金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.204, 1 Nov. 2021(下)
2021-08-29 来源:Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文11篇,涵盖了高熵合金、马氏体等,国内科研单位包括中南大学、合肥固体物理研究所、南京理工大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 204 目录
1. Studies of Cu-Sn interdiffusion coefficients in Cu3Sn and Cu6Sn5 based on the growth kinetics
基于生长动力学的Cu3Sn和Cu6Sn5中Cu-Sn相互扩散系数的研究
2. Hydrogen-induced transgranular to intergranular fracture transition in bi-crystalline nickel
双晶镍中氢致穿晶向晶间断裂转变
3. Short-range ordering governs brittleness and ductility in W-Ta solid solution: Insights from Pugh's shear-to-bulk modulus ratio
W-Ta固溶体中的短程有序控制脆性和延展性:来自Pugh的剪切体积模量比的见解
4. Multicomponent Ni-rich high-entropy alloy toughened with irregular-shaped precipitates and serrated grain boundaries
具有不规则形状析出物和锯齿状晶界的多组元富镍高熵合金
5. Role of thermo-mechanical gyrations on the α/β interface stability in a Ti6Al4V AM alloy
热机械旋转对Ti6Al4V AM合金中α/β界面稳定性的影响
6. Grain boundary relaxation behavior and phase stability of AlCrTiVx (x = 0, 0.5 and 1) high-entropy alloys
AlCrTiVx (x = 0, 0.5 and 1)高熵合金的晶界弛豫行为和相稳定性
7. New mechanism and criterion for forming multi-component solid-solution alloys
形成多组元固溶体合金的新机制和判据
8. 5M and 7M martensitic stability and associated physical properties in Ni50Mn35In15 alloy: first-principles calculations and experimental verification
Ni50Mn35In15合金的5M和7M马氏体稳定性及相关物理性能:第一性原理计算和实验验证
9. Revealing tribo–oxidation mechanisms of the copper–WC system under high tribological loading
揭示高摩擦载荷下Cu-WC系统的摩擦氧化机制
10. Machine learning to predict aluminum segregation to magnesium grain boundaries
机器学习预测铝在镁晶界的偏析
11. In-situ TEM observation and MD simulation of the reaction and transformation of <100> loops in tungsten during H2+ & He+ dual-beam irradiation
H2+和He+双光束辐照过程中钨<100>环反应和转变的原位TEM观察和MD模拟
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114138
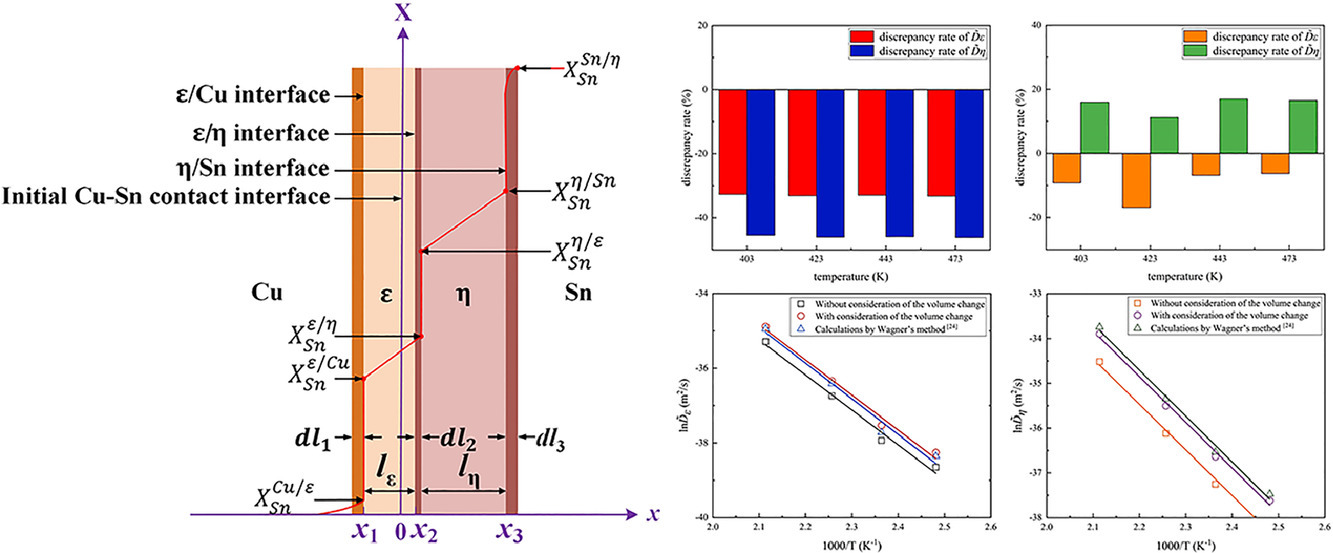
1. Studies of Cu-Sn interdiffusion coefficients in Cu3Sn and Cu6Sn5 based on the growth kinetics
基于生长动力学的Cu3Sn和Cu6Sn5中Cu-Sn相互扩散系数的研究
Yue Wang, Xianwen Peng, Jihua Huang✉, Zheng Ye, Jian Yang, Shuhai Chen
Jihua Huang: jhhuang62@sina.com 北京科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114138
摘要
在这项工作中,我们基于反应/扩散理论建立了Cu3Sn(ε)和Cu6Sn5(η)生长的动力学模型。基于Cu和Sn原子的相互扩散控制生长的理论,建立了ε和η层生长的动力学方程。 在考虑和不考虑相变引起的体积变化的两种情况下推导了动力学方程,其中Cu-Sn相互扩散系数(,
)都被列为主要因素。在此基础上,测定了两种条件下在130~200℃范围内的互扩散系数,结果表明在某种程度上体积变化影响了
和
的计算精度。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114122
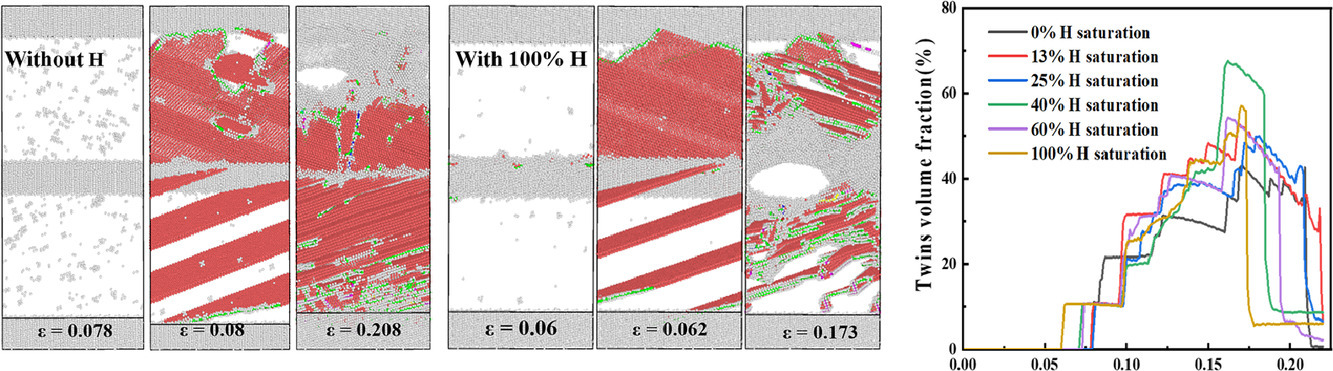
2. Hydrogen-induced transgranular to intergranular fracture transition in bi-crystalline nickel
双晶镍中氢致穿晶向晶间断裂转变
Yu Ding, Haiyang Yu, Kai Zhao, Meichao Lin, Senbo Xiao, Michael Ortiz, Jianying He,
Zhiliang Zhang✉
Zhiliang Zhang: zhiliang.zhang@ntnu.no
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114122
摘要
众所周知,氢会影响金属材料的位错塑性和断裂模式。然而,氢与晶界之间的纳米级相互作用机制在很大程度上仍然不清晰。通过对具有Σ5(210)[001]晶界的双晶Ni进行单轴应变,原子模型阐明了由氢促进的穿晶到晶间断裂转变,并揭示了特定的氢控制塑性机制。研究发现氢在晶界附近形成局部气氛,这会引起局部应力集中并抑制随后在变形过程中晶界处的应力松弛。正是这种局部应力集中促进了位错更早的发展、孪晶演化和更多空位的产生,从而促进了纳米空隙。与无氢样品的穿晶断裂相反,纳米空隙的成核和生长最终导致晶界处的晶间断裂。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114136
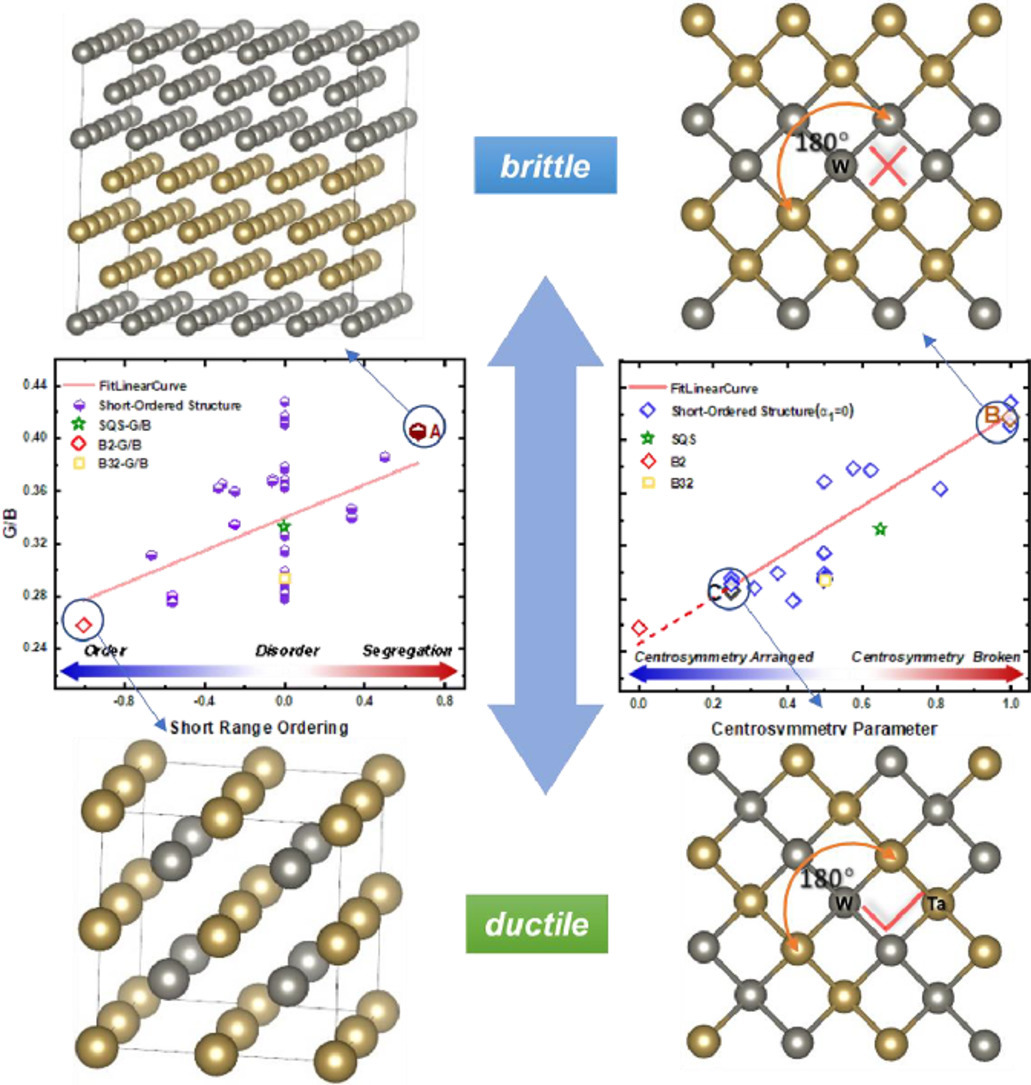
3. Short-range ordering governs brittleness and ductility in W-Ta solid solution: Insights from Pugh's shear-to-bulk modulus ratio
W-Ta固溶体中的短程有序控制脆性和延展性:来自Pugh的剪切体积模量比的见解
Honggang Liu, Sai Tang, YunZhu Ma, Wensheng Liu, Chaoping Liang✉
Chaoping Liang: cpliang@csu.edu.cn 中南大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114136
摘要
在这项工作中,通过第一性原理计算研究了W-Ta固溶体中,从Pugh的剪切体积模量(G/B)比推导出的短程有序对固有脆性和延展性的影响。结果表明,作为脆性指标的G/B值随W-Ta固溶体中Ta浓度的降低而降低。依据G/B值,与理想固溶体和原子偏析结构相比,短程有序结构表现出延展性。这种短程有序结构的延展性源于部分共价W-W键数量的减少和W-Ta固溶体中W-W相互作用的中心对称屏蔽。研究结果表明,短程有序化应该在W固溶体中的固溶软化和辐照硬化现象中起一定作用,这可以用于未来的W合金设计。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114066
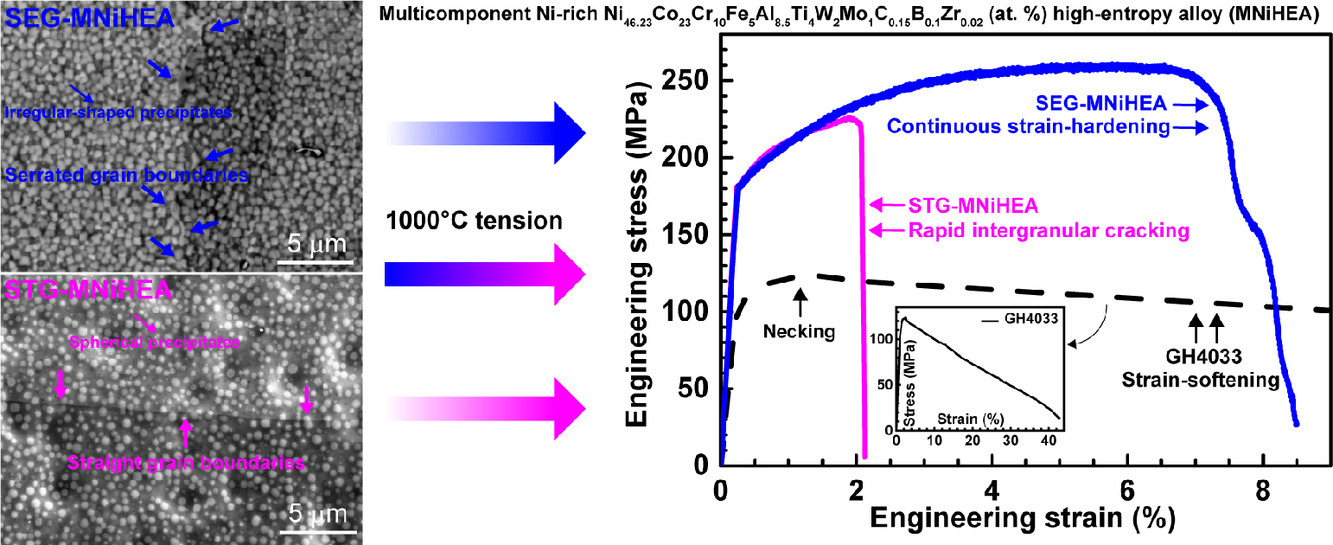
4. Multicomponent Ni-rich high-entropy alloy toughened with irregular-shaped precipitates and serrated grain boundaries
具有不规则形状析出物和锯齿状晶界的多组元富镍高熵合金
S.W. Wu, T. Yang, B.X. Cao, J.H. Luan, Y.F. Jia, L. Xu, Y.K. Mu, T.L. Zhang, H.J. Kong,
X. Tong, J.C. Peng, G. Wang, Q.J. Zhai, J. Lu, C.T. Liu✉
C.T. Liu: chainliu@cityu.edu.hk 深圳福田研究所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114066
摘要
一种新型的沉淀强化多元富镍Ni46.23Co23Cr10Fe5Al8.5Ti4W2Mo1C0.15B0.1Zr0.02 (at.%) 高熵合金(HEA),设计其在1000°C屈服后发生应变硬化而不是应变软化。由于晶间开裂的快速发生,具有球形析出物和垂直晶界的HEA很脆,抗拉强度约220 MPa,均匀伸长率仅为约1.9%。锯齿状晶界结构有效地克服了这种晶间开裂问题。该HEA具有不规则形状的沉淀物和锯齿状的晶界,使其显示出脆性到韧性的转变,具有高达~260 MPa的优异强度和~6.5% 的均匀延伸率。强度和延展性的提高归因于锯齿状晶界对晶间裂纹形核和扩展的抵抗力增强。该研究结果为具有优异机械性能的高温结构材料的创新设计提供了一种新方法。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114134
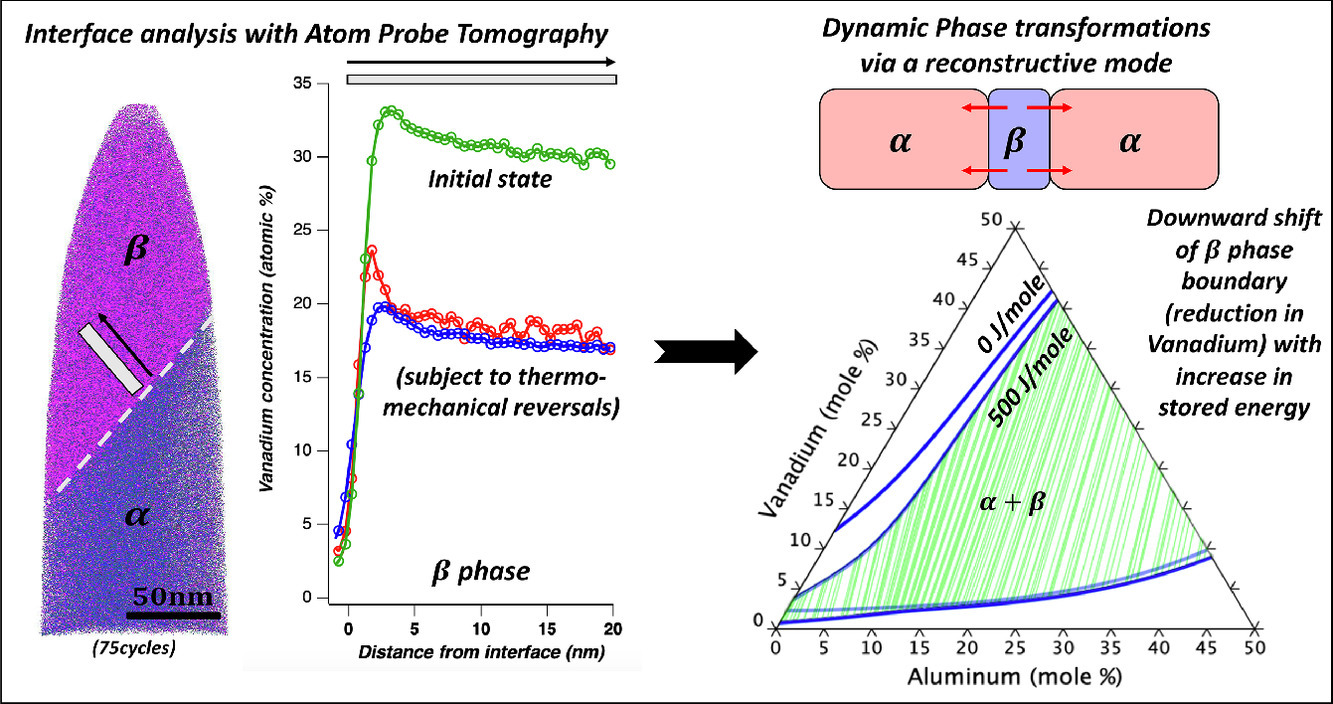
5. Role of thermo-mechanical gyrations on the α/β interface stability in a Ti6Al4V AM alloy
热机械旋转对Ti6Al4V AM合金中α/β界面稳定性的影响
Sabina Kumar✉, Sri Ram Vijayan, Peeyush Nandwana, Jonathan D. Poplawsky, Chen Yan,
Sudaranam Suresh Babu
Sabina Kumar: skumar17@vols.utk.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114134
摘要
增材制造过程中经历的能量波动会导致零件内空间和时间瞬变的演变。一般来说,在制造过程中对这些瞬变的原位监测几乎是不可能的。为了深入了解这些局部热机械瞬变对界面稳定性的影响,在AM Ti6Al4V合金上施加具有已知边界条件的快速热机械反转,这会导致相变从而增加β相稳定性。这项研究的目标是,通过由于塑性应变积累和扩散动力学而产生的储存能量的概念来理解这种相变的动力学。原子探针断层扫描用于研究跨界面的溶质元素的分配。正如预期的那样,经历热机械循环的样品的整个β相中显示出较低的钒浓度。整个界面的浓度分布以及全宽半分析提供了对受热机械旋转影响的α → β转变所涉及的潜在相变动力学的深入了解。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114144
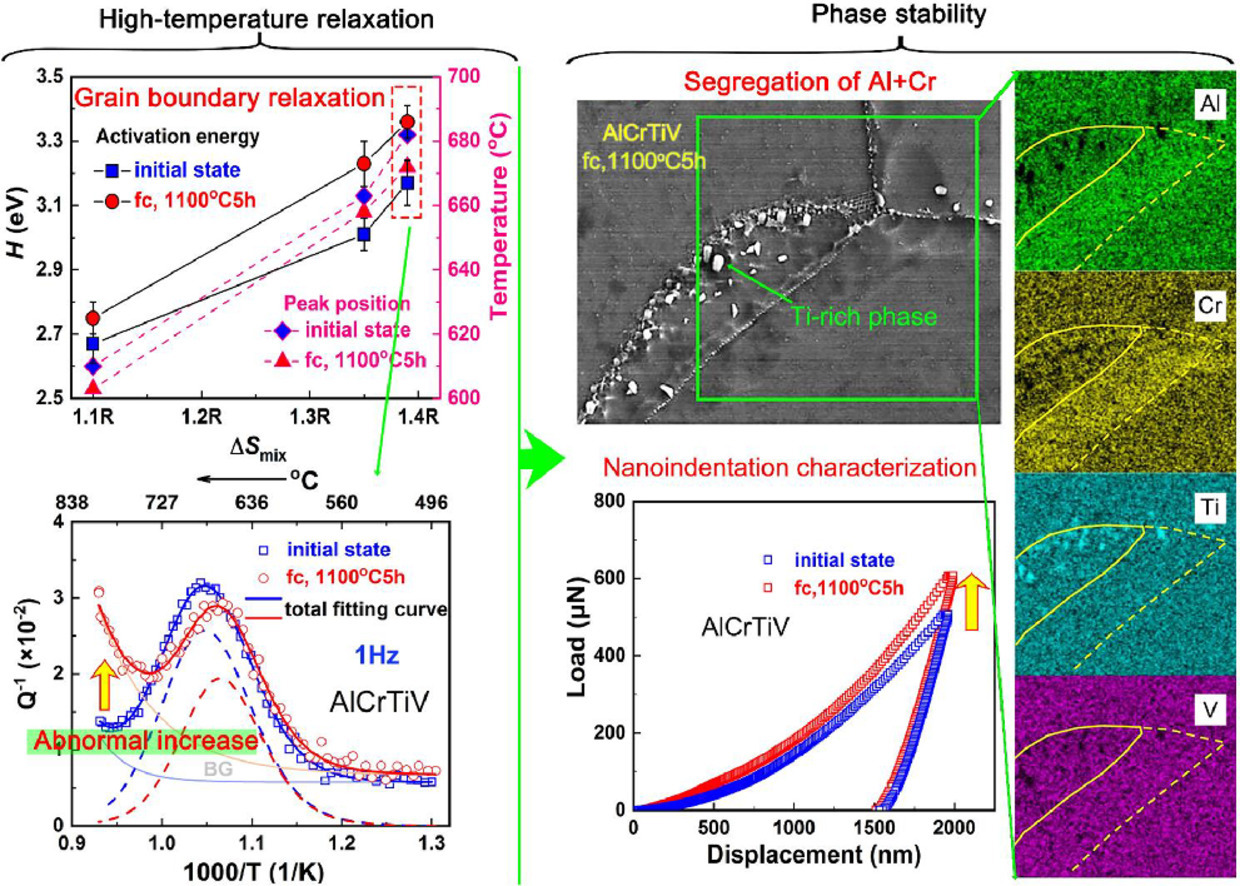
6. Grain boundary relaxation behavior and phase stability of AlCrTiVx (x = 0, 0.5 and 1) high-entropy alloys
AlCrTiVx (x = 0, 0.5 and 1)高熵合金的晶界弛豫行为和相稳定性
Meng Sun✉, Xueqing Liu, Weibin Jiang, Yawei Lei, Jianggang Ke, Rui Liu, Xianping
Wang✉, Xuebang Wu, Qianfeng Fang✉, Changsong Liu
Meng Sun: mengsun@issp.ac.cn 合肥固体物理研究所
Xianping Wang: xpwang@issp.ac.cn 合肥固体物理研究所
Qianfeng Fang: qffang@issp.ac.cn 合肥固体物理研究所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114144
摘要
本文报道了AlCrTiVx(x = 0、0.5 和 1)高熵合金的缺陷弛豫行为。在所有样品中都观察到明显的内摩擦(IF)峰叠加在单调增加的高温背景(HTBG)上,这归因于晶界峰。晶界弛豫的活化能随着V含量的增加而增加,这意味着随着混合熵的增加,原子扩散的复杂性和难度增加。在1100 °C退火5 h后,AlCrTiV合金的HTBG异常增加。微观结构分析证实,这是由于纳米富钛相的析出引起的错配位错的出现。这些发现可能为评估和设计具有高热稳定性的高熵合金提供新的自由度。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114128
7. New mechanism and criterion for forming multi-component solid-solution alloys
形成多组元固溶体合金的新机制和判据
Tsang-Tse Fang✉
Tsang-Tse Fang: ttfang@mail.ncku.edu.tw
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114128
摘要
评估了形成单相多组元固溶体合金(MCSSAs)的一些现有标准,并提出了基于原子堆积拓扑的新标准。提出了一种关于MCSSAs发展的新机制,其中,表面层的多组分效应降低纳米晶核的表面自由能,起着重要的作用。对不同温度退火的CoCrFeMnNi合金的相稳定性提供了更合理的解释。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114140
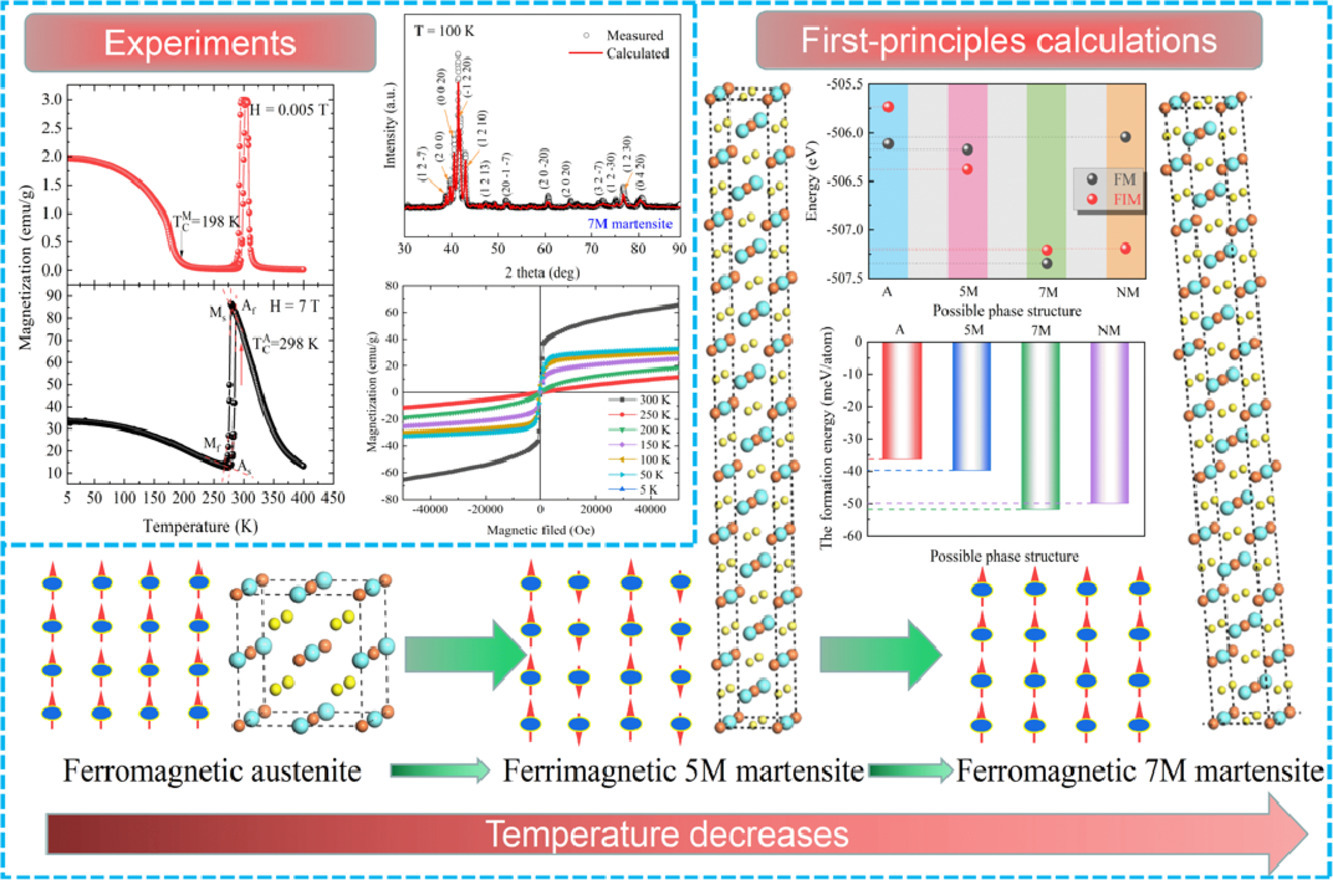
8. 5M and 7M martensitic stability and associated physical properties in Ni50Mn35In15 alloy: first-principles calculations and experimental verification
Ni50Mn35In15合金的5M和7M马氏体稳定性及相关物理性能:第一性原理计算和实验验证
Xinzeng Liang, Xinjun Jiang, Jianglong Gu, Jing Bai✉, Ziqi Guan, Zhenzhuang Li, Haile
Yan, Yudong Zhang, Claude Esling, Xiang Zhao✉, Liang Zuo
Jing Bai: baijing@neuq.edu.cn 东北大学,东北大学秦皇岛分校
Xiang Zhao: zhaox@mail.neu.edu.cn 东北大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114140
摘要
Ni-Mn基铁磁形状记忆合金优异的磁驱动性能本质上与调制马氏体的存在有关。 然而,调制马氏体的亚稳定性阻碍了这些特性的可用性。在此,通过第一性原理计算和实验研究了 Ni50Mn35In15合金中5M和7M调制马氏体的相稳定性和相关物理性能。结果表明,该合金经历了磁结构耦合转变(即铁磁奥氏体→亚铁磁5M马氏体→铁磁7M马氏体)。基于状态密度和微分电荷密度分析,可理解可能相的稳定性。7M马氏体中Ni和Mn原子之间的强键合能力使其成为最稳定的相。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114142
9. Revealing tribo–oxidation mechanisms of the copper–WC system under high tribological loading
揭示高摩擦载荷下Cu-WC系统的摩擦氧化机制
X. Chen✉, Y. Ma✉, Y. Yang, A. Meng, Z.X. Han, Z. Han, Y.H. Zhao✉
X. Chen: xiang.chen@njust.edu.cn 南京理工大学
Y. Ma: y.ma@mpie.de
Y.H. Zhao: yhzhao@njust.edu.cn 南京理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114142
摘要
在高摩擦载荷期间,研究了纯铜相对于碳化钨(WC)球体的近表面结构和化学变化。 在Cu-WC摩擦系统中确定了基本阶段:(i)在最初阶段,高摩擦应力促进了晶粒细化到超细晶粒状态;(ii)极细(~3 nm)富氧铜纳米颗粒在近表层中的成核和氧化铜随后的生长;(iii)具有异质Cu和O分布的连续纳米结构混合层在后期的形成。近表面机械混合可能是高摩擦载荷下化学改性的主要原因。该发现为复杂的摩擦化学修饰提供了原子解释,这是面向材料的摩擦学中最有趣的现象之一。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114150
10. Machine learning to predict aluminum segregation to magnesium grain boundaries
机器学习预测铝在镁晶界的偏析
Joseph Messina, Renjie Luo, Ke Xu, Guanghong Lu, Huiqiu Deng, Mark A Tschopp, Fei
Gao✉
Fei Gao: eigaoum@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114150
摘要
镁合金由于其高的强度重量比而成为许多应用的优质候选材料,但其他性能如耐腐蚀性、可成形性和蠕变仍是问题。在镁铝合金中,Mg17Al12相在晶界(GBs)析出会对机械性能和腐蚀行为产生重要影响。为了更好地理解这些影响,必须首先评估铝对GB的原子偏析的作用。本研究使用原子模拟来量化铝偏析能,以训练机器学习模型。铝原子被反复放置在近30个不同的镁对称倾斜晶界(STGB)的原子位置。结果显示了铝偏析如何受GB结构和局部原子环境的影响。使用机器学习技术计算感兴趣的晶界物理特性可以对晶界科学和工程领域产生广泛的影响。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 204, 1 Nov. 2021, 114154
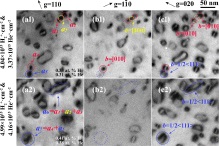
11. In-situ TEM observation and MD simulation of the reaction and transformation of <100> loops in tungsten during H2+ & He+ dual-beam irradiation
H2+和He+双光束辐照过程中钨<100>环反应和转变的原位TEM观察和MD模拟
Yifan Ding, Long Guo, Yipeng Li, Xinyi Liu, Guang Ran✉, Lu Wu, Xi Qiu, Huiqiu Deng,
Xiaoyong Wu, Yuanming Li, Xiuyin Huang
Guang Ran: gran@xmu.edu.cn 厦门大学,福建核工程研究中心
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114154
摘要
低迁移率<100>环显著影响体心立方材料的力学性能,其产生和演化是近年来的研究热点。然而,对于后续辐照过程中形成的<100>环的反应仍然缺乏直接观察,这阻碍了更好地理解辐照引起的机械性能退化。在这里,我们首次报道了钨30 keV H2+和He+双光束照射期间,通过原位TEM观察到了<100>环之间的反应产生了1/2<111>环。分子动力学模拟表明,该反应需要初始<100>环的合适位置和高温,以诱导<100>环分裂成1/2<111>段,然后转化为1/2<111>环。同时,原位观察到<100>环的演变,<100>环的平均尺寸和面数密度被量化为辐射通量的函数。