金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.209,1 May. 2021(上)
2021-06-06 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文12篇,涵盖了高强钢、多元合金、贝氏体等,国内科研单位包括北京科技大学、香港理工大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 209 目录
1. The role of grain-environment heterogeneity in normal grain growth: A stochastic approach
通过随机模型研究局部环境不均匀性对晶粒长大过程的影响
2. Theory of solid solution strengthening of BCC Chemically Complex Alloys
BCC多主元合金的固溶强化理论
3. Eutectoid growth of nanoscale amorphous Fe-Si nitride upon nitriding
纳米非晶Fe-Si氮化物在氮化过程中的共析长大
4. Dislocation-mediated plasticity in the Al2Cu θ-phase
Al2Cu θ相中的位错介导塑性研究
5. Spatial and temporal variation of hardness of a printed steel part
金属打印方法制备钢件的硬度时空演化研究
6. Grain boundary phase transformation in a CrCoNi complex concentrated alloy
CrCoNi多主元合金中的晶界相变
7. Role of cementite and retained austenite on austenite reversion from martensite and bainite in Fe-2Mn-1.5Si-0.3C alloy
渗碳体和残余奥氏体对Fe-2Mn-1.5Si-0.3C马氏体和贝氏体组织奥氏体逆相变的影响
8. Synergistic alloying effects on nanoscale precipitation and mechanical properties of ultrahigh-strength steels strengthened by Ni3Ti, Mo-enriched, and Cr-rich co-precipitates
Ni3Ti、富Mo相和富Cr相共析出的演化及其对超高强钢力学性能的影响
9. Rolling contact fatigue deformation mechanisms of nickel-rich nickel-titanium-hafnium alloys
NiTiHf合金的滚动接触疲劳变形机理研究
10. Wear-induced microstructural evolution of ultra-fine grained (UFGs) aluminum
超细晶铝(UFGs)中的磨损诱导组织演变研究
11. Correlative Synchrotron X-ray Imaging and Diffraction of Directed Energy Deposition Additive Manufacturing
定向能量沉积增材制造的同步X射线成像和衍射技术研究
12. Grain boundary structure-property model inference using polycrystals: The underdetermined case
稀数据条件下的多晶晶界结构-性质模型推断
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116699
1. The role of grain-environment heterogeneity in normal grain growth: A stochastic approach
通过随机模型研究局部环境不均匀性对晶粒长大过程的影响
Thomas Breithaupt✉, Lars N. Hansen, Srikanth Toppaladoddi, Richard F. Katz
T. Breithaupt:thomas.breithaupt@univ.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116699
摘要
晶粒的尺寸分布是多晶材料的基本特征。在无变形情况下,晶粒尺寸分布受正常晶粒长大控制。Hillert提出的晶粒长大模型预测的粒度分布与实验观测存在系统性差异。为此,我们对Hillert模型进行了改进,考虑了晶粒附近环境不均匀性的影响。在本模型中,所有晶粒的演化都主要受其相邻晶粒局部环境的影响,而不优先考虑体系的晶粒分布。每个晶粒的局部环境根据Ornstein-Uhlenbeck随机过程进行演化。结果表明,我们的模型结果与经典晶粒长大动力学模型结果一致。至关重要的是,我们的模型表明,大晶粒会由于局部环境的变化而以随机行走的方式进行演化,这最终导致了比Hillert模型更宽的粒度分布。以上研究表明,非均匀性对材料微观组织演化有重要影响。

ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116758
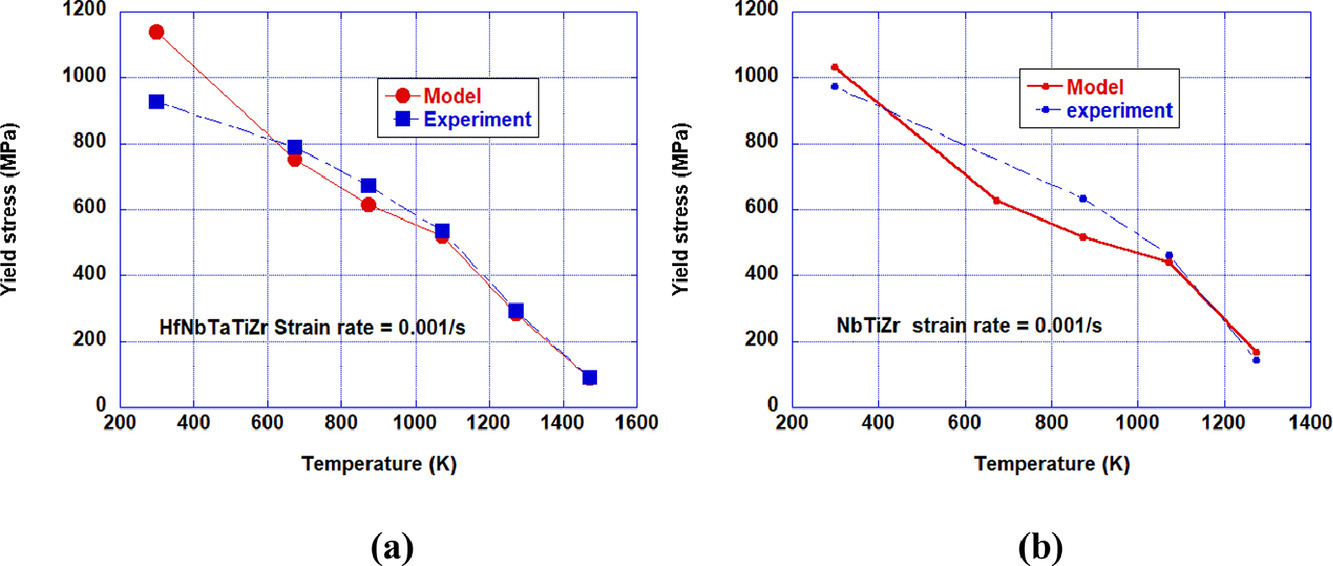
2. Theory of solid solution strengthening of BCC Chemically Complex Alloys
BCC多主元合金的固溶强化理论
S.I. Rao✉, C. Woodward, B. Akdim, O.N. Senkov, D. Miracle
S.I. Rao:srao@ues.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116758
摘要
我们提出了一种基于a/2<111>螺位错迁移的体心立方(BCC)多主元合金强化模型。在较低温度下,我们认为偶极子拖曳是强化的主要速度限制,随着温度的升高,这种机制转变为扭结拖曳机制。尽管Suzuki提出的经典BCC合金强化模型中包含了这两种机制,但仍需要进行一些改进,才能将模型应用于难熔的多主元合金。首先,我们通过三元NbTaTi合金和四种四元合金(MoNbTaTi、WNbTaTi、CrMoNbTi、CrMoTaTi)建立并比较了衡量复杂合金中净化学效应的方法。随后,我们将模型扩展到高温,并应用于分析复杂BCC合金(包括NbTiZr和HfNbTaTiZr)中屈服强度数据随温度(0.15-0.7TL,其中TL是液相线温度)和应变速率(10−5~10−2/s)的变化。我们发现基于这两种机制的模型预测与BCC多主元合金、NbTiZr和HfNbTaTiZr的屈服数据吻合良好。我们也利用了Maresca刃位错模型对这两种BCC多主元合金、NbTaTi和四种四元合金的屈服数据进行了分析。总得来说,本研究中提出的螺位错模型可用于预测BCC多主元合金的高温强度,对航空航天领域高强BCC合金的设计研发具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116774
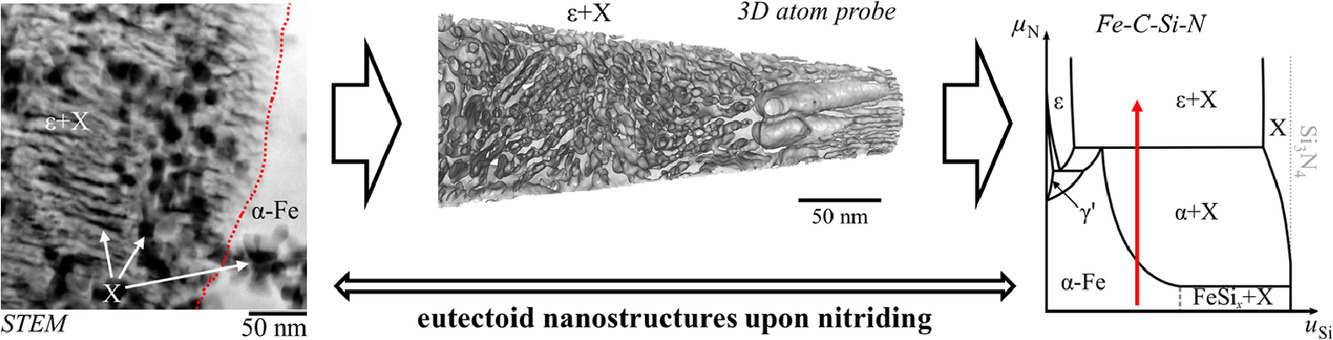
3. Eutectoid growth of nanoscale amorphous Fe-Si nitride upon nitriding
纳米非晶Fe-Si氮化物在氮化过程中的共析长大
Stefan Kante, Philipp Kürnsteiner, Mykhaylo Motylenko, Baptiste Gault, Andreas Leineweber✉
A. Leineweber:andreas.leineweber@iww.tu-freiberg.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116774
摘要
氮化铁在钢、铸铁表面工程和功能材料中具有重要的应用价值。Si对氮化铁形成和生长的影响尚不明确,在ε和γ′ Fe氮化物中的溶解度定量数据缺乏。我们以Fe-C-Si体系为研究对象,研究了富Si α-Fe和珠光体中铁氮化物形成和长大。在N连续供给的条件下,材料中发生了两种等温共析反应,分别是α-Fe或ε相与纳米非晶富Si氮化物的共析长大,反应式为:Fe23Si5C4→α-Fe+XSC和 α-Fe(Si)→ε+Xε。我们利用原子探针技术,首次在氮化后的Fe-3.5C-330Si(wt.%)合金中证明了ε相中存在Si的渗入。共析ε相中Si/Fe原子比< 0.02,对应ε-Fe3(N, C)中约1.5at.%。此外,上述Xε是一种首次报导的非晶Fe-Si混合氮化物,其组成介于Fe2Si5N8和FeSiN2之间,根据电中性条件,可以推测其中含有Si4+、N3−和Fe2+。类似于金属氧化物改性的石英玻璃,Xε的组成可以写作(Si3N4)1-x(Fe3N2)x,其中0.33 < x < 0.43。以上结果表明,现有的Fe(-C)-Si-N热力学相图需要补充和修改,我们在文中大致推导了Fe-C-Si-N相图的示意图。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116748
4. Dislocation-mediated plasticity in the Al2Cu θ-phase
Al2Cu θ相中的位错介导塑性研究
D. Andre✉, Z. Xie, F. Ott, J.T. Pürstl, N. Lohrey, W.J. Clegg, S. Sandlöbes-Haut, S. Korte-Kerzel
D. Andre:andre@imm.rwth-aachen.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116748
摘要
我们通过原子尺度模拟和微柱压缩研究了金属间化合物Al2Cu θ相的变形行为,并发现了{211}和{022}面上的滑移。我们对金属间化合物所有可能的滑移系统进行了分析,并根据滑移系统的有效面间距和有效Burgers矢量提出了滑移系统的激活优先顺序。有效面间距对应于人为确定的面间距离,而有效Burgers向量考虑了潜在的位错分解。最终得到的优先性排序为:{211}½<111>,{022}½<111>和{022}<100>,{110}<001>,{310}<001>,{022}<011>,{110}½<111>,{112}<110>和{112}½<111>。同时,我们对几个滑移系统的临界解剪应力进行了测量。

ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116775
5. Spatial and temporal variation of hardness of a printed steel part
金属打印方法制备钢件的硬度时空演化研究
T. Mukherjee, T. DebRoy✉, T.J. Lienert, S.A. Maloy, P. Hosemann
T. DebRoy:debroy@psu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116775
摘要
部分行业中经常使用金属打印工艺制造复杂零件,在此过程中,需要对零件的微观组织和性能进行调控。大量的工艺参数会影响热循环,从而影响零件的组织和性能。在本研究中,我们发现,可以基于热循环和Johnson-Mehl-Avrami动力学关系计算工具钢零件不同位置的硬度变化。在不同加工条件下,计算得到的硬度值与实验数据吻合良好。在确定的位置,硬度随热循环增加而持续下降。上层沉积过程中,下方堆积层经历持续的热循环,导致材料硬度随着距顶端距离的增加而降低。若激光功率高,扫描速度慢,则输入的热量更大,因此材料的冷却速率更低,温度更高,马氏体回火更明显,硬度也更低。模型可以有效预测硬度随工艺参数的空间变化,因此可以为增材制造加工零件的硬度调控提供有益的指导。

ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116786
6. Grain boundary phase transformation in a CrCoNi complex concentrated alloy
CrCoNi多主元合金中的晶界相变
Fuhua Cao, Yan Chen, Shiteng Zhao, En Ma, Lanhong Dai✉
L. Dai:lhdai@lnm.imech.ac.cn(中国科学院力学研究所/北京理工大学/中国科学院大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116786
摘要
晶界的类相变行为,即晶界的成分、结构和性质不连续变化的行为,是晶界工程中一个重要的研究课题。目前关于这一问题的研究对象主要是纯金属或是稀合金。下一步的研究需要更多地关注成分更加复杂的单相体系。高/中熵合金(H/MEAs),或称为多主元合金(CCAs),符合这方面的要求。我们使用了CoCrNi模型合金来研究多主元合金中的原子间相互作用,及其对晶界元素分布和晶界相变的影响。通过分子动力学模拟和第一性原理计算,我们发现晶界相变温度对晶界原子构型很敏感。具有随机原子排布的多主元合金晶界相比于没有明显组分差异的晶界更容易发生相变,因为这类晶界的相变热力学驱动力更大,扩散动力学更快。而当三种元素在晶界中的分布情况为Ni发生团簇、Co-Cr有序分布时,扩散较为缓慢,从而延缓了晶界相变。我们的研究加深了学界对多主元合金中晶界相变的认识,对于通过晶界工程进行材料设计具有重要指导意义。

ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116772
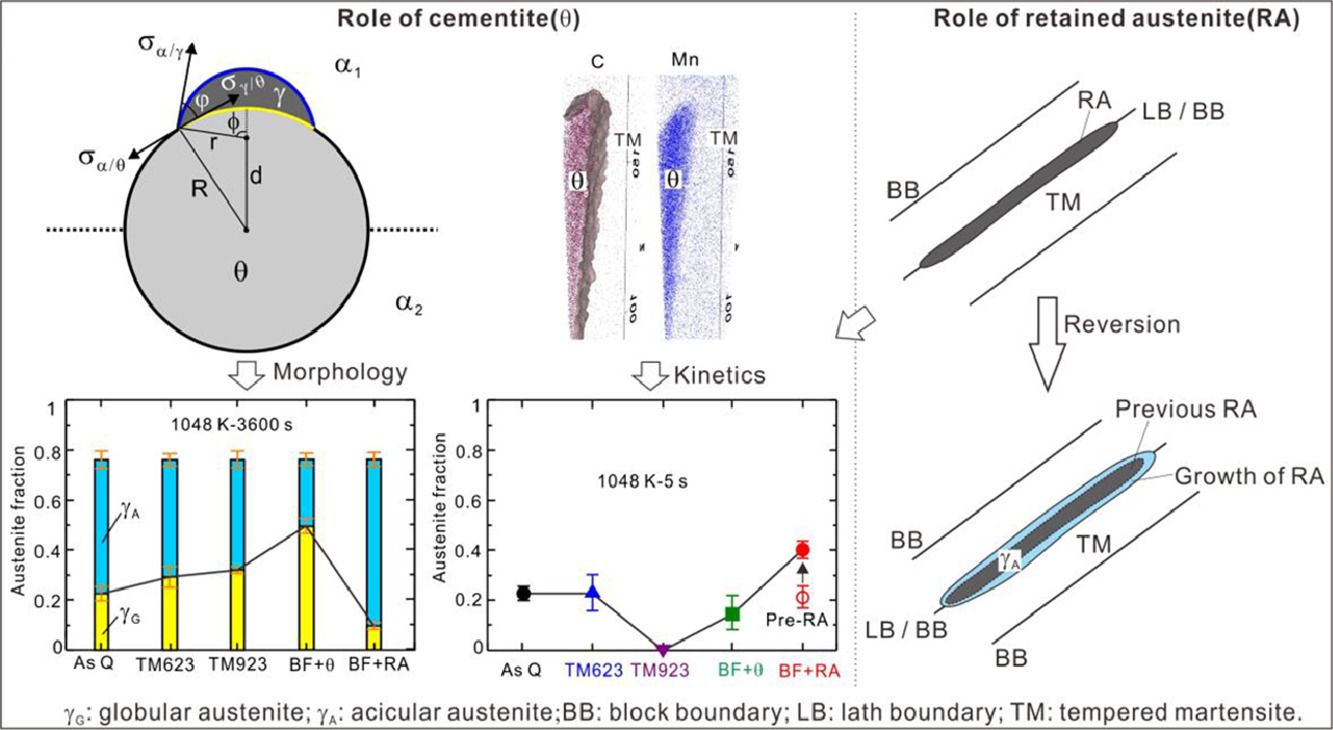
7. Role of cementite and retained austenite on austenite reversion from martensite and bainite in Fe-2Mn-1.5Si-0.3C alloy
渗碳体和残余奥氏体对Fe-2Mn-1.5Si-0.3C马氏体和贝氏体组织奥氏体逆相变的影响
Xianguang Zhang✉, Goro Miyamoto, Yuki Toji, Yongjie Zhang, Tadashi Furuhara
X. Zhang:xgzhang@ustb.edu.cn(北京科技大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116772
摘要
我们研究了Fe-2Mn-1.5Si-0.3C (mass%)淬火马氏体、回火马氏体和贝氏体初始组织中的奥氏体逆相变过程,阐明了渗碳体(θ)和残余奥氏体(RA)对奥氏体(γ)逆相变动力学和组织演变的影响。马氏体预回火或长时间奥氏体等温淬火均会导致θ相析出,并提高高温奥氏体逆相变条件下球形奥氏体的体积分数;而通过短时间等温淬火得到的无碳化物贝氏体+残余奥氏体组织则会抑制θ相形成。高温预回火或长时间等温淬火会减慢奥氏体逆相变动力学,而低温预回火或残余奥氏体则对相变动力学影响很小。在渗碳体/铁素体界面形核的γ相为球形。理论分析表明,粗大的θ相更容易促进球形γ相形核,因此预回火或奥氏体等温淬火等工艺能够促进球形γ相形成。另一方面,当残余奥氏体大量存在时,γ逆相变前θ相析出被抑制,从而抑制了球形γ相的形成。综上所述,高温预回火或奥氏体等温淬火对奥氏体逆相变动力学的减缓作用主要是由于Mn向θ相的富集和θ相的粗化抑制了逆相变奥氏体的长大。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116788
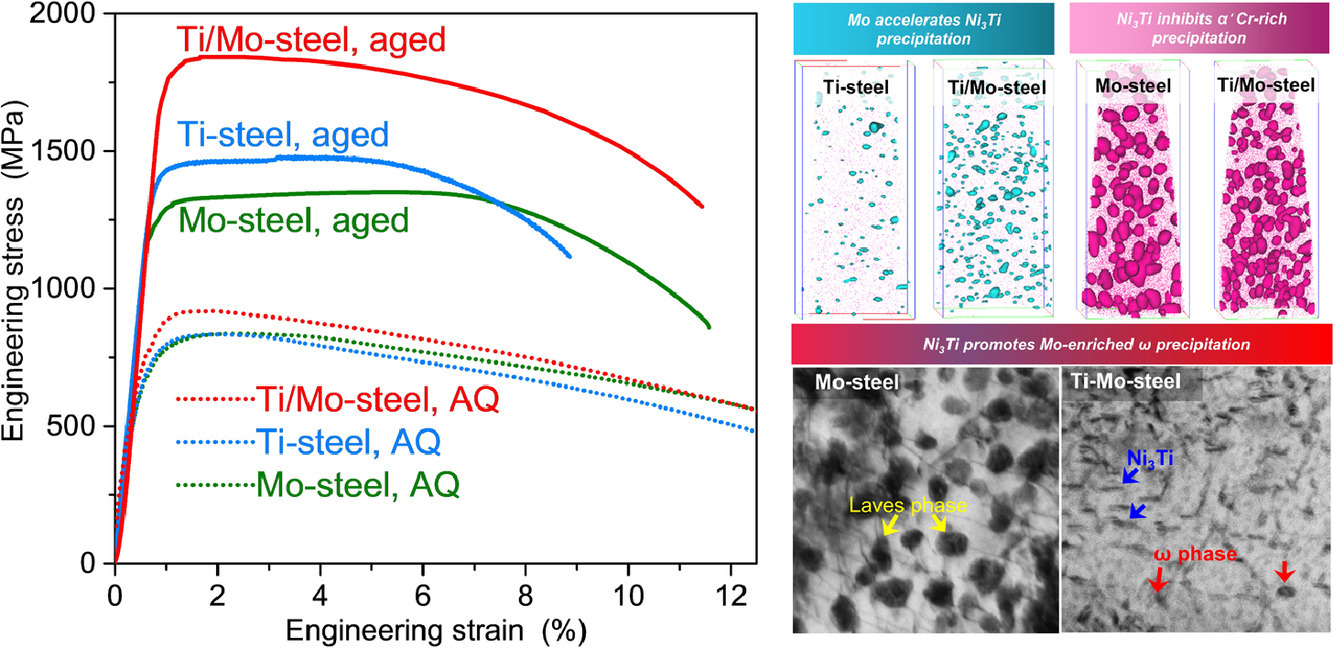
8. Synergistic alloying effects on nanoscale precipitation and mechanical properties of ultrahigh-strength steels strengthened by Ni3Ti, Mo-enriched, and Cr-rich co-precipitates
Ni3Ti、富Mo相和富Cr相共析出的演化及其对超高强钢力学性能的影响
M.C. Niu, L.C. Yin, K. Yang, J.H. Luan, W. Wang✉, Z.B. Jiao✉
W. Wang:wangw@imr.ac.cn(中科院金属所)
Z.B. Jiao:zb.jiao@polyu.edu.hk(香港理工大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116788
摘要
我们通过高分辨率扫描透射电镜、原子探针(APT)、热力学计算、第一性原理和力学试验,系统研究了Mo、Ti和Cr对马氏体时效不锈钢纳米级沉淀和力学性能的协同影响。结果表明,Ni3Ti、富Mo析出相和富Cr析出相的共沉淀路径明显,形成过程中具有显著的相互作用。APT结果表明,在Ni3Ti形成初期,Mo向Ni3Ti析出相中心配分,使得Ni3Ti的析出密度提高近一倍。计算表明,Mo的配分不仅增加了化学驱动力,而且降低了形核的应变能,从而加速了Ni3Ti的析出。随着Ni3Ti析出的进行,Mo从Ni3Ti析出的中心被排至Ni3Ti/基体界面,引起了富Mo析出相在Ni3Ti表面的非均匀形核。这一过程大大细化了富Mo析出相的尺寸。此外,Ni3Ti的形成消耗了基体中的Ni,显著抑制了调幅分解分解,细化了富Cr析出相的尺寸。Ni3Ti、富Mo析出相和富Cr析出相的协同强化作用使得钢铁材料的强度达到了1.8 GPa。我们根据析出相的位错切过和绕过机制,对这些析出相的强化贡献进行了定量分析。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116784
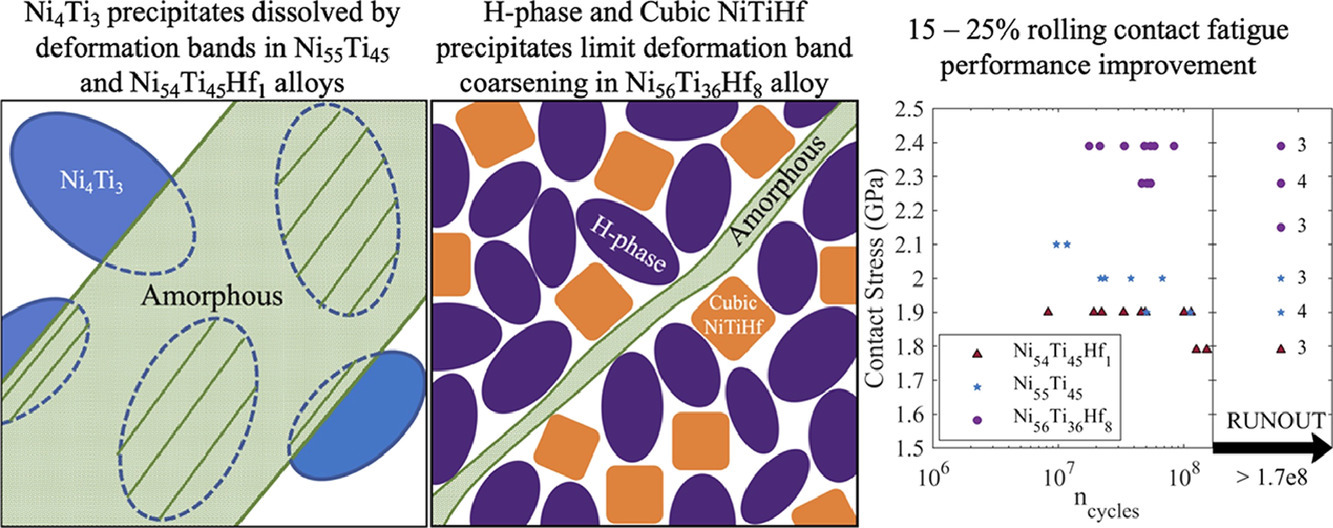
9. Rolling contact fatigue deformation mechanisms of nickel-rich nickel-titanium-hafnium alloys
NiTiHf合金的滚动接触疲劳变形机理研究
Sean H. Mills, Christopher Dellacorte, Ronald D. Noebe, Behnam Amin-Ahmadi✉, Aaron P. Stebner✉
B. Amin-Ahmadi:behnam.aminahmadi@gmail.com
A.P. Stebner:aaron.stebner@gatech.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116784
摘要
我们通过滚动接触疲劳(RCF)测试和透射电镜(TEM)分析,研究了经热处理后Ni55Ti45、Ni54Ti45Hf1和Ni56Ti36Hf8合金的摩擦性能和变形机制。样品经过5×108 次RCF循环后,损伤主要集中在表面下几百纳米到几微米的变形带。这些变形带在B2奥氏体中通过位错滑移的集中形核。对于Ni55Ti45和Ni54Ti45Hf1样品,变形带中的Ni4Ti3溶解和切变导致了进一步的损伤和剥落破坏。随后变形带纳米晶化,包括部分B19’相的应力诱导纳米晶形核,并最终在断裂之前完全非晶化。Ni56Ti36Hf8合金的RCF性能相对提高了15 - 25%,这与表面下的损伤深度较低有关,严重损伤区域向试样中仅扩展了1.5µm,而Ni55Ti45和Ni54Ti45Hf1合金中则大于 6µm。Ni56Ti36Hf8合金的优异抗RCF损伤性能是由于体系中存在大量富Ni的立方NiTiHf和纳米H相析出,使得B2相的体积分数大大减少(≤13%)。这种组织限制了B2奥氏体相内变形带的宽度,使其小于纳米强化相的尺寸,从而抑制了纳米晶化和非晶化之前的析出剪切和溶解过程。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116787
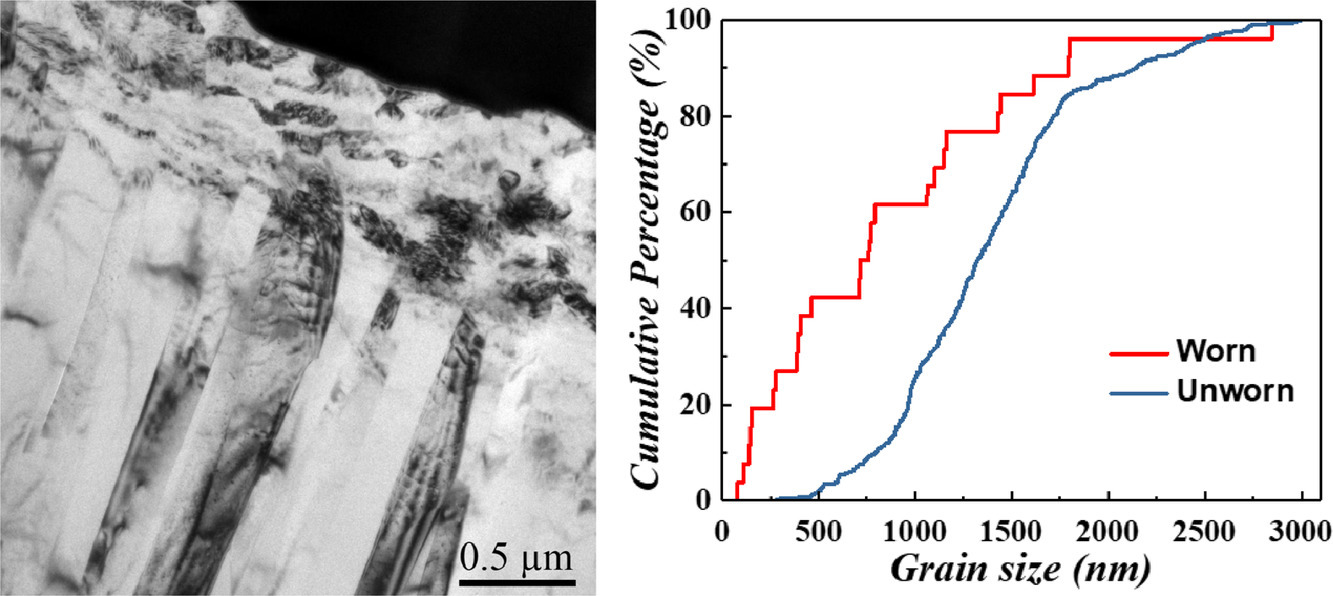
10. Wear-induced microstructural evolution of ultra-fine grained (UFGs) aluminum
超细晶铝(UFGs)中的磨损诱导组织演变研究
S. Wei, H. Zhang✉, C. Tangpatjaroen, J. Tarnsangpradit, A.D. Usta, M. Eriten, J.H. Perepezkoa, I. Szlufarska✉
H. Zhang:zhlcanes@hotmail.com
I. Szlufarska:szlufarska@wisc.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116787
摘要
我们对通过累积叠轧(ARB)和物理气相沉积(PVD)方法制备得到的两种超细晶粒(UFG)铝材试样的硬度和摩擦性能进行了研究。我们首次在这种材料中发现了磨损诱导的晶粒细化。根据平均接触应力的不同,晶粒将发生从长大到细化的转变。这一变化趋势对PVD和ARB样品相同,这意味着它与材料的制备方法无关。材料硬度随晶粒尺寸的减小而增大,但偏离了Hall-Petch关系。在ARB试样中,初始硬度最高的超细晶Al是最耐磨的。而PVD制备的超细晶Al虽是所有样品中最耐磨的,却不是最硬的。原因在于不同方法制备的样品中位错密度不同,随后磨损引起的位错网络演化也不同。我们通过透射电镜分析了超细晶Al的微观组织演变机制,确定其主要为动态再结晶(DRX),包括连续再结晶和不连续再结晶。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116777
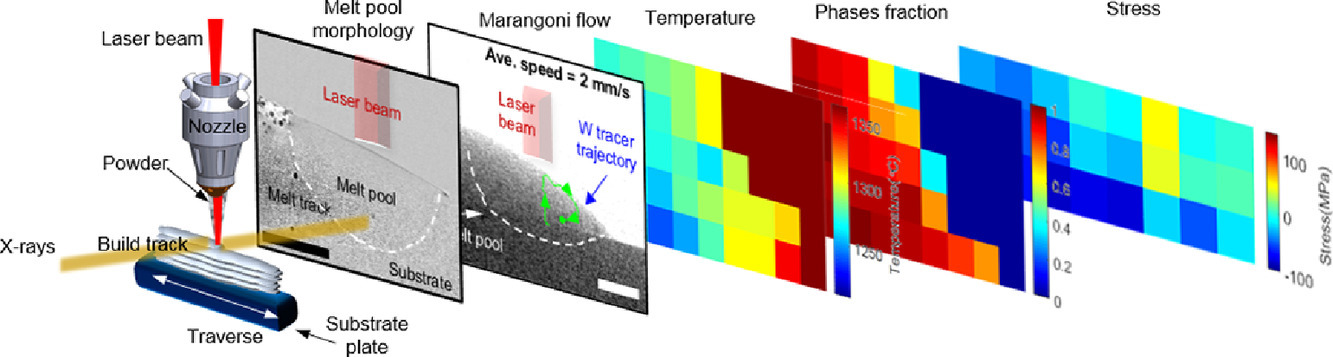
11. Correlative Synchrotron X-ray Imaging and Diffraction of Directed Energy Deposition Additive Manufacturing
定向能量沉积增材制造的同步X射线成像和衍射技术研究
Yunhui Chen✉, Samuel J. Clark, David M. Collins✉, Sebastian Marussi, Simon A. Hunt, Danielle M. Fenech, Thomas Connolley, Robert C. Atwood, Oxana V. Magdysyuk, Gavin J. Baxter, Martyn A. Jones, Chu Lun Alex Leung, Peter D. Lee✉
Y. Chen:yunhui.chen@ucl.ac.uk
D.M. Collins:d.m.collins@bham.ac.uk
P.D. Lee:peter.lee@ucl.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116777
摘要
我们对镍基高温合金IN718进行了原位同步X射线成像和衍射研究,揭示了定向能量沉积增材制造(DED-AM)过程中的性能调控机制。我们采用了一种独特方法,对熔池边界处和凝固过程中的流体力学进行了复现和量化。这种成像方法还可以以100µm的空间分辨率测量相变和应力条件下的组织相演化。通过对热梯度的定量衍射表征使我们可以预测枝晶凝固并将其与应力状态相耦合。快速冷却完全抑制固态组织中二次相或再结晶的形成。凝固冷却过程中,应力迅速增加到屈服强度。结合IN718的较大凝固范围,我们认为材料中积累的塑性应变耗尽了合金的延展性,并导致了开裂。以上研究揭示了在DED-AM过程中形成高度非平衡组织的机制。
ACTA
Vol. 208,15 Apr. 2021, 116769
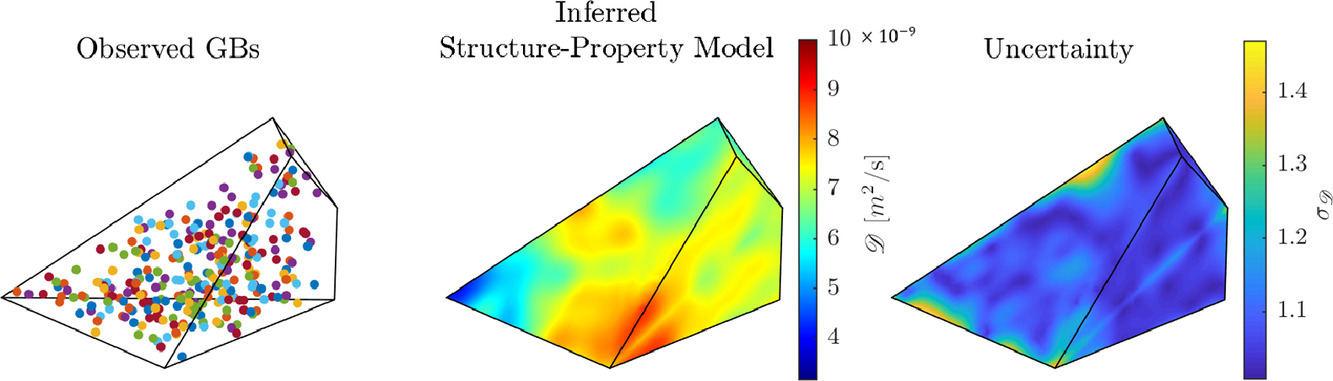
12. Grain boundary structure-property model inference using polycrystals: The underdetermined case
稀数据条件下的多晶晶界结构-性质模型推断
Brandon D. Snow, Sterling G. Baird, Christian Kurniawan, David T. Fullwood, Eric R. Homer, Oliver K. Johnson✉
O.K. Johnson:ojohnson@byu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116769
摘要
建立晶界(GB)结构和材料性能之间的联系一直是学界研究的热点,而这方面的大量尝试主要采用双晶体系进行实验和计算。虽然得到的数据较为精确,但由于表征完整晶界的五维特征需要极高的算力成本,因此,现有数据主要集中在高度对称的局部区域。相比之下,多晶体更加普遍,制备成本低,且包含大量的晶界特征。然而,从多晶性质中提取晶界性质较为困难。本研究中,我们提出了一种贝叶斯方法,希望通过基于间接的多晶测量和少量数据来推断晶界的结构-性能关系。该方法提供了不完全量化的结果。我们通过1DOF和3DOF 结构-性能模型对在二维结构中的晶界扩散进行了测试和验证,并研究了多晶中晶粒数量对性能预测的影响。结果表明,当有大量数据时,双晶体体系的预测更准确;而当数据严重稀缺时,多晶体预测更准确。