金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.214,1 Aug. 2021(上)
2021-08-29 来源:Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文10篇,涵盖了镁合金、珠光体等,国内科研单位包括南京工业大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 214 目录
1. A quantitative study on mechanical behavior of Mg alloys with bimodal texture components
双织构镁合金力学行为的定量研究
2. Atomic diffusivities in amorphous and liquid Cu-Zr: Kirkendall effects and dependence on packing density
非晶态和液态Cu-Zr中的原子扩散速率研究:Kirkendall效应及其与堆垛密度的关系
3. Atomic insights on intermixing of nanoscale nitride multilayer triggered by nanoindentation
纳米压痕导致纳米氮化物多层材料发生混合的原子尺度研究
4. Bridging microstructure and crystallography with the micromechanics of cleavage fracture in a lamellar pearlitic steel
组织和取向对片层珠光体钢中解理断裂微观力学的影响
5. CALPHAD-informed phase-field modeling of grain boundary microchemistry and precipitation in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys
基于CALPHAD的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金晶界成分和偏聚相场模拟
6. Characterizing the microstructural effect of build direction during solidification of laser-powder bed fusion of Al-Si alloys in the dilute limit: A phase-field study
Al-Si合金激光粉末熔炼凝固过程中制备方向对微观组织影响的相场研究
7. Deep learning-based discriminative refocusing of scanning electron microscopy images for materials science
基于深度学习的扫描电子显微镜图像失焦修复技术
8. Effect of size and orientation on stability of dislocation networks upon torsion loading and unloading in FCC metallic micropillars
FCC金属微柱扭转和卸载过程中微柱尺寸和取向对位错网络稳定性的影响
9. Enhanced microstructural stability of γ/γ’-strengthened Co-Ti-Mo-based alloys through Al additions
添加Al引起γ/γ′强化Co-Ti-Mo合金组织稳定性提高的机制研究
10. Faceting diagram for Ag segregation induced nanofaceting at an symmetric Cu tilt grain boundary
Ag偏聚诱导Cu中对称倾侧晶界形成纳米面的机理研究
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117013
1. A quantitative study on mechanical behavior of Mg alloys with bimodal texture components
双织构镁合金力学行为的定量研究
Lingyu Zhao, Bo Guan, Yunchang Xin✉, Xiaoxu Huang, Chenglu Liu, Peidong Wu, Qing Liu
Y. Xin:ycxin@cqu.edu.cn(南京工业大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117013
摘要
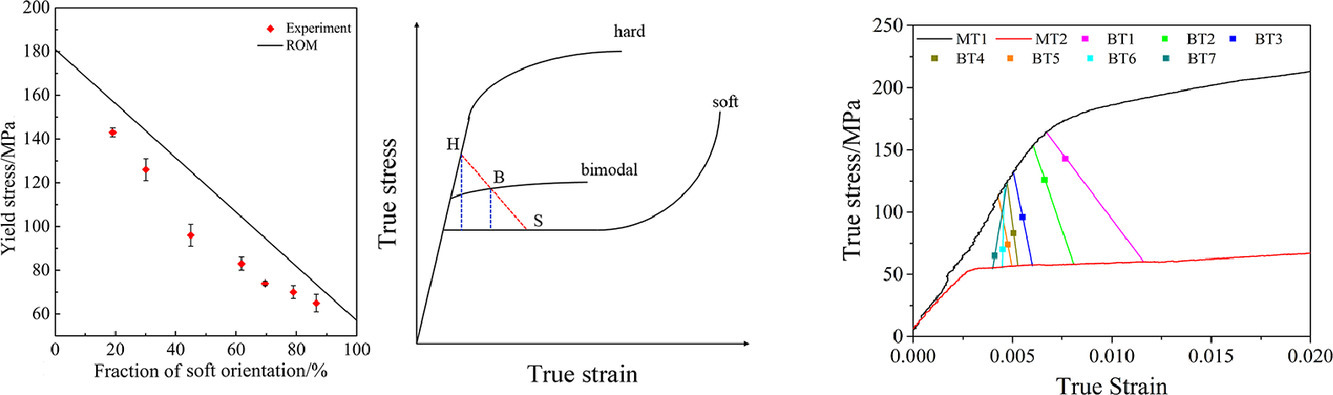
对于单一织构镁合金的力学和孪晶行为目前已有广泛研究,而对于多织构镁合金的研究则较少。我们对AZ31镁合金棒材沿挤压方向(ED)拉伸性能与<0002>// ED(19-87%)、<0002>⊥ED双织构相对比例间的关系进行了系统的定量研究。研究表明,<0002>// ED织构有助于{10-12}孪晶,且是软取向; 而<0002>⊥ED织构有助于棱柱滑移,且是硬取向。结果表明,屈服强度不随软取向占比增加线性下降,与混合定律计算结果存在偏差。当软取向晶粒比例小于50%时,比例增加偏差增大;而当软取向晶粒比例大于50%时,比例增加偏差减小。此外,抗拉强度似乎与软取向占比没有明显关联。基于以上结果,我们讨论了相应机理并提对混合定律进行了修正。双织构使得{10-12}孪晶变体能够在较低的Schmid因子下激活,并且一个晶粒内能够存在更多变体。传统的应变调节理论无法解释这种实验现象。我们采用晶体塑性有限元对此进行了分析。结果表明,比起临近晶粒的变形,孪晶变体间的相互作用对于孪晶的激活起到了更加重要的作用,这一发现为应变调节理论提供了重要补充。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116993
2. Atomic diffusivities in amorphous and liquid Cu-Zr: Kirkendall effects and dependence on packing density
非晶态和液态Cu-Zr中的原子扩散速率研究:Kirkendall效应及其与堆垛密度的关系
S.V. Ketov, Yu.P. Ivanov, B. Putz, Z. Zhang, J. Eckert, A.L. Greer✉
A.L. Greer:alg13@cam.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116993
摘要
我们提出了一种创新性的测量非晶Cu-Zr在其玻璃态转变温度Tg附近原子互扩散率的方法。我们通过TEM和X射线能谱对溅射沉积多层薄膜的横截面进行了表征。通过分析成分的演化推算得到了互扩散系数,结果其在Tg附近的值比预期的要高几个数量级。非晶态和过冷态下层间界面的克根达尔漂移以及液相中的孔洞表明,铜的扩散系数远大于锆。众所周知,非晶态Cu-Zr在特定成分处存在原子堆积密度极大值。本研究中的结果提供了直接证据,证明更加致密的堆积与较低的原子互扩散率有关。当铜扩散较慢时,互扩散速率也较慢。以上研究对于我们理解玻璃成型性和纳米孔隙调控等问题具有重要帮助。

ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117004
3. Atomic insights on intermixing of nanoscale nitride multilayer triggered by nanoindentation
纳米压痕导致纳米氮化物多层材料发生混合的原子尺度研究
Zhuo Chen, Yonghui Zheng, Lukas Löfler, Matthias Bartosik, Ganesh Kumar Nayak, Oliver Renk, David Holec, Paul H. Mayrhofer, Zaoli Zhang✉
Z. Zhang:zaoli.zhang@oeaw.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117004
摘要
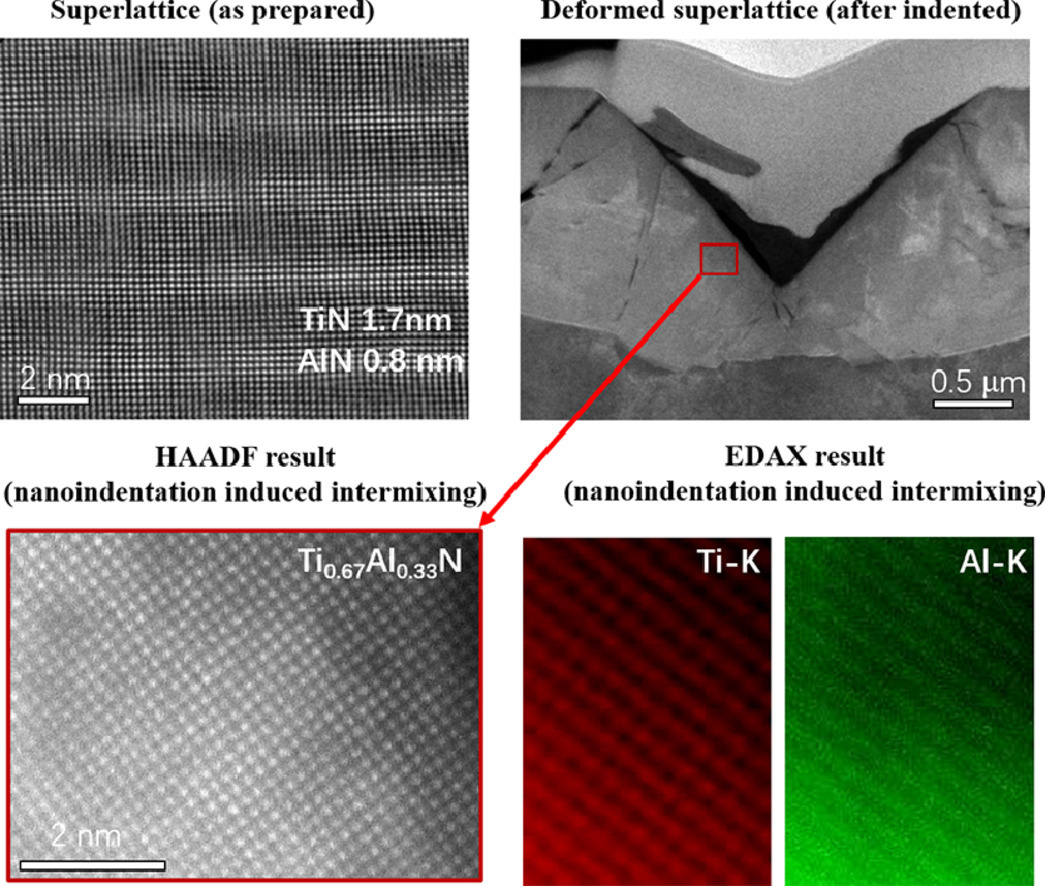
纳米多层涂层的力学性能与界面数量及其特性密切相关。当层厚降低时,一般而言材料的强度和韧性增加,但当层厚减小至只有几纳米时,性能下降。本研究中,我们发现了一种纳米层压入过程中的现象,可以一定程度上解释材料性能的劣化。纳米压痕作为一种常见的涂层硬度表征手段,会导致多层结构产生一定程度的变形和破坏。我们通过SEM表征和原子尺度模拟,证明了纳米压痕会诱发外延过渡金属氮化物超晶格薄膜的混杂。固溶体的形成降低了界面密度,使得位错密度急剧下降。以上研究结果表明,塑性变形会引起氮化物多层结构的失稳,这对于我们进一步认识多层薄膜结构强度机制具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116988
4. Bridging microstructure and crystallography with the micromechanics of cleavage fracture in a lamellar pearlitic steel
组织和取向对片层珠光体钢中解理断裂微观力学的影响
Rakesh Kumar Barik✉, Abhijit Ghosh, Md. Basiruddin Sk, Sankalp Biswal, Amlan Dutta, Debalay Chakrabarti
R.K. Barik:barikrakesh4@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116988
摘要
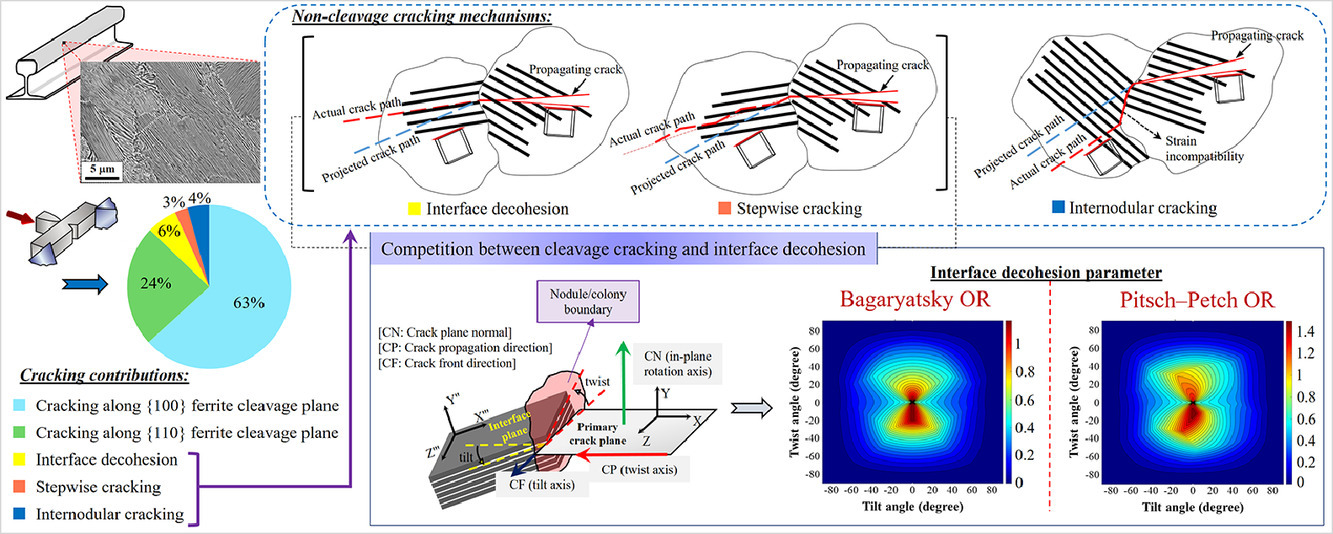
本研究基于显微组织和结晶学形貌,研究了全珠光体钢在夏比冲击实验中的解理裂纹扩展。通过数学模型模拟,结合界面脱粘和裂纹逐步扩展机理,讨论了珠光体片层取向对断裂路径影响。虽然珠光体钢中较为常见的是{100}解理断裂,但沿{110}晶面的裂纹扩展也可以在某些珠光体集落中普遍存在。这可能与层片界面对滑移的限制抑制了裂纹尖端的位错发射有关。此外,珠光体组织中由于弹性模量或Schmid因子的不匹配而导致的应变不均是引起开裂的原因。我们基于断裂力学和实验观测结果,提出了珠光体中不同类型裂脊形成的机制,阐明了片层取向在裂脊处晶体发生切变和弯曲过程中所起的作用。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116966
5. CALPHAD-informed phase-field modeling of grain boundary microchemistry and precipitation in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys
基于CALPHAD的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金晶界成分和偏聚相场模拟
Chuanlai Liu✉, Alistair Garner, Huan Zhao, Philip B. Prangnell, Baptiste Gault, Dierk Raabe, Pratheek Shanthraj✉
C. Liu:c.liu@mpie.de
P. Shanthraj:pratheek.shanthraj@manchester.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116966
摘要
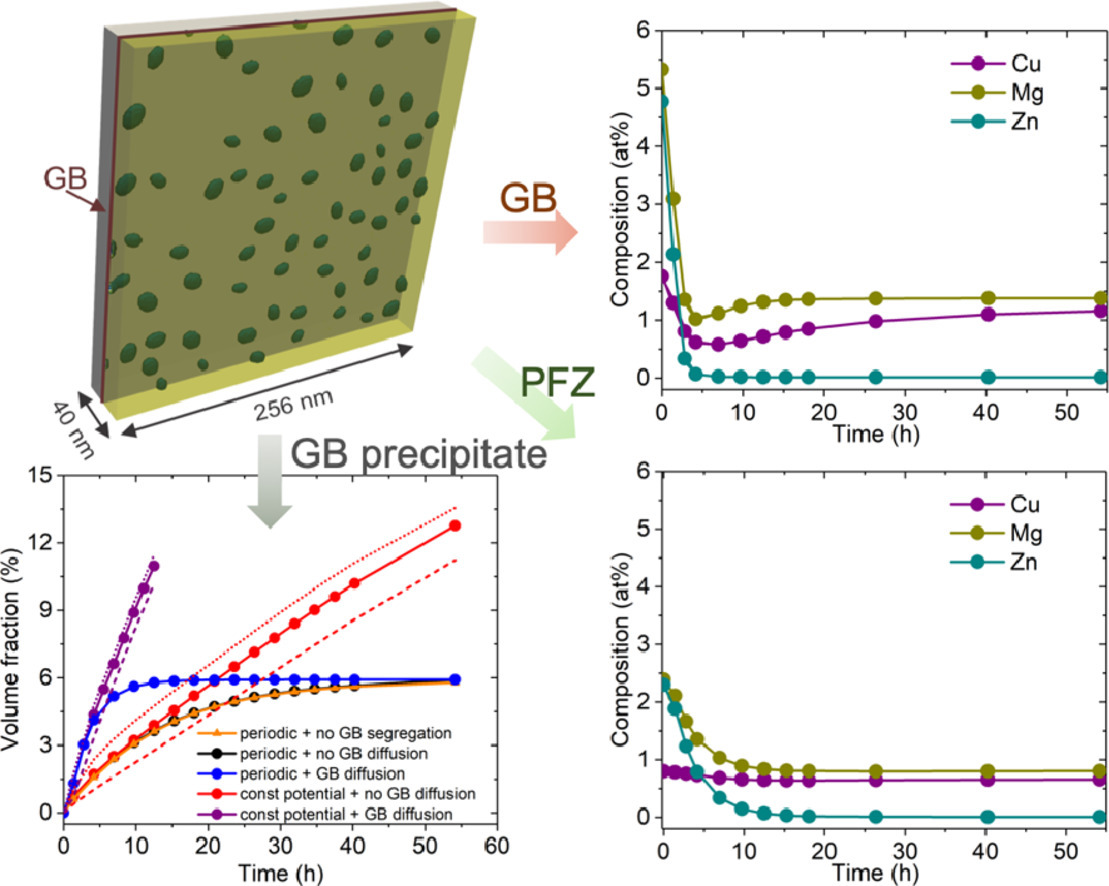
高强Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金的晶界化学成分和析出行为对其力学和电化学性能有重要影响。模拟这类合金中的晶界偏聚、析出和溶质配分需要对这一体系的热力学和动力学进行准确描述。目前开发的CALPHAD数据库能够较好地实现复杂多组分系统中的平衡态热力学计算,且能够和扩散模拟进行结合。本研究中,我们将CALPHAD数据库和相场模型进行了结合,以求实现对合金热处理过程中的非平衡过程进行准确模拟。特别地,我们在一种成分接近AA7050的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu模型合金中,系统研究晶界偏聚、晶界扩散、析出密度和远场基体成分对晶界处η相析出长大的影响。结果表明,在时效早期阶段,晶界的溶质分布极不均匀性,受η析出分布影响很大。在过时效过程中,Mg和Cu在晶界处存在显著偏聚,而Zn则会迅速贫化。这种晶界偏聚显著影响了析出形貌,但对晶界析出整体动力学的影响则相对有限。此外,晶界附近的溶质消耗很大程度上取决于Zn和Mg的扩散,这将影响时效早期无析出区的演化。我们将模拟结果与相似成分中扫描透射电子显微镜和原子探针的实验结果进行了比较,两者吻合较好。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116983
6. Characterizing the microstructural effect of build direction during solidification of laser-powder bed fusion of Al-Si alloys in the dilute limit: A phase-field study
Al-Si合金激光粉末熔炼凝固过程中制备方向对微观组织影响的相场研究
Hossein Azizi✉, Alireza Ebrahimi, Nana Ofori-Opoku, Michael Greenwood, Nikolas Provatas, Mohsen Mohammadi
H. Azizi:haziz@unb.ca, hossein.azizi@mail.mcgill.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116983
摘要
激光粉末熔化(LPBF)增材制造相关研究表明,改变制备方向可以导致凝固组织形貌发生转变,从而实现对材料织构和性能的调控。本研究中,我们通过数值模拟,研究了LPBF过程中制备方向对Al-Si合金组织演变的影响。我们建立了一个有限元热场模型,以考虑垂直和水平打印过程中制备方向对熔池热场特征的影响。随后我们利用多参量相场模型对Al-Si合金的组织演变进行了研究。我们的相场模型可以自洽地模拟晶粒在添加孕育剂后的形核和形貌演变。我们通过对定向凝固Al-Si合金的形貌转变数值检测以及与Hunt的CET模型的比较,验证了相场模型的准确性。相场模拟和晶粒分析结果表明,水平制备样品中的形核速率和等轴晶比例更高,这与实验观测的结果一致。

ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116987
7. Deep learning-based discriminative refocusing of scanning electron microscopy images for materials science
基于深度学习的扫描电子显微镜图像失焦修复技术
Juwon Na✉, Gyuwon Kim✉, Seong-Hoon Kang✉, Se-Jong Kim✉, Seungchul Lee✉
J. Na:juwonna7@postech.ac.kr
G. Kim:gyuwonkim96@postech.ac.kr
S.-H. Kang:kangsh@kims.re.kr
S.-J. Kim:ksj1009@kims.re.kr
S. Lee:seunglee@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116987
摘要
扫描电子显微镜(SEM)在材料组织结构表征中被广泛应用。但由于仪器状态不佳或自动成像错误,图像经常出现失焦,而研究人员需要对这些失焦图像进行检测恢复,以便进一步分析。我们提出了一种基于深度学习的扫描电镜(SEM)图像失焦修复方法,对于二次电子像(SE)效果尤其明显。我们考虑了三个人工智能(AI)实际运用中的重要问题:(1) AI能否在人为设置条件下修复SEM图像? (2) AI能否在无人为设置条件下修复SEM图像?(3) AI在以上两种情况下的修复是否有区别?为此我们通过单尺度卷积神经网络、多尺度卷积神经网络和数据增强多尺度卷积神经网络逐步改进了算法,解决上述问题。研究表明,我们提出的方法不仅可以修复低质量的SEM图像,而且还可以有区别地执行任务,这意味着修复是明确针对失焦区域进行的。我们采用马氏体钢和析出强化合金的SEM图像对算法进行了验证评价,并对深度学习修复的机制进行了解释。以上结果有助于加快SEM的图像采集速度,搭建材料信息化数据平台。
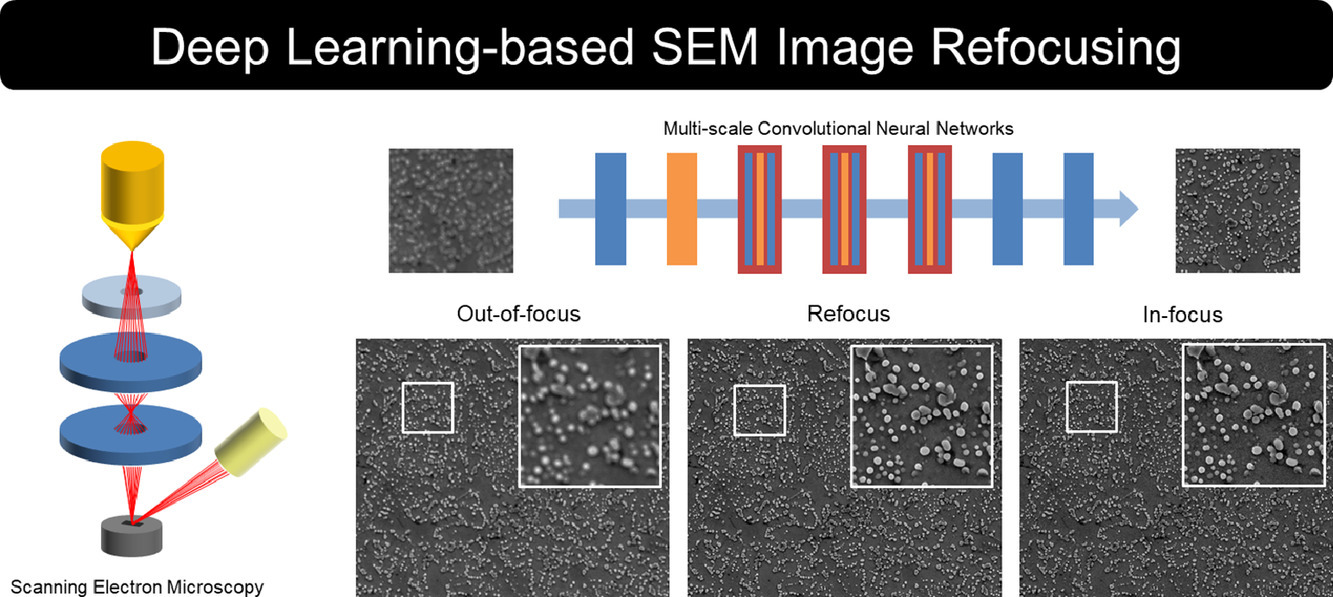

ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117010
8. Effect of size and orientation on stability of dislocation networks upon torsion loading and unloading in FCC metallic micropillars
FCC金属微柱扭转和卸载过程中微柱尺寸和取向对位错网络稳定性的影响
J.D. Gravell, S. Lee, S. Ryub, I. Ryu✉
I. Ryu:ill.ryu@utdallas.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117010
摘要
在连续的长度尺度上,金属材料的力学性能受取向影响不大;然而当样品尺寸减小到微米或纳米尺度时,则经常表现出强烈的各向异性。本研究中,我们通过三维位错动力学模拟研究了亚微米面心立方微柱在扭转作用下塑性与取向的关系。我们基于原子尺度模拟结果,对我[001]、[101]和[111]三个取向上的表面形核进行了修正,重点关注了位错微观结构演化和加载/卸载时的各向异性力学响应的变化。模拟结果表明,在[101]和[111]取向的微柱中分别形成了共轴和六方网络,使材料表现出良好的塑性回复,而[001]取向微柱中的矩形网络则更稳定,因此塑性回复不显著。

ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117011
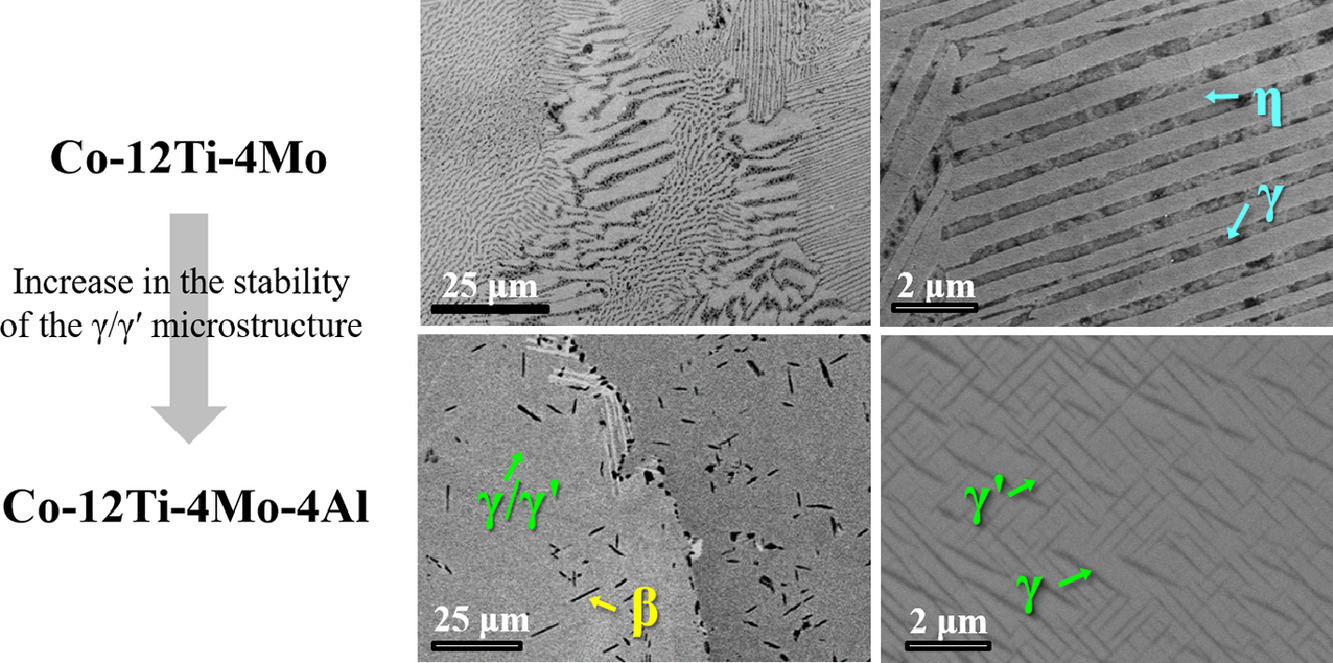
9. Enhanced microstructural stability of γ/γ’-strengthened Co-Ti-Mo-based alloys through Al additions
添加Al引起γ/γ′强化Co-Ti-Mo合金组织稳定性提高的机制研究
Hye Ji Im, Won Seok Choi, KenHee Ryou, Jae Bok Seol, Tae Hyeok Kang, Won-Seok Ko✉, Pyuck-Pa Choi✉
W.-S. Ko:wonsko@ulsan.ac.kr
P.-P. Choi:p.choi@kaist.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117011
摘要
我们通过电子显微镜和密度泛函理论对多种不同成分γ/γ’ Co-Ti-Mo合金(Co-12Ti-4Mo, Co-12Ti-4Mo- 2Al, Co-12Ti-4Mo- 4Al, Co-10Ti-4Mo-2Al, Co-8Ti-4Mo-4Al at.%)的组织稳定性和高温力学性能进行了研究。Co-12Ti-4Mo合金在800℃时效500 h后发生不连续析出,形成FCC (γ)和D019 (χ)相,而Co-12Ti-4Mo- 4al合金则依然维持γ/γ′组织。Al的添加通过在晶界形成L21 (β’)相,降低γ基体的过饱和度和FCC/L12的界面能,提高了γ/γ′组织的稳定性。Co-12Ti-4Mo-4Al合金的屈服强度低于无Al合金,但两种合金间的差异随温度升高而减小。且与其他钴基合金(如MarM302和Co-9Al-9W)相比,材料在高温下屈服强度的显著升高很大程度地抵消了这种下降的影响。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116960
10. Faceting diagram for Ag segregation induced nanofaceting at an symmetric Cu tilt grain boundary
Ag偏聚诱导Cu中对称倾侧晶界形成纳米面的机理研究
Nicolas J. Peter✉, Maria J. Duarte✉, Christoph Kirchlechner✉, Christian H. Liebscher✉, Gerhard Dehm✉
N.J. Peter:peter@mpie.de
M.J. Duarte:duarte@mpie.de
C. Kirchlechner:kirchlechner@mpie.de
C.H. Liebscher:liebscher@mpie.de
G. Dehm:dehm@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116960
摘要
本研究汇中,我们通过扩散偶实验确定了Cu-Ag体系∑5非对称倾侧晶界处纳米面的等温演化。我们研究了银浓度对沿晶界形成纳米面的影响。等温过程中,晶界分解为非对称的贫银部分和对称的富银(210)部分。Ag含量的增加将引起富Ag面段长度增加,而非对称面长度保持不变。基于以上实验结果,我们建立了晶界纳米面图以阐明原子结构、Ag溶质过量和晶面倾斜状态间的关系。


