金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.206,1 Mar. 2021(中)
2021-06-03 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文13篇,涵盖了镁合金、高熵合金、高温合金、复合材料等,国内科研单位包括东北大学、湖南大学、中科院金属所、大连交通大学、中南大学、西安交通大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 206 目录
1. Giant hardening response in AlMgZn(Cu) alloys
AlMgZn(Cu)合金中的巨幅硬化响应研究
2. In situ He+ irradiation of the double solid solution (Ti0.5,Zr0.5)2(Al0.5,Sn0.5)C MAX phase: Defect evolution in the 350–800 °C temperature range
(Ti0.5,Zr0.5)2(Al0.5,Sn0.5)C MAX相在350-800°C范围内He+辐照缺陷演变的原位研究
3. The role of grain colony on secondary recrystallization in grain-oriented electrical steel: New insights from an original tracking experiment
晶粒群落对有取向电工钢二次再结晶影响的跟踪实验研究
4. In-situ TEM investigation of 30 keV He+ irradiated tungsten: Effects of temperature, fluence, and sample thickness on dislocation loop evolution
30keV He+辐照条件下温度、注量和样品厚度对钨中位错环演化影响的原位TEM研究
5. Atomic-resolution studies on reactions of slip dislocations with {10-11} twin boundaries and local plastic relaxation in a Mg alloy
Mg合金中滑移位错与{10-11}孪晶界相互作用及局部塑性松弛的原子尺度研究
6. Characterization of oxidation mechanisms in a family of polycrystalline chromia-forming nickel-base superalloys
有多晶氧化铝形成的镍基高温中氧化机制的表征研究
7. A grand-potential based phase-field approach for simulating growth of intermetallic phases in multicomponent alloy systems
巨势法相场方法对多组分合金体系中金属间化合物长大的模拟研究
8. Controllable additive manufacturing of gradient bulk metallic glass composite with high strength and tensile ductility
高强高塑梯度块体金属玻璃复合材料的增材制造调控制备
9. Coupled segregation mechanisms of Sc, Zr and Mn at θ′ interfaces enhances the strength and thermal stability of Al-Cu alloys
Sc、Zr、Mn在θ′ 界面处的耦合偏聚对Al-Cu合金强度和热稳定性的提升机制
10. Interstitial effects on the incipient plasticity and dislocation behavior of a metastable high-entropy alloy: Nanoindentation experiments and statistical modeling
间隙原子对亚稳高熵合金初始塑性和位错行为的影响的纳米压痕实验和统计模拟研究
11. Dynamic precipitation and the resultant magnetostriction enhancement in [001]-oriented Fe-Ga alloys
[001]取向Fe-Ga合金中的动态析出对磁致伸缩性能的增强作用
12. Suppressing irradiation induced grain growth and defect accumulation in nanocrystalline tungsten through grain boundary doping
通过晶界掺杂抑制纳米晶钨中辐照诱导的晶粒长大和缺陷积累
13. Efficiently exploiting process-structure-property relationships in material design by multi-information source fusion
利用多信息源融合技术高效开发材料设计中的工艺-组织-性能关系
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116617
1. Giant hardening response in AlMgZn(Cu) alloys
AlMgZn(Cu)合金中的巨幅硬化响应研究
Lukas Stemper✉, Matheus A. Tunes, Phillip Dumitraschkewitz, Francisca Mendez-Martin, Ramona Tosone, Daniel Marchand, William A. Curtin, Peter J. Uggowitzer, Stefan Pogatscher✉
L. Stemper:lukas.stemper@unileoben.ac.at
S. Pogatscher:stefan.pogatscher@unileoben.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116617
摘要
我们提出了一种新的热机械加工工艺,能够充分开发AlMgZn(Cu)合金的工业潜力。通过合金设计和加工,不仅能够实现高服役强度和良好加工成形性之间的平衡,而且充分考虑了工艺时间窗口的经济效益。我们主要在商业化EN AW-518合金中分别添加了Zn和Zn+Cu,在100°C短时间失效3小时候,材料的加工硬化能力增加,表现出了较好的成形性能。随后,合金经185°C的短时间热处理(即烤漆)20分钟后,强度提高了约184 MPa,屈服强度达到410 MPa。这种快速硬化响应与时效过程中,形成的前驱体的数量、密度、尺寸分布、化学组成有关,它们是T相前驱体析出的优先形核位点。添加Cu能够显著增加硬化影响。预时效后、最终热处理前的轻微变形(2%)使得析出相能够借助位错形核、长大,进一步促进了析出相的形成。我们采用了拉伸测试、电子显微镜、原子探针和第一性原理计算对材料在热机械加工过程中的组织演变进行了表征和分析。我们对与应变对硬化响应的影响,以及Cu对早起原子团簇形核的作用进行了详细讨论,并通过原位STEM和第一性原理计算对我们的理论进行了验证。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116606
2. In situ He+ irradiation of the double solid solution (Ti0.5,Zr0.5)2(Al0.5,Sn0.5)C MAX phase: Defect evolution in the 350–800 °C temperature range
(Ti0.5,Zr0.5)2(Al0.5,Sn0.5)C MAX相在350-800°C范围内He+辐照缺陷演变的原位研究
B. Tunca✉, G. Greaves, J.A. Hinks, P.O. Å. Persson, J. Vleugels , K. Lambrinou
B. Tunca:bensu.tunca@kuleuven.be
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116606
摘要
我们使用了6 keV 能量的He+离子对(Zr0.5,Ti0.5)2(Al0.5,Sn0.5)C MAX相双固溶体在透射电镜中进行了原位辐照实验,粒子注入量为1.3 × 1017 ions ·cm-2 (~7.5 dpa),实验温度350-800°C。我们利用TEM对样品进行了原位和辐照后表征,以研究辐照缺陷随辐照剂量和温度的变化规律。我们在组织中观察到了球形He泡弦状排列、类似血小板状的He泡、以及位错环,且位错环位于非基面。当辐照温度在450℃以上时,由于He泡偏析,导致晶界局部断裂,但并未进一步导致裂纹穿晶扩展。在450°C和500°C的辐照条件下,选区域电子衍射图样中特定衍射斑的强度减弱,表明晶体的对称性增加。而700℃以上则没有观察到类似现象,表明损伤发生了高温回复。在700°C辐照样品的高分辨率TEM表明,7.5 dpa He+辐照后,MAX相的化学有序和纳米层状结构被保留。我们对血小板状和球形He泡的尺寸、分布随温度和辐照剂量的变化进行了统计分析。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116611
3. The role of grain colony on secondary recrystallization in grain-oriented electrical steel: New insights from an original tracking experiment
晶粒群落对有取向电工钢二次再结晶影响的跟踪实验研究
Hong-Yu Song✉, Yin-Ping Wang, Claude Esling, Guo-Dong Wang, Hai-Tao Liu✉
H.-Y. Song: sohoyu@126.com(东北大学)
H.-T. Liu:liuht@ral.neu.edu.cn, liu_haitao163@163.com(东北大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116611
摘要
二次再结晶是有取向电工钢产生强烈Goss织构({110}<001>)的主要原因。目前大多研究的重点在于确定最终Goss织构的锐度与X射线衍射测得的初级再结晶织构之间的关系,关于微观织构对二次再结晶影响的研究则相对较少。本研究中,我们通过跟踪实验,发现一次再结晶基体中取向相似的晶粒组成的晶粒集落对二次再结晶过程有特殊的影响。γ晶粒(< 111 > / /ND)群落有助于保留基体中那些和{110}< 001 >具有20-45°取向差以及和Goss取向具有较大差的一次再结晶晶粒(≤25µm),从而在二次再结晶发生时促进低偏差角Goss晶粒的异常长大,并最终导致尖锐的Goss织构。与之相反,一次再结晶基体中随机分布的晶粒则会促进高偏差角晶粒的反常长大,从而导致电磁性能劣化。我们基于以上发现,揭示了晶粒集落对二次再结晶的作用,以及一次再结晶织构对最终Goss织构锐度影响的机理。此外,我们还观察到,晶粒群落的形成主要与初始凝固组织、工艺路线、以及γ晶粒的变形、再结晶特征有关。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116618
4. In-situ TEM investigation of 30 keV He+ irradiated tungsten: Effects of temperature, fluence, and sample thickness on dislocation loop evolution
30keV He+辐照条件下温度、注量和样品厚度对钨中位错环演化影响的原位TEM研究
Yipeng Li, Li Wang, Guang Ran✉, Yue Yuan, Lu Wu, Xinyi Liu, Xi Qiu, Zhipeng Sun, Yifan Ding, Qing Han, Xiaoyong Wu, Huiqiu Deng✉, Xiuyin Huang
G. Ran:gran@xmu.edu.cn(厦门大学)
H. Deng:hqdeng@hnu.edu.cn(湖南大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116618
摘要
我们采用30keV的He+对钨进行了原位辐照,研究了辐照温度、注量、预存位错和样品厚度对位错环演化的影响,包括位错环的密度、尺寸和相互作用。在辐照过程中,钨中形成了Burgers矢量为1/2<111>和<100>的位错环。辐照温度、注量、样品厚度和预存位错对<100>位错环的占比有明显影响。高密度氦团簇之间的相互作用可以促进辐照钨中< 100 >环的形成,分子动力学模拟验证了这一点。此外,< 100 >位错环的形成还与两个1/2<111>位错环变体之间的反应有关,这种反应需要长时间高温辐照驱动。我们还发现,预存位错对位错环的尺寸、密度和Burgers矢量有重要影响。辐照缺陷在离子辐照过程中很可能被薄膜样品的表面吸收,导致在表面附近形成剥蚀区。通过对辐照缺陷演化进行原位观察,可以深入了解聚变堆中钨的辐照损伤过程。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116622
5. Atomic-resolution studies on reactions of slip dislocations with {10-11} twin boundaries and local plastic relaxation in a Mg alloy
Mg合金中滑移位错与{10-11}孪晶界相互作用及局部塑性松弛的原子尺度研究
Huhu Su, Xinzhe Zhou, Mengmeng Zhang, Shijian Zheng✉, Hengqiang Ye, Zhiqing Yang✉
S. Zheng:sjzheng@hebut.edu.cn(河北工业大学)
Z. Yang:yangzq@imr.ac.cn (中科院金属所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116622
摘要
我们基于原子尺度的实验观测结合界面缺陷理论,对镁合金{10-11}孪晶界(TB)与滑移位错的反应以及孪晶界处对应的台阶演化进行了研究。研究发现,{10-11}孪晶界可与由1/3〈11-20〉(简称〈a60〉)基底混合位错组成的小角晶界发生反应,形成不对称倾斜晶界。每个〈a60〉-TB反应都将产生一个具有b±3/±2残留位错的台阶并引起一个双层孪晶位错(TD)滑移。具有b±1 /±1残余错位的单层台阶即可以通过{10-11}TB一侧的〈a60〉或〈c+as〉位错与{10-11}TB另一侧的〈a60〉位错反应生成,也可以通过与 {10-11} TB直接反应生成。与双层孪晶位错、〈a60〉位错、 〈c+a60〉位错或1/6〈20-23〉Frank 分位错的反应均会改变{10-11} 孪晶界台阶处的局部原子结构,从而减少台阶处的晶格应变。以上结果可以帮助我们更好地理解{10-11} TBs的塑性弛豫机制。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116626
6. Characterization of oxidation mechanisms in a family of polycrystalline chromia-forming nickel-base superalloys
有多晶氧化铝形成的镍基高温中氧化机制的表征研究
M.T. Lapington✉, D.J. Crudden, R.C. Reed, M.P. Moody, P.A.J. Bagot
M.T. Lapington:mark.lapington@eng.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116626
摘要
我们研究了不同Ti:Nb比的新型多晶镍基高温合金的氧化性能,发现钛含量的增加与氧化动力学加速有关。我们利用SEM/EDX和原子探针对氧化层进行了高分辨率的组织和化学表征,尤其是氧化铬中Ti元素的偏聚,以图确定和解释其中的关联机制。尽管数据点相对分散,但氧化铬层中固溶的Ti含量与合金的名义Ti浓度或合金的氧化性能的相关性很小,这表明氧化率并不依赖于氧化铬中的掺杂水平。我们对氧化层内的一些晶界进行了APT分析,因为这些晶界被认为是短路扩散路径。我们发现,Ti、Nb和Ta向氧化物晶界处偏析,这表明离子迁移速率可能是由晶界掺杂而非体掺杂有关。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116630
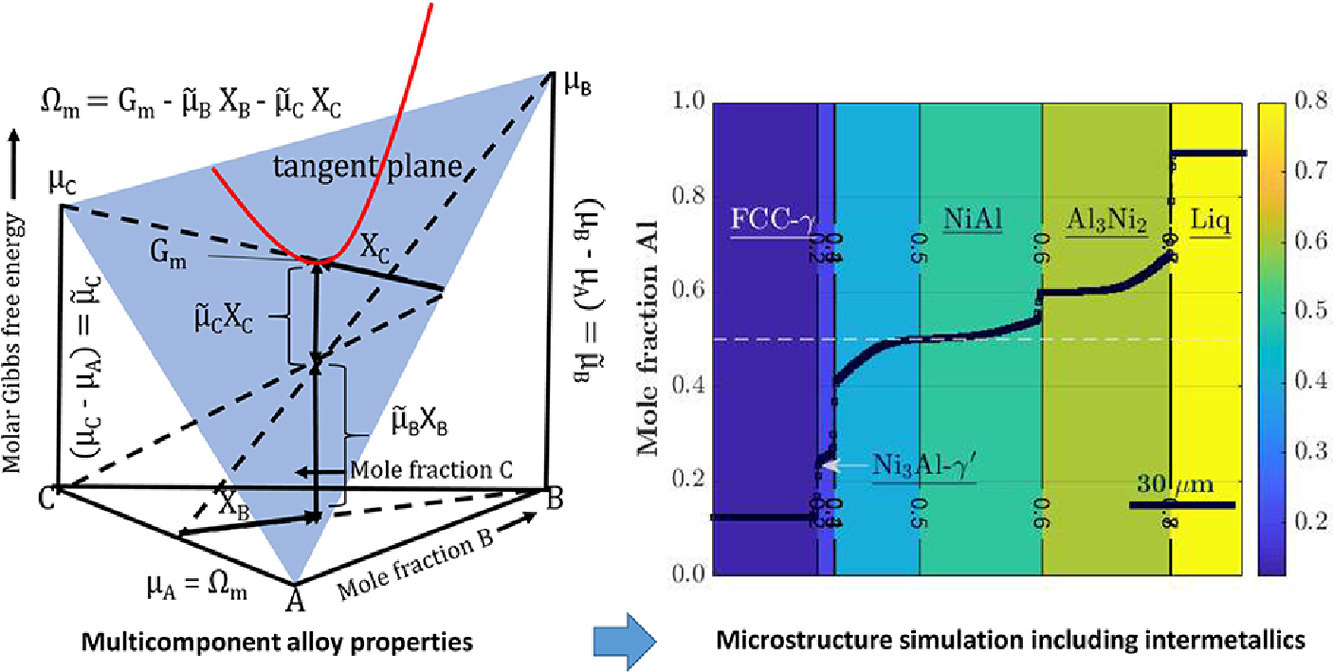
7. A grand-potential based phase-field approach for simulating growth of intermetallic phases in multicomponent alloy systems
巨势法相场方法对多组分合金体系中金属间化合物长大的模拟研究
Sourav Chatterjee✉, Nele Moelans✉
S. Chatterjee:sourav.chatterjee@kuleuven.be
N. Moelans:nele.moelans@kuleuven.be
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116630
摘要
金属间化合物合金,特别是过渡簇金属和铝形成的化合物合金,作为高温结构材料和涂层材料具有优异的潜在应用前景。这类应用通常涉及两种不同材料之间的相互扩散。为了定量地模拟合金的互扩散组织,需要结合CALPHAD数据库求解合金相场模型。然而对于二元以上的多组分金属间化合物,这种耦合仍是一个挑战。在此,我们提出了一种新的方法,成功将多组分相中与扩散势有关的特征耦合到了相场模型中。它提取CALPHAD数据库中预先直接计算出的相性质作为溶质扩散势的离散函数。我们以六种不同的合金为例,从双相四元Al-Cr-Ni-Fe合金到五相二元Ni-Al合金,说明了该模拟方法的应用和准确性。以上例子中,包括了置换相和金属间化合物相。在可以比较的情况下,模拟结果与DICTRA和实验结果吻合良好,从而验证了我们的方法。此外,我们发现DICTRA在三种相场方法可模拟的、涉及有序金属间化合物的情形中失败。进一步研究表明,模型中的界面宽度可变,且不会造成精度损失,因此模型可以在更接近实验实际的时空尺度下进行模拟。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116632
8. Controllable additive manufacturing of gradient bulk metallic glass composite with high strength and tensile ductility
高强高塑梯度块体金属玻璃复合材料的增材制造调控制备
Yunzhuo Lu✉, Shuang Su, Shengbiao Zhang, Yongjiang Huang✉, Zuoxiang Qin, Xing Lu, Wen Chen✉
Y. Lu:luyz@djtu.edu.cn (大连交通大学)
Y. Huang:yjhuang@hit.edu.cn (哈尔滨工业大学)
W. Chen:wenchen@umass.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116632
摘要
在非晶基体中引入韧性枝晶,从而原位制备块体金属玻璃复合材料(BMGCs)是提高金属玻璃(BMGs)韧性的一种有效方法。而对枝晶组织进行调控是这一过程中的难点。BMGs增韧通常需要较高的晶相体积分数,但这会导致材料强塑积的损失。此外,现有的金属玻璃加工技术大多依靠液态金属铸造,由于玻璃形成需要快速冷却,因此对铸件有尺寸限制。在本研究中,我们通过激光增材制造方法(LAM)实现了对于特定位置冷速和组织的调控,从而成功制备了一种枝晶体积分数呈梯度变化的多层Zr基金属玻璃复合材料。梯度BMGC具有优异的屈服强度(>1.3 GPa)和拉伸塑性(~13%)。强塑性耦合的增强主要是由于相邻层间相互作用引起的协同强化和非均匀组织引起的异步形变。借助LAM技术从而得以实现的梯度结构设计理念,为高性能、大尺寸BMGs结构材料研发提供了新的思路。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116634
9. Coupled segregation mechanisms of Sc, Zr and Mn at θ′ interfaces enhances the strength and thermal stability of Al-Cu alloys
Sc、Zr、Mn在θ′ 界面处的耦合偏聚对Al-Cu合金强度和热稳定性的提升机制
Lu Jiang✉, Baptiste Rouxel, Timothy Langan, Thomas Dorin
L. Jiang:l.jiang@deakin.edu.au, 421895030@qq.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116634
摘要
θ′中间相的细化和热稳定性对于新型高强度2系铝-铜(Al-Cu)高温合金至关重要。在此,我们研究了微量添加Sc、Zr、Mn等元素对Al-6.5 wt。% Cu合金中θ′相的细化和稳定作用。研究发现,时效过程中,Al3(Sc, Zr)核/壳结构的形成对θ′相具有显著的细化作用。190°C时效时,Mn的添加可显著提高材料硬度,硬度在280°C时效24小时的情况在仍能保持。TEM表征表明,Mn的添加使θ′相更加细小弥散,显著减缓了θ′相的生长和粗化。热差分析(DSC)实验表明,Mn促进了θ′相的形核,提高其抗粗化能力。原子探针(APT)表征表明,时效强化和热稳定性的提升是由于Mn、Sc、Zr在θ′相半共格和共格界面的独立偏聚机制所致。我们通过计算吉布斯界面过剩量和界面能,对偏聚进行了量化分析。结果表明,Sc和Zr对θ '相的细化起重要作用,而Mn不仅能细化θ '相,而且能大幅提高θ '相的抗粗化能力和合金的热稳定性。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116633
10. Interstitial effects on the incipient plasticity and dislocation behavior of a metastable high-entropy alloy: Nanoindentation experiments and statistical modeling
间隙原子对亚稳高熵合金初始塑性和位错行为的影响的纳米压痕实验和统计模拟研究
Kefu Gan, Dingshun Yan, Shuya Zhu, Zhiming Li✉
Z. Li:lizhiming@csu.edu.cn(中南大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116633
摘要
由于应力载荷下的位错诱导孪晶和/或切变型相变,亚稳态高熵合金(HEA)及其变体表现出了良好的强塑性协同效应。然而,这类新材料中位错形核和塑性启动的基本机制尚不清楚。我们希望通过纳米压痕和统计物理模拟相结合的方法,定量研究亚稳态HEAs中的位错形核,并揭示间隙合金元素在其中的影响。结果表明,我们以FeMnCoCr亚稳态非等原子比 HEA为研究对象,发现位错形核是由单一主原子的热激活位移触发的,基于新生位错环能量的连续力学描述可以推断,位错形核是大体均匀的。此外,基于预先存在的缺陷对形核影响的定量分析,我们发现,单空位-原子交换导致的少量非均匀形核也是可能的。亚稳HEA中位错形核所需的活化体积增大,约0.5 at.% C+1.0 at.% N % C 固溶至面心立方结构。统计模型和纳米压痕结果表明,在强剪应力作用下,间隙C、N原子容易促进肖克利分位错的形核。然而,间隙原子的对这些新生的可动位错具有显著的钉扎作用,减少了它们的平均自由程。因此,借由这类分位错滑移而形成的层错的宽度受到了显著限制,从而阻碍了多原子层上的层错形成,并进一步抑制了C-N共掺杂亚稳HEAs变形过程中的切变型相变。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116631
11. Dynamic precipitation and the resultant magnetostriction enhancement in [001]-oriented Fe-Ga alloys
[001]取向Fe-Ga合金中的动态析出对磁致伸缩性能的增强作用
Junming Gou, Tianyu Ma✉, Ruihua Qiao, Tianzi Yang, Feng Liu, Xiaobing Ren
T. Ma:matianyu@xjtu.edu.cn(西安交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116631
摘要
最近有研究表明,弥散纳米粒子可以在一些功能材料中引起出乎意料的优异性能,比如具有fct纳米析出的bcc Fe-Ga合金就具有显著且敏感的磁致伸缩性能。然而,由于定向凝固过程中产生的内应力可能通过加快原子团簇形成而影响析出行为,因此有必要对析出相形貌的演化和溶质元素的配分进行细致研究。在此,我们研究了[001]取向Fe73Ga27定向凝固合金中的动态析出行为。通过与随机多晶样品在经相同时效处理后进行对比,我们发现[001]取向样品中的fct纳米析出更加稀疏,且有额外的界面omega纳米析出形成。内应力加快了Ga在fct纳米析出和基体间的分配,从而减少了它们的形核位点。此外,内部压力也改变了基体和析出之间的弹性相互作用。在[001]取向样品中,fct析出的Bain应变通过形成富Ga的omega析出和{112}<111>层错得以松弛,而在随机多晶样品中则是通过基体的局部四方扭转。结果表明,取向晶样品的磁致伸缩增强约40%,显著低于随机多晶样品的约165%。以上研究结果阐明了应力对时效后析出相的影响,为超功能合金的微观组织设计提供了指导。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116629
12. Suppressing irradiation induced grain growth and defect accumulation in nanocrystalline tungsten through grain boundary doping
通过晶界掺杂抑制纳米晶钨中辐照诱导的晶粒长大和缺陷积累
W. Streit Cunningham, Khalid Hattar, Yuanyuan Zhu, Danny J. Edwards, Jason R. Trelewicz✉
J.R. Trelewicz:jason.trelewicz@stonybrook.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116629
摘要
纳米结构材料中的高密度掺杂稳定界面为晶体中辐照缺陷的湮灭提供了优先的能量位置。在此,我们以通过重离子辐照,对掺杂了20 at.% Ti的纳米晶W合金中,这种行为的控制机制进行了研究。我们在饱和剂量之前都对缺陷演化进行了原位表征,并基于非原位表征与组织分析对极端剂量的情况进行外推,重点在于定量分析对缺陷状态和离子辐照对纳米晶组织的影响。与纯W纳米晶薄膜相比,20at% Ti钨合金中的缺陷环较小、饱和剂量较高,并在在瞬态损伤累积过程中存在辐照诱导的晶粒长大。我们在级联诱导的峰值条件下模拟了微观组织的演变,结果显示合金中的纳米晶尺寸比纯W中更小,这表明Ti能够稳定纳米晶结构不产生辐照诱导晶粒长大。对于单个晶粒缺陷演化的原位表征证实了样品总体缺陷密度和组织演化之间的关系,揭示了Ti在瞬态缺陷积累和复苏过程中对晶界汇强度的影响。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116619
13. Efficiently exploiting process-structure-property relationships in material design by multi-information source fusion
利用多信息源融合技术高效开发材料设计中的工艺-组织-性能关系
Danial Khatamsaz, Abhilash Molkeri, Richard Couperthwaite, Jaylen James, Raymundo Arróyave, Douglas Allaire, Ankit Srivastava✉
A. Srivastava:ankit.sri@tamu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116619
摘要
材料设计通常需要逆用工艺-组织-性能(PSP)关系,从而研发出具有目标性能的材料。然而,由于算力限制,大多数材料设计框架都不理想。近来,基于贝叶斯优化(BO)的材料设计框架正得到越来越多的应用,因为它们较好地平衡了设计空间的探索和开发。大多数基于BO的框架都假定设计空间可以通过单个信息源(例如实验或仿真)进行查询。而我们研发出了一种对组织敏感、且能够开发多种信息源的BO合金设计框架。传统的设计框架具有一定缺陷,因为它假设最优的组织总是可实现的,并微观组织特征作为设计空间。我们的设计框架回避了这一毫无根据的假设,而把化学成分和加工工艺作为设计空间。我们通过调整成分/工艺参数对铁素体/马氏体双相材料的力学性能进行了优化,证明了框架的有效性。该框架使用热力学来预测组织特征,然后使用各种微观力学模型和基于微观组织的有限元模型来预测力学性能。框架的最后阶段包括模型的具体化和信息融合,以及用于确定最佳设计节点和查询信息源的梯度获取功能。我们对框架和各个组成要素进行了详细讨论,并演示了如何在考虑成本的条件下实现这一框架。


