金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.201, 1 Aug. 2021(上)
2021-06-06 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文14篇,涵盖了高熵合金、奥氏体钢等,国内科研单位包括西北工业大学、清华大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 201 目录
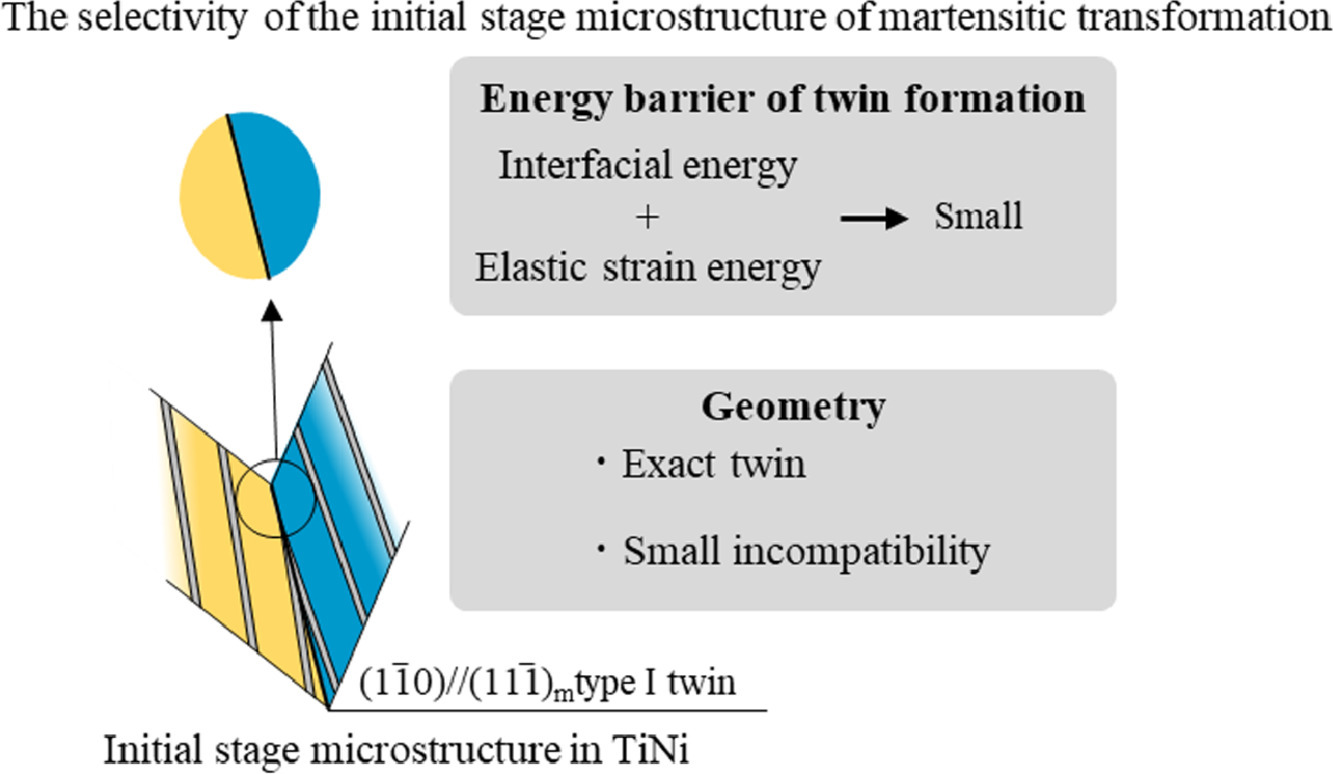
1. Martensitic transformation induced dislocation walls in Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10 high-entropy alloy
Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10高熵合金中马氏体相变诱发位错墙的形成
2. Investigation of the orientation relationship between nano-sized G-phase precipitates and austenite with scanning nano-beam electron diffraction using a pixelated detector
采用具有像素化检测器的扫描纳米束电子衍射研究G相纳米析出与奥氏体的取向关系
3. Remelting induced fully-equiaxed microstructures with anomalous eutectics in the additive manufactured Ni32Co30Cr10Fe10Al18 eutectic high-entropy alloy
增材制造Ni32Co30Cr10Fe10Al18共晶高熵合金中具有异常共晶的重熔诱导全等轴微观组织
4. Effect of alloying elements on the hydrogen diffusion and trapping in high entropy alloys
合金元素对高熵合金中氢扩散和捕获的影响
5. Nanoparticle enabled high performance high modulus steels
纳米颗粒使高性能高模量钢成为可能
6. A statistical model of irradiation hardening induced by non-periodic irradiation defects
非周期辐照缺陷诱导辐照硬化的统计模型
7. Lattice distortion in selective laser melting (SLM)-manufactured unstable β-type Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al alloy analyzed by high-precision X-ray diffractometry
用高精度X射线衍射仪分析选择性激光熔化(SLM)制造的不稳定β型Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al合金的晶格畸变
8. Towards controlling intrinsic heat treatment of maraging steel during laser directed energy deposition
在激光直接能量沉积过程中控制马氏体时效钢的本征热处理
9. Work hardening discrepancy designing to strengthening gradient nanotwinned Cu
加工硬化差异化设计强化梯度纳米孪晶Cu
10. The detrimental effect of elemental contaminants when using B additions to improve the creep properties of a Ni-based superalloy
B添加改善Ni基高温合金蠕变性能时,元素污染物的有害影响
11. A universal configurational entropy metric for high-entropy materials
高熵材料的通用构型熵度量
12. Reducing functional fatigue, transition stress and hysteresis of NiTi micropillars by one-step overstressed plastic deformation
通过一步超应力塑性变形降低NiTi微柱的功能性疲劳、相变应力和滞后
13. Bulk nanostructured Al-Si alloy with remarkable improvement in strength and ductility
强度和塑性显著提高的块体纳米结构Al-Si合金
14. Enhanced ductility of as-quenched martensite by highly stable nano-sized austenite
高稳定纳米奥氏体提高淬火态马氏体的塑性
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113929
1. Martensitic transformation induced dislocation walls in Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10 high-entropy alloy
Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10高熵合金中马氏体相变诱发位错墙的形成
L. Qi, X.D. Huang, A.P. Zhang, H.W. Chen✉, J.F. Nie✉
H. W. Chen: hwchen@cqu.edu.cn 重庆大学
J. F. Nie: jianfeng.nie@monash.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113929
摘要
利用像差校正扫描透射电镜在原子尺度上对Fe42Mn38Co10Cr10 (at.%)冷变形高熵合金中两种迄今未被报道的位错墙进行了表征。两种位错墙均位于两个平行并置的马氏体片层间的界面上,尽管它们分别由全30°混合或全90°刃型肖克利部分位错构成。在这两种位错墙内,两组不同的肖克利部分位错具有大小相同但符号相反的伯氏矢量,并在六角晶格的连续基面上交替排列。包含这种致密位错墙的界面通过各种位错-界面的相互作用,可以改善应变硬化和塑性协调。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113930
2. Investigation of the orientation relationship between nano-sized G-phase precipitates and austenite with scanning nano-beam electron diffraction using a pixelated detector
采用具有像素化检测器的扫描纳米束电子衍射研究G相纳米析出与奥氏体的取向关系
Niels Cautaerts✉, Edgar F. Rauch, Jiwon Jeong, Gerhard Dehm, Christian H. Liebscher
Niels Cautaerts: n.cautaerts@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113930
摘要
采用具有像素化探测器的扫描纳米束电子衍射,研究了辐照诱导的纳米G相(M6Ni16Si7)与奥氏体基体的取向关系。利用该探测器,由细小G相粒子产生的微弱衍射斑可以同时分解为强矩阵反射。采用两阶段模板匹配方案对衍射图形进行分析,即先对基体进行索引,然后在减去基体对衍射图形的贡献后对析出相进行索引。结果表明,G相与奥氏体呈一定的取向关系,这是面心立方(FCC)到体心立方(BCC)转变的特征。本研究表明,具有像素化探测器的纳米束电子衍射技术可以相对轻松地研究其他材料体系中具有复杂晶体结构的纳米析出相的取向关系。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113952
3. Remelting induced fully-equiaxed microstructures with anomalous eutectics in the additive manufactured Ni32Co30Cr10Fe10Al18 eutectic high-entropy alloy
增材制造Ni32Co30Cr10Fe10Al18共晶高熵合金中具有异常共晶的重熔诱导全等轴微观组织
Kexuan Zhou, Junjie Li✉, Qingfeng Wu, Zhilin Zhang, Zhijun Wang✉, Jincheng Wang
Junjie Li: lijunjie@nwpu.edu.cn 西北工业大学
Zhijun Wang: zhjwang@nwpu.edu.cn 西北工业大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113952
摘要
在合金的增材制造中,通常会获得外延生长的粗大柱状晶粒,从而造成各向异性的力学性能甚至热撕裂裂纹的形成。在本研究中,我们提出了一种新的方法,即在增材制造Ni32Co30Cr10Fe10Al18共晶高熵合金中,通过重熔诱导柱状晶向等轴晶转变,从而促进全等轴晶微观组织的形成。与传统铸态和其他打印态的共晶高熵合金相比,我们的工作展示了具有优异的强度和塑性组合的各向同性力学性能。这一新发现可应用于其他共晶体系的增材制造,以调控等轴组织并优化性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113957
4. Effect of alloying elements on the hydrogen diffusion and trapping in high entropy alloys
合金元素对高熵合金中氢扩散和捕获的影响
Sara Correa Marques, Amanda Ventura Castilho, Dilson S. dos Santos✉
Dilson S. dos Santos: dilson@metalmat.ufrj.br
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113957
摘要
研究了合金元素浓度对Fe20Mn20Ni20Co20Cr20和Fe22Mn40Ni30Co6Cr2两种高熵合金中氢扩散率和捕获率的影响。从两种合金的气体渗透试验中得到,氢扩散率为温度的函数(300-550°C)。在两种面心立方合金中均观察到S型行为,遵循菲克第二定律。等原子和非等原子合金的扩散系数分别为D=4.3χ10-7exp()和D=2.8χ10-8exp()。第一性原理模拟结果表明,扩散系数的差异主要是由于Cr含量的降低,Cr在固溶状态下会与氢产生强烈的交互作用。通过对高熵合金和传统钢在Cr含量上的比较,进一步加强了这一分析。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113954
5. Nanoparticle enabled high performance high modulus steels
纳米颗粒使高性能高模量钢成为可能
Shiqi Zheng, Rosalía Rementeria, Wenbin Kan, Mingjie Xu, Jin Huang, Yu Huang, Xiaoqing Pan, Diran Apelian, Yongfeng Liang, Junpin Lin, Marcos Perez, Xiaochun Li✉
Xiaochun Li: xcli@seas.ucla.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113954
摘要
在此,我们提出了一种新的概念,使用低体积分数的纳米颗粒对Fe-Ti-B熔体进行纳米化处理,用于制备新型高性能高模量钢(HMS)。研究了纳米处理后的Fe-Ti-B HMS的微观组织。纳米处理的HMS由细小的TiB2颗粒和出乎意料的超细Fe2B片层组成。由于固有的脆性效应,传统上认为Fe2B相在炼钢过程中是有害的,但本研究表明,有害的Fe2B相可以成功地转变为有利相。纳米处理后的HMS的抗拉强度明显高于常规制备的HMS(950 MPa vs. 510 MPa),同时保持了高的杨氏模量、低的密度和高的塑性。这一新概念有效地证明了在不改变凝固速率的情况下,使用纳米粒子成功地细化了Fe-Ti-B体系的结构。这克服了实现提高机械性能与主流应用制造之间的两难困境,并使刚性HMS能够用于实际应用的轻量化。本文提出了一种在合金熔体中纳米颗粒诱导纳米级溶质富集的新机制,为金属制备提供了新的途径。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113959
6. A statistical model of irradiation hardening induced by non-periodic irradiation defects
非周期辐照缺陷诱导辐照硬化的统计模型
Wei Cui, Yinan Cui✉, Wei Liu✉
Yinan Cui: cyn@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn 清华大学
Wei Liu: liuw@mail.tsinghua.edu.cn 清华大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113959
摘要
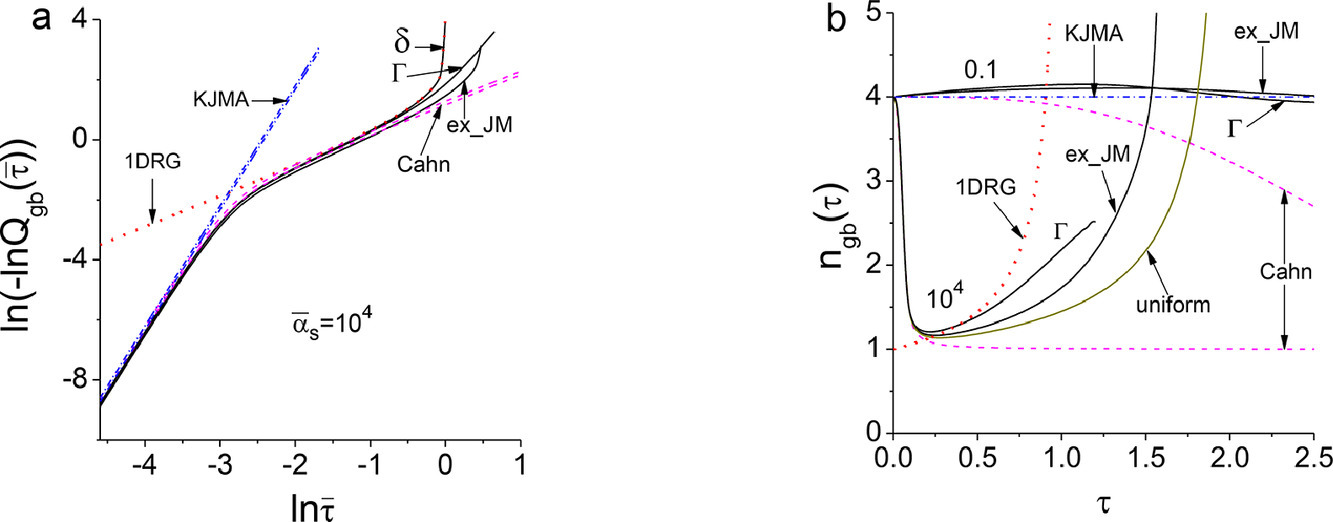
由于辐照硬化模型在核反应堆设计和服役寿命预测中的重要作用,人们为发展辐照硬化模型付出了大量的努力。大多数模型都是基于位错线张力近似,假设有周期性的辐照缺陷排列。随机分布效应通常也从完全确定性的角度考虑,如著名的Bacon-Kocks-Scattergood模型。与以往的研究不同,本研究旨在通过系统地粗化位错与非周期辐照缺陷之间的交互作用机制,建立统计辐照硬化模型。通过解析推导得到了克服辐照缺陷势垒的临界切应力的累积分布函数,并将其集中到二维蒙特卡罗模型中,用于预测辐照材料的力学响应。预测结果与三维离散位错动力学结果和实验数据吻合得很好。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113953
7. Lattice distortion in selective laser melting (SLM)-manufactured unstable β-type Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al alloy analyzed by high-precision X-ray diffractometry
用高精度X射线衍射仪分析选择性激光熔化(SLM)制造的不稳定β型Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al合金的晶格畸变
Aya Takase✉, Takuya Ishimoto, Ryoya Suganuma, Takayoshi Nakano✉
Aya Takase: aya.takase@mat.eng.osaka-u.ac.jp
Takayoshi Nakano: nakano@mat.eng.osaka-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113953
摘要
通过高精度X射线衍射(XRD)分析,首次观察到选择性激光熔化(SLM)制备的不稳定β型Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al中的特殊晶格畸变。经SLM处理后,Ti-15Mo-5Zr-3Al由体心立方结构转变为体心四方结构;c轴比a轴短0.63%。XRD分析表明,试样表面的拉伸残余应力为210±12 MPa。数值模拟表明,SLM过程中存在快速冷却,这可能导致残余应力的产生。通过对部分释放应力的SLM试样和残余应力可忽略的电子束熔铸试样进行比较,发现SLM中快速冷却引起的残余应力导致了晶格畸变。这一发现与之前认为残余应力改变晶格参数而不产生晶格畸变的认识不一样。这项研究为SLM特有的超快冷速和不稳定相共同产生的晶格畸变提供了新的见解。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113973
8. Towards controlling intrinsic heat treatment of maraging steel during laser directed energy deposition
在激光直接能量沉积过程中控制马氏体时效钢的本征热处理
Sasan Amirabdollahian, Faraz Deirmina✉, Luke Harris, Raveendra Siriki, Massimo Pellizzari, Paolo Bosetti, Alberto Molinari✉
Faraz Deirmina: Faraz.deirmina@sandvik.com
Alberto Molinari: Alberto.molinari@unitn.it
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113973
摘要
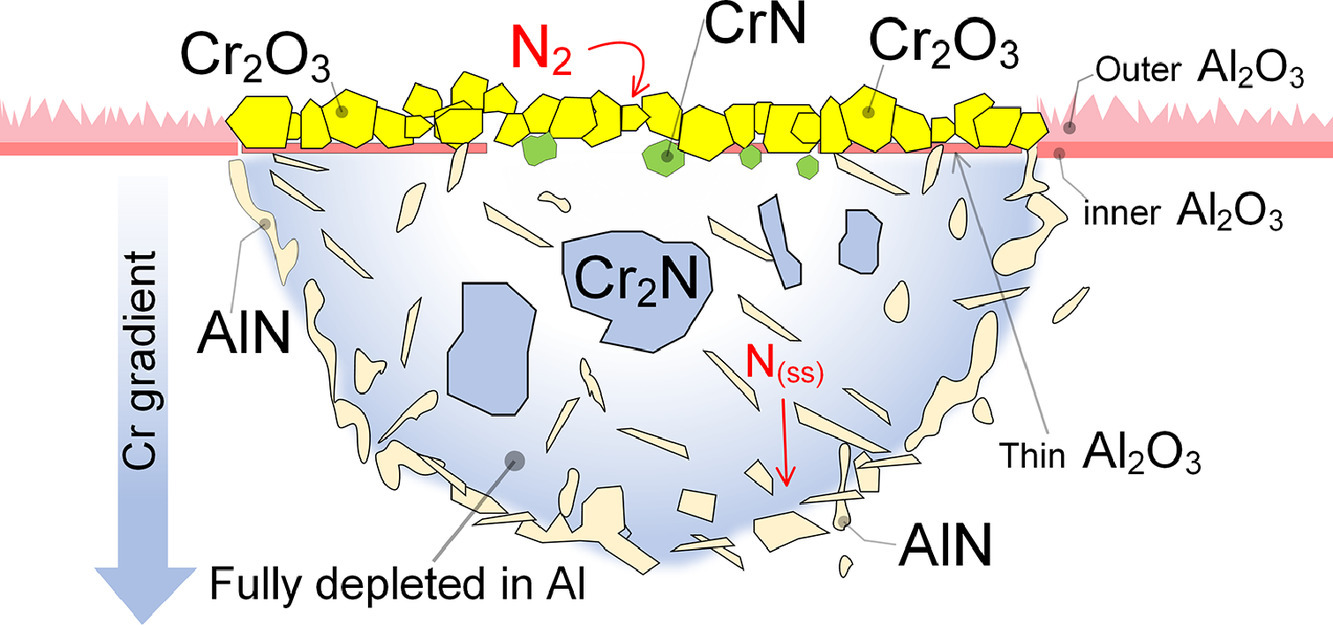
研究了马氏体时效钢粉末在激光直接能量沉积(L-DED)过程中的本征热处理(IHT)。模拟了构筑过程中每一层的热历史,以评估层间暂停对材料经历的最高和最低温度的影响。最低温度随层间停顿而降低,增强了奥氏体向马氏体的转变,从而触发了在随后的层间沉积过程中金属间化合物的析出。随后,制备不同层间停顿的试样,研究了沿构筑方向的硬度分布、抗压强度和微观组织,并与时效曲线进行比较。结果与模拟结果一致,并表明本征热处理可以避免构筑后热处理。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113975
9. Work hardening discrepancy designing to strengthening gradient nanotwinned Cu
加工硬化差异化设计强化梯度纳米孪晶Cu
Tao Wan, Zhao Cheng, Linfeng Bu, Lei Lu✉
Lei Lu: llu@imr.ac.cn 沈阳材料科学国家(联合)实验室
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113975
摘要
本研究通过固定表面硬组分,改变中心层的软组分,以研究夹层梯度纳米孪晶(GNT)铜的力学行为。我们发现,随着构件加工硬化差值的增加,GNT Cu的强度和加工硬化同时增加,与独立构件相比会产生更好的强度-塑性协同效应。力学性能的优化是应变离域化、弹塑性转变时间延长和应变梯度增大的结果,这些因素在界面处诱发了更多的几何必须位错(GNDs)。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113971
10. The detrimental effect of elemental contaminants when using B additions to improve the creep properties of a Ni-based superalloy
B添加改善Ni基高温合金蠕变性能时,元素污染物的有害影响
Martin Detrois✉, Zongrui Pei, Tao Liu, Jonathan D. Poplawsky, Michael C. Gao, Paul D. Jablonski, Jeffrey A. Hawk
Martin Detrois: martin.detrois@netl.doe.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113971
摘要
利用先进的表征技术和第一性原理模拟方法,研究了在不同Si含量下使用B改善Ni基高温合金蠕变性能时Si污染的影响。Si的存在缓解了B沿晶界偏析对蠕变性能的积极影响,Si也表现出类似的偏析倾向。采用密度泛函理论,通过计算晶界解理能进行了验证。Si降低了晶界结合力,抵消了B的积极作用。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113974
11. A universal configurational entropy metric for high-entropy materials
高熵材料的通用构型熵度量
Olivia F. Dippo, Kenneth S. Vecchio✉
Kenneth S. Vecchio: kvecchio@eng.ucsd.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113974
摘要
近年来,高熵材料变得越来越复杂,超越了基于构型熵计算的简单固溶体,也超越了先前建立的对于高、中和低熵的度量。先前的度量标准是基于特定金属的熔化熵和单原子气体的内能的近似,因此不适用于其他材料。本文提出了一种普遍适用于晶体材料的新型熵度量,从简单的固溶高熵合金到具有复杂晶体结构和多个亚晶格的高熵材料。此外,本文还讨论了复杂晶体结构中构型熵的计算方法。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113958
12. Reducing functional fatigue, transition stress and hysteresis of NiTi micropillars by one-step overstressed plastic deformation
通过一步超应力塑性变形降低NiTi微柱的功能性疲劳、相变应力和滞后
Kangjie Chu, Qingping Sun✉
Qingping Sun: meqpsun@ust.hk 香港科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113958
摘要
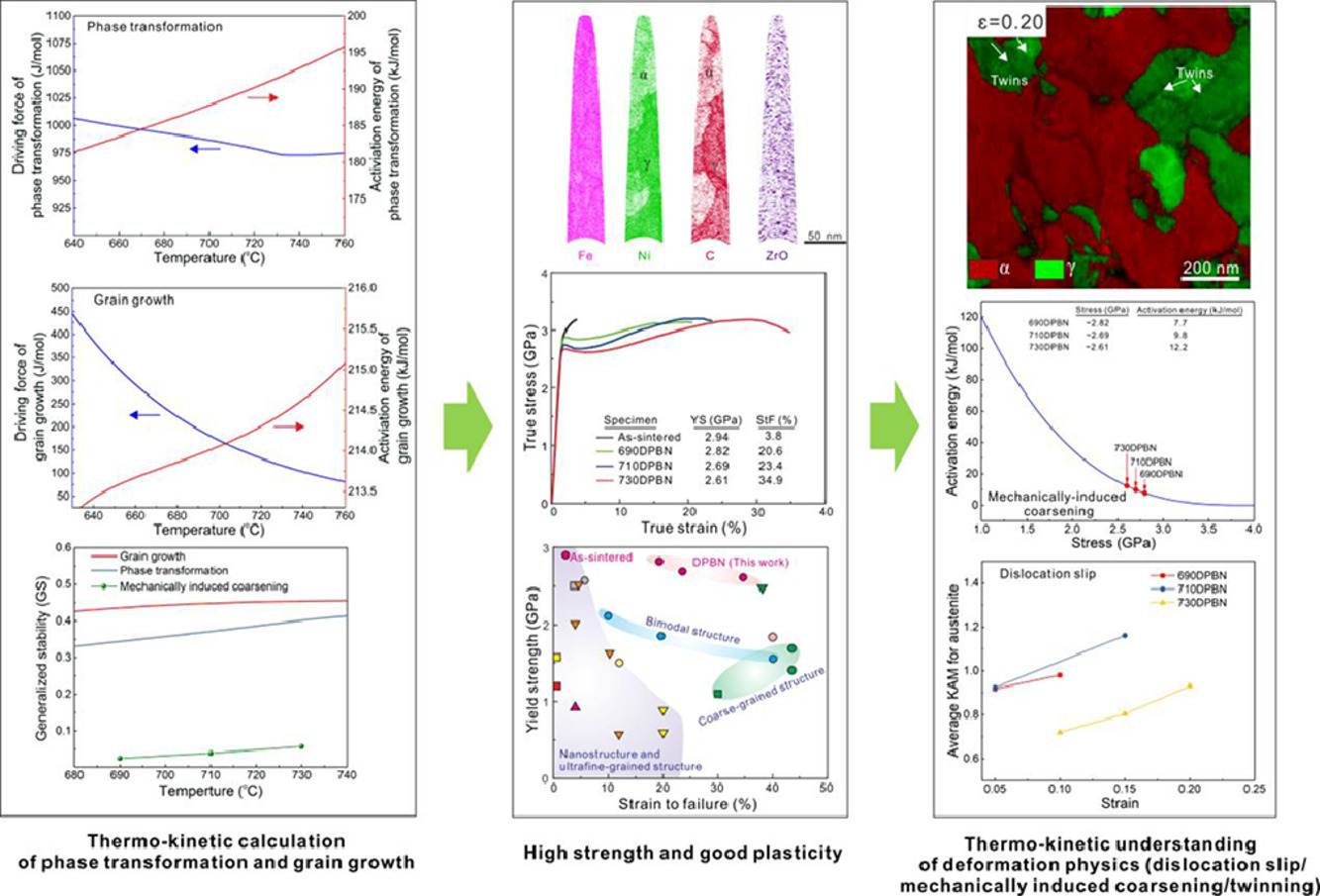
研究了一次超应力压缩塑性变形对多晶NiTi功能性疲劳的影响。立方形的微柱在1.8 GPa条件下进行一次塑性变形,残余应变为3.5%,然后在1 GPa条件下进行106次循环压缩。与初始微柱相比,塑性变形微柱的总残余应变、相变应力和滞后回线面积分别减小了74%、52%和67%。显微组织分析表明,在一次塑性变形过程中,所观察到的变化来源于饱和位错结构和残余纳米马氏体。前者抑制了后续循环相变中位错的进一步形成,从而提高了循环稳定性,而后者通过产生的残余应力和直接的马氏体生长降低了整体相变应力和滞后损耗。该方法简单有效地降低了用于弹热制冷机的NiTi合金的功能性疲劳,提高了NiTi的冷却性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113970
13. Bulk nanostructured Al-Si alloy with remarkable improvement in strength and ductility
强度和塑性显著提高的块体纳米结构Al-Si合金
Maowen Liu, Ruixiao Zheng✉, Wenlong Xiao✉, Jin Li, Guodong Li, Qiuming Peng, Chaoli Ma
Ruixiao Zheng: zhengruixiao@buaa.edu.cn 北京航空航天大学
Wenlong Xiao: wlxiao@buaa.edu.cn 北京航空航天大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113970
摘要
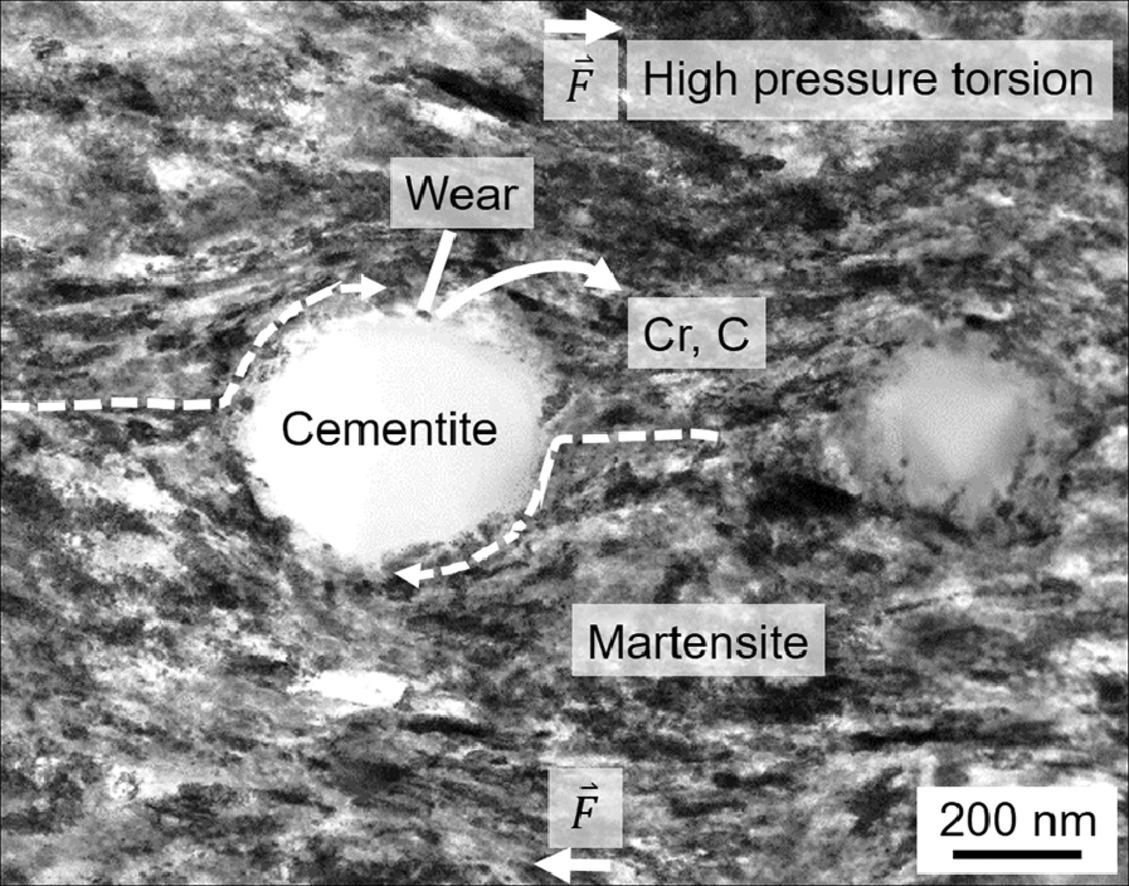
对具有低溶合金元素的金属材料进行微观组织细化一直是一项艰巨的任务。我们提出了一种新的两步法来实现这一目标,该方法已成功地应用于亚共晶Al-Si合金。首先在超高等静压下通过固溶处理制备Al-Si单相合金,然后进行高压扭转,首次获得块体纳米结构亚共晶Al-Si合金。超细的Al晶粒、Si纳米颗粒、浓缩的Si溶质和位错对屈服强度有很大的贡献。同时,通过将Si细化到纳米尺度,避免了普通Al-Si合金中微米级Si相的脆性断裂,显著提高了合金的塑性。因此,纳米结构Al-Si合金表现出403 MPa的高屈服强度和32%的总延伸率。这项工作为实现具有低溶组分的块体纳米结构合金提供了一个有效的途径。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 201, 1 Aug. 2021, 113955
14. Enhanced ductility of as-quenched martensite by highly stable nano-sized austenite
高稳定纳米奥氏体提高淬火态马氏体的塑性
Ji Hoon Kim✉, Guiyoung Gu, Minseo Koo, Eun-Young Kim, Jae-Sang Lee, Dong-Woo Suh
Ji Hoon Kim: kjh8027@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113955
摘要
奥氏体是提高先进高强钢拉伸性能的关键。在本研究中,利用包括富Mn渗碳体和铁素体基体的化学非均质初始组织,在淬火马氏体中形成了纳米尺寸的奥氏体颗粒。富Mn渗碳体在奥氏体化过程中转变为纳米奥氏体,冷却至室温后仍有相当数量的奥氏体保留。奥氏体颗粒具有特殊的稳定性,这不能完全解释为Mn的富集。压应力和配分到奥氏体中的C元素也可能提高奥氏体的稳定性。高稳定性的奥氏体提供了持久的TRIP效应,显著提高了延伸率,而不影响淬火态马氏体的抗拉强度。


