金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.200, 15 July. 2021(上)
2021-06-04 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文12篇,涵盖了高熵合金、复相钢、高温合金、形状记忆合金等,国内科研单位包括北京大学、上海交通大学、西安交通大学、中南大学、湖南大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 200 目录
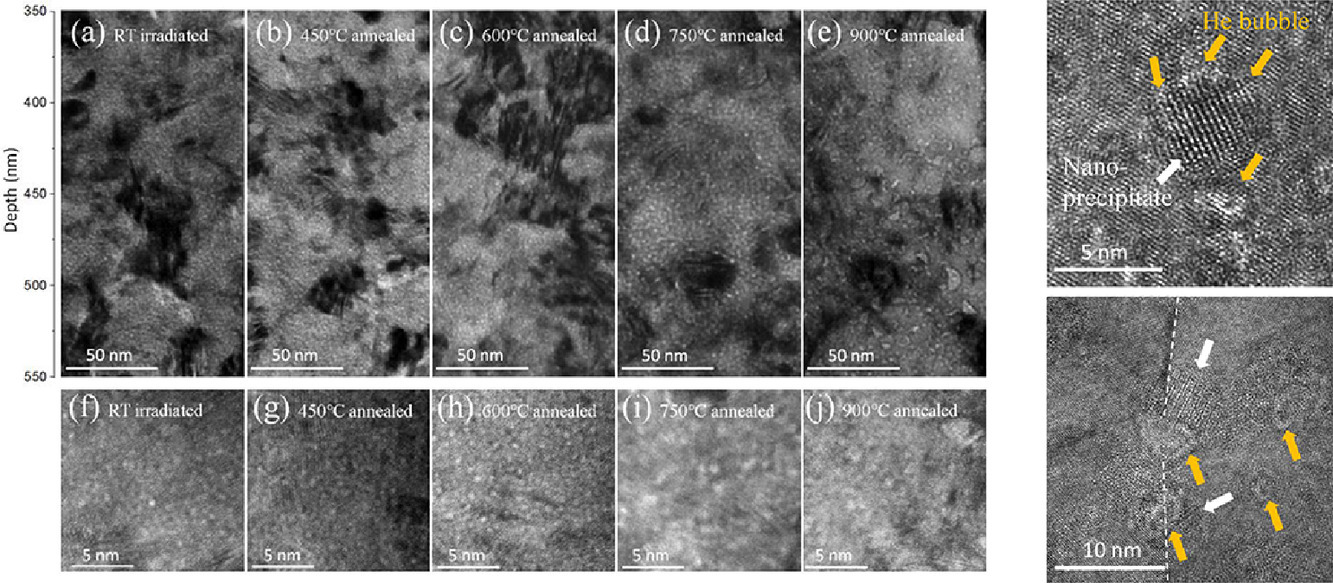
1. Effects of grain boundaries and nano-precipitates on helium bubble behaviors in lanthanum-doped nanocrystalline steel
晶界和纳米析出对掺镧纳米钢中氦泡行为的影响
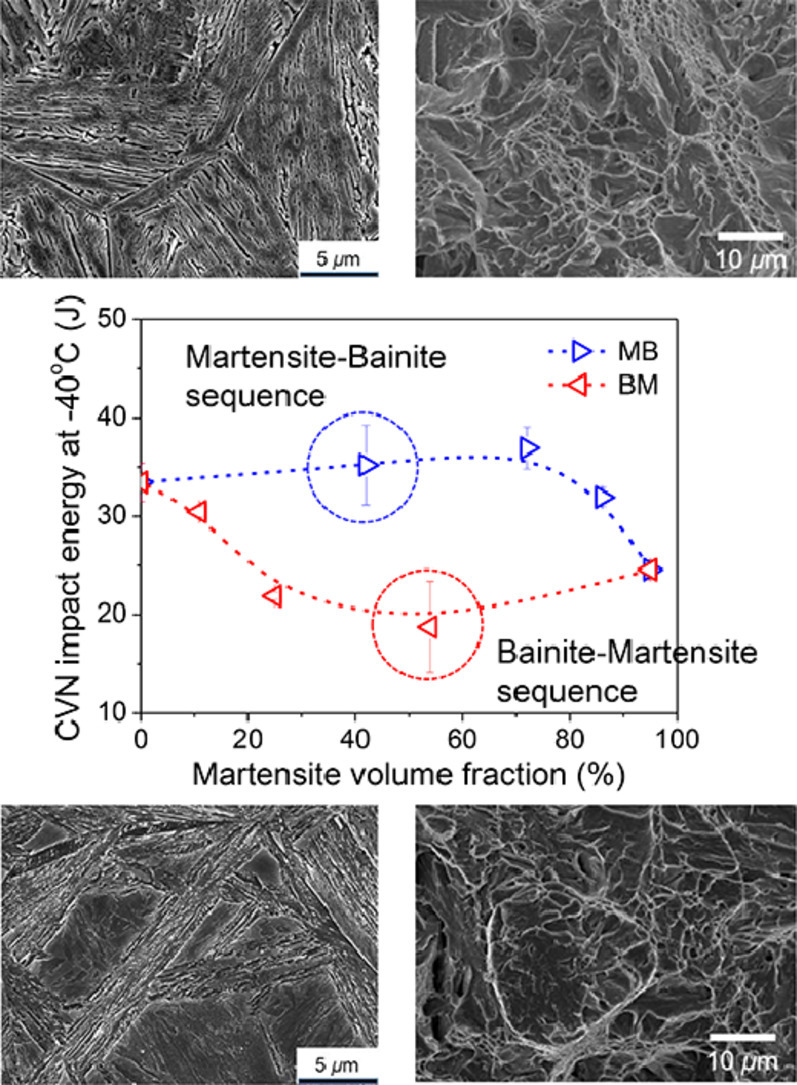
2. Influence of chronological control of transformation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of complex phase steels
相变顺序控制对复相钢组织和力学性能的影响
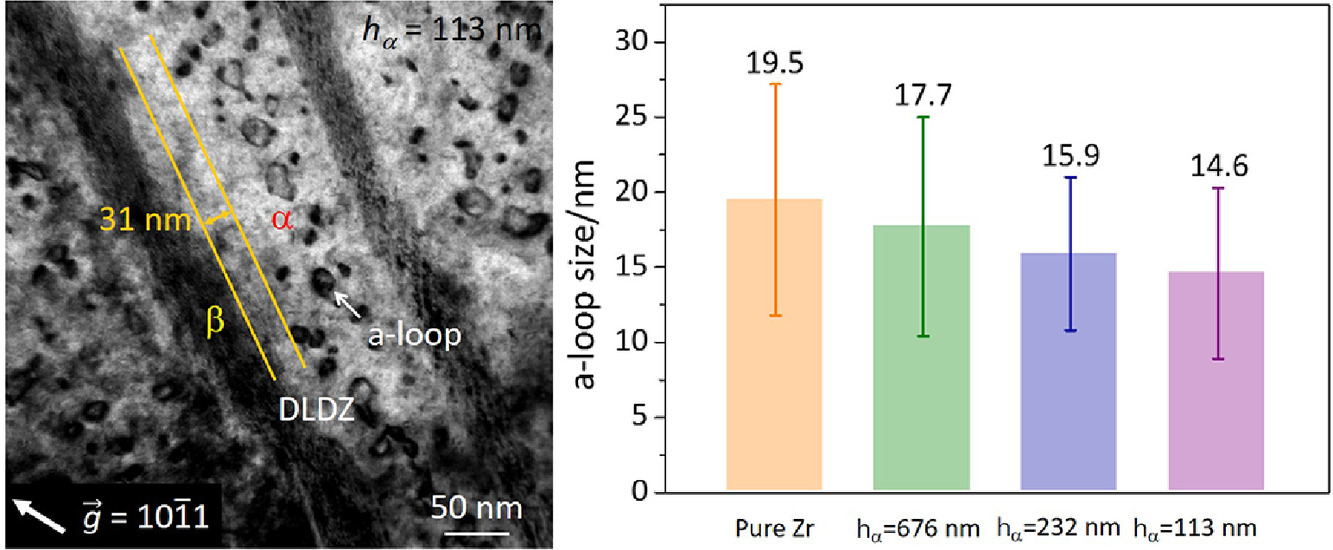
3. Interfaces Reduce Dislocation Loop Formation in Irradiated Nanolayered Zr-2.5Nb
界面减少了辐照纳米层状Zr-2.5Nb中位错环的形成
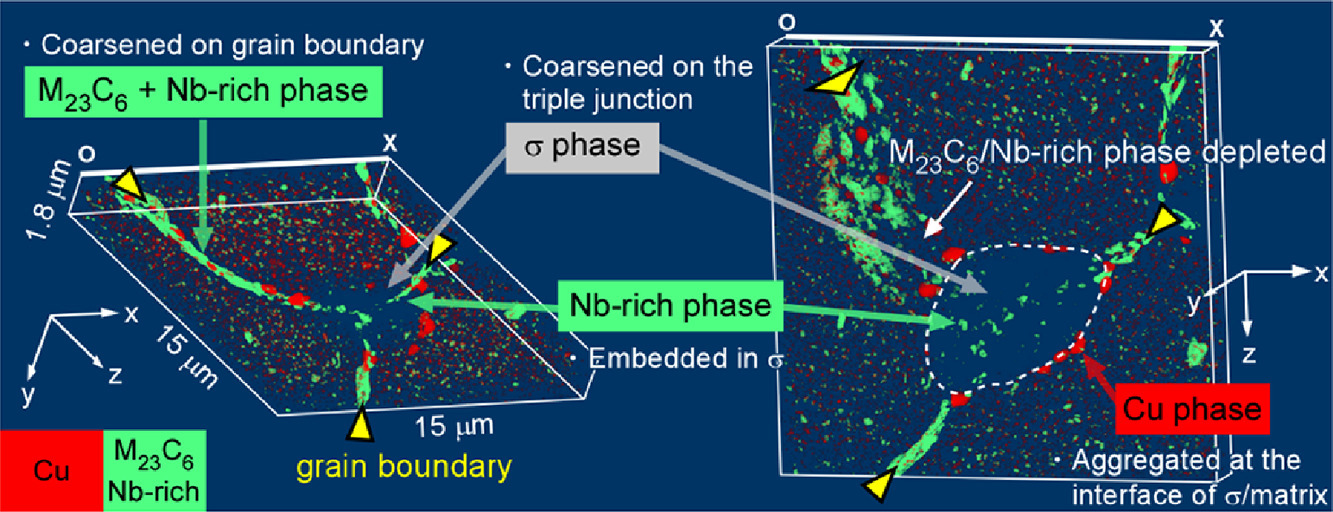
4. Three-dimensional analysis of the precipitation behavior of 18Cr-9Ni-3Cu-Nb-N steel at 973 K
973 K下18Cr-9Ni-3Cu-Nb-N钢析出行为的三维分析
5. In situ synchrotron diffraction study of a crack-free additively manufactured Ni base superalloy
无裂纹增材制造镍基高温合金的原位同步辐射研究
6. Persistent slip observed in TiZrNbHfTa: A body-centered high-entropy cubic alloy
体心立方高熵合金TiZrNbHfTa中观察到的持久滑移
7. Bulk NiTiCuCo shape memory alloys with ultra-high thermal and superelastic cyclic stability
具有超高热稳定性和超弹性循环稳定性的块状NiTiCuCo形状记忆合金
8. Characterization of nano precipitate phase in an as-extruded Zn-Cu alloy
挤压态锌铜合金中纳米析出相的表征
9. Enhancing strength-ductility synergy in a casting non-equiatomic NiCoCr-based high-entropy alloy by Al and Ti combination addition
Al和Ti元素共添加增强铸造非等原子NiCoCr基高熵合金的强塑性协同效应
10. A carbide-reinforced Re0.5MoNbW(TaC)0.8 eutectic high-entropy composite with outstanding compressive properties
具有优异压缩性能的碳化物强化Re0.5MoNbW(TaC)0.8共晶高熵复合材料
11. High temperature in situ SEM assessment followed by ex situ AFM and EBSD investigation of the nucleation and early growth stages of Fe-Al intermetallics
对Fe-Al金属间化合物的形核和早期生长阶段进行高温原位SEM评估与随后的非原位AFM和EBSD研究
12. Microstructure and strengthening mechanisms of nanolamellar structures in ultrastrong drawn iron wires
超强拉拔铁丝中纳米层状结构的微观组织及强化机理
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113900
1. Effects of grain boundaries and nano-precipitates on helium bubble behaviors in lanthanum-doped nanocrystalline steel
晶界和纳米析出对掺镧纳米钢中氦泡行为的影响
Haocheng Liu, Jia Huang, Chenxu Wang, Songqin Xia, Wei Ge, Qingyuan Liu, Yue Su, Zhiying Gao, Shuang Zhao, Congcong Du, Liuxuan Cao, Tongde Shen, Yugang Wang✉
Yugang Wang: ygwang@pku.edu.cn 北京大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113900
摘要
在先进核系统中,氦的积聚会加速结构材料的失效。纳米结构材料可以通过为氦泡提供更多的形核位点来缓解氦效应。掺镧的304奥氏体纳米不锈钢(NC304-La)具有超细且稳定的纳米晶粒(直径~45 nm),并具有高密度的细小纳米析出。本文将氦离子注入NC304-La,并在不同温度下进行退火处理。研究发现,结合了纳米晶钢和氧化弥散强化钢的关键特性,NC304-La展现出优异的抗氦泡膨胀性能。我们表征了氦泡与NC304-La中晶界和纳米析出物这两种特征之间的相互作用。通过对此体系中氦泡的热处理相关行为的详细研究,提出了NC304-La中抗氦泡粗化的机理。
SCRIPTA
Vol.200, 15 July. 2021, 113892
2. Influence of chronological control of transformation on the microstructure and mechanical properties of complex phase steels
相变顺序控制对复相钢组织和力学性能的影响
Hong-Bum Lee, Ho Hyeong Lee, Young-Beum Song, Jinhee Ham, Yong JinKim, Hong-Kyu Kim, Dong-Woo Suh✉
Dong-Woo Suh:dongwoo1@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113892
摘要
我们研究了相变顺序对由贝氏体和马氏体组成的复相钢组织演变和力学性能的影响。当马氏体相变发生在贝氏体相变之前时,最终组织为均匀分布的板条状贝氏体和马氏体;当贝氏体相变发生在马氏体相变之前时,最终组织为板条状贝氏体和富碳的块状马氏体。尽管富碳块状马氏体的存在更有效地提高了合金的强度,但少量马氏体的存在就会显著降低合金的冲击韧性。另一方面,均匀的板条状马氏体和贝氏体的混合可以在马氏体含量高达70%时,保持冲击韧性或者造成其中等程度的降低,这被认为是在不影响冲击韧性的情况下提高复相钢强度的非常有利的选择。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113902
3. Interfaces Reduce Dislocation Loop Formation in Irradiated Nanolayered Zr-2.5Nb
界面减少了辐照纳米层状Zr-2.5Nb中位错环的形成
Jie-Wen Zhang, Si-Mian Liu, Wei-Zhong Han✉
Wei-Zhong Han: wzhanxjtu@mail.xjtu.edu.cn 西安交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113902
摘要
界面工程是减少辐照缺陷在金属中积累的有效方法。本文研究了氦和氪离子辐照纳米层状Zr-2.5Nb中,界面对位错环形成的影响。纳米层状α/β-Zr双相结构在400℃照射至20 dpa后仍保持稳定。在界面处形成了宽30 ~ 40 nm的位错剥蚀区。由于界面加速了点缺陷的复合,纳米层状样品中a环和c环的数量密度和尺寸都变小了。这些结果表明,α/β-Zr界面有效减少了位错环的形成。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113904
4. Three-dimensional analysis of the precipitation behavior of 18Cr-9Ni-3Cu-Nb-N steel at 973 K
973 K下18Cr-9Ni-3Cu-Nb-N钢析出行为的三维分析
Tomotaka Hatakeyama✉, Kota Sawada, Toru Hara, Kaoru Sekido, Kazuhiro Kimura
Tomotaka Hatakeyama: hatakeyama.tomotaka@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113904
摘要
通过观察18Cr-9Ni-3Cu-Nb-N钢蠕变试样在973 K/50214.3 h后断裂的握持部位,探讨了该钢蠕变过程中的显微组织演变。结合聚焦离子束扫描电子显微镜(FIB-SEM)系列切片与机器学习的图像处理相结合,对钢的析出行为进行了三维可视化。结果表明,σ相粗化导致M23C6相在晶界上的消耗和Cu相在σ相与基体界面的聚集。σ相的形成引起了M23C6相的晶界析出强化和Cu相在σ相附近的析出强化贡献的降低,进而导致了长期蠕变过程中的过早失效。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113896
5. In situ synchrotron diffraction study of a crack-free additively manufactured Ni base superalloy
无裂纹增材制造镍基高温合金的原位同步辐射研究
Kartik Prasad✉, Yuuki Horita, Atsushi Ito, Shiro Torizuka
Kartik Prasad: kartik@eng.u-hyogo.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113896
摘要
用原位同步X射线衍射法研究了无裂纹增材制造(AM)Ni基高温合金及其变形(W)合金的拉伸变形行为。为了了解位错特性、位错密度(ρ)、共格散射畴大小(D)和位错排列参数(M)的演化,采用修正的Williamson-Hall和修正的Warren-Averbach方法对前六个{hkl}反射的衍射数据进行了分析。在弹性和塑性变形过程中,AM合金的ρ值均高于W合金。在塑性变形过程中,W合金中刃位错和螺位错的比例几乎相等,而AM合金中螺位错的比例较高。对于AM高温合金中初始ρ值较高和D值无效的特点,提出了对已成型零件进行热处理的建议。
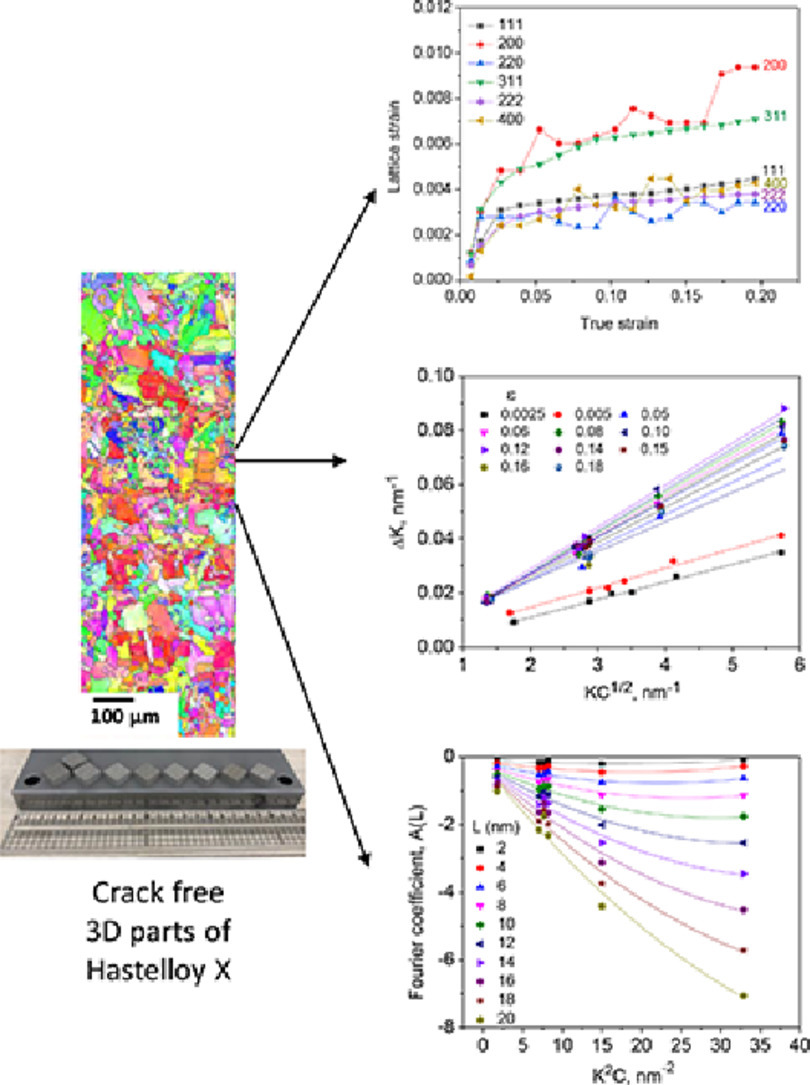
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113895
6. Persistent slip observed in TiZrNbHfTa: A body-centered high-entropy cubic alloy
体心立方高熵合金TiZrNbHfTa中观察到的持久滑移
Masaki Tanaka✉, Shinji Okajo, Shigeto Yamasaki, Tatsuya Morikawa
Masaki Tanaka: masaki@zaiko.kyushu-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113895
摘要
本文评估了TiZrNbHfTa的滑移特性,得出了ψ-χ关系,其中χ定义为最大剪应力平面与(-101)之间的夹角,ψ定义为表观滑移面与(-101)之间的夹角。用聚焦离子束在单个晶粒中制备出微米大小的悬臂梁,进而进行弯曲试验。对于Fe-Si合金来说,滑移带在微米尺度上是连续的,这表明存在持续的滑移。然而,ψ-χ关系表明ψ与χ基本相同,表明不存在持续滑移。用原子力显微镜的详细观察证实,在亚微米尺度上,交滑移是如此频繁,以至于滑移带看起来是连续的,且在微米尺度上观察到了最大剪应力面。在这里,TiZrNbHfTa表现出异常频繁的交滑移,这是体心立方高熵合金的一个新特征。
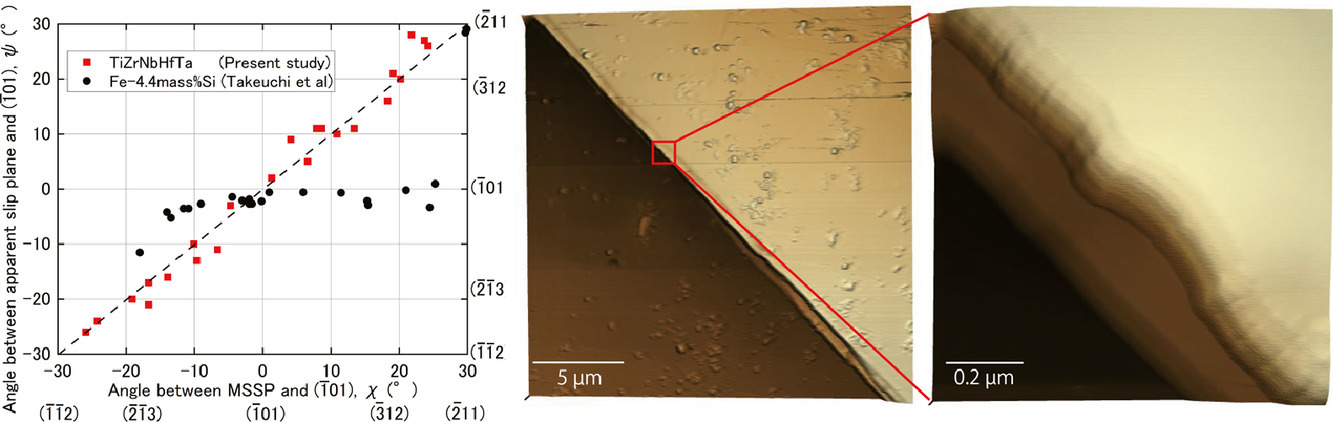
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113899
7. Bulk NiTiCuCo shape memory alloys with ultra-high thermal and superelastic cyclic stability
具有超高热稳定性和超弹性循环稳定性的块状NiTiCuCo形状记忆合金
Aslan Ahadi✉, Amir Sabet Ghorabaei, Hassan Shirazi, Mahmoud Nili-Ahmadabadi
Aslan Ahadi: Aslan.Ahadi@ut.ac.ir
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113899
摘要
在NiTiCuCo薄膜中,形状记忆合金在数百万次循环中依然保持稳定的功能性能。众多学者提出这种超低功能疲劳的机理是由共格Ti2Cu析出相周围的外延应变引起的。尽管充分了解了微观组织的起源,但是这种抗疲劳性能从未在块体NiTiCuCo合金中实现过。在本研究中,我们首次表明,在热相变下,半共格Ti2Cu析出相有助于满足相容性标准。在600°C时效1小时后,块状粗晶Ti54Ni31.7Cu12.3Co2的热稳定性达到了前所未有的水平,其中循环200次相变温度迁移了0.1°C左右。为了获得稳定的超弹性响应,提出了一种热机械加工的方法,获得了嵌入Ti2Cu析出相的均匀纳米晶组织。这种微结构大大改善了超弹性循环稳定性,200次超弹性循环下平台应力改变了~ 22 MPa。
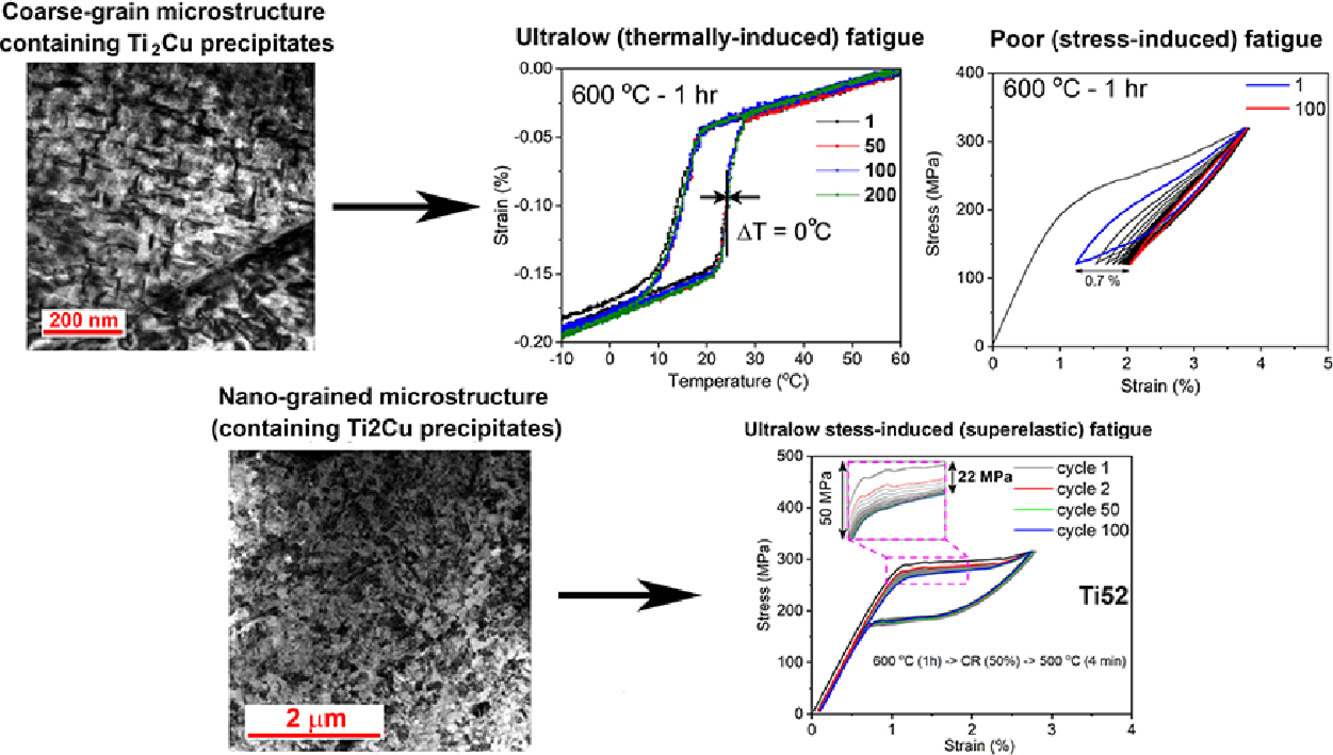
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113907
8. Characterization of nano precipitate phase in an as-extruded Zn-Cu alloy
挤压态锌铜合金中纳米析出相的表征
Jimiao Jiang, Hua Huang✉, Jialin Niu, Zhaohui Jin, Matthew Dargusch, Guangyin Yuan✉
Hua Huang: huangh@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学
Guangyin Yuan: gyyuan@sjtu.edu.cn
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113907
摘要
Zn-Cu基合金具有优异的抗自老化性能、强度与延展性的结合以及良好的生物相容性,是可生物降解心血管支架的重要合金系列,具有广阔的应用前景。一般来说,纳米析出是增强这些合金的有效途径。在Zn-Cu基合金中,先前的研究仅观察到了亚微米或微米尺寸的第二相。本研究中,我们用透射电镜首次表征了挤压态Zn-2.0wt.%Cu合金中纳米析出相,确定了其为富Cu的六方ε (CuZn4)相。此纳米析出相呈棒状,沿[02-21]η方向以特定角度与基体基面对称分布,展现出和基体近似的共格关系。基于自由能最小化理论,分析了这些纳米析出相的形状及其与基体的取向关系。
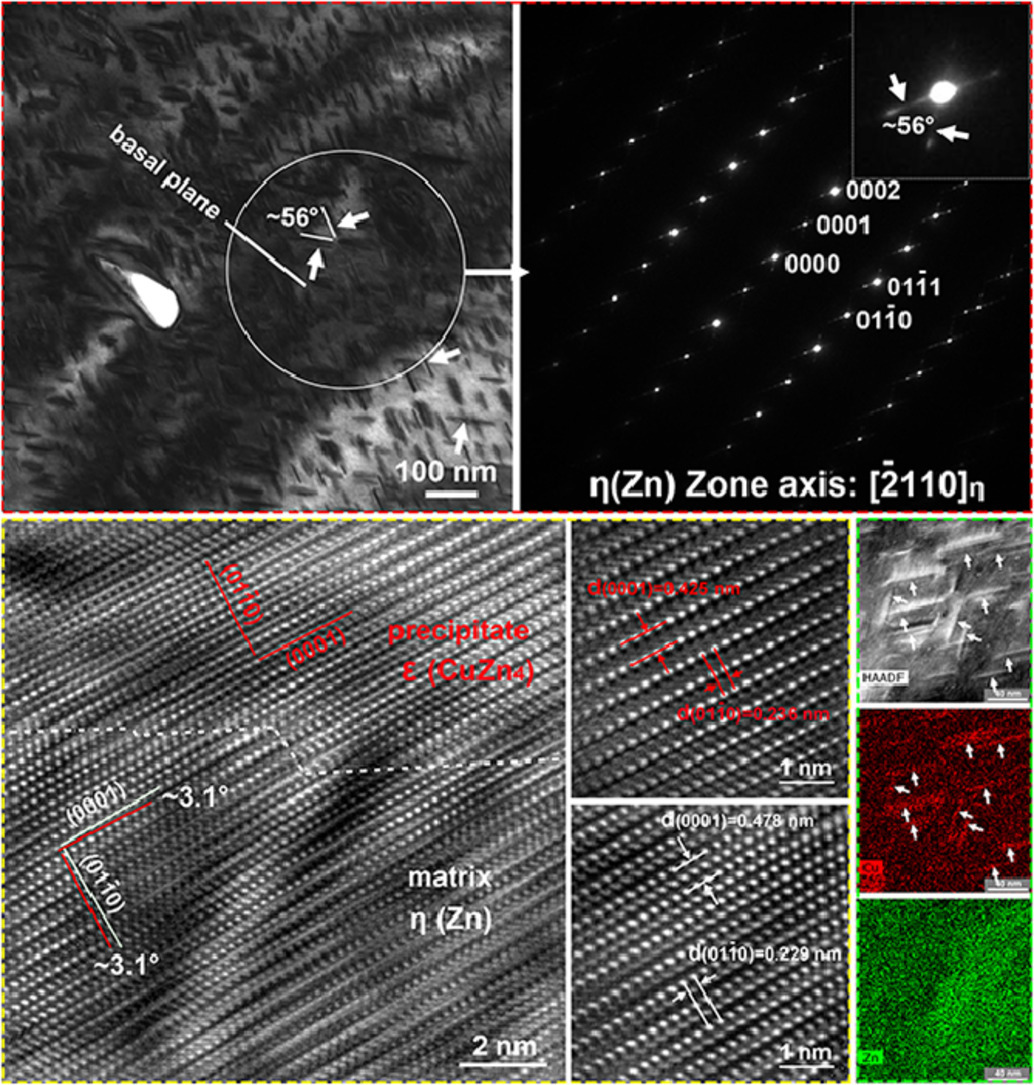
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113898
9. Enhancing strength-ductility synergy in a casting non-equiatomic NiCoCr-based high-entropy alloy by Al and Ti combination addition
Al和Ti元素共添加增强铸造非等原子NiCoCr基高熵合金的强塑性协同效应
Xueling Huang, Lanping Huang, Hailong Peng, Yong Liu, Bin Liu, Song Li✉
Song Li: ls2011sl@csu.edu.cn 中南大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113898
摘要
采用直接电弧熔炼得到了单相面心立方结构(FCC)的非等原子Ni3.5Co3Cr1.5中熵合金(AT0),屈服强度为147 MPa,抗拉强度为447 MPa,断裂总伸长率为78.8%。通过添加Al和Ti,铸态(Ni3.5Co3Cr1.5)90Al5Ti5高熵合金(AT5)表现出增强的强塑性协同效应。与AT0合金相比,AT5合金的屈服强度提高了5倍以上,达到792 MPa,抗拉强度提高了一倍,达到1004 MPa,但仍保持了38.2%的高伸长率。强度的明显提高是由于FCC基体中形成了均匀分布的、高含量且共格的(Ni,Co)3(Al,Ti)型纳米析出。拉伸变形过程中各种位错亚组织的形成和带有Lomer-Cottrell锁的交叉层错(SFs)是AT5合金应变硬化的主要原因。
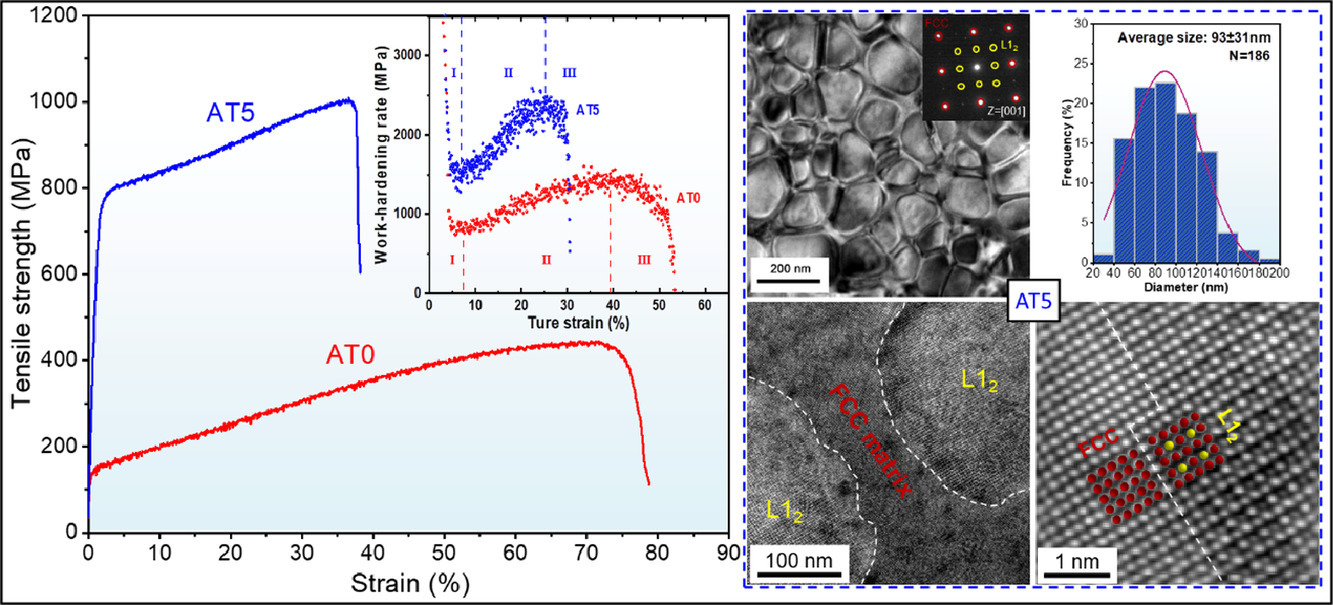
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113909
10. A carbide-reinforced Re0.5MoNbW(TaC)0.8 eutectic high-entropy composite with outstanding compressive properties
具有优异压缩性能的碳化物强化Re0.5MoNbW(TaC)0.8共晶高熵复合材料
Q. Q. Wei, X.D. Xu✉, G.M. Li, G.Q. Luo, J. Zhang, Q. Shen✉, C.L. Wu
X. D. Xu: xiandongxu@hnu.edu.cn 湖南大学
Q. Shen:sqqf@263.net 武汉理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113909
摘要
耐火高熵合金(RHEAs)具有优异的抗软化性能,是一种很有前途的高温材料。然而,大多数在1200℃下能够承受软化的RHEAs往往在室温下表现出明显的脆性。本文采用电弧熔炼法制备了由体心立方和多组元碳化物相组成的高强高韧Re0.5MoNbW(TaC)0.8共晶高熵复合材料(HEC)。HEC具有较高的屈服强度(1340 MPa)、极限抗压强度(2347 MPa)和塑性(8.90%),超过了之前报道的RHEAs和HEC。基于实验观测的定量计算表明,半共格相界面对强度的提高起着至关重要的作用,界面相关强化在界面强化项中占主导地位。基于本研究,我们提出了一种策略,以设计高温应用的高强高韧HECs。
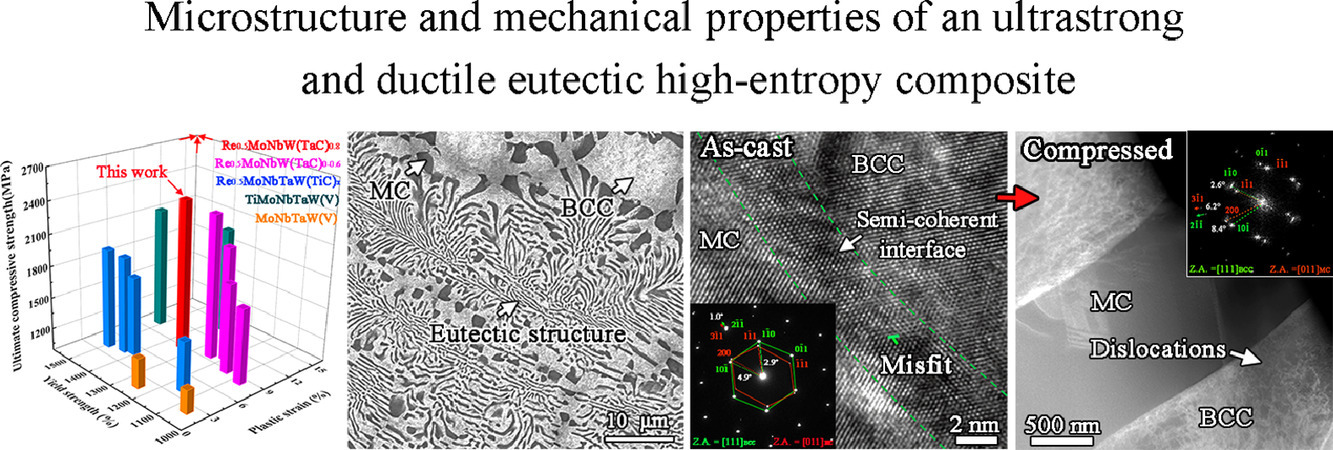
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113910
11. High temperature in situ SEM assessment followed by ex situ AFM and EBSD investigation of the nucleation and early growth stages of Fe-Al intermetallics
对Fe-Al金属间化合物的形核和早期生长阶段进行高温原位SEM评估与随后的非原位AFM和EBSD研究
T. Sapanathan✉, I. Sabirov, P. Xia, M.A. Monclús, J.M. Molina-Aldareguía, P.J. Jacques, A. Simar
T. Sapanathan: thaneshan.sapanathan@uclouvain.be
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113910
摘要
使用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)中的专用原位加热设置以及后续的非原位原子力显微镜(AFM)和电子背散射衍射(EBSD)对596℃下Fe-Al金属间化合物(IMs)的形核和早期生长阶段进行了表征。位置跟踪被用来解释进一步的特征。非原位AFM观察表明,IMs在形核开始时有轻微的收缩和平面外突起,随后定向生长。用非原位EBSD对形成的界面IM化合物进行了鉴定。结果清楚地表明,在扩散控制的η相生长之前,θ相先形核。θ相普遍存在于金属间化合物层中。
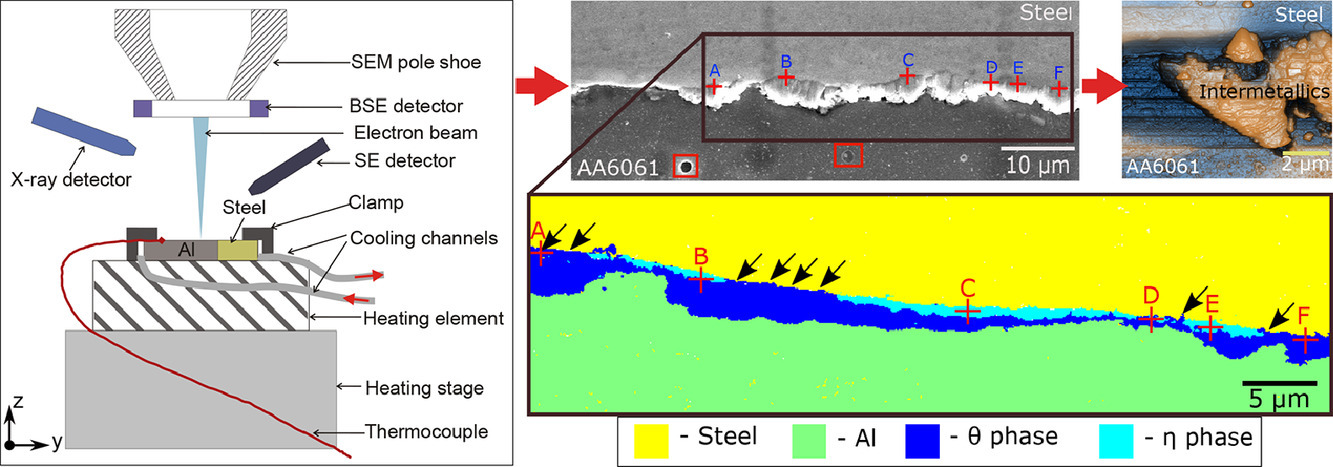
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113906
12. Microstructure and strengthening mechanisms of nanolamellar structures in ultrastrong drawn iron wires
超强拉拔铁丝中纳米层状结构的微观组织及强化机理
Hanchen Feng, Linfeng Wang, Shiyun Cui, Niels Hansen, Feng Fang✉, Xiaodan Zhang✉
Feng Fang: fangfeng@seu.edu.cn 东南大学
Xiaodan Zhang: xzha@mek.dtu.dk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113906
摘要
本工作制备了超强纯铁丝,当拉拔应变为10.35时强度为1.8 GPa。通过微观组织观察和量化的结构参数,分析了强化机理和强度-组织关系。当拉伸应变超过8.89时,由于界面结运动,<110>丝织构强度、界面间距和界面取向差趋于饱和。在不饱和拉拔应变为10.35时,铁素体胞/板条中的位错密度增加到~ 3.6 × 1015 m-2。基于系统的微观组织表征和定量分析,讨论了d-1或(2d)-0.5界面强化和森林硬化能。


