金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.210,15 May. 2021(上)
2021-06-20 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文11篇,涵盖了不锈钢、中熵合金、增材制造等,国内科研单位包括国立清华大学、北京科技大学、金属所等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 210 目录
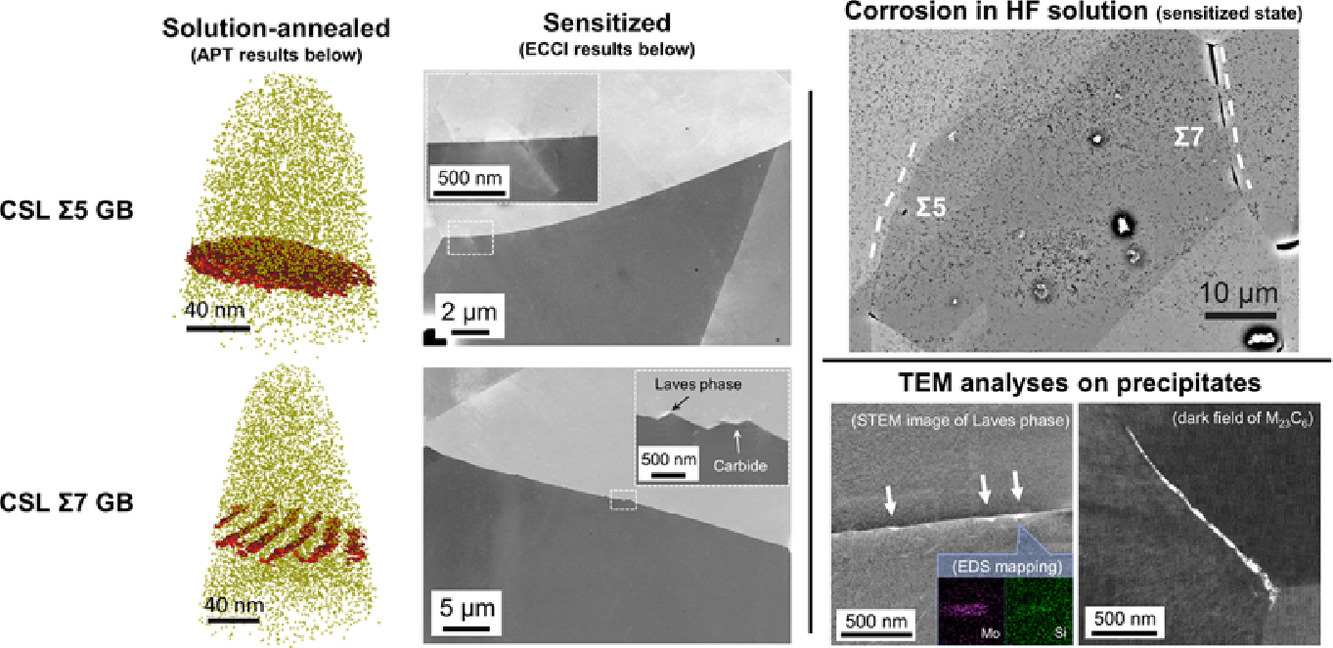
1. Precipitation formation on ∑5 and ∑7 grain boundaries in 316L stainless steel and their roles on intergranular corrosion
316L不锈钢中的∑5和∑7晶界析出及其对晶间腐蚀的影响
2. Importance of deformation-induced local orientation distributions for nucleation of recrystallisation
变形引起的局部取向分布对再结晶形核的影响
3. Mechanism of twinning induced plasticity in austenitic lightweight steel driven by compositional complexity
奥氏体轻量化钢中复杂成分驱动的孪晶诱导塑性机制研究
4. Stress of misfit dislocation at Fe/MgO interface drives the annihilation of radiation induced defects
错配位错应力引起的Fe/MgO界面辐照缺陷湮灭
5. Ideal superelasticity in Ni-based Heusler alloys
Ni基Heusler合金的超弹性研究
6. Digital materials design by thermal-fluid science for multi-metal additive manufacturing
基于热流体科学的金属材料增材制造数字化设计
7. Fe−Ni−N based alloys as rare-earth free high-performance permanent magnet across α'' to L10 phase transition: A theoretical insight
无稀土元素添加Fe-Ni-N基合金高性能永磁体的α″→L10相变理论研究
8. Ordering effects on deformation substructures and strain hardening behavior of a CrCoNi based medium entropy alloy
有序化对CrCoNi基中熵合金变形亚结构和应变硬化行为的影响
9. Phase evolution in two-phase alloys during severe plastic deformation
双相合金在严重塑性变形过程中的相变研究
10. Anisotropic strengthening of nanotwin bundles in heterogeneous nanostructured Cu: Effect of deformation compatibility
变形相容性对非均匀纳米Cu结构中纳米孪晶各向异性强化的的影响
11. Effect of micro-segregation of alloying elements on the precipitation behaviour in laser surface engineered Alloy 718
合金元素微观偏析对激光表面加工718合金析出行为的影响
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116822
1. Precipitation formation on ∑5 and ∑7 grain boundaries in 316L stainless steel and their roles on intergranular corrosion
316L不锈钢中的∑5和∑7晶界析出及其对晶间腐蚀的影响
Shao-Pu Tsai✉, Surendra Kumar Makineni, Baptiste Gault, Kaori Kawano-Miyata, Akira Taniyama, Stefan Zaefferer✉
S.-P. Tsai:s.tsai@mpie.de
S. Zaefferer:s.zaefferer@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116822
摘要
在HF溶液敏化(700°C 10h)AISI316L不锈钢中,∑7晶界通常受到腐蚀而∑5晶界则不被腐蚀。这种不同的腐蚀行为可能与不同晶界的析出行为有关,取决于晶界的自身特征。研究表明,∑5晶界虽然在宏观和微观观测下都呈现出弯曲特点,但既没有多边形面也没有析出,且与退火状态相比,敏化∑5晶界处有明显的偏聚。而∑7晶界在退火和敏化状态下都有明显的表面,并在其中一个面的方向上存在强烈的偏聚,其他面则没有偏聚。我们基于晶界能量各向异性对实验现象进行了解释。C14和M23C6的析出是导致两种不同的腐蚀形态的原因之一。它们应该也与∑7晶界的表面形貌和各向异性偏聚有关。通过痕量分析手段,我们发现∑7的{111}方向是碳化物的优先形核位点。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116808
2. Importance of deformation-induced local orientation distributions for nucleation of recrystallisation
变形引起的局部取向分布对再结晶形核的影响
Romain Quey✉, Guo-Hua Fan, Yubin Zhang, Dorte Juul Jensen
R. Quey:romain.quey@mines-stetienne.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116808
摘要
我们对冷轧40%的三晶粒铝材中的形核进行了研究。我们制备了多组状态一致的样品。其中一些用于分析形变组织,另一些用于分析退火组织。结果表明,形核只发展在三个晶体中的一个,而不发生在晶界。我们随后分析了晶体取向对局部形核密度以及变形组织的影响。一般认为,形核会继承母相取向。而我们发现,通常被认为是再结晶成核驱动力的存储能量不能为实验样品的再结晶形核提供可靠的判据。相反,高度各向异性的尖锐带状亚结构处的形核密度是最高的。综上所述,我们提出了一种新的再结晶形核能量判据,并将其称“初级存储能”(primary stored energy),它由存储能量和取向各向异性共同决定。

ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116814
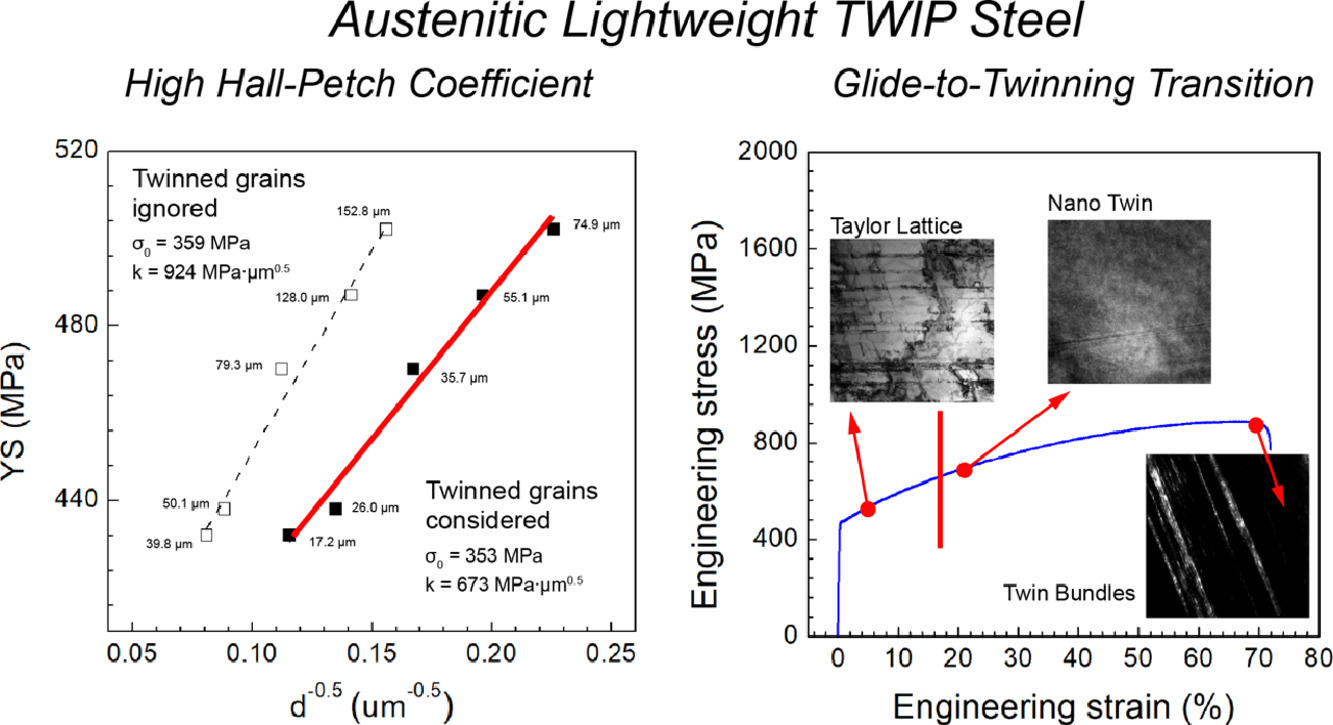
3. Mechanism of twinning induced plasticity in austenitic lightweight steel driven by compositional complexity
奥氏体轻量化钢中复杂成分驱动的孪晶诱导塑性机制研究
Zen-Hao Lai, Yi-Hsuan Sun, Yi-Ting Lin, Jui-Fan Tu, Hung-Wei Yen✉
H.-W. Yen:homeryen@ntu.edu.tw(台湾大学/国立清华大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116814
摘要
我们研究了一种新型轻量化奥氏体Fe-Mn-Al-Si-C钢的机械性能,它同时具备了轻量化钢和TWIP钢的特点。材料设计的关键在于协同添加Al和Si,从而同时实现49.5mJ/m2的层错能、短程有序和低密度。材料通过微变形带的塑性滑移实现初始应变硬化。Hall-Petch系数为673MPa·μm0.5。在变形后期,虽然层错能不低,但当应力到达临界应力时,仍会引起层错和孪晶的形成。这是首次在轻量化钢中察到这种转变,并最终使材料实现了约2.4GPa加工硬化率。本研究中的轻量化TWIP钢密度为g/cm3 , 抗拉强度800-950MPa,总伸长率为67-77%。此外,我们建立了一个位错模型以阐明材料从位错滑移到机械孪晶的机制转变。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116798
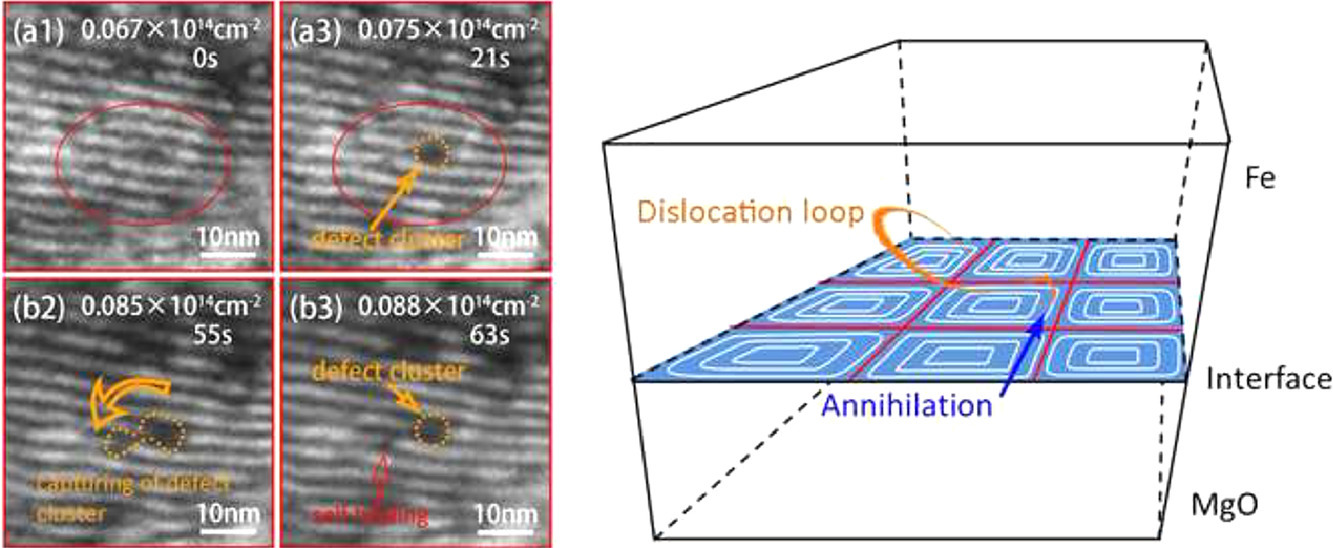
4. Stress of misfit dislocation at Fe/MgO interface drives the annihilation of radiation induced defects
错配位错应力引起的Fe/MgO界面辐照缺陷湮灭
J.L. Du, H.Q. Chen, C. Xu, Y. Fan, Y.H. Qiu, H. Wang✉, E.G. Fu✉
H. Wang:qinghe5525@163.com(中国核动力研究所)
E.G. Fu:efu@pku.edu.cn(北京大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116798
摘要
界面能够有效地捕获和复合在辐照级联碰撞过程中产生的Frenkel缺陷对。深入了解辐照条件下界面与缺陷的相互作用机制能够帮助我们更好地设计具有优异抗辐射性能的材料。我们利用原位辐照实验,研究了界面捕获和复合辐照缺陷的机理。我们观察到了辐照缺陷簇(DCs)的湮灭,计算了具有错配位错阵列的Fe/MgO界面的应力场,并讨论了其对辐照缺陷的影响。我们根据实验和计算结果,确定了界面与辐照缺陷的作用效率。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116816
5. Ideal superelasticity in Ni-based Heusler alloys
Ni基Heusler合金的超弹性研究
Peiyu Cao, Fuyang Tian✉, Wei Li, Levente Vitos, Yandong Wang
F. Tian:fuyang@ustb.edu.cn(北京科技大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116816
摘要
应力诱导一阶马氏体相变引起的超弹性过程中的迟滞现象对材料性能不利。我们通过第一性原理计算系统研究了化学成分和晶体无序性对Ni50-xCoxM25Ga25 (M = Mn, Fe)合金超弹性的影响。我们通过合金中应力-应变关系的计算重现了近来实验上在一定成分和有序性范围内观测到的非迟滞超弹性结果。我们对布洛赫谱函数进行了估计,以研究与非迟滞超弹性有关的费米表面拓扑。我们提出了由Landau-de Gennes模型决定的临界参数Pc, 用于预测迟滞超弹性材料的组成范围。对于铁磁性L21 Ni50-xCoxMn25Ga25合金和B2 Ni50-xCoxFe25Ga25合金,理论上当x分别在16和28以上时,将出现的非迟滞超弹性现象。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116825
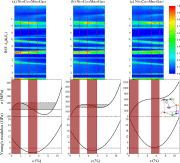
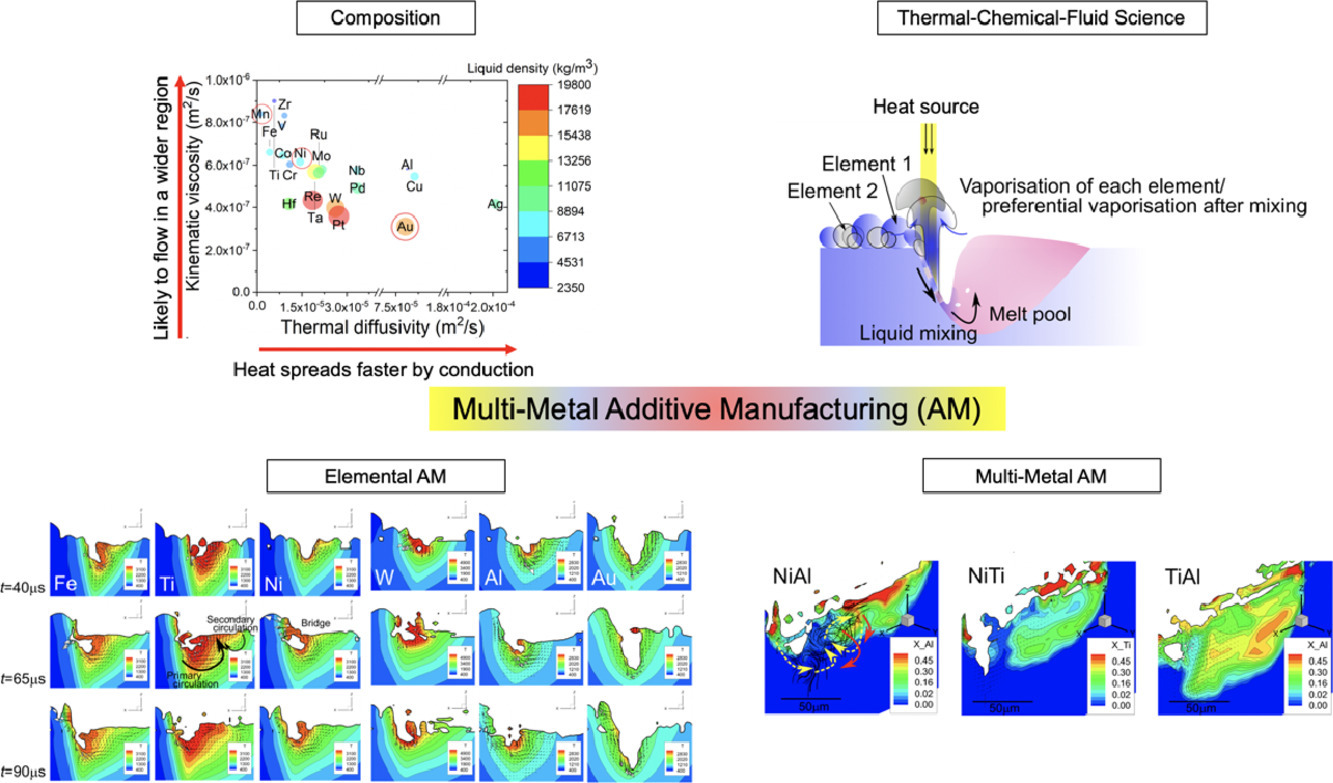
6. Digital materials design by thermal-fluid science for multi-metal additive manufacturing
基于热流体科学的金属材料增材制造数字化设计
Junji Shinjo, Chinnapat Panwisawas✉
C. Panwisawas:chinnapat.panwisawas@leicester.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116825
摘要
增材制造是制备复杂结构先进金属部件的有效手段。这一方法中的主要难点在于熔体动力学、合金混合和蒸汽质量损失的控制,它们对部件成品质量至关重要。在此,我们提出了一套高保真的热溶流体建模方法,可以精确地跟踪表面形状、热毛细管动力学和汽化过程。并且这一方法也适用于多组分金属模拟。我们基于该方法,研究了21种过渡金属和3种二元合金蒸汽质量损失与溶体流动过程的物理联系。结果表明,质量损失率受流体动力学中的雷诺数控制,呈现简单的比例关系,而在原位混合制备的二元合金中这一关系则更加复杂。通过数字化建模可以帮助我们深入理解溶体动力学,从而帮助我们进行材料工艺设计。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116807
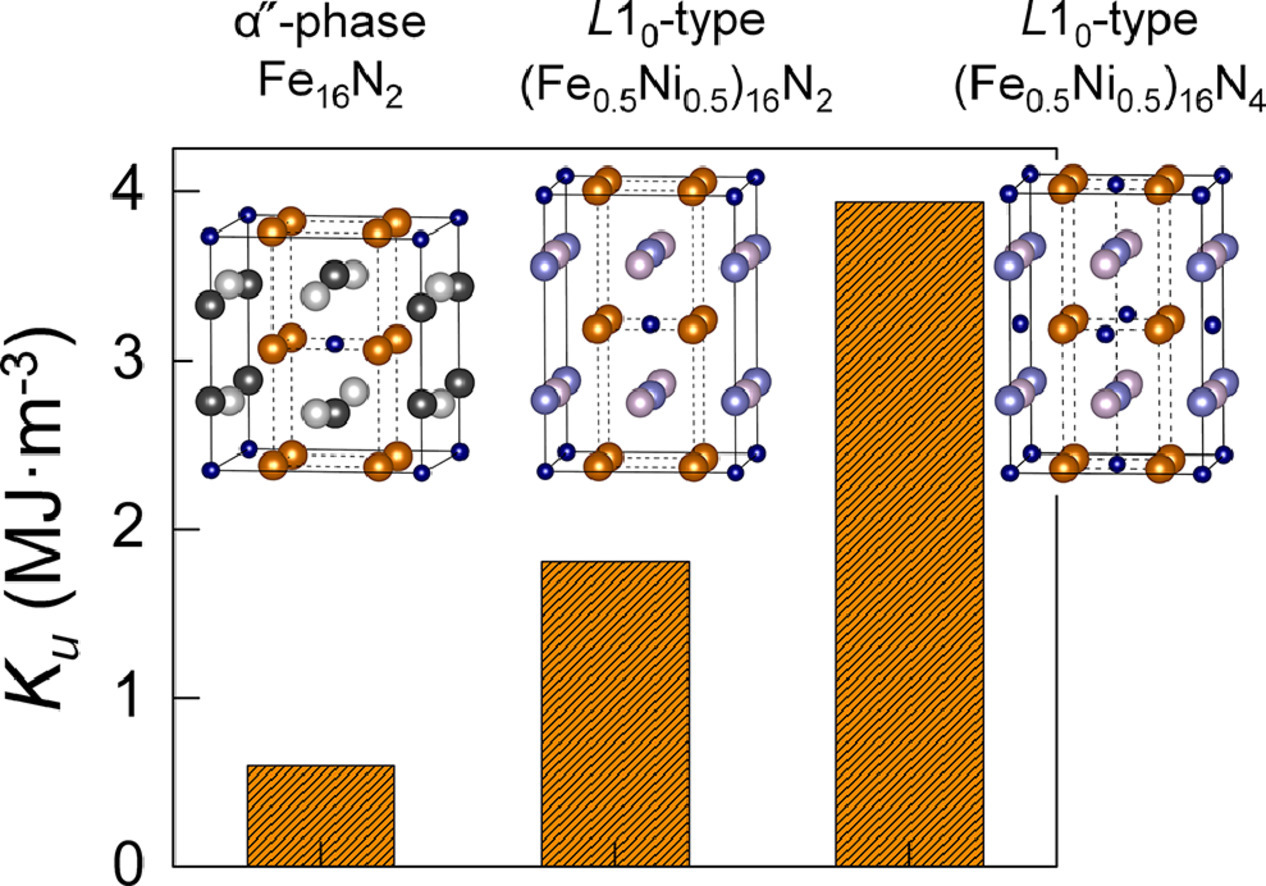
7. Fe−Ni−N based alloys as rare-earth free high-performance permanent magnet across α'' to L10 phase transition: A theoretical insight
无稀土元素添加Fe-Ni-N基合金高性能永磁体的α″→L10相变理论研究
D. Tuvshin, T. Tsevelmaa, S.C. Hong✉, D. Odkhuu✉
S.C. Hong:schong@ulsan.ac.kr
D. Odkhuu:odkhuu@inu.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116807
摘要
多年来,在不添加其他重元素或稀土元素的条件下,同时增强3d族金属的能量密度和热稳定性一直是永磁领域的一个巨大挑战。在本研究中,我们利用密度泛函理论和蒙特卡罗模拟研究了(Fe1-xNix)16N2(x=0−1)合金在α″→L10相变过程中的结构稳定性和固有磁性。我们从理论上阐明了L10 (Fe0.5Ni0.5)16N2合金单轴磁各向异性(Ku)的增强可高达1.8MJ·M-3,约三倍于α″-Fe16N2(0.6MJ·M-3)和L10-FeNi(0.68MJ·m-3)。同时,预测结果表明,L10 Fe0.5Ni0.5)16N2相在能量上比α″-Fe16N2相更稳定。进一步计算表明,在添加额外间隙N原子的情况下,L10 (Fe0.5Ni0.5)16N2的Ku可增加至近3.9MJ·m-3。综上所述,经过设计调控的Fe16N2基化合物是极有潜力的无稀土永磁材料。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116829
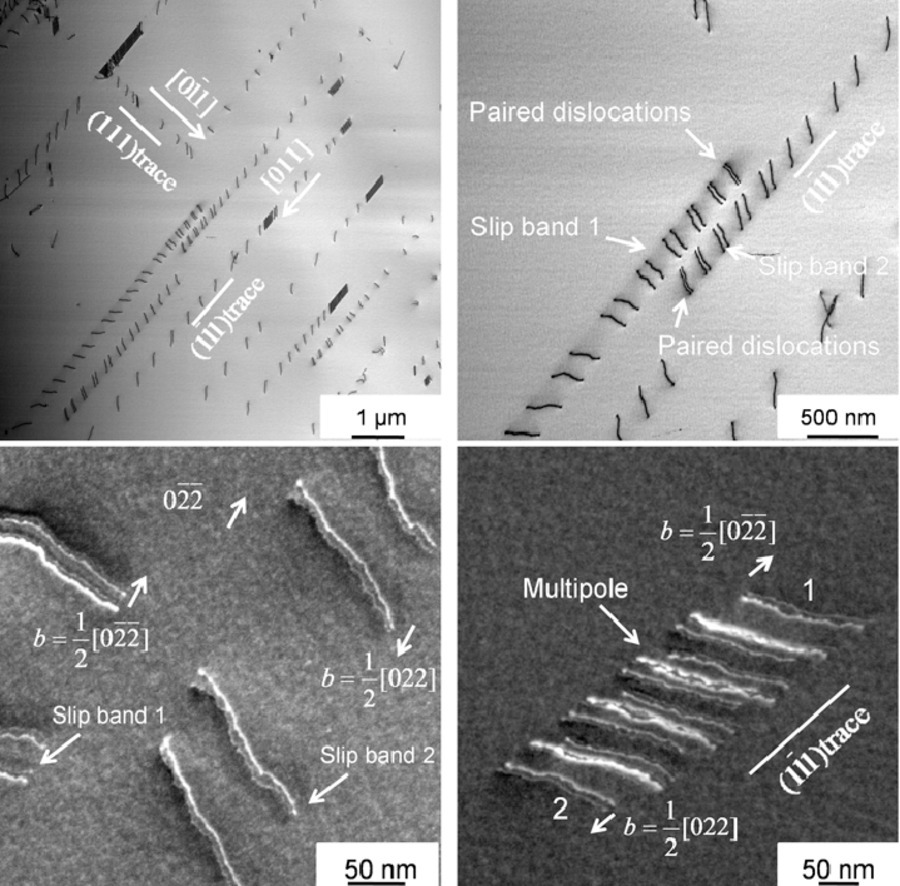
8. Ordering effects on deformation substructures and strain hardening behavior of a CrCoNi based medium entropy alloy
有序化对CrCoNi基中熵合金变形亚结构和应变硬化行为的影响
Jiashi Miao✉, Connor Slone, Sriswaroop Dasari, Maryam Ghazisaeidi, Rajarshi Banerjee, Easo P. George, Michael J. Mills✉
J. Miao:miao.152@osu.edu
M.J. Mills:mills.108@osu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116829
摘要
少量添加了Ti、Al、Nb元素的淬火态CrCoNi基中熵合金(可表示为(CrCoNi)93Al4Ti2Nb)可在室温下表现出与等原子比CrCoNi合金相当的拉伸性能。透射电镜(TEM)暗场像、原子分辨率高角环形扫描透射电镜(HAADF-STEM)暗场像和原子探针(APT)表征表明,合金中存在长程有序的L12 畴。我们通过背散电子衍射(EBSD)、电子隧穿比对成像(ECCI)和扫描透射电镜(STEM)弱束暗场成像技术,对合金中的塑性变形亚结构演化进行了表征。研究表明,塑性变形是通过a/2<110>位错滑移发生的,它们在{111}滑移面上分解为Shockley分位错。(CrCoNi)93Al4Ti2Nb合金中的分离间距比等原子比CrCoNi合金中小的多。且这种合金中的位错滑移具有明显的平面滑移特征。由于长程有序畴的存在,滑移带中的头部位错成对滑移。相邻{111}滑移平面上相反位错的滑移形成多极子。这些多极子形成了具有细小滑移带的亚晶界结构。塑性变形过程中,滑带之间的距离不断缩小。滑移带的动态细化在应变硬化过程起关键作用。此外,我们对LRO畴对平面位错滑移、形变孪晶抑制和应变硬化的影响进行了讨论。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116826
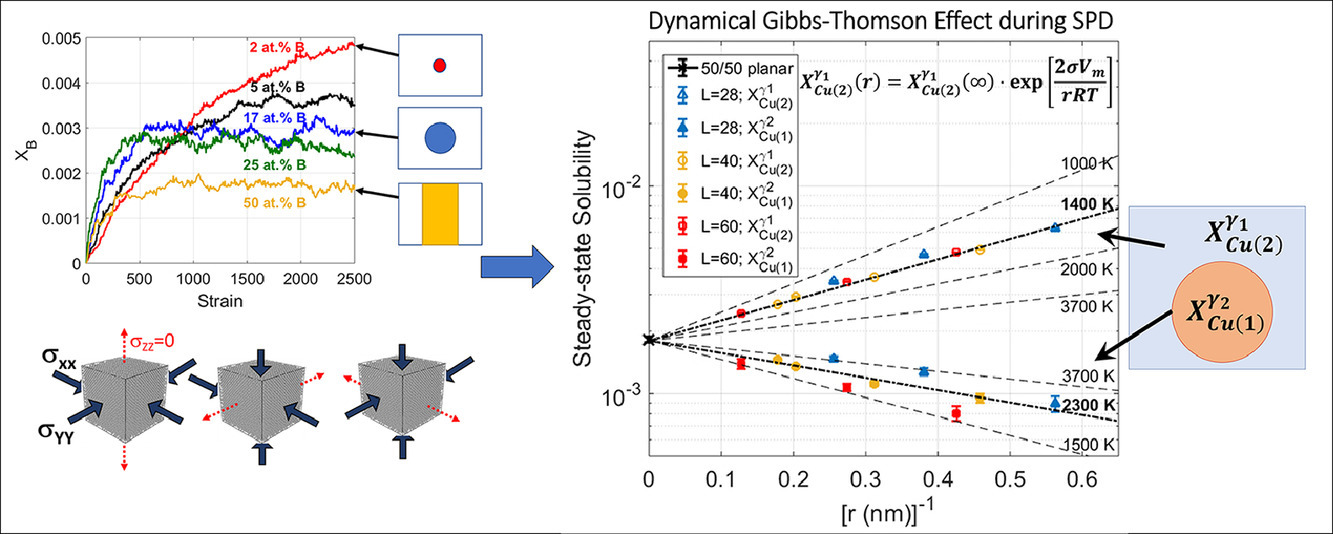
9. Phase evolution in two-phase alloys during severe plastic deformation
双相合金在严重塑性变形过程中的相变研究
Nirab Pant✉, Nisha Verma, Yinon Ashkenazy, Pascal Bellon, Robert S. Averback
N. Pant:pant4@illinois.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116826
摘要
我们利用分子动力学模拟研究了具有强相互作用合金成分的FCC金属在严重塑性变形过程中的相变,包括合金稳态组织、超饱固溶体中的析出形核和长大、以及非饱和固溶体中的析出溶解。我们将结果与改进后的等效温度模型进行了比较,描述了模型背后的原子尺度的物理过程并阐述了模型的优缺点。这项工作取得的重要成果包括:100K下SPD过程中析出的形核长大;持续剪切作用下稳态溶解度和析出尺寸的类吉布斯-汤姆逊关系;有效温度和剪切模量之间的直接关系;以及析出长大过程中团簇的影响。研究还表明,化学混合机制与析出大小有关,这增加了描述非均匀系统的有效温度模型的复杂性。模拟结果与文献报导的实验结果取得了半定量的一致。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116830
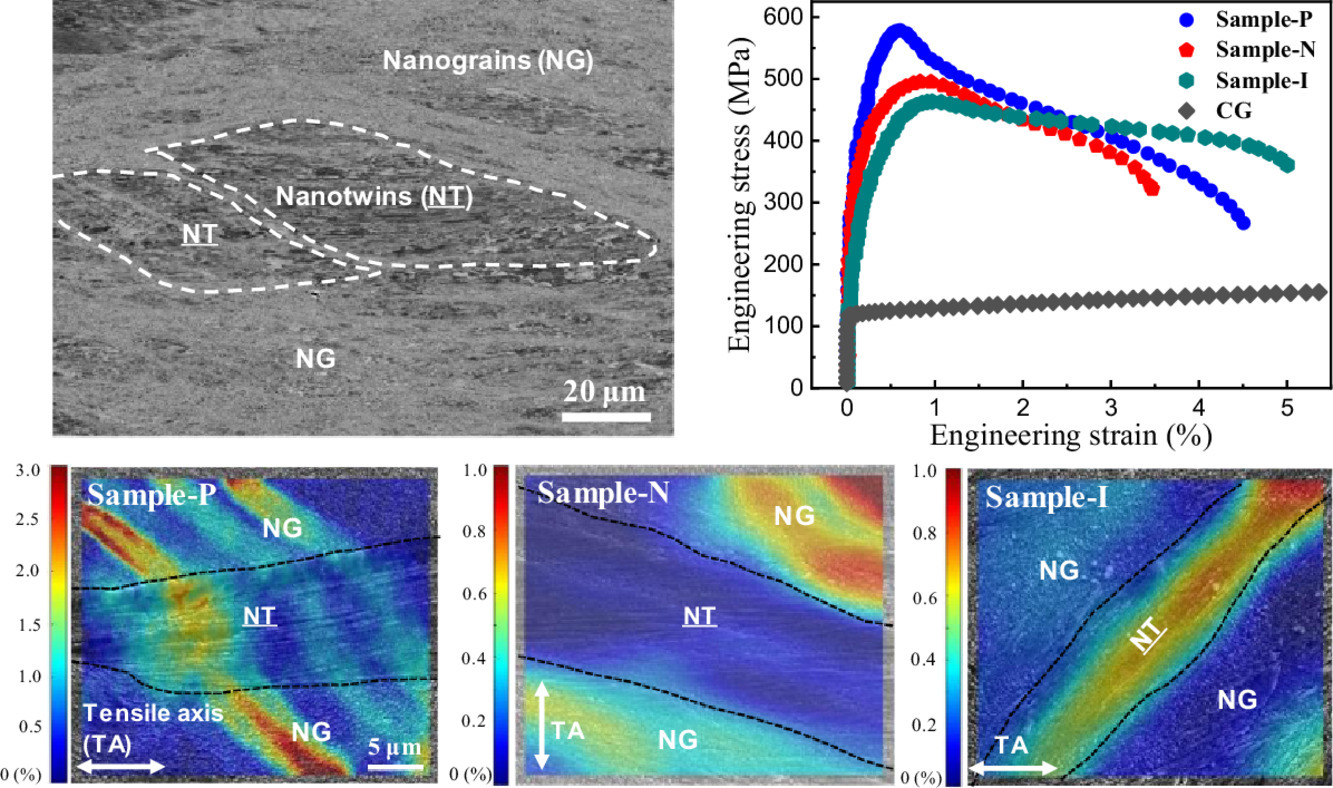
10. Anisotropic strengthening of nanotwin bundles in heterogeneous nanostructured Cu: Effect of deformation compatibility
变形相容性对非均匀纳米Cu结构中纳米孪晶各向异性强化的的影响
H.Z. Zhao, Z.S. You, N.R. Tao, L. Lu✉
L. Lu:llu@imr.ac.cn(金属所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116830
摘要
我们在平行、垂直和45°加载条件下研究了由各向同性纳米晶基体和各向异性纳米孪晶组成的非均匀纳米铜结构的拉伸行为。与均匀纳米孪晶对比组表现出的各向异性强化作用不同,异质结构在平行张力下强度最高,在垂直张力下强度中等。高分辨数字图像分析(DIC)表明,纳米孪晶和基体之间存在各向异性的的变形相容性,即在平行取向上相容,而在与孪晶界垂直和45°方向上显著不相容。研究表明,纳米孪晶在异质纳米结构中的强化作用不仅依赖于自身的强度,而且受到周围结构变形相容性的影响。纳米晶基体中各向同性剪切带与纳米孪晶各向异性变形的相互作用导致了最终的变形相容性与取向有关。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116844
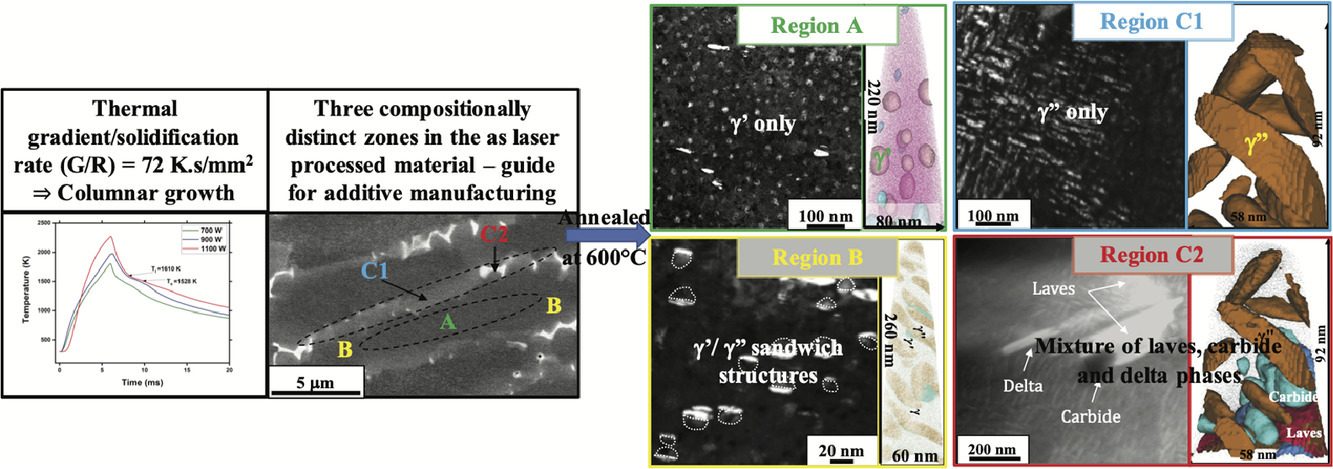
11. Effect of micro-segregation of alloying elements on the precipitation behaviour in laser surface engineered Alloy 718
合金元素微观偏析对激光表面加工718合金析出行为的影响
Srinivas Aditya Mantri, Sriswaroop Dasari, Abhishek Sharma, Talukder Alam,Mangesh V. Pantawane, Mayur Pole, Shashank Sharma, Narendra B. Dahotre, Rajarshi Banerjee✉, Srikumar Banerjee✉
R. Banerjee:raj.banerjee@unt.edu
S. Banerjee:sbanerjee1946@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116844
摘要
激光表面工程已被广泛用于调控718合金增材制造时的组织演化,特别是在熔化和凝固过程中。表面激光熔化区域的合金元素偏聚对局部析出相形成具有重要影响。通过快速熔化和凝固形成的枝晶组织可被分为3个不同区域:1)核心区 2)枝晶外围 3)枝间通道。其中核心区主要形成 γ′ [Ni3(Al, Ti, Nb)] 析出;枝晶外围主要在奥氏体中形成γ″ [Ni3(Nb, Mo)]析出和γ′/γ″复合析出);而富Nb、 Mo、C的枝间通道则含有离散的LAVES相和碳化物团簇,是δ相的优先形核位置。通道中的Nb富集引起了后续退火处理是的高密度γ″析出。我们使用SEM、TEM和APT等表征手段,揭示了成分非均匀718合金中的析出特征,这些特征在激光增材制造构件中广泛存在。此外,我们利用三维原子探针对合金元素在纳米尺度上的偏聚进行了表征和解释。