金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.206,1 Mar. 2021(下)
2021-06-04 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文13篇,涵盖了形状记忆合金、不锈钢、高熵合金、高温合金等,国内科研单位包括哈尔滨工业大学、台湾国立交通大学、浙江大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 206 目录
1. Competing Interactions between Mesoscale Length-Scales, Order-Disorder, and Martensitic Transformation in Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys
铁磁形状记忆合金中中尺度相变、有序-无序转变和马氏体相变之间的相互竞争
2. Role of Hydrogen in the Separation of Interfaces in S13Cr Supermartensitic Stainless Steel
氢在S13Cr超级马氏体不锈钢界面失效中的作用
3. Enhanced strength in pure Ti via design of alternating coarse- and fine-grain layers
通过粗晶、细晶交替叠层结构设计提高纯钛的强度
4. Effect of thermal stress on anisotropic grain growth in nano-twinned and un-twinned copper films
热应力对纳米孪晶和无孪晶铜薄膜中晶粒各向异性长大的影响
5. Characteristics and mechanisms of hydrogen-induced quasi-cleavage fracture of lath martensitic steel
板条马氏体钢氢致准解理断裂的特征及机理研究
6. Mechanical response of dislocation interaction with grain boundary in ultrafine-grained interstitial-free steel
超细晶无间隙钢中位错与晶界的相互作用和力学响应研究
7. Chemical-Affinity Disparity and Exclusivity Drive Atomic Segregation, Short-Range Ordering, and Cluster Formation in High-Entropy Alloys
化学亲和力差异和排斥对高熵合金中元素偏聚、短程有序和团簇形成的驱动作用
8. The nucleation sequence of α-Al on TiB2 particles in Al-Cu alloys
Al-Cu合金中α-Al在TiB2颗粒上的形核顺序研究
9. The nature of yielding and anelasticity in metals
金属屈服和滞弹性的本质
10. Critical cooling rates for amorphous-to-ordered complexion transitions in Cu-rich nanocrystalline alloys
富铜纳米合金中非晶-有序转变的临界冷却速率
11. Formative and controlled mechanisms of nano-sized γ′ precipitates with local phase-transition within dislocation networks of nickel-based single crystal superalloys
镍基单晶高温合金中位错网络局域相变过程中纳米γ′析出的形成及控制机制
12. Deformation modes during room temperature tension of fine-grained pure magnesium
细晶纯镁室温拉伸的形变模式研究
13. Enhancing the flow resistance and sound absorption of open-cell metallic foams by creating partially-open windows
通过开窗设计增强金属泡沫的流体阻力和吸声能力
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116616
1. Competing Interactions between Mesoscale Length-Scales, Order-Disorder, and Martensitic Transformation in Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys
铁磁形状记忆合金中中尺度相变、有序-无序转变和马氏体相变之间的相互竞争
D. Salas, Y. Wang, T.C. Duong, V. Attari, Y. Ren, Y. Chumlyakov, R. Arróyave, I. Karaman✉
I. Karaman:ikaraman@tamu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116616
摘要
我们研究了NiCoMnIn超磁形状记忆合金的组成、热处理及由此引起的组织演化对其马氏体相变和铁磁转变的影响。这一合金体系在较宽的温度范围内进行热处理过程中,都可观测到马氏体相变起始温度随热处理时间呈非单调变化,且这种非单调变化的特征也根据成分不同而不同。这一行为不能简单地用析出、析出引起的局部成分变化和/或材料整体的有序度变化解释。在此,我们通过系统的制备、热处理、热物性能测量、透射电子显微镜和原位同步X射线衍射表征,对非单调变化的铁磁转变和马氏体相变温度,与有序-无序转变引起的L21畴演化之间的关系进行了研究。将磁性-结构转变的热力学模型与经典形核理论相结合,进一步确定了组织的空间尺度对马氏体相变开始温度的影响。本研究为基于热力学和动力学对NiCoMnIn超磁形状记忆合金的耦合磁性-结构转变进行调控提供了指导。
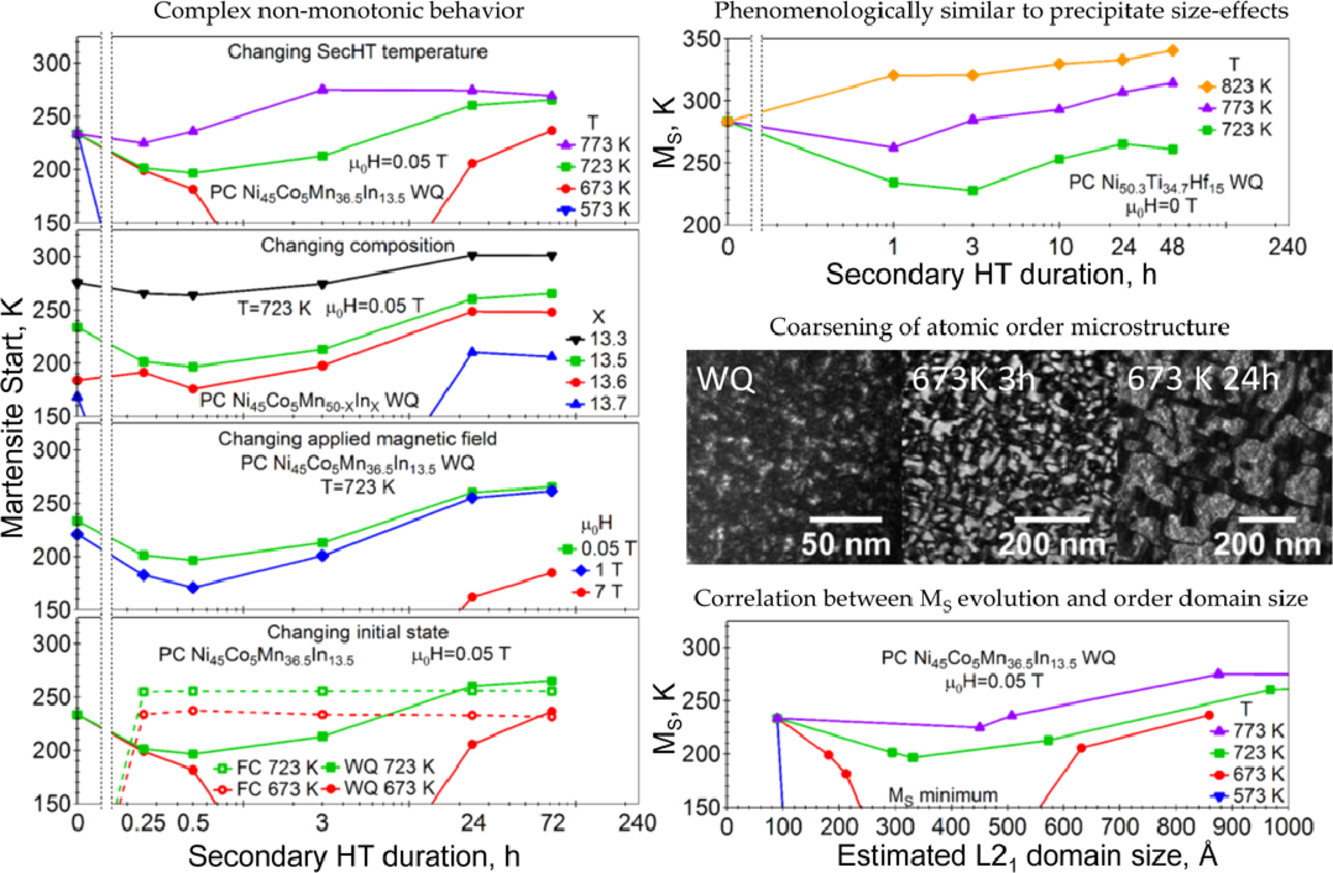
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116614
2. Role of Hydrogen in the Separation of Interfaces in S13Cr Supermartensitic Stainless Steel
氢在S13Cr超级马氏体不锈钢界面失效中的作用
Debora Lima Molter, Mario Augusto Lopes de Castro, Dilson Silva dos Santos✉
D. Silva dos Santos:dilson@metalmat.ufrj.br
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116614
摘要
我们对S13Cr超级马氏体不锈钢(SMSS)在不同阴极电位下进行了氢脆(HE)实验和数值分析。我们采用双恒电位法(DPM)和步进法(SM)两种电化学技术以及热吸收光谱(TDS)研究了氢的扩散行为,测得表观氢扩散系数为1.4 × 10−13 ~ 4.7 × 10−12 m2/s。TDS实验表明存在较深的H陷阱,例如析出相界面、残余奥氏体/铁素体界面等。我们通过拉伸试验和断口分析,研究了氢脆对材料韧性的影响。在-1.5 V/SCE和-1.7 V/SCE的预充测试样品中,延伸率最大降低约14%,且沿整个截面观察到大量脆性断裂。我们基于试验数据,进行了有限元模拟,对韧性损失进行了预测。模型采用了静态结构条件下的断裂控制方法,在试样延伸率的降低与临界断裂能的降低之间建立联系,其中临界断裂能的降低通过热力学过剩变量的平均场方法计算得到。结果表明,S13Cr具有良好的抗氢脆性能,计算模型可靠,实验和模拟结果之间的误差约为5%。
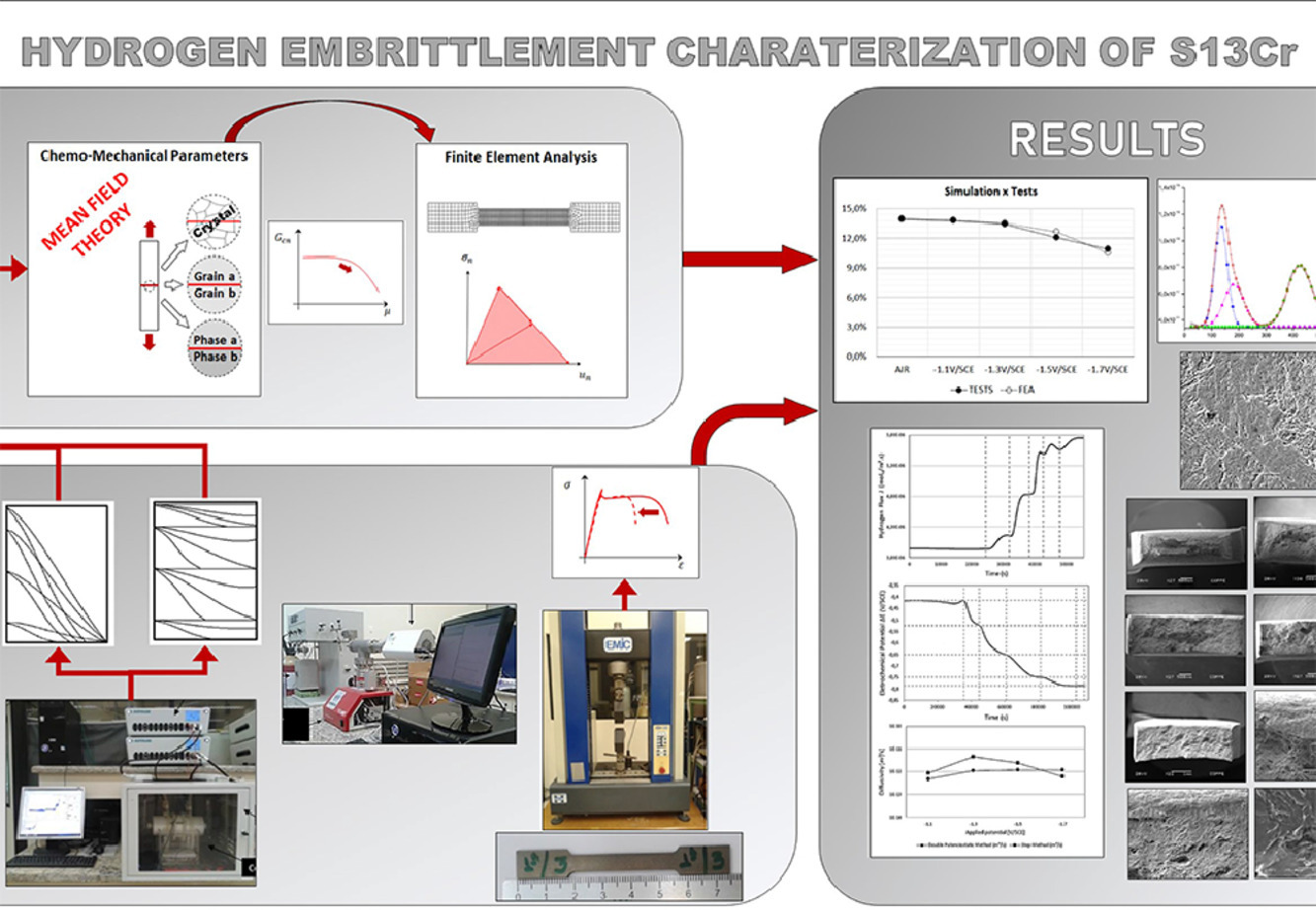
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116627
3. Enhanced strength in pure Ti via design of alternating coarse- and fine-grain layers
通过粗晶、细晶交替叠层结构设计提高纯钛的强度
Danyang Li, Guohua Fan✉, Xiaoxu Huang, Dorte Juul Jensen, Kesong Miao, Chao Xu, Lin Geng✉, Yubin Zhang, Tianbo Yu✉
G. Fan:ghfan@njtech.edu.cn(南京工业大学)
L. Geng:genglin@hit.edu.cn(哈尔滨工业大学)
T. Yu:tiyu@mek.dtu.dk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116627
摘要
金属的屈服强度与平均晶粒尺寸有关,遵循Hall-Petch公式,而层状复合材料的强度则通常遵循混合规则(ROM)。在本研究中,我们制备了一种经特别设计的Ti基多层复合材料。该复合材料又交替的细晶层和粗晶层组成,且不论是细晶层还是粗晶层,层厚均与晶粒尺寸相当。材料实现了极高的屈服强度,远超Hall-Petch公式和混合规则的预测值。我们通过多种实验表征手段,包括使用纳米硬度仪测量硬度、使用拉伸过程中的原位同步辐射XRD测量晶格应变、使用TEM测量材料屈服后的位错结构,对这种多层复合材料的强化机制进行了研究。我们发现,粗晶层中层界面附近的硬度明显高于层中区域,屈服后只在界面区域观察到了<c+a>位错和密集的<a>位错堆积。这说明,在HCP材料的变形过程中,界面具有很强的约束作用,<a>滑移和<c+a>滑移的临界剪切应力之间存在较大差异。粗晶/细晶多层复合Ti结构可以同时实现细晶的强度和粗晶的韧性,这为单相HCP材料的性能优化提供了一种新的设计策略。
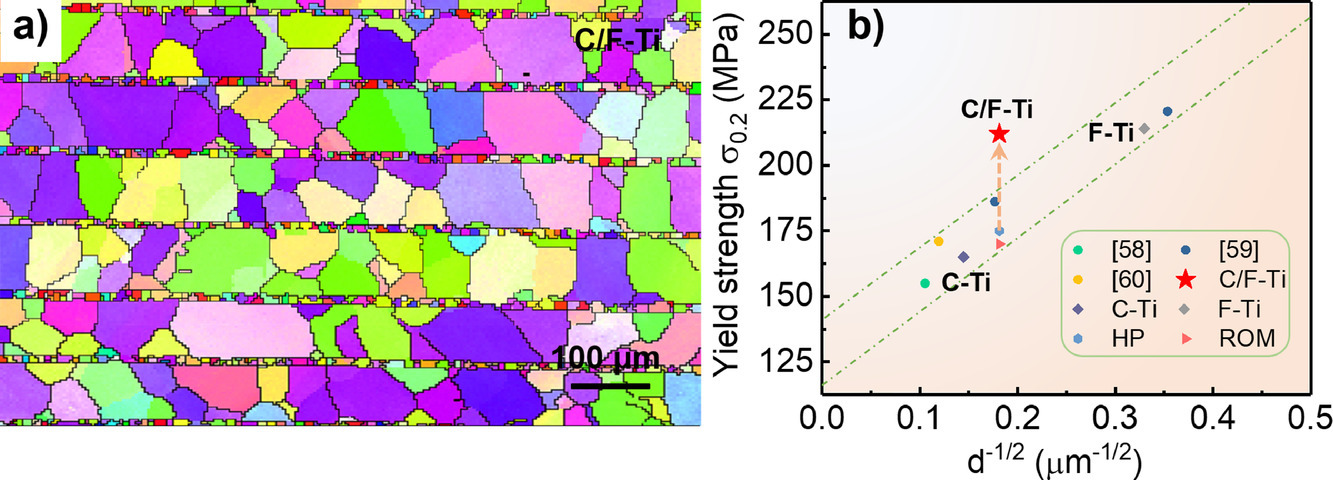
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116637
4. Effect of thermal stress on anisotropic grain growth in nano-twinned and un-twinned copper films
热应力对纳米孪晶和无孪晶铜薄膜中晶粒各向异性长大的影响
I-Hsin Tseng, Yun-Ting Hsu, Jihperng Leu, K N Tu, Chih Chen✉
C. Chen:chih@mail.nctu.edu.tw (台湾国立交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116637
摘要
我们在Si基底上电化学沉积了3.8µm厚的特定取向的纳米孪晶铜(nt-Cu)。我们采用弯曲梁法在室温到400℃范围内对其进行了热应力测量,并研究了铜薄膜经热处理后的微观组织演化。结果表明,150℃时,最大压应力达到150 MPa,(111)取向的纳米孪晶铜开始向(200)取向转变。超过150°C,(200)晶粒的各向异性生长加快。我们发现,纳米孪晶铜薄膜能承受比无纳米孪晶的随机取向铜薄膜大1.5倍的压应力。这一巨大的热应力为定向纳米孪晶Cu晶粒的各向异性生长提供了驱动力,晶粒尺寸最终可达几百µm。
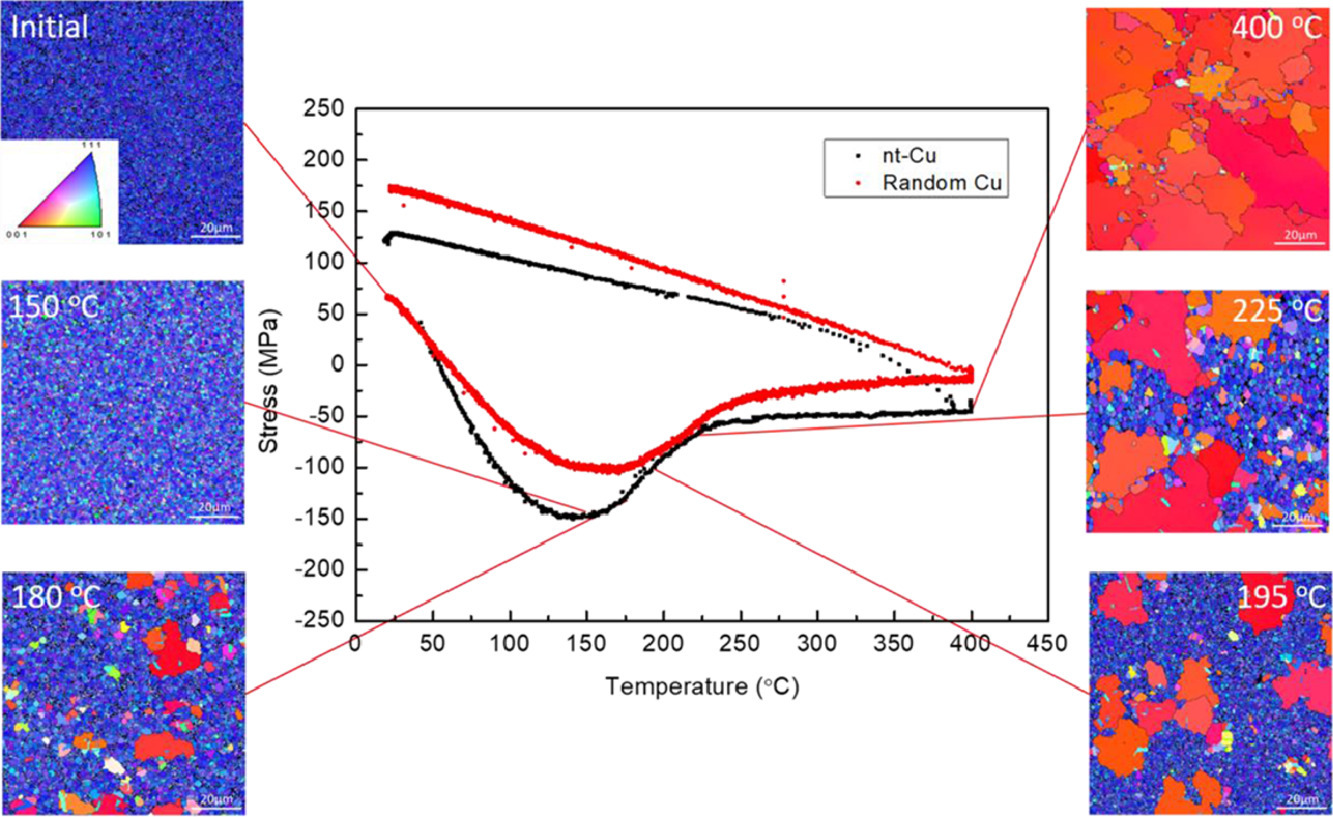
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116635
5. Characteristics and mechanisms of hydrogen-induced quasi-cleavage fracture of lath martensitic steel
板条马氏体钢氢致准解理断裂的特征及机理研究
L. Cho✉, P.E. Bradley, D.S. Lauria, M.L. Martin, M.J. Connolly, J.T. Benzing, E.J. Seo, K.O. Findley, J.G. Speer, A.J. Slifka
L. Cho:lawrence.cho@nist.gov, cyc616@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116635
摘要
我们对淬火态22MnB5的板条马氏体组织、晶体取向和氢致准解理断裂下的位错进行了深入表征。我们采用了扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、背散电子衍射(EBSD)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、透射菊池衍射(TKD)等多种手段对氢脆马氏体试样的断口进行了分析。氢影响区的主要断裂方式为准解理断裂,撕裂脊附近有塑性区,准解理面存在高密度位错。马氏体的组织尺寸、变体取向和界面均对准解理表面形貌有一定影响。断口形貌表明,{100}α'理穿过马氏体板条,随后演化为相对“平坦”的准解理面,同时板条和区块边界处出现{110}α'裂纹,并沿非解理面断裂。随着马氏体组织尺寸的增大,形成相对“平坦”的准解理面的可能性也增大。在氢致解理断裂{100}α'面的断口下方,马氏体区块内的{112}α'滑移面上形成了大量的位错带。我们发现,准解理面上的河流条纹起源于复杂且层次分明的板条马氏体组织。准解理面上的台阶和脊通常与各种马氏体界面相连,表明它们是由于裂纹在这些边界处的偏离而产生的。我们基于Cottrell解理模型,结合氢的作用,对马氏体的准解理机制和断裂路径进行了讨论。
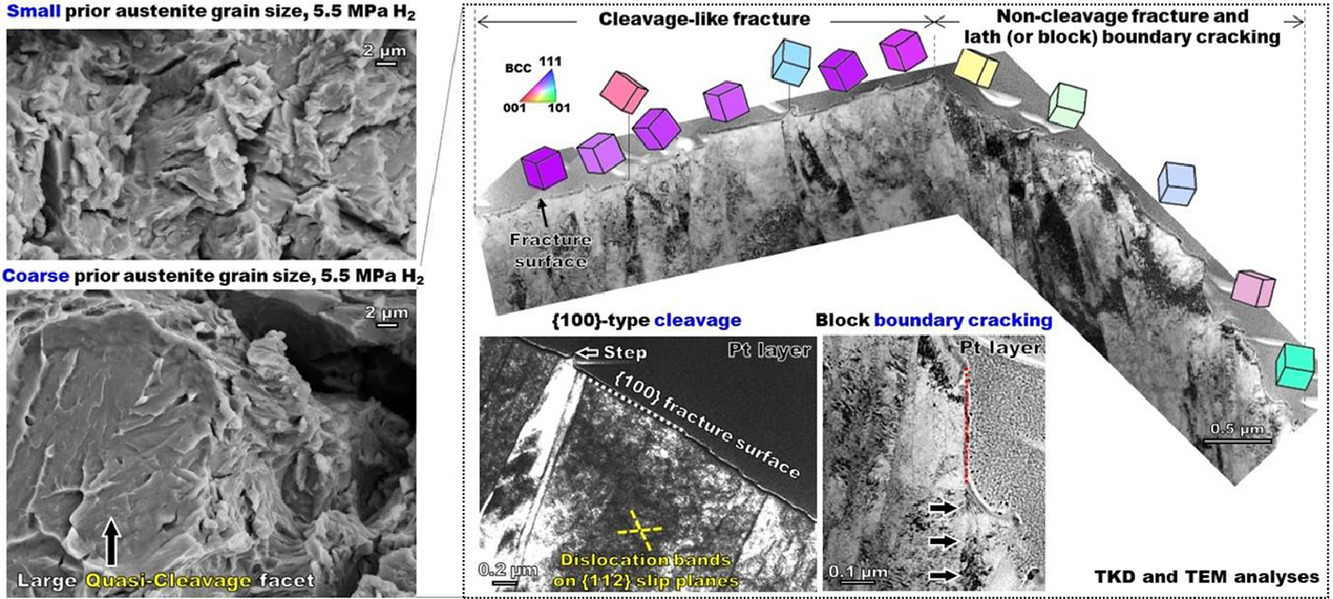
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116621
6. Mechanical response of dislocation interaction with grain boundary in ultrafine-grained interstitial-free steel
超细晶无间隙钢中位错与晶界的相互作用和力学响应研究
Hongxing Li✉, Si Gao, Yo Tomota, Seiichiro Ii, Nobuhiro Tsuji, Takahito Ohmura
H. Li:Li.Hongxing@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116621
摘要
我们以超细晶(UFG)无间隙(IF)钢为研究对象,阐明了Hall-Petch曲线表现出的“超硬化”行为和轴向拉伸试验中不连续屈服行为的潜在机制。我们采用透射电子显微镜(TEM)对不同拉伸应变下的超细晶IF钢试样进行了观察,发现在宏观屈服前,1.0%的微观拉伸应变后,晶粒内部的位错密度降低。宏观屈服后,晶粒内部位错密度增大,最终颈缩区的微观拉伸应变为15%。我们通过TEM微柱原位压缩试验,对超细晶IF钢中的位错运动及其与晶界的相互作用进行了直接观测。宏观屈服前,晶内位错向晶界移动,在晶界处被吸收。在预屈服过程中,位错密度由于湮没而显著降低,同时伴随载荷增加。微柱晶粒内位错密度的降低与块体样品中的观测结果一致。宏观屈服后,晶界处出现爆发式的位错发射,导致了屈服应力降低和不连续屈服行为。通过结合Orowan模型和Johnston-Gilman模型,可以较好地从位错密度的变化的角度,理解超细晶IF钢的高屈服应力和屈服下降行为。
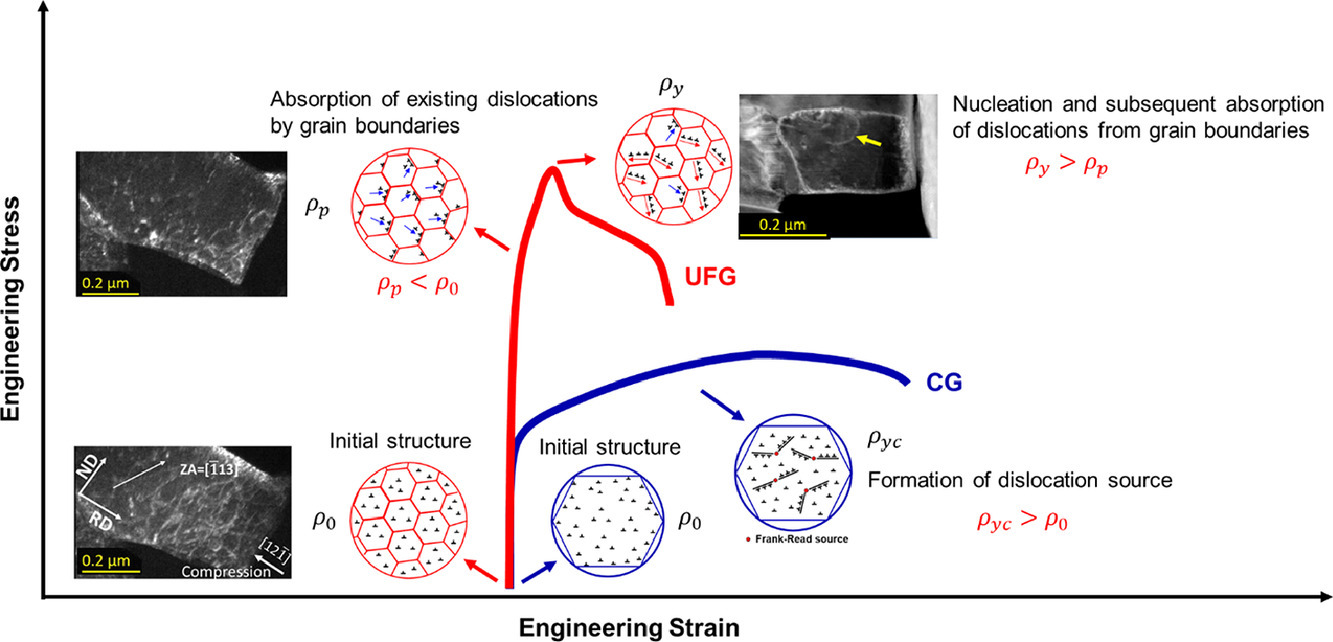
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116638
7. Chemical-Affinity Disparity and Exclusivity Drive Atomic Segregation, Short-Range Ordering, and Cluster Formation in High-Entropy Alloys
化学亲和力差异和排斥对高熵合金中元素偏聚、短程有序和团簇形成的驱动作用
Shuai Chen, Zachary H. Aitken, Subrahmanyam Pattamatta, Zhaoxuan Wu, Zhi Gen Yu, Rajarshi Banerjee, David J. Srolovitz✉, Peter K. Liaw✉, Yong-Wei Zhang✉
D.J. Srolovitz:srol@cityu.edu.sg(香港城市大学)
P.K. Liaw:pliaw@utk.edu
Y.-W. Zhang:zhangyw@ihpc.a-star.edu.sg
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116638
摘要
根据已有文献报导,在实验中观察到了高熵合金(HEAs)中的元素偏聚、近程有序和团簇形成。原子大小和元素的电负性差异被认为是这类现象的根本原因。我们使用了蒙特卡罗方法结合分子动力学模拟,对于两种高熵合金,CoCuFeNiPd和CoCuFeNiTi,进行了研究。结果表明,尽管Ti与其它元素之间的尺寸及电负性差异比Pd大,但CoCuFeNiPd中的元素偏聚和短程有序比CoCuFeNiTi更加显著,这表明仅仅原子尺寸和电负性的差异不足以解释模拟结果。我们发现,Ti(Pd)与其他元素之间的化学亲和力的差异和排斥性引起了这两种合金中不同的聚类行为。我们确定了出现显著元素偏聚和近程排序的三个条件:1. 化学元素之间的化学亲和力差异较大 ;2. 低、中、高能团簇具有较高的化学元素排斥性;3. 中、低能量团簇的形成会导致体系的能量减少,从而补偿高能团簇形成导致的能量增加。我们的研究结果与文献中报道的实验结果一致,强调了化学亲和力差异和排斥性高熵合金微观组织的影响,解释了高熵合金中高能团簇的成因,为高性能高熵合金的设计提供了指导。
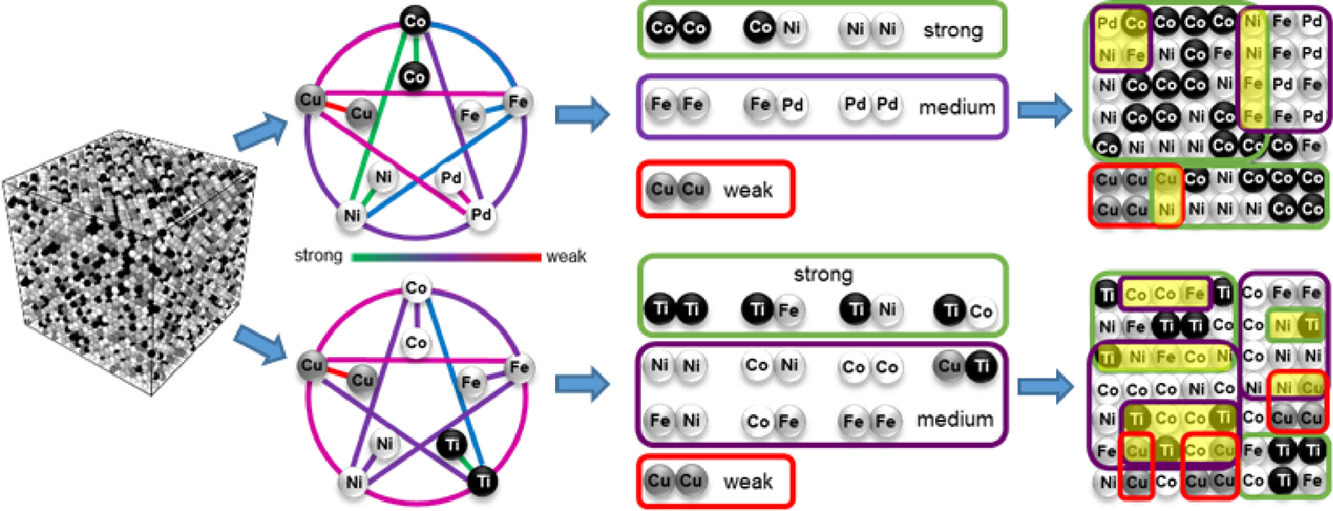
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116652
8. The nucleation sequence of α-Al on TiB2 particles in Al-Cu alloys
Al-Cu合金中α-Al在TiB2颗粒上的形核顺序研究
Jiehua Li✉, Fredrik S. Hage, Quentin M. Ramasse, Peter Schumacher
J. Li:jiehua.li@unileoben.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116652
摘要
近几十年来,TiB2对铝合金的细化作用在工业界和学术界都得到了广泛的研究。为了获得更好的晶粒细化能力,需要添加其他溶质元素,从而对TiB2颗粒界面处的非均匀形核进行调控。在此,我们报导了Al-Cu合金中TiB2非均匀形核界面的原子尺度实验结果,以及Al-5Ti-1B对Al-Cu合金的细化作用。其中着重研究了主要溶质元素(Ti、Cu)的偏聚对TiB2界面的影响,并试图其与其他成核、长大的影响因素分开。在Al-5Ti-1B细化剂中,TiB2粒子的基面上可以明显观察到Ti的偏聚,这一富Ti层为Al3Ti二维化合物,这与之前文献中的记录一致。在Al-Cu合金体系中,TiB2基面也普遍存在Ti的偏聚,当Cu浓度较高时,还存在原子尺度的富Cu层。基于以上观察,我们在添加了Al-5Ti-1B晶粒细化剂的Al-Cu合金中,提出了一种可能的成核顺序。Al在TiB2的富Ti层表面形核,当Cu含量足够时,这些核心借助共晶反应形成一层富Cu层,从而在随后的包晶反应中被保存下来。这一形核顺序有可以帮助我们在TiB2基面上的Al3Ti层与凝固后的工艺条件之间建立联系。虽然很难确切地知道,在凝固后组织中观测到的TiB2粒子在多大程度上对凝固过程中的非均匀形核起到了激活作用,但本研究着重强调了Cu的偏聚在Al-5Ti-1B细化Al-Cu 合金晶粒过程中的作用。

ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116625
9. The nature of yielding and anelasticity in metals
金属屈服和滞弹性的本质
Dayong Li, Robert H. Wagoner✉
R.H. Wagoner:wagoner.2@osu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116625
摘要
最近有文献指出,金属在所有应力条件下,屈服前的应力-应变曲线总存在一定的非线性和迟滞性。这使得我们需要思考金属变形的中的一些基本问题。是否存在一个临界应力,在该应力以下位错是不动的?是否存在一个发生永久形变对应的临界应力?滞弹性和弹性、塑性有什么区别?为此,我们对11种商用合金板材(9种高强钢、2种Mg合金)施加了不同的预应变,随后进行了加载-卸载循环拉伸试验。我们提出了一个位错滞弹性耗散模型,模型与实验结果吻合较好。我们发现,材料施加预应变后,存在一个有限的屈服应力,在此应力之下不会发生永久变形或硬化。滞弹性不同于弹性和塑性:它是可恢复和耗散的;机械可逆而热力学不可逆。相应的初始加载试验得出了截然不同的结论。没有预应变时,材料在近零应力下,即发生塑性变形。基于以上结果,我们对弹性、塑性和滞弹性变形的局部和非局部相互作用提出了假设。
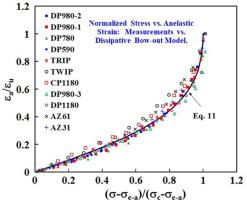
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116650
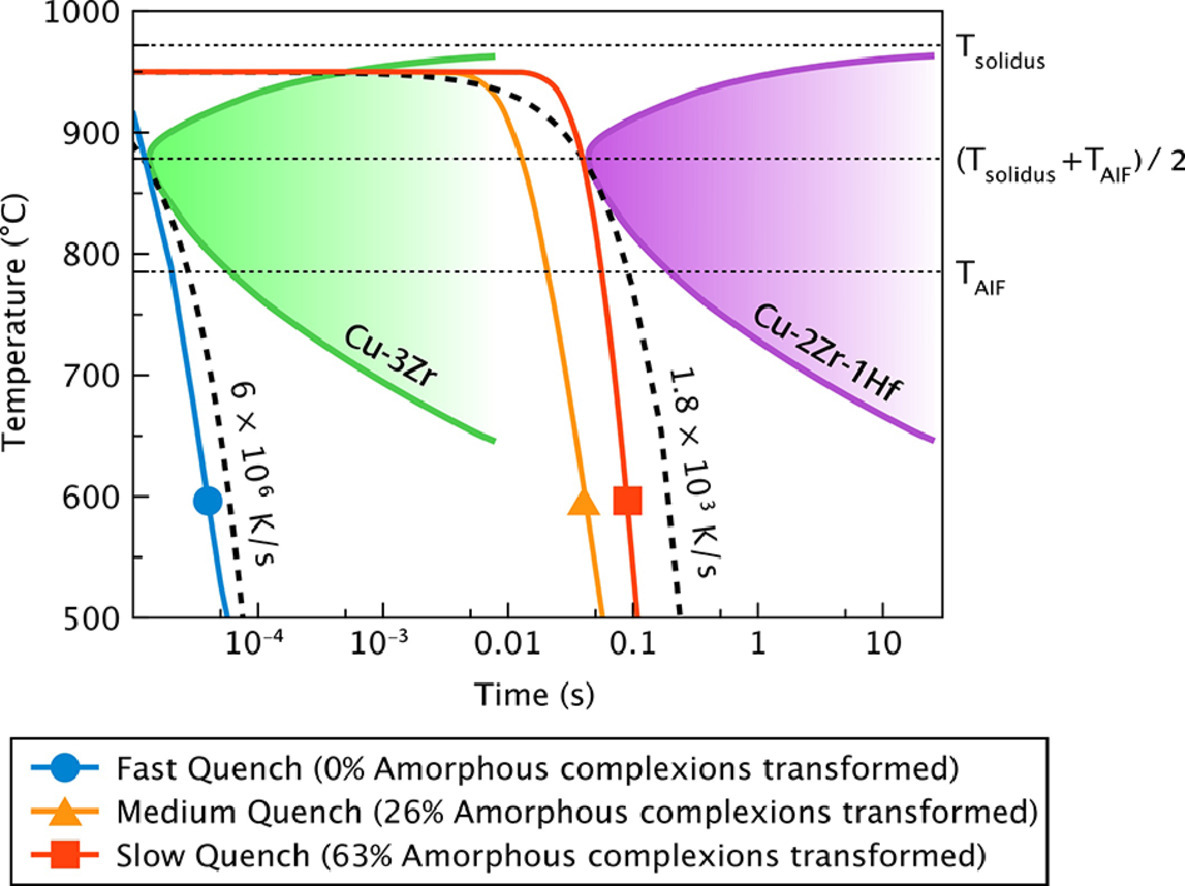
10. Critical cooling rates for amorphous-to-ordered complexion transitions in Cu-rich nanocrystalline alloys
富铜纳米合金中非晶-有序转变的临界冷却速率
Charlette M. Grigorian, Timothy J. Rupert✉
T.J. Rupert:trupert@uci.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116650
摘要
纳米晶金属中的非晶相能够提高材料的机械性能、抗辐照性能以及抑制晶粒长大。本文通过观察从高温冷却过程中,冷却速率对二元和三元铜基合金非晶态-有序态相变的影响,研究了非晶相的稳定性。我们首先对Cu-Zr和Cu-Zr- hf合金试样进行了退火使晶界预熔,随后将样品进行淬火。淬火过程中,采取特殊工艺使试样高度方向的局部冷却速度存在梯度。研究发现,Cu-Zr- hf合金中的非晶厚度分布与局部冷却速率无关,而Cu-Zr合金在缓慢冷却区的非晶层较薄,这表明Cu-Zr- hf合金中非晶相的稳定性优于Cu-Zr合金。我们基于实验结果绘制了二元和三元合金非晶态-有序态相变的时间-温度-相变图,加深了冷却速率和晶界化学对相变影响的认识。三元合金的临界冷却速率比二元合金至少慢三个数量级。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116653
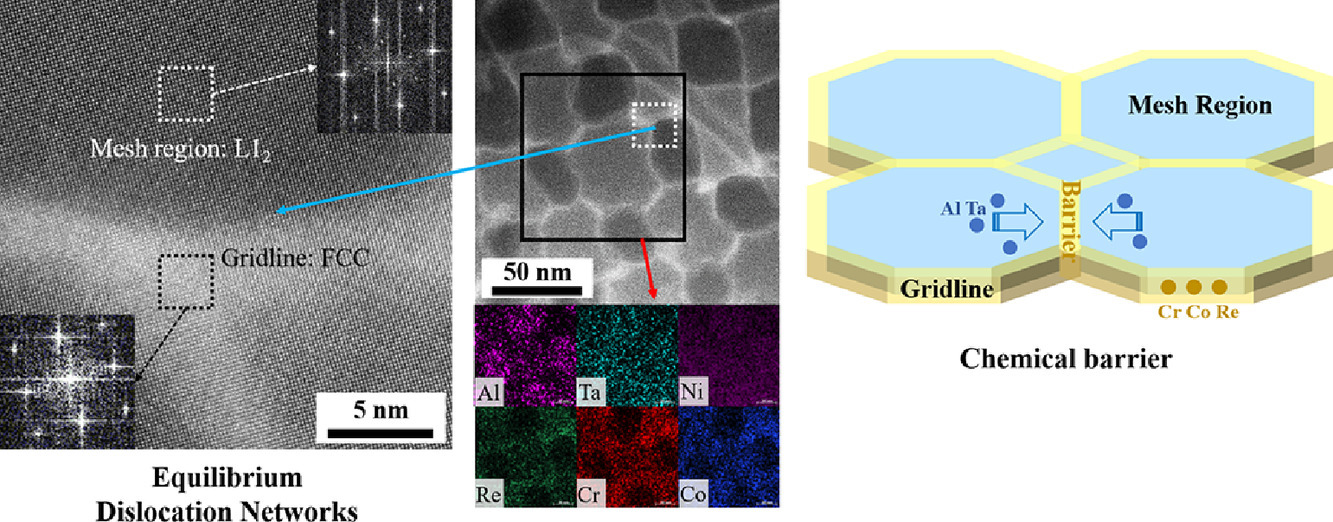
11. Formative and controlled mechanisms of nano-sized γ′ precipitates with local phase-transition within dislocation networks of nickel-based single crystal superalloys
镍基单晶高温合金中位错网络局域相变过程中纳米γ′析出的形成及控制机制
Wanshun Xia, Xinbao Zhao✉, Quanzhao Yue, Liang Yue, Jiangwei Wang, Qingqing Ding, Hongbin Bei, Ze Zhang✉
X. Zhao:superalloys@zju.edu.cn(浙江大学)
Z. Zhang:zezhang@zju.edu.cn(浙江大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116653
摘要
我们对镍基单晶高温合金在1373K、137MPa蠕变过程中位错网络的成分和结构演化进行了研究。位错网络中的区域可分为两部分:网格线和中间的网格区域。随着位错网络的演化,网格区有纳米级γ′相(γ′n)析出,而网格线始终为FCC γ相。Cr、Co和Re在网格线处偏析增加,使网格区Al等γ′形成元素含量增加,引起了FCC-L12的局域相变,形成γ′n相。γ′n 的进一步长大需要大量的γ′形成元素扩散,然而这种扩散被网格线处Cr、Co、Re偏聚形成的化学屏障所阻挡。网格区域的γ′相和网格线处的γ相互相支撑,形成了一种稳定的蠕变位错结构。在较大的局部晶格失配条件下,枝晶内更容易形成更加致密的位错网络,从而促进γ/γ′亚结构的形成,提高材料的抗蠕变抗性能。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116648
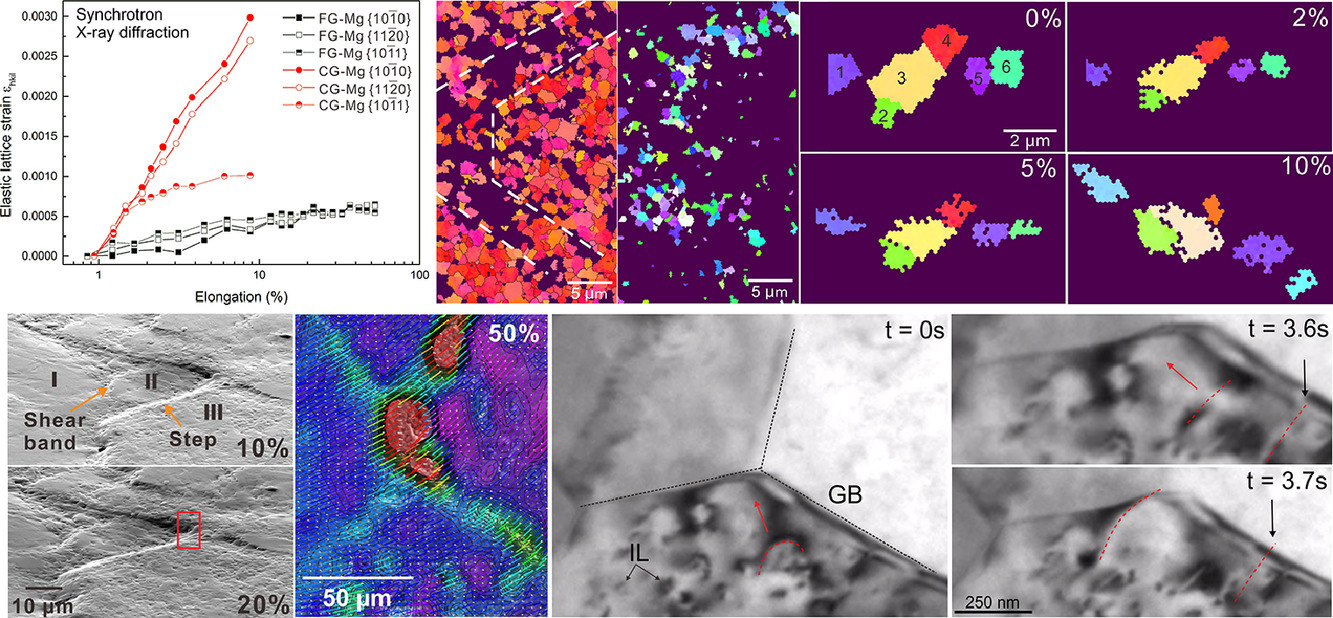
12. Deformation modes during room temperature tension of fine-grained pure magnesium
细晶纯镁室温拉伸的形变模式研究
Zhuoran Zeng✉, Mengran Zhou, Peter Lynch, Frédéric Mompiou, Qinfen Gu, Mohsen Esmaily, Yuanming Yan, Yao Qiu, Shiwei Xu, Hidetoshi Fujii, Chris Davies, Jian-Feng Nie, Nick Birbilis
Z. Zeng:zhuoran.zeng@anu.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116648
摘要
挤压成型的细晶(晶粒尺寸~1.2 µm)多晶纯镁尽管存在较强的织构,但在室温下的延伸率仍可超过100%。在本研究中,我们通过多尺度原位表征技术揭示了其变形模式,以图揭示这种超塑性的成因。同步辐射XRD结果表明,当伸长率为55%时,细晶样品的弹性晶格应变比粗晶样品低3-10倍,表明细晶内没有明显的应变积累,样品内部没有晶间形变。原位SEM证实了晶间变形的主导作用,进一步揭示了晶间形变是由具有相似取向晶粒之间的相对滑移引起的。这种滑移引起的形变是巨大的,位于滑移晶粒组之间的晶粒通过旋转,使得位错滑移容易发生。原位TEM进一步证实了位错滑移的调节模式。位错容易向晶界滑移,并在晶界处湮灭。以上结果表明,细晶Mg的变形模式主要是由晶粒旋转和位错滑移导致的成组晶间滑移,这与粗晶Mg中的位错滑移模式显著不同。协调变形抑制了局部应力集中,从而大幅提高了纯Mg的室温塑性。
ACTA
Vol. 206,1 Mar. 2021, 116666
13. Enhancing the flow resistance and sound absorption of open-cell metallic foams by creating partially-open windows
通过开窗设计增强金属泡沫的流体阻力和吸声能力
Xiang Yu, Zhenbo Lu, Wei Zhai✉
W. Zhai:mpezwei@nus.edu.sg
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116666
摘要
具有高流体阻力的金属泡沫是一种实用的吸声材料。在此,我们报导了一种新型金属泡沫材料,该材料在相互连接的泡沫孔之间采用部分打开的窗口形貌,从而提高了流体阻力和吸声系数。这种组织是在制备过程中利用金属浆料的剪切剪薄行为形成的。我们还建立了一种新的微观组织模型,考虑了窗口处特定表面积的增加,以模拟这种新型泡沫材料的渗透率。模型的输入参数包括材料胞结构的几何形状,这一参数可以通过材料的形貌表征获取。结果表明,这种新型金属泡沫的流体阻力显著提高(1.5倍),且孔隙率损失较小(< 2.3%)。声学实验表明,材料在整个频率范围内的吸声系数均有所提升(平均为0.2)。以上研究展示了一种特殊微结构泡沫金属的设计方法,材料具有高流体阻力和高孔隙率(93%~97%)开路结构。提出的流体模型在其他的设计和表征方面也具有优异的应用潜力。


