金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.209,1 May. 2021(下)
2021-06-20 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文11篇,涵盖了镁单晶、高熵合金、锆合金等,国内科研单位包括哈尔滨工业大学、中科院金属所等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 209 目录
1. Effects of electric current on the plastic deformation behavior of pure copper, iron, and titanium
电流对纯铜、铁、钛塑性变形行为的影响
2. The (110) and (320) surfaces of a Cantor alloy
Cantor合金的(110)和(320)表面表征
3. Doping distribution in Skutterudites with ultra-high filling fractions for achieving ultra-low thermal conductivity
通过调控CoSb3中的高浓度掺杂分布实现超低热导
4. On the origin of the Hall–Petch law: A 3D-dislocation dynamics simulation investigation
通过三维位错动力学模拟探究Hall-Petch定律的物理起源
5. Anomalous dislocation core structure in shock compressed bcc high-entropy alloys
冲击压缩BCC高熵合金中的特殊位错核结构表征与研究
6. An origin of corrosion resistance changes of Zr alloys: effects of Sn and Nb on grain boundary strength of surface oxide
Sn、Nb对Zr合金表面氧化物晶界强度及Zr合金耐蚀性的影响
7. Dynamic observation of dual-beam irradiated Fe and Fe-10Cr alloys at 435 °C
435 °C双束辐照下Fe和Fe-10Cr合金的动态观测
8. Surprising increase in yield stress of Mg single crystal using long-period stacking ordered nanoplates
通过长周期堆垛有序结构显著提高Mg单晶的屈服应力
9. A critical relative density and a break-and-reconnect model for annealing-induced densification in nanoporous gold
纳米多孔金退火致密化的临界相对密度和断裂-重连模型
10. The effect of hydrogen content and yield strength on the distribution of hydrogen in steel: a diffusion coupled micromechanical FEM study
基于扩散耦合微观力学有限元模型研究氢含量和屈服强度对钢中氢分布的影响
11. Synchrotron X-ray imaging and ultrafast tomography in situ study of the fragmentation and growth dynamics of dendritic microstructures in solidification under ultrasound
超声凝固过程中枝晶破碎和长大动力学的原位同步X射线成像和超快断层扫描研究
ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116776
1. Effects of electric current on the plastic deformation behavior of pure copper, iron, and titanium
电流对纯铜、铁、钛塑性变形行为的影响
C. Rudolf✉, R. Goswami, W. Kang, J. Thomas
C. Rudolf:christopher.rudolf@nrl.navy.mil
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116776
摘要
我们对多晶纯铜、纯铁和纯钛试样在不同直流电和对应纯温度条件下进行了单轴拉伸试验。实验过程中,样品标距段的应变、电流密度和温度条件保持均匀。结果表明,只在纯钛Ti样品中发现了非热电流效应。与无电流纯温度对比组样品相比,材料的抗拉强度下降了20%,且晶粒生长不均匀。而在纯温度下变形或有电流无变形的试样中,都观察不到明显的组织变化。电子漂流和焦耳热效应引起的电辅助变形(EAD)机制无法解释如此显著的实验现象。热声子导致的位错散射和样品径向、轴向的热流引起的电子运动可能是潜在的机制。以上实验结果和热声子/电子散射间的可能联系为我们研究金属中EAD效应提供了新的思路。

ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116790
2. The (110) and (320) surfaces of a Cantor alloy
Cantor合金的(110)和(320)表面表征
J. Ledieu✉, M. Feuerbacher, C. Thomas, M.-C. de Weerd, S. Šturm, M. Podlogar, J. Ghanbaja, S. Migot, M. Sicot, V. Fournée
J. Ledieu:julian.ledieu@univ-lorraine.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116790
摘要
我们通过利用表面技术手段和透射电子显微镜(TEM)研究了单相FeCrMnNiCo固溶体的(110)和(320)表面,测定了高熵合金表面在不同溅射条件、退火温度和退火时间下的结构和化学演化。角分辨X射线光电子能谱结果显示,873 K时,表面存在明显的Mn、Ni共偏聚。我们认为Mn的表面偏聚是由其较低的表面能驱动的。而Mn和Ni之间的吸引相互作用促进了Ni的偏析,并随Mn向表面扩散。低能电子衍射和扫描隧道显微镜表征表明,合金的(320)表面呈阶梯状形貌的有序结构。相反,(110)表明则显示出明显的结构无序和局部重构。其形貌高度各向异性,且似沿[001]方向传播。873 K以上,Mn发生脱附,Ni含量随温度呈线性增加。TEM分析表明,即使经过多次退火和溅射循环,高熵合金也没有分解成金属相或金属间化合物。上述结果表明,存在一个上限温度,该温度以上,材料的表面化学计量显著偏离五元高熵合金的概念,因此,本研究对于明确FeCrMnNiCo基涂层在航空航天等领域内的应用温度范围具有重要意义。

ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116791
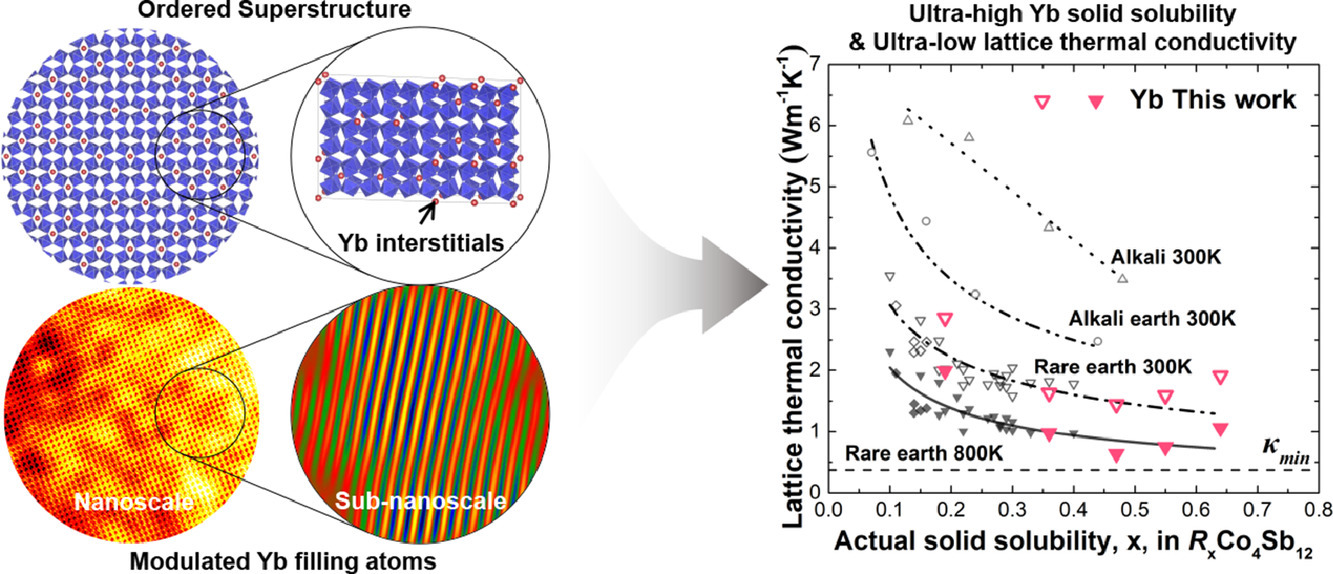
3. Doping distribution in Skutterudites with ultra-high filling fractions for achieving ultra-low thermal conductivity
通过调控CoSb3中的高浓度掺杂分布实现超低热导
Wei Ren, Yan Sun, Jialun Zhang, Yiping Xia, Huiyuan Geng✉, Lixia Zhang✉
H. Geng:genghuiyuan@hit.edu.cn(哈尔滨工业大学)
L. Zhang:zhanglxia@hit.edu.cn, hitzhanglixia@163.com(哈尔滨工业大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116791
摘要
热电材料和热障材料需要具有低晶格导热系数。可以向基体晶格中添加间隙或置换型原子引入点缺陷,从而散射声子,但这仍不足以实现如同玻璃般的热传性能。本研究中,我们制备了超高含量Yb掺杂的CoSb3结构,其中有序超结构和纳米/亚纳米尺度的不均匀Yb间隙原子共存。在高含量Yb掺杂、有序超结构、纳米尺度的不均匀Yb填充、以及高密度晶格应变的作用下,声子散射显著增强,从而使得材料的晶格热导率接近玻璃极限。以上研究为通过调控掺杂原子的分布,设计超低热导的热电、热障材料提供了新的思路。
ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116783
4. On the origin of the Hall–Petch law: A 3D-dislocation dynamics simulation investigation
通过三维位错动力学模拟探究Hall-Petch定律的物理起源
Maoyuan Jiang✉, Ghiath Monnet, Benoit Devincre
M. Jiang:maoyuan.jiang@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116783
摘要
我们对1 ~ 10µm的立方晶粒进行了三维位错动力学(3D-DD)模拟,以探究Hall-Petch定律的物理起源。特别是,我们对晶界处累积的极化位错密度(GNDs)引起的长程应力(背应力)、以及与森位错密度(SSDs)相关的短程应力分别进行了区分和量化。研究表明,在低应变下,背应力和相应的应变硬化与晶粒尺寸无关。因此,在位错动力学模拟框架下,晶粒的尺寸效应主要受随晶粒尺寸减小而增加的CRSS控制。CRSS幅值的演化受两种相互竞争的强化机制调控,与模拟和实验中观察到的Hall-Petch定律的一般形式相互印证。

ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116801
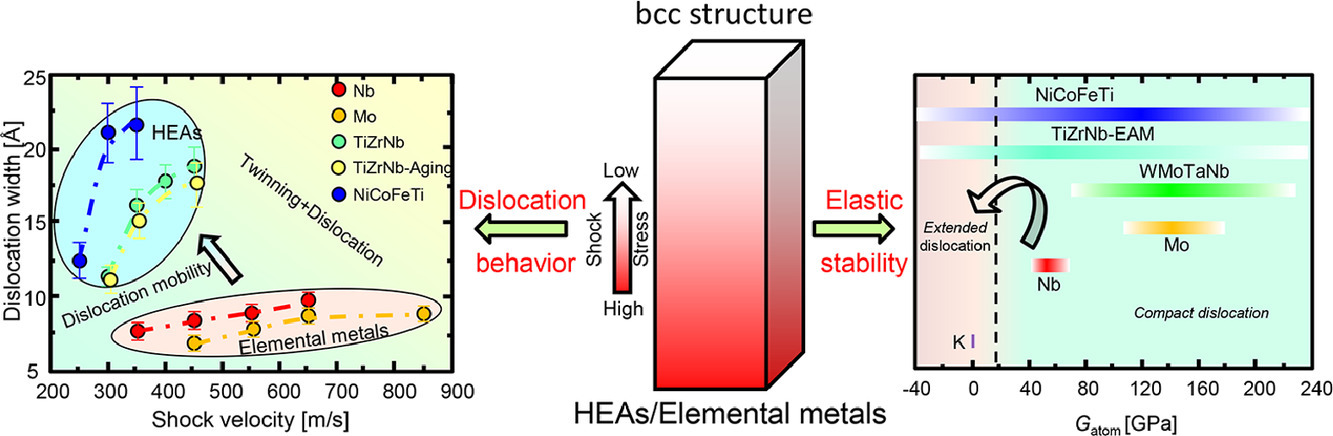
5. Anomalous dislocation core structure in shock compressed bcc high-entropy alloys
冲击压缩BCC高熵合金中的特殊位错核结构表征与研究
Long Zhao, Hongxiang Zong✉, Xiangdong Ding, Turab Lookman
H. Zong:zonghust@mail.xjtu.edu.cn(西安交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116801
摘要
研究表明,在多主元合金中,由于成分/结构的不均匀性,存在特殊的位错核结构和位错运动模式。然而目前尚不清楚极端添条件下,多主元合金中仍存在这些现象。因为在极端条件下,固溶效应会被巨大的驱动力所抵消。本研究中,我们通过大规模分子动力学模拟,研究了BCC高熵合金(HEAs)经冲击后的位错结构。与BCC纯金属相比,我们在冲击压缩TiZrNb和NiCoFeTi 高熵合金中发现了具有高度稳定性的特殊“扩展”刃位错结构。这种独特的位错结构有利于位错的快速运动,从而抑制变形早期发生孪晶形核。结合连续介质弹性理论,我们发现“扩展”位错结构的形成主要是由于高熵合金中纳米尺度的成分非均匀性导致了低弹性稳定性的局部结构。此外,我们说明了原子间作用势对位错结构的影响。
ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116804
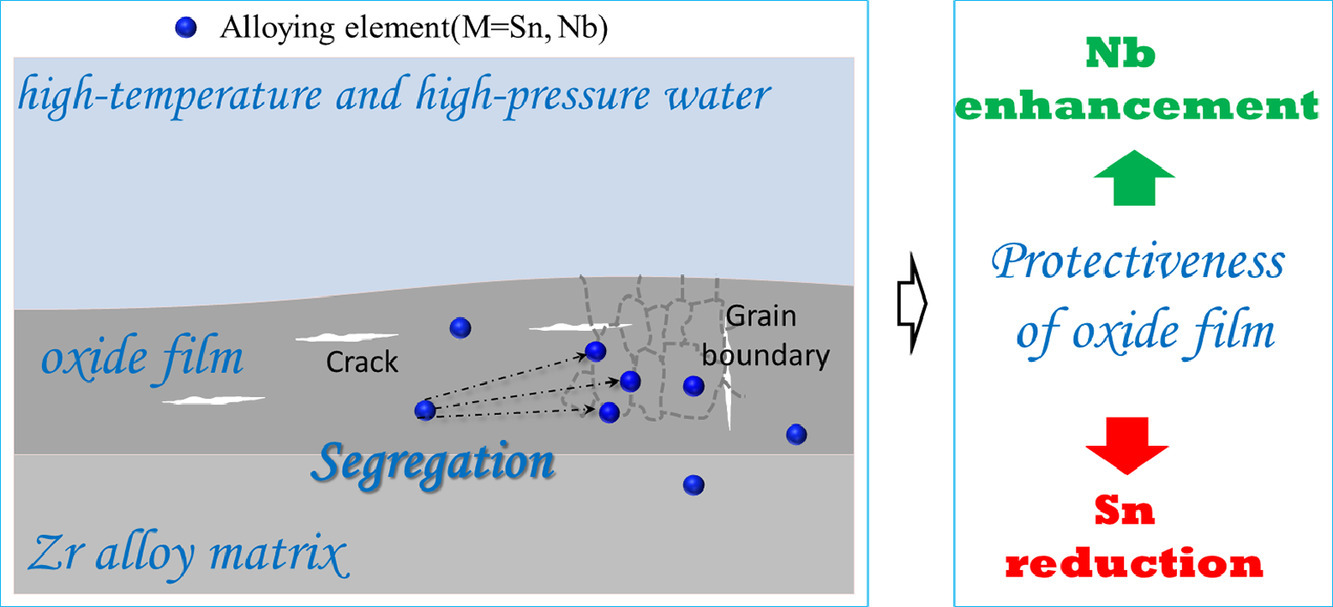
6. An origin of corrosion resistance changes of Zr alloys: effects of Sn and Nb on grain boundary strength of surface oxide
Sn、Nb对Zr合金表面氧化物晶界强度及Zr合金耐蚀性的影响
Rong Yuan, Yao-Ping Xie✉, Tong Li, Chen-Hao Xu, Mei-Yi Yao, Jing-Xiang Xu, Hai-Bo Guo, Bang-Xin Zhou
Y.-P. Xie:ypxie@shu.edu.cn(上海大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116804
摘要
Zr合金作为核燃料包层结构材料,需要具备良好的抗腐蚀性能。几十年来,通过调整Sn和Nb的含量,已经研制出了几代具有优良耐腐蚀性能的Zr合金。但Sn和Nb对合金耐蚀性的影响机理尚不清楚。我们通过计算模拟,发现Sn或Nb会在氧化膜晶界(GB)处偏聚,引起晶界结合力的变化,从而影响耐蚀性。第一性原理计算表明,Sn偏聚降低晶界结合力,减弱了氧化膜的保护性;而Nb偏聚则增强晶界结合力,提高氧化膜的保护性。因此降低Sn或增加Nb可以提高Zr合金的耐蚀性。以上研究结果加深了我们关于合金元素对Zr合金耐蚀性影响的理解,为新型Zr合金的设计提供了指导。
ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116793
7. Dynamic observation of dual-beam irradiated Fe and Fe-10Cr alloys at 435 °C
435 °C双束辐照下Fe和Fe- 10cr合金的动态观测
Yan-Ru Lin✉, Wei-Ying Chen✉, Meimei Li✉, Jean Henry✉, Steven John Zinkle✉
Y.-R. Lin:ylin52@vols.utk.edu
W.-Y. Chen:wychen@anl.gov
M. Li:mli@anl.gov
J. Henry:jean.henry@cea.fr
S.J. Zinkle:szinkle@utk.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116793
摘要
铁素体/马氏体钢具有良好的力学性能和抗辐照肿胀性能,是一种优秀的先进核反应堆备选结构材料。而辐照后Fe和Fe- Cr合金中b=½<111>和b=<100>两种位错环的比例一直是引起研究者兴趣的一个问题。学界虽然对< 100 >位错环的形成机制进行了大量的模拟研究,但事实上,我们对于Fe(Cr)合金的基本辐照实验过程的理解仍不深入。我们在435 °C的双束(1 MeV Kr + 10 appm He/dpa)辐照下,研究了高纯度Fe和Fe- 10Cr合金在0 ~ 20dpa损伤范围内的组织演化。实验表明,< 100 >位错环的形成机制可能不遵循传统理论,即由两个½<111>环发生简单的位错反应形成。动态形成和演化的缺陷包括黑点、位错环粗化、位错环装饰、位错网络和孔洞。结果表明,Cr和He能够抑制位错环运动。我们对各类缺陷额尺寸/密度演化、以及½<111>位错环和< 100 >位错环的相对比例进行了定量分析。随着损伤的增加,½<111>位错环逐渐占据主导。值得注意的是,< 100 >环只在纯Fe中的晶界附近占据主导,而Fe-10Cr合金中则大量观察到组成< 100 >环的纳米级黑点缺陷阵列。

ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116797
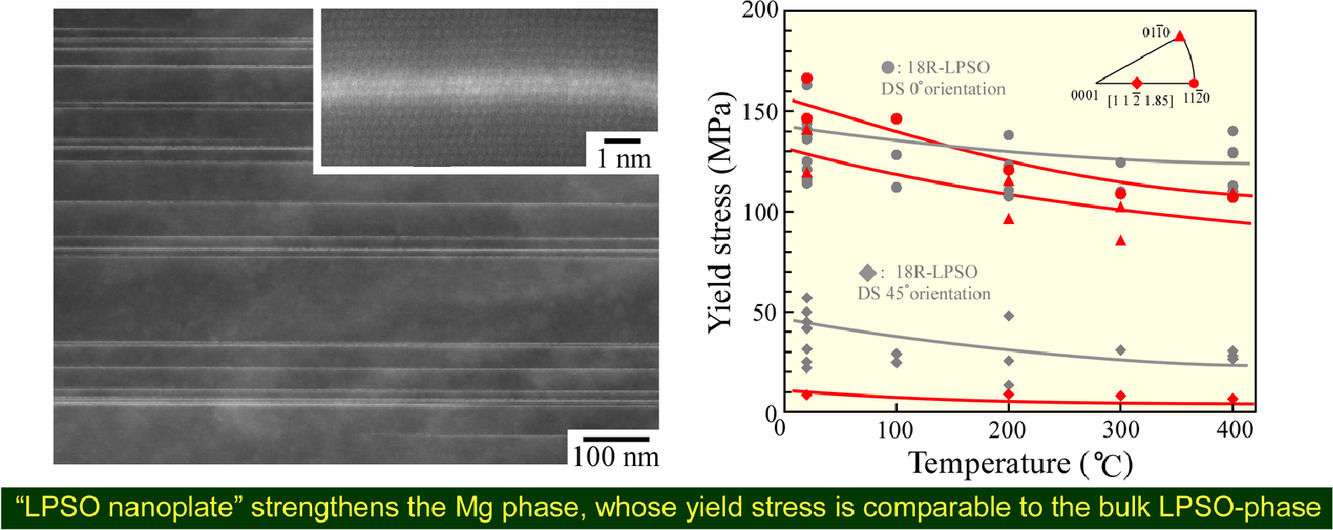
8. Surprising increase in yield stress of Mg single crystal using long-period stacking ordered nanoplates
通过长周期堆垛有序结构显著提高Mg单晶的屈服应力
Koji Hagihara✉, Ryohei Ueyama, Michiaki Yamasaki, Yoshihito Kawamura, Takayoshi Nakano
K. Hagihara:hagihara@mat.eng.osaka-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116797
摘要
具有长周期堆垛有序结构(LPSO)的Mg-Zn-Y三元合金具有优异的力学性能。一般认为LPSO相是强化相。在本研究中,我们首次发现Mg/LPSO双相合金中基体Mg固溶体的力学性能与纯Mg有显著区别,而Mg99.2Zn0.2Y0.6单晶(基体Mg固溶体)的屈服强度与LPSO单相合金的屈服强度基本相同。这是由于组织中形成了类似层错的缺陷,我们将其称为“LPSO纳米板”。Mg99.2Zn0.2Y0.6在变形过程中如同LPSO相一样形成了扭结带,从而提高了强度和塑性。因此,必须根据组织特征重新考虑Mg/LPSO双相合金的强化机制。此外,研究结果还表明,通过适当控制“LPSO纳米板”的微观结构,可以开发出具有较低Zn、Y含量,但力学性能优于Mg/LPSO双相合金的新型超高强度镁合金。
ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116806
9. A critical relative density and a break-and-reconnect model for annealing-induced densification in nanoporous gold
纳米多孔金退火致密化的临界相对密度和断裂-重连模型
Hui Xie, Huai Guan, Ling-Zhi Liu, Hai-Jun Jin✉
H.-J. Jin:hjjin@imr.ac.cn(中科院金属所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116806
摘要
一般认为,用脱合金方法制备的单晶或粗晶纳米多孔金(NanoPorous Gold,NPG)在退火过程中是稳定的,不受烧结或致密化的影响。我们研究发现,这种现象仅适用于相对密度(φ)超过临界值0.31的高密度NPG,在密度在退火过程的变化不显著。而在φ < 0.31的低密度NPG中,退火引起收缩,且收缩程度随φ的减小而增大。晶界烧结可以解释高密度NPG致密度的略微增加,但不能解释低密度NPG的过度收缩。对于φ< 0.3的低密度NPG而言,致密度的增加可能与多孔金中的连接带断裂有关。然而,连接带断裂并不直接导致材料的致密化。相反,我们认为连接带的再附着才是NPG收缩的原因。这种断裂-重连得到了准原位SEM观察等实验的证实。以上研究结果表明,将纳米多孔金属的相对密度提高到0.31以上可以有效抑制退火引起的致密化,这对其组织和性能调控具有重要意义。

ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116799
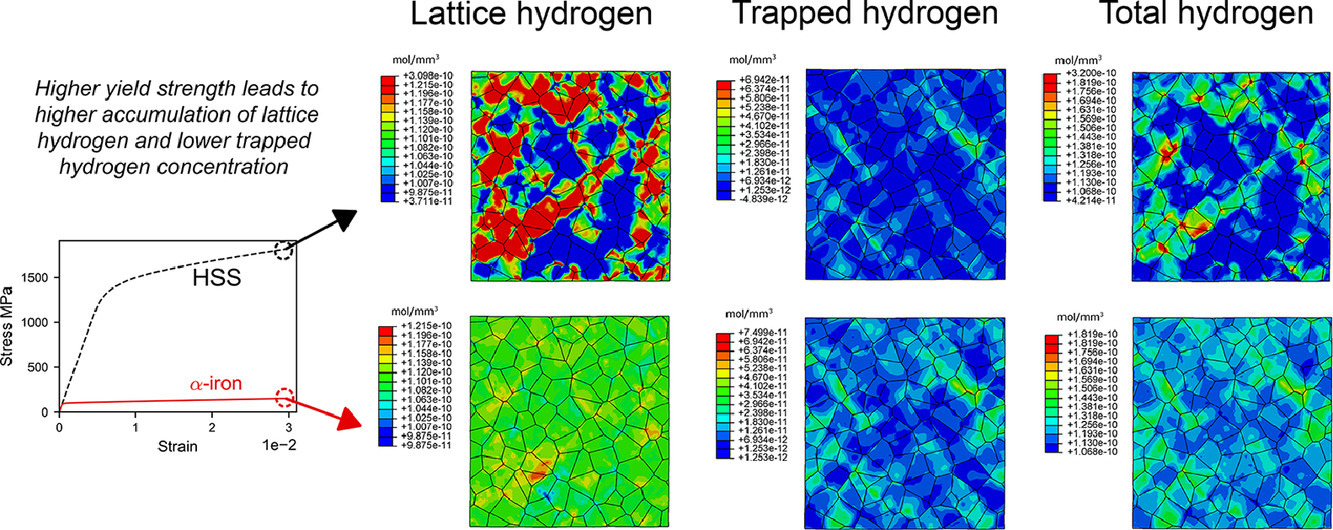
10. The effect of hydrogen content and yield strength on the distribution of hydrogen in steel: a diffusion coupled micromechanical FEM study
基于扩散耦合微观力学有限元模型研究氢含量和屈服强度对钢中氢分布的影响
Abdelrahman Hussein✉, Alfons H.M. Krom, Poulumi Dey, Gagus K. Sunnardianto, Othonas A. Moultos, Carey L. Walters✉
A. Hussein:a.h.a.hussein@tudelft.nl
C.L. Walters:c.l.walters@tudelft.nl
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116799
摘要
在本研究中,我们基于扩散耦合晶体塑性模型研究了晶粒各向异性引起的非均匀微观应力场对氢分布的影响。我们采用具有周期边界条件的代表性体积单元模拟组织,研究了拉伸载荷、初始氢含量和屈服强度对晶格中H和位错捕获H再分布的影响。研究发现,非均匀的微观应力场导致H在晶界处发生偏聚。这表明除了众所周知的晶界捕获外,非均匀应力和塑性应变的相互作用也会促进氢在晶界的积累。材料的屈服强度较高时,由于塑性变形较弱,因此位错捕获的H减少。另一方面,较高的静应力也促进了晶格中H从压缩区向拉伸区的扩散,这些晶格H增加的区域被认为是潜在的损伤萌发区。这与高强度钢比低强度钢更易受氢脆影响的实验结果一致。
ACTA
Vol. 209,1 May. 2021, 116796
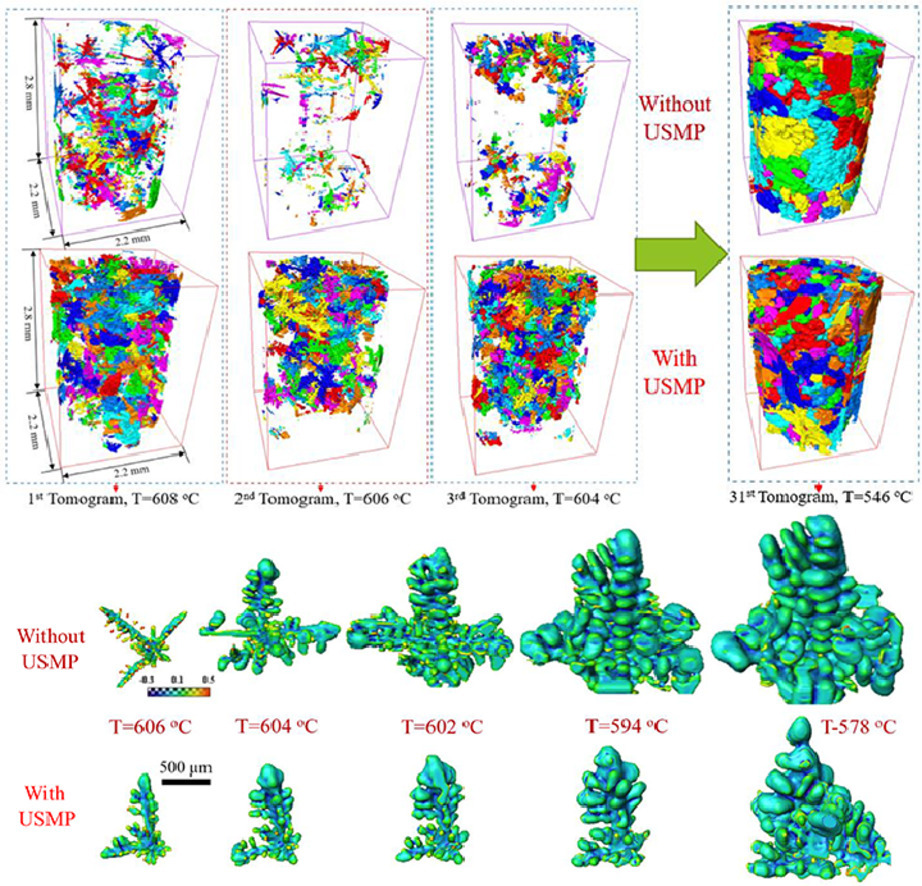
11. Synchrotron X-ray imaging and ultrafast tomography in situ study of the fragmentation and growth dynamics of dendritic microstructures in solidification under ultrasound
超声凝固过程中枝晶破碎和长大动力学的原位同步X射线成像和超快断层扫描研究
Zhiguo Zhang, Chuangnan Wang, Billy Koe, Christian M. Schlepütz, Sarah Irvine, Jiawei Mi✉
J. Mi:J.Mi@hull.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116796
摘要
我们利用高速同步X射线成像和超快断层扫描技术,原位实时研究了Al-15%Cu合金凝固过程中枝晶组织的破碎和生长动力学。我们在合金熔体中应用30kHz、振幅为29µm的超声,产生了~0.3 m/s的强涡旋声流。振动引起了枝晶的高效破碎,其主要机制是热扰动重熔加上机械断裂和分离效应。声流疲劳冲击和碰撞效应在枝晶破碎中起次要作用。与未超声条件相比,凝固早期仅应用超声波10 s,枝晶碎片的数量就增加了约100%,从而使凝固样品的平均晶粒尺寸减小了20~25%。初始枝晶碎片的数密度及分布主要影响枝晶形态和尖端生长速度。本研究中获得的系统和实时数据为相关数值模型提供了有价值的4D信息,对工业化超声熔体加工的工艺优化具有指导意义。