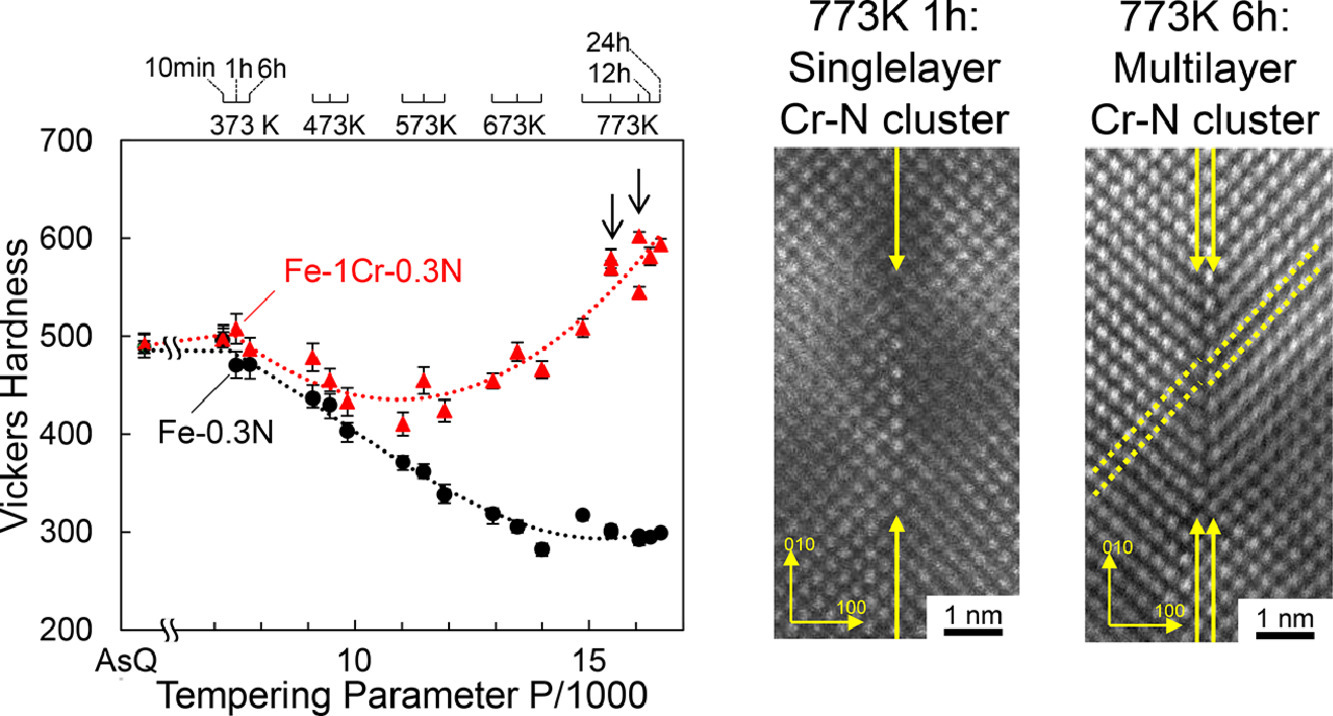
我们对气相氮化+淬火制备得到的Fe-0.3mass%N-1mass%M (M: Cr, Mo, Mn, Si)马氏体在高温回火过程中的氮化物析出行为进行了研究。与Fe-N二元合金相比,Si的添加并没有在回火软化方面引起明显变化,Mn、Cr、Mo的添加减少了材料的回火软化,并且回火温度高于673K时,Cr、Mo合金发生了二次硬化。X射线衍射和TEM表征表明,773K回火过程中,存在氮化铁(γ′-Fe4N)和其他氮化物的析出。球差矫正STEM-HAADF表征表明,在Cr、Mo合金中,沿{001}α'平面形成了亚稳单层氮-合金元素团簇,并且这种团簇最终增厚形成为B1型MN沉淀。我们在含Mn合金中发现了B1型Mn氮化物,它可随厚度增加而转变为η-Mn3N2。3DAP分析证实,氮与合金元素的比值与STEM-HAADF所推导的结构一致。进一步分析表明,体系中还存在无法通过STEM-HAADF和3DAP明确表征的细小团簇。通过分析析出和位错强化对材料回火后硬度的贡献,我们推测,未检测到的Cr- N团簇同样有助于提高合金的硬化。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116520
9. Slip-twinning interdependent activation across phase boundaries: An in-situ investigation of a Ti-Al-V-Fe (α+β) alloy
α+β双相Ti-Al-V-Fe合金中滑移-孪生相互激活的原位研究
Shaolou Wei, Gaoming Zhu, Cemal Cem Tasan✉
C.C. Tasan:tasan@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116520
摘要
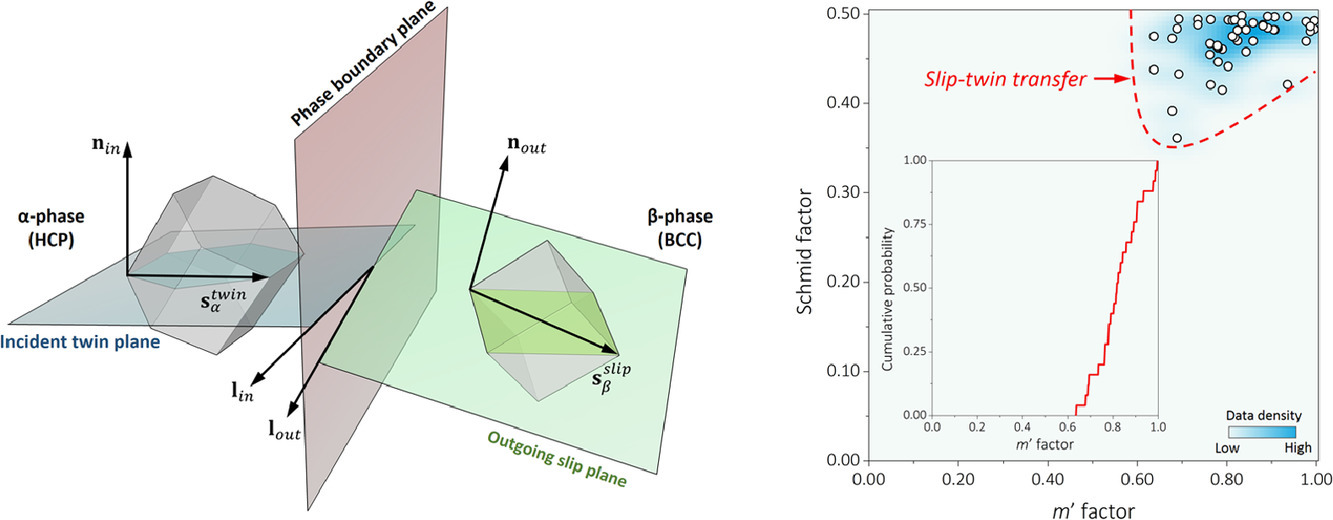
即使在单相合金中,组织塑性应变分布的演化也具有高度不均匀性。跨晶界/相界的滑移/孪晶迁移是引起这种非均匀性的重要因素之一。在这方面,跨晶界迁移的基本原理已经受到了广泛关注,而对相界的研究仍较少。我们认为(α+β)钛合金是研究这一现象的优秀材料,因为:(1)在相近的微观应变下,两相都可以表现出塑性变形;(2)位错滑移和机械孪晶的发生都可以松弛塑性应变。在本研究中,我们证实了一种包含β相中的位错滑移和α相中的{101-2}孪晶的形变传递单元。通过晶体学计算,我们发现可以使用Schmid因子结合Luster-Morris相容性,对滑动-孪晶迁移的发生倾向进行量化。我们采用了原位应变映射方法,证明了这种迁移有助于缓解应变集中,从而促进材料均匀变形。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116595
10. Segregation and precipitation stabilizing an ultrafine lamellar-structured Al-0.3%Cu alloy
偏聚和析出对Al-0.3%Cu超细层状组织的稳定性影响研究
Linfei Shuai, Tianlin Huang✉, Tianbo Yu✉, Guilin Wu, Niels Hansen, Xiaoxu Huang
T. Huang:huangtl@cqu.edu.cn(重庆大学)
T. Yu:tiyu@mek.dtu.dk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116595
摘要
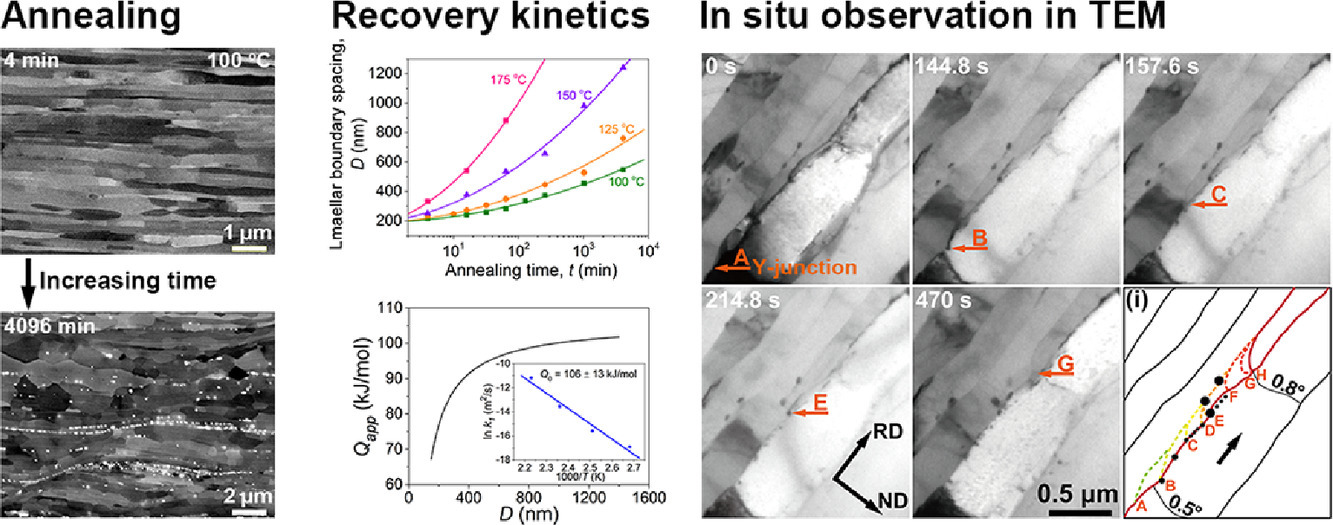
理解通过大应变变形制备的超细叠层合金在退火过程中的粗化机制和溶质原子的作用,对于调控其组织和力学性能至关重要。本研究中,我们采用冷轧方法(压下量98%)制备了界面间距为200 nm的Al-0.3%Cu合金层状结构。组织中的Cu偏聚在高角度层界。在100 ~ 175℃的退火过程中,细小的Al2Cu颗粒在片层边界处优先析出。我们通过测量退火样品的层间距,对合金的回复动力学进行了分析,发现回复过程中表观活化能从初期的77 kJ/mol增加末期的106 kJ/mol。通过透射电子显微镜下的原位观察,我们发现,粗化主要是由片层边界形成的Y形结的运动导致,运动受到位错、位错边界和粒子不同程度的钉扎影响。随着位错界面取向差的增大、Al2Cu颗粒的粗化以及相互连接的界面和颗粒的共同作用,这种局部钉扎逐渐增强。以上研究结果表明了合金元素在变形和退火过程中对精细层状组织稳定性的重要影响,为稳定超细层状结构的制备提供了指导。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116609
11. Ultrahigh tribocorrosion resistance of metals enabled by nano-layering
金属多层纳米结构的耐磨损腐蚀性能研究
Wenbo Wang, Kaiwen Wang, Zhengyu Zhang, Jia Chen, Tianyou Mou, F. Marc Michel, Hongliang Xin, Wenjun Cai✉
W. Cai:caiw@vt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116609
摘要
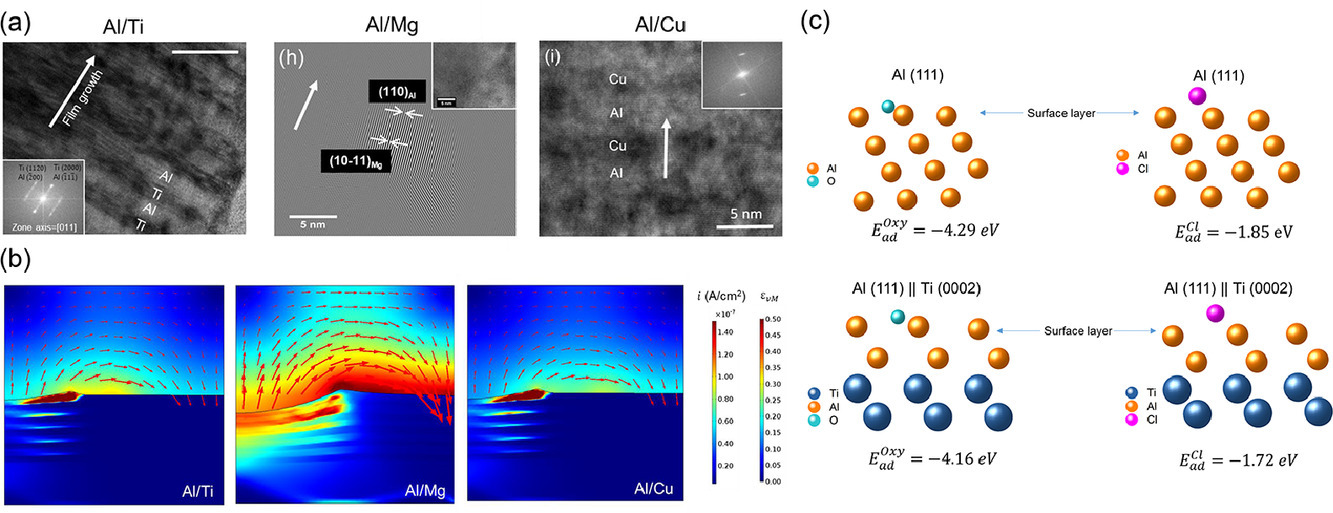
金属表面的磨损腐蚀是其在腐蚀环境中长期服役所需面临的挑战之一。在本研究中,我们发现,金属多层纳米薄膜结构(NMMs)由于具有大量界面和纳米尺度的化学作用,能够有效限制塑性变形,减少微电腐蚀和表面活性,从而表现出优异的抗磨损腐蚀性能。我们主要研究了Al/X (X = Ti、Mg、Cu)等间距多层纳米薄膜结构材料(单层厚度~3nm)在室温下、0.6 M NaCl水溶液中的磨损腐蚀行为。我们采用了微纳力学和电化学测量方法,结合先进的材料表征技术,研究了组分对材料变形和失效机制的影响。结果表明,在磨损腐蚀过程中,Al/Mg和Al/Cu NMMs主要发生材料的腐蚀,而Al/Ti NMM则由于表面持续钝化而发生严重的塑性变形。我们通过有限元(FE)模拟验证了所有NMMs的磨损腐蚀行为,结果表明磨损和腐蚀的协同作用加速了材料在层界面和磨损裂纹边缘的损耗。最后,我们通过密度泛函理论(DFT)计算,揭示了纳米材料耐蚀性的成因。结果表明,纳米层化提高了铝的表面功函数,相比于纯铝,Cl的吸附强度降低,因此铝的表面反应活性和点蚀敏感性降低。以上研究结果为极端环境下多层、多相金属材料的选择和设计提供了指导。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116620
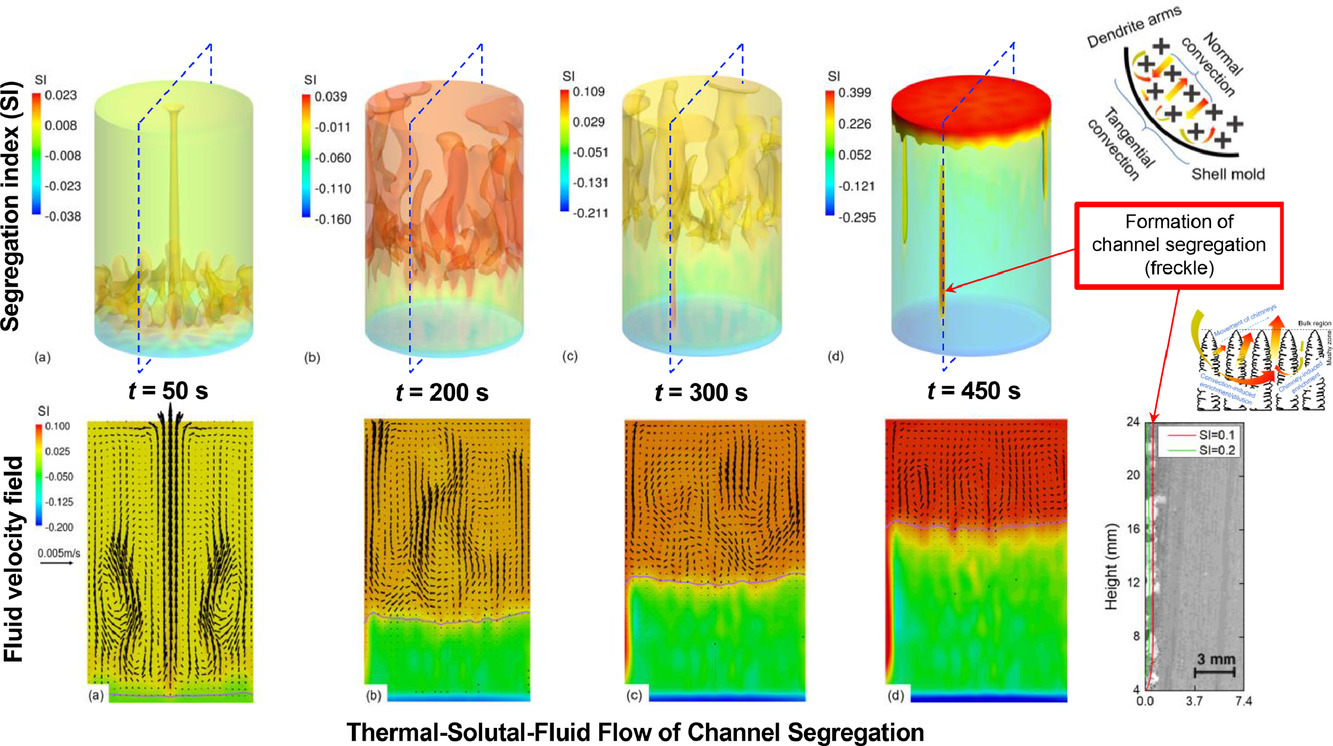
12. Thermal-solutal-fluid flow of channel segregation during directional solidification of single-crystal nickel-based superalloys
镍基单晶高温合金定向凝固过程中通道偏析的热流-溶质-流体流动
Neng Ren, Jun Li, Chinnapat Panwisawas, Mingxu Xia, Hongbiao Dong, Jianguo Li✉
J. Li:li.jun@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116620
摘要
通道偏析(即斑点现象)是模铸造单晶涡轮叶片最复杂的缺陷之一,严重限制了叶片的力学性能。斑点现象是由凝固过程中热流-固相-液相流的不稳定引起的。因此我们需要深入理解模铸过程中的流体流动、传热和物质迁移。本研究中,我们建立了一种三维欧拉两相模型,对CMSX-4镍基单晶高温合金定向凝固过程中的烟道效应和通道偏析演化进行研究。结果表明,通道仅分布在钢锭表面,模型预测的通道偏析形貌与实验观测到的斑点形貌一致。在忽略横向热流的情况下,瑞利数准则对通道偏析的预测有所偏差,因为在显著扰动下,并不是所有的烟囱都能发展为通道偏析。在糊状区,从水平方向到铸造方向的溶体对流扰动将导致已有烟道消失,从而加剧通道偏析。一旦形成稳定的通道偏析,热溶质对流引起的溶质富集会进一步促进偏析。通道偏析很难在棒材中心持续形成,而在沿铸造方向的侧壁附近更容易发生。以上研究表明,较弱的侧向热流可以抑制通道偏析的形成,从而有效减少单晶铸造过程中的斑点现象。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116624
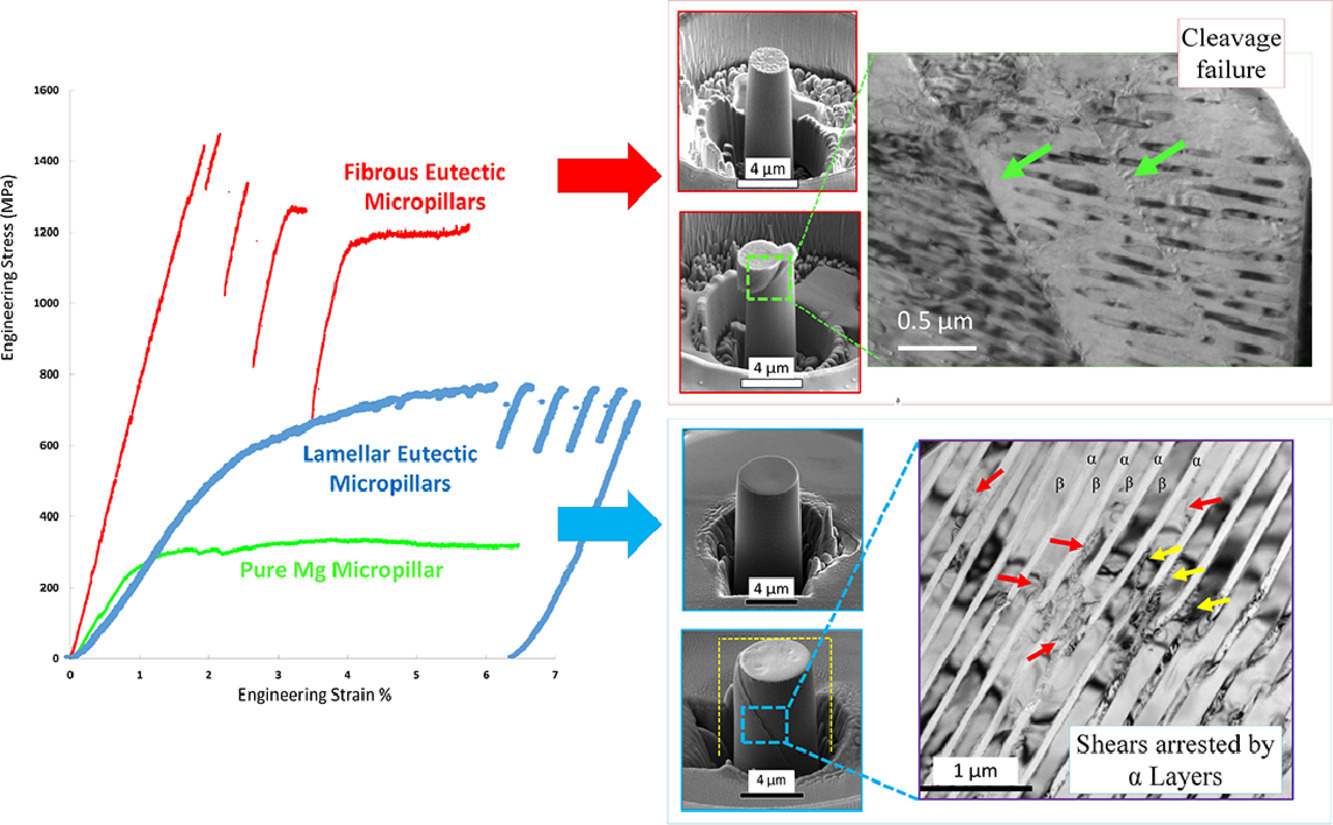
13. Strength and plasticity of lamellar vs. fibrous eutectic Mg-Al nanocomposites: An in-situ microcompression study
层状与纤维状共晶Mg-Al纳米复合材料强度和塑性的原位微柱压缩比较研究
Soodabeh Azadehranjbar✉, Bingqiang Wei✉, Dongyue Xie✉, Kaisheng Ming✉, Jian Wang✉, Jeffrey E Shield✉
S. Azadehranjbar:sranjbar@huskers.unl.edu
B. Wei:bwei5@huskers.unl.edu
D. Xie:dyxlux@gmail.com
K. Ming:ming@unl.edu
J. Wang:jianwang@unl.edu
J.E. Shield:jshield@unl.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116624
摘要
镁合金由于其低密度和高强重比,而在汽车和航空工业中具有很大的应用潜力。强度低和室温成形性差是镁合金的主要缺陷。两相纳米结构是改善镁合金力学性能的一种可能方案。根据工艺参数的不同,可以通过共晶转变形成纤维或片层形貌。我们通过原位SEM微柱压缩实验,研究了这两种不同形貌对材料力学响应的影响。与纤维形貌相比,片层形貌的强塑积更佳。且两者的强度都显著高于纯Mg,前者是纯Mg的5倍,后者是纯Mg的12倍。纤维状共晶以牺牲了部分塑性,获得了更高的强度。对变形微柱的HR/TEM分析表明,片层形貌塑性较高主要是由于以下两点:(1)α相和β相均有较强的位错活动,引起层片的协调变形;(2)α层对β层的切变不稳定性具有重要的制约作用。而在纤维形态中则没有观察到这两种影响,因此它们通常沿β相晶体的密排面发生解理失效。