金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.208,15 Apr. 2021(上)
2021-06-06 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文15篇,涵盖了铝合金、高温合金、形状记忆合金、高熵合金等,国内科研单位包括大连理工大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 208 目录
1. Role of tantalum concentration, processing temperature, and strain-rate on the mechanical behavior of copper-tantalum alloys
钽含量、加工温度和应变速率对铜钽合金力学行为的影响
2. Critical factor triggering grain boundary cracking in non-weldable superalloy Alloy713ELC fabricated with selective electron beam melting
不可焊高温合金713ELC晶界开裂的关键影响因素
3. The effects of stress, temperature and facet structure on growth of {101-2} twins in Mg: A molecular dynamics and phase field study
应力、温度和晶面结构对Mg{101-2}孪晶长大影响的分子动力学和相场研究
4. Manipulation of solute partitioning mechanisms for nanocrystalline stability
纳米晶稳定性的溶质配分机制调控
5. Thermal stability of immiscible Cu-Ag/Fe triphase multilayers with triple junctions
非混溶Cu-Ag/Fe三相多层结构的热稳定性研究
6. Composition-dependent solidification cracking of aluminum-silicon alloys during laser powder bed fusion
铝硅合金激光粉末熔炼过程中化学成分对凝固开裂的影响
7. Impact of crystallography at Ni/NiAl interfaces on the nucleation of Ni3Al
Ni/NiAl界面的晶体学特征对Ni3Al形核的影响
8. High entropy alloy nanocomposites produced by high pressure torsion
基于高压扭转方法制备高熵合金纳米复合材料
9. Quantities and distribution of strain-induced vacancies and dislocations enhanced by hydrogen in iron
氢对铁中应变诱导空位和位错的数量、分布的影响研究
10. Strain-sensitive topological evolution of twin interfaces
孪晶界面应变敏感的拓扑演化研究
11. Elemental segregation to lattice defects in the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy during high temperature exposures
高温下CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金中元素在晶格缺陷处的偏聚研究
12. Evolution of elastic constants of the NiTi shape memory alloy during a stress-induced martensitic transformation
NiTi形状记忆合金在应力诱导马氏体相变过程中弹性常数的演化
13. Three-dimensional atomic scale characterization of {11-22} twin boundaries in titanium
钛中{11-22}孪晶界的三维原子尺度表征
14. A model to unravel the beneficial contributions of trace Cu in wrought Al–Mg alloys
微量铜添加对铝镁合金变形性能增益的模型研究
15. Revealing the mechanisms for the nucleation and formation of equiaxed grains in commercial purity aluminum by fluid-solid coupling induced by a pulsed magnetic field
脉冲磁场条件下工业纯铝中等轴晶形核长大的机理研究
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116706
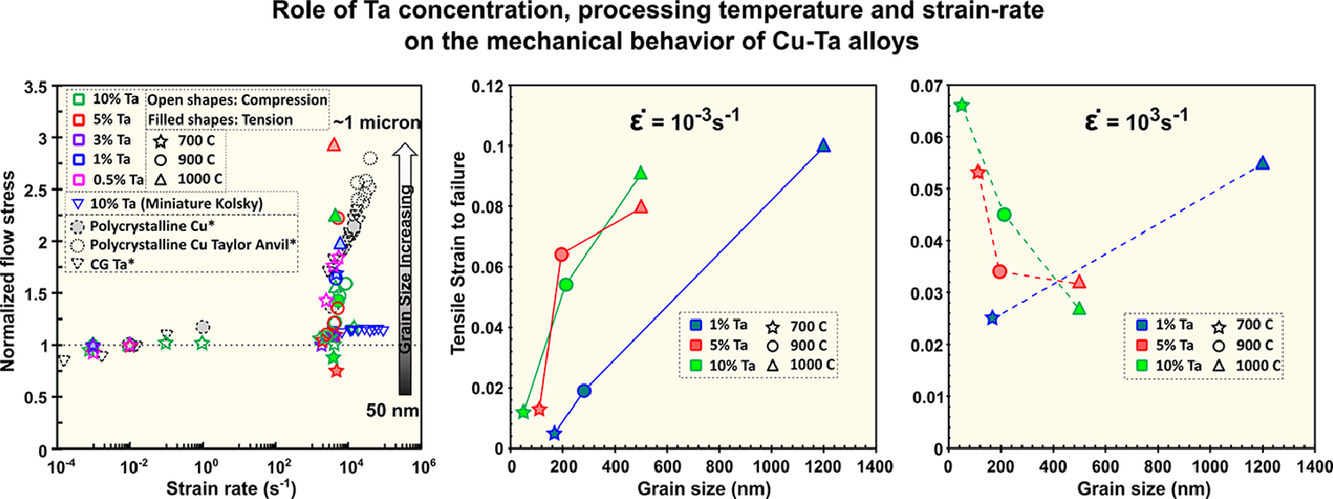
1. Role of tantalum concentration, processing temperature, and strain-rate on the mechanical behavior of copper-tantalum alloys
钽含量、加工温度和应变速率对铜钽合金力学行为的影响
S. Srinivasan, S. Sharma, S. Turnage, B.C. Hornbuckle, C. Kale, K.A. Darling, K. Solanki✉
K. Solanki:kiran.solanki@asu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116706
摘要
传统纳米晶的组织不稳定性使得我们难以深入研究极端条件下(如高温、快速加载等)晶粒尺寸对力学行为的影响。我们研究了Ta浓度和温度对粉末加工成型的致密Cu-Ta合金组织的影响以及合金在不同应变率下的拉伸和压缩行为,从而探索通过调控组织对流变应力上升进行控制的可能性。研究结果表明,存在一个临界尺寸,即在晶粒尺寸较小且和团簇间距合适的条件下,这种应变上升被抑制。实验观测到的流变应力的变化与高速率塑性的变化一致,两者均在临界长度尺度以下呈增长趋势。此外,纳米晶Cu-Ta合金的拉压不对称性也受到抑制,而当晶粒尺寸从纳米晶变为超细晶时,这种不对称性开始逐渐凸显。总的来说,这项工作提出了一种系统的方法,对高加载速率下合金的流变应力上升行为进行调控。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116695
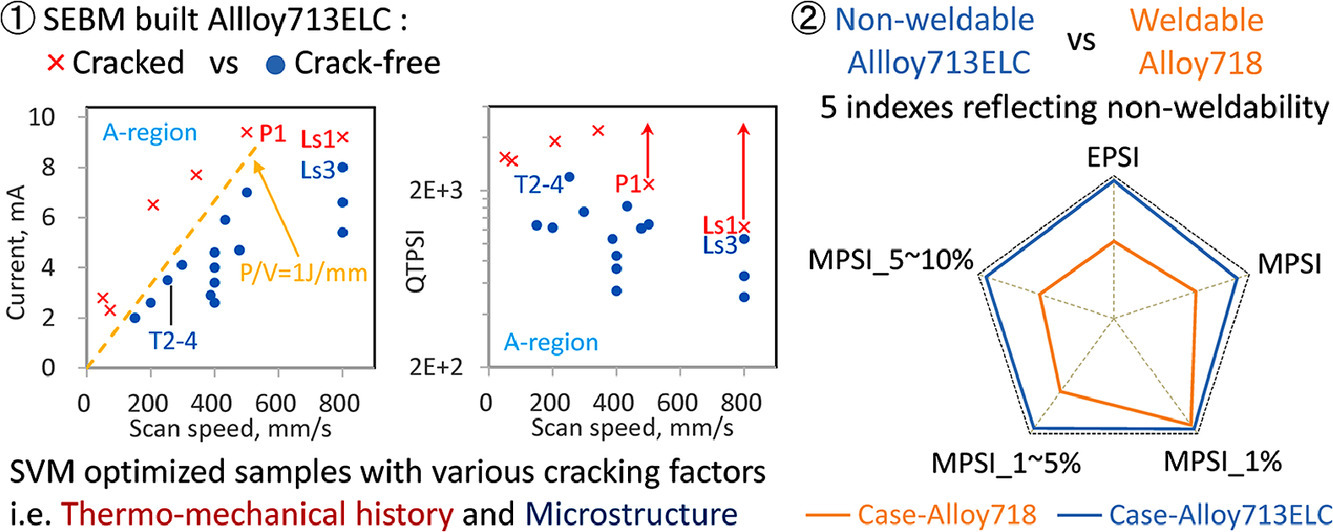
2. Critical factor triggering grain boundary cracking in non-weldable superalloy Alloy713ELC fabricated with selective electron beam melting
不可焊高温合金713ELC晶界开裂的关键影响因素
Yuchao Lei, Kenta Aoyagi✉, Kinya Aota, Kosuke Kuwabara, Akihiko Chiba
K. Aoyagi:k.aoyagi@imr.tohoku.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116695
摘要
电子选区熔炼制备的难焊高温合金中的晶界裂纹是应力、成分等多种因素共同作用的结果。在本研究中,我们采用机器学习方法在高维参数空间中构建了难焊高温合金713ELC的工艺图。通过排除工艺缺陷对开裂的影响,我们可以在优化后的参数条件下制备出有裂纹和无裂纹的样品。通过样本间的比较,我们发现,细柱状晶样品中裂纹容易萌生;粗柱状晶样品中裂纹则不易萌生。在扫描速度 ≤800 mm/s条件下制备的样品,其开裂可能性可以通过热力学分析计算得到的准全塑性应变指数(QTPSI)进行排名。全塑性应变水平是开裂的关键影响因素之一。扫描速度增加可以提高总塑性应变,当应变超过QTPSI可衡量范围时,预测出现较大偏差。此外,713ELC合金难焊性主要是由于其热膨胀效应,这种效应与材料中的Al含量较高有关。在此基础之上,进一步结合熔化效应和应变时效开裂,可以帮助我们更加深入地揭示713ELC合金难焊的原因。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116603
3. The effects of stress, temperature and facet structure on growth of {101-2} twins in Mg: A molecular dynamics and phase field study
应力、温度和晶面结构对Mg{101-2}孪晶长大影响的分子动力学和相场研究
Mingyu Gong, J. Graham, Vincent Taupin, Laurent Capolungo✉
L. Capolungo:laurent@lanl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.116603
摘要
本文主要研究了组织、应力和温度对Mg中孪晶畴迁移率和{101-2}孪晶长大动力学的影响。我们首先使用了分子动力学模拟(MD)研究了界面结构、应力、温度和迁移率之间的关系。由于孪晶畴面可以有不同的原子结构,因此我们还对位错引起的应力松弛对基面-棱柱界面迁移率的影响进行了量化。我们基于分子动力学数据,收集了10种界面的不同参数,引入各向异性相场模型,从而进一步预测温度和应力对{101-2}孪晶形貌和长大动力学的影响。研究结果表明,三维孪晶生长过程中,孪晶界面的效迁移率与单独多面体界面显著不同。这主要是由于孪晶中复杂的三维内应力状态和相互耦合的界面运动导致的。综上所述,通过使用分子动力学模拟不同温度和应力条件下孪晶的形貌的长大动力学,结合响应的拟合分析,我们可以很好地判别控制孪晶形貌和动力学的界面,并对其有效迁移率进行测量。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116662
4. Manipulation of solute partitioning mechanisms for nanocrystalline stability
纳米晶稳定性的溶质配分机制调控
Xuyang Zhou, Ankit Gupta, Garritt J. Tucker, Gregory B. Thompson✉
G.B. Thompson:Gthompson@eng.ua.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116662
摘要
我们报导了一种通过控制退火温度和化学成分在同一Ni(P)合金中激活两种不同的纳米晶稳定机制的方法。我们采用了两步加热法,Ni-1at%P合金在低温退火(350°C/1 h)过程中发生溶质元素的晶界(GBs)修饰,从而在较高温度(550°C)实现热力学稳定。原子探针分析发现溶质元素的浓度很低(< 0.2 at.%), 间接证明了这种稳定机制。如果不进行第一步低温退火而直接将样品升至高温(550°C),材料中将析出稳定的Ni3P相并钉扎晶界。而在第二相形成之前,晶粒已发生明显粗化。而如果使用Ni-4at.%P,则无论是两步退火(350°C/1 h后升至550°C)还是一步退火(直接升至550°C),溶质元素都会析出形成Ni3P相并引起Zener钉扎机制。通过比较热力学稳定和Zener钉扎两种稳定机制,我们发现,尽管热力学稳定机制下的晶粒更细,但溶质均匀分布的钉扎强度低于Zener钉扎。我们进一步通过原子尺度模拟对以上结果进行了分析讨论。
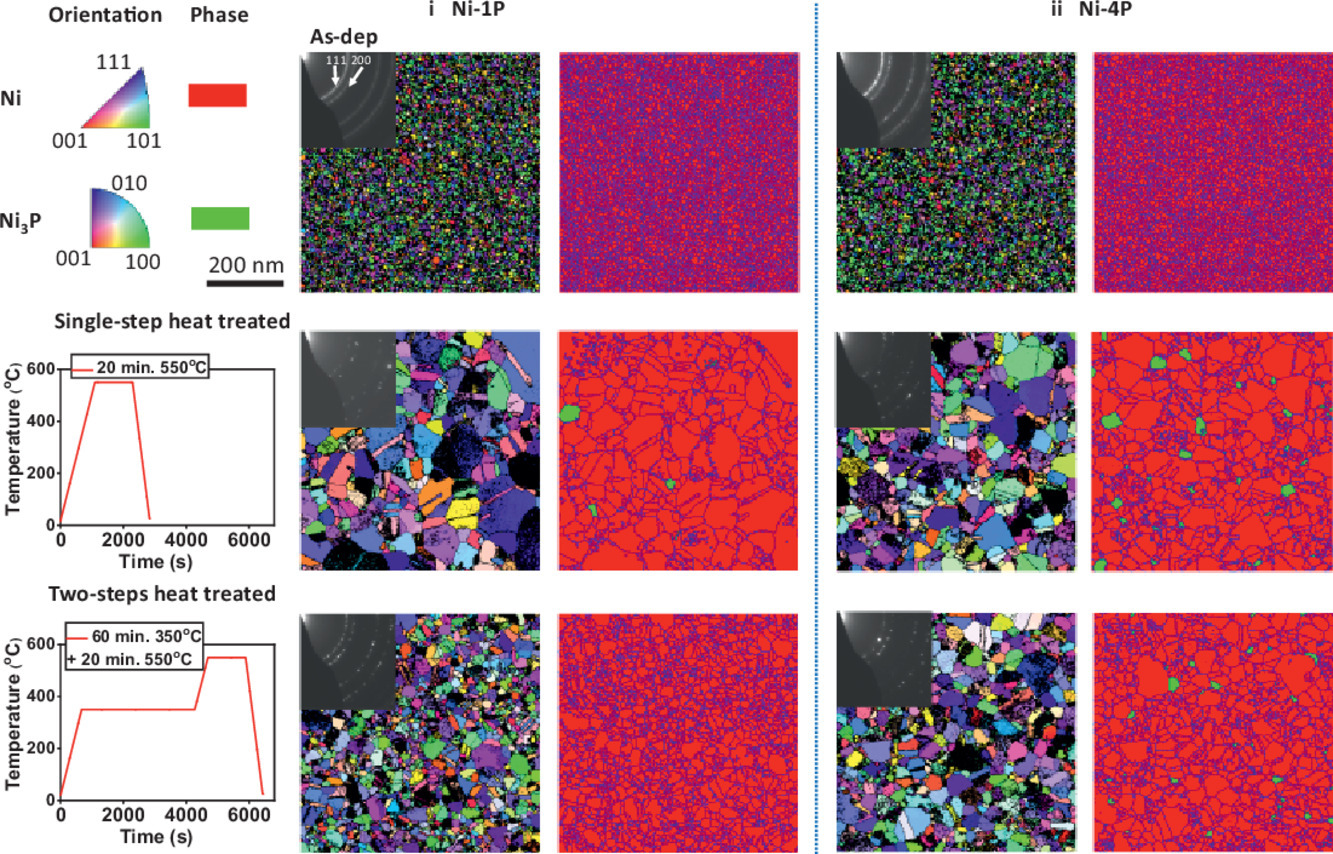
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116679
5. Thermal stability of immiscible Cu-Ag/Fe triphase multilayers with triple junctions
非混溶Cu-Ag/Fe三相多层结构的热稳定性研究
Tongjun Niu, Yifan Zhang, Jaehun Cho, Jin Li, Haiyan Wang, Xinghang Zhang✉
X. Zhang:xzhang98@purdue.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116679
摘要
金属纳米多层材料由于其高机械强度而受到广泛关注。然而,它们在高温下常常出现热开槽和层断等现象,导致组织不稳定。在本文中,我们报道了一种具有三重结点的三相互不相溶Cu-Ag/Fe多层结构材料,它比Cu/Fe多层结构具有更高的热稳定性。Cu/Fe多层结构在500℃下出现了明显的热缺陷和快速的晶粒长大,600℃时多层结构完全断裂,并伴随组织球化。相比之下,Cu-Ag/Fe三相多层结构在600℃时仍保持稳定,晶粒粗化不明显。我们对三相多层结构中热沟槽的动力学和材料的高热稳定性机理进行了讨论。本研究为高温稳定纳米多层结构的设计提供了新的思路。
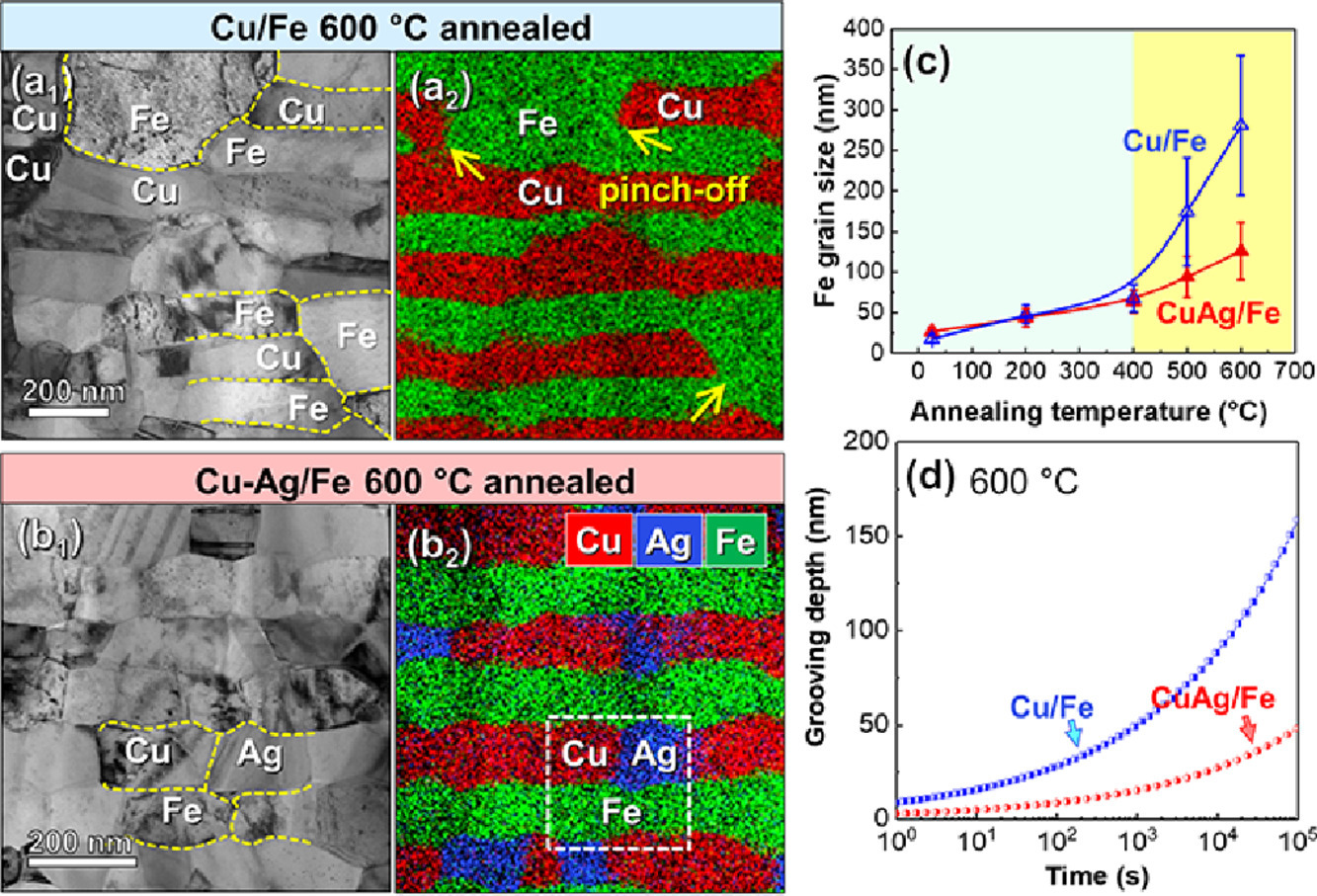
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116698
6. Composition-dependent solidification cracking of aluminum-silicon alloys during laser powder bed fusion
铝硅合金激光粉末熔炼过程中化学成分对凝固开裂的影响
Holden Hyer, Le Zhou, Abhishek Mehta, Sharon Park, Thinh Huynh, Shutao Song, Yuanli Bai, Kyu Cho, Brandon McWilliams, Yongho Sohn✉
Y. Sohn:yongho.sohn@ucf.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116698
摘要
我们以AlSi10Mg和Al12Si为例,研究了Al-Si合金的激光粉末熔炼(LPBF)制备工艺。制备得到的工程部件致密且无凝固裂纹。这些合金能够成功制备主要是由于它们的成分接近共晶,且冻结范围较小。为了阐明这一观察结果,我们利用Scheil-Gulliver凝固模型,通过计算热裂敏感性|dT/dfS1/2|来说明材料的断裂敏感性。我们选择了亚共晶、近共晶和过共晶成分的六种二元Al-Si合金,雾化制粉后进行激光熔炼,对热裂敏感性的计算结果进行了验证。结果表明,只有Si含量为1.0和2.0 wt.%的Al-Si合金出现了裂纹,这与这两种合金的|dT/dfS1/2|值较大相吻合。Si在胞状结构界面处发生偏析,形成亚胞结构。对于特定成分合金,通过表征胞状结构,可以估计冷却速率为106-107 K•s−1。在不产生凝固裂纹的合金中,抗拉强度随Si含量增加而增加,延性则降低。胞状结构的形成和胞界面处的Al-Si共晶是引起这种力学行为差异的主要原因。
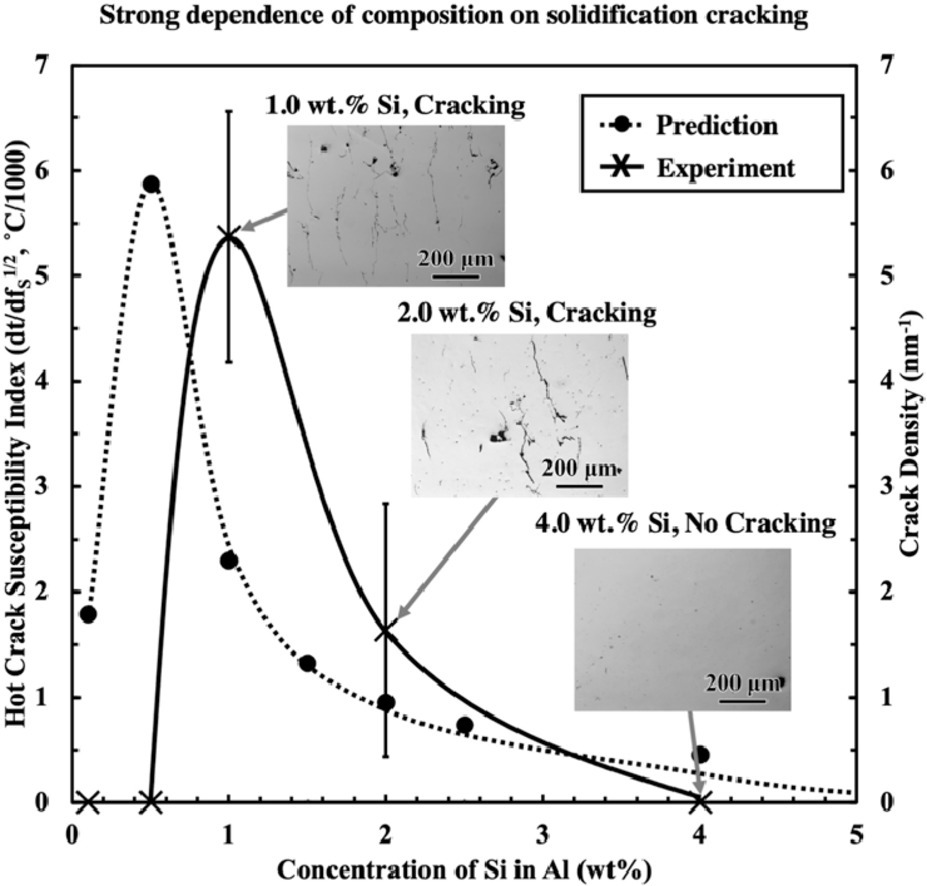
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116713
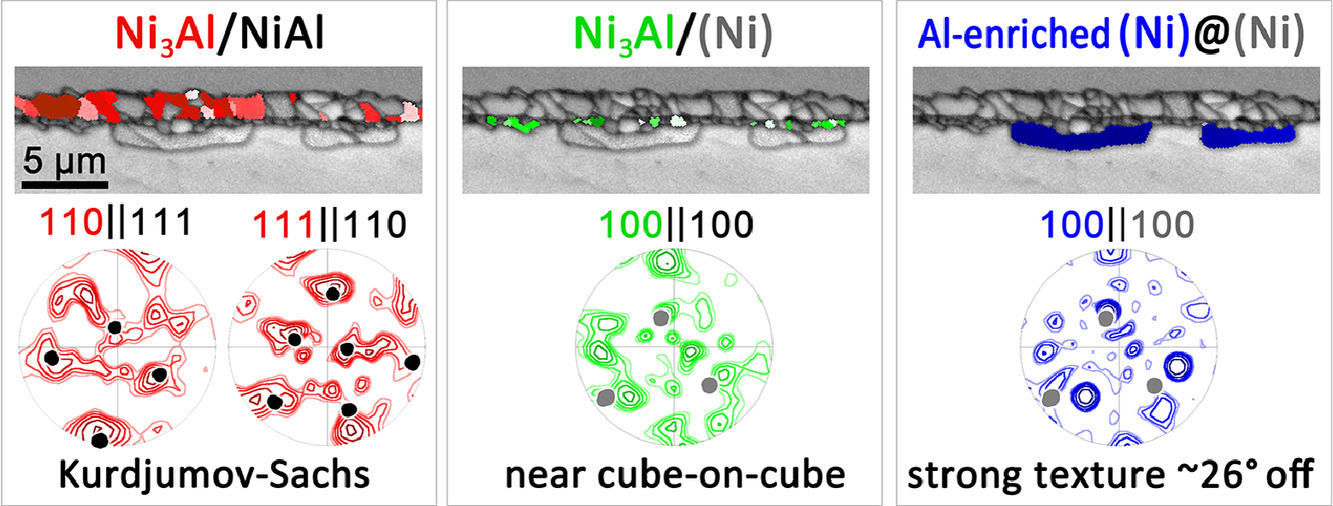
7. Impact of crystallography at Ni/NiAl interfaces on the nucleation of Ni3Al
Ni/NiAl界面的晶体学特征对Ni3Al形核的影响
M. Seyring✉, M. Rettenmayr
M. Seyring:martin.seyring@uni-jena.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116713
摘要
我们研究了具有不同晶体构型的(Ni)/NiAl界面处的相变早期过程。与其他工作不同的是,我们在研究中采用了扩散偶和650℃的低退火温度。我们采用了EBSD和STEM EDX相结合的统计方法,研究了Ni3Al相的形貌、Ni3Al相与不同(Ni)/NiAl界面的晶体学关系以及Ni3Al的长大动力学。Ni3Al相呈层片状形成,主要向着NiAl相生长,并与相邻相形成特定的晶体学关系。向着NiAl相生长的大部分Ni3Al为K-S位向关系。第二层Ni3Al中的晶粒主要以近立方-立方取向关系(取向差< 15°)向着Ni生长。我们在(Ni)/Ni3Al界面处观察到了富Al的(Ni)晶粒形成,我们认为这可以解释为扩散诱导的再结晶过程。

ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116714
8. High entropy alloy nanocomposites produced by high pressure torsion
基于高压扭转方法制备高熵合金纳米复合材料
Shabnam Taheriniya✉, Farnaz A. Davani, Sven Hilke, Marco Hepp, Christian Gadelmeier, Mohammed Reda Chellali, Torben Boll, Harald Rösner, Martin Peterlechner, Christoph Gammer, Sergiy V. Divinski, Benjamin Butz, Uwe Glatzel, Horst Hahn, Gerhard Wilde
S. Taheriniya:s_tahe01@uni-muenster.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116714
摘要
我们采用高压扭转方法对两种等原子比单相高熵合金圆盘,FCC的CoCrFeMnNi和BCC的 HfNbTaTiZr,进行了连接。经15转后,CoCrFeMnNi的细长纳米晶与HfNbTaTiZr的部分非晶态纳米晶交错形成了块体纳米复合材料,其微观结构复杂,具有大量的漩涡状区域。FCC相中的元素分布较为均匀,而BCC高熵合金则分离成富Ta和贫Ta两相。这种在约束条件下对不同高熵合金进行的连接,可以为我们通过非平衡工艺进行高熵合金复合材料设计提供新的思路。
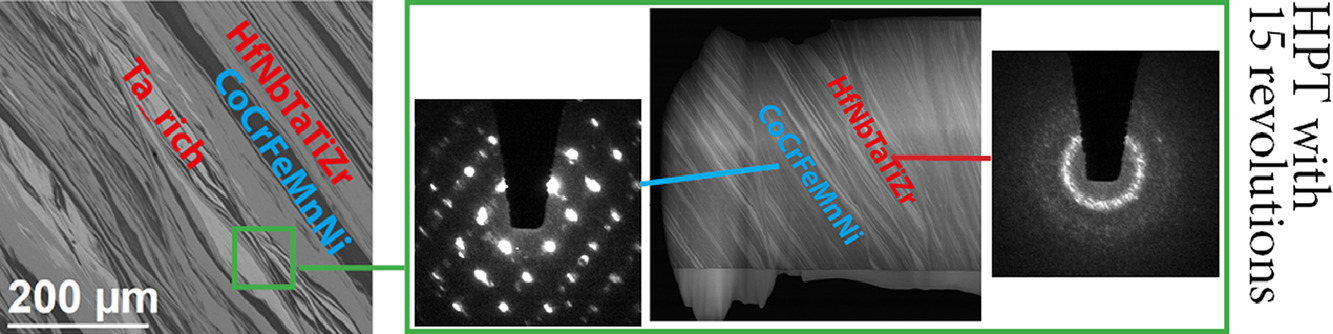
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116663
9. Quantities and distribution of strain-induced vacancies and dislocations enhanced by hydrogen in iron
氢对铁中应变诱导空位和位错的数量、分布的影响研究
Yuri Sugiyama, Kenichi Takai✉
K. Takai:takai-k@sophia.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116663
摘要
我们利用低温热吸收光谱(L-TDS)对纯铁试样中,由塑性应变引起各种晶格缺陷形成过程中氢的作用进行了研究。该光谱可以从−200℃开始测量。我们分别在有氢和无氢条件下,对试样进行了不同应变量的塑性形变。我们使用L-TDS对氢饱和试样的应变诱导晶格缺陷,包括空位和位错核,进行了定量分析。L-TDS谱包含两个氢释放峰:一个与位错有关的低温峰和一个与空位有关的高温峰。各峰值对应的氢含量随塑性应变的增大而增大。我们发现,当应变量为25%时,氢含量对低温峰(即位错对应峰)无影响;而含氢样品的高温峰(即空位对应峰)则增加了6倍,而当应变量为40%,这一数值则达7倍。电子隧穿对比成像(ECCI)和背散电子衍射(EBSD)分析表明,有氢条件下,应变为25%时,应变铁素体晶界附近存在应变集中。因此,我们认为氢在塑性应变过程中不影响位错的形成数量,但会促进空位形成和晶界处的位错集中。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116716
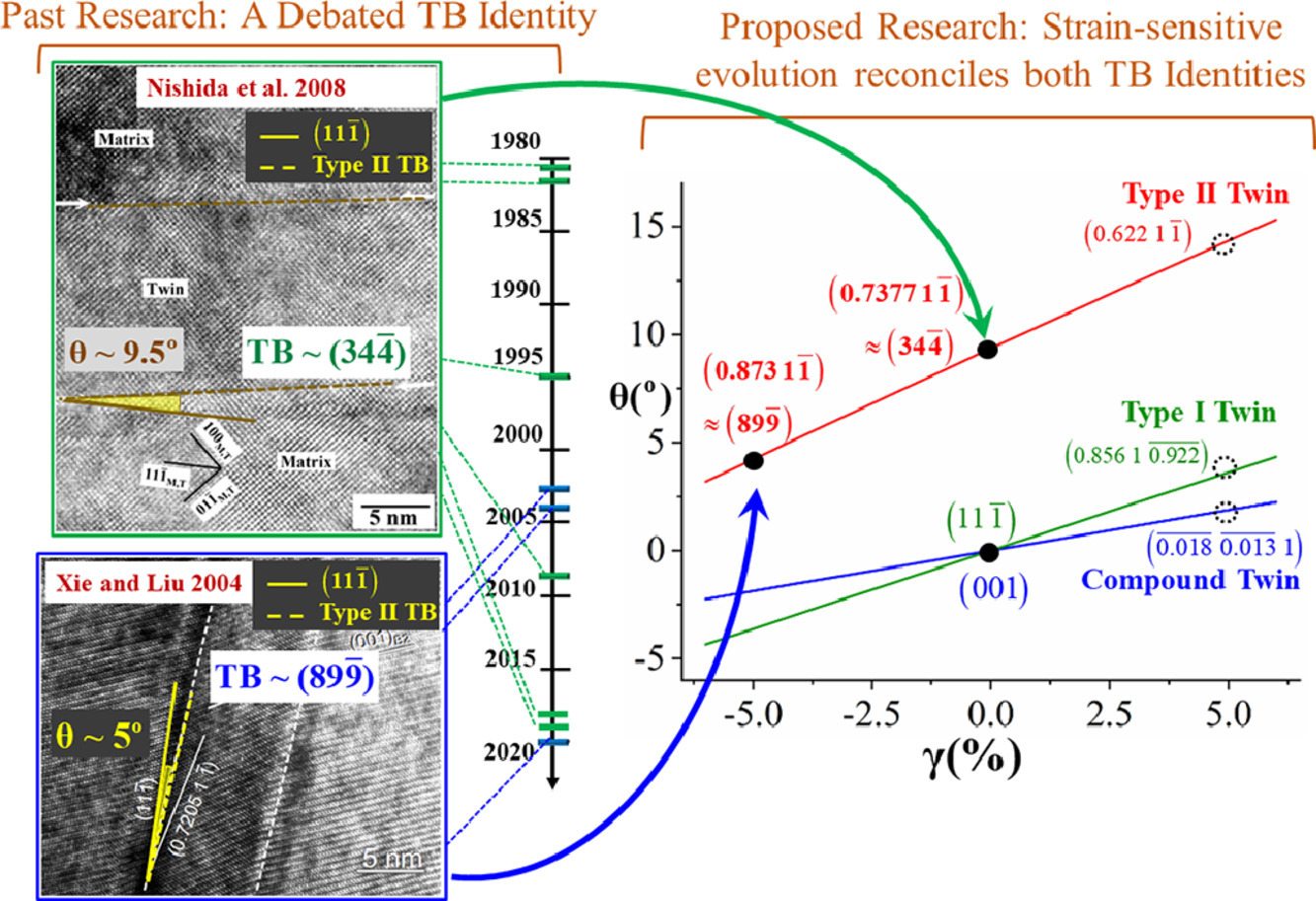
10. Strain-sensitive topological evolution of twin interfaces
孪晶界面应变敏感的拓扑演化研究
Ahmed Sameer Khan Mohammed, Huseyin Sehitoglu✉
H. Sehitoglu:huseyin@illinois.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116716
摘要
孪晶界是材料科学中的基本界面,历经了一个多世纪的研究,仍不断有这方面的新发现。该领域中一个长期存在的异常现象是:NiTi体系中一个II型孪晶界的实验观测结果具有两种不同的表示:(0.7205 1 -1) ≈(3 4 -4)和(8 9 -9)。在过去的40年里,人们对这种界面的结构提出了各种主张。在本研究中,我们考虑了多个尺度上的能量,通过分子静力学模拟和各向异性弹性模型,创建了一个阶梯-断开(TD)拓扑结构,作为能量最小的纳米结构;并进一步建立了一个基于连续的应变-能量参数的理论框架,来研究组织应变和局部孪晶体积分数对界面拓扑结构的影响。结果表明,在两个参数的耦合影响下,拓扑结构趋向于在连续的指标谱上演化。因此,我们认为迄今为止的实验观察结果是该谱系内的不同状态,并可将其作为II型孪晶界演化的证据。这种拓扑演化本质上是由应变导致的位错间距变化(等效于界面位错密度变化)引起的。我们进一步指出,这种演化行为在NiTi中的I型和复合孪晶界中普遍存在,表现为共格态和半共格态间的无缝过渡。这种演化将引起位错密度的显著变化(高达8倍),并使材料在非零应变下出现无理Miller指数。这一“界面演化”理论是对拓扑建模理论的扩展,使我们能够在非零应变和非对称孪晶体积分数下确定拓扑平衡。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116719
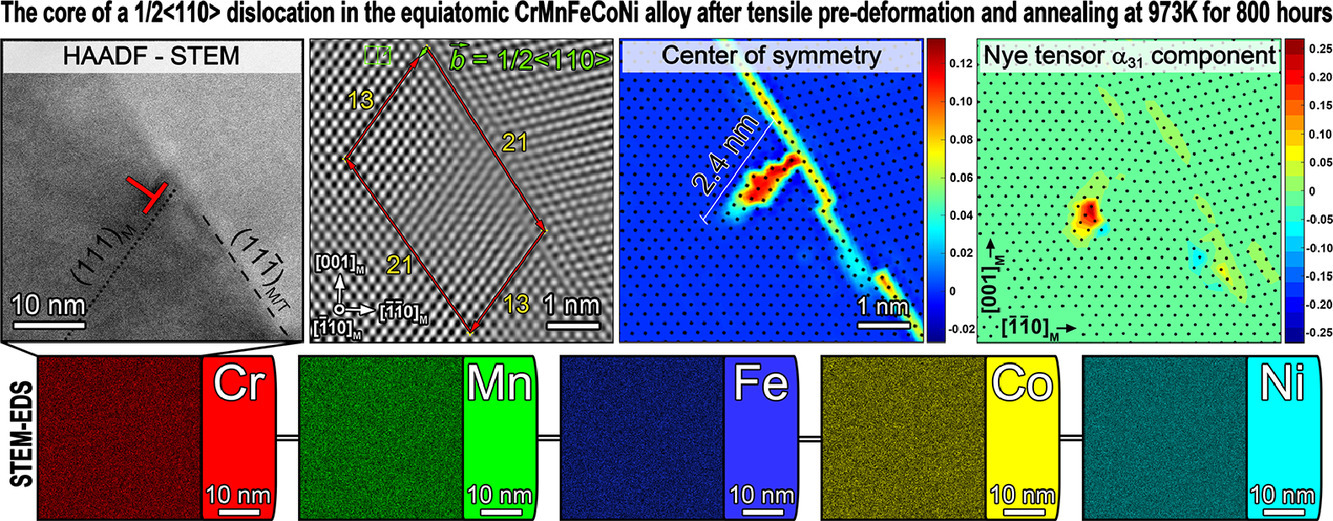
11. Elemental segregation to lattice defects in the CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloy during high temperature exposures
高温下CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金中元素在晶格缺陷处的偏聚研究
Milan Heczko✉, Veronika Mazánová, Roman Gröger, Tomáš Záležák, Mohammad S. Hooshmand, Easo P. George, Michael J. Mills, Antonín Dlouhý
M. Heczko:heczko.2@osu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116719
摘要
我们研究了少量塑性预应变对等原子比CrMnFeCoNi面心立方固溶体高温稳定性和组织的影响。其中,我们特别关注了合金元素在位错处的偏聚。我们首先将CrMnFeCoNi样品在室温进行拉伸变形,塑性应变分别为0.2%和2.3%,随后将样品在973 K退火800小时。研究表明,预应变激活了{111}滑移面上1/2<110>位错的平面滑移。这种平面滑移与特殊的Σ3晶界相互作用,形成了大量适合采用HR-STEM进行分析的<110>位错段。1/2<110>位错的核心向晶界堆积,形成近致密构型。在EDS能谱的灵敏度范围内,位错附近没有检测到溶质元素浓度梯度,这表明在预变形和退火后没有合金元素在位错核偏聚。然而,在退火过程中,富Cr的四方σ相会在三叉晶界处形核长大,且这一过程并没有因预应变后位错密度增大而加快。在晶界附近的贫Cr区存在明显的Cr梯度,这表明Cr是从基体缓慢扩散到晶界,再沿晶界较快扩散到析出。伴随着Cr在晶界附近耗尽,Ni、Mn发生富集,从而促进了长时间退火后晶界上L10 NiMn相的形成。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116718
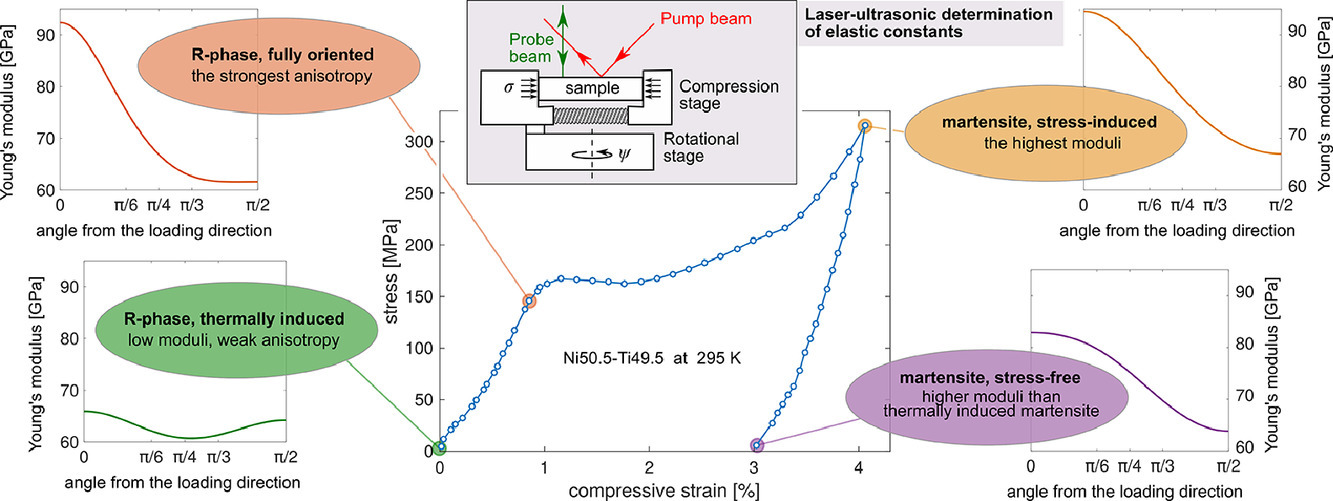
12. Evolution of elastic constants of the NiTi shape memory alloy during a stress-induced martensitic transformation
NiTi形状记忆合金在应力诱导马氏体相变过程中弹性常数的演化
Tomáš Grabec, Petr Sedlák✉, Kristýna Zoubková, Martin Ševcík, Michaela Janovská, Pavla Stoklasová, Hanuš Seiner
P. Sedlák:psedlak@it.cas.cz
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116718
摘要
我们对多晶NiTi形状记忆合金的假塑性应变进行了原位超声表征,对应力诱导奥氏体→R相→B19’马氏体相变过程中横向各向同性多晶的全弹性张量进行了测量。结果表明,在低应变状态下,R相具有较强的各向异性。这种各向异性在整个R相→马氏体相变过程中保持不变,甚至在卸载后的无应力马氏体中也能保持。通过基于均匀化方法的微观力学模型,我们发现这种强各向异性可能与R相和马氏体中的孪晶界有关,而与晶胞的各向异性和晶体织构无关。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116707
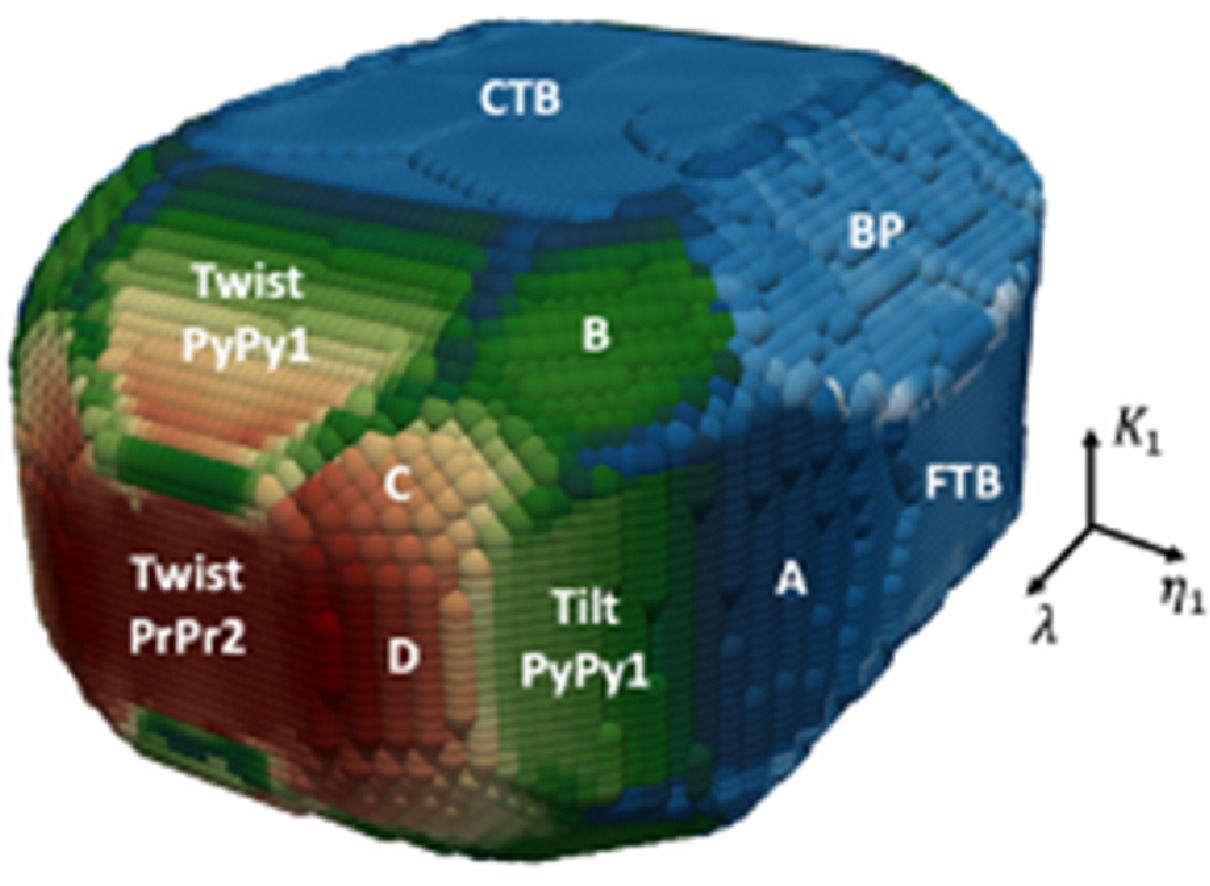
13. Three-dimensional atomic scale characterization of {11-22} twin boundaries in titanium
钛中{11-22}孪晶界的三维原子尺度表征
Shujuan Wang, Khanh Dang, Rodney J. McCabe✉, Laurent Capolungo, Carlos N. Tomé
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116707
摘要
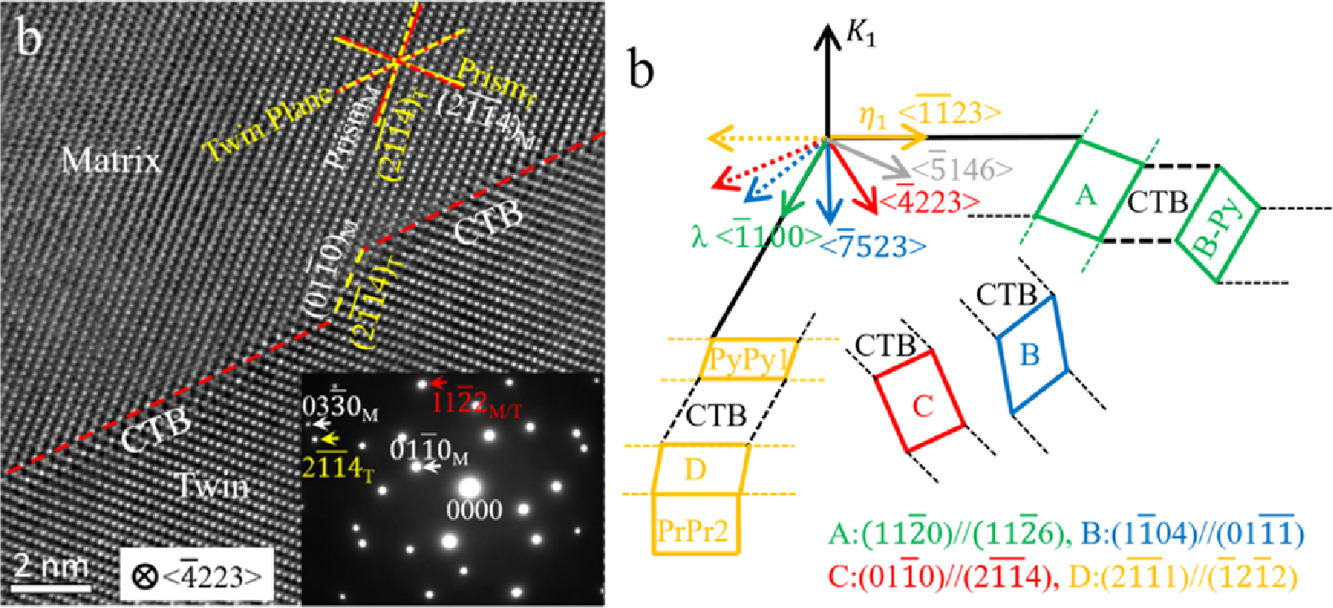
在Ti中,{11-22}<112-3>压缩孪晶可以适应c轴压缩下的大量应变。然而,与{10-12}<-1011>拉伸孪晶不同,{11-22}<112-3>压缩孪晶的结构尚未被完全表征。本研究中,我们结合了HR-TEM表征、拓扑分析和原子尺度模拟对Ti中{11-22}<112-3>孪晶多面体界面进行了研究。除了目前已知的晶面外 (CTB和B-Py),我们通过TEM首次从原子尺度沿5个晶体学方向观察到了六个新的晶面。它们分别是:(11-20)//(11-26), PrPr1, PyPy1, (2-1-11)//(-12-11), (1-104)//(01-1-1), 和 (01-10)//(2-1-14)。拓扑分析和计算结果与HRTEM结果吻合较好。研究表明:(1)观测到的面在孪晶和基体中都与低指数界面对齐 (2)低能表面能够形成扩展界面 (3)孪晶尖端处存在高能表面,这是孪晶尖端区域内面形结构总能量最低导致。这些结果不仅增进了我们对Ti中{11-22}<112-3>压缩孪晶三维结构的了解,而且验证了分子动力学方法和其中采用的Ti原子间相互作用势的有效性。这对于进一步研究{11-22}孪晶的孪晶迁移率、以及{11-22}孪晶与其他缺陷的相互作用具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116734
14. A model to unravel the beneficial contributions of trace Cu in wrought Al–Mg alloys
微量铜添加对铝镁合金变形性能增益的模型研究
S. Medrano, H. Zhao, B. Gault, F. De Geuser, C.W. Sinclair✉
C.W. Sinclair:chad.sinclair@ubc.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116734
摘要
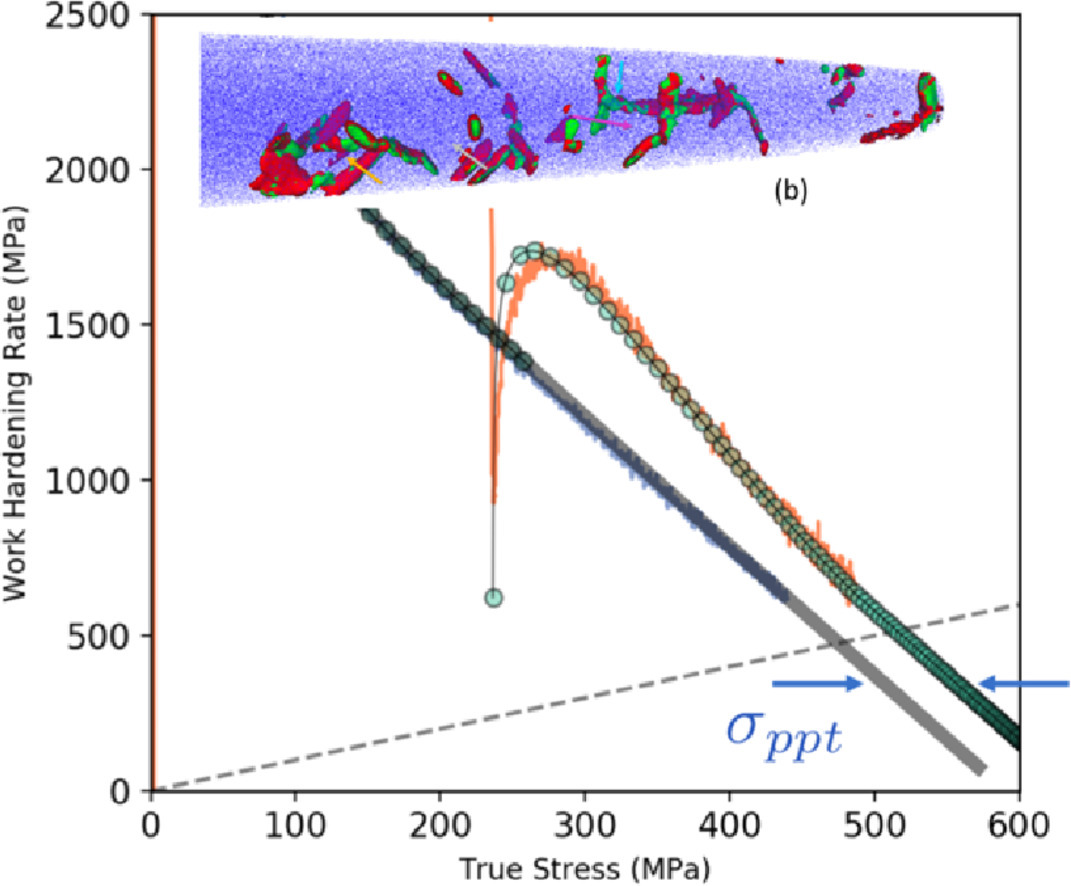
我们通过显微组织、力学性能测试结合模型对经预变形和时效的Al-3Mg-5Cu(wt .%)合金中软化和强化的贡献进行了分析。我们发现,分别单独考虑了回复和析出影响的加工硬化唯象模型可以较好地量化合金中的析出强化贡献。值得注意的是,Cu含量(在低Cu含量的情况下)、预变形水平或时效温度对合金的力学响应影响不大,这表明合金性能对于成分变化不敏感。从合金设计的角度来看,这对于合金的一些加工(如烤漆)和回收再利用是十分有利的。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116747
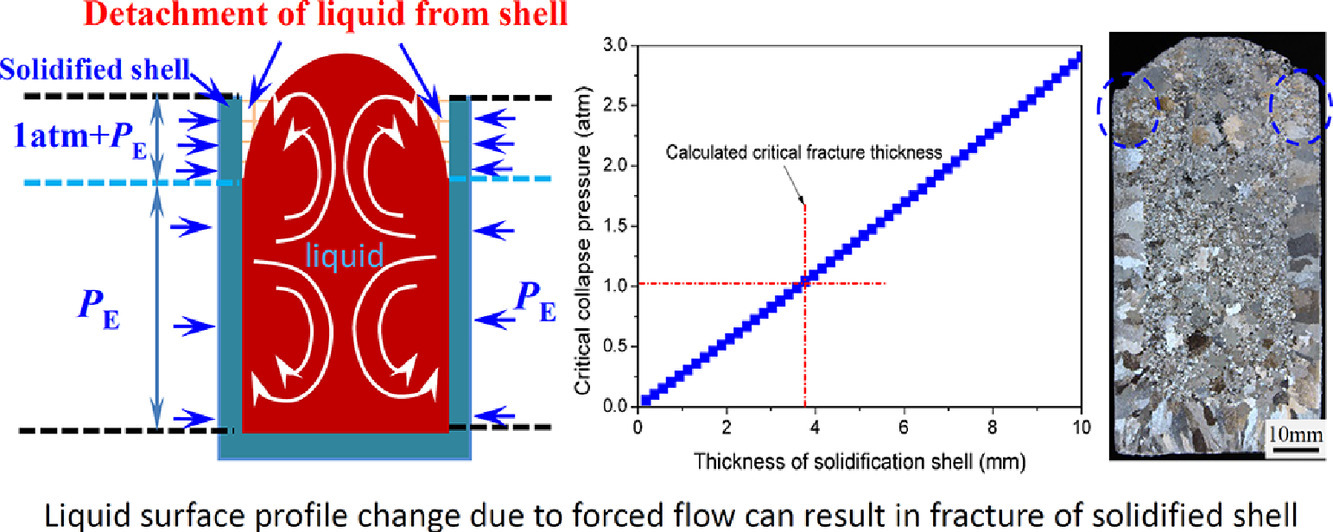
15. Revealing the mechanisms for the nucleation and formation of equiaxed grains in commercial purity aluminum by fluid-solid coupling induced by a pulsed magnetic field
脉冲磁场条件下工业纯铝中等轴晶形核长大的机理研究
J.C. Jie✉, S.P. Yue, J. Liu, D.H. StJohn, Y.B. Zhang, E.Y. Guo, T.M. Wang, T.J. Li
J.C. Jie:jiejc@dlut.edu.cn(大连理工大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116747
摘要
我们研究了工业纯铝在脉冲磁场(PMF)条件下凝固过程中晶粒组织的影响因素。结果表明,纯金属根据铸造条件的不同,会在PMF条件下以不同的形核和长大机制形成等轴晶。其中一种机制出现在PMF被应用于熔点以上时。当达到熔点时,器壁上大量形核,随后这些小晶粒被每100毫秒一次的脉冲分离。PMF产生的洛伦兹力使熔体中的晶粒在整个铸造过程中形成细化的等轴晶组织。另一种机制是,在应用PMF之前,器壁上已经形成了一层柱状晶核的壳。一旦施加了洛伦兹力,就会引起固液耦合。壳厚较薄时,这种耦合会将壳层分离;而壳厚较厚时,壳体的最上方几毫米将从器壁分离。由于晶界上的富铁液相熔点较低,分离的壳层破碎形成大块晶粒。在这种情况下,暴露的器壁将依照第一种机制产生细晶填充大块晶粒间的间隙,因此材料中将形成双峰晶粒尺寸。综上所述,在熔点以上应用PMF是细化晶粒的最佳工艺,这样可确保在整个铸造过程中形成细小的等轴晶组织。