金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.199, 1 July. 2021(上)
2021-06-03 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文8篇,涵盖了高熵合金、奥氏体、形状记忆合金等,国内科研单位包括重庆大学、天津大学、香港城市大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 199 目录
1. Influence of parent Nb-alloy grain morphology on the layer formation of Nb3Sn and its flux pinning characteristics
母相Nb合金晶粒形貌对Nb3Sn层形成及其钉扎特性的影响
2. Oxidation mechanisms of an intermetallic alloy at high temperatures
金属间化合物在高温下的氧化机理
3. In situ monitoring nanoscale solid-state phase transformation of Ag nanowire during electrochemical reaction
电化学反应中银纳米线在纳米尺度固态相变的原位监测
4. A novel L12-strengthened multicomponent Co-rich high-entropy alloy with both high γ′-solvus temperature and superior high-temperature strength
具有高γ'固溶温度和优异高温强度的新型L12强化多组分富钴高熵合金
5. Revisiting the formation mechanism of intragranular κ-carbide in austenite of a Fe-Mn-Al-Cr-C low-density steel
重论Fe-Mn-Al-Cr-C低密度钢奥氏体中晶内κ-碳化物的形成机制
6. Nucleation of coupled body-centered-cubic and closed-packed structures in liquid Ni-Cr alloys
液态Ni-Cr合金中体心立方和密堆积结构的耦合形核
7. Martensite phase structure of Mg-Sc lightweight shape memory alloy and the effect of rare earth elements doping
Mg-Sc轻质形状记忆合金的马氏体相结构及稀土元素掺杂的影响
8. Influence of element distribution on mechanical properties in the bonding zone of explosively welded steels
爆炸焊接钢结合区元素分布对力学性能的影响
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113822
1. Influence of parent Nb-alloy grain morphology on the layer formation of Nb3Sn and its flux pinning characteristics
母相Nb合金晶粒形貌对Nb3Sn层形成及其钉扎特性的影响
Nobuya Banno✉, Taro Morita, Tsuyoshi Yagai, Shigeki Nimori
Nobuya Banno: banno.nobuya@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113822
摘要
用基础方法阐明了母相Nb合金晶粒形貌对Nb3Sn层的形成及其钉扎特性的影响。本文采用Nb-Ta-Hf,其回复温度超过700℃,高于Nb3Sn相的形成温度。首先,制备了Cu/ Nb-4at % Ta-1at %Hf单芯复合导线(外部为Cu)。随后,切下两片,其中一片在再结晶温度下进行中间退火。然后,通过电镀将Sn吸附在两个样品的表面,并对样品进行热处理,形成Nb3Sn层。显然,冷拔后的Nb合金层晶粒明显细化,具有更好的钉扎力性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113852
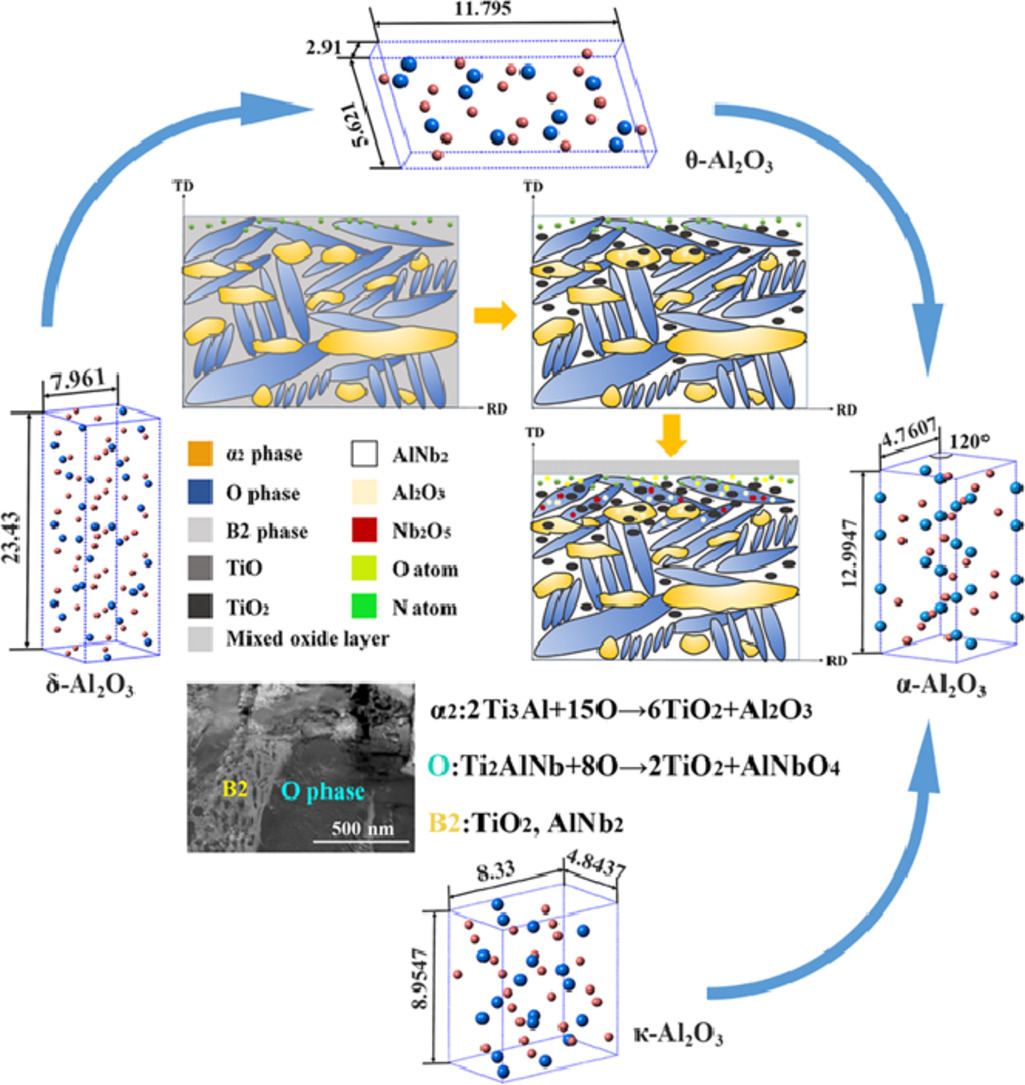
2. Oxidation mechanisms of an intermetallic alloy at high temperatures
金属间化合物在高温下的氧化机理
A. Chen, Q. Chen, S.J. Qu✉, H.P. Xiang, C. Wang, J.B. Gao, A.H. Feng, D.L. Chen✉
A. J. Qu: qushoujiang@tongji.edu.cn 同济大学
A. L. Chen: dchen@ryerson.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113852
摘要
本研究的目的是通过透射电子显微镜、X射线衍射和热力学计算对氧化层/基体界面进行详细分析,确定Ti2AlNb基合金的高温氧化机理。氧首先吸附在合金表面,与B2相反应生成TiO2。B2相中钛的耗竭促使剩余的铝和铌形成AlNb2,从而阻止了B2相的进一步氧化反应。α2相易被氧化形成TiO2和Al2O3。O相的氧化产物为TiO2和AlNbO4,它们是由Nb2O5和Al2O3进一步反应形成的。通过基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理计算,证实了反应的可能性,建立了Al2O3由亚稳态向稳态转变的两条路径:δ-Al2O3→θ-Al2O3→α-Al2O3和κ-Al2O3→α-Al2O3。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113835
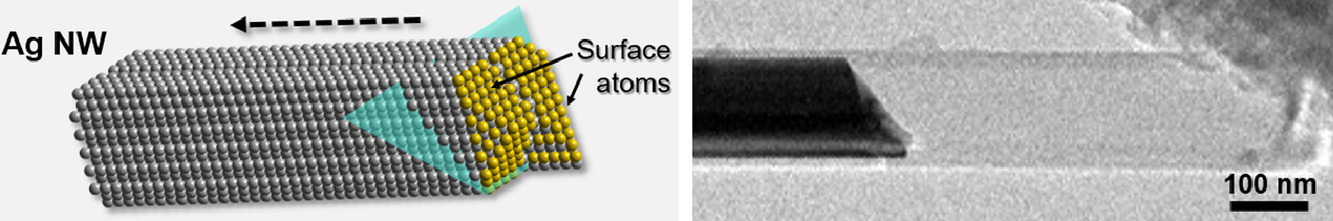
3. In situ monitoring nanoscale solid-state phase transformation of Ag nanowire during electrochemical reaction
电化学反应中银纳米线在纳米尺度固态相变的原位监测
Lei Xu, Youran Hong, Jiangwei Wang✉, Langli Luo✉
Jiangwei Wang: jiangwei_wang@zju.edu.cn 浙江大学
Langli Luo: luolangli@tju.edu.cn 天津大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113835
摘要
金属和合金在电化学过程中纳米尺度的固态相变对于腐蚀、电化学加工和碱金属电池等应用是至关重要的。然而,传统表征技术缺少具有高空间分辨率的位点特定信息,无法检测到金属表面和界面处纳米尺度的相和化学转变。在这里,我们使用原位透射电子显微镜来验证Ag纳米线与Li在电化学合金化时的一种独特相变。它的特点是Ag的电化学锂化的表面反应,然后Ag快速重新分配到嵌入Li2O的小纳米颗粒中。Ag-Li合金化反应通过表面反应模式进行,且与表面切面有很强的依赖性。AgLi和TEM柱中残存的O2之间的弱键合使形成的Ag-Li合金立即转变为一种分散良好的Ag纳米粒子的Li2O壳层。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113826
4. A novel L12-strengthened multicomponent Co-rich high-entropy alloy with both high γ′-solvus temperature and superior high-temperature strength
具有高γ'固溶温度和优异高温强度的新型L12强化多组分富钴高熵合金
A. X. Cao, H.J. Kong, Z.Y. Ding, S.W. Wu, J.H. Luan, Z.B. Jiao, J. Lu, C.T. Liu✉, T. Yang✉
A. T. Liu: chainliu@cityu.edu.hk 香港城市大学
A. Yang: taoyang6-c@my.cityu.edu.hk 香港城市大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113826
摘要
本文开发了一种具有良好组织稳定性的L12强化多组分富钴高熵合金。在800~1100℃等温时效后,合金基体中形成了高密度的立方γ′颗粒;长期热暴露后,在晶界和晶内均未形成脆性金属间化合物相。原子探针分析表明,Ta和Nb元素优先配分到γ′金属间化合物中,这对L12有序晶体结构的稳定具有重要作用。更重要的是,该合金具有较高的γ′-固溶温度(1125°C)和较低的质量密度(8.28 g cm-3),并具有优异的高温抗拉强度(800°C时为755 MPa, 900°C时为664 MPa)。该研究结果为设计基于Co的具有更广泛温度性能的先进L12强化高温合金提供了基本范式。
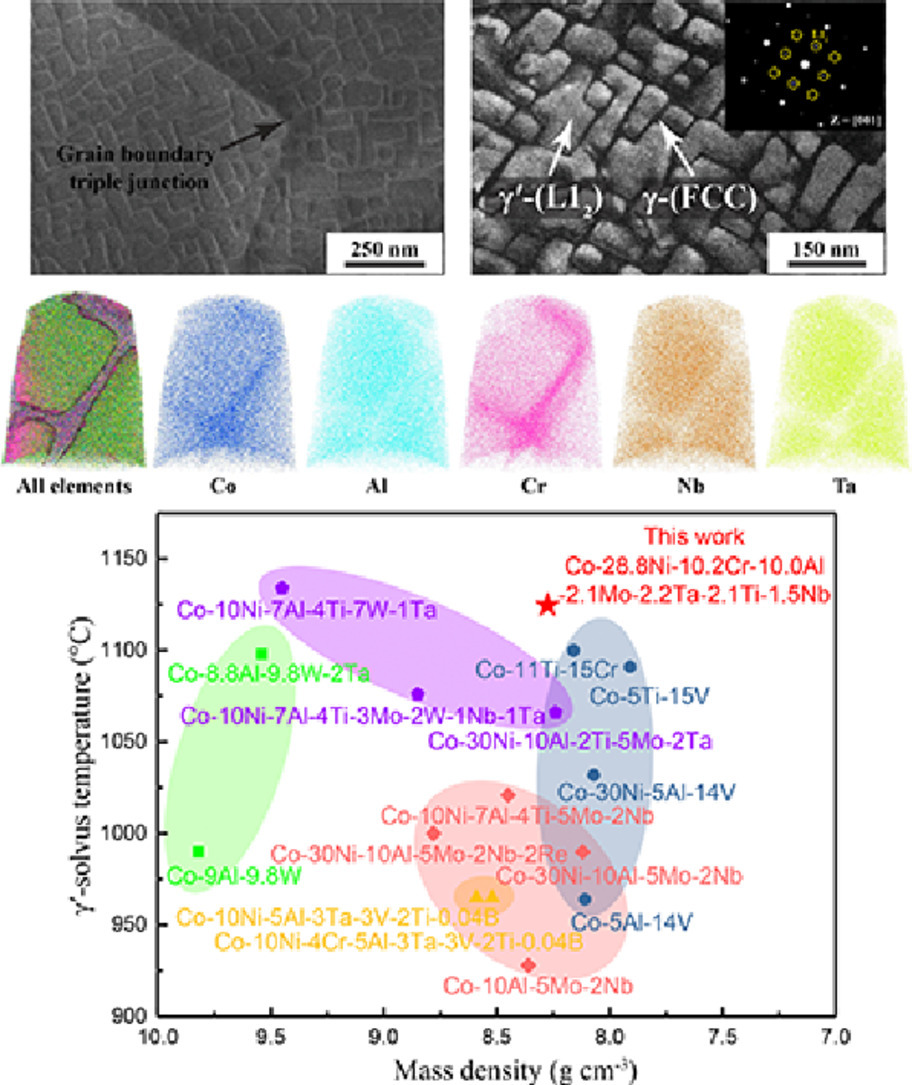
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113836
5. Revisiting the formation mechanism of intragranular κ-carbide in austenite of a Fe-Mn-Al-Cr-C low-density steel
重论Fe-Mn-Al-Cr-C低密度钢奥氏体中晶内κ-碳化物的形成机制
Jianlei Zhang, Yueshan Jiang, Weisen Zheng, Yuxiang Liu, Ahmed Addad, Gang Ji✉, Changjiang Song✉, Qijie Zhai
Gang Ji: gang.ji@univ-lille.fr
Changjiang Song: riversong@shu.edu.cn 上海大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113836
摘要
通常认为γ-奥氏体中晶内κ-碳化物的形成是由于调幅分解和随后的有序反应。在本工作中,我们用高分辨透射扫描显微镜和原子探针断层扫描对奥氏体基Fe-20Mn-9Al-3Cr-1.2C(wt.%)低密度钢进行了近原子尺度的表征,结果表明初步形成的κ碳化物(颗粒尺寸为2-3nm)为有序的L′12结构,但是没有检测到元素的配分。在400 ~ 800℃温度范围内,热力学计算表明FCC相的吉布斯能随Al和C含量的变化始终呈现出正曲率(即(d2G/dx2)< 0)。这两个结果都表明,有序的κ-碳化物核心可以直接在无序的γ-奥氏体中形成,而不是由于众所周知的调幅分解有序机制。γ-奥氏体基体与κ-碳化物具有相似的晶格结构、相同的成分和完全的共格性,这导致了极低的形核势垒。
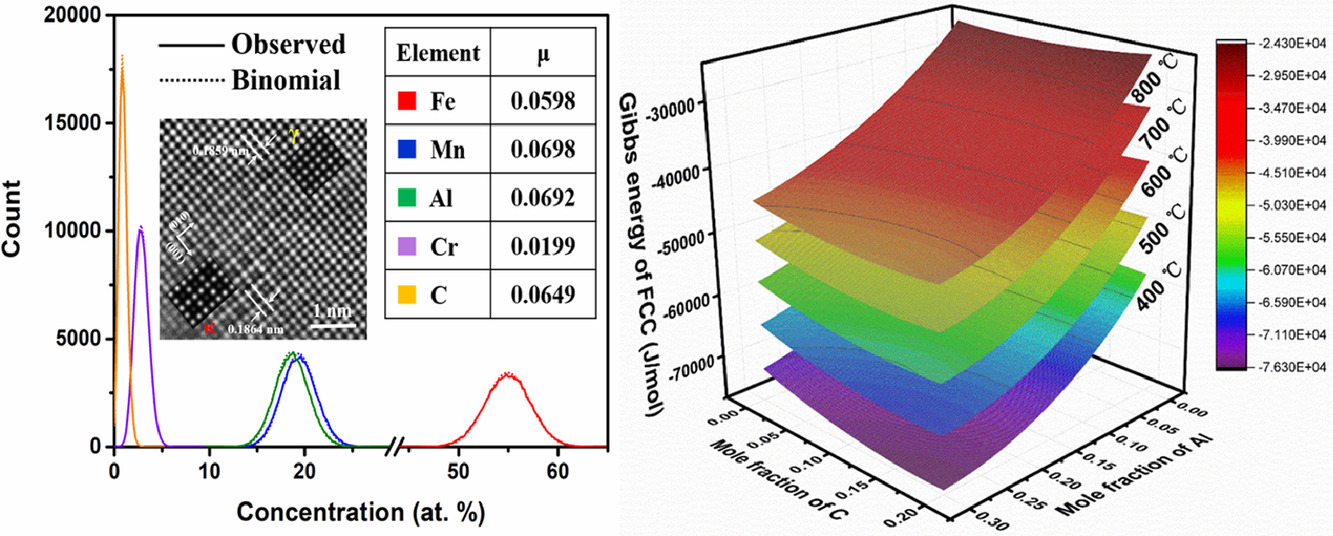
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113857
6. Nucleation of coupled body-centered-cubic and closed-packed structures in liquid Ni-Cr alloys
液态Ni-Cr合金中体心立方和密堆积结构的耦合形核
Deep Choudhuri✉, Skyler Matteson, Reilly Knox
Deep Choudhuri: deep.choudhuri@nmt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113857
摘要
在过去的四十年中,对单组分面心立方(FCC)材料液相内的预临界固态核心的结构进行了广泛的研究。这些研究表明,平衡FCC的形成是由亚稳态体心立方(BCC)结构的预临界核心介导的。然而,目前未知这种形核机理是否适用于以FCC和BCC结构作为平衡相的多组分结构合金。我们通过分子动力学模拟,以Ni-35at.%Cr和Ni-50at.%Cr二元合金为对象对此问题进行了研究。结果表明,预临界和临界晶核由富Cr的BCC和富Ni的密堆积(FCC和六方密堆积)结构组成。通过将合金熔体预先分离成富Cr和富Ni的液袋,可以促进这种多结构预临界晶核的形成。晶核内的BCC和密排区域由随时间演变的非平衡成分组成。因此,浓缩Ni-Cr合金中的非传统形核机理使其能够凝固成FCC-BCC微观结构。
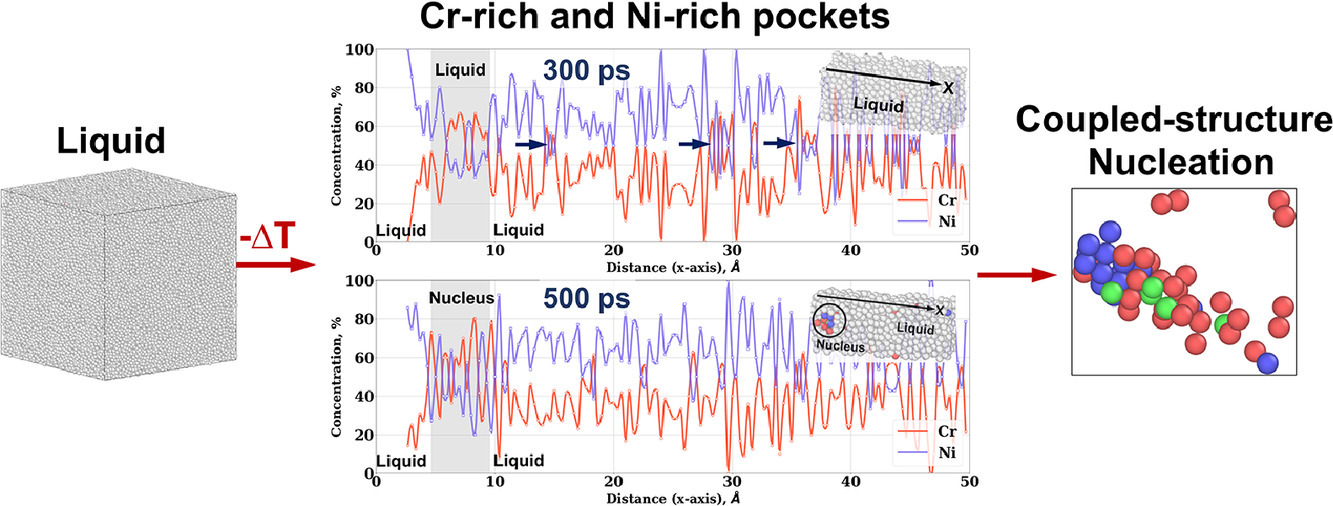
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113863
7. Martensite phase structure of Mg-Sc lightweight shape memory alloy and the effect of rare earth elements doping
Mg-Sc轻质形状记忆合金的马氏体相结构及稀土元素掺杂的影响
Wenbin Zhao, Erjun Guo, Kun Zhang✉, Xiaohua Tian, Changlong Tan
Kun Zhang: kunzhang@hrbust.edu.cn 哈尔滨理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113863
摘要
随着轻量化形状记忆合金(SMAs)应用需求的不断增加,Mg-Sc合金作为一种新型形状记忆合金受到了人们的广泛关注。然而,Mg-Sc合金不明确的马氏体组织,不明确的相变路径以及低的马氏体相变温度(Tm)等问题仍然存在。本文系统研究了Mg-Sc合金的马氏体组织和相变路径。通过形成能确定了马氏体相为正交晶相。此外,为了改善Tm,研究了稀土元素的掺杂对Tm的影响;在1.25 at.% Gd掺杂下,Tm提高了28.2 K。总态密度表明,相稳定性决定了Tm的增加。此外,偏态密度表明,d轨道电子在Sc和Gd原子之间的耦合导致了Tm的变化。我们的研究结果为设计新型Mg-Sc基轻量化SMAs提供了坚实的基础。
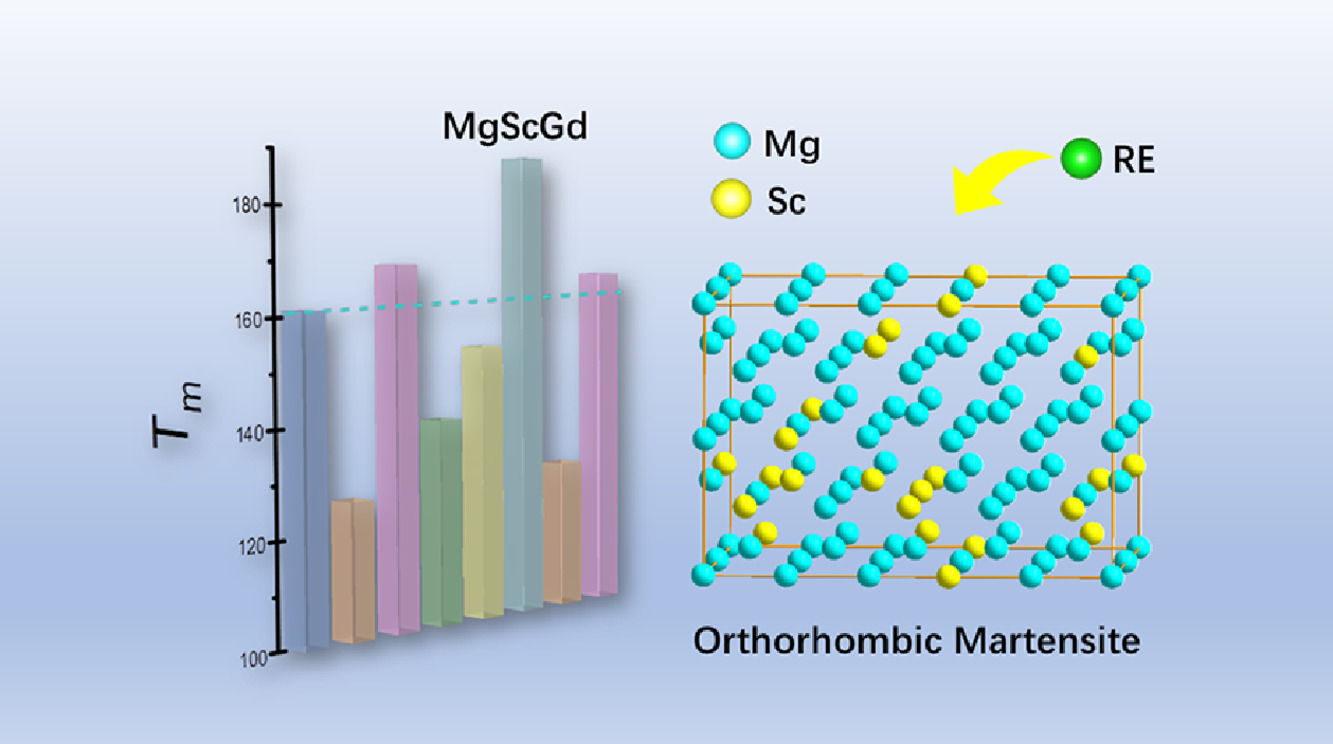
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113860
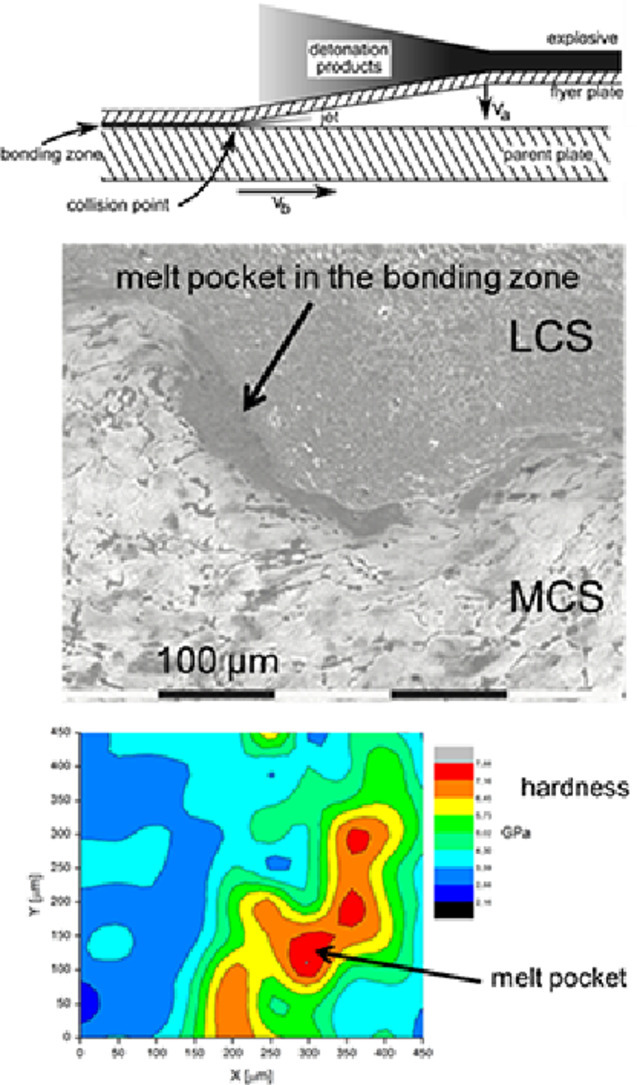
8. Influence of element distribution on mechanical properties in the bonding zone of explosively welded steels
爆炸焊接钢结合区元素分布对力学性能的影响
A. Borchers✉, J. Arlt, C. Nowak, F. Gärtner, M. Hammerschmidt, H. Kreye, C.A. Volkert, R. Kirchheim
A. Borchers: cborche@uni-goettingen.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113860
摘要
利用激光辅助原子探针层析技术研究了中碳钢与低碳钢爆炸焊接结合过程中结合区的熔袋特征。结果表明,该区域具有纳米晶结构,亚晶界富含碳元素。熔袋中的高硬度值归因于(亚)晶粒尺寸和碳分布的共同作用。