金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.214,1 Aug. 2021(下)
2021-10-07 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文10篇,涵盖了马氏体、奥氏体、高温合金等,国内科研单位包括燕山大学、重庆大学、上海交通大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 214 目录
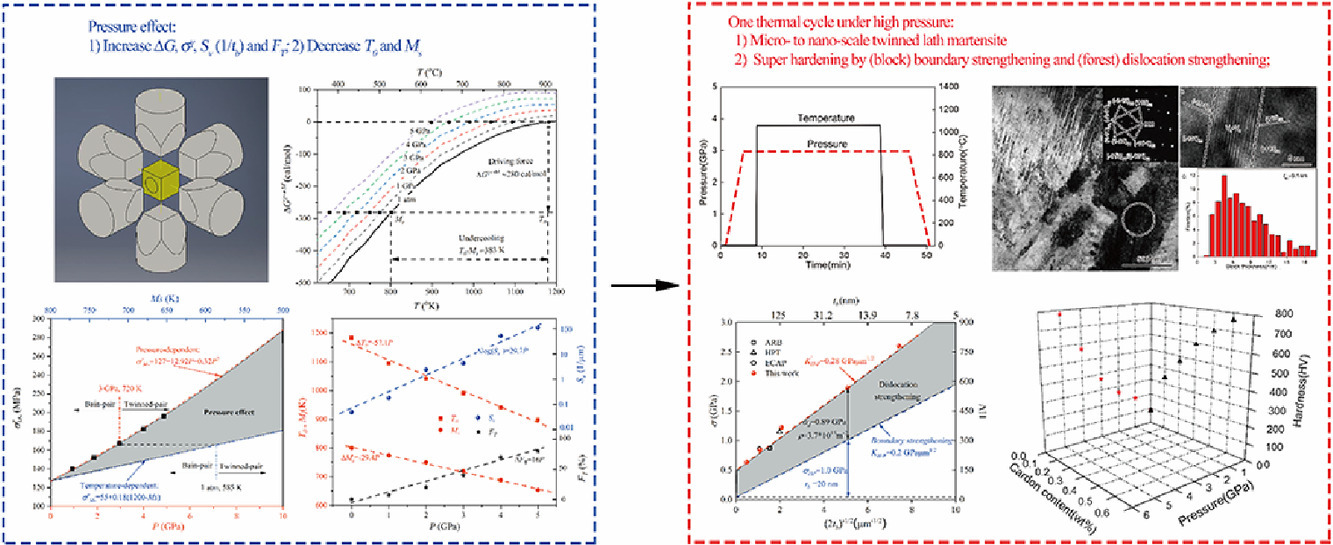
1. High pressure effect on the substructure and hardness of IF steel during martensitic transformation
高压对IF钢马氏体相变组织和硬度的影响
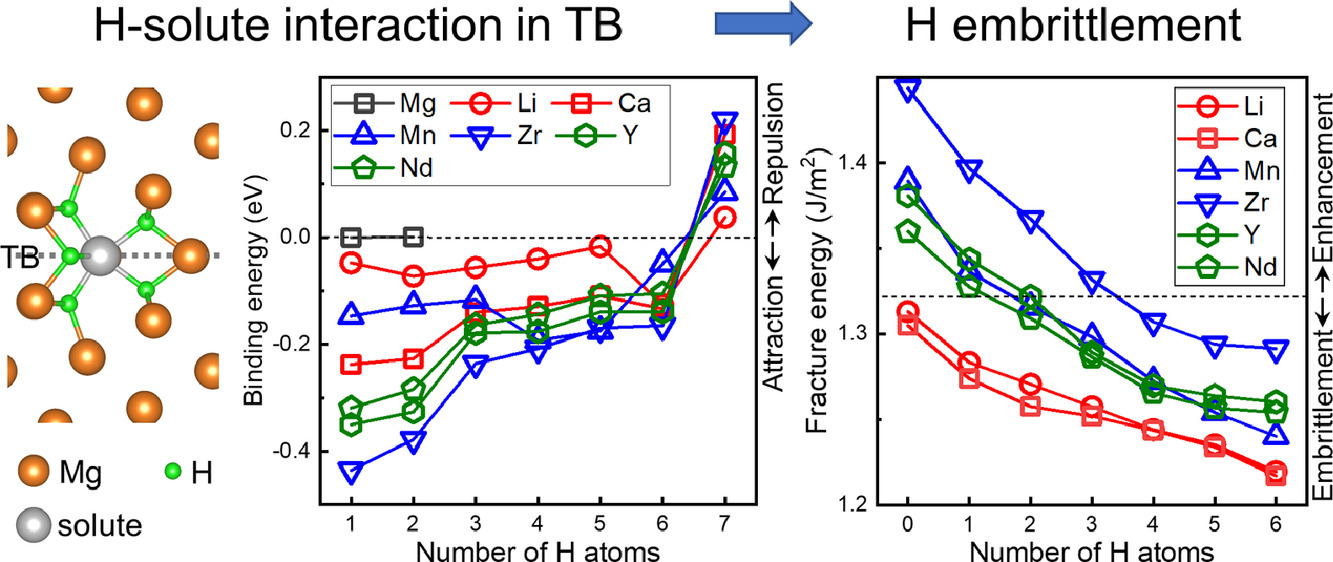
2. Interaction between hydrogen and solute atoms in {10-12} twin boundary and its impact on boundary cohesion in magnesium
镁{10-12}孪晶界处氢与溶质原子的相互作用及其对晶界结合力的影响
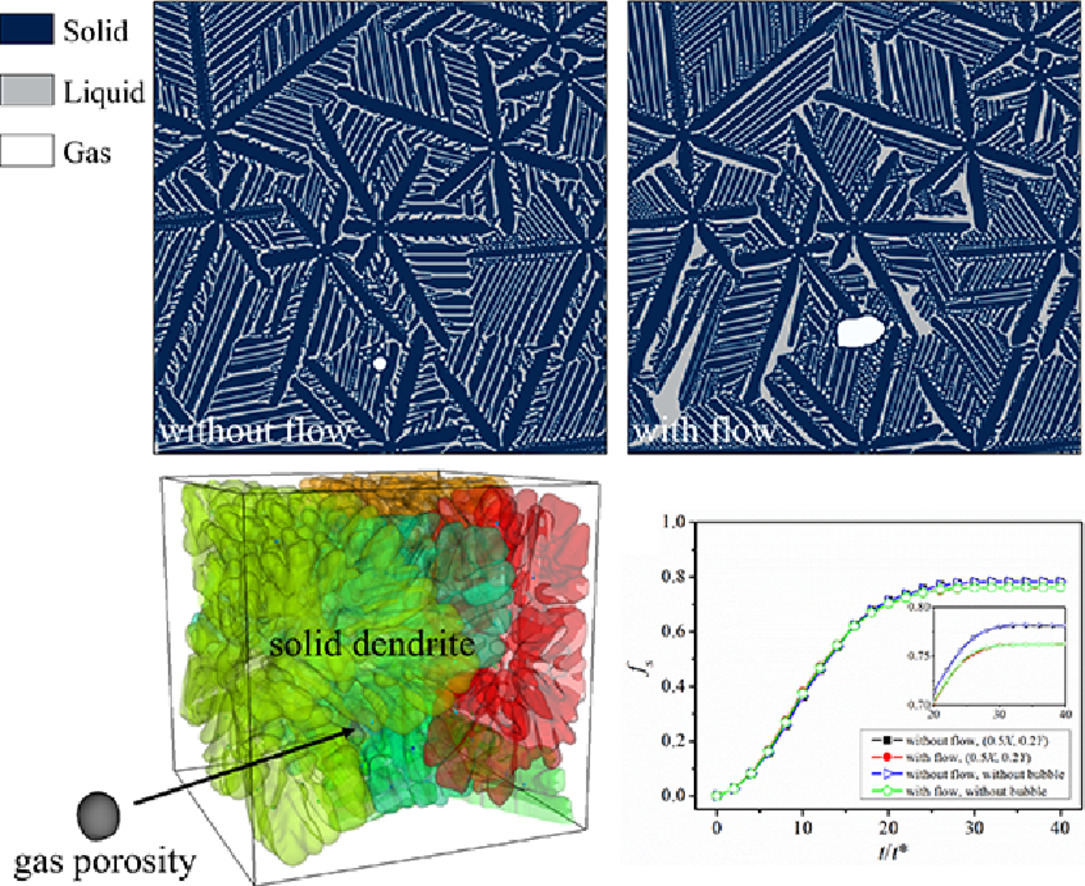
3. Multiphase and multiphysics modeling of dendrite growth and gas porosity evolution during solidification
凝固过程中枝晶生长和气孔演化的多相物理模型
4. Origins of size effects in initially dislocation-free single-crystal silver micro- and nanocubes
无位错单晶银微纳米立方体中尺寸效应的原因
5. Representative volume elements for plasticity and creep measured from high-resolution microscale strain fields
基于微观应变场的高分辨表征测量材料塑性和蠕变的代表体积元
6. Role of the local stress systems on microstructural inhomogeneity during semisolid injection
铸造过程中局部应力对微观组织不均匀性的影响研究
7. Segmentation of experimental datasets via convolutional neural networks trained on phase field simulations
利用相场模拟训练的卷积神经网络实现对实验数据集的图像分割
8. Studying the micromechanical behaviors of a polycrystalline metal by artificial neural networks
多晶金属微观力学行为的人工神经网络研究
9. Tailoring the metastable reversed austenite from metastable Mn-rich carbides
通过富锰碳化物调控亚稳逆相变奥氏体
10. Understanding creep of a single-crystalline Co-Al-W-Ta superalloy by studying the deformation mechanism, segregation tendency and stacking fault energy
基于变形机制、合金元素偏聚和层错能研究单晶Co-Al-W-Ta高温合金的蠕变性能
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116978
1. High pressure effect on the substructure and hardness of IF steel during martensitic transformation
高压对IF钢马氏体相变组织和硬度的影响
Zuohua Wang, Haidong Sun, Changji Li, Ning Liu, Shuai Zhang, Pinwen Zhu, Dongli Yue, Hongwang Zhang✉
H. Zhang:hwzhang@ysu.edu.cn(燕山大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116978
摘要
我们对1050°C保温30 min,随后10°C/s冷却至室温的IF钢进行了1- 5GPa等静压处理,并研究了这一过程中的组织演化和硬化。实验结果表明,材料中形成了典型的板条马氏体,硬度从80HV大幅提高至780HV。马氏体表现出板条束-板条块-板条的层级结构,与奥氏体之间遵循经典K-S取向关系。压力对马氏体变体的倾向和尺寸有调控作用。当压力从1 GPa增加到5 GPa时:(1)单变体马氏体半条块逐渐被同一Bain组的双变体马氏体半条块取代 (2)与孪晶有关的变体逐渐增加(3)异体厚度从微米级减小到纳米级。我们假设界面强化和位错强化的贡献可进行线性叠加,对硬化机制进行了分析。以上研究表明,高压作为一种不依赖合金元素的马氏体相变调控方法,具有巨大的开发潜力。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117009
2. Interaction between hydrogen and solute atoms in {10-12} twin boundary and its impact on boundary cohesion in magnesium
镁{10-12}孪晶界处氢与溶质原子的相互作用及其对晶界结合力的影响
Zhifeng Huang, Jian-Feng Nie✉
J.-F. Nie:jianfeng.nie@monash.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117009
摘要
氢是镁合金中常见的杂质或添加元素,对于沿晶界的裂纹扩展有重要影响。关于氢原子与晶界偏聚的其他合金元素间的相互作用及其对镁合金界面结合力的影响目前尚不清楚。我们通过第一性原理计算,对氢与Mg合金中常见的18种合金元素在{10-12}孪晶界的相互作用,及其对{10-12}孪晶界结合力的影响进行了研究。结果表明,氢倾向于与Mg晶格和孪晶界中的Li、Ca、Mn、Zr、Y、La、Pr、Nd、Sm、Gd、Tb、Dy、Ho等溶质原子结合,而不易与Al、Sn、Bi、Zn、Ag结合。因此,当{10-12}孪晶界处存在Al、Bi、Zn、Ag等元素时,氢不易向孪晶界处偏聚;而当孪晶界处已有 Li、Ca、Mn、Zr、Y、Nd等元素的偏聚时,氢很容易与他们形成氢-溶质原子对。偏聚溶质原子及其与氢原子的相互作用对孪晶界结合力的增强或减弱与Mg原子和偏聚溶质原子间的电子相互作用密切相关。Mn、Zr、Y、Nd等原子在没有氢偏聚的条件下,由于溶质原子d电子与Mg原子p电子间的强烈相互作用,可以显著增强孪晶界的结合力。然而,与氢原子形成原子对后,发生的电子转移会减弱这种强化效果,从而使界面的抗断裂能力发生劣化。本研究从氢与合金元素相互作用的角度揭示了氢致界面断裂,这对于深入理解镁合金中的氢脆具有重要意义。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117005
3. Multiphase and multiphysics modeling of dendrite growth and gas porosity evolution during solidification
凝固过程中枝晶生长和气孔演化的多相物理模型
Ang Zhang✉, Zhipeng Guo, Bin Jiang✉, Jinglian Du, Cuihong Wang, Guangsheng Huang, Dingfei Zhang, Feng Liu, Shoumei Xiong, Fusheng Pan
A. Zhang:angzhang@cqu.edu.cn(重庆大学/清华大学)
B. Jiang: jiangbinrong@cqu.edu.cn(重庆大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117005
摘要
气孔缺陷会极大地劣化铸件的力学性能。本研究中,我们建立了固-液-气多相场晶格-玻尔兹曼模型来描述凝固过程中复杂的多相相互作用。模型放宽了纯金属体系假设,简化了气泡形状和纯扩散条件,可以考虑固相生长、气泡运动、界面变形、成分输运、熔体流动以及合金溶质和溶解气体的配分。我们从质量守恒、双相模型映射、气泡动力学等方面对模型进行了验证。通过将其与其他四种模型以及实验进行比较,进一步评价了模型的有效性。模型成功地描述了镁合金中气孔与枝晶间的相互作用。我们通过定量分析熔体过冷度、界面流动性、气泡压力等特征参数对相分数的影响,深入讨论了多相平衡问题。该模型是对现有模型的补充,特别适合用于涉及固-液-气多相的复杂问题。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117020
4. Origins of size effects in initially dislocation-free single-crystal silver micro- and nanocubes
无位错单晶银微纳米立方体中尺寸效应的原因
Claire Griesbach, Seog-Jin Jeon, David Funes Rojas, Mauricio Ponga, Sadegh Yazdi, Siddhartha Pathak, Nathan Mara, Edwin L. Thomas, Ramathasan Thevamaran✉
R. Thevamaran:thevamaran@wisc.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117020
摘要
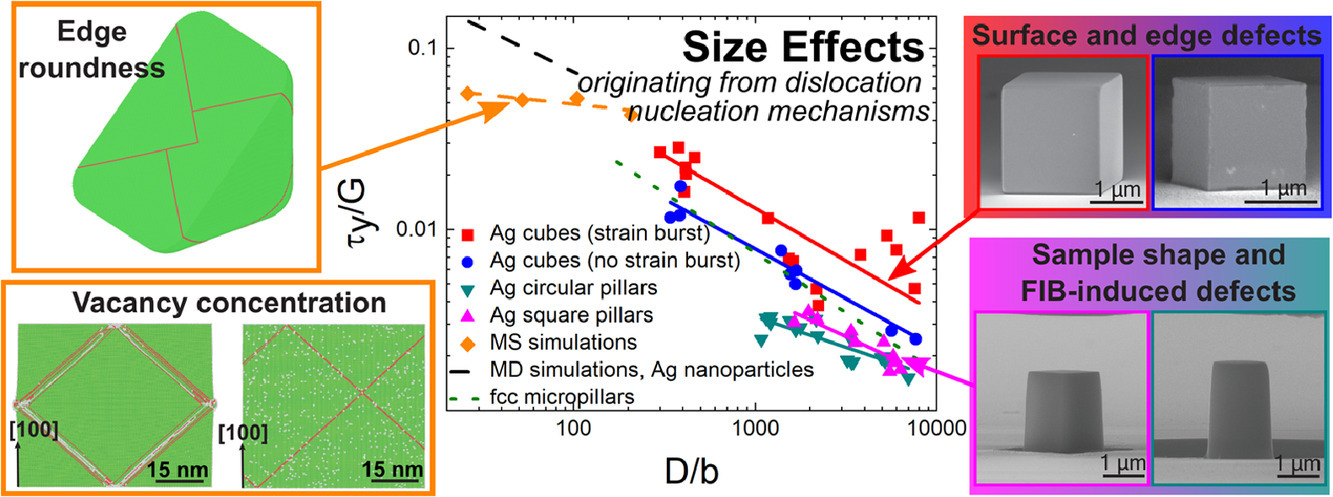
我们通过多步形核-长大工艺制备得到了无位错的银纳米立方,该材料在随后的微柱压缩试验中表现出了惊人的屈服强度——高达银理论强度的四分之一。材料极高的强度和屈服瞬间应变是单晶样品位错自发形核的结果。若样品微柱是通过聚焦离子束制备的,则压缩时不会发生剧烈的应变爆发,其屈服强度只有对比组样品的四分之一。无论测试前样品的缺陷状态如何,尺寸效应都很明显——屈服强度随着样品尺寸的减小而增加。由于位错贫乏和单源机制都不能解释尺寸效应对无位错样品屈服强度的影响,因此我们通过实验观测和分子静力学模拟从位错形核机制的角度进行了研究。研究表明,破坏材料对称性的因素,如表面缺陷、边缘圆度、样品形状或高空位浓度,都会影响位错形核,从而导致尺寸对无位错样品的屈服强度产生影响。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117021
5. Representative volume elements for plasticity and creep measured from high-resolution microscale strain fields
基于微观应变场的高分辨表征测量材料塑性和蠕变的代表体积元
R.B. Vieira, H. Sehitoglu, J. Lambros✉
J. Lambros:lambros@illinois.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117021
摘要
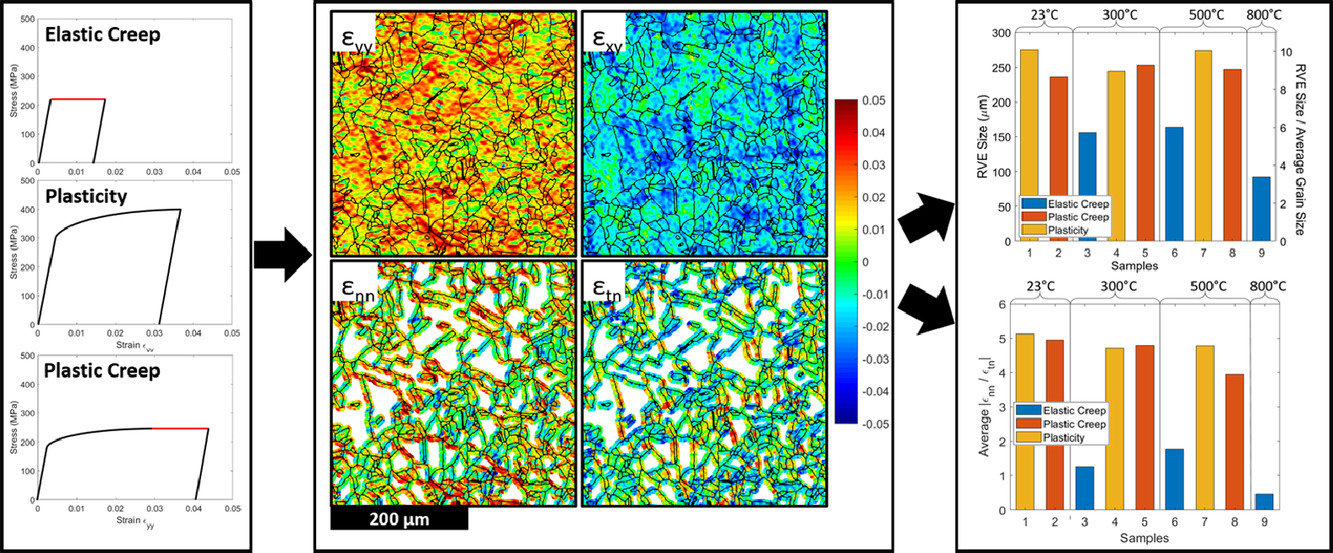
均匀化方法被广泛应用于放大显微尺度的数值结果,以预测材料的宏观性能。均匀化通常是基于代表体积元(RVE)进行的,因此,准确测量RVE尺寸和阐明RVE尺寸的影响因素是材料建模成功的关键。本研究中,我们通过不同参数条件下的塑性和蠕变实验对奥氏体不锈钢的RVE尺寸进行了实验测定。我们通过高分辨率数字图像关联(DIC)方法,对材料在微观尺度上的残余应变不均匀性进行了识别。此外,结合背散电子电子衍射(EBSD)获取的材料的表面组织信息,可以进一步对晶界附近的局域应变进行区分,从而对引起应变积累的变形机制进行定量分析。最后,我们通过对比不同加载参数下的RVE尺寸,以及局部正应变和剪应变的相对比例,研究了晶界滑移与应变不均匀性之间的关系。高温下,晶界滑移是材料的主要变形机制,此时RVE尺寸约为平均晶粒尺寸的4-6倍,明显小于不明显发生滑移的样品(约为平均晶粒尺寸的10倍)。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117015
6. Role of the local stress systems on microstructural inhomogeneity during semisolid injection
铸造过程中局部应力对微观组织不均匀性的影响研究
S. Bhagavath, Z. Gong, T. Wigger, S. Shah, B. Ghaffari, M. Li, S. Marathe, P.D. Lee✉, S. Karagadde✉
P.D. Lee:peter.lee@ucl.ac.uk
S. Karagadde:s.karagadde@iitb.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117015
摘要
高压金属铸造是一个冷却速率和压强变化很大的动态过程,这导致在铸造过程中同一件铸件的不同部分往往具有不同的固相状态和形变特征。工艺参数及参数间复杂的相互作用共同决定了凝固组织中的缺陷。本研究中,我们通过快速同步X射线成像技术对铝合金高压压铸过程中,研究了固态体积分数、加载状态和熔体流动对局部组织不均匀性的影响。虽然已有文献中报导的原位变形速率可达10 μm/s,但我们对更快填充和凝固条件下(~100 μm/s)的过程进行了研究。结果表明,当固态体积分数较低时,熔体的变形具有以下两种典型特征:(1)中间晶粒尺寸较大,近器壁晶粒尺寸较小,(2)由于Cu在液相中的富集导致在固液界面附近发生重熔。我们对固态体积分数较大的样品进行了非原位扫描和数字图像分析,揭示了基于局部应力状态、微观组织和补缩的孔隙形成机制。我们发现熔体可以分为具有以下四种不同特征的区域:(1)塞流区 (2)致密浆料区 (3)剪切区 (4)块体区。以上研究对于压铸过程中不同区域缺陷形成的数值模拟具有指导意义。

ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116990
7. Segmentation of experimental datasets via convolutional neural networks trained on phase field simulations
利用相场模拟训练的卷积神经网络实现对实验数据集的图像分割
Jiwon Yeom, Tiberiu Stan, Seungbum Hong✉, Peter W. Voorhees
S. Hong:seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116990
摘要
对大型图像数据集的快速分析能力对于先进材料的表征和设计至关重要,而图像分割是分析过程中最主要和耗时的步骤。卷积神经网络(CNNs)是一种很有前景的分割方法。然而这一方法的主要难点在于前期需要人工地对数据集进行分类和标记,从而实现对CNN算法的训练过程。本研究中,我们发现仅使用简单的相场模拟对CNN算法进行训练,就可能实现对于实验数据集的图像分割。我们以Al-Zn合金原位凝固的实验图像为例,对相场模拟进行了参数化。以下训练能够帮助CNN算法有效地捕获图像中最重要的组织特征:(1)识别粒子和背景的弥散边缘 (2)噪声的优化 (3)去除图像边缘的粒子 (4) 枝晶上假象的识别。经过相场模拟图像训练的CNN算法对实验图像的分割准确率为99.3%,与直接在实验数据上训练的准确率相当。这种利用计算机生成图像训练算法的方法能够极快地快速新材料的设计研发。

ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117006
8. Studying the micromechanical behaviors of a polycrystalline metal by artificial neural networks
多晶金属微观力学行为的人工神经网络研究
Wei Dai, Huamiao Wang✉, Qiang Guan, Dayong Li, Yinghong Peng, Carlos N. Tomé
H. Wang:wanghm02@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117006
摘要
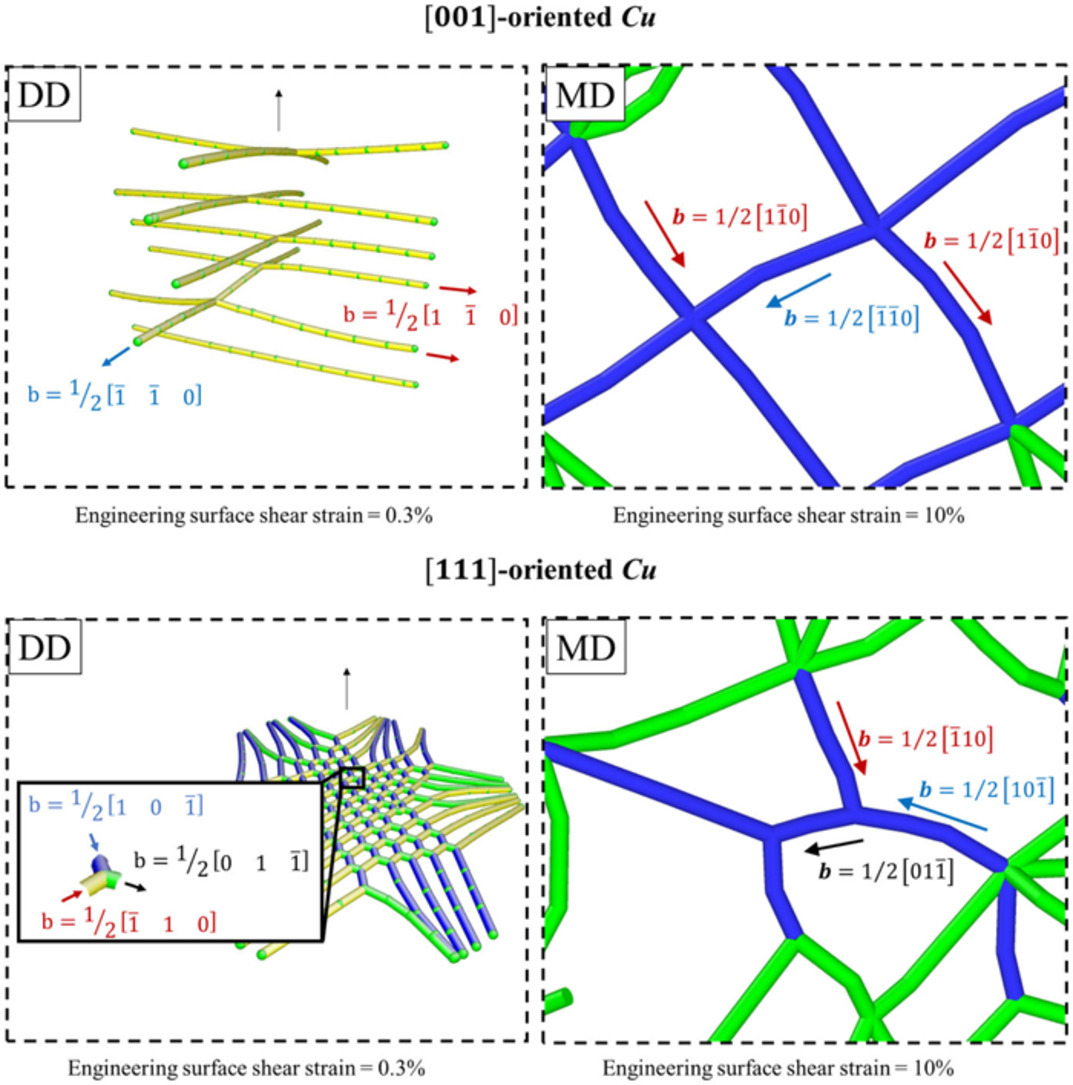
尽管基于物理的晶体塑性模型能够准确预测复杂载荷下的材料力学响应,但其较高的计算成本极大地限制了工程应用。另一方面,机器学习技术目前已被广泛用于数据的分析预测,且比传统技术在计算效率方面更具优势。本研究中,我们在OFHC铜中根据物理粘塑性自洽(VPSC)模型得到的数据库基础上,开发了人工神经网络(ANN)模型,并对模型进行了训练。结果表明,ANN模型能够成功地预测具有任意织构的多晶铜在不同加载路径下的微观力学行为,甚至其泛化能力超出了数据集的边界。ANN模型的精度没有显著降低,但计算效率大幅提升。因此,基于物理模型的人工神经网络在工程上具有极大的应用前景。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 116986
9. Tailoring the metastable reversed austenite from metastable Mn-rich carbides
通过富锰碳化物调控亚稳逆相变奥氏体
Yuantao Xu, Wei Li✉, Hao Du, Huisheng Jiao, Binggang Liu, Yun Wu, Wei Ding, Yi Luo, Yihong Nie, Na Min, Wenqing Liu, Xuejun Jin✉
W. Li:weilee@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
X. Jin:jin@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116986
摘要
我们设计了两步回火-配粉工艺,用于调控冷轧中锰钢中的碳、锰等奥氏体稳定元素。材料经450℃回火0.5h和1h后,三维原子探针表征表明,存在大量的亚稳态富锰M12C析出和NiAl纳米析出,且大量的碳在NiAl析出附近的界面和位错上偏聚。M12C碳化物与位错/界面之间的竞争抑制了亚稳态M12C向更稳定碳化物的转变。在随后630℃,0.5h的配分过程中,亚稳M12C溶解,在M12C上形核的细小奥氏体中呈现出明显的Mn梯度。亚稳态奥氏体继承了M12C中的大量锰和碳(Mn: 18.1 at.%, C: 1.56 at.%),且分布弥散(9.8 μm−2)和尺寸细小(50-200 nm)。由于这些奥氏体兼具硬质和可相变的特点,因此同时为材料提供了Orowan强化和形变诱导马氏体相变(TRIP)强化,力学性能可达屈服强度~1350 MPa,总延伸率~30%。综上所述,我们提出了一种有创新性的高强度钢设计策略,使得亚稳奥氏体除了TRIP效应外,还能够通过第二相强化材料。
ACTA
Vol. 214,1 Aug. 2021, 117019
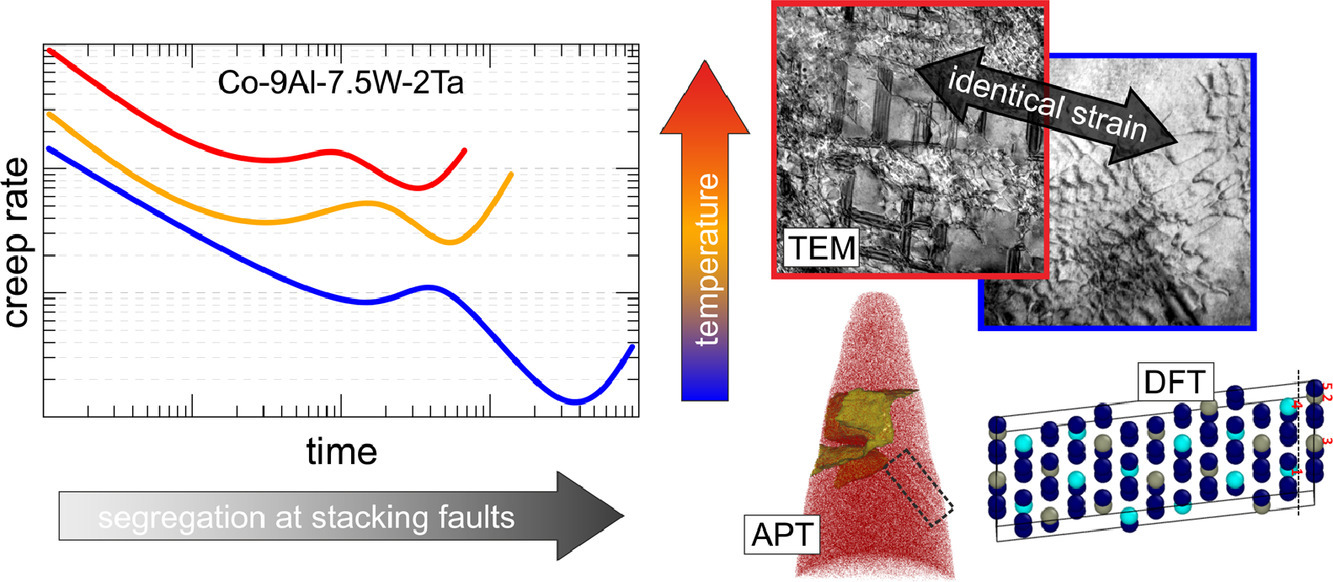
10. Understanding creep of a single-crystalline Co-Al-W-Ta superalloy by studying the deformation mechanism, segregation tendency and stacking fault energy
基于变形机制、合金元素偏聚和层错能研究单晶Co-Al-W-Ta高温合金的蠕变性能
N. Volz✉, F. Xue, C.H. Zenk, A. Bezold, S. Gabel, A.P.A. Subramanyam, R. Drautz, T. Hammerschmidt, S.K. Makineni, B. Gault, M. Göken, S. Neumeier
N. Volz:nicklas.volz@fau.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117019
摘要
我们对Co-9Al-7.5W-2Ta单晶钴基高温合金在950、975和1000℃下的压缩蠕变性能进行了系统,揭示了温度和Al、W和Ta等元素扩散速度对变形机制的影响。在所有的温度条件下,均能观测到两个蠕变率最小值,因此这种现象的变形机制应当是相似的。原子探针分析表明,蠕变过程中,γ′相中形成的层错处存在溶质元素偏析。密度泛函理论计算表明,W和Ta有向层错偏聚的趋势,且能显著降低层错能。高温下元素扩散加快,因此偏聚也加快。这使得合金的软化显著加快,因为偏聚能够在蠕变早期促进分位错切过γ′析出。透射电子显微镜表征证实了上述机制。因此,高温下析出体积分数的减小和扩散对分位错剪切γ′相的促进作用共同导致了材料蠕变性能的劣化。以上研究对高温合金设计具有指导意义。