金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.200, 15 July. 2021(下)
2021-06-06 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文11篇,涵盖了高熵合金、奥氏体钢、高温合金等,国内科研单位包括上海交通大学、吉林大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 200 目录
1. Mn-stabilized austenitic steel strengthened by nano-scale β-NiAl (B2), FCC-Cu, and carbides via ICME design
通过ICME设计,采用纳米尺度β-NiAl(B2),FCC-Cu和碳化物强化Mn稳定的奥氏体钢
2. A binary beta titanium superalloy containing ordered-beta TiFe, alpha and omega
一种包含有序β-TiFe,α和ω的二元β钛高温合金
3. Origin of high tension-compression yield asymmetry in as-extruded pure zinc
挤压态纯锌高拉伸-压缩屈服不对称性的成因
4. Novel eutectoid Ti-5Ni alloy fabricated via direct energy deposition
采用直接能量沉积制备新型共晶Ti-5Ni合金
5. Hardening induced by dislocation core spreading at disordered interface in Cu/Nb multilayers
Cu/Nb多层膜中无序界面处位错核扩展引起的硬化
6. On temperature and strain-rate dependence of flow serration in HfNbTaTiZr high-entropy alloy
HfNbTaTiZr高熵合金流动锯齿的温度和应变速率依赖性研究
7. The {10-12} non-cozone twin-twin interactions in Mg: A stability and mobility study using 3-D atomistic simulations
Mg中{10-12}非同域孪生相互作用:使用三维原子模拟的稳定性和迁移率研究
8. Yielding behavior of a single-crystalline γ'-strengthened Co-Ti-Cr superalloy
单晶γ'强化Co-Ti-Cr高温合金的屈服行为
9. New Ms-formula for exact microstructural prediction of modern 3rd generation AHSS chemistries
新的Ms公式可精确预测不同化学成分的第三代AHSS的微观组织
10. Plastic deformation of solid-solution strengthened Hf-Nb-Ta-Ti-Zr body-centered cubic medium/high-entropy alloys
固溶强化Hf-Nb-Ta-Ti-Zr体心立方中/高熵合金的塑性变形
11. Pre-strain mediated fast natural aging in a dilute Mg-Zn-Ca-Sn-Mn alloy
预应变介导的Mg-Zn-Ca-Sn-Mn稀释合金的快速自然时效
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113903
1. Mn-stabilized austenitic steel strengthened by nano-scale β-NiAl (B2), FCC-Cu, and carbides via ICME design
通过ICME设计,采用纳米尺度β-NiAl(B2),FCC-Cu和碳化物强化Mn稳定的奥氏体钢
Colin A. Stewart✉, Richard W. Fonda, Keith E. Knipling
Colin A. Stewart: colin.stewart.ctr@nrl.navy.mil
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113903
摘要
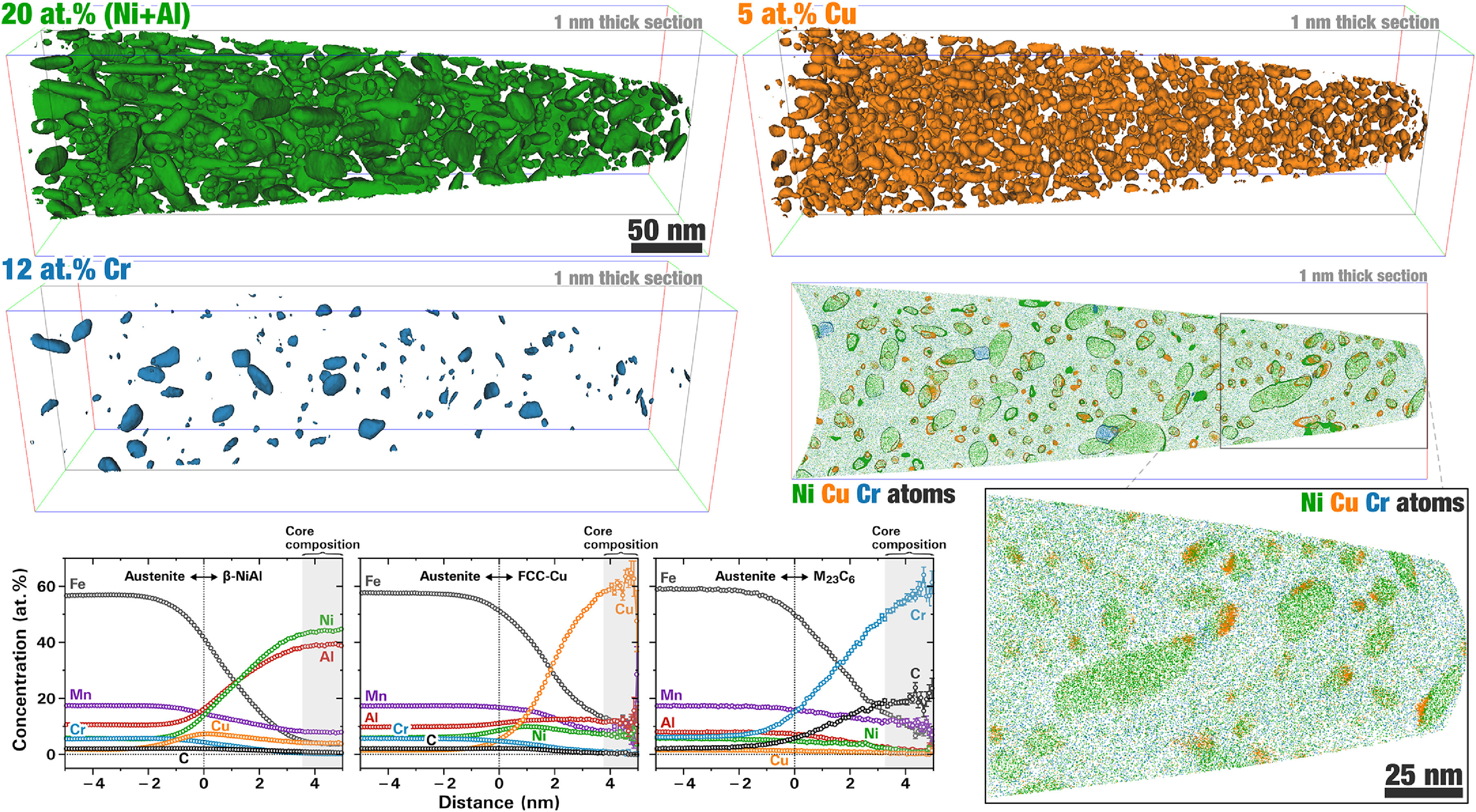
采用集成计算材料工程(ICME)的方法设计了由β-NiAl、FCC-Cu和M23C6碳化物这三种纳米尺度析出相强化的Mn稳定全奥氏体钢。采用Thermal-Calc预测了Ni、Al和Cu对Fe-17.7Mn-4.7Cr-0.48C (wt.%)基奥氏体成分相稳定性的影响。通过实验(1)合成Cu、Ni+Al或Cu+Ni+Al改性的奥氏体基合金,(2)通过微压痕测量力学性能,(3)通过原子探针断层扫描(APT)表征纳米尺度的微观结构,验证了上述预测。根据Thermal-Calc模型,在580℃时效后,Cu或Ni+Al改性的样品只有轻微的硬化。Cu+Ni+Al复合合金展现出强烈的硬化效果(强度为490 HV,σy≈1200 MPa),这主要归因于FCC-Cu和β-NiAl纳米相的形成。
SCRIPTA
Vol.200, 15 July. 2021, 113905
2. A binary beta titanium superalloy containing ordered-beta TiFe, alpha and omega
一种包含有序β-TiFe,α和ω的二元β钛高温合金
R. D. Jones✉, A.J. Knowles, W.J. Clegg
R. D. Jones: robert.jones48@ntlworld.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113905
摘要
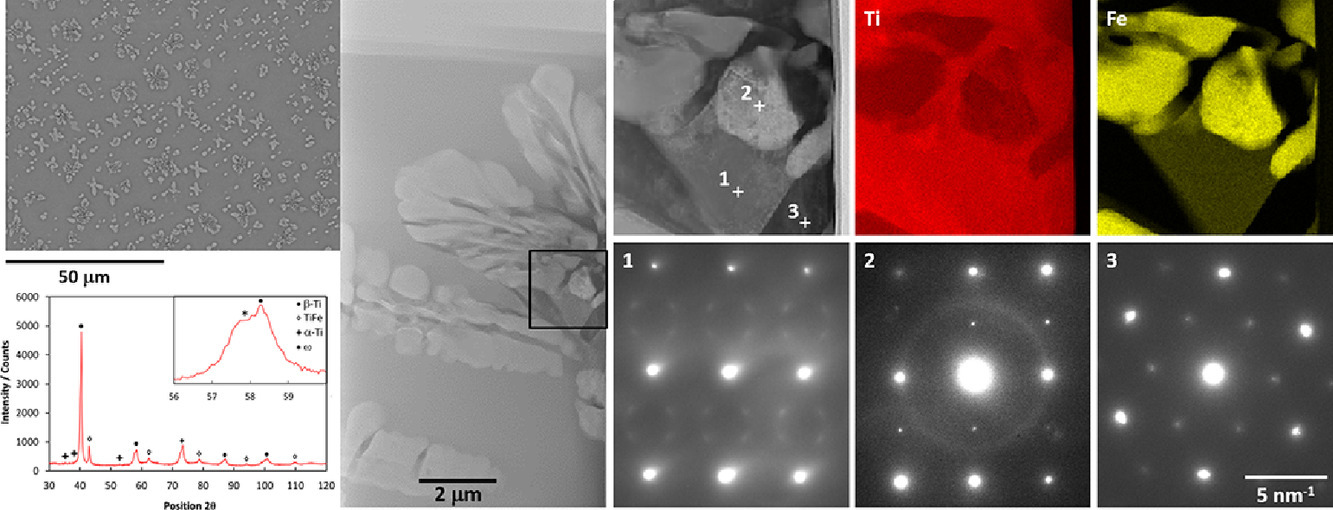
α-β钛合金适用于航空发动机,但通常限制在~550°C。另一种策略是用有序β- TiFe金属间化合物增强“β-Ti高温合金”,然而,目前对二元体系中TiFe析出的研究很少。本研究将Ti-20Fe (at.%)合金在β-Ti相区进行1050°C的均匀化处理,然后在600°C进行时效,时效过程中Fe的过饱和促进了TiFe的析出。结果表明,随着TiFe体积分数的增加,合金的硬度降低,主要原因是:(1) 时效过程中β-Ti Fe含量降低至16.2%,Fe的固溶强化降低;(2) 透射电镜观察发现,均匀化的β-Ti母相中类ω的不相称调制域在时效后,其尺寸和结构发生变化,导致ω析出的强化减弱;(3) 从较硬的ω强化β-Ti母相析出较软的TiFe和α-Ti相而发生软化。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113922
3. Origin of high tension-compression yield asymmetry in as-extruded pure zinc
挤压态纯锌高拉伸-压缩屈服不对称性的成因
Chun Chen, Hua Huang✉, Jialin Niu, Jian-Feng Nie✉, Guangyin Yuan✉
Hua Huang: huangh@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学
Jian-Feng Nie: jianfeng.nie@monash.edu
Guangyin Yuan: gyyuan@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113922
摘要
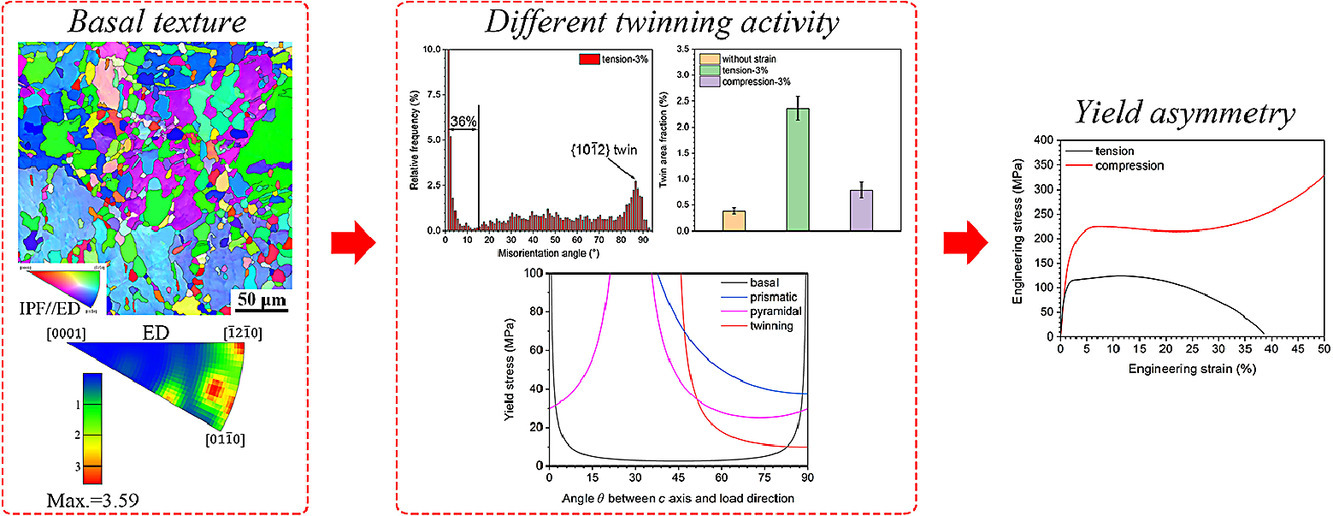
锌及其合金因其作为生物可降解植入物的潜力而受到越来越多的关注。然而,锌及其合金在塑性成形后存在明显的拉-压屈服不对称性,这是不希望出现的。本文研究了挤压态纯锌中强烈的拉伸-压缩屈服不对称性,揭示了拉伸状态下较高的{10-12}⟨-1011⟩孪晶活性是其根本原因。在此基础上,我们提出弱化织构和细化晶粒是降低拉-压屈服不对称性的有效策略。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113918
4. Novel eutectoid Ti-5Ni alloy fabricated via direct energy deposition
采用直接能量沉积制备新型共晶Ti-5Ni合金
P. L. Narayana, Jae H. Kim✉, Sangwon Lee, Jong Woo Won, Chan Hee Park, Jong-Taek Yeom, N.S. Reddy, Jae-Keun Hong✉
Jae H. Kim: jaehkim@kims.re.kr
Jae-Keun Hong: jkhong@kims.re.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113918
摘要
直接能量沉积Ti-5Ni (wt.%)合金促进了显著的晶粒细化,具有细小的等轴晶粒(~ 30-50 μm);具有不连续的晶界α、细小共晶α条(宽度约1 μm)和α+Ti2Ni相。在低于β转变温度下进行24 h的后处理,促进了近等轴相α的形成,温度显著影响了组织组成,包括预共析相α+保留相β+Ti2Ni(760°C)、预共析相α+α' +Ti2Ni(800°C)和完全α' +Ti2Ni(850°C)。与其他常规处理的Ti-Ni二元共晶合金相比,制备态和热处理态合金的拉伸性能显著提高。因此,本文提出的方法为更高效率制备其他共析成形合金系统开辟了新的机会和可能性,这可以克服其他制备工艺的局限性。
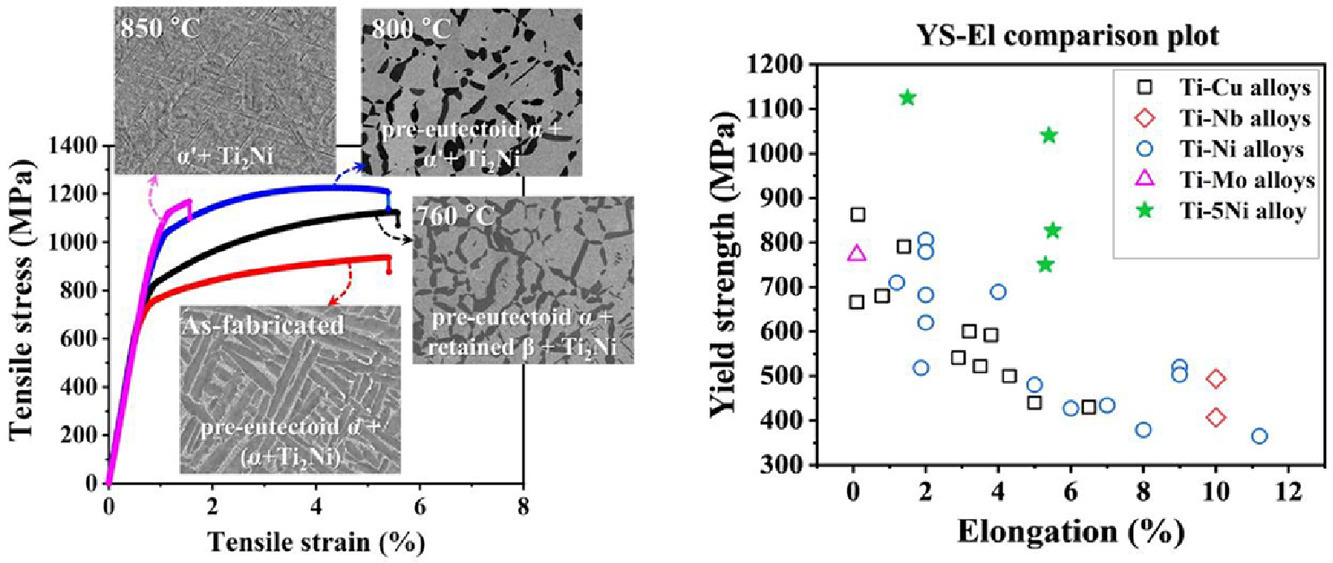
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113917
5. Hardening induced by dislocation core spreading at disordered interface in Cu/Nb multilayers
Cu/Nb多层膜中无序界面处位错核扩展引起的硬化
Wenfan Yang, Mingyu Gong, Jiahao Yao, Jiangwei Wang, Shijian Zheng✉, Xiuliang Ma
Shijian Zheng: sjzheng@hebut.edu.cn 沈阳材料科学国家实验室;河北工业大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113917
摘要
原子尺度界面结构可以调整界面处的位错行为,并强化界面。在本研究中,我们通过在Cu/Nb多层膜中引入超薄非晶层来设计无序界面。与尖锐界面相比,无序界面可以松弛平面内和平面外的伯氏矢量,涂抹钉扎的位错,从而在Cu/Nb多层膜中引起显著的硬化。这一发现不仅证明了位错界面涂抹所引起的硬化效应,而且为采用无序界面开发超高硬度先进材料提供了思路。
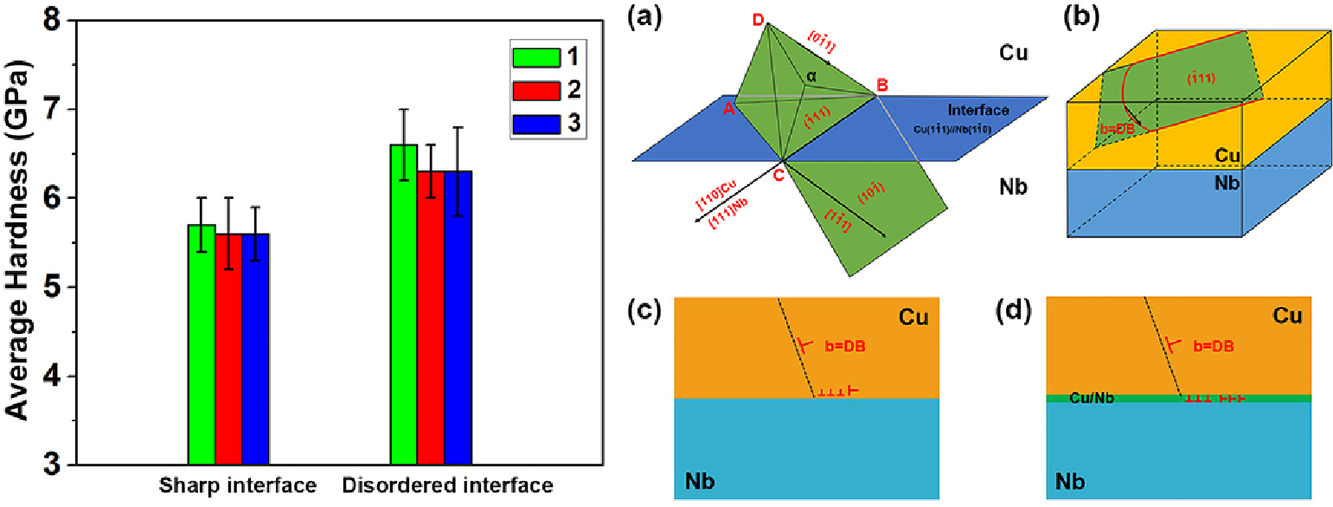
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113919
6. On temperature and strain-rate dependence of flow serration in HfNbTaTiZr high-entropy alloy
HfNbTaTiZr高熵合金流动锯齿的温度和应变速率依赖性研究
Shuying Chen, Weidong Li✉, Fanchao Meng, Yang Tong, Hua Zhang, Ko-Kai Tseng, Jien-Wei Yeh, Yang Ren, Fei Xu, Zhenggang Wu✉, Peter K. Liaw✉
Weidong Li: wli20@utk.edu
Zhenggang Wu: zwu9@hnu.edu.cn 湖南大学
Peter K. Liaw: pliaw@utk.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113919
摘要
金属合金在应力-应变曲线上表现为锯齿状流动的塑性失稳现象通常不利于合金的加工和制造。本文报道了HfNbTaTiZr合金中的流动锯齿,并通过实验研究了其对于温度(573-823K)和应变速率(5×10-5 s-1-1× 10-3 s-1)的依赖关系。在一定的应变速率下,随着温度的升高,锯齿状流动的起始应变由下降(正态)向上升(逆态)的显著转变被理论框架成功地模拟了出来。该模型成功地预测了起始应变作为温度和应变速率的函数,这表明在理论上为受测合金建立处理窗口的可能性。
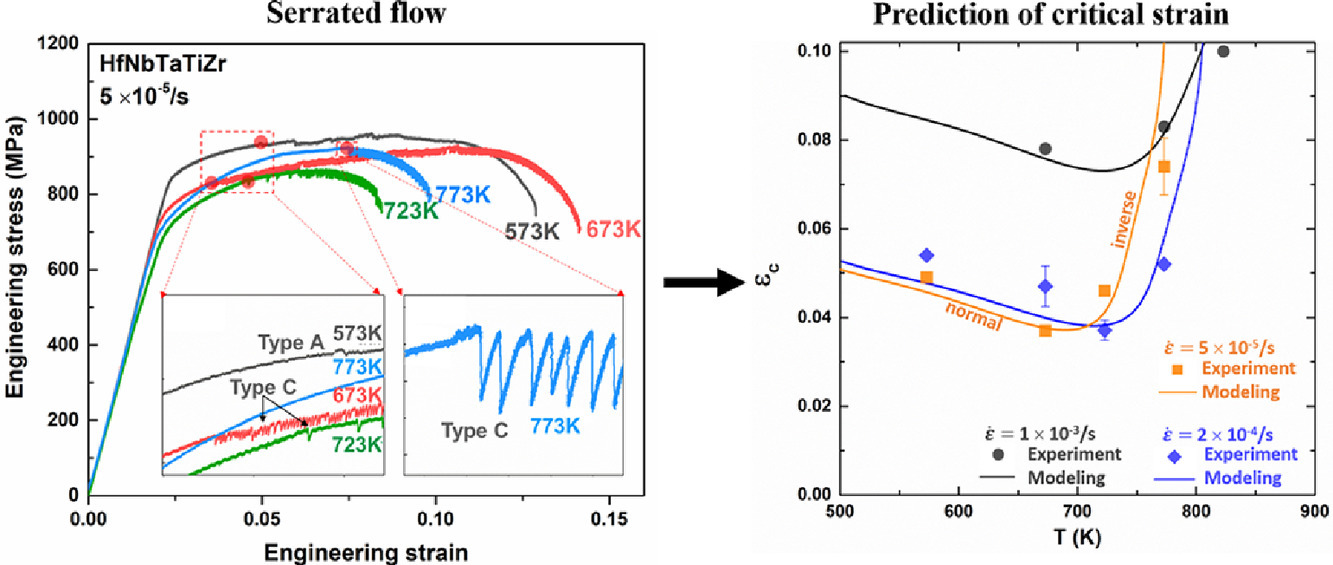
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113913
7. The {10-12} non-cozone twin-twin interactions in Mg: A stability and mobility study using 3-D atomistic simulations
Mg中{10-12}非同域孪生相互作用:使用三维原子模拟的稳定性和迁移率研究
Khanh Dang✉, Carlos N. Tomé, Laurent Capolungo
Khanh Dang: kqdang@lanl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113913
摘要
由于Mg中拉伸孪晶容易激活,多个{10-12}孪晶变体可以相互作用,在塑性变形过程中形成孪晶界。之前使用二维模拟的研究只提供了这些相互作用的部分理解,特别是非同域的交互作用。本文采用原子模拟方法研究了非同域{10-12}孪晶结的三维结构特征和演化过程。研究表明,基底棱柱和具有共格孪晶界的共轭孪晶界面发生相互作用后,会形成新的孪晶界(TTBs),如TTBBP和TTBK2。对于两种非共域孪生相互作用,{-12-12}TTB及其相关的孪晶结对{10-12}孪晶的稳定性和迁移率起着重要作用。特别地,在相互作用过程中它们促进了三维孪晶在法向和正向上的生长,在卸载时阻碍了去孪晶过程。
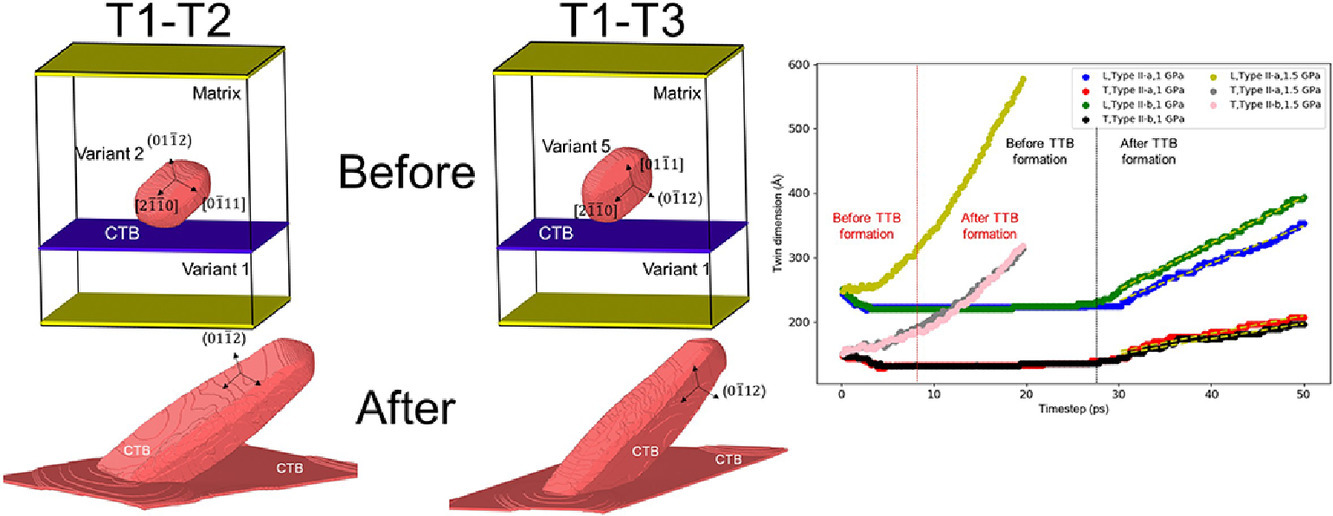
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113928
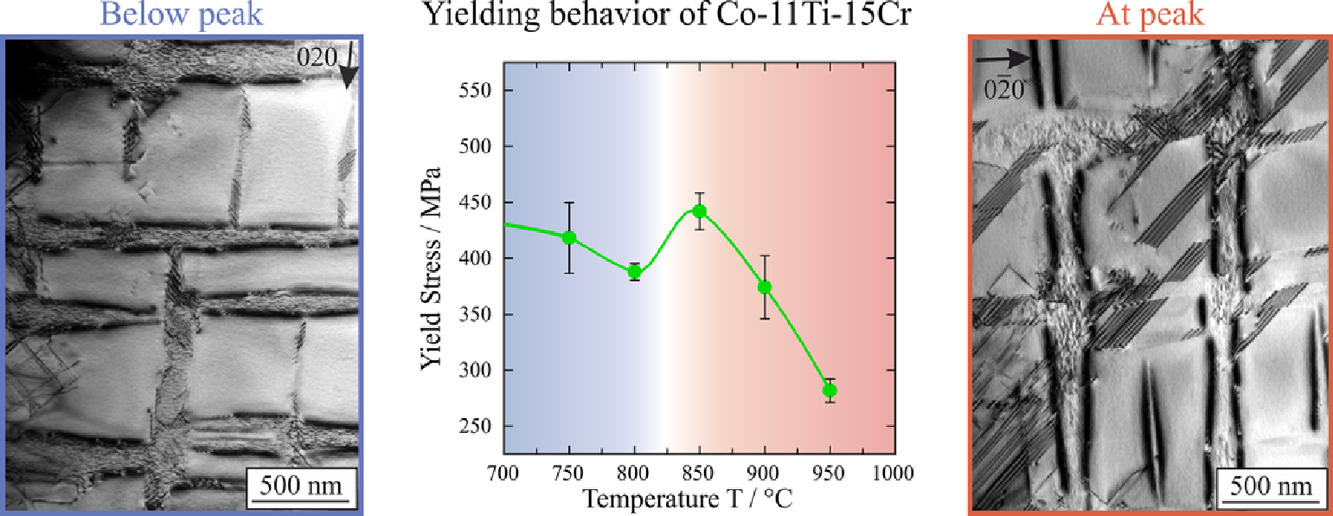
8. Yielding behavior of a single-crystalline γ'-strengthened Co-Ti-Cr superalloy
单晶γ'强化Co-Ti-Cr高温合金的屈服行为
A. Bezold✉, N. Volz, M. Lenz, C.H. Zenk, E. Spiecker, M. Mills, M. Göken, S. Neumeier
A. Bezold: andreas.bezold@fau.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113928
摘要
Ni3Al或Ni基高温合金的异常屈服行为可以用不可动位错构型来解释,这是由反相界耦合位错对的交滑移形成的。本文用透射电镜对单晶Co-11Ti-15Cr高温合金的反常屈服行为进行了系统研究,发现在屈服初期没有形成类似的不动位错构型。γ′析出相在峰值温度下的主要变形机制是超晶格层错的形成。此外,高密度的超晶格层错及其相互作用也导致了明显的加工硬化异常。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113923
9. New Ms-formula for exact microstructural prediction of modern 3rd generation AHSS chemistries
新的Ms公式可精确预测不同化学成分的第三代AHSS的微观组织
Simone Kaar✉, Katharina Steineder, Reinhold Schneider, Daniel Krizan, Christof Sommitsch
Simone Kaar: simone.kaar@fh-wels.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113923
摘要
对于第三代先进高强度钢(AHSS)来说,精确调整各个微观组织组成,特别是亚稳残余奥氏体(RA)的最佳体积分数是非常必要的。此外,避免在最终冷却时形成新鲜马氏体(α′)是至关重要的,否则将导致这些新钢种的力学性能发生明显恶化。因此,准确估算马氏体相变起始温度(Ms)对这组钢的建模和发展是至关重要的。在此背景下,本文基于第三代AHSS化学成分,提出了一个具有宽成分范围的Ms温度预测的新关系。此外,新的Ms公式可以精确预测极低和非常高C含量钢种的Ms温度,这是文献中已知的任何Ms公式所不能实现的。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113927
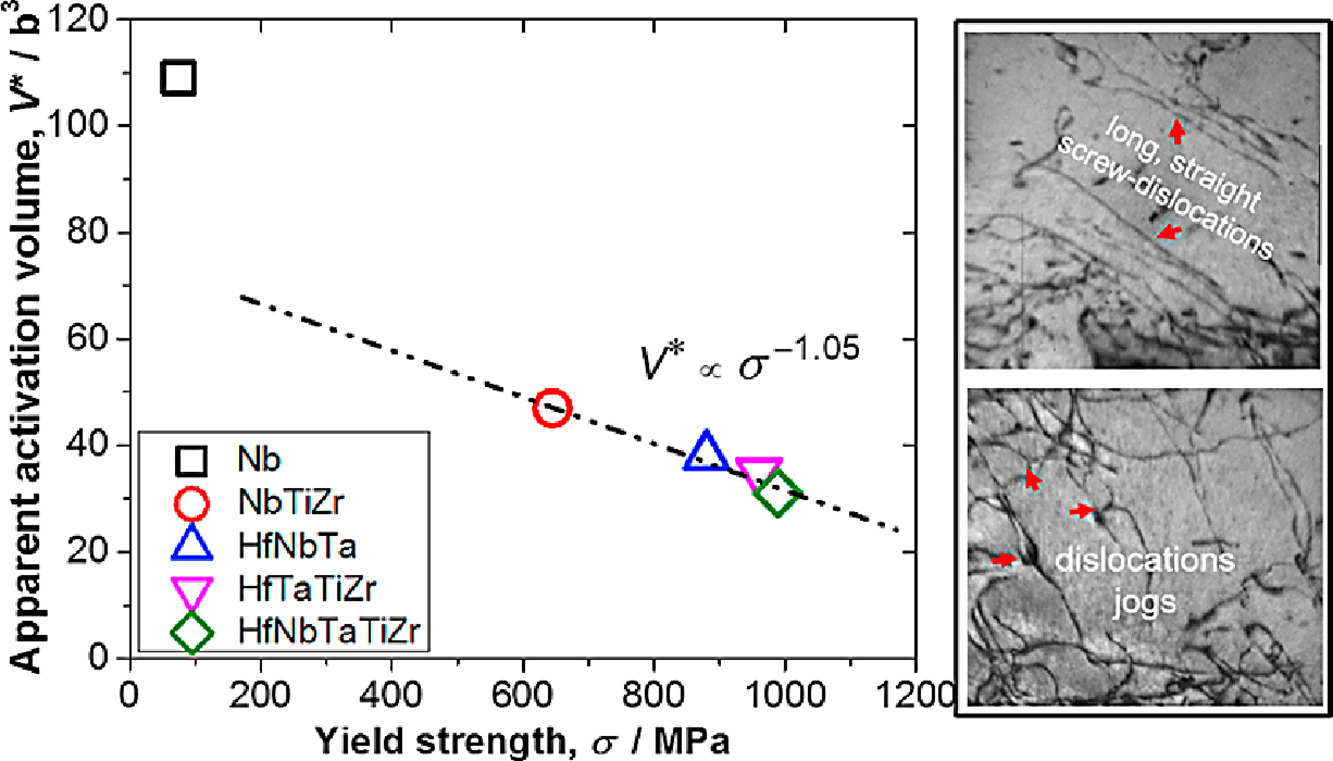
10. Plastic deformation of solid-solution strengthened Hf-Nb-Ta-Ti-Zr body-centered cubic medium/high-entropy alloys
固溶强化Hf-Nb-Ta-Ti-Zr体心立方中/高熵合金的塑性变形
Rajeshwar R. Eleti✉, Nikita Stepanov, Nikita Yurchenko, Denis Klimenko, Sergey Zherebtsov
Rajeshwar R. Eleti: rajeshwar.eleti@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113927
摘要
研究了不同体心立方(BCC)中/高熵合金(MEAs/HEAs)在300K拉伸变形过程中的塑性变形和速率控制机制。微观组织观察显示长而直的螺位错,偶尔由割阶组成。变形的亚结构与评估的激活体积(V*)一致,表明螺位错运动克服Peierls-Nabarro应力阻碍作为速率控制机制。V*值与屈服强度成反比。V*作为屈服强度函数的单调行为表明BCC-MEAs/HEAs的位错运动必须同时克服涉及多个/群置换溶质原子的能垒。此外,首次在BCC-MEAs/HEAs中观察到应力等效现象。研究结果描述了固溶强化BCC-MEAs/HEAs的热激活位错滑移机制取决于应力而不是合金的化学复杂性。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 200, 15 July. 2021, 113924
11. Pre-strain mediated fast natural aging in a dilute Mg-Zn-Ca-Sn-Mn alloy
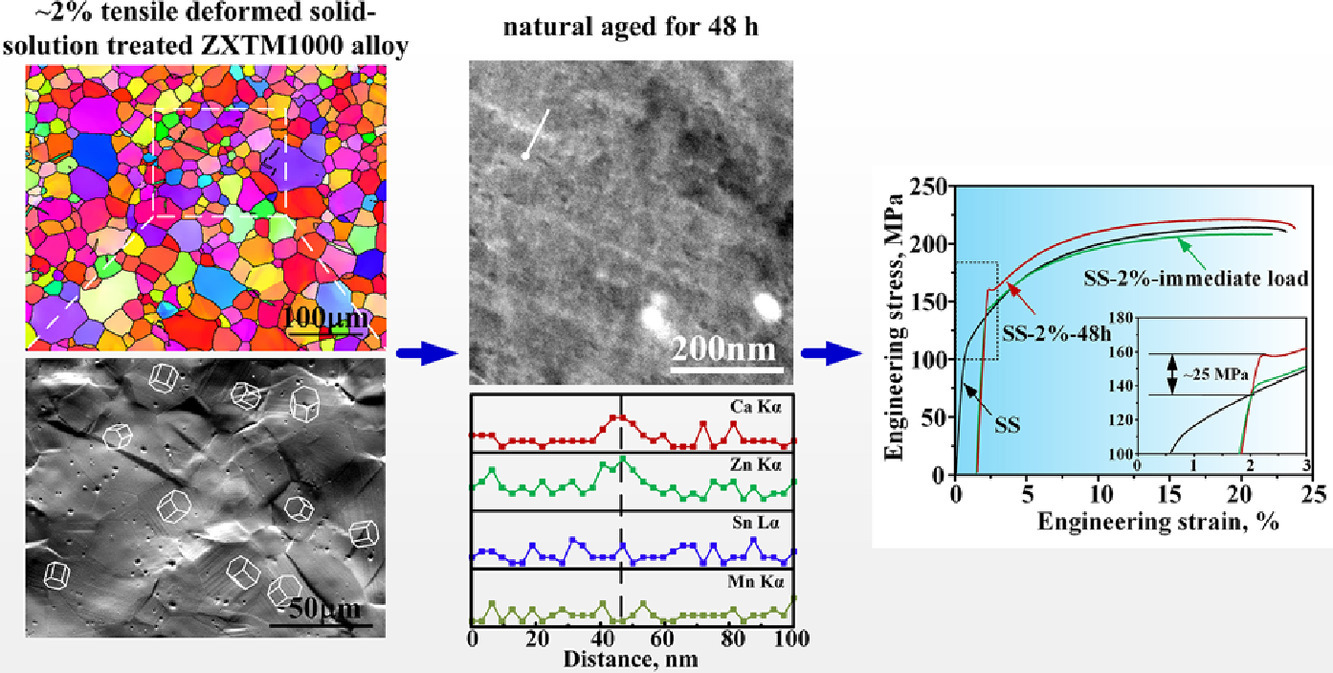
预应变介导的Mg-Zn-Ca-Sn-Mn稀释合金的快速自然时效
Zhen-Ming Hua, Mei-Xuan Li, Cheng Wang✉, Xiao Shi, Zhao-Yuan Meng, Yi-Jia Li, Hai-Long Jia, Min Zha, Hui-Yuan Wang✉
Cheng Wang: chengwang@jlu.edu.cn 吉林大学
Hui-Yuan Wang: wanghuiyuan@jlu.edu.cn 吉林大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113924
摘要
稀释Mg-1.0Zn-0.45Ca-0.33Sn-0.2Mn (wt.%,ZXTM1000)合金板材经预应变处理后,产生了显著的自然时效(NA)响应,在48小时内流应力从~138 MPa明显增加到了~163 MPa。预应变变形引入了大量基底为<a>的位错和过饱和非平衡空位,有利于溶质扩散过程,从而导致能量最小化的非均匀溶质分布。Zn和Ca原子的共偏析阻碍了位错运动,这是强化效应的主要原因。本工作揭示了在稀释镁合金中由于晶体缺陷的引入而出现的明显NA现象,同时也揭示了环境温度下相关的组织演变,为高性能低成本镁合金的设计提供了一种新的策略。