金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.208,15 Apr. 2021(下)
2021-06-06 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文16篇,涵盖了镁合金、钛合金、高温合金、形状记忆合金、高熵合金等,国内科研单位包括西北工业大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 208 目录
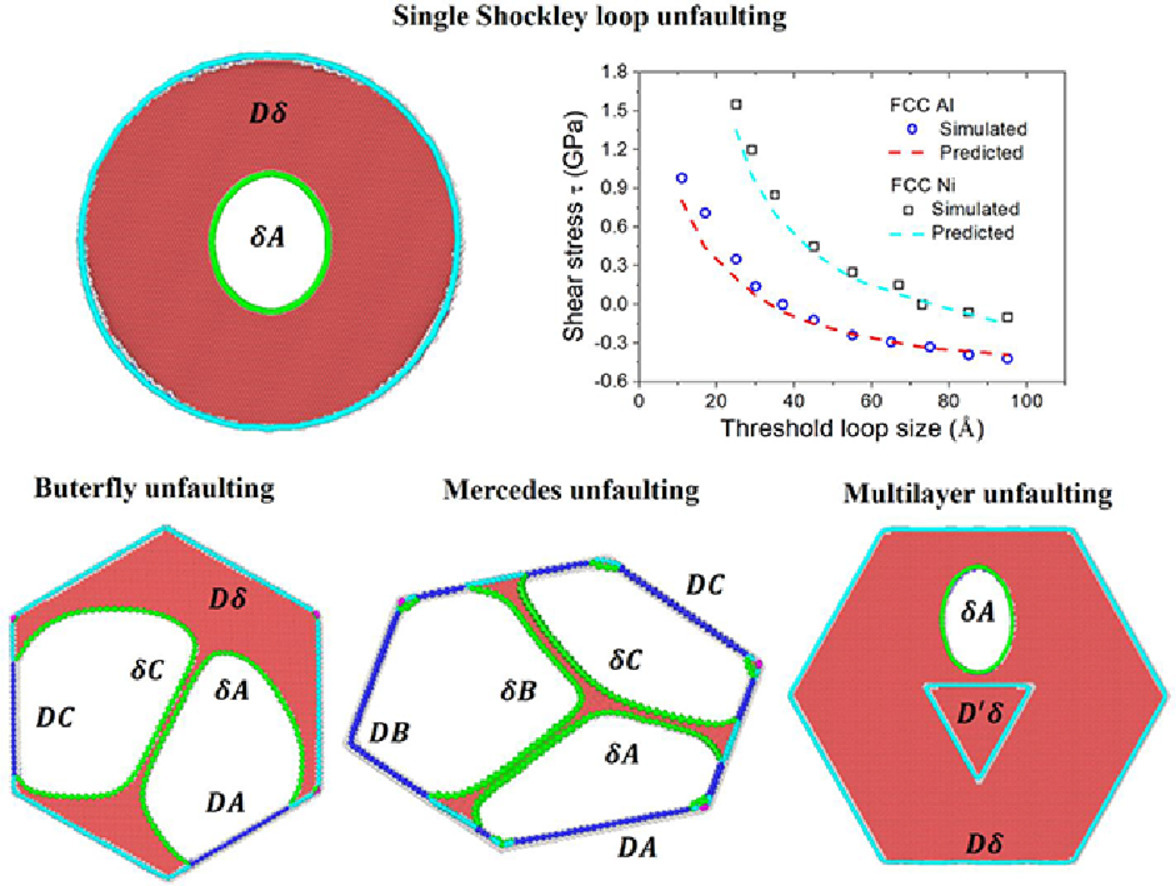
1. Comprehensive study of vacancy frank loop unfaulting: atomistic simulations and predictive model
空位Frank环脱缺陷过程的原子尺度模拟和预测
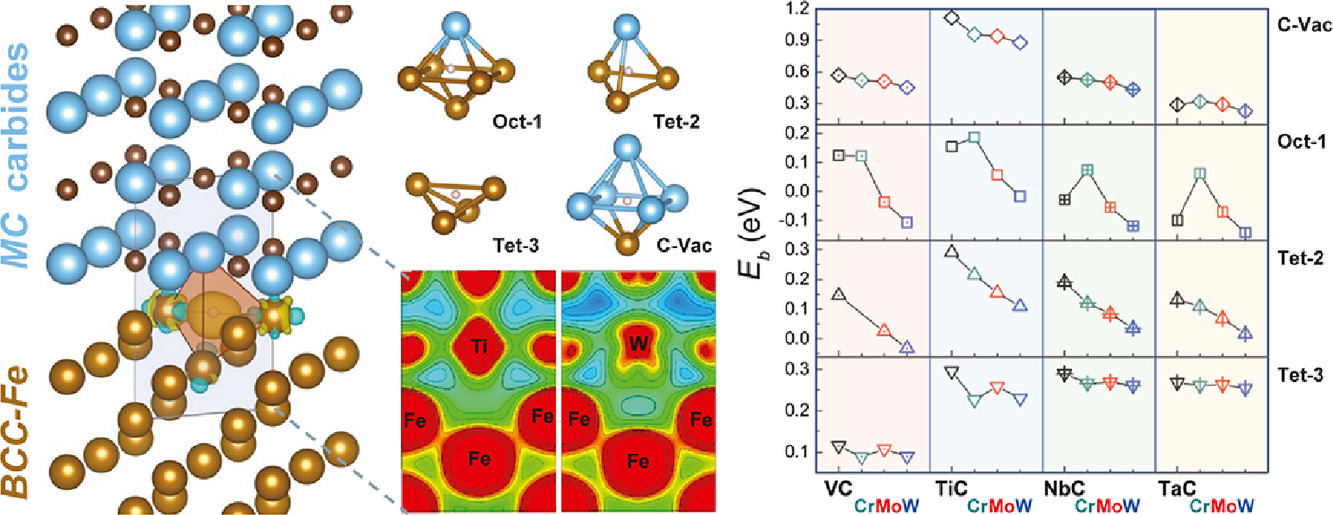
2. Atomistic insight into hydrogen trapping at MC/BCC-Fe phase boundaries: The role of local atomic environment
局部环境对MC/BCC-Fe相界捕氢能力影响的原子尺度研究
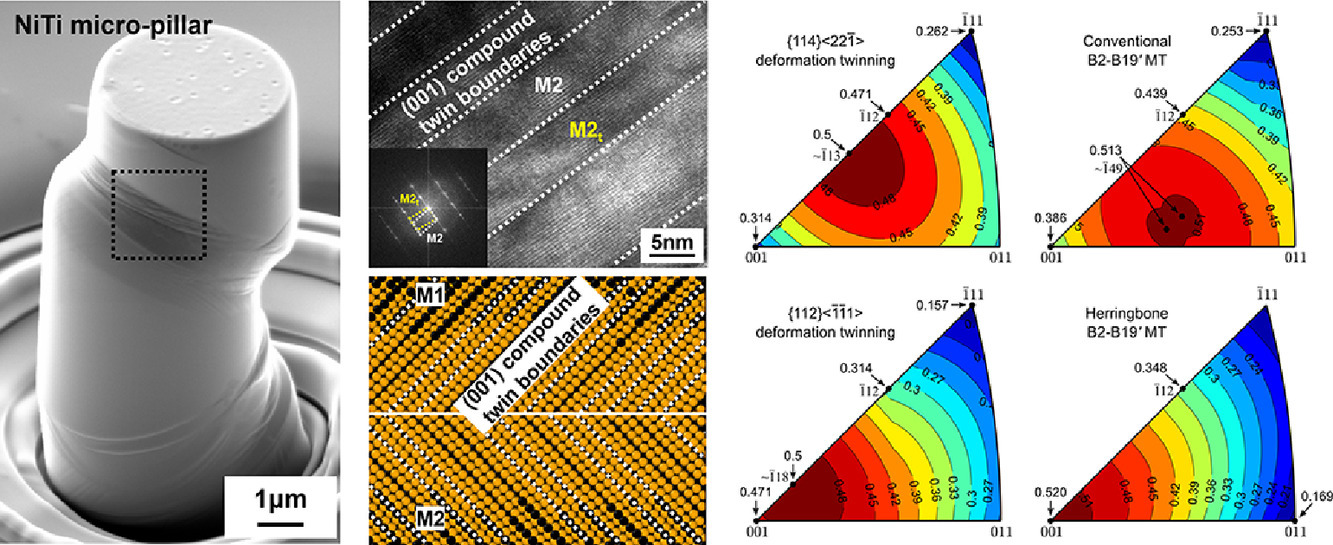
3. Orientation-dependent plastic deformation mechanisms and competition with stress-induced phase transformation in microscale NiTi
NiTi中塑性变形机制与取向的关系及其与应变诱导相变之间竞争的微观尺度研究
4. H-phase precipitation and its effects on martensitic transformation in NiTi-Hf high-temperature shape memory alloys
高温形状记忆合金中H相析出及其对马氏体相变的影响
5. Large-deformation plasticity and fracture behavior of pure lithium under various stress states
纯锂在不同应力状态下的大变形塑性和断裂行为研究
6. The role of Ti addition on the evolution and stability of γ/γ′ microstructure in a Co-30Ni-10Al-5Mo-2Ta alloy
Ti的添加对Co-30Ni-10Al-5Mo-2Ta合金中γ/γ′组织演化和稳定性的影响
7. Experimental and theoretical investigations on the phase stability and mechanical properties of Cr7Mn25Co9Ni23Cu36 high-entropy alloy
Cr7Mn25Co9Ni23Cu36高熵合金稳定性和力学性能的实验和理论研究
8. Microstructural damage behaviour of Al foams
泡沫铝的微观结构损伤行为研究
9. A crystal plasticity investigation of grain size-texture interaction in magnesium alloys
镁合金中晶粒尺寸与织构相互作用的晶体塑性模型研究
10. Grain boundary co-segregation in magnesium alloys with multiple substitutional elements
镁合金中多种置换型合金元素的晶界共偏析研究
11. A Multiscale Adhesion Model for Deposition Prediction in Laser Enhanced Nanoparticle Deposition Process
激光增强纳米颗粒沉积过程的多尺度粘附模型
12. Estimating single-crystal elastic constants of polycrystalline β metastable titanium alloy: A Bayesian inference analysis based on high energy X-ray diffraction and micromechanical modeling
通过高能X射线衍射和微观力学模型的贝叶斯分析估算多晶β亚稳钛合金的弹性常数
13. Enhanced mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of 316L stainless steel by pre-forming a gradient nanostructured surface layer and annealing
通过梯度纳米结构表面和退火处理提高316L不锈钢的力学性能和耐腐蚀性能
14. Micropillar compression deformation of single crystals of Fe3Ge with the L12 structure
L12 结构Fe3Ge单晶微柱的压缩变形行为研究
15. Improved elastocaloric cooling performance in gradient-structured NiTi alloy processed by localized laser surface annealing
通过局部激光表面退火改善梯度NiTi合金的热弹性冷却性能
16. On the cross-slip of screw dislocations in zirconium
锆中螺位错的交滑移研究
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116745
1. Comprehensive study of vacancy frank loop unfaulting: atomistic simulations and predictive model
空位Frank环脱缺陷过程的原子尺度模拟和预测
Cheng Chen✉, Jing Zhang, Jun Song✉
C. Chen:cheng.chen@nwpu.edu.cn(西北工业大学)
J.Song:jun.song2@mcgill.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116745
摘要
我们采用原子模拟结合连续介质模型对两种模型体系(Al、Ni)中通过Shockley分位错环使得空位Frank环脱缺陷的过程进行了研究。我们提出了一种普适的方法,用于构建不同的位错构型。研究表明,当封闭的Shockley位错环超过临界尺寸时,空位Frank环将发生脱缺陷,且这一临界尺寸与Frank环的尺寸无关。我们建立了连续介质模型来定量预测Shockley环的几何参数和脱缺陷临界条件。连续介质模型的预测结果与原子模拟结果高度吻合,并且我们发现,这一模型使用于单一或多个并被证明适用于包括单个或多个Shockley环的各种情况。我们的模拟可以复现实验观测到的Butterfly和Mercedes六方形貌,阐明了潜在的位错反应,并确定了其后续转变为棱柱位错环的竞争机制。综上所述,本研究提供了普适且灵活的计算工具,用于深入理解Frank环的缺陷反应和演化机制以及淬火和辐照材料中存在的二次缺陷。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116744
2. Atomistic insight into hydrogen trapping at MC/BCC-Fe phase boundaries: The role of local atomic environment
局部环境对MC/BCC-Fe相界捕氢能力影响的原子尺度研究
Boning Zhang, Jie Su, Maoqiu Wang, Zhenbao Liu, Zhigang Yang, Matthias Militzer, Hao Chen✉
H. Chen:hao.chen@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn(清华大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116744
摘要
深入理解微观组织缺陷(如晶界、相界等)对氢的捕获作用对抗氢脆(HE)材料设计至关重要。相界处的原子环境比晶界更加复杂,因此相界的氢捕获机制目前尚不清楚。本文中,我们通过系统的密度泛函理论计算(DFT)揭示了BCC铁和NaCl型碳化物(MCs)相界面处氢捕获的物理机制。研究表明,MC/BCC-Fe 相界处的氢结合能不仅与氢陷阱的局部体积膨胀有关,而且与陷阱处的局部原子环境有关。尽管有研究指出,通过晶格应变、几何体积、电荷密度等参数,可以有效预测晶界对氢的捕获,但它们无法对MC/BCC-Fe相界处的氢捕获进行量化。我们分析了相界处的电子相互作用,发现它们与氢的结合能密切相关。另一方面,氢的Bader体积可以较为普适地用于估计氢在相界处的俘获能量。本研究为从原子和电子尺度上研究组织中的氢阱提供了新的视角,对氢陷阱和抗氢脆金属设计具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116731
3. Orientation-dependent plastic deformation mechanisms and competition with stress-induced phase transformation in microscale NiTi
NiTi中塑性变形机制与取向的关系及其与应变诱导相变之间竞争的微观尺度研究
Won Seok Choi✉, Edward L. Pang, Won-Seok Ko, Hosun Jun, Hyuk Jong Bong, Christoph Kirchlechner, Dierk Raabe, Pyuck-Pa Choi✉
W.S. Choi:w.s.choi@kaist.ac.kr
P.-P. Choi:p.choi@kaist.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116731
摘要
在细微尺度上理解NiTi形状记忆合金取向对变形行为的影响对于微纳电子机械系统设计具有重要意义。然而,我们对于对NiTi形状记忆合金中各种滑移、孪晶和马氏体相变模式之间的竞争机制,以及这种竞争与取向、尺寸的关系理解尚不深入,特别是在微米级试样中。本研究中,我们对Ti-49.9at.% Ni 合金的[001]、[112]取向微柱进行了微压缩试验。TEM表征表明,微柱的塑性变形机制为{011}<100>滑移和{114}<22-1>孪晶,它们与马氏体相变相互竞争,并且这种竞争与晶体取向有关。此外,在实验和分子动力学模拟中,我们都在由细间距(001)B19’孪晶组成的人字形组织中发现了残余B19’马氏体,而不是一般在块体样品中的[011]B19’ II型孪晶。这表明实际的马氏体相变模式可能与尺寸有关。我们对压缩过程中所有常见滑移、孪晶和马氏体相变模式的Schmid因子随晶体取向的变化进行了计算,从而合理解释了取向对这些变形模式竞争的影响。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116651
4. H-phase precipitation and its effects on martensitic transformation in NiTi-Hf high-temperature shape memory alloys
高温形状记忆合金中H相析出及其对马氏体相变的影响
Taiwu Yu, Yipeng Gao, Lee Casalena, Peter Anderson,Michael Mills, Yunzhi Wang✉
Y. Wang:wang.363@osu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116651
摘要
B2母相中的析出对NiTi基高温形状记忆合金(HTSMAs)的马氏体相变起始温度Ms、温度和应力滞后、输出功、尺寸稳定性和功能疲劳等性能具有重要影响。为了理解其中的机制从而优化时效工艺和材料性能,我们系统地研究了纳米级共格析出对马氏体相变的力学和化学影响。以NiTi-Hf高温形状记忆合金为例,我们首先研究了H相析出的平衡形状和应力应变场随尺寸的变化。随后,我们定量地研究了析出相和由单一变体或多个自适应变体组成的马氏体间的弹性相互作用能。同时,我们计算了H相析出生长过程中的浓度场变化。最后,我们量化并比较了H相析出周围应力场和浓度场对Ms的影响。结果表明,应力场是长时效条件下的主要控制因素,而浓度场是短时效条件下的主要控制因素。由于模型是时效温度和时效时间的函数,因此可以通过设计合适的热处理工艺对材料的Ms进行调控。
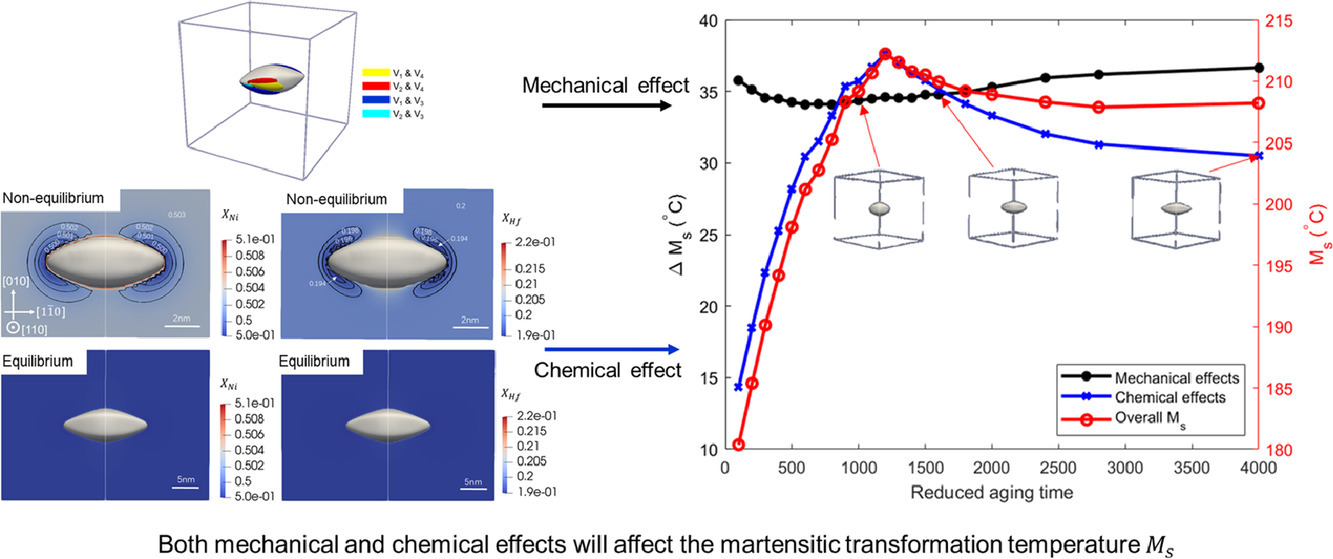
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116730
5. Large-deformation plasticity and fracture behavior of pure lithium under various stress states
纯锂在不同应力状态下的大变形塑性和断裂行为研究
Tobias Sedlatschek✉, Junhe Lian✉, Wei Li✉, Menglei Jiang,✉ Tomasz Wierzbicki✉, Martin Z. Bazant✉, Juner Zhu✉
T. Sedlatschek:tose@mit.edu
J. Lian:lianjh@mit.edu
W. Li:weili17@mit.edu
M. Jiang:mengleij@mit.edu
T. Wierzbicki:wierz@mit.edu
M.Z. Bazant:bazant@mit.edu
J. Zhu:zhujuner@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116730
摘要
虽然锂金属阳能够提高在锂电池的相关研究中受到了广泛关注,但关于纯锂的力学性能研究还远远不够。首先,现有数据大多聚焦单晶锂的微纳尺度或块体材料的宏观尺度。其次,力学实验通常为单轴测试,应力状态较为简单,或是直接使用纳米压痕。本研究的主要目的是通过在小试样上各种应力状态下的系统实验,建立能够描述纯锂力学响应特征的塑性模型。基于实验和计算结果,我们首次对不同应力状态下锂的变形和破坏机制及其塑性各向异性进行了定量的分析。为了制备五种不同的应力状态(单轴拉伸、两种半径的缺口拉伸、中心孔拉伸和简单剪切)试验所需的复杂形状试样,我们开发了一种在氩气气氛下激光切割厚锂箔的方法。我们分别在氩气和空气中进行了拉伸试验,以阐明氧化对锂强度的影响。通过对样品的组织表征,我们观察到两个主动滑移系统和交叉滑移。当试样的厚度由于局部颈缩而减少到零时,锂以一种完美的塑性方式断裂。数字图像分析(DIC)表明,虽然锂箔在平面内各向同性,但在厚度方向上具有高度各向异性。我们通过速率相关的横向各向同性模型,对实验结果进行了较好的预测。
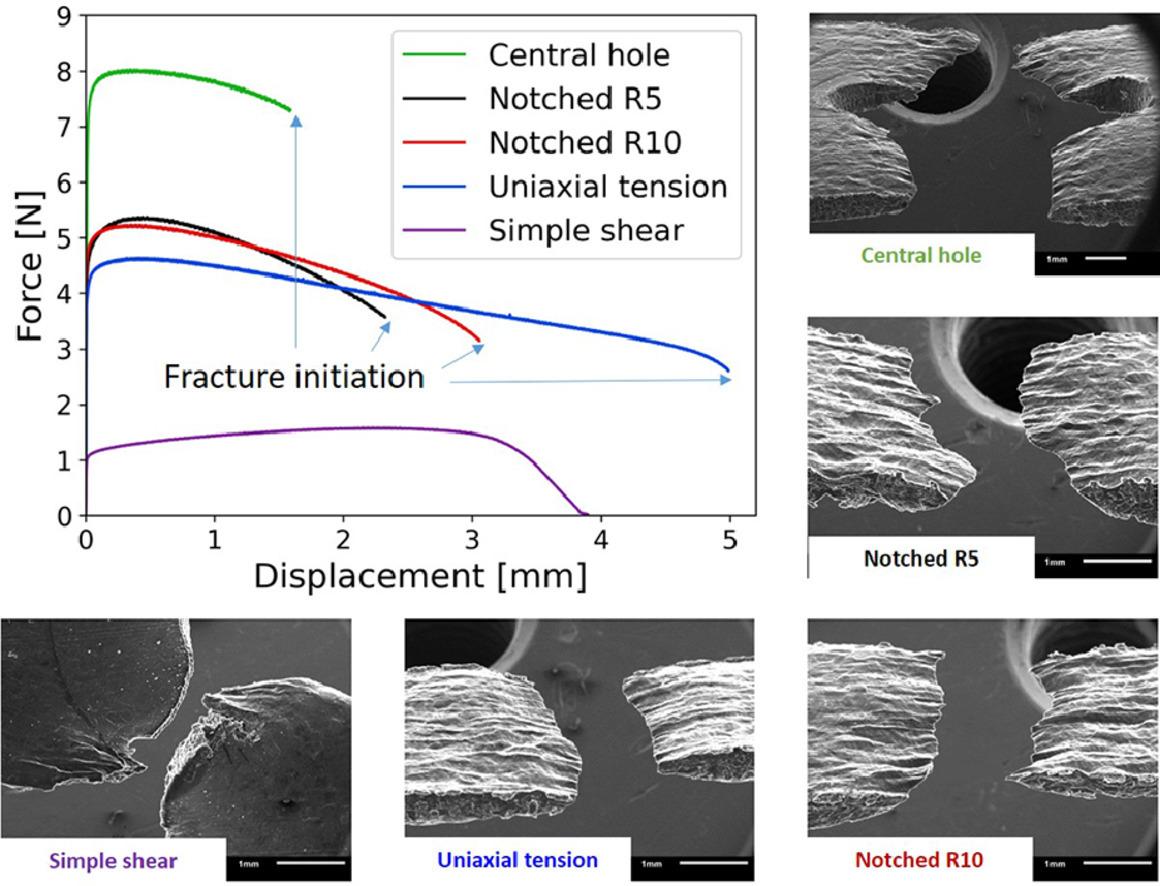
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116736
6. The role of Ti addition on the evolution and stability of γ/γ′ microstructure in a Co-30Ni-10Al-5Mo-2Ta alloy
Ti的添加对Co-30Ni-10Al-5Mo-2Ta合金中γ/γ′组织演化和稳定性的影响
Semanti Mukhopadhyay, Prafull Pandey✉, Nithin Baler, Krishanu Biswas, Surendra Kumar Makineni✉, Kamanio Chattopadhyay✉
P. Pandey:prafull1011@gmail.com
S.K. Makineni:skmakineni@iisc.ac.in
K. Chattopadhyay:kamanio@iisc.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116736
摘要
本文研究了Ti对Co-30Ni-10Al-5Mo-2Ta-xTi (x = 0, 1, 2和4 at.%) γ/γ '双相Co基高温合金的影响。经固溶(1300℃,25 h)和淬火后,组织中的γ′相在γ基体内呈细小的球形分布。当材料在900°C时效时,γ′相形貌由球型转变为立方型,同时与固溶合金相比,γ/γ′晶格失配增加。然而,这种晶格失配随Ti含量的增加而减小。通过使用原子探针对时效后的γ/γ′界面进行成分分析,我们发现Ti优先向γ′相配分。这一现象解释了4 at.% Ti合金中γ′固溶温度的上升(升至1166℃)。此外,Ti含量的增加也降低了Mo向γ′的配分。实验还观测到,在900℃和950℃时,高Ti合金γ′相粗化速率显著增加。γ′粗化的初始阶段遵循扩散控制的LSW动力学;而在粗化后期,可以观察到粒子出现团簇倾向。添加3 和 4 at.% Ti后,材料在1000℃时的高温强度提高,分别为 360和 400 MPa。
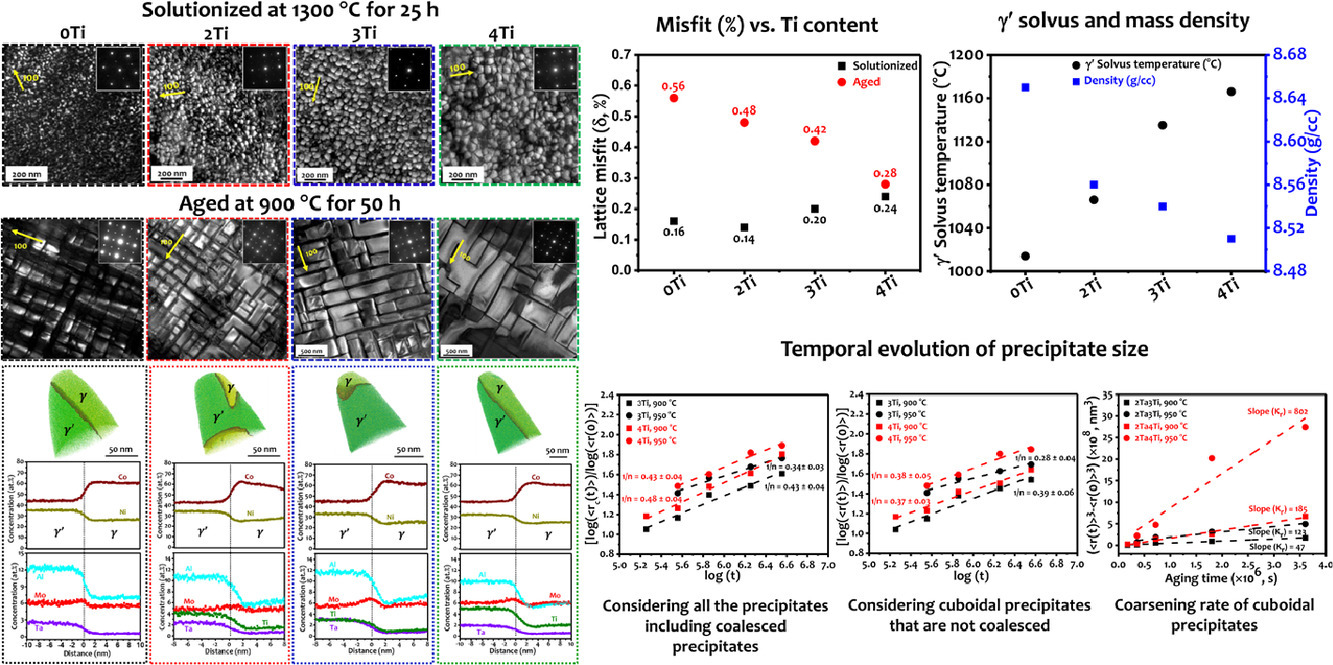
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116763
7. Experimental and theoretical investigations on the phase stability and mechanical properties of Cr7Mn25Co9Ni23Cu36 high-entropy alloy
Cr7Mn25Co9Ni23Cu36高熵合金稳定性和力学性能的实验和理论研究
Gang Qin, Ruirun Chen✉, Huahai Mao, Yan Yan, Xiaojie Li, Stephan Schönecker, Levente Vitos, Xiaoqing Li
R. Chen:ruirunchen@hit.edu.cn(哈尔滨工业大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116763
摘要
深入理解结构材料中组成相的形成机制及其对力学性能的影响十分重要。在此,我们研究了Cr7Mn25Co9Ni23Cu36(原子百分比)高熵合金在热处理过程中的相分解、二次相形成、以及组织变化对拉伸性能的影响。研究表明,经800℃/ 2h和600℃/ 8h热处理后,组织中形成sigma相,而当材料经600℃及以下热处理2h时后,未发现sigma相。我们将实验观测到的相组成与相图进行了比较,并基于热力学和动力学对实验现象进行了分析。第一性原理计算表明,合金分解成两相比单一固溶相在能量上更低,这可能是相分解的主要原因。
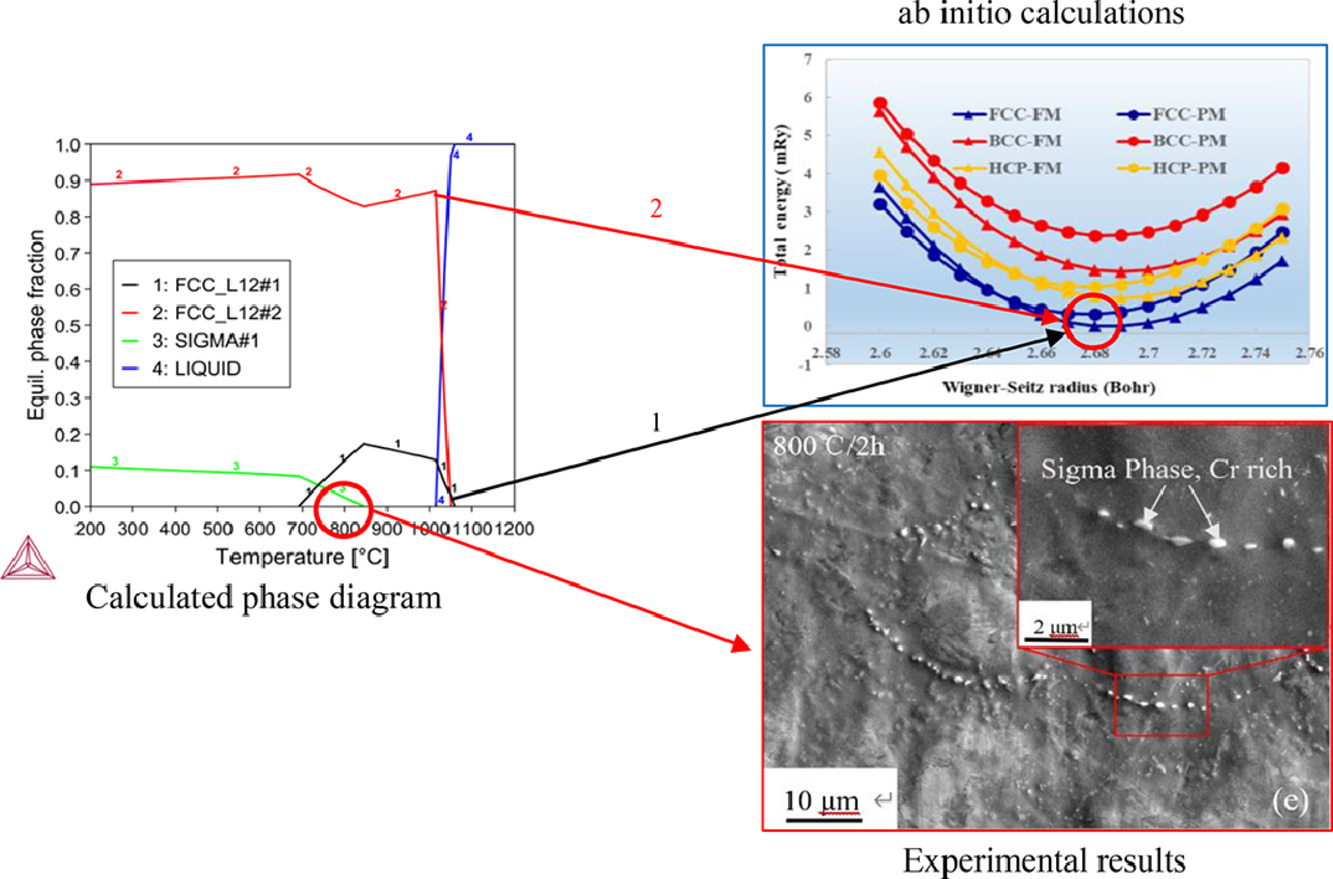
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116739
8. Microstructural damage behaviour of Al foams
泡沫铝的微观结构损伤行为研究
Jutta Luksch, Thomas Bleistein, Kristian Koenig, Jérôme Adrien, Eric Maire, Anne Jung✉
A. Jung:anne.jung@mx.uni-saarland.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116739
摘要
微观非均匀材料(比如泡沫金属)的性能与组织具有密切关系。金属泡沫的宏观性能取决于孔隙几何形状、支撑网络的几何形状和组织特征。由于支撑网络的晶粒组织与块体材料不同,因此对局部网络进行微拉伸试验尤为重要。关于泡沫铝的已有文献指出,这种微观力学特征的测试方差很大。泡沫金属铸造过程中产生的网络中的微孔和夹杂是这种不稳定性的可能原因。在本研究中,我们采用了异位和原位微拉伸试验,对单一网格杆微拉伸试验中力学性能方差产生的原因进行了研究。我们通过原位拉伸试验结合高分辨率X射线计算重构阐明了泡沫铝微观组织的破坏机理。我们通过异位拉伸和低分辨率X射线计算重构对大量样品进行了分析,进一步从统计层面对结果进行了验证。研究表明,微观孔隙和夹杂是引起泡沫铝微观力学性能差异的主要原因。
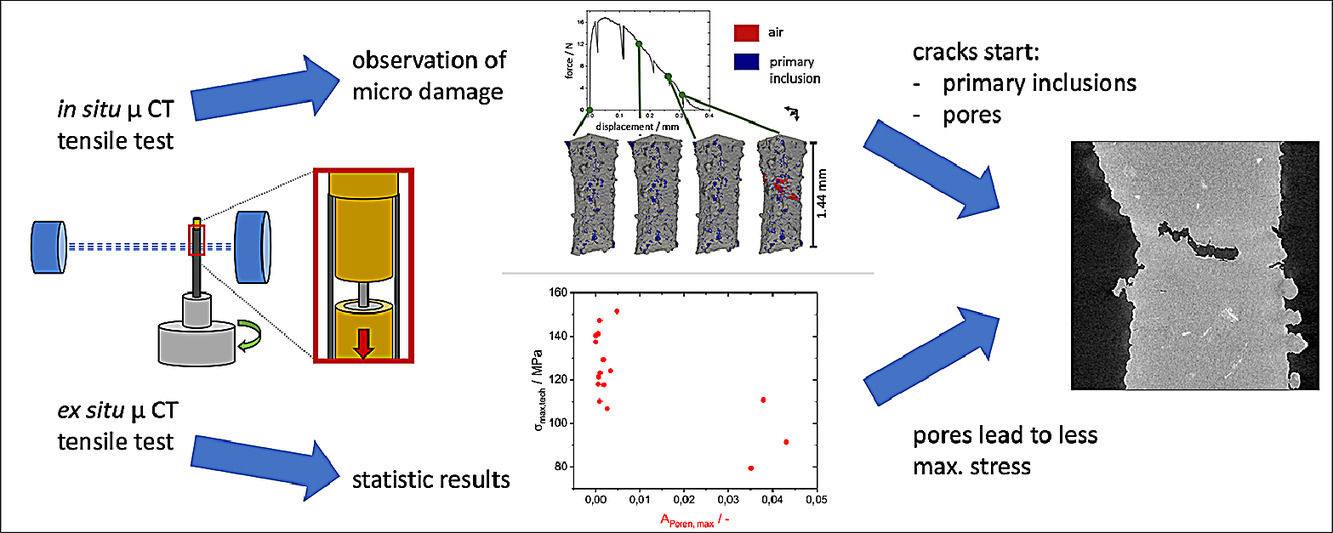
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116743
9. A crystal plasticity investigation of grain size-texture interaction in magnesium alloys
镁合金中晶粒尺寸与织构相互作用的晶体塑性模型研究
Babak Ravaji✉, Shailendra P. Joshi
B. Ravaji:bravaji@uh.edu
S.P. Joshi:shailendra@uh.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116743
摘要
本文研究了镁(Mg)的微观结构与性能之间的联系,重点探讨了晶粒尺寸、织构和加载取向之间的相互作用。我们在单晶塑性模拟框架中引入了带有激活阈值的Hall-Petch模型,从而在较宽的晶粒尺寸和织构范围内对材料组织进行模拟。模拟得到的宏观趋势与实验结果一致,揭示了组织间的协同调控对材料宏观力学行为的影响。模拟结果表明,尽管孪晶的Hall-Petch系数小于非基滑移,但随着晶粒细化,扩展孪晶减少。晶粒细化和织构弱化通常会降低材料的塑性各向异性和拉压不对称性,但降低的程度受加载取向影响。以上研究结果初步揭示了织构和晶粒尺寸在镁合金组织损伤行为中的作用
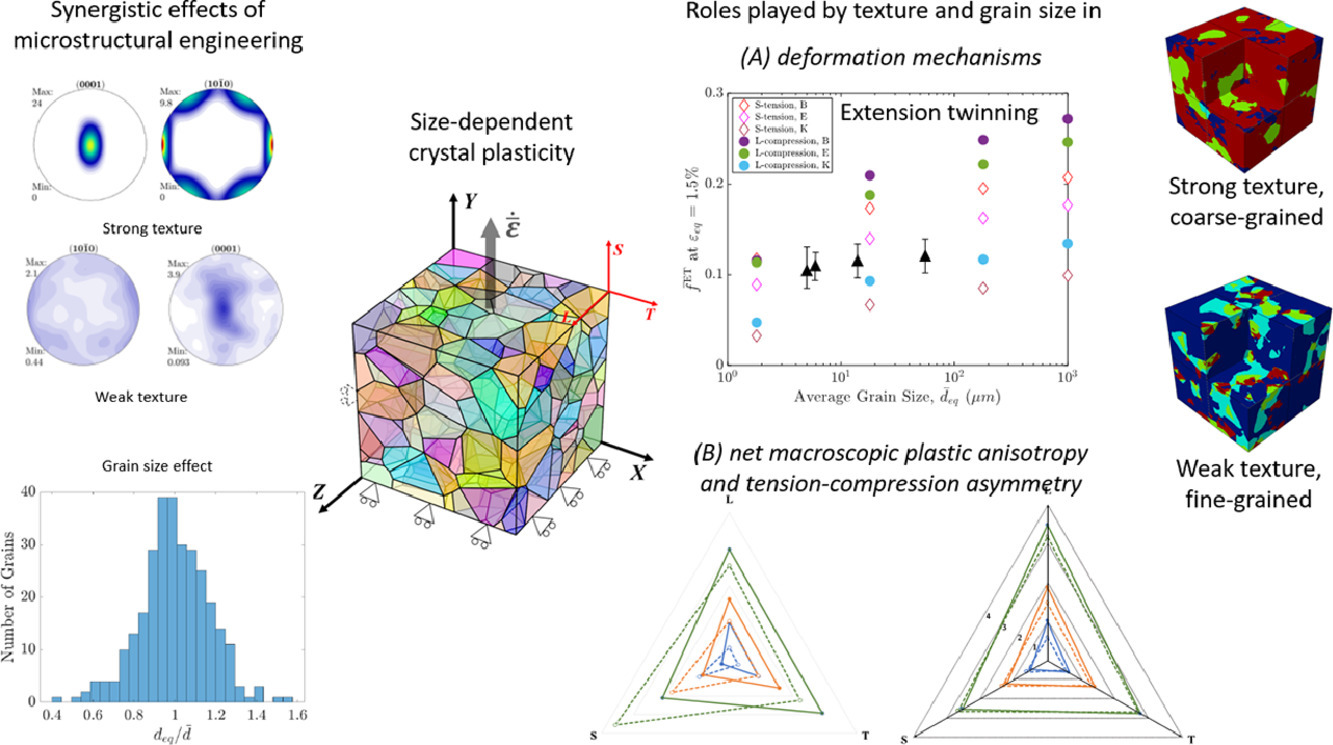
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116749
10. Grain boundary co-segregation in magnesium alloys with multiple substitutional elements
镁合金中多种置换型合金元素的晶界共偏析研究
Risheng Pei✉, Yongchun Zou, Daqing Wei, Talal Al-Samman
R. Pei:pei@imm.rwth-aachen.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116749
摘要
在镁合金添加合金元素可以改变材料再结晶过程中的织构,且这种调控作用于合金元素的固溶度和析出行为有关。在已有文献理论的基础上,我们希望更深入地理解合金元素添加引起的再结晶阻力与退火织构间的联系。本研究中,我们对一种含有多种置换型元素的Mg-3Al-1Zn-0.3Ca(wt.%)镁合金进行了形变和退火,研究了溶质元素浓度对偏聚和析出行为的影响。我们重点研究了溶质元素向晶界的偏聚,发现偏析的类型和水平在控制生长行为中起着关键作用,能够限制基织构晶粒的择优生长。通过有针对性的热处理调控溶质元素浓度,从而调控第二相析出和晶界偏聚,可以成为一种有效的合金设计策略。
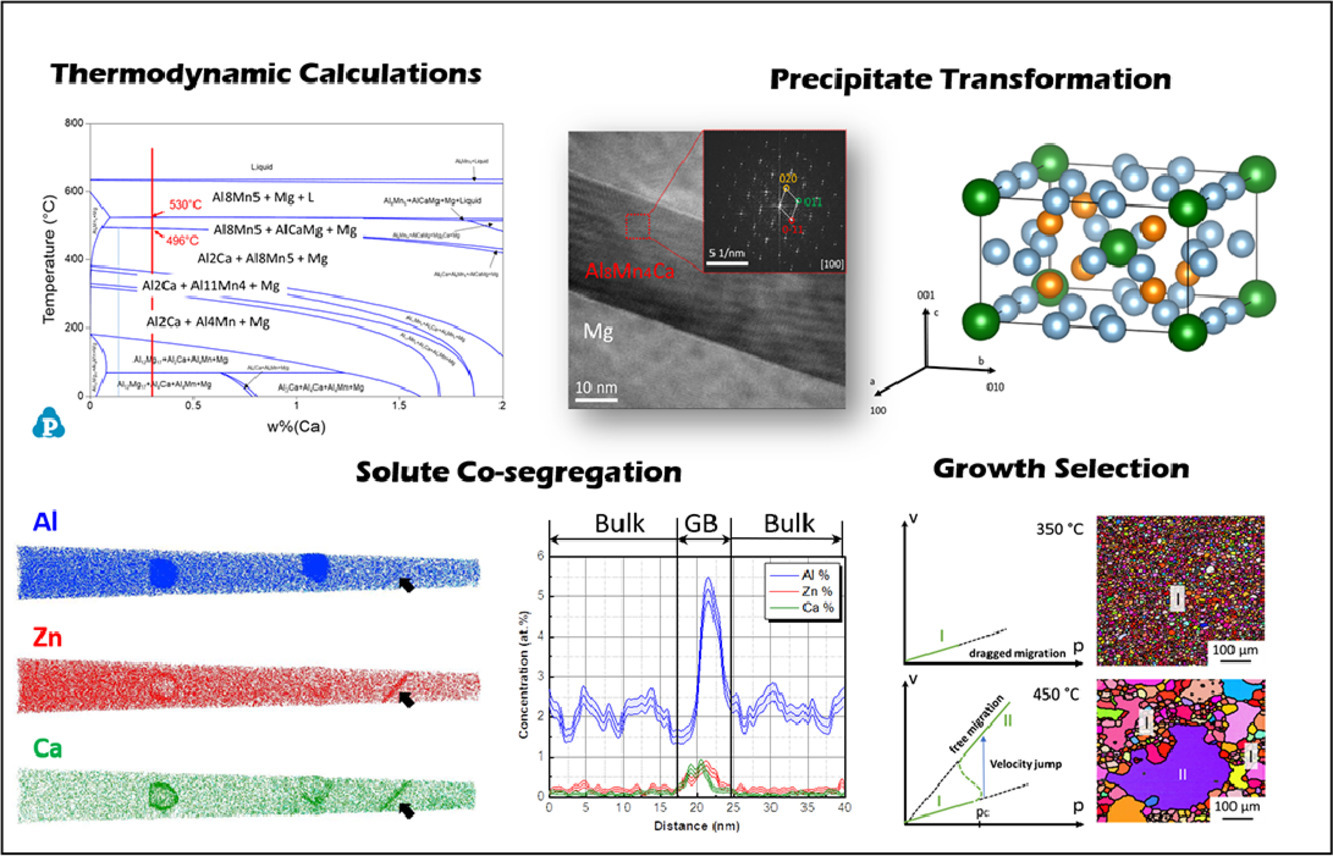
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116740
11. A Multiscale Adhesion Model for Deposition Prediction in Laser Enhanced Nanoparticle Deposition Process
激光增强纳米颗粒沉积过程的多尺度粘附模型
Ji-Hyeon Song, Sung-Hoon Ahn, Yan Wang✉
S.-H. Ahn:ahnsh@snu.ac.kr
Y. Wang:yan-wang@gatech.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116740
摘要
纳米颗粒沉积工艺有潜力在不使用有毒溶剂的情况下实现大面积快速打印,而激光加工已成为提高沉积性能的辅助方法。然而,目前没有有效的工艺模型来预测沉积的质量。在本研究中,我们提出了一个多尺度粘着模型来评估激光增强纳米颗粒沉积过程的沉积性能。模型考虑了激光辐照引起的热能和粒子动能,基于颗粒大小、颗粒速度、激光功率等方面有效地预测了沉积效应。此外,我们通过分子动力学模拟,预测了纳米粒子与温度和尺寸相关的弹塑性特性。我们通过实验对模型预测进行了验证。
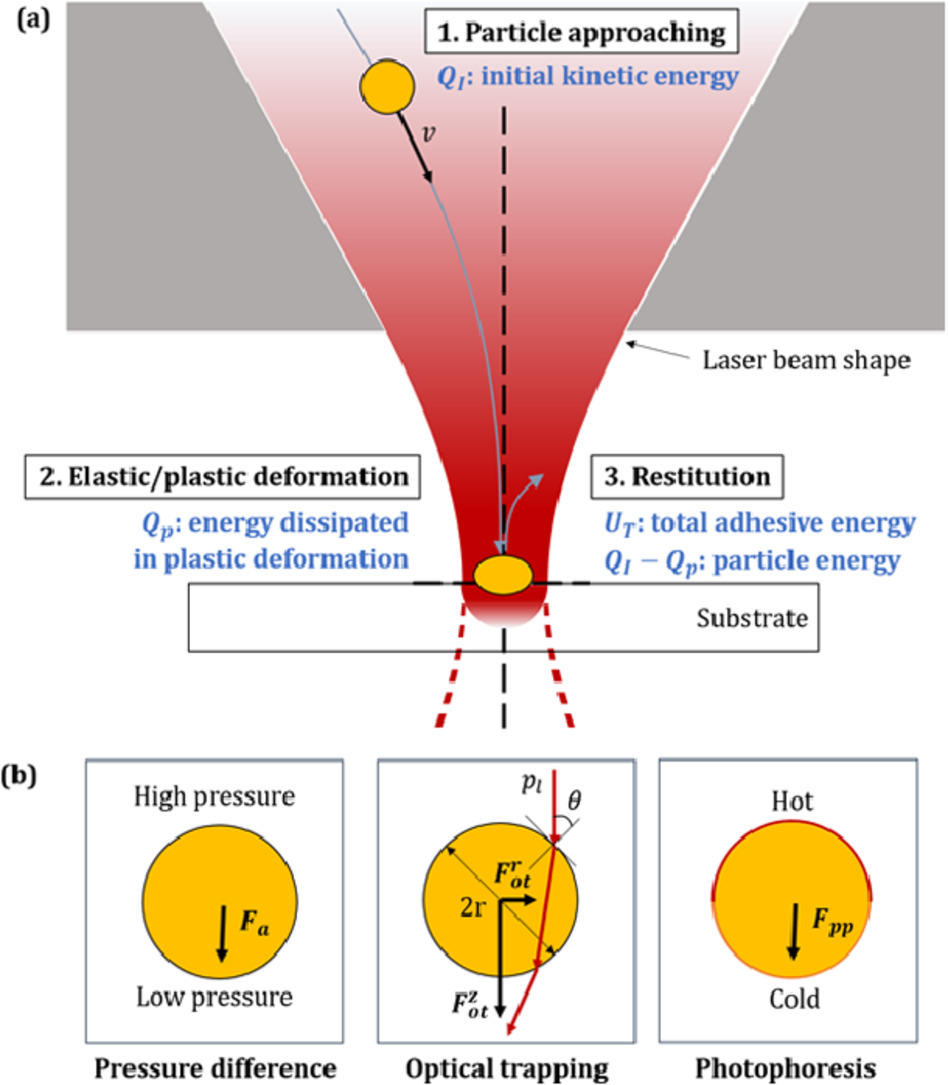
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116762
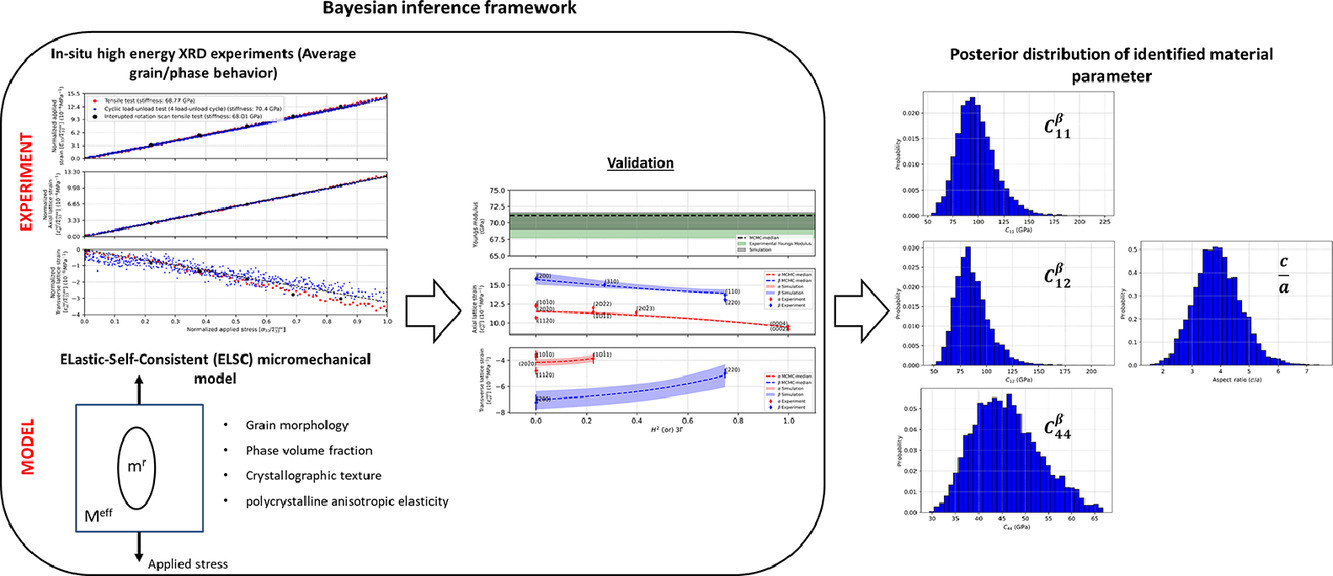
12. Estimating single-crystal elastic constants of polycrystalline β metastable titanium alloy: A Bayesian inference analysis based on high energy X-ray diffraction and micromechanical modeling
通过高能X射线衍射和微观力学模型的贝叶斯分析估算多晶β亚稳钛合金的弹性常数
Ravi Raj Purohit Purushottam Raj Purohit✉, Thiebaud Richetona,c, Stephane Berbenni, Lionel Germain, Nathalie Gey, Thomas Connolley, Olivier Castelnaue
R.R.P. Purushottam Raj Purohit:ravi-raj-purohit.purushottam-raj-purohit@univ-lorraine.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116762
摘要
我们以两相近β相铸态钛合金(Ti-10V-2Fe-3Al,或Ti-1023)为例,说明了用贝叶斯模型识别单晶弹性常数(SEC)的可行性。我们采用了高能同步X射线衍射(HE-XRD)对样品在弹性区拉伸过程中不同取向晶粒的晶格应变演化进行了研究,并用弹性自洽(ELSC)均匀模型对样品的形变和晶粒变形进行了估计。我们用贝叶斯模型对XRD数据和微观力学模拟进行了进一步分析,系统地研究了不同材料参数(晶体结构、形貌、相分数等)对微观力学模型的影响以及XRD数据偏差对β相SEC常数分析的影响。在此基础上,我们推导了Ti-1023合金β相(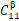 ,
,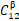 ,
,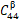 )的三个立方弹性常数及误差。我们发现,在文献中未引起重视的ELSC模型的晶粒长宽比,对SEC的分析具有重要影响。贝叶斯模型对非球形晶粒(长宽比~3.8±0.8)具有高置信率:
)的三个立方弹性常数及误差。我们发现,在文献中未引起重视的ELSC模型的晶粒长宽比,对SEC的分析具有重要影响。贝叶斯模型对非球形晶粒(长宽比~3.8±0.8)具有高置信率: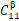 = 92.6±19.1GPa,
= 92.6±19.1GPa, 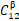 = 82.5±16.3GPa,
= 82.5±16.3GPa, 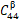 = 43.5±7.1GPa。而采用贝叶斯模型确定的剪切模量如下:μ′=
= 43.5±7.1GPa。而采用贝叶斯模型确定的剪切模量如下:μ′=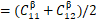 介于1-3GPa之间,μ″=
介于1-3GPa之间,μ″=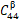 约7 GPa,而体积模量
约7 GPa,而体积模量 的不确定性更大,为17 ~ 24 GPa。
的不确定性更大,为17 ~ 24 GPa。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116773
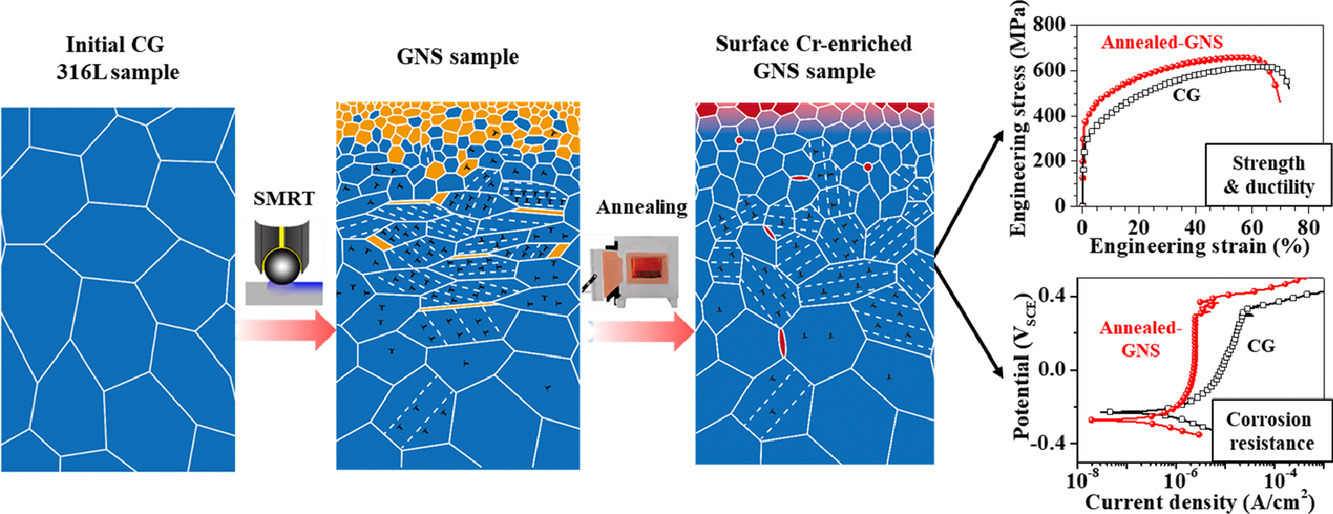
13.Enhanced mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of 316L stainless steel by pre-forming a gradient nanostructured surface layer and annealing
通过梯度纳米结构表面和退火处理提高316L不锈钢的力学性能和耐腐蚀性能
Y.B. Lei, Z.B. Wang✉, B. Zhang, Z.P. Luo, J. Lu, K. Lu
Z.B. Wang:zbwang@imr.ac.cn(沈阳金属所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116773
摘要
不锈钢具有优异的机械性能和耐腐蚀性能,在航空航天等行业中具有广阔的应用前景。本研究中,我们采用表面机械球磨方法(SMRT)制备了表面纳米梯度结构(GNS)316L不锈钢,随后将材料在700℃退火。拉伸试验表明,退火后的SMRT试样的具有优异的强塑性耦合,且GNS层的晶粒尺寸和硬度保持稳定。此外,退火后的GNS表层有明显的Cr富集,使得材料的耐腐蚀性能显著增强。我们对退火后SMRT试样的组织、成分和相变进行了表征,并分析了它们对形变和腐蚀性能的影响。以上研究为采用简单的热机械方法制备具有优异机械性能和耐蚀性的不锈钢材料提供了新的思路。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116779
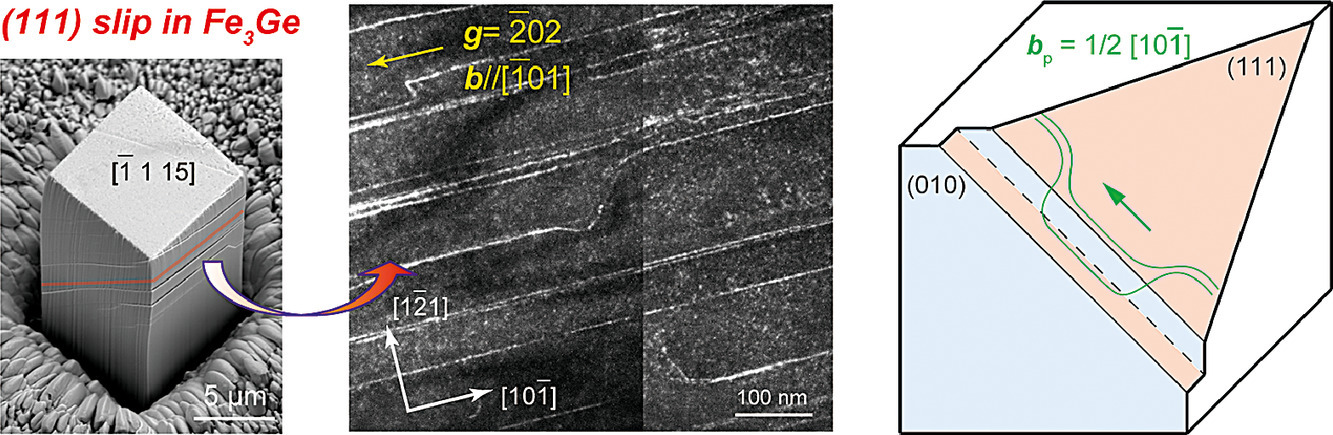
14. Micropillar compression deformation of single crystals of Fe3Ge with the L12 structure
L12 结构Fe3Ge单晶微柱的压缩变形行为研究
Zhenghao Chen✉, Haruyuki Inui
Z. Chen:chen.zhenghao.6e@kyoto-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116779
摘要
我们通过微柱压缩试验研究了L12结构Fe3Ge单晶室温下塑性变形行为与晶体取向的关系。除(010)面上的滑移外,我们首次在Fe3Ge中观察到了(111)面上的滑移。我们通过外推法对(111)[101]滑移的临界剪切应力(CRSS)进行了估算,~240MPa,几乎是(010)[101]滑移估算值(~ 40MPa)的6倍。在(010)和(111)面上,b=[10-1]的超晶格位错均被证实为APB(anti-phase boundary,即反相界)型,这与之前预测的(111)面上的SISF(超晶格内秉层错)方案不同,我们认为这是由于APB不稳定所致。虽然超晶格位错在(010)上滑移时没有任何的优先排列方向,但在(111)上滑移时则可观察到其沿螺型排列。研究表明,这一现象由于热激活交叉滑移形成Kear-Wilsdorf锁导致的,这也是许多其他L12化合物(如Ni3Al)中出现异常屈服的原因。我们基于实验结果和对Fe3Ge中一些重要的变形特征进行了讨论。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116741
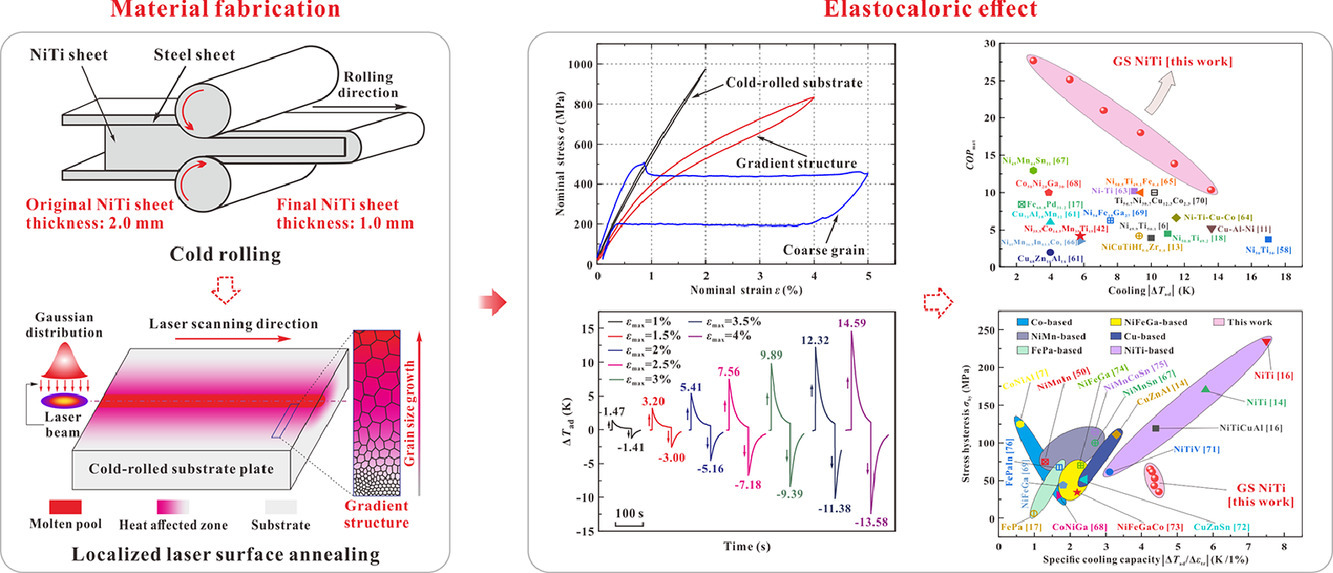
15. Improved elastocaloric cooling performance in gradient-structured NiTi alloy processed by localized laser surface annealing
通过局部激光表面退火改善梯度NiTi合金的热弹性冷却性能
Junyu Chen, Leilei Xing, Gang Fang✉, Liping Lei, Wei Liu
G. Fang:fangg@tsinghua.edu.cn (清华大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116741
摘要
材料的COPmat系数,即热效应与能量耗散的比值,是固态制冷剂的一个关键性能指标。而材料的固有滞回特性会显著降低这一系数。在本研究中,我们采用了局部激光表面退火的方法,在强烈变形的基底上制备了一种具有梯度结构(晶粒尺寸梯度从~ 10 nm到~ 3500nm)的低迟滞NiTi制冷剂,用于热弹性冷却。与均匀粗晶NiTi相比,具有梯度结构(GS)的NiTi在绝热温度变化(ΔTad)相当的情况下,COPmat提高了约83%,并且材料的使用下限温度从283 K降至了243 K。此外,梯度NiTi具有大比冷(~ 4.5 K/1%)、窄应力滞后(~ 60 MPa)和高力学性能(高强度、高延展性和高稳定性)的特点,这使得梯度NiTi在制冷性能和效率方面优于大多数热弹性材料。此外,梯度结构具有良好的协同强化效果和均匀的相变模式,因此显著提高了NiTi的冷却性能和力学性能。以上研究为弹性热交换材料的性能优化提供了一种新的设计策略,并显示了梯度NiTi在固态冷却方面的巨大工业潜力。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116764
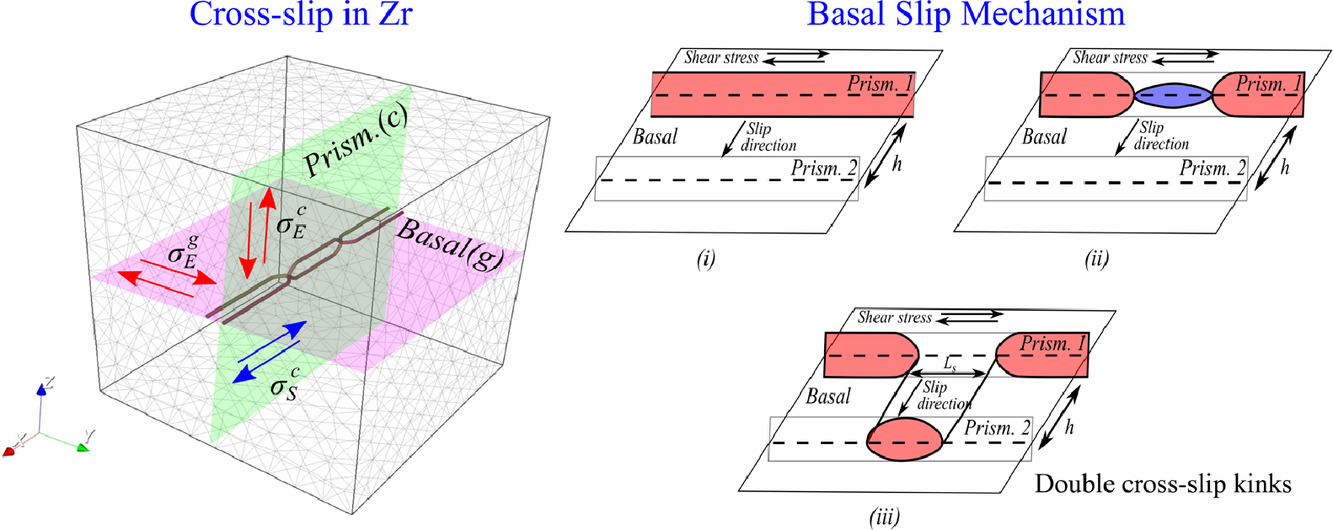
16. On the cross-slip of screw dislocations in zirconium
锆中螺位错的交滑移研究
Yang Li✉, Sabyasachi Chatterjee, Enrique Martinez, Nasr Ghoniem✉, Giacomo Po✉
Y. Li:yangli0401@ucla.edu
N. Ghoniem:ghoniem@ucla.edu
G. Po:gpo@miami.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116764
摘要
我们基于离散位错动力学和分位错的显式表示,建立了锆的交滑移模型。研究发现,基底-棱柱交滑移在能量上总是有利的。相应的无应力激活焓约为0.5eV,临界形核长度接近于零。主平面上的Escaig应力是影响活化焓的主要因素。相比之下,棱柱-基底交滑移只有当共轭平面上的Schmid应力大于1GPa时才会被激活,激活焓大于5 eV。我们认为Zr中〈a〉型螺旋位错的基滑移是借助双交叉滑移过程中形成的扭结对及其侧向迁移发生的。我们通过将模型预测的临界解析剪应力(CRSS)随温度和〈a〉型基滑移运动的变化与实验观测进行比较,对模型的有效性进行了验证。