金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.207,1 Apr. 2021
2021-06-04 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文18篇,涵盖了铝合金、形状记忆合金、双相钢等,国内科研单位包山东大学、西安交通大学、中国科学院大学、上海大学、香港城市大学、上海交通大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 207 目录
1. Temperature-dependent cavity swelling in dual-ion irradiated Fe and Fe-Cr ferritic alloys
双离子辐照条件下铁素体Fe和Fe- Cr合金的肿胀性能随温度的变化
2. Combinatorial structural-analytical models for the prediction of the mechanical behaviour of isotropic porous pure metals
通过组合结构-分析模型预测各向同性多孔纯金属的力学行为
3. Effects of solid solution and grain-boundary segregation of Mo on hydrogen embrittlement in 32MnB5 hot-stamping steels
Mo的固溶和晶界偏聚对32MnB5热冲压钢氢脆性能的影响
4. Influence of Ni4Ti3 precipitation on martensitic transformations in NiTi shape memory alloy: R phase transformation
Ni4Ti3析出相对NiTi形状记忆合金中马氏体相变的影响
5. Effect of Si content on the uniaxial tensile behavior of Mo-Si solid solution alloys
Si含量对Mo-Si合金单轴拉伸性能的影响
6. Analysis and characterization of dynamic recrystallization and grain structure evolution in friction stir welding of aluminum plates
铝合金搅拌摩擦焊过程中动态再结晶以及组织演化的表征与分析研究
7. Solute cluster evolution during deformation and high strain hardening capability in naturally aged Al–Zn–Mg alloy
自然时效Al-Zn-Mg合金变形过程中溶质原子团簇的演化及其对应变硬化性能的影响
8. Significant disparity of non-basal dislocation activities in hot-rolled highly-textured Mg and Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy under tension
热轧强织构Mg和Mg- 3Al-1Zn合金在拉伸过程中非基位错活动差异的比较研究
9. Multiscale prediction of microstructure length scales in metallic alloy casting
金属合金铸件组织特征长度的多尺度预测
10. Significant reduction of phase-transition hysteresis for magnetocaloric (La1-xCex)2Fe11Si2Hy alloys by microstructural manipulation
通过组织调控显著降低磁热(La1-xCex)2Fe11Si2Hy合金的相变滞后
11. A combinatorial approach to study the phase constitution of the Ni-Al-Pt system
Ni-Al-Pt体系中组成相演化的高通量研究
12. Structural and chemical disorder enhance point defect diffusion and atomic transport in Ni3Al-based γ′ phase
结构和化学无序对Ni3Al基γ′相中点缺陷扩散和原子迁移的促进作用
13. Density-based grain boundary phase diagrams: Application to Fe-Mn-Cr, Fe-Mn-Ni, Fe-Mn-Co, Fe-Cr-Ni and Fe-Cr-Co alloy systems
以Fe-Mn-Cr、Fe-Mn-Ni、Fe-Mn-Co、Fe-Cr-Ni和Fe-Cr-Co等合金系为例阐述基于密度的晶界相图应用
14. Abnormal grain growth in a Zn-0.8Ag alloy after processing by high-pressure torsion
高压扭转Zn-0.8Ag合金中晶粒的异常长大研究
15. A semi-physical α-β model on bainite transformation kinetics and carbon partitioning
贝氏体相变动力学和碳配分的半物理α-β模型
16. Abnormal dynamic behavior and structural origin of Cu-Ag eutectic melt
Cu-Ag共晶熔体的异常动力学行为及其机理研究
17. Indentation size effect, geometrically necessary dislocations and pile-up effects in hardness testing of irradiated nickel
辐照后镍硬度测试中的压痕尺寸效应、几何必要位错和堆积效应研究
18. Outstanding cracking resistance of fibrous dual phase steels
纤维双相钢的抗裂性能研究
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116660
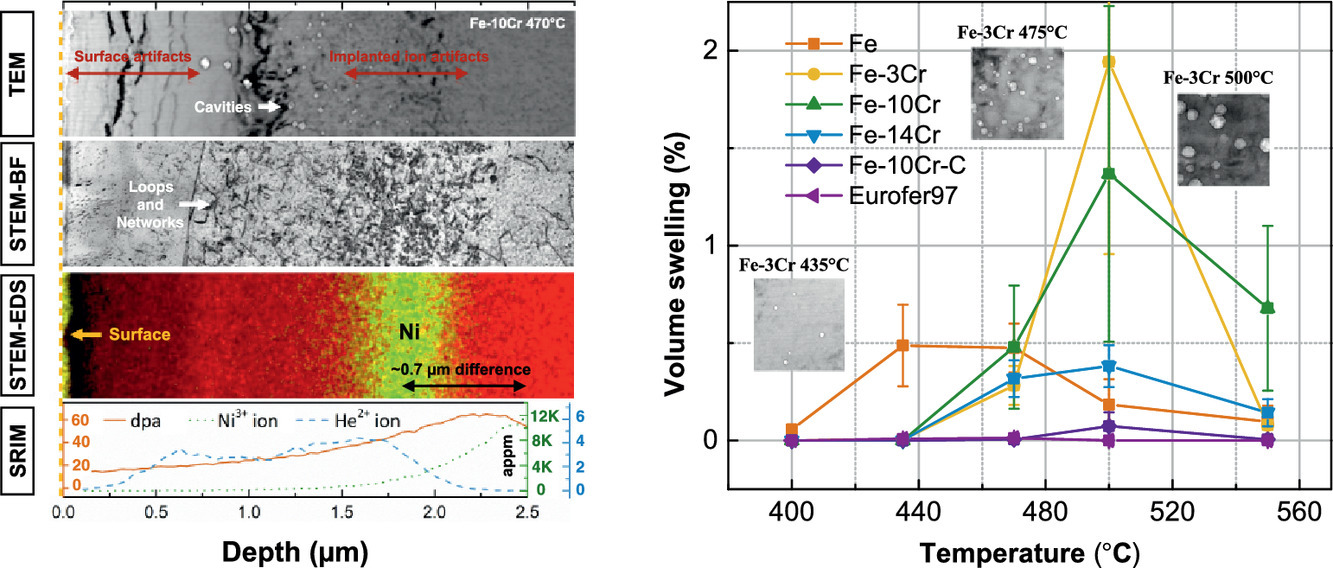
1. Temperature-dependent cavity swelling in dual-ion irradiated Fe and Fe-Cr ferritic alloys
双离子辐照条件下铁素体Fe和Fe- Cr合金的肿胀性能随温度的变化
Yan-Ru Lin✉, Arunodaya Bhattacharya✉, Da Chen✉, Ji-Jung Kai✉, Jean Henry✉, Steven J. Zinkle✉
Y.-R. Lin:ylin52@vols.utk.edu
A. Bhattacharya:bhattacharya@ornl.gov
D. Chen:dachen5-c@my.cityu.edu.hk
J.-J. Kai:jijkai@cityu.edu.hk
J. Henry:jean.henry@cea.fr
S.J. Zinkle:szinkle@utk.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116660
摘要
Fe-Cr铁素体-马氏体(FM)钢具有良好的力学性能和抗肿胀性能,是聚变和先进裂变反应堆的理想结构材料。但离子辐照条件下溶质元素和辐照温度对孔洞肿胀的影响与中子辐照条件下存在显著差异。本研究中,我们使用了双离子辐照(8 MeV Ni3+和3.5 MeV He2+)对高纯Fe、Fe-Cr合金(3-14 wt.% Cr)、Fe-10 wt.% Cr-780 wt.ppm C和Eurofer97 FM钢的肿胀行为进行了定量研究。辐照温度范围为400 ~ 550℃,辐照剂量~30dpa,He注入率为0.1 appm/dpa。通过透射电子显微镜表征,我们发现,由于纯Fe的空位迁移率更高,因此纯Fe的肿胀峰值温度比Fe- Cr合金低~50°C。Cr在470°C以下对Fe-Cr合金的溶胀有明显抑制作用,而在470°C以上对肿胀影响不大,甚至略有增强作用。我们在所有400-550°C辐照样品中都观察到了孔洞。这表明之前研究中所发现的预离子辐照Fe-Cr样品只能在较窄的温度范围内观察孔洞,可能只是因离子能量较低(< 5MeV)而造成的表象,显著的表面效应和粒子注入效应一定程度上抑制了中等深度的肿胀,特别是在高温条件下。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116664
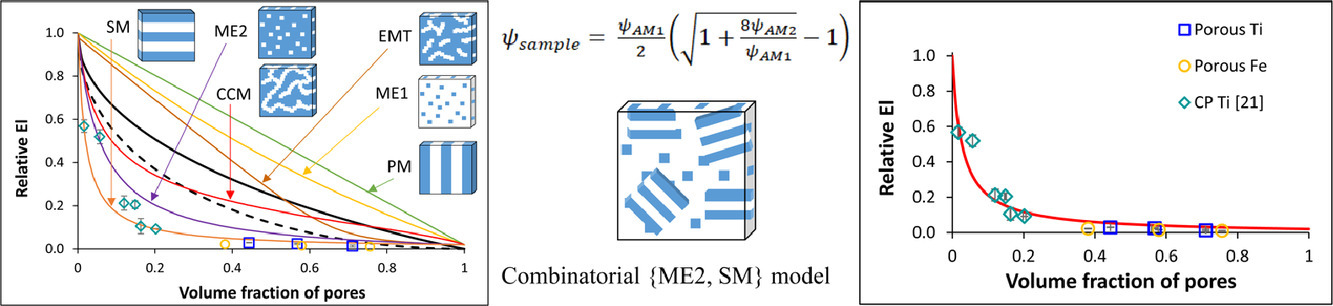
2. Combinatorial structural-analytical models for the prediction of the mechanical behaviour of isotropic porous pure metals
通过组合结构-分析模型预测各向同性多孔纯金属的力学行为
L. Bolzoni✉, J.K. Carson, F. Yang
L. Bolzoni:leandro@waikato.ac.nz
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116664
摘要
多孔金属(如金属泡沫)是先进的工程材料,模型预测可以帮助我们更好地对其进行性能优化。然而,对多孔金属力学性能的估计通常依赖于半经验模型,这使得模型仅适用于特定材料(即金属类型+内部结构类型+单一性能),并且需要确定经验常数。本研究对使用经验模型和结构分析模型预测各向同性多孔纯金属的力学行为提供了一些见解,并提出了两种新的结构-分析模型。在以往的所有结构-分析模型中,对称和互联骨架结构(SISS)模型能够在较宽的孔洞体积分数(0.4-1.0)范围内给出较好的预测结果,但往往会高估材料的断裂延伸率。在本研究中,我们对新的结构-分析模型进行了推导,该模型能够快速、准确地预测材料在整个孔隙体积分数范围内的杨氏模量、抗拉强度和断裂延伸率。模型具有物理基础,因此不需要花费大量的时间和计算成本,并且对微观组织不确定的材料预测也能达到可接受的精度。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116661
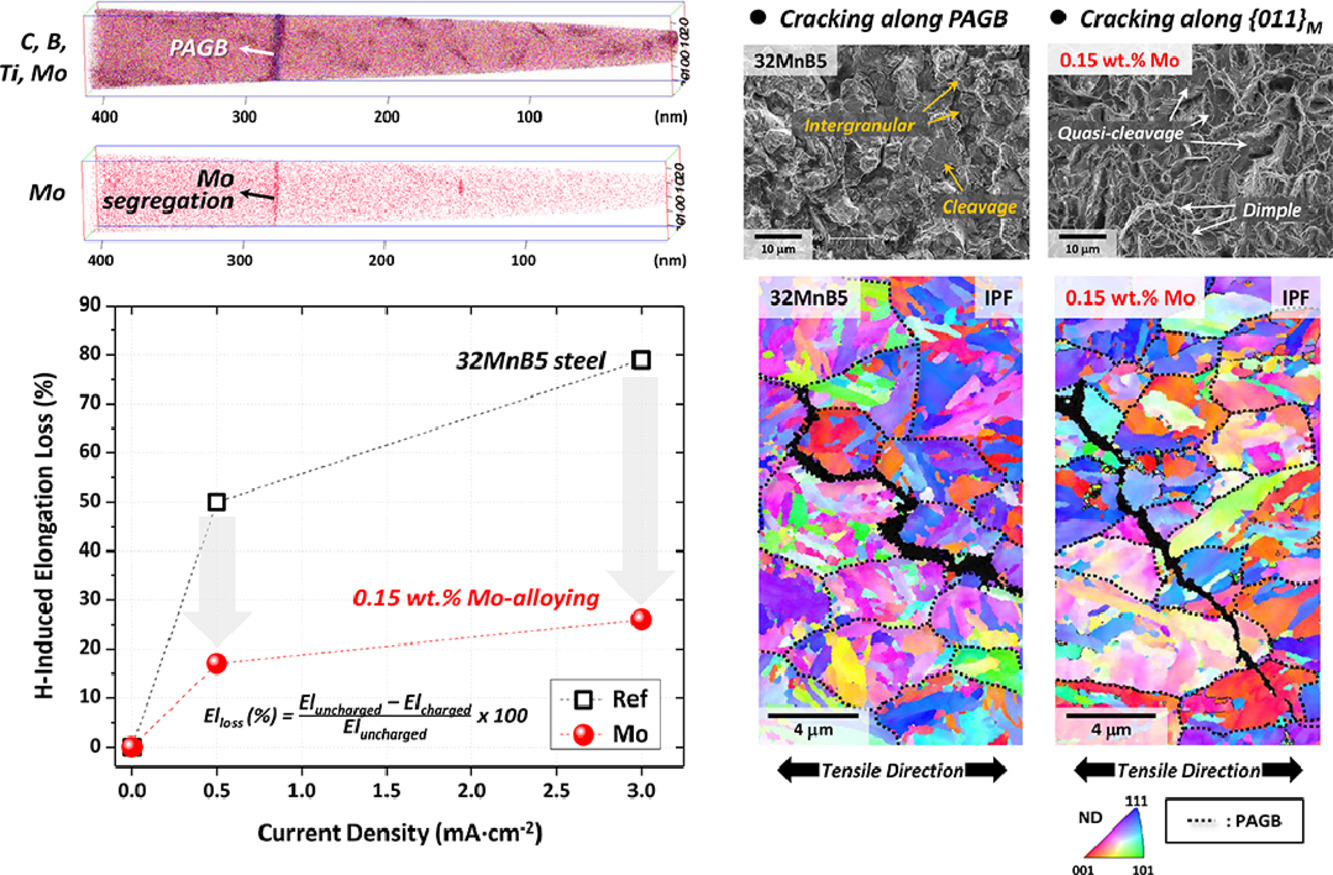
3. Effects of solid solution and grain-boundary segregation of Mo on hydrogen embrittlement in 32MnB5 hot-stamping steels
Mo的固溶和晶界偏聚对32MnB5热冲压钢氢脆性能的影响
Jisung Yoo, Min Chul Jo, Min Cheol Jo, Seongwoo Kim, Sang-Heon Kim, Jinkeun Oh, Seok Su Sohn✉, Sunghak Lee✉
S.S. Sohn:sssohn@korea.ac
S. Lee:shlee@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116661
摘要
氢脆已成为超高强度汽车钢中的一个重要问题。在商用32MnB5热冲压钢中添加Mo能够提高钢的强度,且延性损失较小。然而,关于Mo对32MnB5氢脆影响的研究却很少,且大多为Mo在Fe晶格中结合能的理论计算。本研究中,我们在32MnB5中添加了0.15 wt % Mo,并通过电化学充H实验对其氢脆性能进行了研究。充H后32MnB5的延性损失较大(50-79%),而Mo的添加显著降低了延性损失(17-26%),且材料具有足够的断后伸长率,表明了Mo的添加能够有效增强抗氢脆性能。这是由于Mo的原子尺寸较大,对H的亲和力更高,应变场更显著,从而降低了H的扩散系数。对裂纹扩展的直接观测表明, 裂纹路径发生了改变,从原奥晶界(PAGBs)变为了晶内滑移面。这是由于Mo溶质原子减少了PAGBs上的应变集中,且Mo的偏聚增强了晶界结合力。综上所述,钼的添加能够显著提高超高强钢的拉伸和抗氢脆性能。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116665
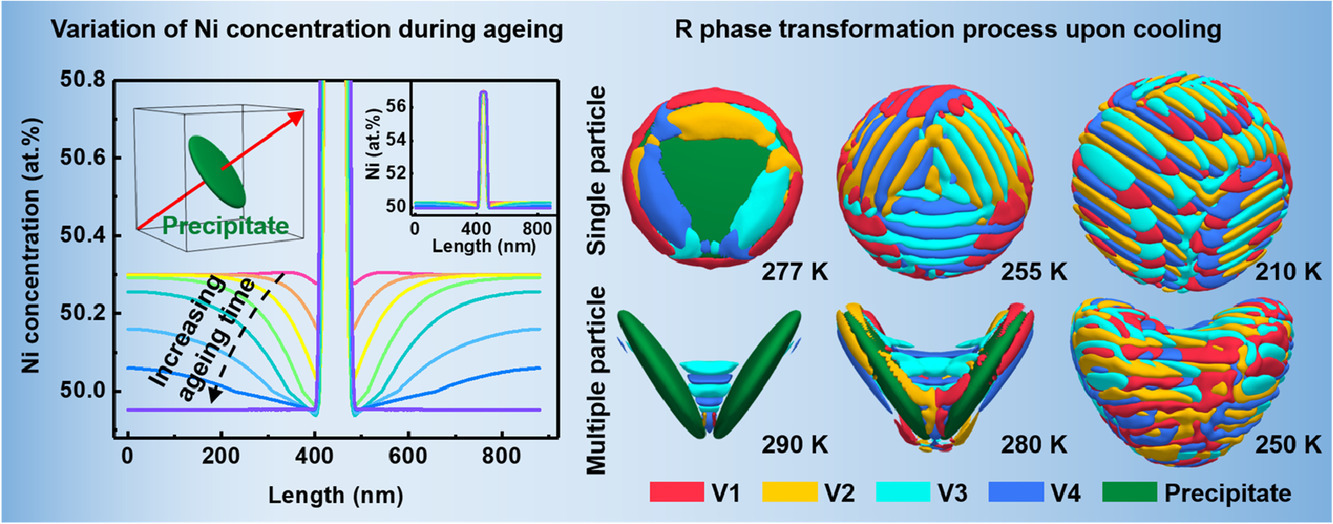
4. Influence of Ni4Ti3 precipitation on martensitic transformations in NiTi shape memory alloy: R phase transformation
Ni4Ti3析出相对NiTi形状记忆合金中马氏体相变的影响
Jiaming Zhu✉, Hong-Hui Wu, Yuan Wu, Haoliang Wang, Tianlong Zhang, Hu Xiao, Yunzhi Wang✉, San-Qiang Shi✉
J. Zhu:zhujiaming@sdu.edu.cn(山东大学/香港理工大学)
Y. Wang:wang.363@osu.edu
S.-Q. Shi:san.qiang.shi@polyu.edu.hk(香港理工大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116665
摘要
Ni4Ti3析出相能够有效调控NiTi形状记忆合金(SMAs)中的马氏体相变(MTs)。然而,关于Ni4Ti3对马氏体相变影响的几个基本问题目前仍不清楚。我们利用相场模拟,研究了 析出过程中的组织演变及其对B2→R马氏体相变的影响。其中,我们重点分析了B2基体中的Ni浓度梯度的作用以及组织中的应变场。结果表明,Ni4Ti3析出引起的B2基体中Ni浓度梯度显著改变了局部马氏体相变的起始温度和整体的马氏体相变行为,而应力场则通过变体选择影响马氏体结构。后者使得通过应力时效对析出相进行调控从而研发因瓦合金成为可能。以上研究结果加深了我们对含析出形状记忆合金中马氏体相变机理的理解,为进一步的组织和工艺设计提供了指导。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116654
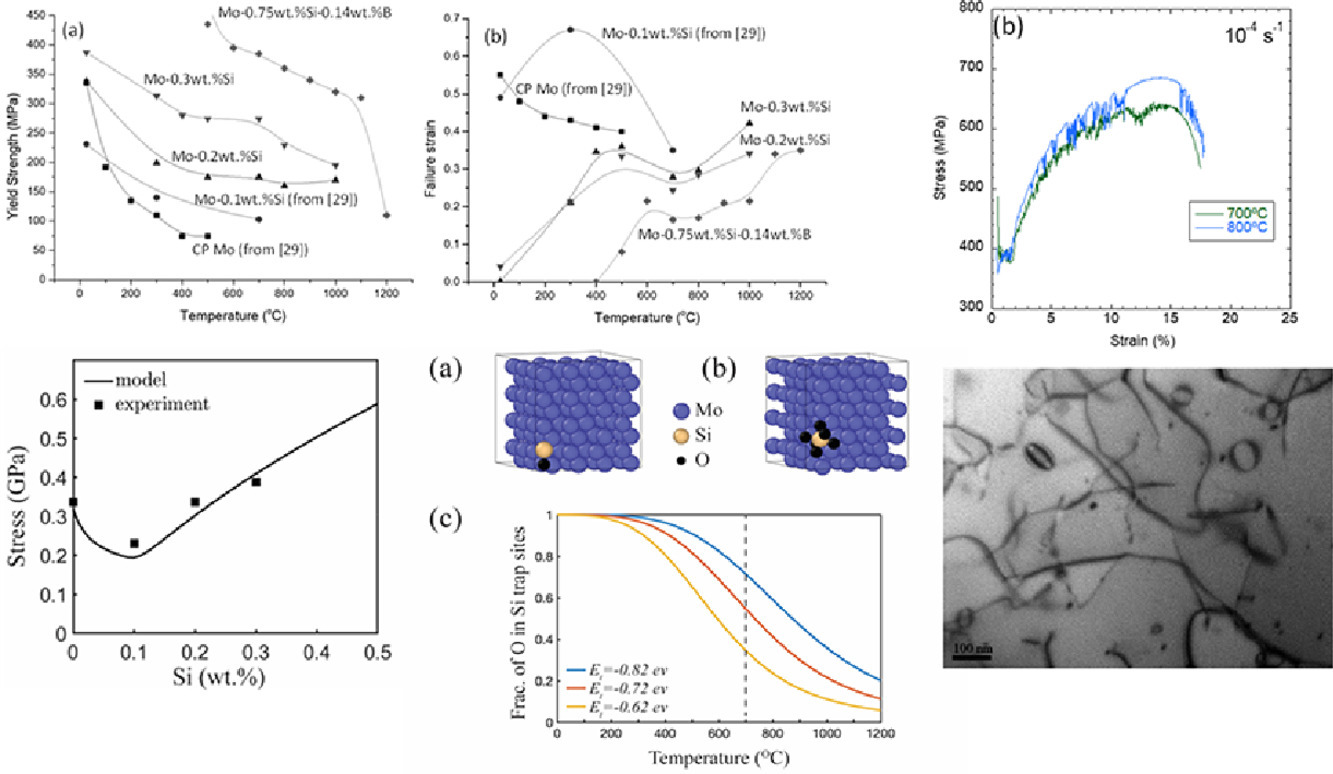
5. Effect of Si content on the uniaxial tensile behavior of Mo-Si solid solution alloys
Si含量对Mo-Si合金单轴拉伸性能的影响
Xiang Yu, Zhi Li, Padam Jain, Huajian Gao, Sharvan Kumar✉
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116654
摘要
我们对再结晶二元Mo-0.2Si、Mo-0.3Si和三元Mo-0.75Si-0.14B (wt%)合金在真空条件下的单轴拉伸性能随温度的变化进行了研究,并将结果与再结晶纯 Mo和二元Mo-0.1Si (wt%)合金进行了比较。研究表明,在除室温外的所有试验条件下,材料的屈服强度随Si含量的增加而增加。原子尺度模拟表明以上行为与Si的偏聚以及材料中的扭结形核。室温下,随着Si含量增加,合金的拉伸塑性迅速下降。Mo-0.3Si合金在300℃时的伸长率~10%,并在此后随温度升高迅速增加。材料在600℃~800℃温度范围内出现锯齿状流变,幅度随Si含量的增加而增大。模拟表明,固溶原子Si对O有捕获作用,随后在较高温度下将O释放出来,这可能是Mo-Si合金中锯齿状流变的起始温度高于纯Mo原因。锯齿状流变伴随着显著的加工硬化。对700℃以上断裂的试样的观测表明,位错缠结、偶极子和棱柱环的是引起加工硬化的主要原因。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116692
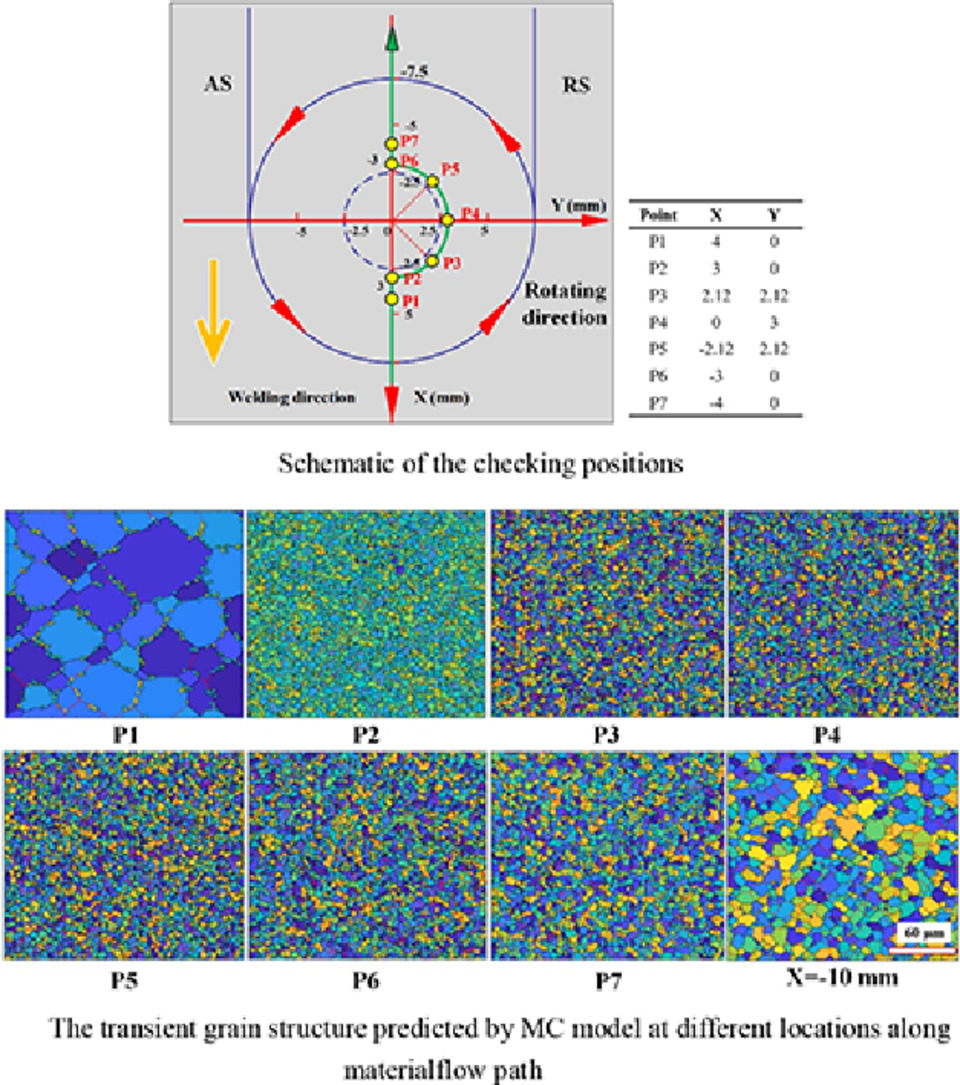
6. Analysis and characterization of dynamic recrystallization and grain structure evolution in friction stir welding of aluminum plates
铝合金搅拌摩擦焊过程中动态再结晶以及组织演化的表征与分析研究
Pengfei Yu, ChuanSong Wu✉, Lei Shi
C. Wu:wucs@sdu.edu.cn(山东大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116692
摘要
搅拌摩擦焊过程中的动态再结晶(DRX)和晶粒结构演变对焊接接头的最终组织和性能具有重要影响。本研究中,我们采用了蒙特卡罗方法建立了铝合金搅拌摩擦焊中动态再结晶的数值模拟模型。我们选择了适合蒙特卡洛方法的再结晶形核模型,并阐明了蒙特卡罗模拟步长与实际时间之间的关联。数值模拟成功预测了焊接过程中晶粒组织的瞬态演化和最终分布,计算得到的晶粒尺寸与实验结果吻合良好。我们将有限元模拟、蒙特卡罗模拟与背散电子衍射表征结果结合,分析了1060铝合金在搅拌摩擦焊过程中的动态再结晶机理。发现在摩擦焊过程中,在材料流动路径上不同区域的再结晶机制不同。工具的旋转速度决定了什么类型的再结晶更加容易发生。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116682
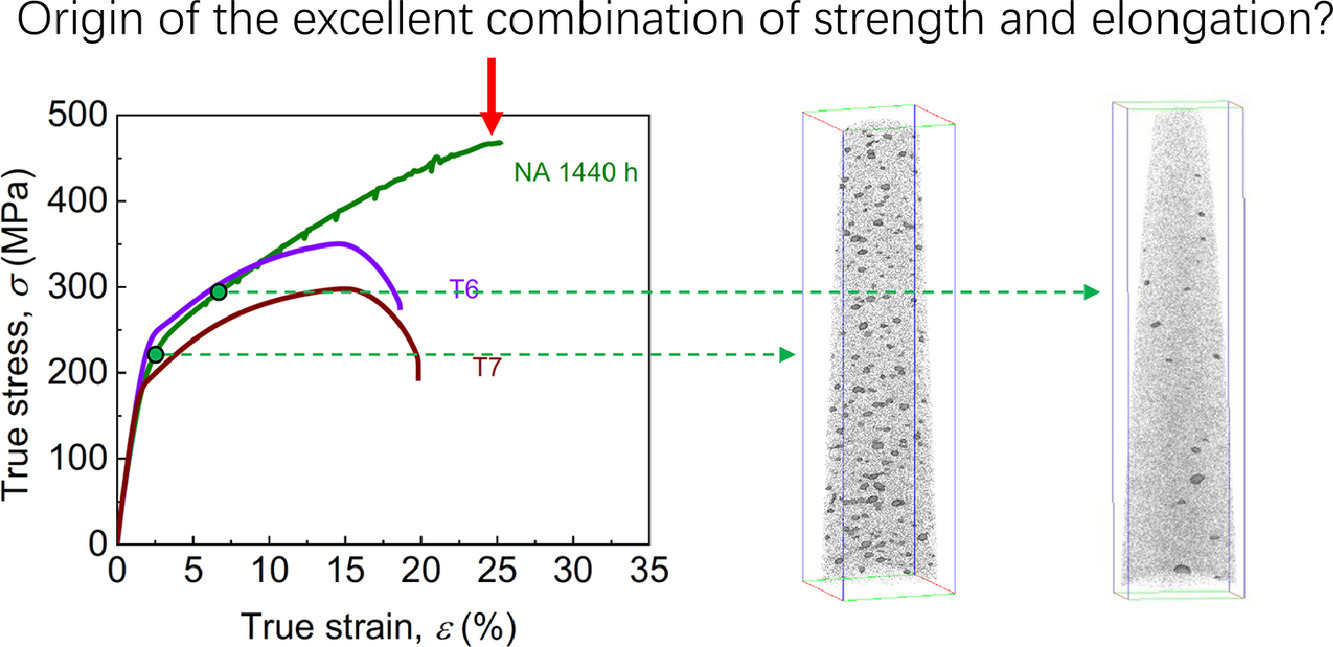
7. Solute cluster evolution during deformation and high strain hardening capability in naturally aged Al–Zn–Mg alloy
自然时效Al-Zn-Mg合金变形过程中溶质原子团簇的演化及其对应变硬化性能的影响
Peng Zhang, Kunkun Shi, Jianjun Bian, Jinyu Zhang, Yong Peng, Gang Liu✉, Alexis Deschamps✉, Jun Sun✉
G. Liu:lgsammer@mail.xjtu.edu.cn(西安交通大学)
A. Deschamps:alexis.deschamps@grenoble-inp.fr
J. Sun:Junsun@mail.xjtu.edu.cn(西安交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116682
摘要
我们对一种商业化Al-Zn-Mg合金的自然时效(NA)响应进行了跟踪,以研究溶质原子团簇对力学性能的影响。研究发现,由于应变硬化能力提高,自然时效过程中屈服强度的提高并不一定导致均匀延伸率降低。与含析出相的人工时效Al-Zn-Mg合金相比,具有高密度溶质原子团簇的Al-Zn-Mg合金的屈服强度、应变硬化能力和均匀拉伸性能更佳。我们通过同步辐射X射线和原子探针技术,系统研究了溶质原子团簇对应变硬化的积极影响。结果表明:位错的增殖主导了自然时效合金的整个变形过程直至失效;但溶质团簇对位错密度演化没有影响。另一方面,溶质团簇本身发生剧烈演化,在变形过程中先后发生溶解和粗化,相关动力学模型可以对此进行一定解释。实验证据表明位错的储存和应变诱导的溶质原子团簇演化不足以解释材料的高应变硬化速率,我们对其他可能机制的贡献进行了半定量估计。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116691
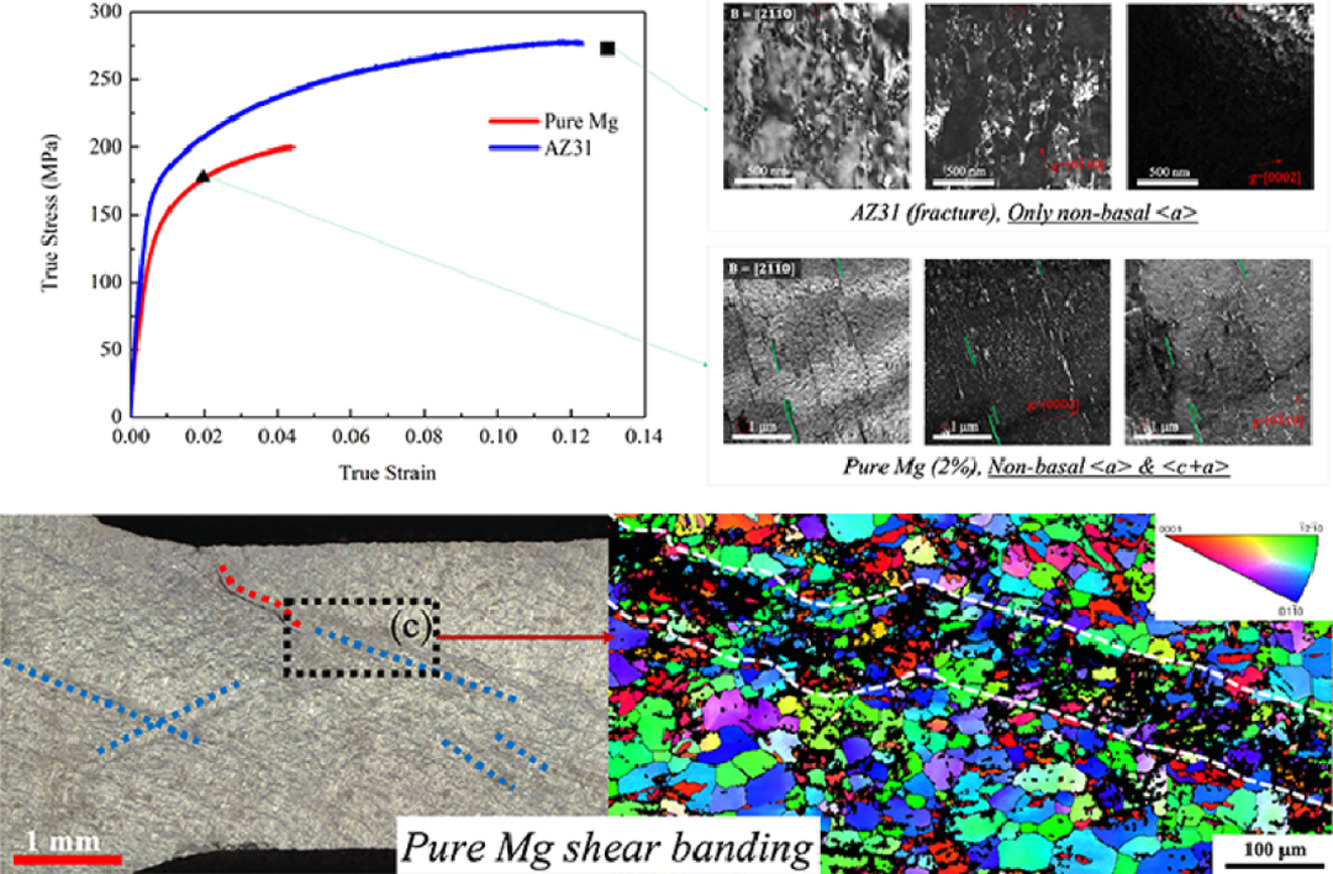
8. Significant disparity of non-basal dislocation activities in hot-rolled highly-textured Mg and Mg-3Al-1Zn alloy under tension
热轧强织构Mg和Mg- 3Al-1Zn合金在拉伸过程中非基位错活动差异的比较研究
Dexin Zhao, Xiaolong Ma, Abhinav Srivastava, Griffin Turner, Ibrahim Karaman, Kelvin Y. Xie✉
K.Y. Xie:kelvin_xie@tamu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116691
摘要
Mg- 3Al - 1Zn (AZ31)合金的拉伸性能明显优于纯Mg。而引起这种差异的位错相关机制却少有研究。本文中,我们对具有相似初始组织(即晶粒尺寸和织构)的强织构纯Mg和AZ31热轧样品沿轧制方向进行了拉伸。结果表明,只有纯Mg样品从变形初期就出现了明显的剪切带。裂纹容易沿剪切带扩展,因此纯Mg的延性较低。而变形后的AZ31试样中未发现明显的剪切带。我们利用透射电子显微镜从错演化的角度对变形机制进行了研究。系统的倾斜实验和不同应变下的多晶粒统计分析表明,纯Mg和AZ31的非基位错活动存在显著差异。在塑性变形早期,纯Mg中的<c + a>位错就被激活。而在AZ31中,所有应变条件下,甚至断裂样品中,都几乎观察不到<c + a>位错,而仅观察到非基<a>位错,包括棱柱位错和锥体位错。非基<a>位错的活跃和<c+a>位错的缺失使得AZ31能够发生持久硬化,因此与纯Mg相比,AZ31的延性显著提高,且不存在明显的剪切带。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116686
9. Multiscale prediction of microstructure length scales in metallic alloy casting
金属合金铸件组织特征长度的多尺度预测
B. Bellón, A.K. Boukellal, T. Isensee, O.M. Wellborn, K.P. Trumble, M.J.M. Krane, M.S. Titus c, D. Tourret a, J. LLorca✉
J. LLorca:javier.llorca@imdea.org, javier.llorca@upm.es
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116686
摘要
材料组织中的一些特征长度,如铸态合金中的枝晶间距,对材料构件的性能具有重要作用。因此,利用模拟对这类长度进行定量预测对通过集成计算材料工程(ICME)对合金进行设计和优化非常重要。目前,合金初生枝晶臂间距(PDAS)的实验和定量模拟主要局限于薄试样的定向凝固和稀合金的相场模拟。本研究中,我们将铸造实验和模拟结合,提出了一种新的多尺度建模方法,来预测合金在工业条件下凝固后的局部初生枝晶间距。为此,我们首先对含1 wt.%和4 wt.% Cu的Al-Cu合金的初生枝晶间距进行了实验测量,并将其与相场(PF)和枝晶针状网络(DNN)模型的模拟结果进行了比较。我们发现,在DNN模拟中引入相场计算得到的枝晶尖端选择常数后,PF和DNN模型对于Al-1 wt.%Cu合金的模拟结果非常类似。由于非稀合金中尖端半径和扩散距离之间的尺度差异较大,使得相场模型的计算量大幅增加,因此相场模型无法实现对Al-4 wt.%Cu合金的定量预测。然而,非稀Al-Cu合金的DNN模拟结果大致与我们的实验以及文献主流观测结果一致。模拟表明,随着温度梯度的降低,合金初生枝晶臂间距的稳定范围会随着组织从胞状枝晶向高度发达的次级枝晶转变而扩大。
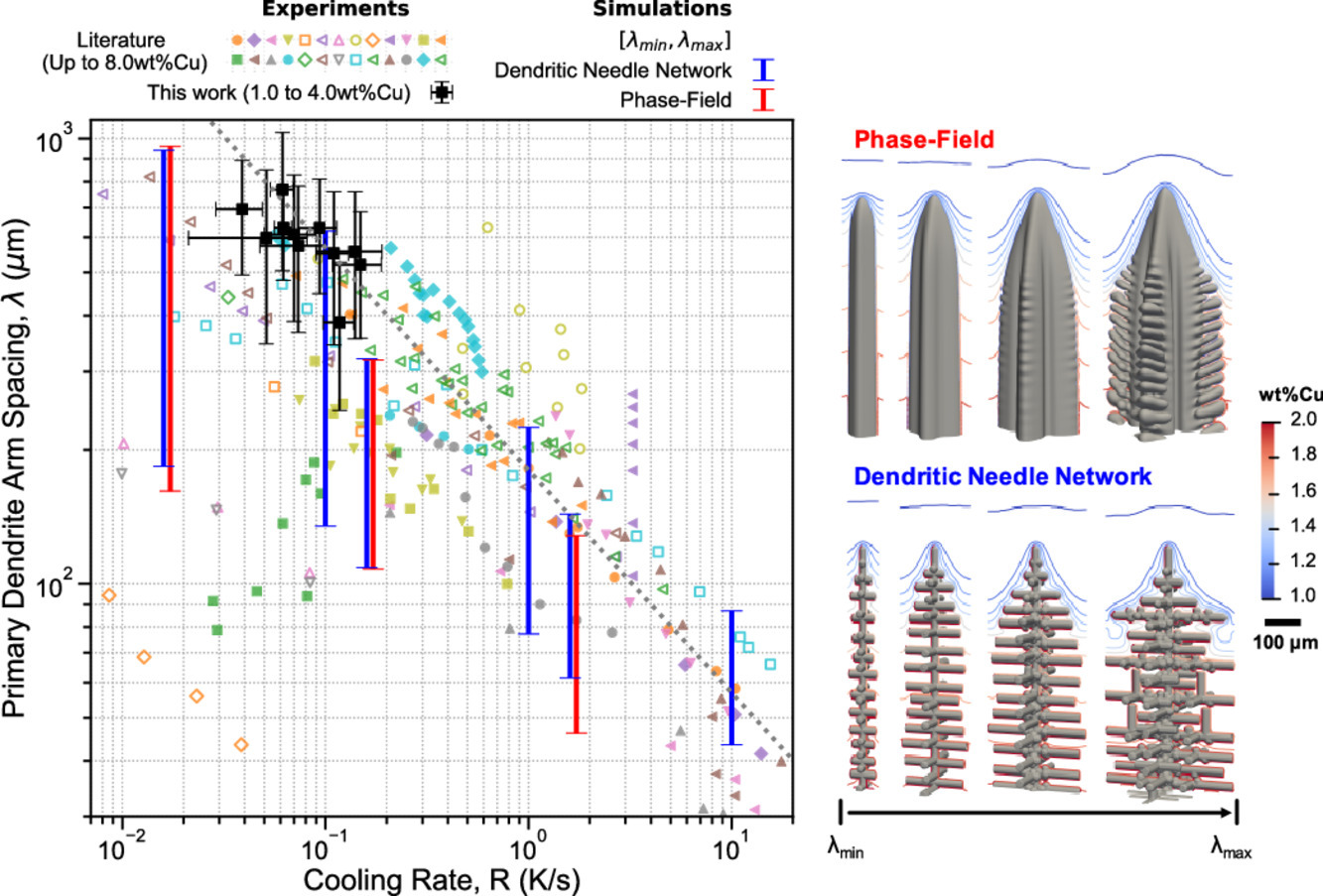
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116687
10. Significant reduction of phase-transition hysteresis for magnetocaloric (La1-xCex)2Fe11Si2Hy alloys by microstructural manipulation
通过组织调控显著降低磁热(La1-xCex)2Fe11Si2Hy合金的相变滞后
Yanfeng Liu, Xiaoqian Fu, Qian Yu, Mingxiao Zhang, Jian Liu✉
J. Liu:liujian@nimte.ac.cn(中国科学院大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116687
摘要
一级磁性相变不可避免地伴随着较大的滞后效应,这一现象引起的能量损耗是巨磁热效应(MCE)材料在磁冷却技术应用中面临的主要挑战。本研究中,我们提出了一种新方法来减少La-Fe-Si基MCE合金的磁滞,同时通过调控其微观结构保持材料的巨熵变化。我们采用大角度环形暗场扫描透射电子显微镜、三维原子探针和几何相分析等手段对材料的微观结构演变进行了系统研究。我们在Ce和H原子共掺杂的LaFe13-xSix体系中观察到了5 - 50nm纳米晶,且其组成与主流报导完全不同。这种组织细化可能是由于氢原子分布不均匀引起的内应力释放所致。随着纳米晶的形成,(La1-xCex)2Fe11Si2Hy的磁滞损耗从48.3单调降至0.6 J kg−1。更重要的是,(La1-xCex)2Fe11Si2Hy的磁性转变仍为明显的一级相变,使其在1.3 T、105次磁循环的绝热条件下温度变化可达2.03 K,可逆制冷量达89.4 J kg−1。
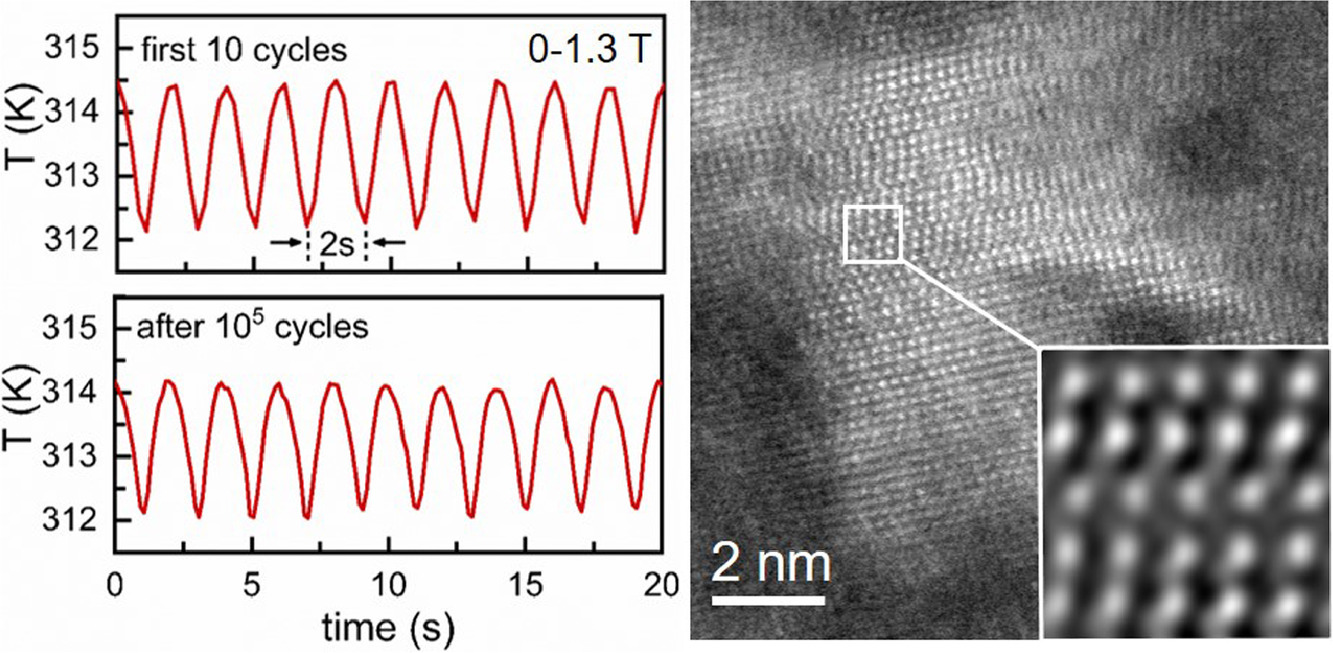
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116703
11. A combinatorial approach to study the phase constitution of the Ni-Al-Pt system
Ni-Al-Pt体系中组成相演化的高通量研究
G.H. Cao✉, Z. Zhang, X. Li✉, W. Skrotzki, E. Müller, R. Schneider, D. Gerthsen
G.H. Cao:ghcao@shu.edu.cn(上海大学)
X. Li:lx_net@sina.com(上海大学/上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116703
摘要
铂对提高热障涂层表面氧化铝的附着能力,抑制α -氧化铝长大具有有益作用。然而,在使用过程中,由于涂层与镍基高温合金基体之间的扩散,会导致Ni、Al和Pt之间形成复杂相。采用高通量方法研究具有珍贵成分的合金相平衡是一种高效且节约成本的方法。我们通过透射电镜和电子探针对1100℃退火96 h后水淬的Ni-Al-Pt三元扩散偶的微观组织演变进行了表明。结果表明,由于Ni的溶解,高温下Pt3Al(h)相十分稳定,因此Ni是Pt3Al(h)的稳定剂。我们在(Ni,Pt)3Al附近观察到了三元 L12结构Ni2PtAl相的存在,此外,我们也观察到了L10结构的四方方NiPt2Al相。冷却过程中,富镍的β-(Ni,Pt)Al相发生了β'马氏体相变,转变为L10结构。我们发现在β′-(Ni,Pt)Al马氏体会形成结构的斜方(Ni,Pt)5Al3相,晶格常数a=0.747 nm, b=0.682 nm, c=0.376 nm。
与β′相的取向关系为(100)[010]
// (100)[001] β′。我们在(Ni,Pt)5Al3片层中观察到了(221)孪晶,并对β′-(Ni,Pt)Al中形成(Ni,Pt)5Al3的机理进行了分析。
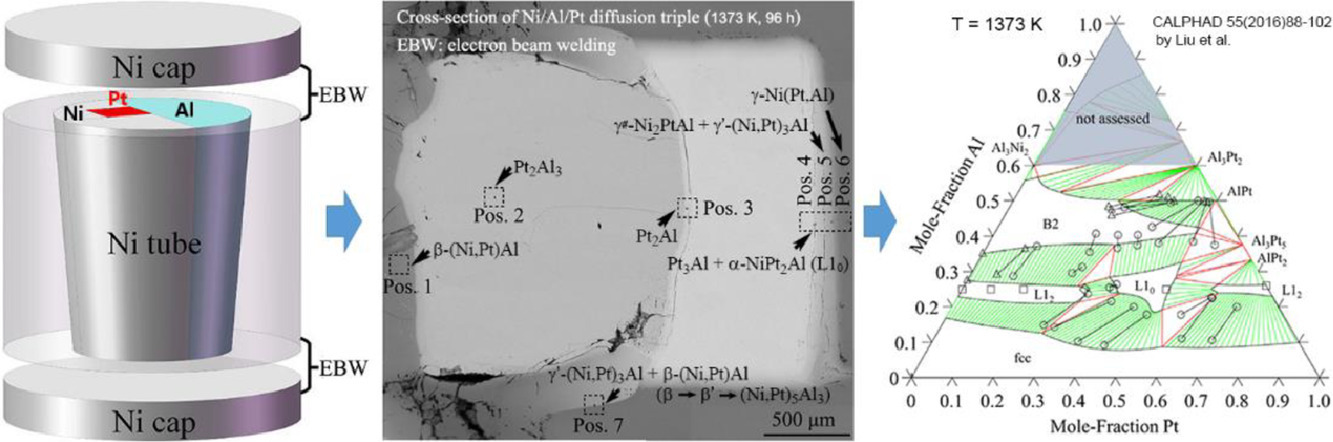
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116704
12. Structural and chemical disorder enhance point defect diffusion and atomic transport in Ni3Al-based γ′ phase
结构和化学无序对Ni3Al基γ′相中点缺陷扩散和原子迁移的促进作用
Shijun Zhao✉, Yuri Osetsky✉
S. Zhao:shijzhao@cityu.edu.hk(香港城市大学)
Y. Osetsky:osetskiyyn@ornl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116704
摘要
有序L12 γ ' Ni3Al金属间化合物是镍基高温合金和高熵合金中常见的强化相。根据合金基体元素的不同,γ′相的成分通常会有一定的变化。本文研究了具有化学无序和结构无序特征的NiCo3Al γ′相中的元素配分及其对原子迁移性质的影响。通过将蒙特卡罗方法和分子静态技术结合,我们首次确定了这种组成复杂的γ′相中的元素分布。结果表明,Co原子有偏聚的趋势,这会对材料的能量和扩散性质产生重要影响。通过分子动力学模拟热激活原子的扩散,我们发现,与严格遵循化学计量比的γ ' Ni3Al相比,Co引起的化学无序可以促进空位扩散,从而显著抑制间隙原子迁移。进一步研究表明,以上现象与体系中的缺陷能量密切相关。我们的研究较好地阐明了无序、长程有序和短程有序对多组分金属间化合物扩散性能的影响,对于理解其稳定性,从而在退火、辐照等条件下进行γ′强化设计具有重要意义。
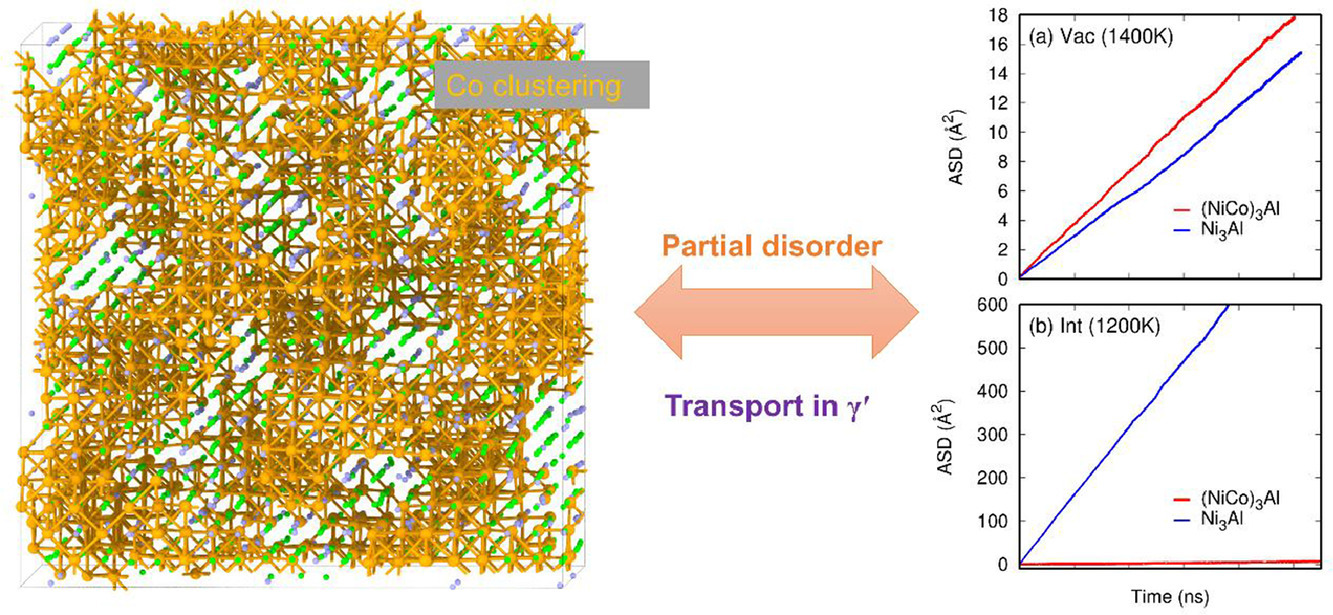
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116668
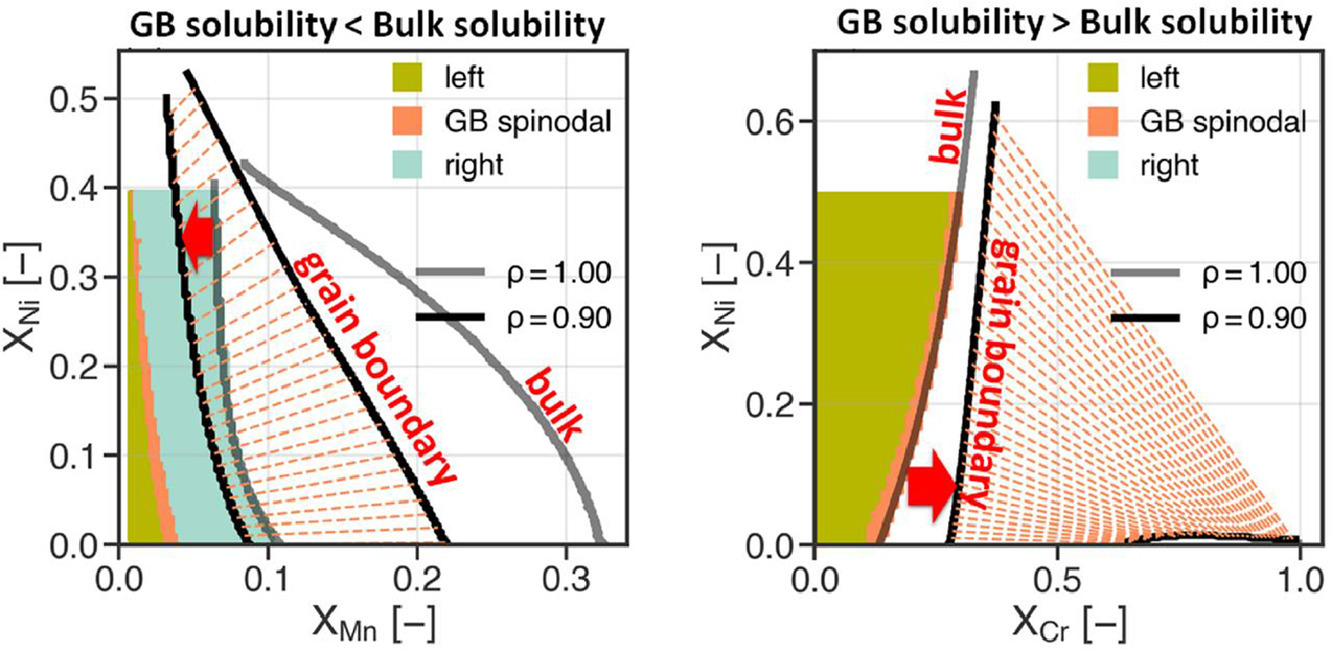
13. Density-based grain boundary phase diagrams: Application to Fe-Mn-Cr, Fe-Mn-Ni, Fe-Mn-Co, Fe-Cr-Ni and Fe-Cr-Co alloy systems
以Fe-Mn-Cr、Fe-Mn-Ni、Fe-Mn-Co、Fe-Cr-Ni和Fe-Cr-Co等合金系为例阐述基于密度的晶界相图应用
Lei Wang, Reza Darvishi Kamachali✉
R. Darvishi Kamachali:reza.kamachali@bam.de, reza.kamachali@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116668
摘要
相图是材料设计的基础。与体相类似,晶界也可以具有不同的相,但它们的相图在很大程度上仍是未知的。在本研究中,我们设计了一种策略,基于密度模型和体相的热力学数据(CALPHAD),计算多组分材料的晶界相图。我们以Fe-Mn-Cr、Fe-Mn-Ni、Fe-Mn-Co、Fe-Cr-Ni和Fe-Cr-Co体系为研究对象,因为它们是许多钢铁材料和高熵合金的最主要的三元基体。通过对Fe-Mn-X合金的研究我们发现,尽管晶界存在溶质元素偏聚,但晶界处的合金元素溶解度极限低于相应的体相,这将促使界面发生化学分解。出现这种反直觉特征的原因主要有两点,分别是磁性有序效应和Mn溶质元素的低结合能。我们对三元合金这种界面相的稳定性和晶界处的元素共偏聚也进行了研究。结果表明,溶质浓度梯度的能量贡献减弱了偏聚,但增加了晶界溶解度极限,从而抑制了化学分解,稳定了晶界。晶界相图的研究为系统研究界面相演化提供了指导,对晶界处的缺陷调控具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116667
14. Abnormal grain growth in a Zn-0.8Ag alloy after processing by high-pressure torsion
高压扭转Zn-0.8Ag合金中晶粒的异常长大研究
Wiktor Bednarczyk✉, Jakub Kawałko, Bogdan Rutkowski, Maria W ˛atroba, Nong Gao, Marco J. Starink, Piotr Bała, Terence G. Langdon
W. Bednarczyk:bednarczyk@agh.edu.pl
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116667
摘要
我们采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、背散电子衍射(EBSD)、高分辨透射电子显微镜(HR-TEM)和显微硬度等测试手段,对高压扭转(HPT)方法制备的Zn-0.8Ag (wt%)合金中的晶粒异常长大(AGG)进行了系统研究。经HPT变形的合金在不进行任何额外热处理的情况下,在室温下表现出晶粒异常长大。EBSD分析表明,初始(0001)线织构的{11-20}< 0001 >方向发生晶粒定向形核,这一现象符合最大能量释放模型。新晶粒的取向沿最小杨氏模量方向(c轴),平行于剪切方向。应变诱导的纳米Zn3Ag析出相溶解是该合金中晶粒异常长大的主要驱动力。异常长大发生和结束所需的应变分别为~4.0和~5.0。由于固溶强化的作用,使得材料的硬度从中心细晶的~47 HK增加到粗晶区的~84 HK。对Hall-Petch公式的相关分析表明,晶粒细化的强化作用在晶粒尺寸23µm以下发生减弱。以上研究首次对室温下经强烈塑性变形后,金属中的晶粒异常长大进行了全面描述。

ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116701
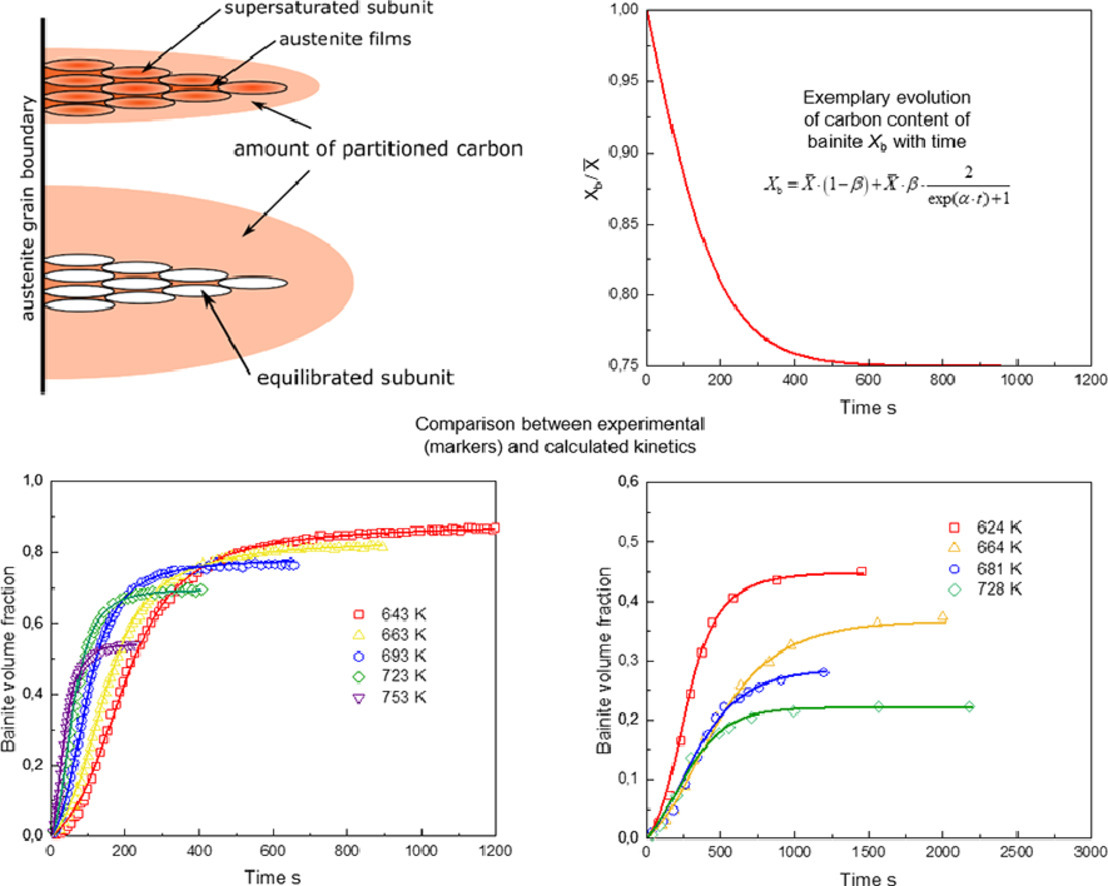
15. A semi-physical α-β model on bainite transformation kinetics and carbon partitioning
贝氏体相变动力学和碳配分的半物理α-β模型
Wenwen Wei✉, Philipp Retzl, Ernst Kozeschnik, Erwin Povoden-Karadeniz✉
W. Wei: wen.wei@tuwien.ac.at, johnsonwenz24@gmail.com
Erwin Povoden-Karadeniz:erwin.povoden-karadeniz@tuwien.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116701
摘要
我们提出了一个含有双可调参数的半物理模型,用于预测钢中等温贝氏体相变和碳的二次配分。模型采用费米-狄拉克统计函数,结合贝氏体碳浓度的演化方程,成功实现了对贝氏体中碳含量演化和残余奥氏体中碳富集的唯像描述。其中α参数反映了碳原子从贝氏体束扩散至邻近大体积奥氏体中的概率,而β参数描述了贝氏体对大体积奥氏体中碳富集的潜在贡献。我们从碳扩散和碳捕获的角度,对α参数对贝氏体相变动力学的影响进行了解释,结果表明,这种影响具有显著的温度依赖性。模型通过调整α和β参数,能够实现对一系列不同钢种中贝氏体相变动力学的模拟。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116705
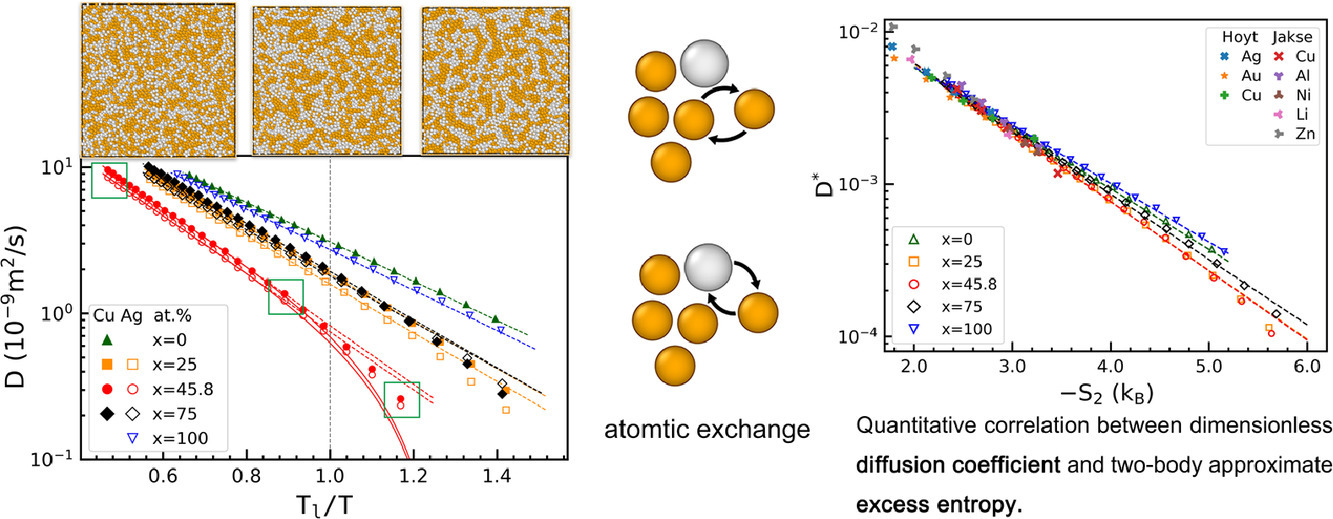
16. Abnormal dynamic behavior and structural origin of Cu-Ag eutectic melt
Cu-Ag共晶熔体的异常动力学行为及其机理研究
B.Q. Wu, L.T. Kong, J.F. Li✉
J.F. Li:jfli@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116705
摘要
我们采用分子动力学模拟研究了Cu(100-x)Agx (x = 0,25, 45.8, 75, 100)熔体的动力学特性和微观结构。在除纯铜和纯银外的其他熔体中,我们都发现了阿仑尼乌斯-非阿仑尼乌斯转变和Stokes-Einstein关系失效。Cu75Ag25和Cu25Ag75熔体的临界温度Tc低于液相线温度,与之不同的是,Cu54.2Ag45.8共晶熔体的Tc高于共晶温度约115 K。在临界温度附近,我们观察到了溶体动态非均匀性的突然增加和Stokes-Einstein关系的时效。化学短程有序和局部拓扑结构分析表明,慢粒子数量的快速增加、局部原子结构差异的急剧变化以及由此引起的扩散机制转变是引起该异常动力学行为的原因。同种原子在较低的温度下更容易聚集成团簇。Ag原子的迁移能力不随其在Ag团簇中的位置而变化;而由于Cu原子团簇的有序程度较高,因此团簇中心的Cu原子迁移速度较慢。基于扩展标度定律,我们粗略揭示了Cu-Ag熔体的无量纲动态性质D*与过量熵S2之间的经验关系。以上研究对于深入了解共晶熔体的动力学具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116702
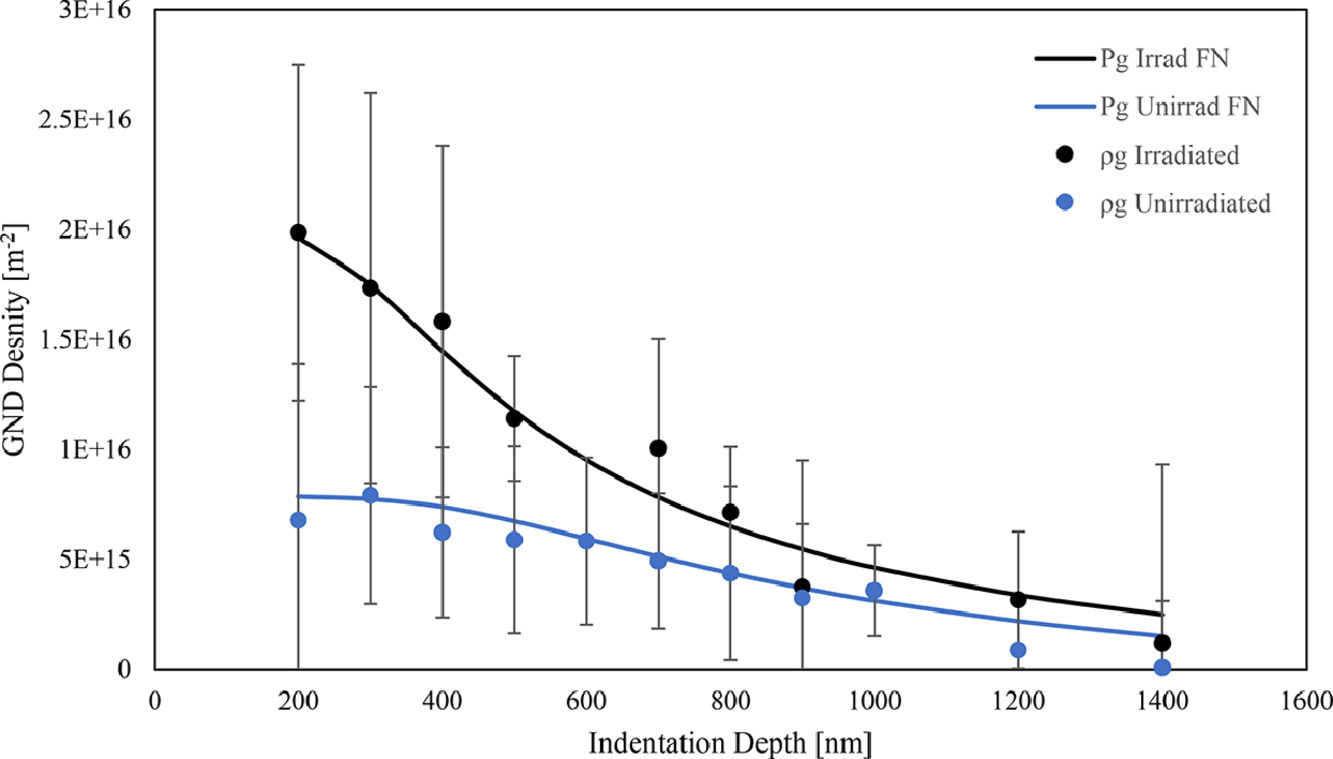
17. Indentation size effect, geometrically necessary dislocations and pile-up effects in hardness testing of irradiated nickel
辐照后镍硬度测试中的压痕尺寸效应、几何必要位错和堆积效应研究
M.A. Mattucci, I. Cherubin, P. Changizian, T. Skippon, M.R. Daymond✉
M.R. Daymond:daymond@queensu.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116702
摘要
我们通过对比实验,从位错密度的角度,研究了经120°C质子辐照(粒子能量6MeV,辐照剂量0.1dpa)后的商业纯Ni的压痕尺寸效应。我们对样品进行了辐照缺陷TEM表征和微纳压痕试验,采用Nix-Gao (NG)模型计算了辐照缺陷引起的屈服强度增加,结果与考虑了层错和位错环的Bacon-Kocks-Scattergood (BKS)模型吻合良好。我们同时在辐照和未辐照材料的NG模型中观察到了双线性趋势,这表明在纳米尺度下,压痕变形机制发生了转变。而如果考虑和测量了压痕堆积的影响,则这种趋势就大幅减小。因此,在这种材料中,当测量深度低于500nm时,我们必须对解释辐照缺陷引起的硬度增加格外小心。应变梯度塑性模型和SEM/EBSD分析表明,与未辐照材料相比,辐照材料的压痕变形组织中的几何必要位错(GND)密度更高。有研究者认为,Frank位错环能够阻碍位错运动,引起压头尖端变形集中,从而抑制塑性变形。这导致当我们使用纳米压痕量对材料硬度进行测量时,辐照和未辐照样品间的差异比块体硬度测试中的更大。通过考虑压痕堆积,可以对辐照材料纳米压痕中几何必要位错密度的增加进行解释。
ACTA
Vol. 207,1 Apr. 2021, 116700
18. Outstanding cracking resistance of fibrous dual phase steels
纤维双相钢的抗裂性能研究
Karim Ismail, Astrid Perlade, Pascal J. Jacques, Thomas Pardoen✉
T. Pardoen:thomas.pardoen@uclouvain.be
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116700
摘要
双相(DP)钢因其优异的强度-韧性-成本组合而受到广泛应用。然而,双相钢的抗裂纹扩展性能限制了其一部分需要复杂成形的结构应用。研究表明,与等轴晶组织相比,具有“托马斯-纤维”型血小板形貌马氏体的DP钢具有更加优异的抗裂纹扩展性能,且马氏体体积分数和厚度各异的薄、厚试样均能表现出这种优异性能。我们通过断口形貌和组织表征,结合裂纹尖端颈缩和断裂功的计算对薄板的断裂进行了分析,发现变形过程中片晶的排列和其较小的尺寸能够显著抑制裂纹的形核。以上研究结果为在不改变DP钢强度和化学成分的条件下优化DP钢的断裂韧性提供了一条新的途径。


