金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.205, 1 Dec. 2021(上)
2021-12-03 来源:Goal Science

本期包含金属材料领域论文9篇,涵盖了钛合金、铝合金、增材制造、马氏体等,国内科研单位包括西北工业大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 205 目录
1. Heat-affected coarsening of β grain in titanium alloy during laser directed energy deposition
激光定向能量沉积钛合金中β晶粒的热影响粗化
2. A molecular dynamics study of path-dependent grain boundary properties in nanocrystals prepared using different methods
使用不同方法制备的纳米晶体中路径相关晶界特性的分子动力学研究
3. The mechanical response of additively manufactured IN625 thin-walled structures
增材制造IN625薄壁结构的机械响应
4. Predicting the energetics and kinetics of Cr atoms in Fe-Ni-Cr alloys via physics-based machine learning
通过基于物理的机器学习预测Fe-Ni-Cr合金中Cr原子的能量学和动力学
5. Observation of Portevin-le Chatelier effect in aluminum alloy 7075-w under a heterogeneous stress field
7075-w铝合金非均质应力场下Portevin-le Chatelier效应的观察
6. Cyclic response of additive manufactured 316L stainless steel: The role of cell structures
增材制造316L不锈钢的循环响应:胞状结构的作用
7. Impact of Ni alloying on Fe-C martensite ageing: an atomistic investigation
Ni合金化对Fe-C马氏体时效的影响:一项原子尺度研究
8. Aperiodic structures of rod-shaped precipitates in a Mg-Zn-Al alloy
Mg-Zn-Al合金中棒状析出物的非周期性结构
9. Giant magnetic-field-induced bending effect in Ni-Mn-Ga-Co-Cu melt-spun ribbons
Ni-Mn-Ga-Co-Cu熔纺薄带中的巨大磁场诱导弯曲效应
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114180
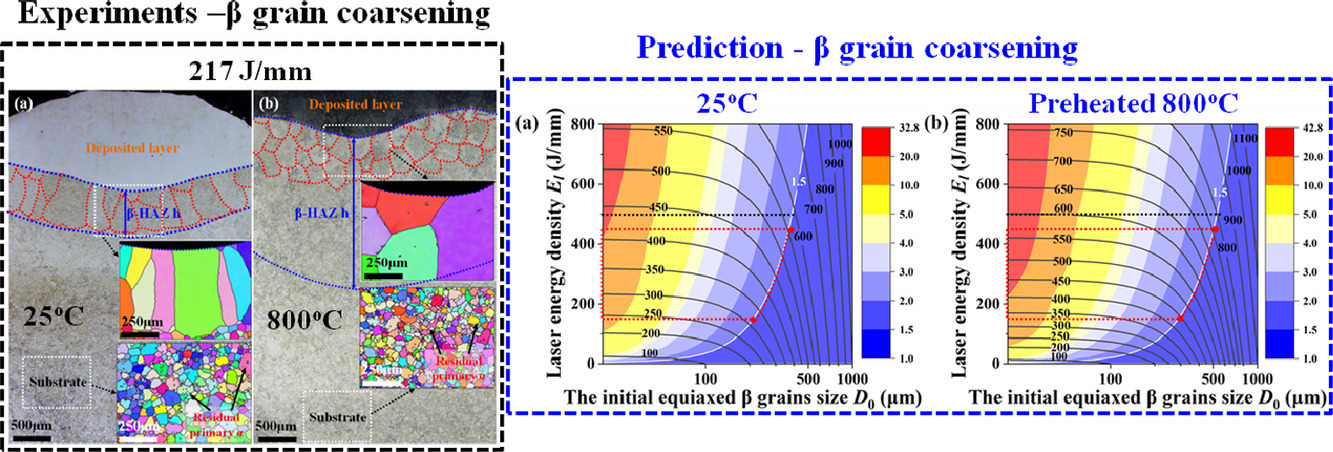
1. Heat-affected coarsening of β grain in titanium alloy during laser directed energy deposition
激光定向能量沉积钛合金中β晶粒的热影响粗化
Aitang Xue✉, Xin Lin, Lilin Wang, Xufei Lu, Hanlin Ding, Weidong Huang
Aitang Xue: atxue@mail.nwpu.edu.cn (西北工业大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114180
摘要
钛合金中β晶粒在增材制造 (AM) 过程中会受热影响而粗化,这极大影响了实现像锻造态的细β晶粒,但过去的研究忽视了这点。在项工作,我们报告了Ti6Al4V等轴β晶粒的显着粗化发生在激光定向能量沉积过程中的瞬时高温(β转变温度以上)热循环下。 特别是初始β晶粒越小,能量密度越大,预热温度越高,粗化越显著。同时,提出了一种用于预测增材制造钛合金中粗化的β晶粒的尺寸的修正模型。 这些发现为增材制造条件下的β晶粒提供了更全面的认识,并对具有细等轴β晶粒的增材制造钛合金的成分设计提供了重要指导。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114183
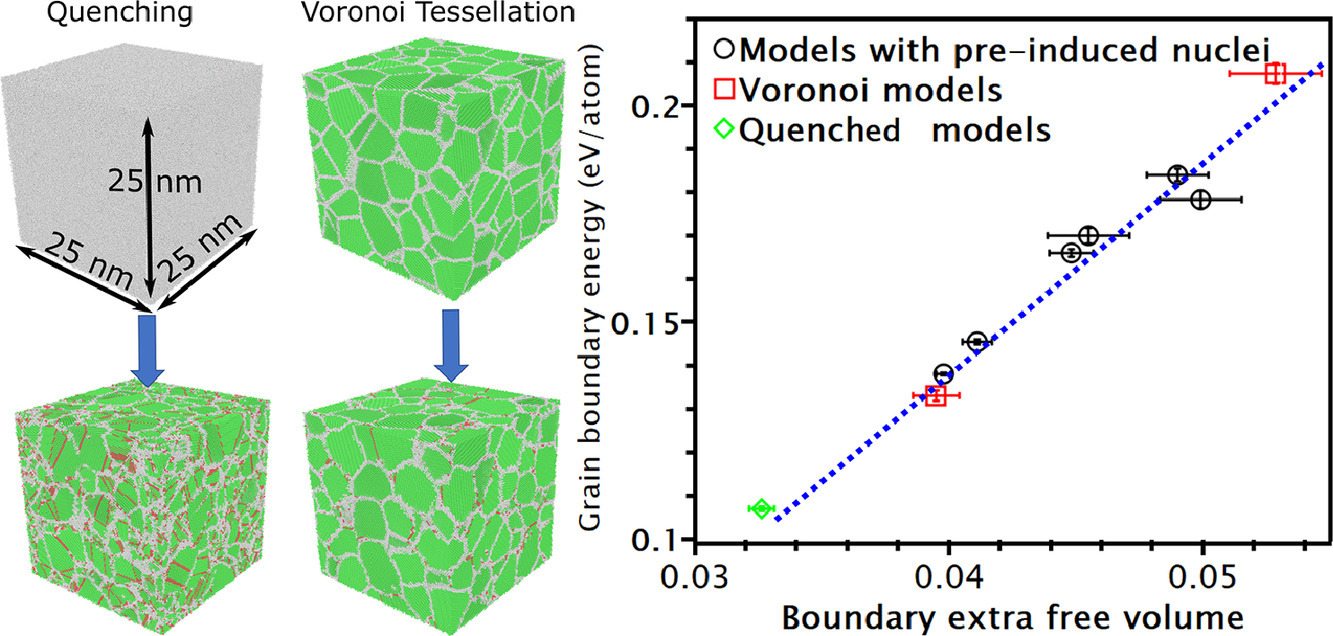
2. A molecular dynamics study of path-dependent grain boundary properties in nanocrystals prepared using different methods
使用不同方法制备的纳米晶体中路径相关晶界特性的分子动力学研究
Hao Sun✉, Laurent Karim Beland✉
Hao Sun: hs126@queensu.ca
Laurent Karim Beland: laurent.beland@queensu.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114183
摘要
晶界在热力学上是不稳定的,因此,它们的特性应该是与路径相关的,使用不同方法制备的纳米晶中的晶界可能表现出不同的特性。使用分子动力学模拟,我们分别研究了通过淬火、预诱导成核位点凝固和Voronoi镶嵌形成的不同纳米体的晶界,并发现一些与路径有关的特性:淬火模型的每个原子边界能量较低,每个原子的边界过剩自由体积较小,晶粒生长速度比Voronoi模型慢。我们推测这些差异归因于淬火模型中大量的退火孪晶。此外,一些属性与路径无关,例如杨氏模量、泊松比以及晶界能量与过剩自由体积之间的比率。本研究的结果进一步加深了对纳米晶结构-性能关系的理解,并为未来基于模拟的纳米晶材料研究提供了指导。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114188
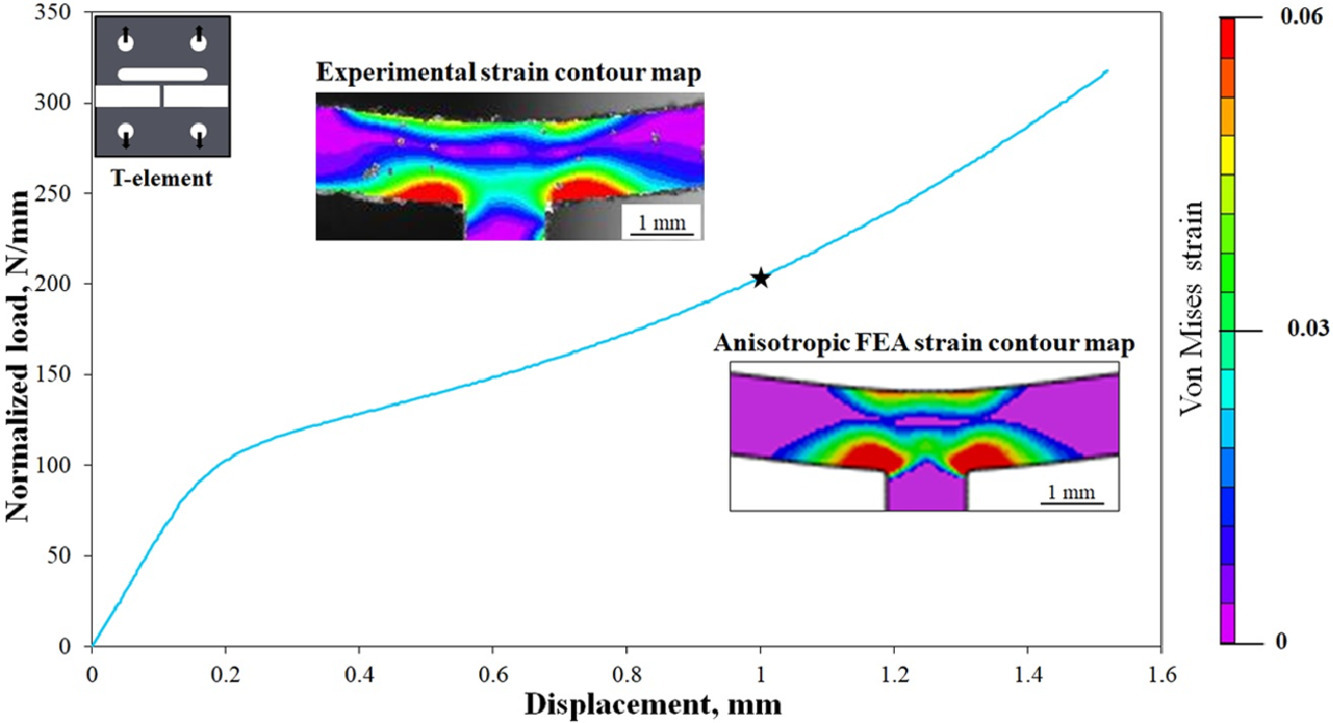
3. The mechanical response of additively manufactured IN625 thin-walled structures
增材制造IN625薄壁结构的机械响应
Arunima Banerjee, Sara Messina, Matthew R. Begley, Edwin J. Schwalbach, Michael A. Groeber, William D. Musinski, Paul A. Shade, Marie E. Cox, Jonathan D. Miller, Kevin J. Hemker✉
Kevin J. Hemker: hemker@jhu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114188
摘要
与传统制造相比,增材制造提供了增强的设计和拓扑复杂性,非常适合制造复杂的结构。这项工作中,我们提出了一种新的毫米级测试方法来评估激光粉床打印的 Inconel 625薄壁结构的特定位置的机械响应。通过高分辨率数字图像与环境温度毫级测试相结合,以了解T形试样中塑性变形的进展。塑性应变集中在水平和垂直韧带的交叉处,这意味着它们在设计过程中的重要性。EBSD图像阐明了几何结构在平面纹理发展中的作用。各向同性有限元模型无法完全预测打印样本的力学性能响应,但由纹理测量驱动的各向异性模型产生了更好的一致性。这项工作说明了局部加工和微观结构对增材制造部件的机械响应的重要性。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114177
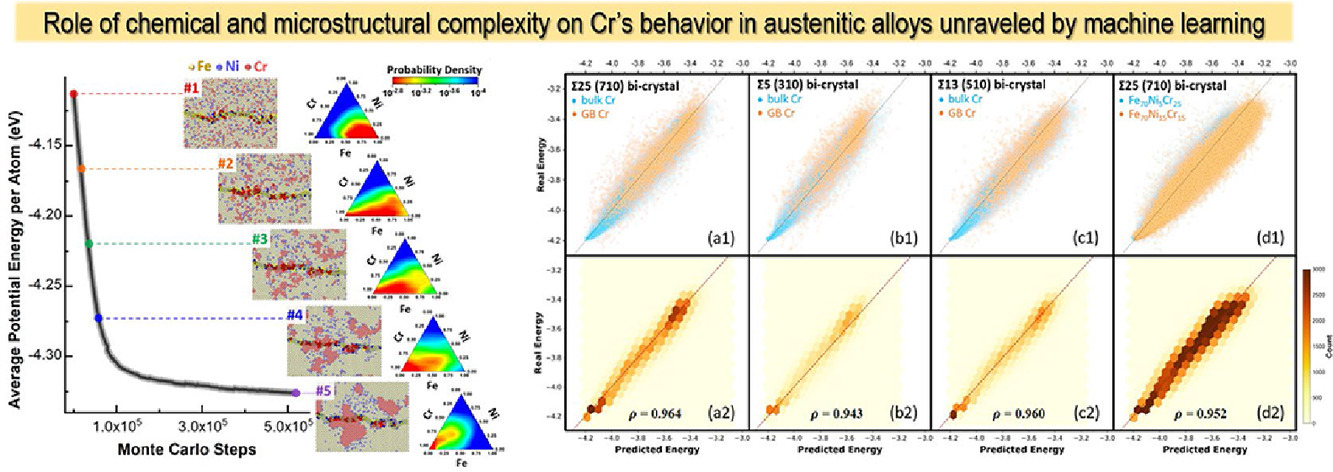
4. Predicting the energetics and kinetics of Cr atoms in Fe-Ni-Cr alloys via physics-based machine learning
通过基于物理的机器学习预测Fe-Ni-Cr合金中Cr原子的能量学和动力学
Yuchu Wang, Bita Ghaffari, Christopher Taylor, Simon Lekakh, Mei Li, Yue Fan✉
Yue Fan: fanyue@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114177
摘要
奥氏体合金中Cr原子的能量和激活势垒的分布在多种化学(例如固溶体与偏析状态)和显微结构(例如块体与晶界)环境中的多类型样品上进行了研究。借助基于物理的机器学习算法,发现可以根据局部电负性(χ)和局部原子堆积的自由体积 (Vv) 可靠地预测Cr原子的热力学和动力学行为,并建立了χ-Vv参数空间中相应的预测图。这些图与现有实验结果一致,并通过具有不同原子间力场的并行建模进行了验证。同时讨论了本研究在指导具有所需性能的奥氏体合金设计方面的潜力。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114178
5. Observation of Portevin-le Chatelier effect in aluminum alloy 7075-w under a heterogeneous stress field
7075-w铝合金非均质应力场下Portevin-le Chatelier效应的观察
Yumi Choi, Jinjin Ha✉, Myoung-Gyu Lee, Yannis P. Korkolis
Jinjin Ha: jinjin.ha@unh.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114178
摘要
针对固溶热处理的AA7075铝板研究了Portevin-Le Chatelier(PLC)带在使用平头冲头扩孔过程中的动力学。该实验在准静态应变率和室温下进行,整个变形过程中孔周边的全应变场由立体数字图像相关系统测量。PLC带活动的观察是基于厚度应变率场。每个单独的PLC带似乎沿径向排列,跨越不同的应力状态,并在从成核到耗散的寿命期间沿圆周方向传播。此外,在实验过程中记录了所有PLC带的成核位置,这表明PLC带的成核频率受塑性各向异性的影响,并且与厚度应变水平成比例增加。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114190
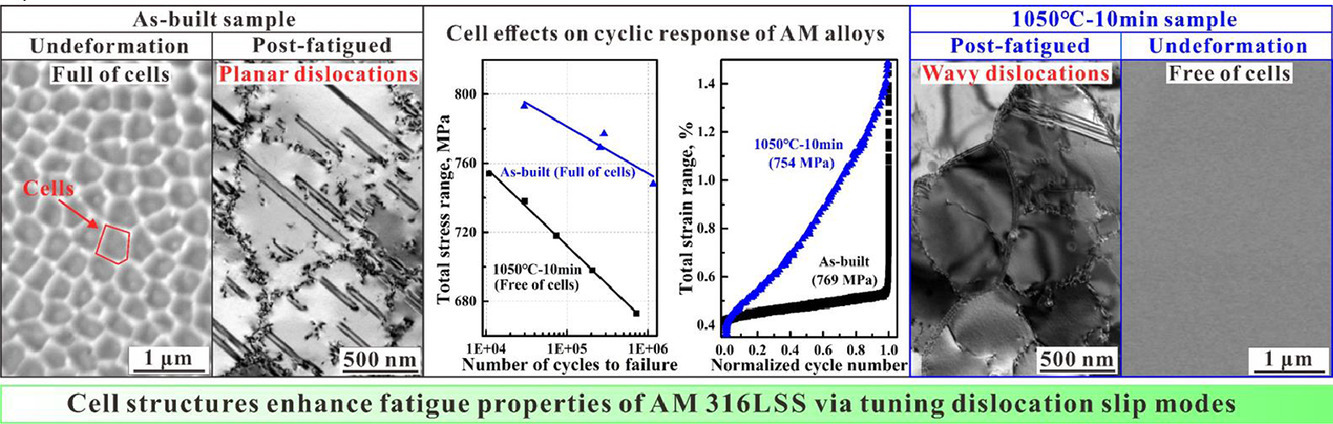
6. Cyclic response of additive manufactured 316L stainless steel: The role of cell structures
增材制造316L不锈钢的循环响应:胞状结构的作用
Luqing Cui✉, Fuqing Jiang, Dunyong Deng, Tongzheng Xin, Xiaoyu Sun, Reza Taherzadeh Mousavian, Ru Lin Peng, Zhiqing Yang✉, Johan Moverare✉
Luqing Cui: luqcu85@liu.se
Zhiqing Yang: yangzq@imr.ac.cn(中国科学院金属研究所)
Johan Moverare: johan.moverare@liu.se
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114190
摘要
我们报告了胞状结构对增材制造(AM)316L不锈钢(316LSS)疲劳行为的影响。与无胞状结构样品相比,全胞状结构样品的疲劳过程仅包括稳定和过载阶段,没有初始软化阶段。此外,全胞状结构样品具有更高的强度、更低的循环软化率和更长的寿命。显微分析显示了晶粒取向、尺寸和形状没有差异。然而,全胞状结构样品显示出平面位错结构,而无胞状结构样品显示出波状位错结构。胞状结构的存在促进了平面滑移的激活,延迟了局部应变,最终增强了AM 316LSS的疲劳性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114182
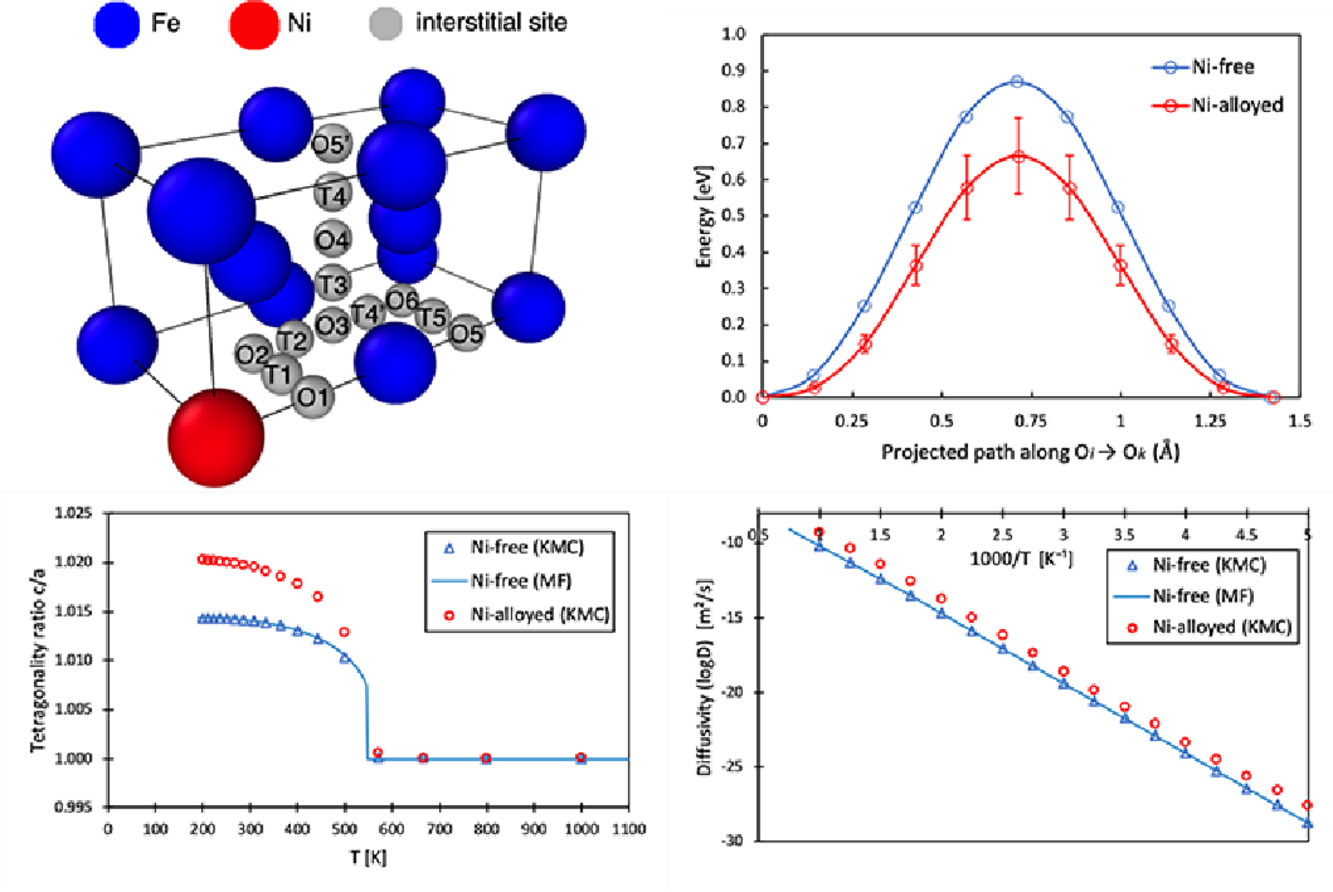
7. Impact of Ni alloying on Fe-C martensite ageing: an atomistic investigation
Ni合金化对Fe-C马氏体时效的影响:一项原子尺度研究
Paul Eymeoud✉, Liangzhao Huang, Philippe Maugis
Paul Eymeoud: paul.eymeoud@univ-amu.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114182
摘要
该工作在原子尺度上对Ni合金化对Fe-C马氏体时效的影响进行计算。使用 Climbing Image Nudged Elastic Band 技术,我们展示了α-铁中Ni-C成对相互作用的排斥性,并证明了Ni合金化降低了与α-铁中的间隙碳相关的迁移能和力偶极张量分量。成对相互作用、迁移能量和偶极子分量的计算值用于实施动力学蒙特卡罗方法。 我们发现镍合金化:(i)对马氏体热力学稳定性的影响可以忽略不计,(ii)通过增加碳扩散率来加速时效动力学。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114189
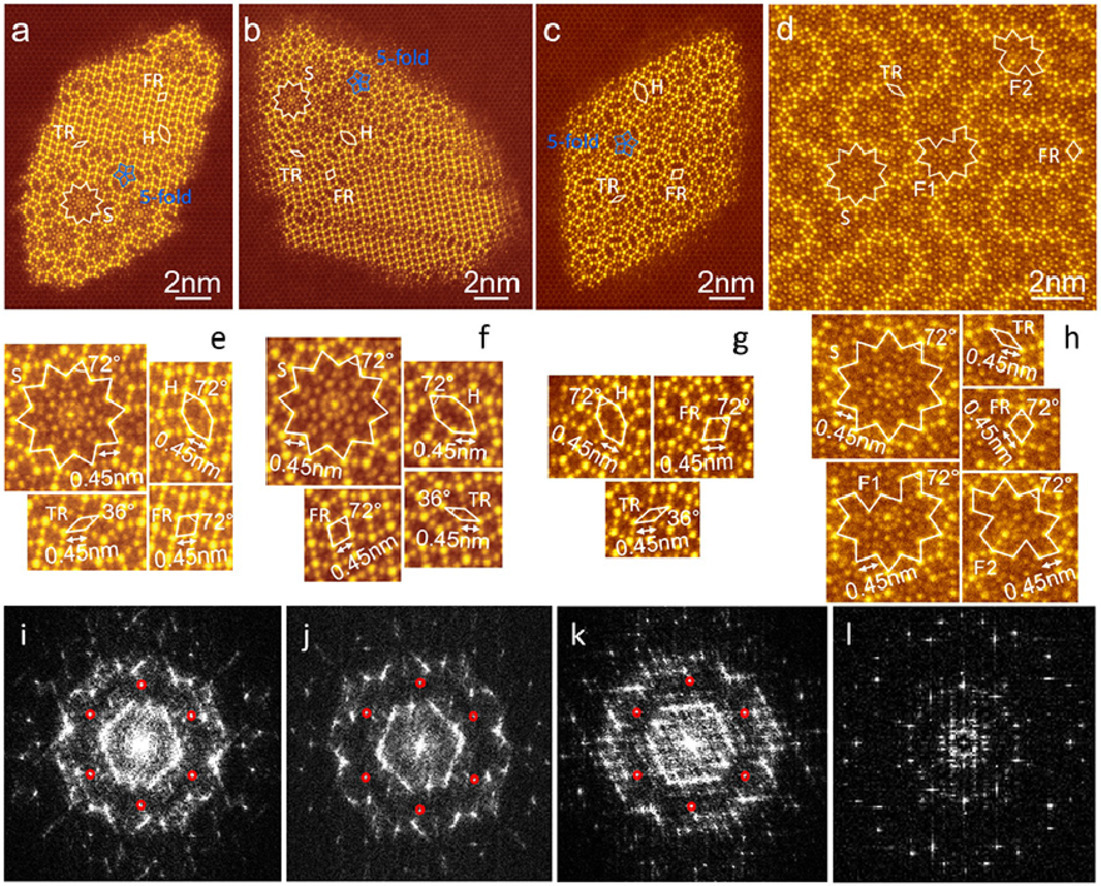
8. Aperiodic structures of rod-shaped precipitates in a Mg-Zn-Al alloy
Mg-Zn-Al合金中棒状析出物的非周期性结构
Yunhe Zheng, Laure Bourgeois, Jian-Feng Nie✉
Jian-Feng Nie: jianfeng.nie@monash.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114189
摘要
长轴平行于[0001]α的棒状析出物通常在Mg-Zn-Al合金中形成,提供强化效果。这些析出物是亚稳态的,通常被认为是MgZn2和/或Mg4Zn7相。在本文中,使用高角度环形暗场扫描透射电子显微镜在原子尺度上检查了时效ZA84合金中析出棒状物的横截面结构。发现这些沉淀物既不是纯MgZn2也不是纯Mg4Zn7。棒状析出物的结构在垂直于棒长轴的二维投影平面上不具有长程平移对称性和长程5重旋转对称性。 然而,这些结构可以通过不同形状的平铺来描述,最常见的是四种这样的形状。这项工作中揭示的结构细节可能有助于使Mg-Zn-Al和Mg-Zn合金中的许多复杂析出物结构合理化。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114203
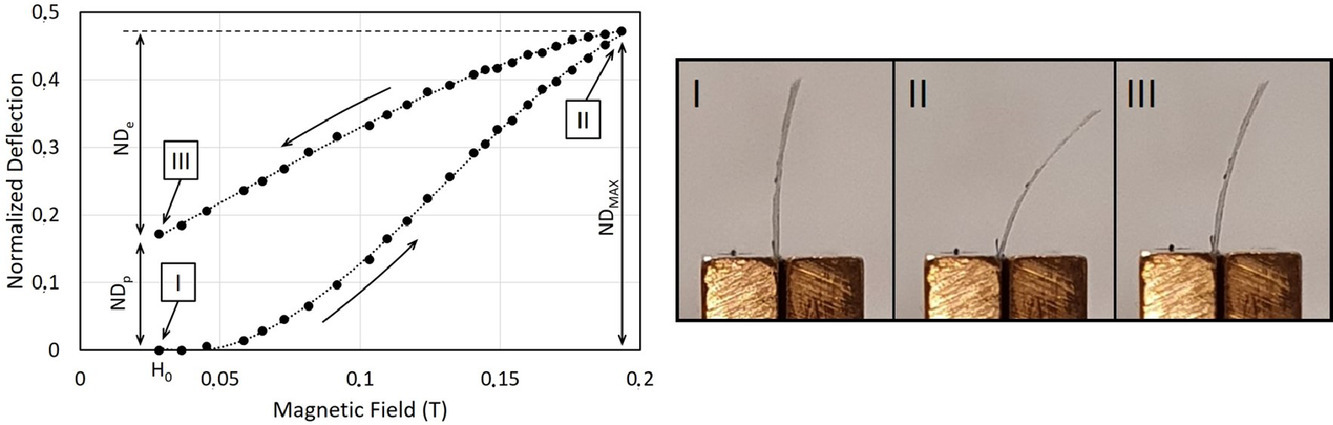
9. Giant magnetic-field-induced bending effect in Ni-Mn-Ga-Co-Cu melt-spun ribbons
Ni-Mn-Ga-Co-Cu熔纺薄带中的巨大磁场诱导弯曲效应
M.J. Szczerba✉
M.J. Szczerba: m.szczerba@imim.pl
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114203
摘要
该文章首次报告了对通过熔体纺丝技术生产的Ni-Mn-Ga-Co-Cu合金的巨磁场诱导弯曲效应。在使用在1173 K下退火60分钟以释放内应力的带材进行弯曲实验期间观察到了这种效果。在0.06T的极低磁场下观察到弯曲效应的开始。小于0.2T的外部磁场产生的整体变形由塑性和弹性的贡献组成。第一次是在初始弯曲周期中观察到的,而后者占主导地位。