金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.210,15 May. 2021(下)
2021-07-04 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文11篇,涵盖了马氏体、高熵合金、形状记忆合金等,国内科研单位包括香港城市大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 210 目录
1. Highly pressurized helium nanobubbles promote stacking-fault-mediated deformation in FeNiCoCr high-entropy alloy
高压纳米氦泡对FeNiCoCr高熵合金层错介导变形的促进作用
2. On aliovalent cations control of α-alumina growth on doped and undoped NiAl
通过共价阳离子调控掺杂/未掺杂NiAl合金表面α-氧化铝的生长
3. Optimal transportation of grain boundaries: A forward model for predicting migration mechanisms
预测晶界迁移机制的向前模型研究
4. Screening of generalized stacking fault energies, surface energies and intrinsic ductile potency of refractory multicomponent alloys
基于层错能、表面能和本征延性对多组分高熔点合金进行快速筛选
5. Stasis mechanism of γ → ε martensitic transformation in Fe-17Mn alloy
Fe-17Mn合金中的γ → ε马氏体相变停滞效应机理研究
6. Effect of sink strength on coherency loss of precipitates in dilute Cu-base alloys during in situ ion irradiation
原位离子辐照过程中汇强度对Cu基合金中析出相共格性损失的影响
7. Tuning Magnetocaloric Effect of a Mn-Cr-Sb-Ga alloy by the Nonvolatile Residual Strain of a Ti-Ni Shape Memory Alloy
通过Ti-Ni形状记忆合金的残余应变调控Mn-Cr-Sb-Ga合金的磁热效应
8. Statistical modeling of microstructure evolution in a Ti-6Al-4V alloy during isothermal compression
Ti-6Al-4V合金等温压缩过程中组织演化的统计模型
9. Effects of local stress, strain, and hydrogen content on hydrogen-related fracture behavior in low-carbon martensitic steel
局部应力、应变和氢含量对低碳马氏体钢氢致断裂行为的影响
10. In-situ investigation of anisotropic crystalline and bulk negative thermal expansion in titanium alloys
钛合金中各向异性晶体或块体负热膨胀系数的原位研究
11. On a new Ti-carbooxinitride redistribution driven microcrack healing mechanism in an annealed 14YWT nanostuctured ferritic alloy
借助Ti的碳氮化物重新分布实现14YWT纳米铁素体合金中退火后的微裂纹愈合
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116843
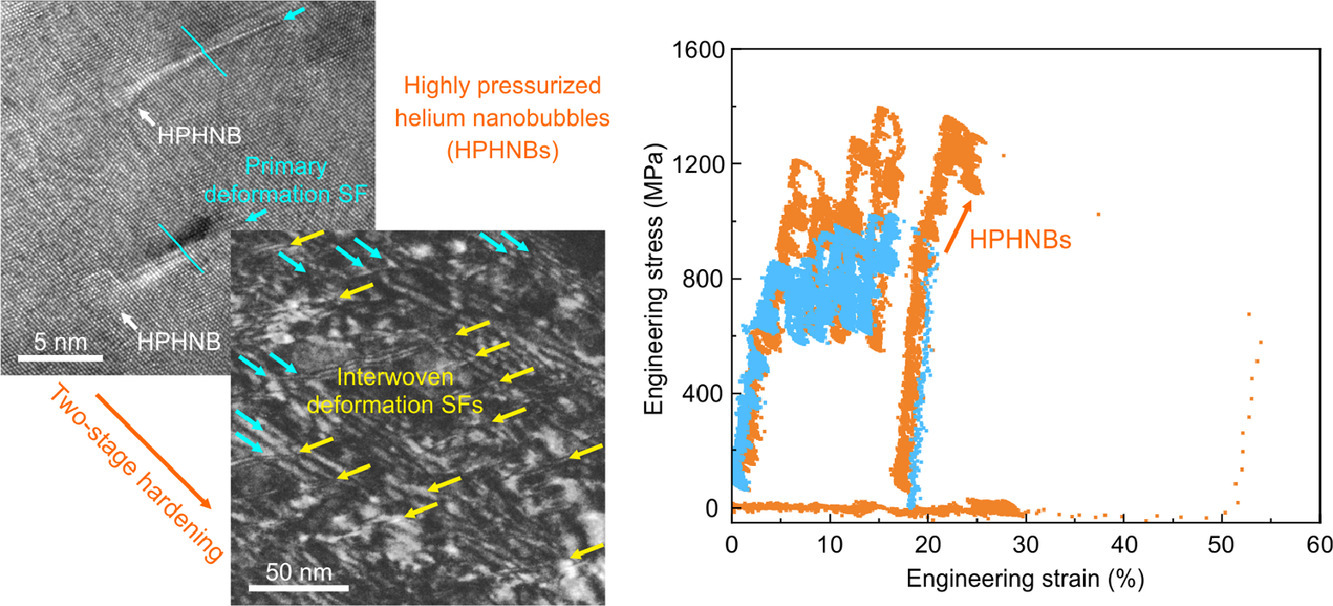
1. Highly pressurized helium nanobubbles promote stacking-fault-mediated deformation in FeNiCoCr high-entropy alloy
高压纳米氦泡对FeNiCoCr高熵合金层错介导变形的促进作用
W.T. Lin, D. Chen, C.Q. Dang, P.J. Yu, G. Wang, J.H. Lin, F.L. Meng, T. Yang, Y.L. Zhao, S.F. Liu, J.P. Du, G.M. Yeli, C.T. Liu, Y. Lu✉, S. Ogata✉, J.J. Kai✉
Y. Lu:yanglu@cityu.edu.hk(香港城市大学)
S. Ogata:ogata@me.es.osaka-u.ac.jp
J.J. Kai:jijkai@cityu.edu.hk, jjkai34280@gmail.com(香港城市大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116843
摘要
纳米缺陷调控对于合金组织设计与性能优化至关重要。与主流增韧机制(如机械孪晶和形变诱导相变)不同,我们在等原子比FeNiCoCr高熵合金(HEA)中,通过可控地引入高压纳米氦泡,实现了一种特别的层错介导变形机制。通过原位透射电镜力学测试,我们证明了纳米氦泡不仅可以作为位错障碍提高强度,还可以通过促进层错的增殖和相互作用来提高应变硬化能力,增强材料塑性。我们通过原子尺度模拟揭示了高压有助于降低纳米氦泡表面分位错的形核能垒,从而提高了位错的形核率并为保持延性提供了可持续的层错源。我们的研究结果为高熵合金性能调控提供了一种新的设计策略。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116809
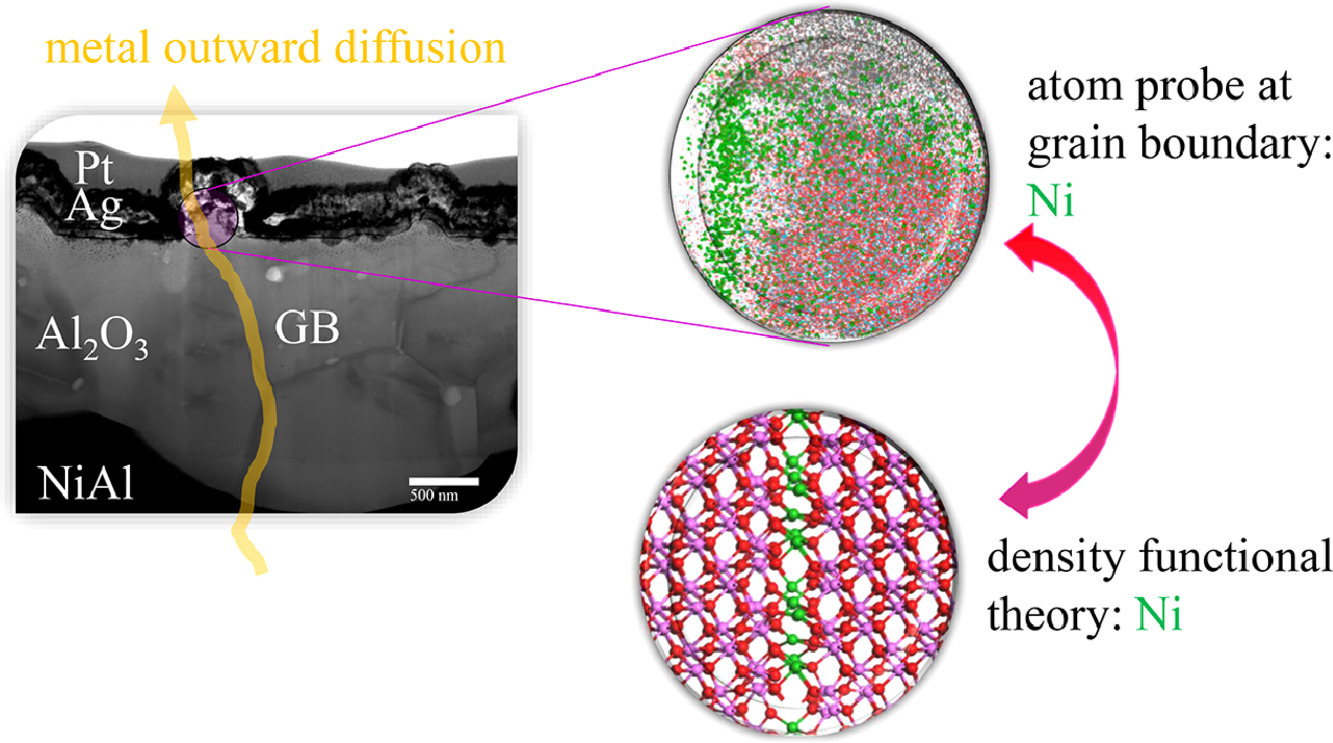
2. On aliovalent cations control of α-alumina growth on doped and undoped NiAl
通过共价阳离子调控掺杂/未掺杂NiAl合金表面α-氧化铝的生长
Torben Boll, Vedad Babic✉, Itai Panas, Olof Bäcke, Krystyna Stiller
V. Babic:vedadb@chalmers.se
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116809
摘要
镍基高温合金表面的氧化铝包覆对其高温抗氧化性能至关重要。通过两步法可以对在1100°形成的氧化物外沿生长和氧化铝晶界覆盖过程进行分析。本研究中,我们以无掺杂50Ni50Al(at%)合金作为对照组,通过原子探针定量研究了具有相互作用的元素(Zr和Hf)对扩散过程的影响。研究发现,在氧化铝晶界中存在单层镍。此外,由于相互作用元素的影响,铝和镍的扩散率下降了两个数量级。我们使用密度泛函理论对Ni(II)、Zr(IV)和Hf(IV)等阳离子在α−氧化铝的作用进行了计算。计算结果表明,Ni不仅可以装饰氧化铝的晶界,还可以促进电子和氧空位的传输,从而促进了氧化物的生长。而相互作用元素会促进氧空位的湮灭,消除带隙中的杂态,从而降低了氧化物的生长速率。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116823
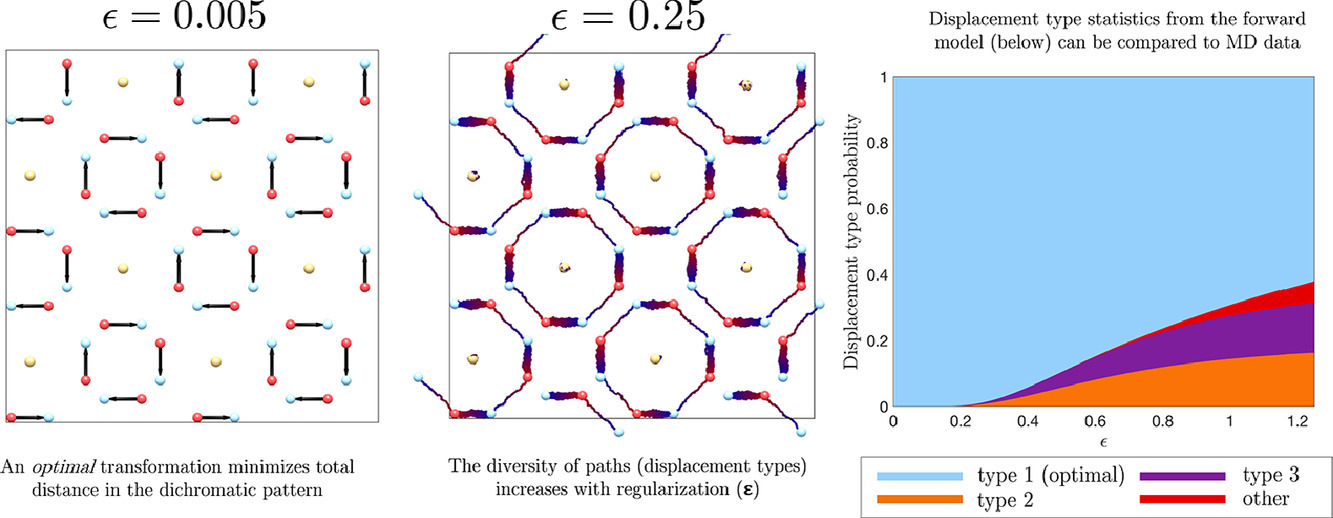
3. Optimal transportation of grain boundaries: A forward model for predicting migration mechanisms
预测晶界迁移机制的向前模型研究
Ian Chesser✉, Elizabeth Holm✉, Brandon Runnels✉
I. Chesser:ichesser@andrew.cmu.edu
E. Holm:eaholm@andrew.cmu.edu
B. Runnels:brunnels@uccs.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116823
摘要
据推测,晶界(GB)迁移过程中原子位移最少的机制是最有可能的原子重排机制。本研究中,我们将晶界迁移过程中的原子位移最小化问题重新表述为一个最优迁移(OT)问题。我们假设原子重排的势垒较小,则晶界迁移的平稳作用原则可以简化为确定两点间距的Wasserstein度量集。为了验证最小距离假设,我们将基于正则化向前OT模型预测的最优位移模式与各种晶界在不同温度下的分子动力学(MD)迁移数据进行了比较。我们进一步对最小距离假设的适用性和OT模拟得到的有趣结果进行了讨论。该向前模型可用于预测任意不连续模式或亚稳态下的原子位移,对多模态GB迁移数据分析具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116800
4. Screening of generalized stacking fault energies, surface energies and intrinsic ductile potency of refractory multicomponent alloys
基于层错能、表面能和本征延性对多组分高熔点合金进行快速筛选
Yong-Jie Hu, Aditya Sundar, Shigenobu Ogata, Liang Qi✉
L. Qi:qiliang@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116800
摘要
高熔点BCC多组分合金因其在高温下的优异强度而备受关注。如何通过优化合金成分,同时实现高强度和高室温延展性是合金设计的难点。在巨大的成分空间中,对材料性能相关性进行系统预测,可以大幅加速合金研发。在研究中,我们通过特殊准随机(SQS)方法进行了第一性原理计算,对106种含有Ti、Zr、Hf、V、Nb、Ta、Mo、W、Re、Ru等元素的二元、三元或四元合金中的(1-10)[111]滑动系统不稳定层错能(γusf)和(1-10)面表面能(γsurf)进行了计算。此外,基于第一性原理计算结果和一组物理描述符,我们开发了可以准确、有效预测10维组分空间中高熔点BCC合金γusf和γsurf的统计回归模型。尽管我们借助二元和三元合金数据对模型进行了搭建,但模型在高阶系统中仍表现出出色的预测能力。基于γsurf和γusf的比值,可以建立基于裂纹尖端变形的延性预测模型。因此,我们对超过112,378种合金成分的γusf、γsurf及其比值进行了快速计算,并筛选出了可能发生强度-延性协同增强的合金成分。我们也通过第一性原理对筛选结果进行了验证。
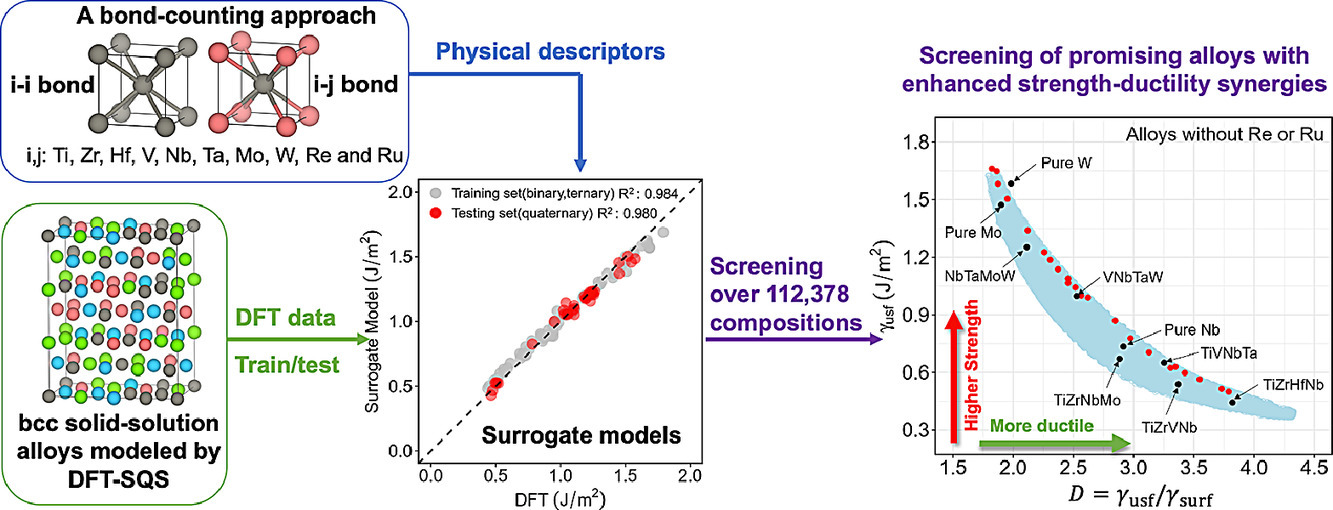
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116846
5. Stasis mechanism of γ → ε martensitic transformation in Fe-17Mn alloy
Fe-17Mn合金中的γ → ε马氏体相变停滞效应机理研究
Jin-Sung Hong, Seon-Min Choi, Young-Kook Lee✉
Y.-K. Lee:yklee@yonsei.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116846
摘要
我们观察到了Fe-17Mn合金中的不完全马氏体转变,即连续冷却过程中,γ奥氏体→ε马氏体相变在一定温度下停止,ε相分数不再随温度的进一步降低而增加。我们通过对不同γ晶粒尺寸的Fe-17Mn样品进行微观组织观察、热力学计算和拉伸试验,研究了这种相变停滞的机理。在所有样品中,不论γ晶粒大小,都能观察到相变停滞现象,并且相变停滞温度随γ晶粒尺寸的减小而降低。相变停滞是由动态晶粒细化导致的,ε马氏体将γ晶粒分割成多个亚晶粒。亚晶周围的γ/ε相界对γ→ε相变具有比γ晶界更强的抑制效应。因此,在相同的亚晶尺寸下,因为γ晶界比例更高,因此γ晶粒尺寸小的样品表现出更活跃的γ→ε转变。我们考虑了γ晶界与γ/ε相界之间的特征差异,重新计算了γ→ε相变的驱动力,对相变停滞现象进行了解释。
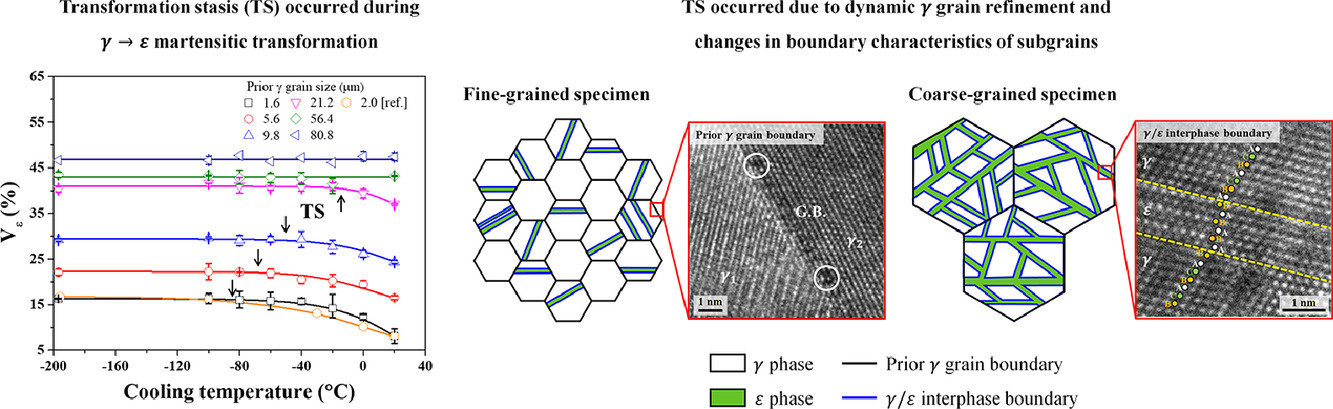
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116812
6. Effect of sink strength on coherency loss of precipitates in dilute Cu-base alloys during in situ ion irradiation
原位离子辐照过程中汇强度对Cu基合金中析出相共格性损失的影响
Ling Wang✉, David Martin, Wei-Ying Chen, Peter M. Baldo, Meimei Li, Brian D. Wirth, Steven J. Zinkle
L. Wang:lwang85@vols.utk.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116812
摘要
我们采用原位辐照实验研究了含有均匀弥散共格析出的Cu-0.9Co, Cu-0.9Fe 和 Cu-0.8Cr 合金中,初始汇强度、损伤剂量和辐照温度对析出相共格性的影响。实验采用1 MeV Kr离子,实验温度50~613K,辐照通量为1014/cm2(~1.25 dpa.)。我们采用了具有不同点缺陷汇强度(2πNd,其中N、d分别为析出密度和直径)的共格析出来研究点缺陷吸收过程中的差异。在所有实验中,低剂量辐照(<~1dpa)都显著引起了析出共格性的损失。在低汇强度的情况(~1013m−2)下,~0.01dpa辐照即可导致析出共格性损失。这表明,由于小尺寸析出的拉伸应变,可能存在一种中等应变诱导间隙缺陷吸收机制,从而导致了析出汇强度较低的情况下共格性的快速损失。析出汇强度(~1014m−2)较高时,材料对共格性损失的抵抗能力较强,(需~1dpa辐照),这可能是由于在高析出汇强度条件下,到达析出界面的间隙原子和空位缺陷几乎相等。此外,我们发现析出的共格性损失与辐照温度的关系不显著。分子动力学模拟证实了析出汇强度对间隙原子吸收的强烈影响。
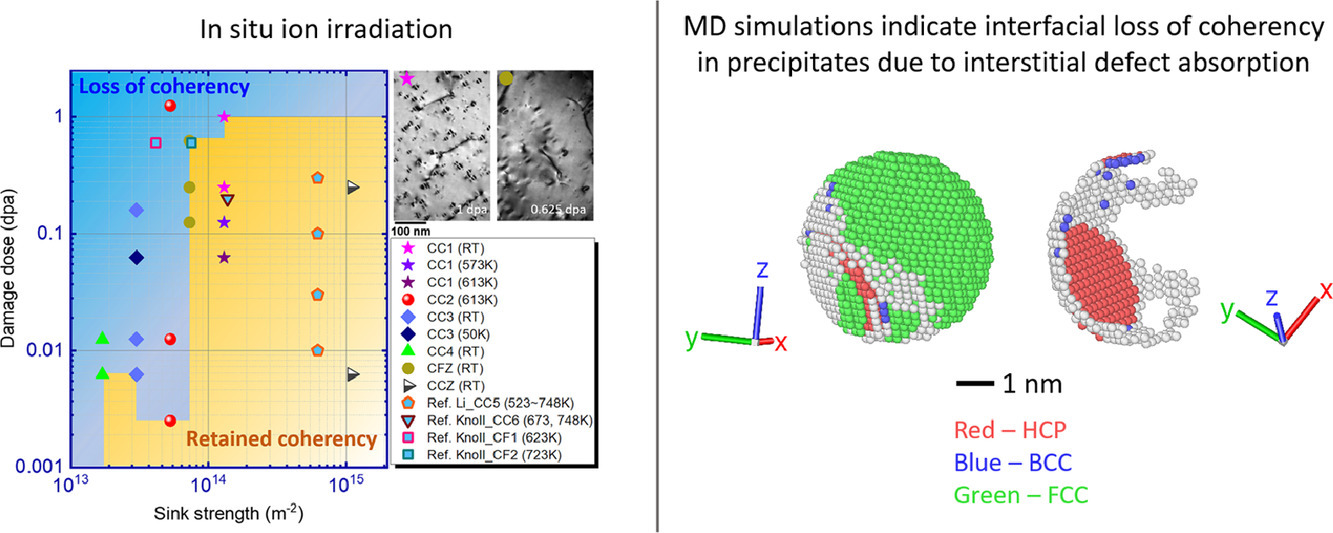
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116849
7. Tuning Magnetocaloric Effect of a Mn-Cr-Sb-Ga alloy by the Nonvolatile Residual Strain of a Ti-Ni Shape Memory Alloy
通过Ti-Ni形状记忆合金的残余应变调控Mn-Cr-Sb-Ga合金的磁热效应
Fei Cheng, Sai Ma, Yu Wang✉, Xiaoqing Ke, Jingmin Wang, Sen Yang
Y. Wang:yuwang@mail.xjtu.edu.cn(西安交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116849
摘要
在压电基体上沉积一层磁热材料(MCMs)制备得到的多铁复合结构能够通过压电基体的应力调整磁热效应(MCE),从而实现高效的小范围制冷。对于相变温度TM对应力敏感的合金而言,压电基体的极小应变就足以实现对磁热效应的控调。然后,以上设计对于应力不敏的MCM则不够有效。本研究中,我们在Ti50Ni50形状记忆合金基板上制备了Mn1.95Cr0.05Sb0.95Ga0.05带状结构,得到了一种新的复合材料。Ti50Ni50基板可以产生比压电基板更大的应力,因此尽管Mn1.95Cr0.05Sb0.95Ga0.05的应力灵敏性较低,但仍可以很好地调控其MCE。当Ti50Ni50基底的残余应变达2%时,Mn1.95Cr0.05Sb0.95Ga0.05的TM增加了~6K,达到了Mn1.95Cr0.05Sb0.95Ga0.05/PMN-PT复合材料的~7.5倍。通过在0%到2%范围内调控Ti50Ni50基板的残余应变,可在1T低磁场下可获得31K的工作温度窗口。此外,该复合材料在不同应力下的制冷能力相对恒定且迟滞较小,有利于均匀传热,提高了工作效率。本研究提出了一种新的方法,可以有效调控应力不敏感MCMs的MCE,对于小型化制冷具有重要意义。
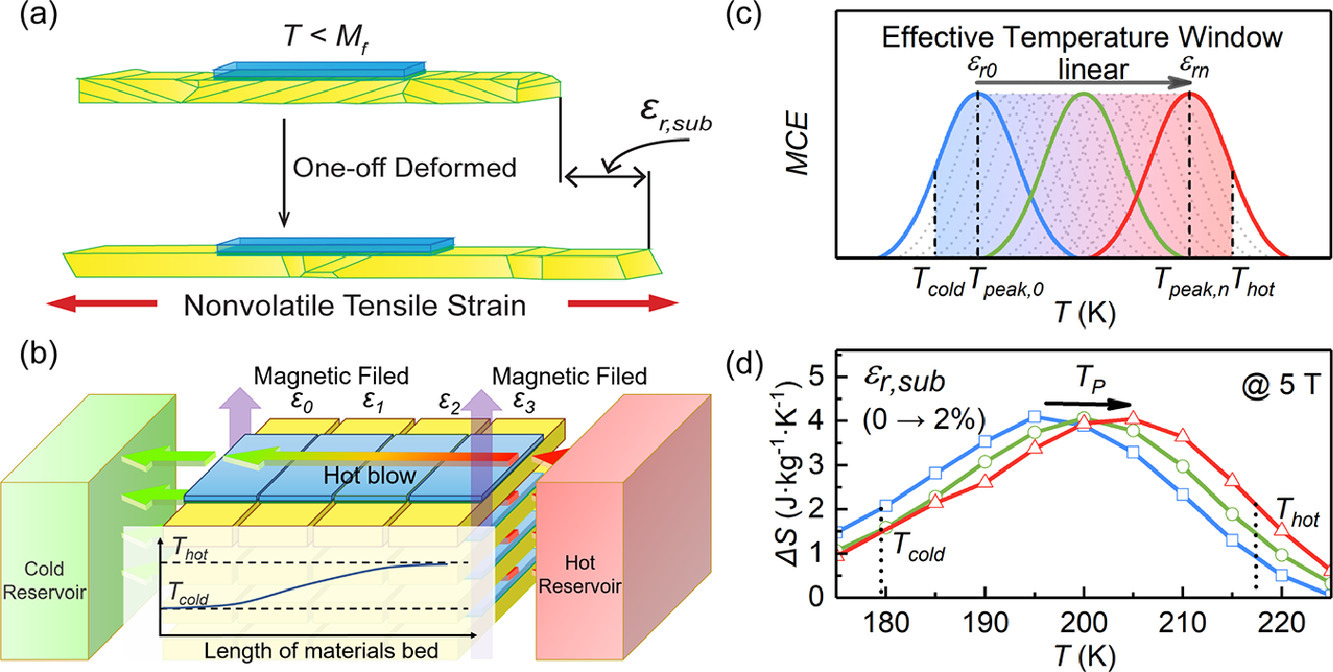
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116827
8. Statistical modeling of microstructure evolution in a Ti-6Al-4V alloy during isothermal compression
Ti-6Al-4V合金等温压缩过程中组织演化的统计模型
Eric Hoar✉, Souvik Sahoo, Mostafa Mahdavi, Steven Liang, Shibayan Roy, Hamid Garmestani
E. Hoar:eric_hoar@yahoo.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116827
摘要
我们建立了一种基于统计学的连续体模型,利用Ti-6Al-4V双相合金的组织信息来模拟其在等温热压缩过程中的组织演化。目前的组织预测模型通常使用有限元方法。而本模型不依赖有限元方法,并可以在不牺牲预测精度的情况下运行更快,消耗算力更少。该方法使用两点统计数据来描述与相分布、晶粒尺寸和晶粒形貌等有关的组织信息。公式采用宏观应变率张量来预测变形。随后利用变形量计算的形变微组织的两点统计数据。最后,我们将模拟的两点统计数据与背散电子衍射模式下的扫描电子显微图像实验结果进行了比较。
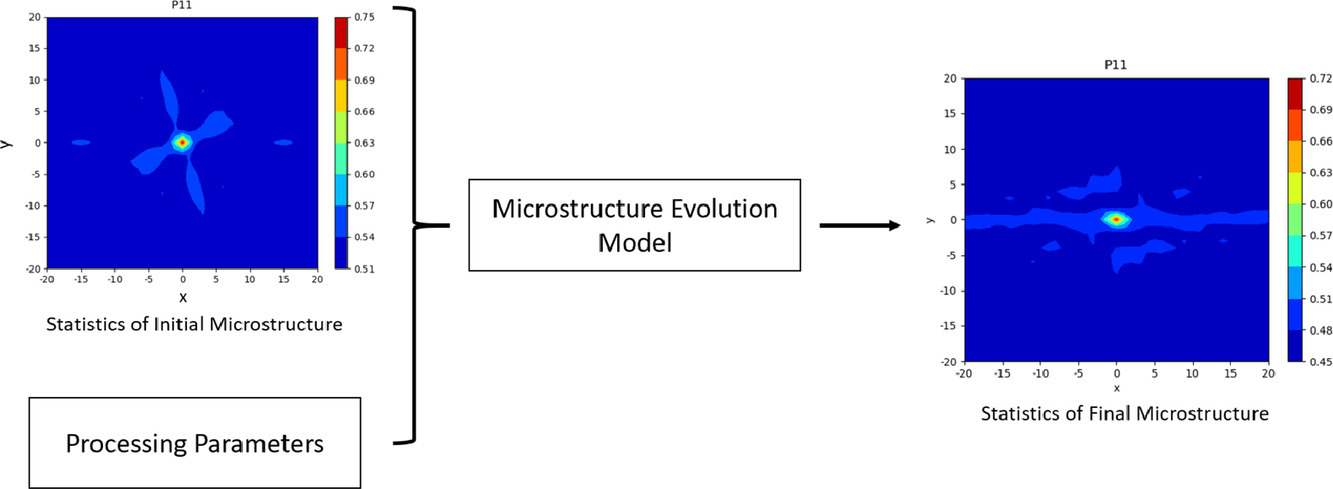
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116828
9. Effects of local stress, strain, and hydrogen content on hydrogen-related fracture behavior in low-carbon martensitic steel
局部应力、应变和氢含量对低碳马氏体钢氢致断裂行为的影响
Akinobu Shibata✉, Takashi Yonemura, Yuji Momotani, Myeong-heom Park, Shusaku Takagi, Yazid Madi, Jacques Bessond, Nobuhiro Tsuji
A. Shibata:SHIBATA.Akinobu@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116828
摘要
我们通过微观组织表征、有限元(FE)模拟和数字图像关联(DIC)分析,研究了具有不同应力浓度因子试样的氢致断裂行为。实验材料为具有全马氏体结构的Fe-0.2C二元模型合金。结果表明,当氢浓度较高(2.21 wt ppm/121 at ppm)时,裂纹沿原奥氏体晶界萌发并扩展。通过FE模拟,我们发现裂纹起始位置对应于高应力、高氢含量区域。虽然应力浓度因子不同,但裂纹起始点的应力水平和氢含量几乎相同,这表明与氢致晶间断裂是由于应力降低了原奥氏体晶界的结合力导致的。对于氢浓度较低(0.41 wt ppm/22.5 at ppm)的试样,准裂纹在样品表面沟槽底部形成并沿{011}面扩展。FE模拟表明,在准裂纹的起始位点为塑性应变最大的位置。此外,我们通过DIC证实了氢的存在增强了局部塑性变形。由于准裂纹萌生位置的最大主应力、塑性应变和局部氢含量随应力浓度系数不同而改变,因此准裂纹起始的关键定量条件非常复杂。
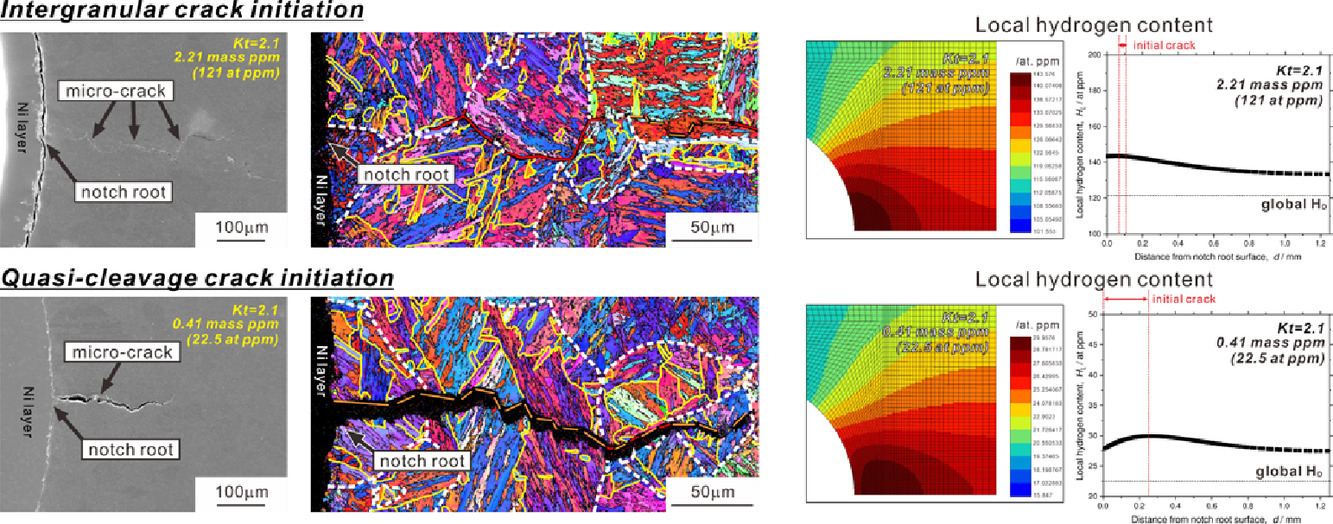
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116847
10. In-situ investigation of anisotropic crystalline and bulk negative thermal expansion in titanium alloys
钛合金中各向异性晶体或块体负热膨胀系数的原位研究
Dominic Gehring, Yang Ren, Zeina Barghouti, Ibrahim Karaman✉
I. Karaman: ikaraman@tamu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116847
摘要
基于晶体学各向异性热膨胀系数效应,我们可以通过马氏体相变对多晶TiNb合金的热膨胀系数(CTE)在负值到较大正值的范围内进行调控。然而,Nb含量、温度和变形等因素对于多晶热膨胀系数各向异性的影响仍不清楚。在本研究中,我们利用原位高能同步辐射X和迭代张力实验,系统地研究了含15-24 at%Nb的TiNb中织构、CTE各向异性和多晶CTE的演化。研究表明,在给定温度下,Ti76Nb24合金的CTE各向异性和多晶CTE最大,在90°C时可达+/-40ppmK−1。降低Nb含量可以在提高CTE各向异性的上限温度,但会牺牲多晶材料整体的CTE。增加形变会降低CTE各向异性。Ti76Nb24合金在应变下织构发生了明显变化,使其在5%应变后沿拉伸方向的CTE就从8 ppmK−1变为了-30 ppmK−1。低Nb合金在给定应变下表现出较低的CTE且织构演化不明显,因此Ti75Nb15的CTE没有明显变化。我们认为这是由于低铌合金中的马氏体二次取向伴随发生位错塑性。织构和拉伸实验的分析表明,不同TiNb合金中的应变水平、织构演化和CTE最低值之间存在直接关系。
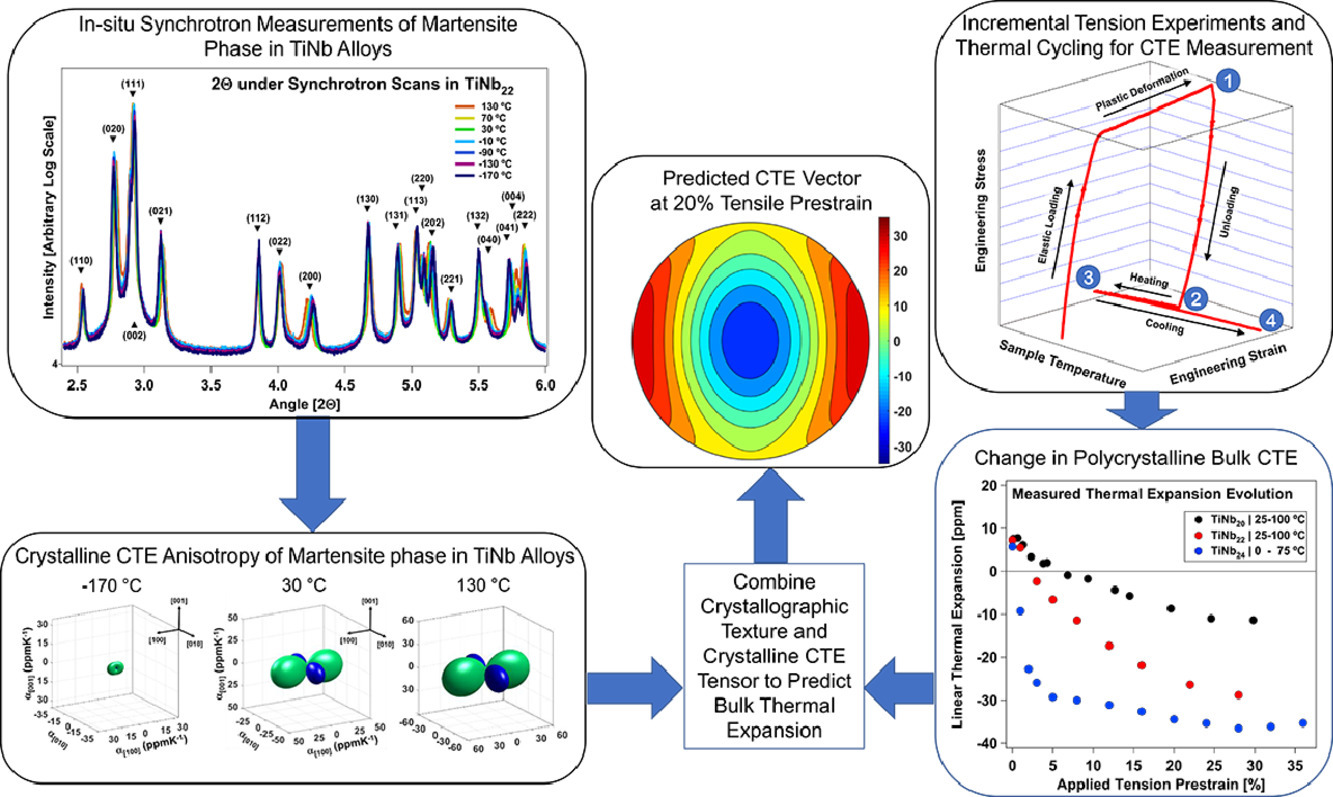
ACTA
Vol. 210,15 May. 2021, 116842
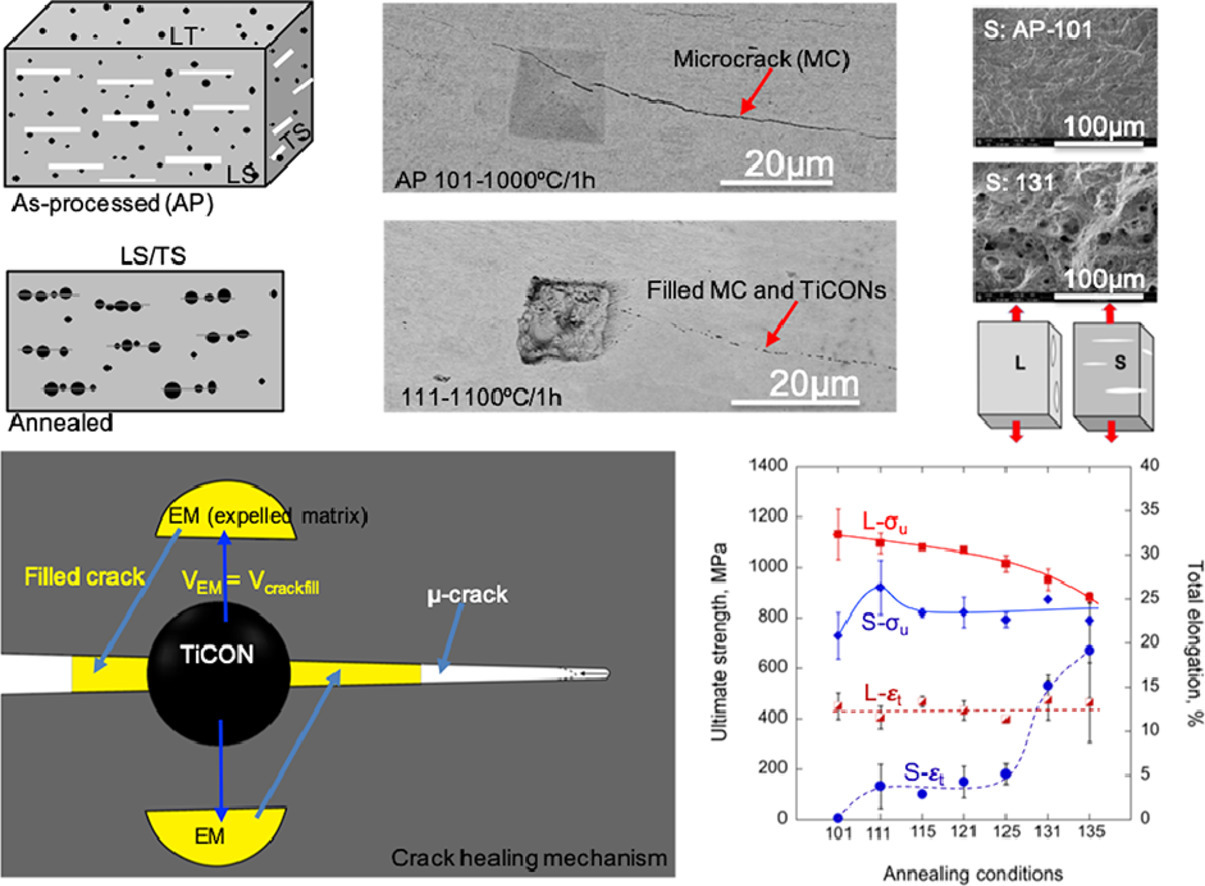
11. On a new Ti-carbooxinitride redistribution driven microcrack healing mechanism in an annealed 14YWT nanostuctured ferritic alloy
借助Ti的碳氮化物重新分布实现14YWT纳米铁素体合金中退火后的微裂纹愈合
M.E. Alam✉, S. Pal✉, N.J. Cunningham✉, G.R. Odette✉
M.E. Alam:alam@ucsb.edu
S. Pal:soupitak@ucsb.edu
N.J. Cunningham:Nicholas.Cunningham@ATImetals.com
G.R. Odette:odette@ucsb.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116842
摘要
FCRD NFA-1是Y2Ti2O7纳米氧化物强化Fe-14Cr铁素体合金(NFA)的大尺度制件。NFA-1采用氩雾化Fe-14Cr-3W-0.35Ti-0.25Y(wt.%)粉末制备,经850°C热压,1000°C 1h退火和交叉轧制,制成约10mm厚板。交叉轧制产生了大量平行于板面的{001}<110>系统微裂纹(MCs)。我们将材料在1100°C到1300°C间进行了一系列高温真空退火,以研究材料的微裂纹和宏观疲劳裂纹是否可能发生自我修复。结果我们发现了一种借由原始态下细小的Ti、C、O和N析出(TiCONs)在裂纹表面桥接位点重新分布和粗化而实现的裂纹自愈合机制。重新分布的TiCONs长大粗化,从而消耗了大量临近的Fe-Cr基体。基体原子的扩散进一步填补了裂纹。显微组织表征和力学测试结果,微裂纹在1100°C/1h开始自愈,自愈程度随着退火时间和温度升高而增加,直到1300°C完成自愈。NFA-1晶粒和织构相对稳定。然而,在1300°C纳米氧化物的粗化和位错的回复会导致材料发生显著软化。