金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.215,15 Aug. 2021(中)
2021-12-10 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文13篇,涵盖了中熵合金、高熵合金、铜合金等,国内科研单位包括南京理工大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 215 目录
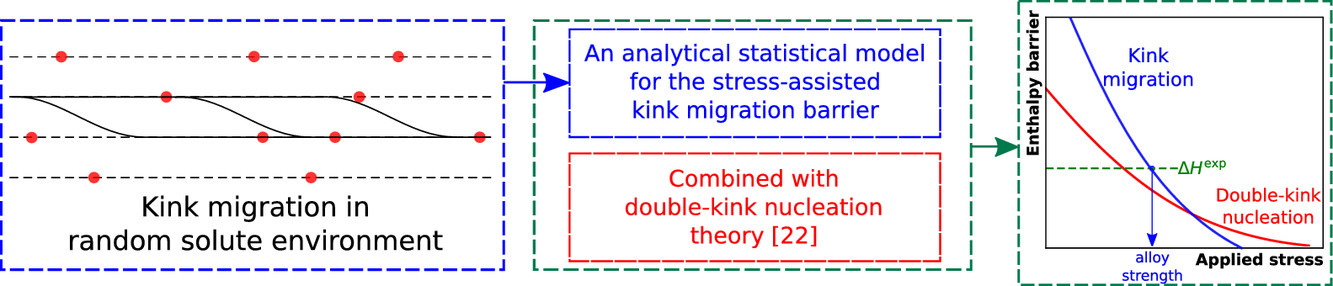
1. Theory of kink migration in dilute BCC alloys
稀释BCC合金中的扭结迁移理论
2. Unraveling dual phase transformations in a CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy
阐明CrCoNi中熵合金双相相变
3. Grain boundary mediated plasticity: A blessing for the ductility of metallic thin films?
晶界介导的塑性:金属薄膜延展性的福音?
4. Interlamellar boundaries govern cracking
层间边界控制开裂
5. Anisotropic microstructural evolution and coarsening in free sintering and constrained sintering of metal film by using FIB-SEM tomography
利用 FIB SEM 断层扫描技术研究金属薄膜自由烧结和约束烧结中的各向异性组织演变和粗化问题
6. Effect of the Pt concentration on microstructures of Ti-Pt alloys using the first-principles phase field method
利用第一性原理相场法研究铂金浓度对Ti-Pt合金组织的影响
7. Enhanced oxidation resistance of (Mo95W5)85Ta10(TiZr)5 refractory multi-principal element alloy up to 1300°C
增强(Mo95W5)85Ta10(TiZr)5 耐火多元素合金在1300°C下的抗氧化性
8. Multimodal 3D characterization of voids in shock-loaded tantalum: Implications for ductile spallation mechanisms
冲击载荷钽中空隙的多模态三维表征: 对延展性剥落机制的影响
9. Evaluating the grain-scale deformation behavior of a single-phase FCC high entropy alloy using synchrotron high energy diffraction microscopy
利用同步辐射高能衍射显微镜评估单相 FCC高熵合金的晶粒尺度变形行为
10. Machine learning assisted composition effective design for precipitation strengthened copper alloys
机器学习辅助下的沉淀强化铜合金成分有效设计
11. Phase transformation pathways in Ti-6Al-4V manufactured via electron beam powder bed fusion
电子束粉末床熔合的Ti-6Al-4V合金的相变途径
12. Lattice transformation in grain boundary migration via shear coupling and transition to sliding in face-centered-cubic copper
面心立方铜中通过剪切耦合的晶界迁移中的晶格转变和向滑动的过渡
13. First-principles study of the effect of Al and Hf impurities on Co3W antiphase boundary energies
Al和Hf杂质对Co3W反相边界能量影响的第一性原理研究
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117078
1. Theory of kink migration in dilute BCC alloys
稀释BCC合金中的扭结迁移理论
Alireza Ghafarollahi✉, W.A.Curtin
Alireza Ghafarollahi: alireza.ghafarollahi@epfl.ch
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117078
摘要
元素BCC 金属和稀土合金的塑性变形受沿螺纹位错的扭结对成核和扭结迁移过程的缓慢控制。在合金中,成核过程被促进,而迁移过程被抑制,导致浓度和温度相关的从成核优势到迁移优势的转变。本文建立并验证了稀BCC合金中应力依赖性扭结迁移势垒的统计分析模型。势垒只取决于一个明确定义的溶质/螺型位错相互作用参数、扭结宽度和位错长度。通过全原子轻推弹性带计算和模型Fe-Si合金的随机模拟,广泛验证了分析模型的有效性。结合最近经过验证的双扭结成核理论,获得了与温度和浓度相关的流动应力的全解析模型,其中包括从成核到迁移控制的转变。利用独立确定的材料特性,将整个模型应用于Fe-Si和W-Re,并在一系列浓度和温度的实验中获得了良好的一致性。总的来说,这两种理论代表了对稀BCC合金中螺型位错强度的统一的、全统计的、无参数的理解。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117112
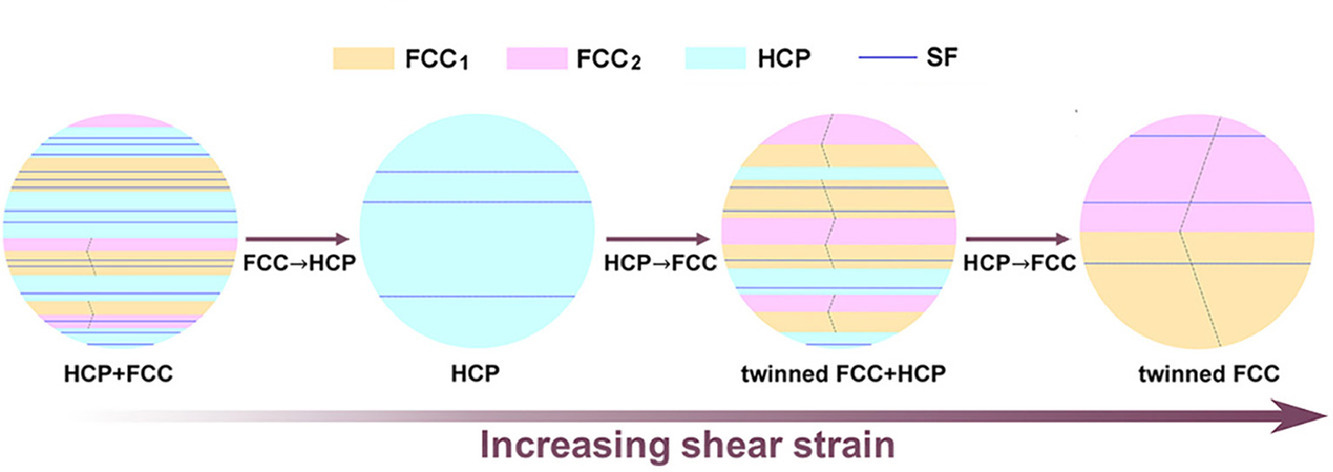
2. Unraveling dual phase transformations in a CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy
阐明CrCoNi中熵合金双相相变
Yujie Chen, Dengke Chen, Xianghai An✉, Yin Zhange, Zhifeng Zhou, Song Lu, Paul Munroe, Sam Zhang, Xiaozhou Liao✉, Ting Zhu✉, Zonghan Xie.
Xianghai An: xianghai.an@sydney.edu.au
Xiaozhou Liao: xiaozhou.liao@sydney.edu.au
Ting Zhu: ting.zhu@me.gatech.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117112
摘要
多主元素合金(MPEAs)的出现为高性能金属材料的发展带来了巨大的希望。然而,MPEAs是否能提供以前未知的变形机制以大幅提高其机械性能,目前仍不清楚。本文报道了CrCoNi中熵合金(MEA)中由面心立方(FCC)相到六方紧密堆积(HCP)相,再由纳米孪晶返回FCC相的机械诱导双相变形机制。相变过程中,在相同< 110 > FCC∥< 11-20 > HCP方向上,沿不同的{111}FCC∥(0001)HCP面发生连续剪切,总剪切应变高达70%。双相变源于FCC和HCP相中紧密堆积的{111}FCC∥(0001)HCP原子层之间的独特滑移能力,导致这些紧密堆积层具有低堆积错能的灵活堆积顺序。本文表明了MPEAs 可以提供非常规的变形机制,如CrCoNi MEA中的双相转化,从而为提高先进合金的力学性能提供了机会。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117079
3. Grain boundary mediated plasticity: A blessing for the ductility of metallic thin films?
晶界介导的塑性:金属薄膜延展性的福音?
Jan P.Liebig, Mirza Mačković, Erdmann Spiecker, MathiasGöken, Benoit Merle✉
Benoit Merle: benoit.merle@fau.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117079
摘要
金属薄膜的有限延展性(<1%)给MEMS 和柔性电子的应用带来了挑战。本文报告了独立的金样品,该样品具有出色的适应≥10%的塑性变形的能力,同时保持了高强度。在透射电子显微镜下使用原位纳米力学测试中,这种异常高的延展性可追溯到超薄厚度、柱状微结构和(111)纤维纹理的组合。在这样的条件下,变形主要是由晶界通过晶界滑动和剪切耦合晶界迁移介导的。由于这些非常规机制保留了试样的横截面厚度,从而延缓了颈缩,使试件达到了较高的延性。由于这些机理是在室温和应变率条件下得到证实的,这为利用微观结构工程开发韧性金属薄膜开辟了广阔的前景。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117091
4. Interlamellar boundaries govern cracking
层间边界控制开裂
Shitan Yan, Zhixiang Qi, YangChen, YuedeCao, Jinpeng Zhang, Gong Zheng, Fengrui Chen, Ting Bian, Guang Chen✉.
Guang Chen: gchen@njust.edu.cn, 南京理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117091
摘要
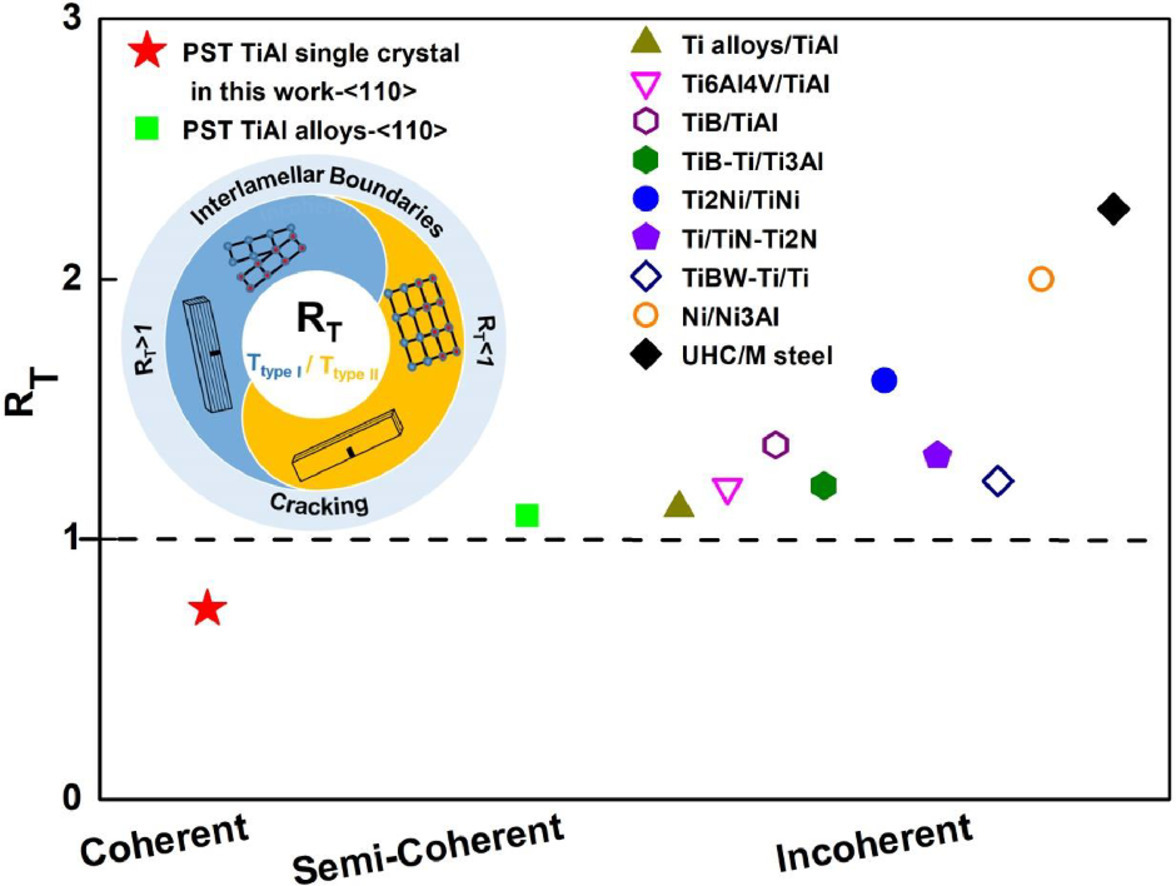
本文在聚合成双晶TiAl单晶中发现了一种新的现象,即带有裂纹分裂器(II型)的试样比带有裂纹止裂器(I型)的试样具有更高的韧性,与以往对层状材料开裂行为的研究相反。结合微观表征和理论计算,我们揭示了这种矛盾是由层间边界的相干性造成的。对于具有共格层间晶界的PST TiAl单晶,共格晶界抑制了I型试样的分层,裂纹倾向于沿变形孪晶面穿透片层。而II型试样中产生的固着位错阻碍了其他位错的进一步运动,导致裂纹尖端钝化。因此,II型试样比I型试样具有更高的断裂韧性。本文提出了韧性比 RT=Ttype I / Ttype II 来评估层状材料中不同水平边界相干性的开裂行为。在以前的研究中,RT>1,因为它们的边界是不连贯的,这促进了分层和裂纹尖端钝化。本文揭示了层间边界和裂纹扩展的关系,这为层状材料的发展提供了一个新的视角。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117087
5. Anisotropic microstructural evolution and coarsening in free sintering and constrained sintering of metal film by using FIB-SEM tomography
利用 FIB SEM 断层扫描技术研究金属薄膜自由烧结和约束烧结中的各向异性组织演变和粗化问题
Gaku Okuma✉, Ryo Miyaki, Kan Shinobe, Anna Sciazko, Takaaki Shimura, Zilin Yan, Shotaro Hara, Toshinori Ogashiwa, Naoki Shikazono, Fumihiro Wakai
Gaku Okuma: OKUMA.Gaku@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117087
摘要
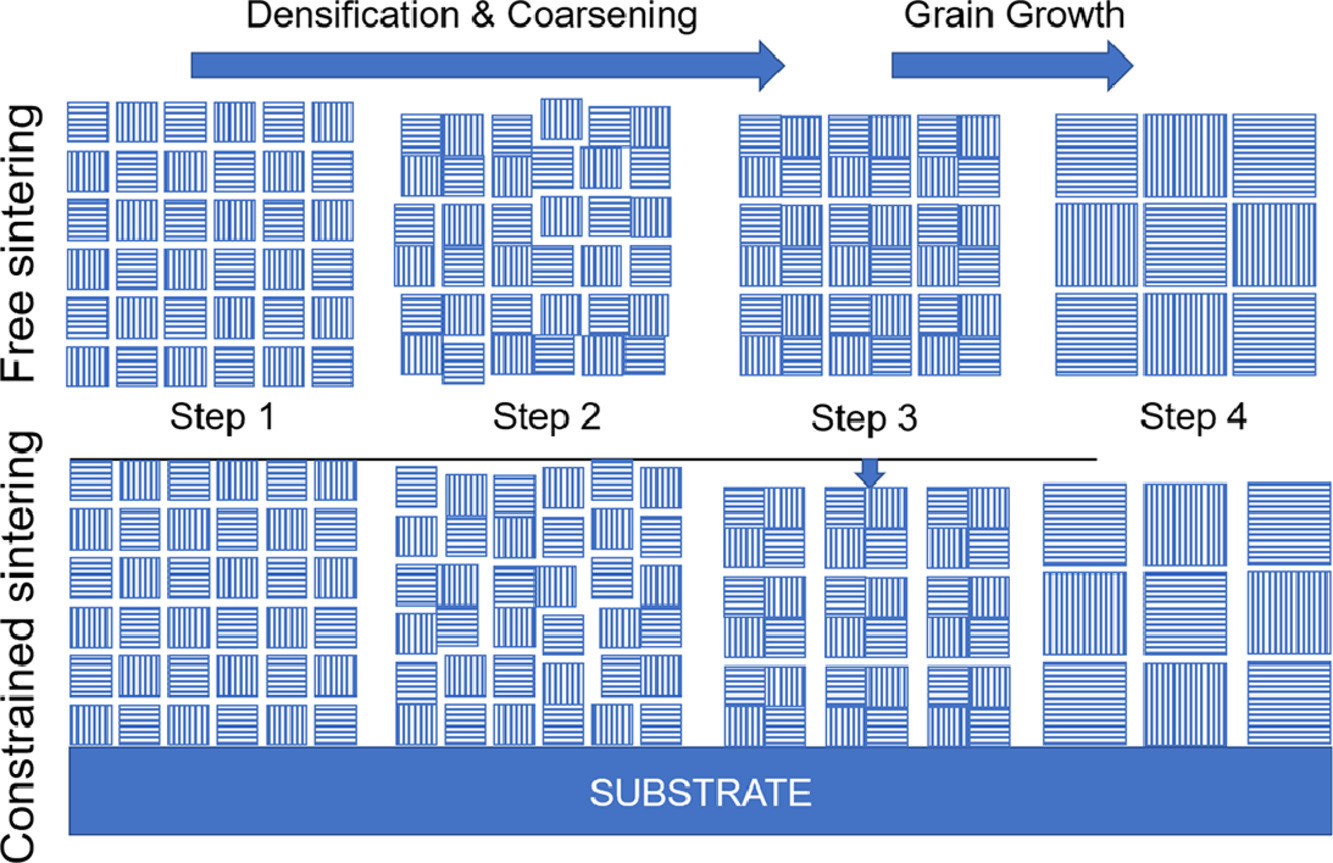
在粉末加工和约束烧结过程中会形成各向异性组织。采用扫描电镜(FIB-SEM)对金亚微米粒子在自由烧结和约束烧结过程中的微观组织演变进行了研究。致密化过程中总表面积减小,固相截距增大,固相粗化。用面积加权组构张量表征了铸态引起的球形颗粒的各向异性堆积结构,该张量表征了颗粒的键向和接触面积的各向异性。在自由烧结中,填充结构的初始各向异性随致密化程度的增加而减小。在约束烧结中,孔隙平均截距长度所观察到的初始各向异性在后期发生了逆转。显微组织沿厚度方向发生演化,形成细长孔洞。本文提出了一个开放孔隙结构模型来解释中间阶段的微观结构演化。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117050
6. Effect of the Pt concentration on microstructures of Ti-Pt alloys using the first-principles phase field method
利用第一性原理相场法研究铂金浓度对Ti-Pt合金组织的影响
Thi Nu Pham, Kaoru Ohno✉, Ryoji Sahara, Riichi Kuwahara, Swastibrata Bhattacharyya
Kaoru Ohno: ohno@ynu.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117050
摘要
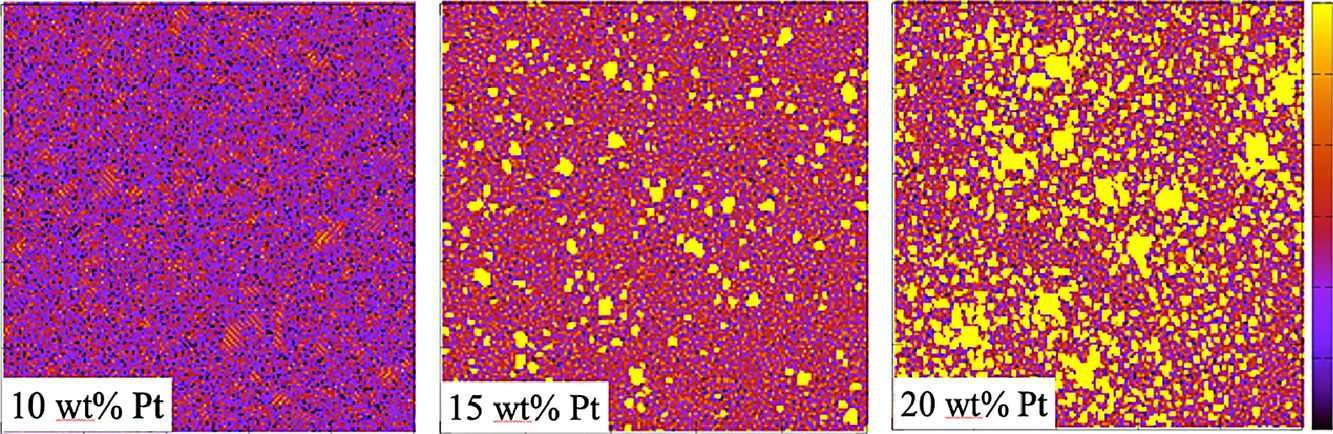
本文采用第一性原理相场(first-principle phase field, FPPF)方法研究了Pt浓度对Ti-Pt合金微观组织的影响,使我们能够从第一性原理研究微观组织的演变,而无需使用热力学经验参数。该方法首先结合密度泛函理论、包含原子空位的团簇膨胀理论和势重正化理论,构造了相场模拟所需的局部自由能。将这种FPPF方法应用于Ti1−xPtx合金在800℃薄膜上,我们证实随着Pt浓度增加为5、10、15和20 wt%, Ti-Pt合金的微观结构会发生剧烈变化,这与Song等人的实验观察结果一致(Materials 7 (2014) 3990)。当铂浓度小于10%时,组织呈片状或波状。当Pt浓度分别为15和20 wt%时,α-Ti相中出现片状或波状的点状Ti3Pt析出相。并且这些结果在二维和三维模拟中得到了证实。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117114
7. Enhanced oxidation resistance of (Mo95W5)85Ta10(TiZr)5 refractory multi-principal element alloy up to 1300°C
增强(Mo95W5)85Ta10(TiZr)5 耐火多元素合金在1300°C下的抗氧化性
Ranran Su, Hongliang Zhang, Gaoyuan Ouyang, Longfei Liu, Will Nachlas, Jun Cui, Duane D.Johnson, John H.Perepezko✉
John H.Perepezko: perepezk@engr.wisc.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117114
摘要
难熔金属基合金由于其在极高温下具有优异的机械强度,是目前镍基高温合金的潜在替代品。然而,高温工作环境中的严重氧化限制了它们的应用。为了解决这一难题,本文对一种新型难熔多主元素合金(RMPEA) (Mo95W5)85Ta10(TiZr)5采用了两步涂层工艺(包括Mo预涂层和Si-B包层胶结)。该涂层是由一个铝硼硅玻璃层在一个RMPEA-Si-B多层结构的顶部。该涂层有效地保护RMPEA在高温环境中免受氧化,这一点在不需要任何强制冷却系统的最新系统中得到了证明,该涂层在更高10-20%的温度下运行稳定。在 1300°C的等温曝晒后,涂层样品的重量变化遵循准线性动力学, 50小时后有4.2mg/cm2的轻微失重。在 1300°C 和室温之间的空气中进行热循环试验, 450次循环后总重量仅增加 2.6mg/cm2。该涂层与基体具有良好的粘附性,硼化物层作为屏障保持涂层的完整性。这种两步Mo-Si-B涂层方法适用于提供环境抗性范围广泛的RMPEA。

ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117057
8. Multimodal 3D characterization of voids in shock-loaded tantalum: Implications for ductile spallation mechanisms
冲击载荷钽中空隙的多模态三维表征: 对延展性剥落机制的影响
Toby Francis, Paul F.Rottmann, Andrew T.Polonsky, Marie-Agathe Charpagne, McLean P.Echlin✉, VeronicaAnghel, David R.Jones, George T.GrayIII, MarcDe Graef, Tresa M.Pollock.
McLean P.Echlin: mechlin@ucsb.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117057
摘要
预测结晶材料在高应变率下的失效需要了解基本的失效机制及其对微观结构的依赖性。在本研究中,对高纯度钽进行了板块冲击部分剥落前后的 3D-EBSD 表征实验,这允许对早期空洞周围的微观结构区域进行统计评估。在分析所得到的包含 5884 个晶粒和 467 个空洞的数据集时,观察到空洞大致是球形的,且大小一致。孔洞最可能分布在四重点、三重交界处、晶界和晶粒内部,其分布顺序依次递减。此外,空隙倾向于在具有高度塑性不相容性的晶粒边界形成,生长到塑性软的晶粒中,但方向主要与加载方向一致或垂直。从这些三维微观结构数据的分析中得到的统计数据支持了韧性剥落的动态空化模型。

ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117120
9. Evaluating the grain-scale deformation behavior of a single-phase FCC high entropy alloy using synchrotron high energy diffraction microscopy
利用同步辐射高能衍射显微镜评估单相 FCC高熵合金的晶粒尺度变形行为
J.V.Gordon✉, R.E.Lim, M.J.Wilkin, D.C.Pagan. R.A.Lebensohn, A.D.Rollett
J.V.Gordon: jerardvg@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117120
摘要
虽然高熵合金(HEA)的变形行为在宏观上得到了广泛的研究,但这些合金的许多重要特性在微观上还没有被探索出来,因此阻碍了对损伤和失效过程的准确预测。本文采用同步辐射高能衍射显微镜(HEDM)和基于快速傅里叶变换的晶体塑性建模,研究了单相FCC HEA 内约1900个组成晶粒在1%外加应变下的三维(3D)晶粒解析微观力学响应。晶粒分辨弹性应变、晶格重定向和最大分辨剪应力(mRSS)的演化被评估以量化弹性、屈服和完全塑性行为。总体而言,发现通过原位 HEDM 和相应建模确定的初始临界分辨剪切应力 (CRSS) 比使用经典多晶泰勒因子 (M = 3.06) 估计的高出了 20%。然而一个基于平均晶粒溶解泰勒因子(M¯)的描述性参数被发现与在 HEDM 数据集中观察到的塑性屈服行为有很好的一致性。与 EVP-FFT 模拟和 FCC 多晶体的经典预测相比, HEDM的晶格重定向被发现有明显的偏差,突出了在晶粒尺度上将局部晶格重定向、Taylor和Schmid因子与这种材料的塑性反应联系起来的复杂性。因此,预计本研究中三维晶粒溶解特性的总体趋势和参数识别可以作为继续对成熟的和新开发的 Cantor like HEAs 进行中间尺度研究的重要基础。

ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117118
10. Machine learning assisted composition effective design for precipitation strengthened copper alloys
机器学习辅助下的沉淀强化铜合金成分有效设计
Hongtao Zhang, Huadong Fu✉, Shuaicheng Zhu, Wei Yong, Jianxin Xie
Huadong Fu: hdfu@ustb.edu.cn, 北京科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117118
摘要
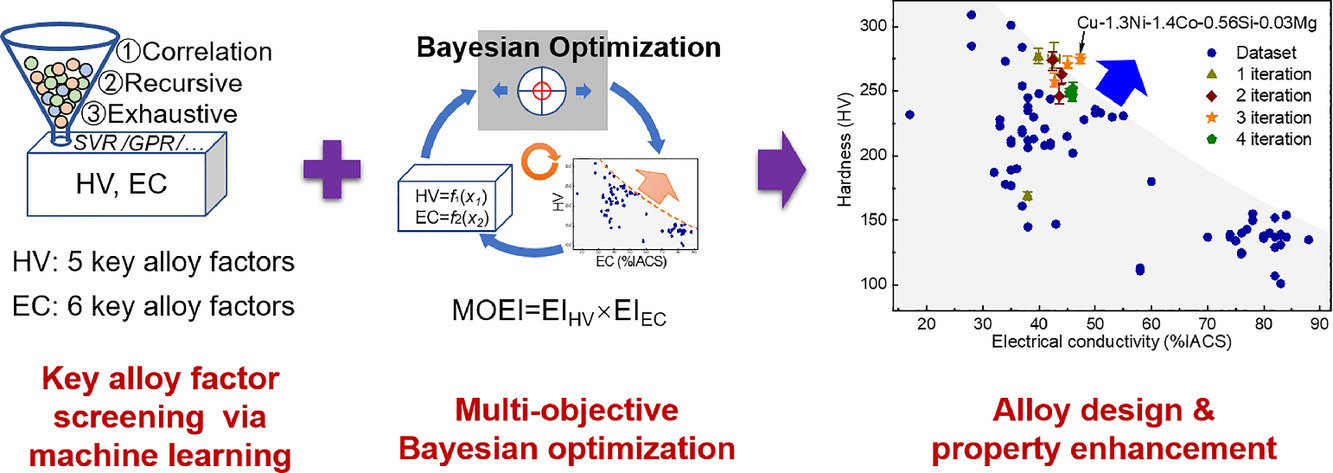
通过传统的试错方法一直难以优化多种复杂合金的成分并改善其相互冲突的力学和电学性能。本文提出了一种机器学习策略,通过相关性筛选、递归消除和详尽筛选关键合金因素,然后通过贝叶斯优化迭代设计成分,从而设计出具有良好性能的合金。以沉淀强化铜合金为例,通过筛选合金因素得到了影响硬度(HV)的 5 种关键合金因素和影响电导率(EC)的6种关键合金因素。分别建立了误差小于7% 的“HV-关键合金因素模型”和误差小于 9%的“EC- 关键合金因素模型”。然后利用贝叶斯优化和迭代优化实验对新型铜合金进行有效设计。设计的Cu-1.3Ni-1.4Co-0.56Si-0.03Mg合金具有良好的综合力学性能和电学性能,实测的极限抗拉强度(UTS)为858 MPa, EC为47.6%IACS。而且,其性能结果优于文献报道的沉淀强化铜合金,实现了同时改善相互矛盾的力学和电学性能。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117131
11. Phase transformation pathways in Ti-6Al-4V manufactured via electron beam powder bed fusion
电子束粉末床熔合的Ti-6Al-4V合金的相变途径
William J.Davids, Hansheng Chen, Keita Nomoto, Hao Wang, Sudarsanam Babu, Sophie Primig, Xiaozhou Liao, Andrew Breen✉, Simon P.Ringer✉,
Andrew Breen: andrew.breen@sydney.edu.au
Simon P.Ringer: simon.ringer@sydney.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117131
摘要
设计具有定制机械性能的增材制造金属合金需要详细了解整个印刷过程中的微观组织演变。在 Ti-6Al-4V 中,这涉及到复杂的相变组合,导致在单一的制造过程中出现微观组织和性能变化。这种性质变化的起源和在循环加热和冷却过程中发生的相变顺序仍然不确定。本文通过跟踪β相生长如何在构建中变化来研究相变途径。使用电子显微镜和原子探针断层扫描技术分析通过电子束粉末床融合制造的样品。证明了在一个给定的构建平面内发生了显著的 β 相分数的变化。研究发现,高温 β 相可以分为两类,取决于它是在 β 相变温度以上的冷却过程中保留下来的,还是在这个温度以下成核的。这是第一个直接证明在 T i-6Al-4V 中两种类型的 β 转化产物共存的证据。增材制造过程的突然循环性质促进了这种不寻常的转化序列。在这些观察的基础上,该论文对相变途径进行了完整的、一般性的描述,且讨论了与化学变化和氧气吸收有关的相变途径对硬度的影响。

ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117127
12. Lattice transformation in grain boundary migration via shear coupling and transition to sliding in face-centered-cubic copper
面心立方铜中通过剪切耦合的晶界迁移中的晶格转变和向滑动的过渡
Bin Li✉, Jane lLeung
Bin Li: binl@unr.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117127
摘要
通过剪切耦合的对称倾斜晶界(GBs)的迁移已经在实验和模拟中得到了广泛的研究。据报道,剪切耦合在高温下转变为 GB 滑移,但这种转变在低温下如何发生还没有被研究过。而且在剪切耦合过程中原子尺度上的晶格转变还没有被充分理解。在本文中,通过跟踪原子模拟中相应平面的位置,仔细研究了100K时面心立方铜中具有 [001] 倾斜轴的对称倾斜 GB 在平行于边界平面的剪切应变下的运动模式,并观察到 GB 运动的新特征。结果表明,两个低指数平面(110)和 (100)与边界平面之间的角度可以用来定义名义剪切强度。近似地的结果表明,如果这两个平面之一的 s 值 <0.5 ,则发生剪切耦合,该平面为活动不变平面;如果 0.5 < s< 0.6 ,则 GB 通过剪切耦合+滑移,即剪切耦合过渡到滑移的混合模式;如果两个平面的值都是 s> 0.6 ,则只发生 GB 滑移。仔细的结构分析表明,对于所有发生剪切耦合的GB,部分GB原子平面保持不变,非常类似于变形孪生中的第一个不变平面,而其他GB原子平面则通过高度协调和复杂的原子置换来交换它们在GB法线方向的位置。这种行为允许识别被重新定向到相邻晶粒的转化单元。确定了晶格转变的速率限制因子,并可用于推导剪切耦合的动力学模型。

ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117075
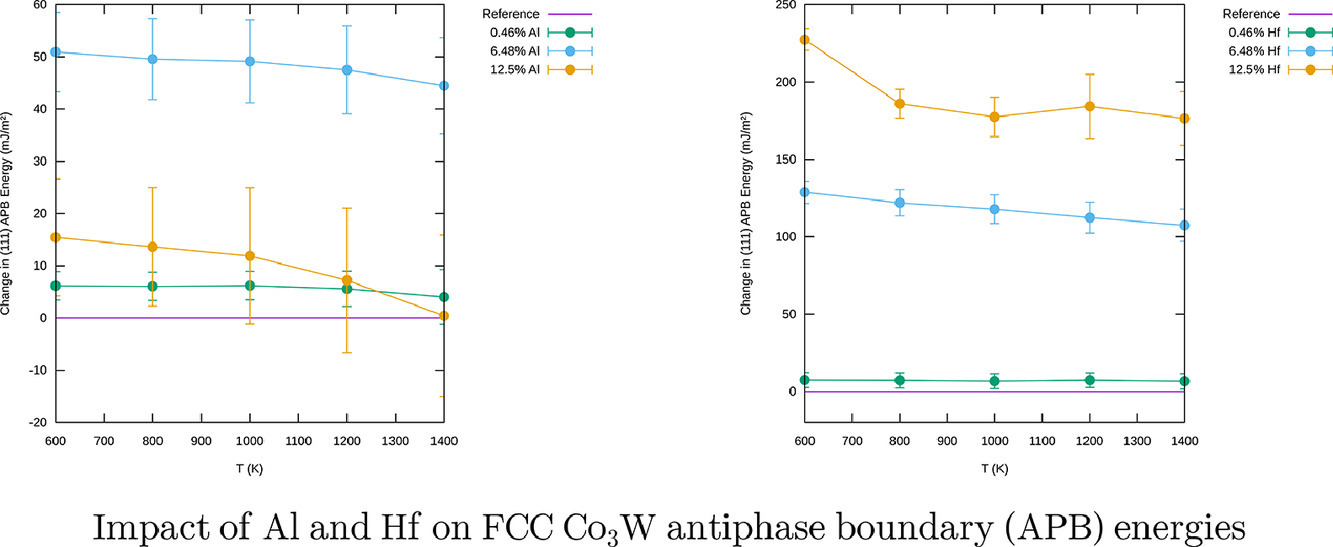
13. First-principles study of the effect of Al and Hf impurities on Co3W antiphase boundary energies
Al和Hf杂质对Co3W反相边界能量影响的第一性原理研究
Chiraag Nataraj✉, Ruoshi Sun✉, Christopher Woodward✉, Axelvan de Walle✉
Chiraag Nataraj: chiraag_nataraj@brown.edu
Ruoshi Sun: rs7wz@virginia.edu
Christopher Woodward: christopher.woodward@us.af.mil
Axelvan de Walle: avdw@brown.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117075
摘要
本文通过第一性原理计算了Al和 Hf 杂质对可转移的 FCC Co3W 的 (111) 反相边界 (APB) 能量的影响。在相关温度下通过蒙特卡洛模拟用团簇展开法来预测含有非稀释浓度的杂质的超单元的总能量,给出了每个三元体系的 APB 能量与杂质浓度和温度的关系。通过与纯 L12 Co3W超单元的直接能量计算相比较,验证了团簇展开的有效性,并比较了每种杂质的影响。进一步对每个系统常数比(Co和W之间的常数比)和牺牲W (Co常量)的两组组成进行了探索。结果表明,在两种体系中,牺牲W组分比常数比组分(考虑到FCC晶格的限制)更能稳定L12结构,因此应该选择牺牲W组分。在牺牲 W 的成分中, Hf 增加的 APB 能量远远大于Al ,特别是在杂质浓度较高的情况下,这两个体系在温度方面的变化很小。进一步结果表明,在较高的 Hf 浓度下,尤其是Co3(W0.5Hf0.5),Hf 和 W 倾向于分离成交替的平面,这与相应的 Co3(W0.5Al0.5) 不同,这也解释了这两种杂质对 APB 能量的不同影响。最后,本文研究了牺牲W组分的(111)与(100)APB能量的比值,以了解这两种三元体系的交叉滑移行为。