金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.204, 1 Nov. 2021(上)
2021-08-08 来源:Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文9篇,涵盖了高熵合金、高温合金、形状记忆合金等,国内科研单位包括吉林大学、西安交通大学、西北工业大学、北京科技大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 204 目录
1. Enhanced ductility and strength of Mg-1Zn-1Sn-0.3Y-0.2Ca alloy achieved by novel micro-texture design
新型微织构设计提高Mg-1Zn-1Sn-0.3Y-0.2Ca合金的延展性和强度
2. A novel bulk eutectic high-entropy alloy with outstanding as-cast specific yield strengths at elevated temperatures
在高温下具有出色的铸态比屈服强度的新型块状共晶高熵合金
3. The environmental degradation behavior of FeNiMnCr high entropy alloy in high temperature hydrogenated water
FeNiMnCr高熵合金在高温氢化水中的环境降解行为
4. Role of in-situ splat sintering on elastic and damping behavior of cold sprayed aluminum coatings
原位飞溅烧结对冷喷涂铝涂层弹性和阻尼行为的影响
5. Hierarchical phase evolution in a lamellar Al0.7CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy involving competing metastable and stable phases
层状Al0.7CoCrFeNi高熵合金中包含竞争亚稳相和稳定相的分层相演化
6. Unveiling the Re segregation at γ/γ′ interface in Ni-based superalloy
揭示Re在镍基高温合金γ/γ′界面的偏析
7. Anomalous stress-strain behavior of NiTi shape memory alloy close to the border of superelastic window
NiTi形状记忆合金超弹窗边界附近的异常应力应变行为
8. High-throughput approach for estimation of intrinsic barriers in FCC structures for alloy design
用于合金设计的FCC结构内势垒估计的高通量方法
9. Achieving excellent superelasticity and extraordinary elastocaloric effect in a directionally solidified Co-V-Ga alloy
在定向凝固的Co-V-Ga合金中实现出色的超弹性和非凡的弹性热效应
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114119
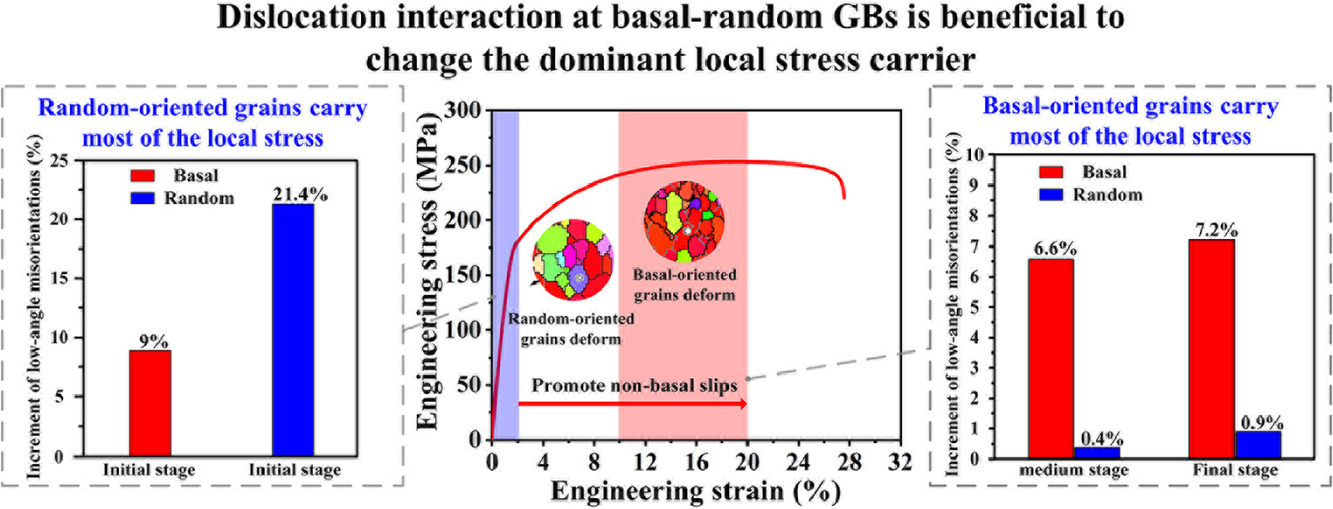
1. Enhanced ductility and strength of Mg-1Zn-1Sn-0.3Y-0.2Ca alloy achieved by novel micro-texture design
新型微织构设计提高Mg-1Zn-1Sn-0.3Y-0.2Ca合金的延展性和强度
Cheng Wang, Hong Ning, Shi Liu, Jiang You, Tong Wang, Hong-Jie Jia, Min Zha, Hui-Yuan
Wang✉
Hui-Yuan Wang: wanghuiyuan@jlu.edu.cn 吉林大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114119
摘要
织构弱化是提高镁合金延展性的主要方法之一。在这项工作中,我们通过精确控制的高压下轧制,设计并制造了具有新型基底随机异质(BRH)织构的Mg-1Zn-1Sn-0.3Y-0.2Ca (wt. % ZTWX1100)合金,该合金均匀分布着基底和随机取向晶粒。与基底织构样品相比,BRH织构同时提高了延展性和抗拉强度,这是由于基底取向晶粒内非基底滑移的作用以及基底随机晶界贡献的强加工硬化能力。此外,BRH织构中的基底-随机晶界通过将局部应力的主要载体从原始随机取向晶粒转变为基底取向晶粒,有利于提高变形相容性。这项工作旨在为通过织构协调变形改善镁合金的力学性能提供新的思路。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114132
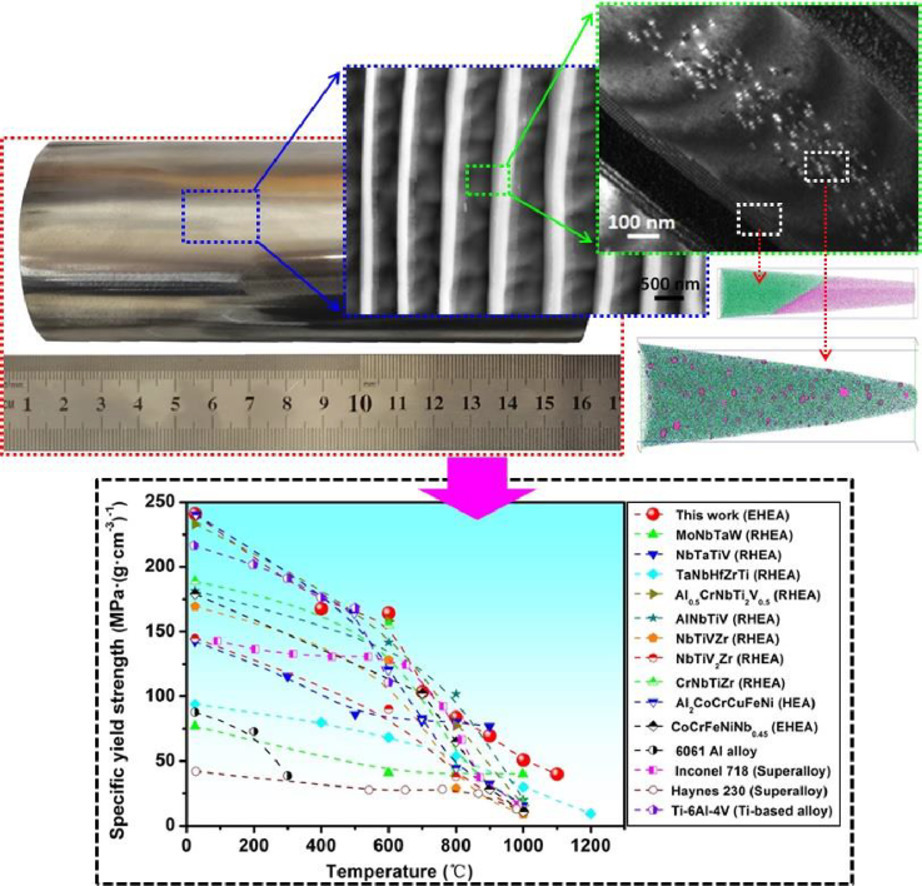
2. A novel bulk eutectic high-entropy alloy with outstanding as-cast specific yield strengths at elevated temperatures
在高温下具有出色的铸态比屈服强度的新型块状共晶高熵合金
Mingliang Wang, Yiping Lu✉, Tongmin Wang, Chuan Zhang, Zhiqiang Cao, Tingju Li,
Peter K. Liaw
Yiping Lu: luyiping@dlut.edu.cn 大连理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114132
摘要
由于其优异的性能和巨大的工业应用潜力,共晶高熵合金(EHEAs)在过去几年中一直是研究热点。本研究报告了一种新型AlCr1.3TiNi2 EHEA,具有低的密度和优异的高温机械性能。首先通过直接凝固法制备了具有均匀超细L21和BCC层状结构(层间距~ 400 nm)的千克级EHEA锭。与大多数报道的难熔高熵合金(RHEA)、EHEA和传统的镍基和钛基合金相比,铸态AlCr1.3TiNi2 EHEA表现出更高的室温和高温硬度和比屈服强度值。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114127
3. The environmental degradation behavior of FeNiMnCr high entropy alloy in high temperature hydrogenated water
FeNiMnCr高熵合金在高温氢化水中的环境降解行为
Jiuyang Dong, Xingyu Feng, Xianchao Hao, Wenjun Kuang✉
Wenjun Kuang: wjkuang66@gmail.com 西安交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114127
摘要
无钴高熵合金(HEA)28%Fe-27%Ni-27%Mn-18%Cr具有良好的抗辐照性能,可作为核电工业潜在的候选材料。这项工作研究了该HEA在高温氢化水中的环境降解行为。该HEA在恒定拉伸速率拉伸试验后出现广泛的晶间裂纹,表明它非常容易引发应力腐蚀开裂 (SCC)。微观结构分析表明,Mn和Cr在氧化过程中沿晶界向外扩散,导致晶界迁移。Cr助熔剂促进在晶界上方形成富含Cr的氧化层,从而在样品无应力时防止晶间氧化。然而,Mn在氧化物中不稳定并倾向于溶解到溶液中,使氧化物多孔。当受到压力时,多孔氧化物很容易破裂,从而引发SCC。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114125
4. Role of in-situ splat sintering on elastic and damping behavior of cold sprayed aluminum coatings
原位飞溅烧结对冷喷涂铝涂层弹性和阻尼行为的影响
Tanaji Paul, Pranjal Nautiyal, Cheng Zhang, Benjamin Boesl, Arvind Agarwal✉
Arvind Agarwal: agarwala@fiu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114125
摘要
冷喷涂6061铝涂层的动态弹性行为被研究,以了解从环境温度到400°C的原位飞溅烧结对空气和氦气喷涂涂层的内在作用。喷涂状态下,空气喷涂涂层具有更高的表面能和更低的扁平率,使得溅射烧结过程中致密率达28%,而热处理氦气喷涂的致密率仅为15%。弹性模量和阻尼行为可以根据烧结和渐进式板间结构分为三个不同的温度范围。本工作建立了理论分析,表明归一化弹性模量是板间孔隙度的指数函数。该研究确定了在高温下,板间热现象与涂层动态机械性能之间的相关性。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114137
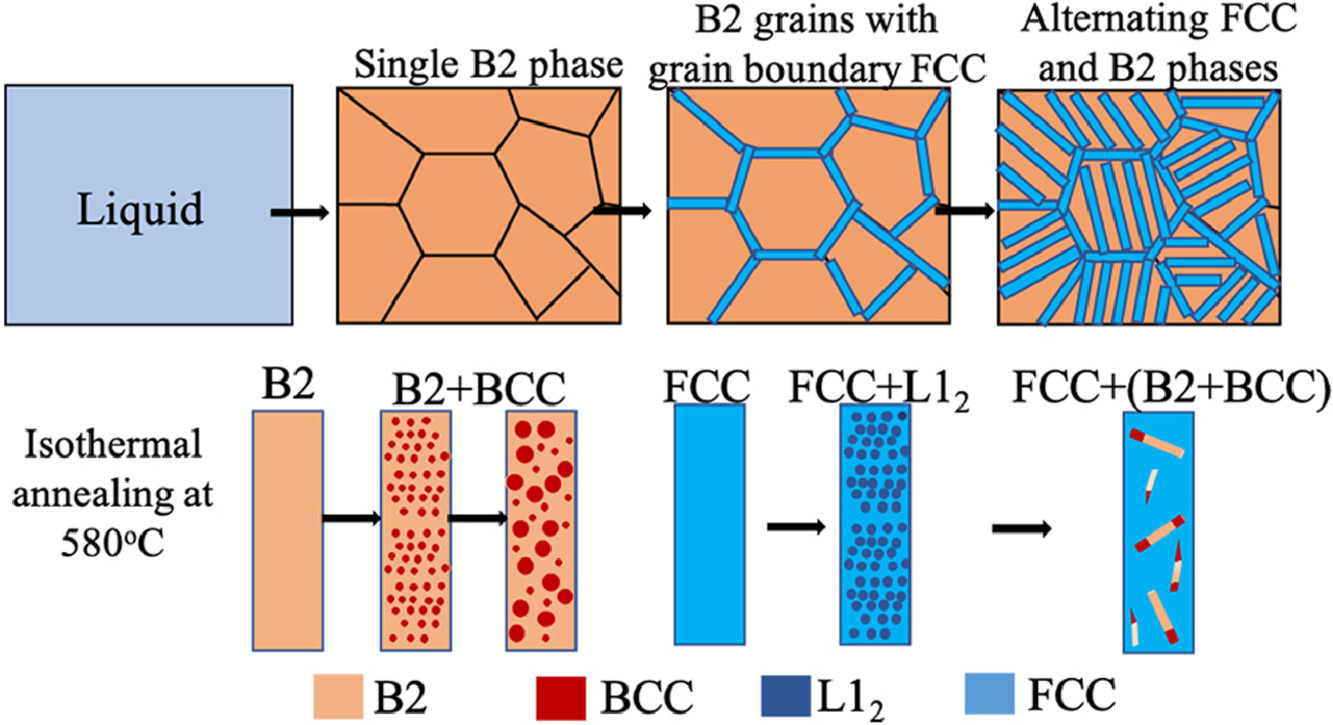
5. Hierarchical phase evolution in a lamellar Al0.7CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy involving competing metastable and stable phases
层状Al0.7CoCrFeNi高熵合金中包含竞争亚稳相和稳定相的分层相演化
K. Srimark, S. Dasari, A. Sharma, P. Wangyao, B. Gwalani, T. Rojhirunsakool, S. Gorsse, R.
Banerjee✉
R. Banerjee: raj.banerjee@unt.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114137
摘要
在溶液热力学模型和详细的实验表征的指导下,本研究确定了Al0.7CoCrFeNi高熵合金中交替的FCC和BCC层状微观结构是,从液相到单B2相的非平衡无分配凝固并接着通过固态分解的结果。 Widmanstätten FCC片晶是由B2晶界处的同素异形FCC沉淀形成,最终导致了含两个不同的子系统的层状微观结构。等温退火通过使有序金属间相沉淀,进一步推动了这些单独的子系统达到平衡。FCC片晶的转变开始于在较短的退火时间内形成的亚稳定L12沉淀物,最终被平衡的BCC和B2相取代,在长期退火时形成复合B2+BCC板条。这些结果进一步说明了,有趣的转变途径导致HEAs内的分层状微观结构,以及这些合金的加工条件通常远离平衡。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114131
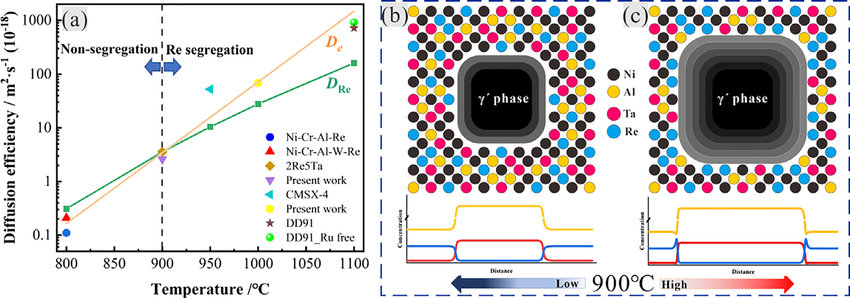
6. Unveiling the Re segregation at γ/γ′ interface in Ni-based superalloy
揭示Re在镍基高温合金γ/γ′界面的偏析
Jiachen Zhang, Taiwen Huang✉, Fan Lu, Kaili Cao, Dong Wang, Jian Zhang, Jun Zhang,
Haijun Su, Lin Liu✉
Taiwen Huang: taiwen_h@nwpu.edu.cn 西北工业大学
Lin Liu: linliu@nwpu.edu.cn 西北工业大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114131
摘要
通过原子探针断层扫描不同热处理后的镍基单晶高温合金确定Re的分布。在较高温度(950-1100℃)下,γ基体中的Re扩散率小于为γ΄生长的实际有效扩散率,这导致Re在随后的冷却和界面迁移过程中不够扩散并保持积累,并在γ/γ΄界面形成偏析。而在低温(800-900℃)下,Re扩散能够平衡γ΄生长的有效扩散。通过对不同Re含量和不同时效温度的合金进行研究,发现Re的偏析与Re含量无关,但高度依赖于温度。这些结果为理解Re对Ni基高温合金中γ΄生长的影响提供了新的视角,对于提高γ/γ΄共晶稳定性和设计高性能高温合金具有重要价值。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114135
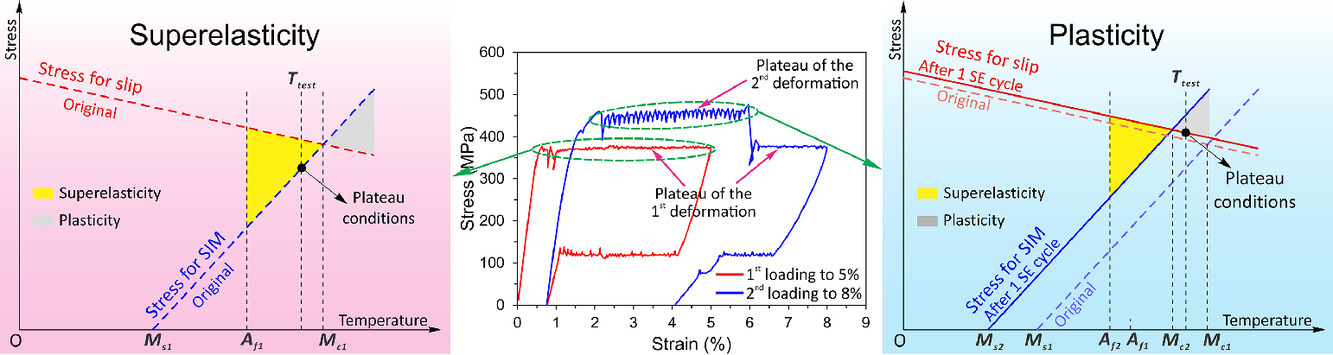
7. Anomalous stress-strain behavior of NiTi shape memory alloy close to the border of superelastic window
NiTi形状记忆合金超弹窗边界附近的异常应力应变行为
Xiebin Wang✉, Xiayang Yao, Dominique Schryvers, Bert Verliden, Guilong Wang, Guoqun
Zhao, Jan Van Humbeeck, Sergey Kustov
Xiebin Wang: wangxiebin@sdu.edu.cn 山东大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114135
摘要
这项工作报告了NiTi形状记忆合金在接近超弹性窗口边界温度下变形时的超弹性循环异常现象,发现了新的意想不到的效果——(i)在第二次加载循环期间诱导马氏体转变的临界应力高于第一次循环;(ii)当应变超过第一个循环的极限时,第二个循环的平台应力会下降到原来的水平;(iii)从第一个循环中良好的超弹性过渡到第二个循环中的完全不可逆应变。 我们提出在靠近超弹性窗口边界的第一个超弹性循环期间产生的缺陷阻碍了应力诱导的马氏体转变,导致临界应力增加并超过B2基体的屈服应力,从而导致NiTi合金的功能疲劳。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114126
8. High-throughput approach for estimation of intrinsic barriers in FCC structures for alloy design
用于合金设计的FCC结构内势垒估计的高通量方法
K.V. Vamsi✉, M.A. Charpagne, T.M. Pollock
K.V. Vamsi: kvvamsi@ucsb.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114126
摘要
广义堆积/平面断层能(GSFE/GPFE)曲线为FCC结构中的塑性变形提供了内在能垒 (IEB)。 在这项研究中,我们提出了一种估计这些IEB的新方法。对于大量纯FCC金属,显示出{111}平面上的不稳定断层能和剪切模量之间的强相关性。有趣的是,文献中的数据对于各种FCC固溶体也遵循这种相关性。对于纯FCC金属和FCC (Ni0.5Co0.5)1-xRux (x=0-0.5),展示了将这些相关性与稳定故障能量的多层扩散故障模型相结合的IEB的高通量估算。此外,还估算了合金设计的其他重要参数,包括滑移和孪晶的临界应力。这种新方法为基于孪生和变形路径倾向的多主元素合金(MPEA)的高通量设计开辟了道路。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114123
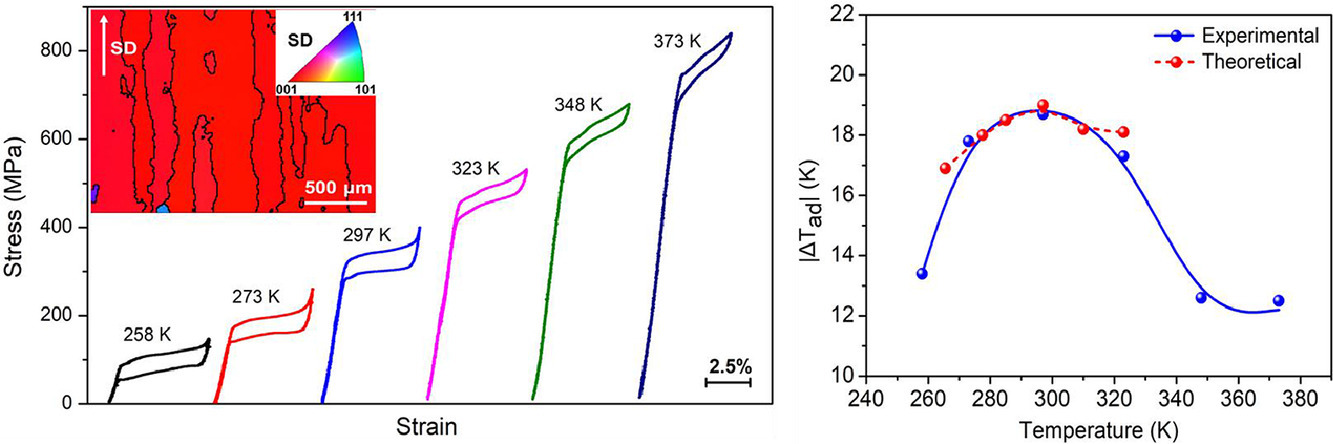
9. Achieving excellent superelasticity and extraordinary elastocaloric effect in a directionally solidified Co-V-Ga alloy
在定向凝固的Co-V-Ga合金中实现出色的超弹性和非凡的弹性热效应
Yurong Niu, Haiyang Chen✉, Xiangyu Zhang, Shengwei Li, Daoyong Cong, Tianyu Ma,
Shilei Li, Junping Lin, Yan-Dong Wang✉
Haiyang Chen: haiyang_chen123@163.com 北京科技大学
Yan-Dong Wang: ydwang@ustb.edu.cn 北京科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114123
摘要
定向凝固的Co50.7V33.3Ga16合金中展示了出色的超弹性和巨大的弹性热效应。由于形成了[001]A择优取向的柱状晶粒,凝固合金显示出近乎完美的超弹性行为:完全可逆的压缩应变高达5.4%,窄应力滞后约为40 MPa以及258-373 K的宽温度范围。同时,通过在室温下去除400 MPa的单轴应力,获得了-18.7 K的绝热温度变化(ΔTad),这与基于Maxwell关系式(-19.0 K)和量热法的理论值非常吻合。在至少115 K的宽温度范围获得了一个大于12.5 K的|ΔTad|。此外,超弹性和弹性热效应均保持良好的功能稳定性,并在100次循环中没有任何明显的消退。