金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.199, 1 July. 2021(下)
2021-06-03 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文7篇,涵盖了高熵合金、铝合金、形状记忆合金等,国内科研单位包括北京科技大学、三峡大学、北京理工大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 199 目录
1. Quantitative monitoring of the environmental hydrogen embrittlement of Al-Zn-Mg-based aluminum alloys via dynamic hydrogen detection and digital image correlation
采用动态氢检测和数字图像相关技术定量监测Al-Zn-Mg基铝合金的环境氢脆
2. Ultrafast solution treatment to improve the comprehensive mechanical properties of superalloy by pulsed electric current
通过脉冲电流进行超快速固溶处理以改善高温合金的综合机械性能
3. Optimization of conflicting properties via engineering compositional complexity in refractory high entropy alloys
通过工程成分复杂性优化耐火高熵合金“相矛盾”的性能
4. Quantitative mapping of nanotwin variants in the bulk
纳米孪晶变体的定量测绘
5. A new infinite solid solution strategy to design eutectic high entropy alloys with B2 and BCC structure
设计具有B2和BCC结构的共晶高熵合金的新型无限固溶策略
6. Temperature dependent deformation behavior and stacking fault energy of Fe40Mn40Co10Cr10 alloy
Fe40Mn40Co10Cr10合金的温度相关变形行为和层错能
7. Novel high-entropy alloys with high-density ε-D019 and abnormal phase transformation
具有高密度ε-D019和异常相变的新型高熵合金
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113853
1. Quantitative monitoring of the environmental hydrogen embrittlement of Al-Zn-Mg-based aluminum alloys via dynamic hydrogen detection and digital image correlation
采用动态氢检测和数字图像相关技术定量监测Al-Zn-Mg基铝合金的环境氢脆
Keitaro Horikawa✉
Keitaro Horikawa: horikawa@me.es.osaka-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113853
摘要
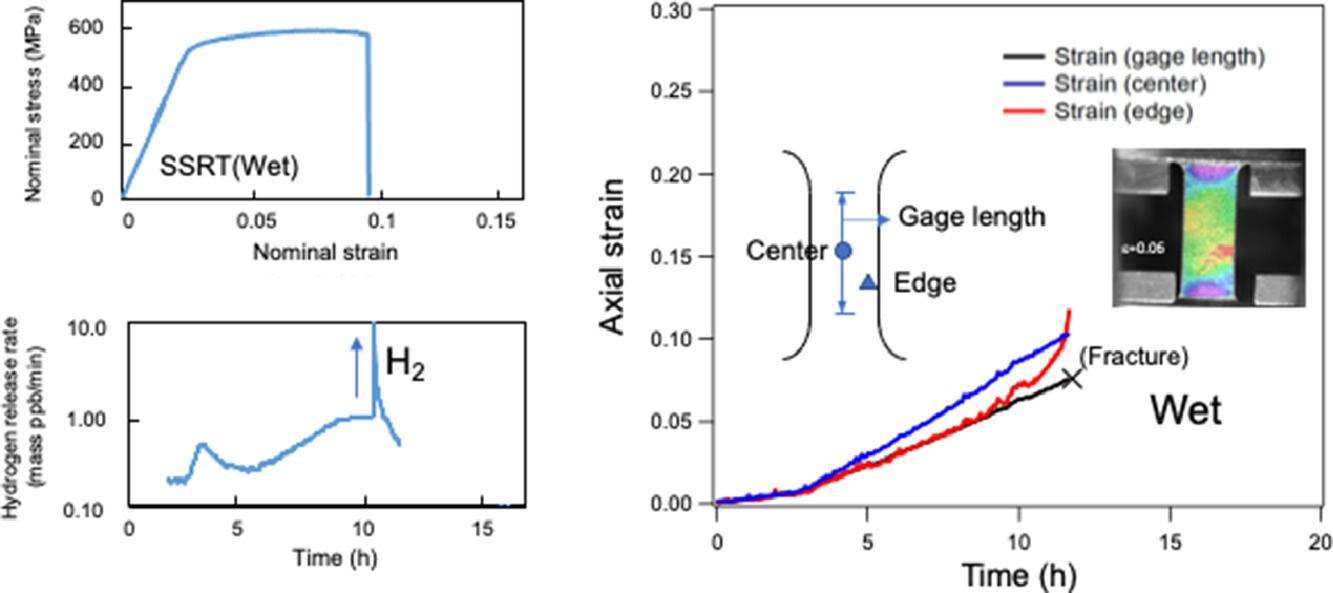
本研究开发了一种新型的分析系统,在大气压力下动态定量地监测Al-Zn-Mg基铝合金的环境氢脆。该系统包括基于SnO2的半导体氢传感器的气相色谱法,数字图像相关步骤,并使用慢应变率试验机。该系统的应用表明,Al-Zn-Mg合金在塑性变形过程中,由于空气中的水蒸气与无氧化膜的合金表面发生化学反应而产生氢原子。数字图像相关技术也证实了产生的氢原子在试样表面造成了大量局部晶界裂纹,导致局部晶界断裂。脆化断口的氢原子数量是未脆化断口的2.7倍。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113879
2. Ultrafast solution treatment to improve the comprehensive mechanical properties of superalloy by pulsed electric current
通过脉冲电流进行超快速固溶处理以改善高温合金的综合机械性能
Shuyang Qin, Jianqiao Hao, Longge Yan, Xinfang Zhang✉
Xinfang Zhang: xfzhang@ustb.edu.cn 北京科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113879
摘要
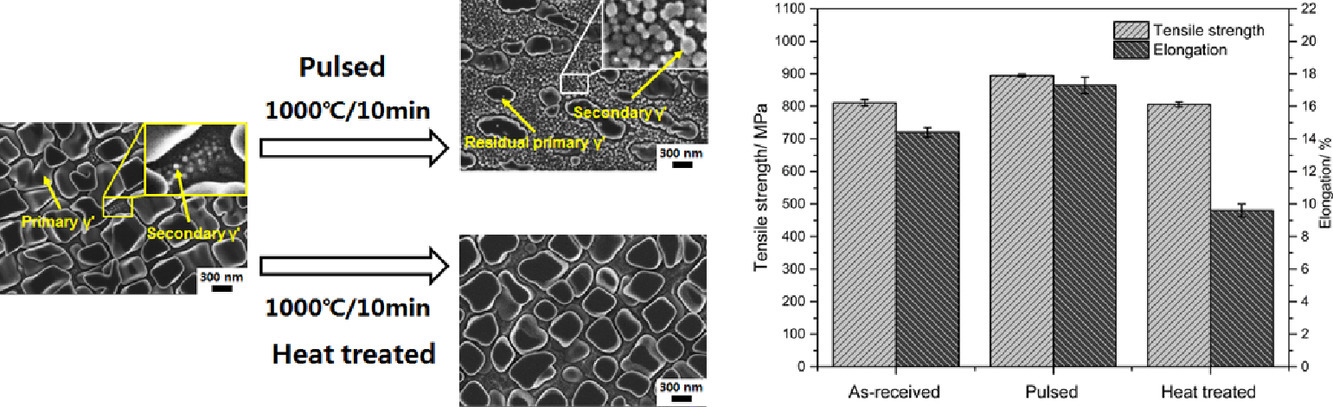
传统的固溶(1120°C/4 h)和时效(845-1080°C/24 h)工艺是K417G高温合金获得预期微观组织和保证优良力学性能的关键。研究发现,1000℃/10分钟的脉冲固溶处理可以得到所研究的微观组织。同时,脉冲过程可以快速改变有害γ/γ′共晶相的形貌,使共晶相附近的裂纹扩展由直接型向锯齿型转变,有利于提高性能。理论分析和计算结果表明,非均质相之间存在的高电流密度区域和系统热力学势垒的降低是初生γ′溶解和γ/γ′共晶形貌演变的根本原因。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113839
3. Optimization of conflicting properties via engineering compositional complexity in refractory high entropy alloys
通过工程成分复杂性优化耐火高熵合金“相矛盾”的性能
Il Hwan Kim, Hyun Seok Oh✉, Kwang Seok Lee, Eun Soo Park✉
Hyun Seok Oh: hsoh@mit.edu
Eun Soo Park: espark@snu.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113839
摘要
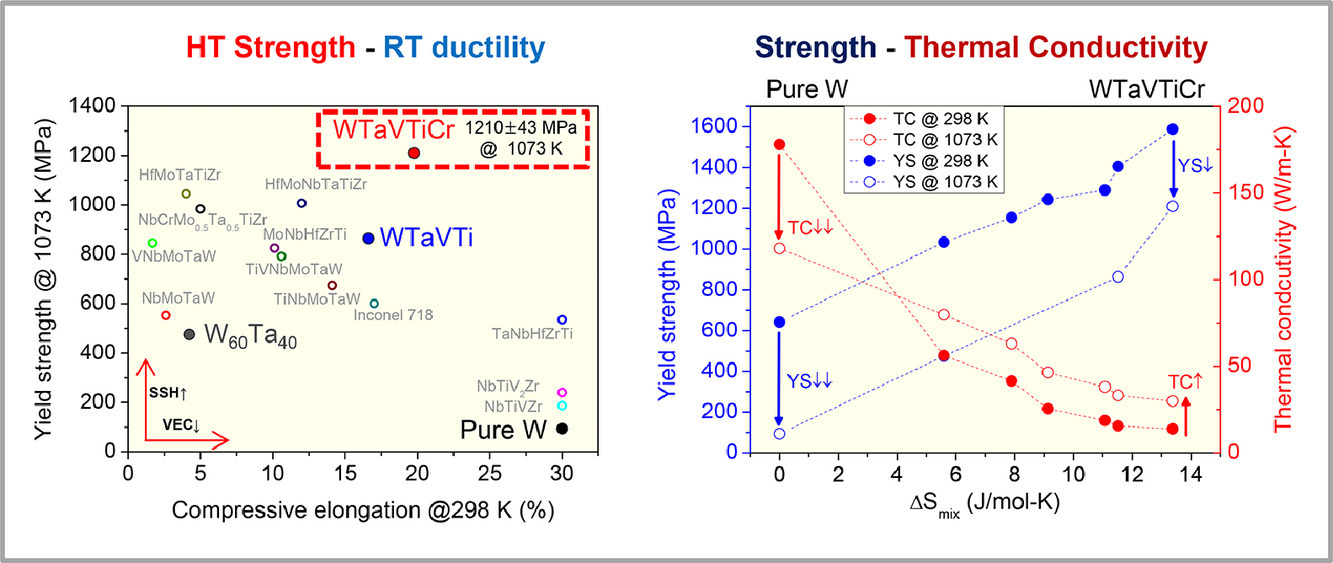
由于成分空间有限,在大多数传统合金中,强度-塑性(或热导率)的平衡是不可避免的。在此,我们提出了一种基于机理的设计策略,通过考虑固溶硬化和晶格畸变的原子尺寸不匹配以及剪切不稳定性的价电子浓度,同时优化高温(HT)强度、室温(RT)塑性和高温热导率。作为测试案例,我们将二元W-Ta合金的成分空间扩展到W-Ta-V-Ti-Cr耐火高熵合金(RHEAs),现有的RHEAs(例如WTaVTiCr)表现出优越的HT强度(1073 K时为1210±43 MPa)和RT塑性(23.4±5.7%)。研究还表明,随着温度的升高,该材料的导热率增加,理论上在2000 K时可以达到纯W导热系数的40%。因此,本工作提供了RHEAs的通用设计规则,使成分复杂性能够有效地加以运用。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113878
4. Quantitative mapping of nanotwin variants in the bulk
纳米孪晶变体的定量测绘
Jan Schultheiß✉, Lukas Porz, Lalitha Kodumudi Venkataraman, Marion Höfling, Can Yildirim, Phil Cook, Carsten Detlefs, Semën Gorfman, Jürgen Rödel, Hugh Simons
Jan Schultheiß: jan.schultheiss@ntnu.no
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113878
摘要
从镁合金到压电材料,晶体孪晶对许多材料的性能都是至关重要的。由于孪晶形成的开始阶段对三轴力学边界条件非常敏感,因此需要采用非破坏性的体显微技术。弹性应变可以通过100-200纳米分辨率的X射线衍射绘制。然而,这种方法不能用来表征应变与纳米孪晶的相互作用。本文介绍了一种基于暗场X射线显微镜的方法,用于量化毫米尺度样品中纳米孪晶变体的密度,孪晶片的尺寸可小至几十纳米,位于嵌入的子体积(70 × 200 × 600 nm3)中。通过对高性能压电材料中孪晶变体的局部密度与长距离应变场的相关性分析,验证了该方法的有效性。该方法便于对纳米尺度结构变化及其弹性驱动场进行直接和原位地测绘及量化,这是在纳米尺度控制和设计材料性能的关键。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113886
5. A new infinite solid solution strategy to design eutectic high entropy alloys with B2 and BCC structure
设计具有B2和BCC结构的共晶高熵合金的新型无限固溶策略
Xicong Ye✉, Jinyan Xiong, Xin Wu, Chang Liu, Dong Xu, Wen Zhang, Dong Fang✉, Bo Li
Xicong Ye: yexc@ctgu.edu.cn 三峡大学
Dong Fang: hill988@163.com 三峡大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113886
摘要
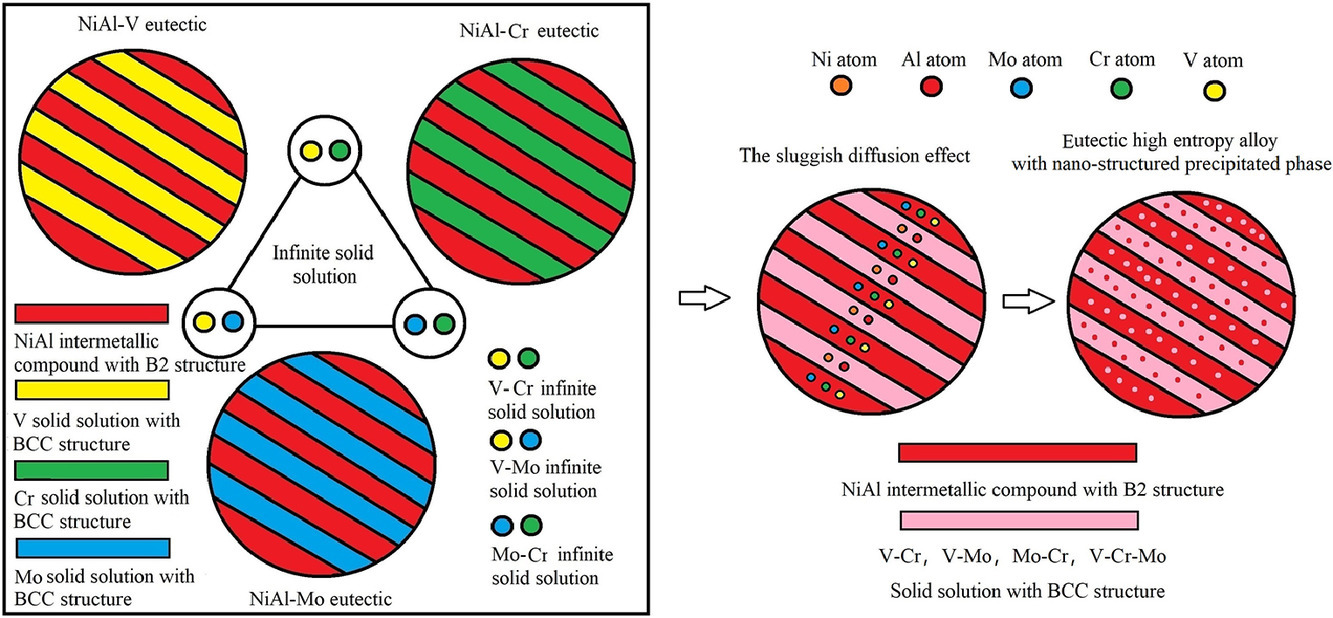
共晶高熵合金(EHEAs)因其优良的铸造性能、细小且可控的微观组织而受到金属材料界的广泛关注。然而,共晶EHEAs的设计方法仍然是一个挑战。本文提出了一种新型的无限固溶体策略来设计EHEAs。采用这种策略,成功地制备了一系列由有序体心立方相(B2)和体心立方相(BCC)组成的EHEAs,且组织中存在纳米结构的析出相。在本工作中,设计的一些合金展示出了良好的压缩力学性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113891
6. Temperature dependent deformation behavior and stacking fault energy of Fe40Mn40Co10Cr10 alloy
Fe40Mn40Co10Cr10合金的温度相关变形行为和层错能
Article 113891
A. K. Chandan, S. Tripathy, B. Sen, M. Ghosh, S. Ghosh Chowdhury✉
A. Ghosh Chowdhury: 无联系方式
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113891
摘要
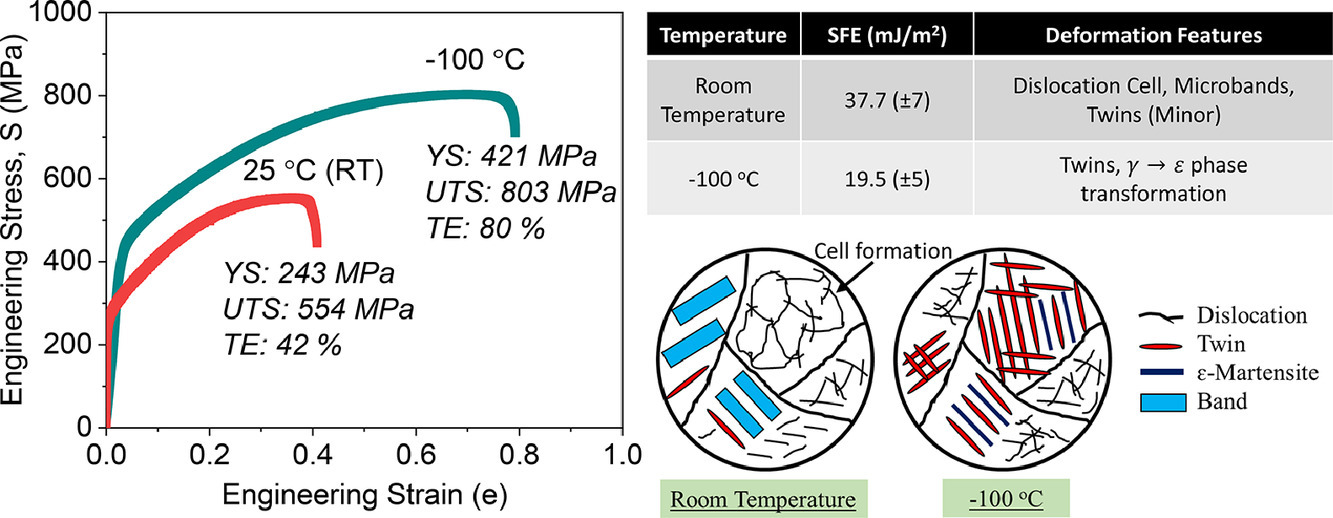
对Fe40Mn40Co10Cr10高熵合金的层错能(SFE)随温度的变化进行了实验研究。利用透射电子显微镜(TEM)弱束暗场(WBDF)技术测量部分位错之间的距离。该系统在室温(RT)和-100℃下的SFE分别为37.7(±7)mJ/m2和19.5(±5)mJ/m2。由于SFE的降低,变形行为从RT时有限的孪晶形成和滑移主导转变为-100℃下的FCC→HCP转变和孪晶的混合模式。在-100℃条件下,孪晶和形变诱发马氏体相变的同时发生使试样具有了优越的强塑性结合。室温下,该合金的SFE比等原子FeMnCoCrNi合金高42%。通过考虑合金化学成分的重新调整对ΔGγ→ε的影响可以理解在去除了Ni元素的条件下SFE的增加。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 199, 1 July. 2021, 113893
7. Novel high-entropy alloys with high-density ε-D019 and abnormal phase transformation
具有高密度ε-D019和异常相变的新型高熵合金
A. H. Xia, Z.L. Ma✉, Z.Q. Xu, M. Wang, X.W. Cheng✉, H.N. Cai
A. L. Ma: z.l.ma@bit.edu.cn 北京理工大学
A. W. Cheng: chengxw@bit.edu.cn 北京理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113893
摘要
析出强化被认为是改善工程结构材料的最有效途径之一。然而,在合金中引入高密度的纳米析出是一个巨大的挑战。本工作利用晶格失配设计的概念,开发出了含有高密度ε-D019纳米析出的CoFeNiVTa(Nb)高熵合金,该纳米析出具有Widmanstätten图案和与基体共格的界面。通过原子分辨率能量色散光谱分析,发现高度共格的六方ε-D019相的成分为(Co, Ni, Fe)3(V, Nb, Ta, Fe),且该相为亚稳相,可以异常转化为δ-D0a相而不是η-D024相。用第一性原理计算证实了δ相比ε相具有优越的热力学稳定性。高密度的Widmanstätten型ε-D019析出物有助于改善CoFeNiVTa(Nb)高温合金的强度和摩擦性能。


