金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.216,1 Sep. 2021
2021-12-18 来源:GS-Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文18篇,涵盖了高温合金、不锈钢、高熵合金等,国内科研单位包括香港城市大学、东北大学、北京理工大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 216 目录
1. Grain size dependent microstructure and texture evolution during dynamic deformation of nanocrystalline face-centered cubic materials
纳米晶面心立方材料动态变形过程中与晶粒尺寸有关的微观组织和织构演变
2. In-situ and ex-situ microstructure studies and dislocation-based modelling for primary creep regeneration response of 316H stainless steel
316H不锈钢初期蠕变再生响应的原位和非原位微观组织研究及基于位错的模型设计
3. Understanding the role of local texture variation on slip activity in a two-phase titanium alloy
了解局部纹理变化对两相钛合金中滑移活动的作用
4. How grain boundary characteristics influence plasticity close to and above the critical temperature of ultra-fine grained bcc Ta2.5W
晶界特性如何在接近或高于临界温度时影响超细晶bcc Ta2.5W的塑性
5. Stability and stoichiometry of L12 Al3(Sc,Zr) dispersoids in Al-(Si)-Sc-Zr alloys
Al-(Si)-Sc-Zr合金中L12 Al3 (Sc,Zr)分散体的稳定性和化学计量学研究
6. In-situ TEM irradiation creep experiment revealing radiation induced dislocation glide in pure copper
原位透射电镜辐照蠕变实验揭示了辐射诱导的纯铜位错滑移
7. Complexions and grain growth retardation: First-principles modeling of phase boundaries in WC-Co cemented carbides at elevated temperatures
配位和晶粒生长迟缓:高温下WC-Co硬质合金相界的第一性原理建模
8. Understanding chemical short-range ordering/demixing coupled with lattice distortion in solid solution high entropy alloys
了解固溶高熵合金中的化学短程有序/分层与晶格畸变的关系
9. Enhancing co-deformation ability of nanograined Ni-W layers in the Ni/Ni-W laminated composites
增强 Ni/Ni-W层压复合材料中纳米晶粒Ni-W层的共变形能力
10. Theory of twin strengthening in fcc high entropy alloys
fcc高熵合金中的孪晶强化理论
11. Element-resolved local lattice distortion in complex concentrated alloys: An observable signature of electronic effects
复杂浓缩合金中元素分辨的局部晶格畸变:电子效应的可观察特征
12. Nickel-based superalloy single crystals fabricated via electron beam melting
电子束熔化法制备单晶镍基高温合金
13. Precipitation and micromechanical behavior of the coherent ordered nanoprecipitation strengthened Al-Cr-Fe-Ni-V high entropy alloy
共格有序纳米析出相强化Al-Cr-Fe-Ni-V高熵合金的析出和微观力学行为
14. Under-stoichiometric cementite in decomposing binary Fe-C pearlite exposed to rolling contact fatigue
在滚动接触疲劳下分解二元Fe-C珠光体的低化学计量渗碳体
15. A half-shear-half-shuffle mechanism and the single-layer twinning dislocation for {11-22}<11-2-3> mode in hexagonal close-packed titanium
六方紧密堆积钛中{11-22} <11-2-3>模式下的半剪切-半侧滑机制和单层孪晶位错
16. Non-thermal melting of tungsten under intense electronic excitations
钨在强电子激发下的非热熔化
17. The role of nitrogen in the oxidation behaviour of a Ti6242S alloy: a nanoscale investigation by atom probe tomography
氮在Ti6242S合金氧化行为中的作用:通过原子探针断层扫描进行的纳米级研究
18. Towards superior high temperature properties in low density ferritic AlCrFeNiTi compositionally complex alloys
在低密度铁素体 AlCrFeNiTi 成分复杂合金中实现优异的高温性能
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117088
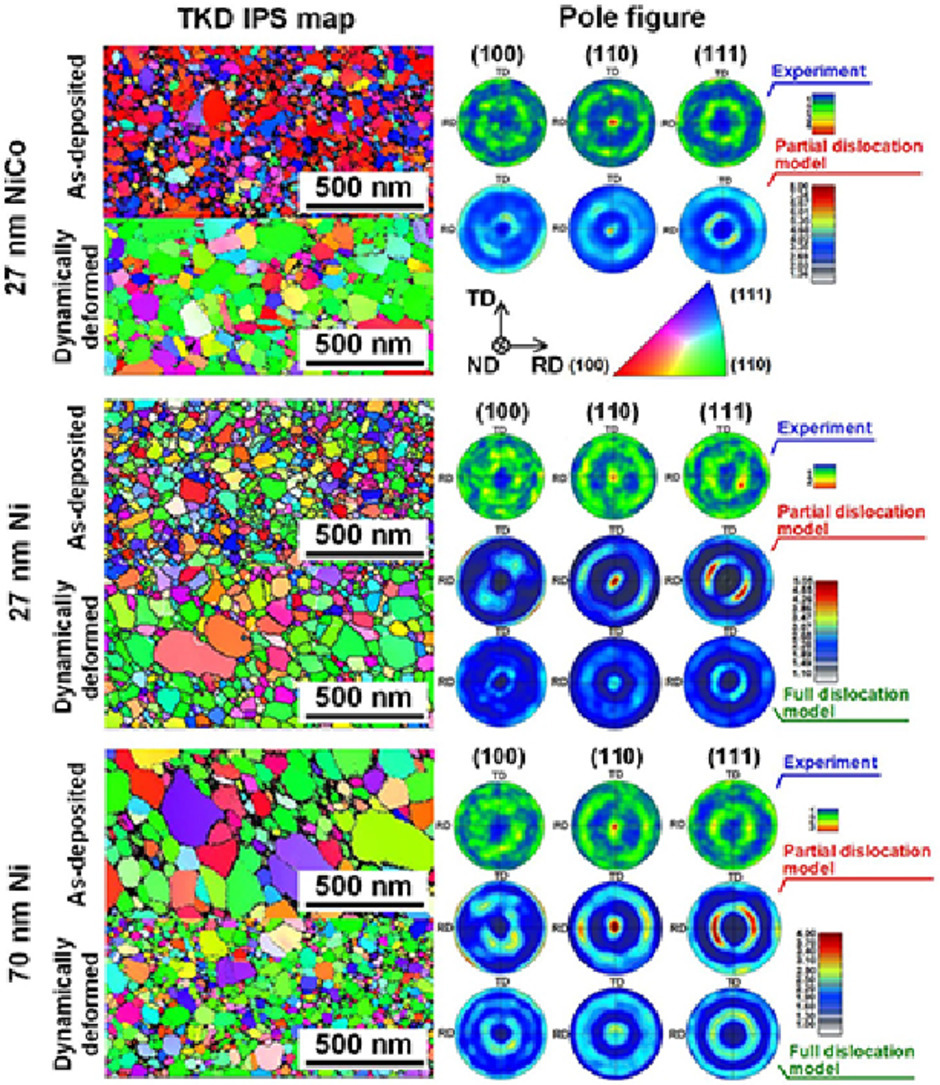
1. Grain size dependent microstructure and texture evolution during dynamic deformation of nanocrystalline face-centered cubic materials
纳米晶面心立方材料动态变形过程中与晶粒尺寸有关的微观组织和织构演变
Heng Li, Tianju Chen, Weilin Li, Hualei Zhang, Shuang Han✉, Caizhi Zhou✉, Zibin Chen✉, Emmanuel A.Flores-Johnson, Luming Shen, Jianshe Lian, Irene J.Beyerlein, Xiaozhou Liao
Shuang Han: shuanghan@jlu.edu.cn, 吉林大学
Caizhi Zhou: caizhi@mailbox.sc.edu
Zibin Chen: z.chen@sydney.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117088
摘要
本文研究了纳米晶体(nc)面心立方材料在高应变速率压缩下的微观组织和织构的演变。采用霍普金森扭杆技术,在高应变速率(8000-23000 s-1)下对晶粒尺寸或层错能不同的三种纳米晶材料进行实验,包括27nm的Ni、70 nm的Ni和27nm的NiCo。采用透射菊池衍射技术和离散晶体塑性有限元(D-CPFE)模拟来评估组织演变。实验结果表明,在初始晶粒尺寸较小和较大的样品中,晶粒分别发生长大和细化,而所有变形材料均演变为(110)织构。在没有拟合参数的情况下,基于晶粒尺寸的数控变形的D-CPFE模拟表明,局部位错滑移比全位错滑移引起的织构演化更快。实验和模拟结果之间的比较表明,在27 nm和70 nm的Ni样品中,(110) 织构主要由完全位错滑移和部分位错滑移联合产生,而在 NiCo 合金中仅由部分位错滑移产生。形变孪晶对观察到的织构演化几乎没有影响。晶界介导的变形有利于晶粒粗化,而部分位错活动有助于促进纳米晶粒的动态稳定和进一步细化。动态变形过程中组织和织构的高度耦合演化受晶粒尺寸和应变速率效应的协同控制。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117130
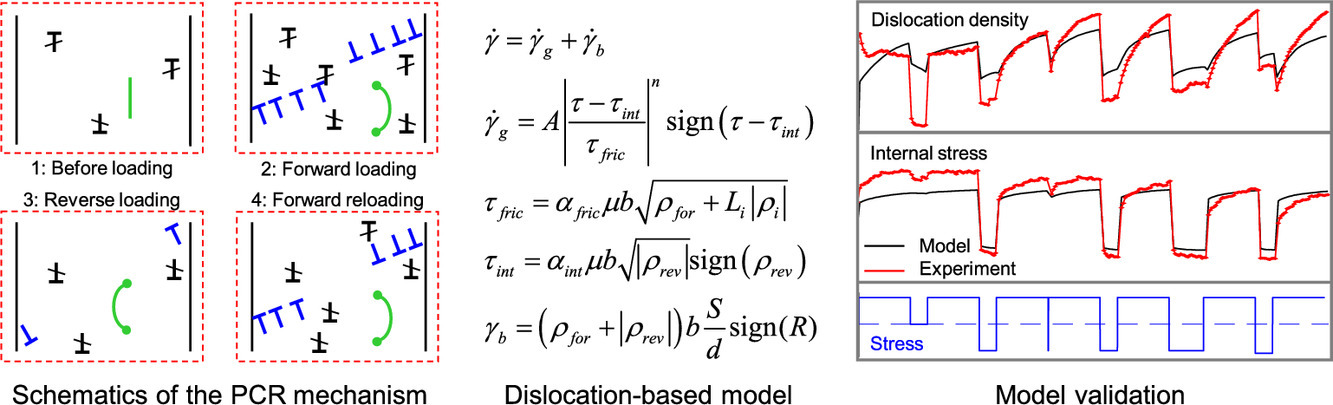
2. In-situ and ex-situ microstructure studies and dislocation-based modelling for primary creep regeneration response of 316H stainless steel
316H不锈钢初期蠕变再生响应的原位和非原位微观组织研究及基于位错的模型设计
X. Li, S.R. Holdsworth, S. Kalácska, L. Balogh, J.-S. Park, Y. Arroyo Rojas Dasilva, X. Maeder, A. Cocks, E. Mazza, E. Hosseinia✉
E. Hosseinia: ehsan.hosseini@empa.ch
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117130
摘要
可再生能源的出现具有可变性和不可预测性,除了工作日与周末的能源需求的变化,还要求火电厂需要灵活运行。因此,这一特性将电厂高温部件的典型稳态蠕变载荷转变为应力变化或循环蠕变状态。已经发现,引入的瞬态载荷会影响蠕变合金的应变硬化记忆,并可能导致多次蠕变再生(PCR)。因此,在这种条件下,蠕变应变积累会大大增加。传统蠕变本构模型基于应变或时效硬化假设,对PCR现象的考虑超出了其能力范围。本文对316H不锈钢进行了原位和非原位实验。各种显微组织检测技术,如同步辐射高能x射线和中子衍射,以及背散射和透射电子显微镜,用于表征合金在应力变化和循环蠕变条件下位错组织的演变和内部晶格应变/应力状态的演变。位错堆积的形成/湮灭和位错线的弯曲/不弯曲被认为是PCR的主要机制。本文也建立了一个基于位错的模型,该模型能够很好地描述钢在650℃下进行的实验中测量到的微观组织演变和力学响应。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117111
3. Understanding the role of local texture variation on slip activity in a two-phase titanium alloy
了解局部纹理变化对两相钛合金中滑移活动的作用
D. Lunt, R. Thomas, M.D. Atkinson, A. Smith, R. Sandala, J. Quinta da Fonseca, M. Preuss
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117111
摘要
在具有hcp 晶体结构的工程合金的塑性变形过程中,可以激活具有不同临界解析剪切应力的滑移系统。在Ti-6Al-4V等两相钛合金的情况下,已经确定各种 和
和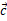 +
+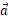 类型的滑移系统可以在α相中被激活,而α相在这种合金中占主导地位。然而,在比较具有相似的临界解析剪切应力值的棱形
类型的滑移系统可以在α相中被激活,而α相在这种合金中占主导地位。然而,在比较具有相似的临界解析剪切应力值的棱形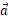 和基底
和基底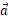 滑移时,它们的相对可能性却没有得到很好的证实。通过结合基于EBSD的晶粒取向映射和高分辨率数字图像,在两种不同的显微织构的Ti-6Al-4V样品的小水平塑性后,进行了晶粒特定的剪切应变映射和Burgers矢量方向分析。这使得不同类型的应变异质性和应变模式能够与潜在的微观组织和微观织构联系起来。详细的分析表明,特定的
滑移时,它们的相对可能性却没有得到很好的证实。通过结合基于EBSD的晶粒取向映射和高分辨率数字图像,在两种不同的显微织构的Ti-6Al-4V样品的小水平塑性后,进行了晶粒特定的剪切应变映射和Burgers矢量方向分析。这使得不同类型的应变异质性和应变模式能够与潜在的微观组织和微观织构联系起来。详细的分析表明,特定的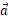 型滑移模式的主导地位随着局部织构的变化而大不相同,当软宏观区(类似取向的晶粒簇)存在时,剪切应变模式延伸到许多晶粒。本文强调,相对位移比分析通过减少模糊解的情况,显著改善了hcp晶体的滑移轨迹分析,而且晶粒邻域对滑移系统激活的影响比Schmid因子更大。
型滑移模式的主导地位随着局部织构的变化而大不相同,当软宏观区(类似取向的晶粒簇)存在时,剪切应变模式延伸到许多晶粒。本文强调,相对位移比分析通过减少模糊解的情况,显著改善了hcp晶体的滑移轨迹分析,而且晶粒邻域对滑移系统激活的影响比Schmid因子更大。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117110
4. How grain boundary characteristics influence plasticity close to and above the critical temperature of ultra-fine grained bcc Ta2.5W
晶界特性如何在接近或高于临界温度时影响超细晶bcc Ta2.5W的塑性
J. Kappacher✉, O. Renk, D. Kiener, H. Clemens, V. Maier-Kiener
J. Kappacher: johann.kappacher@unileoben.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117110
摘要
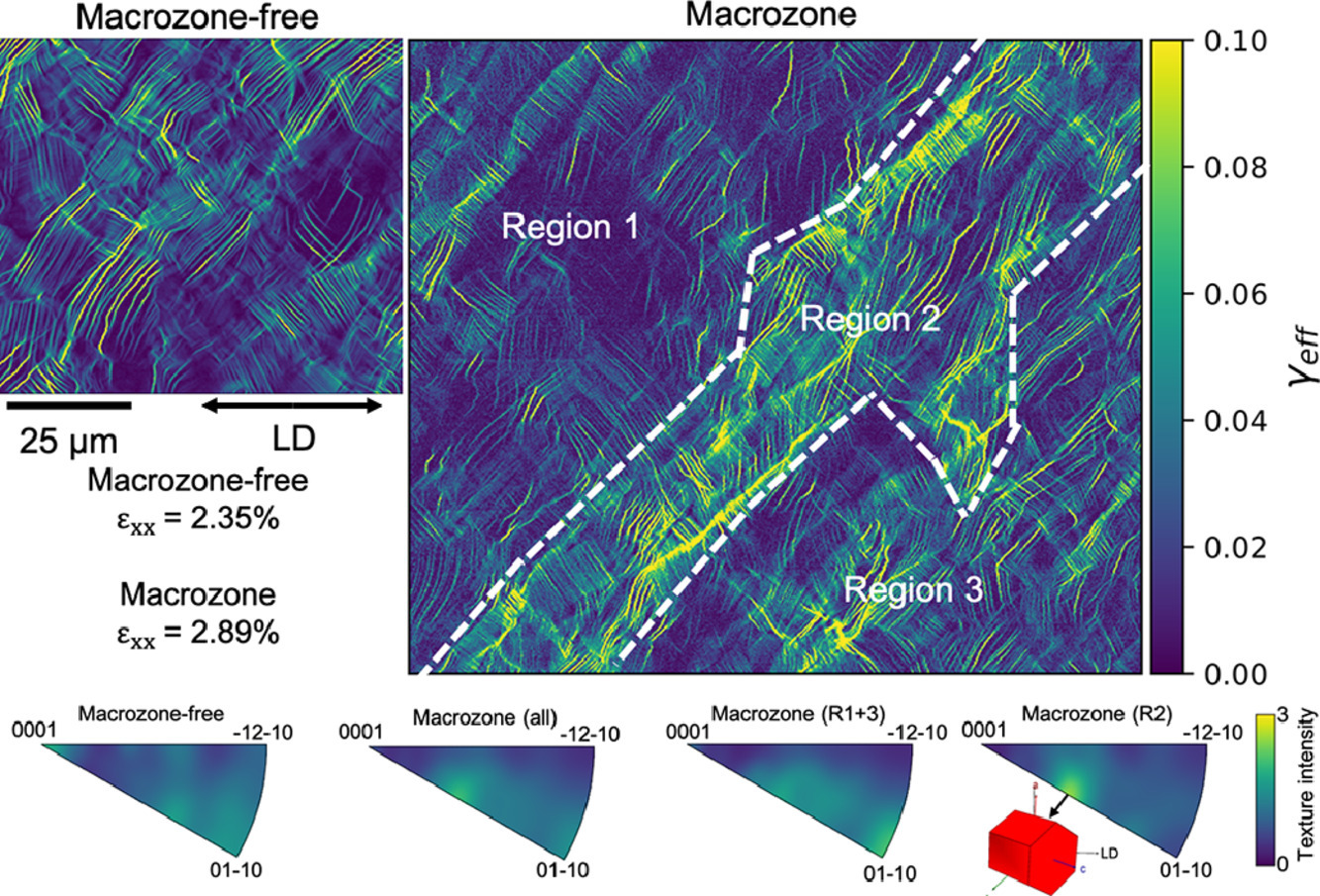
位错-晶界相互作用被广泛认为是超细晶粒 bcc 金属在临界温度以上高温变形阶段中的速率控制过程。然而,不同类型的晶界的影响至今仍未被广泛研究。为此,本文对Ta2.5W 试样进行了先进的高温纳米压痕研究,该试样包括两种截然不同的晶界类型,但具有相似的亚微米平均间距。其中一组样品主要由高角度边界组成,而第二组样品则主要包含低角度边界。完全再结晶的样品作为粗粒度的参考批次。在高达823K的高温下使用先进的纳米压痕技术进行实验,我们发现低角度晶界样品的硬度随温度变化保持不变,而高角度晶界样品的硬度具有很强的温度依赖性。这强调了晶界扩散系数对于界面应力松弛过程的重要性。从473K 到773K中,粗晶组织中观察到了位错与氧杂质原子的明显相互作用,并且直到573K都产生了锯齿状流动,这是Portevin-Le Chatelier 效应的指标。两种晶界类型对位错-杂质相互作用均有显著影响,因此高角度晶界抑制了离散流动特性。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117117
5. Stability and stoichiometry of L12 Al3(Sc,Zr) dispersoids in Al-(Si)-Sc-Zr alloys
Al-(Si)-Sc-Zr合金中L12 Al3 (Sc,Zr)分散体的稳定性和化学计量学研究
T. Dorin✉, S. Babaniaris, L.Jiang, A. Cassel, C.P. Race, A. Eggeman, D.J. Kelly, S.J. Haigh, J.D. Robson
T. Dorin: thomas.dorin@deakin.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117117
摘要
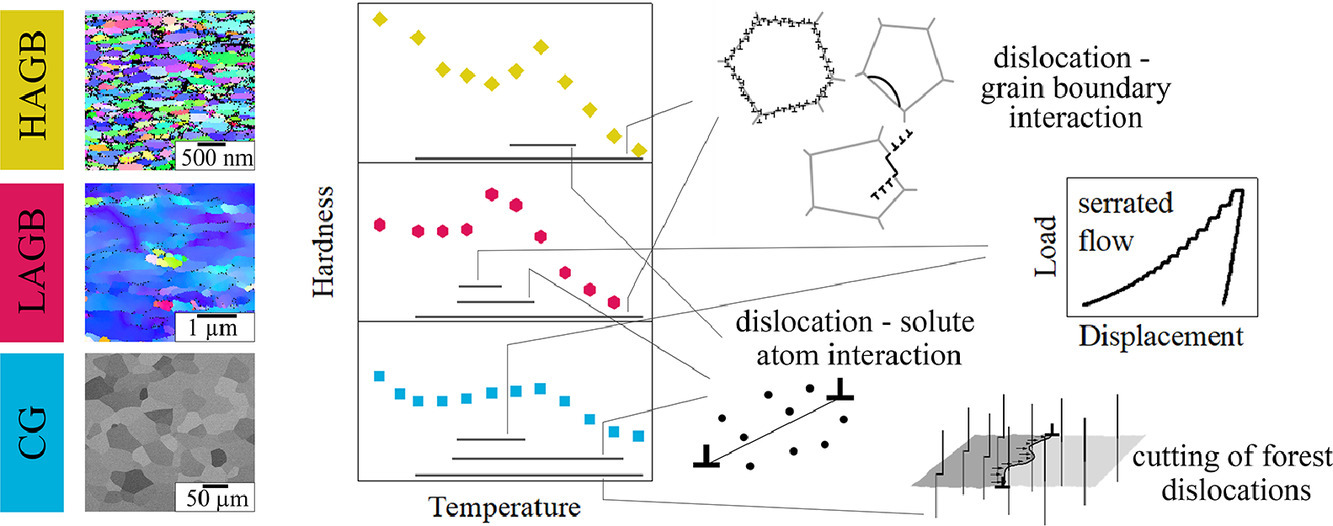
本文研究了添加0.5wt.%的Si对贫Al-Sc-Zr合金中Al3(Sc,Zr) L12 析出相形成的影响。在有Si存在的情况下,在300℃ 和375℃时效时,析出动力学明显加快。在375℃时,硬度的峰值在几分钟内出现,并在375℃时保持长达200小时。高分辨率的TEM 显示了尺寸约为5nm的非常精细的核壳L12 分散体的存在,在375℃下保持稳定达200小时。使用高分辨率的能量色散X 射线光谱(EDX)和原子探针断层扫描(APT),在弥散体的核心部分检测到Si 和Fe 的存在,它们的含量随着时效时间的增加而减少。无论整体Si的含量如何,在两种合金的弥散体中都观察到了类似的Si和Fe的成分。在L12 结构中,Si 和Fe 都被发现对Al 位点有偏好,这也得到了密度函数理论(DFT)计算结果的验证。DFT计算还发现了Si 和Fe 随着时间的推移而减少的情况,表明在L12 结构中没有使Si 或Fe 存在的热力学驱动力。相反,Si 和Fe 被发现在聚集的早期阶段起着关键作用,但当它们稳定在L12结构中时,会从颗粒中排出去。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117096
6. In-situ TEM irradiation creep experiment revealing radiation induced dislocation glide in pure copper
原位透射电镜辐照蠕变实验揭示了辐射诱导的纯铜位错滑移
Nargisse Khiara, Fabien Onimus✉, Stéphanie Jublot-Leclerc, Thomas Jourdan, Thomas Pardoen, Jean-Pierre Raskin, Yves Bréchet
Fabien Onimus: fabien.onimus@cea.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117096
摘要
本文在纯铜上进行了原位TEM 应变实验,研究重离子辐照和高外加应力水平下的位错活动。在应力水平略低于无辐照情况下的位错滑行的临界应力的情况下,在辐照下观察到位错从辐照缺陷中解脱出来后滑行。这一现象首次在铜中被发现,并且使用数字图像处理进行了统计分析。然后对钉扎寿命进行了定量分析,表明级联相关机制可以解释辐射引起的位错滑行。本文也为研究高应力水平下辐照蠕变的提供了新的思路。

ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117128
7. Complexions and grain growth retardation: First-principles modeling of phase boundaries in WC-Co cemented carbides at elevated temperatures
配位和晶粒生长迟缓:高温下WC-Co硬质合金相界的第一性原理建模
Erik Fransson✉, Martin Gren✉, Göran Wahnström✉
Erik Fransson: erikfr@chalmers.se
Martin Gren: martin.gren@chalmers.se
Göran Wahnström: goran.wahnstrom@chalmers.se
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117128
摘要
WC-Co硬质合金结合了超强的硬度和高韧性,使其成为金属加工和耐磨工具的理想材料。在烧结过程中,控制 WC 晶粒尺寸是很重要的,因为晶粒尺寸对材料的力学性能起着关键作用。实验研究已经观察到富W和富C的材料有不同的生长速度和晶粒形态,但这背后的机制尚未阐明。在本文中,我们考虑了在硬质合金的 WC/Co 相界上存在界面稳定状态的可能性,即具有立方结构的WC薄膜。使用从头计算和第一原理建模得出了界面相图。采用聚类扩展法对碳空位进行建模,采用Monte Carlo模拟法对构型熵进行模拟。力常数拟合被用来提取基态结构的谐波自由能,非谐波和电子激发的影响被有效地纳入关于WC体相的配套研究中。本文进一步预测,在液相烧结温度下,薄的立方WC薄膜会稳定下来,但只有在富含W的条件下。这与实验结果一致,在富含W的材料中主要观察到具有立方体堆积的薄膜。并且利用这一知识对观察到的富含W和富含C的硬质合金的不同生长速度和晶粒形态提出了一个解释。
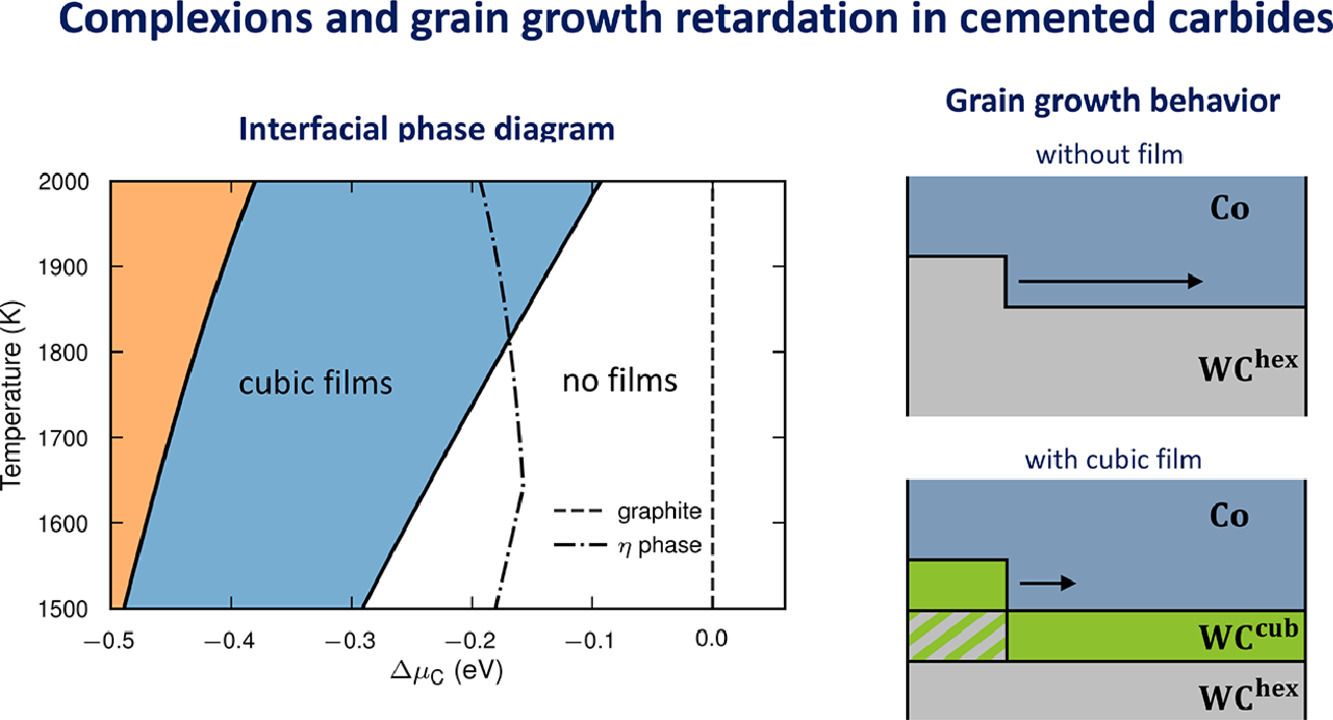
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117140
8. Understanding chemical short-range ordering/demixing coupled with lattice distortion in solid solution high entropy alloys
了解固溶高熵合金中的化学短程有序/分层与晶格畸变的关系
Q.F. He✉, P.H. Tang, H.A. Chen, S. Lan, J.G. Wang, J.H. Luan, M. Du, Y. Liu, C.T. Liu, C.W. Pao✉, Y. Yang✉
Q.F. He: quanfenhe2-c@my.cityu.edu.hk, 香港城市大学
C.W. Pao: cwpao@gate.sinica.edu.tw, 中央研究院
Y. Yang: yonyang@cityu.edu.hk, 香港城市大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117140
摘要
固溶体高熵合金(HEA)中的化学短程有序(CSRO)或分层是一个尚未完全理解的基本问题。在这项工作中,我们首先建立了一个广义的准化学固溶模型,该模型能够定量计算固溶体HEA中的局部化学有序或分层。之后,我们对CoCrFeNi模型合金进行了同步辐射衍射实验、广泛的反向Monte Carlo(RMC)模拟和第一性原理计算,以研究长时间热退火后局部化学环境的发展。综合研究的结果表明, CoCrFeNi中局部化学有序或分层的发展不仅受到不相容原子之间混合热的影响,而且还与局部晶格畸变相关。
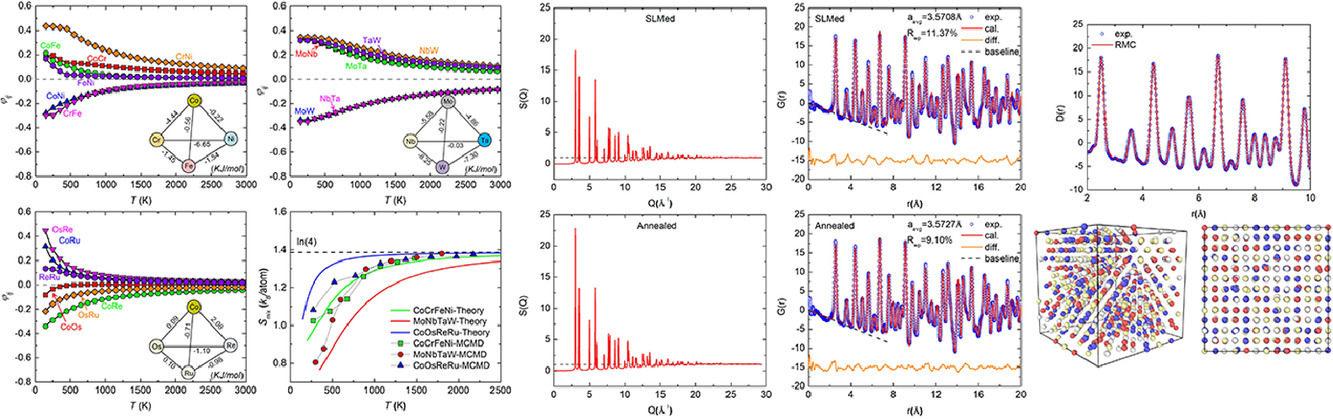
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117138
9. Enhancing co-deformation ability of nanograined Ni-W layers in the Ni/Ni-W laminated composites
增强 Ni/Ni-W层压复合材料中纳米晶粒Ni-W层的共变形能力
Fei Liang, Zhe-Xuan Wang, Yan-Wen Luo, Bin Zhang✉, Xue-Mei Luo, Guang-Ping Zhang✉
Bin Zhang: zhangb@atm.neu.edu.cn, 东北大学
Guang-Ping Zhang: gpzhang@imr.ac.cn, 中科院沈阳金属所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117138
摘要
本文系统地研究了不同Ni层与Ni-W层厚度比的Ni/Ni-W层状复合材料的拉伸性能和塑性变形行为。实验结果表明,与单层Ni相比,大厚度比的Ni/Ni-W层压复合材料的强度/韧性协同性得到了改善,这归因于随着Ni-W层厚度的降低,纳米晶粒Ni-W层的共变形能力得到了增强。原始层厚度小的Ni-W层在界面约束下通过稳定的晶界滑动实现了连续减薄。此外,随着Ni-W层厚度的降低,Ni-W层的断裂行为有一个明显的过渡,即从通道裂缝和微观剪切带并存转变为微观剪切带。有限元模拟结果表明Ni-W层厚度的减少导致复合材料对缺陷的敏感性降低,这与裂纹尖端的应力集中程度降低相对应。基于能量准则,评估了由 Ni-W层的长度尺度和流动应力控制的塑性变形图。这一发现可能为设计和开发用于高温微电子机械系统的高性能材料提供了一个潜在的策略。

ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117119
10. Theory of twin strengthening in fcc high entropy alloys
fcc高熵合金中的孪晶强化理论
R.E.Kubilay✉, W.A.Curtin
R.E.Kubilay: recep.kubilay@epfl.ch
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117119
摘要
fcc高熵合金(HEAs)中的孪晶已经被认为是一种可能的硬化机制,能够增强延展性。在本文中,我们建立了一个类似于最近的屈服应力理论的孪晶应力理论。具体来说,确定了在随机多组分合金中移动孪生位错的应力,即沿着预先存在的孪晶边界移动的fcc部分位错。然后引入了一个降低弹性理论,其中原子与孪晶位错压力场和孪晶边界相互作用。利用原子间势和弹性理论的结果,将该理论应用于NiCoCr。结果也被用来预测(i)留下滞后的堆垛层错的单个局部位错和(ii)参与孪晶成核的相邻部分位错运动的应力增加。预测所有参与fcc孪晶成核和生长的过程的强度都会增加。然后与室温下的单晶实验进行比较,表明孪晶是由孪晶成核控制的,并具有合理的定量一致性。当溶质/断层相互作用被忽略时,该理论显示孪晶和晶格流动应力是相关的。该理论还提供了其他稀溶质添加如何抑制孪晶的见解,正如实验发现的。
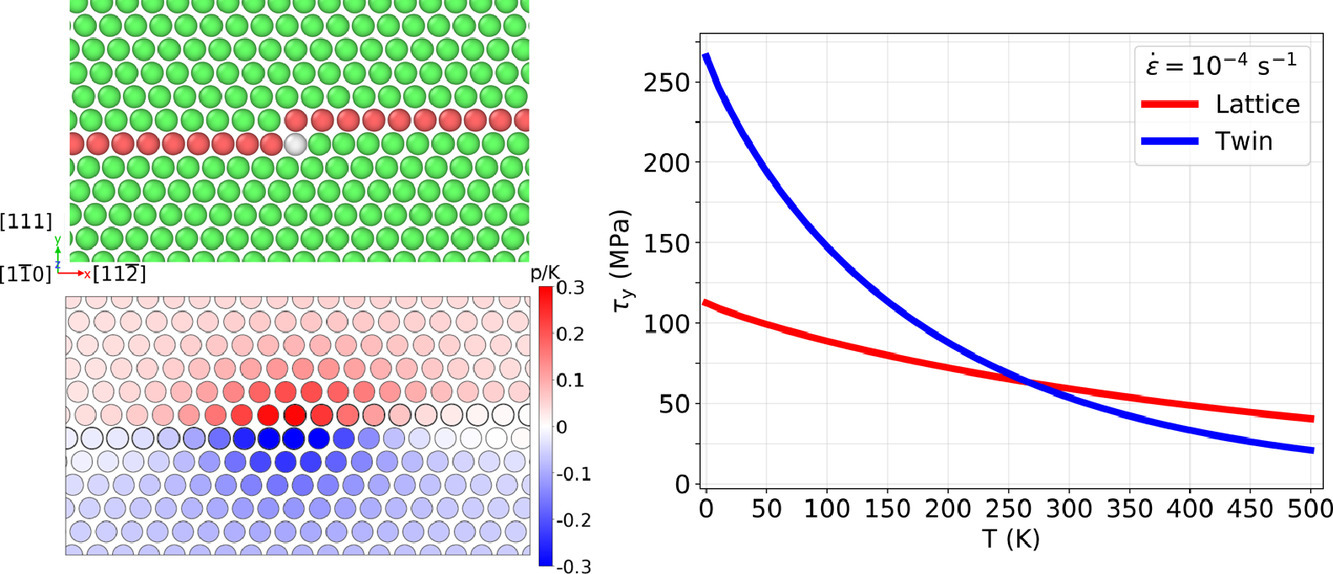
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117135
11. Element-resolved local lattice distortion in complex concentrated alloys: An observable signature of electronic effects
复杂浓缩合金中元素分辨的局部晶格畸变:电子效应的可观察特征
Hyun Seok Oh, Khorgolkhuu Odbadrakh, Yuji Ikeda, Sai Mu, Fritz Körmann, Cheng-Jun Sun, Heh Sang Ahn, Kook Noh Yoon, Duancheng Ma, Cemal Cem Tasan✉, Takeshi Egami✉, Eun SooPark✉
Cemal Cem Tasan: tasan@mit.edu
Takeshi Egami: egami@utk.edu
Eun SooPark: espark@snu.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117135
摘要
复杂浓缩合金(CCAs)由于其优异的力学性能,超过了传统合金的性能极限,因此越来越受到关注。虽然其优异的性能通常归因于严重的晶格畸变,但迄今为止尚不清楚是什么控制了晶格畸变以及它如何影响CCA的力学性能。在本文中,我们通过扩展的X射线吸收精细结构实验和密度泛函理论计算,研究了3d过渡金属元素(3d CCAs)中的元素分辨局部晶格畸变(ELLD)。研究表明ELLD主要取决于元素之间的电荷转移,并通过原子级压力和轨道跃迁影响其特性。ELLD为解释元素的特定特性和宏观特性提供了一个有效原子尺寸的定性测量。
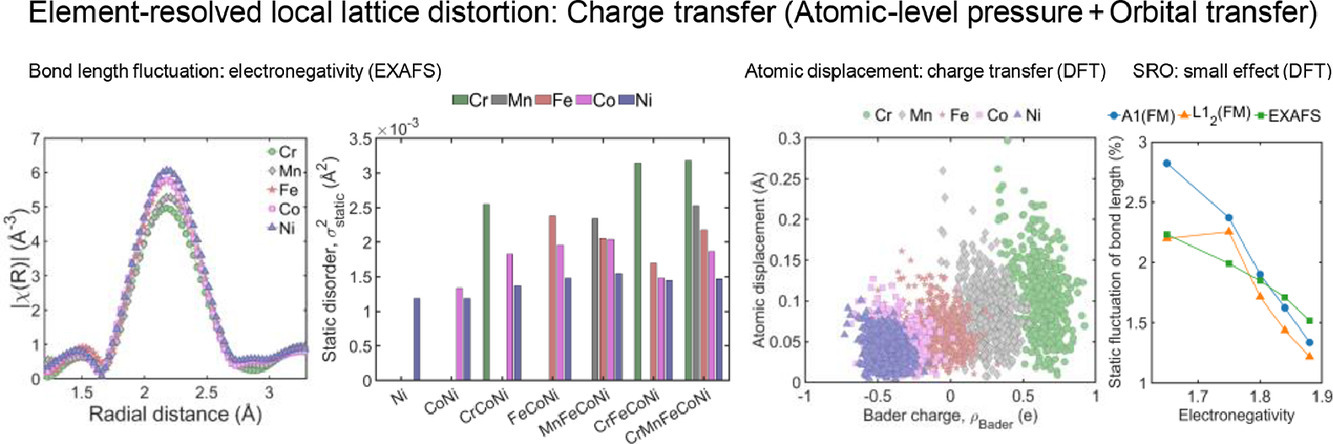
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117133
12. Nickel-based superalloy single crystals fabricated via electron beam melting
电子束熔化法制备单晶镍基高温合金
Patxi Fernandez-Zelaia✉, Michael M. Kirka✉, Andrés Márquez Rossy✉, Yousub Lee✉, Sebastien N.Dryepondt✉
Patxi Fernandez-Zelaia: fernandezzep@ornl.gov
Michael M. Kirka: kirkamm@ornl.gov
Andrés MárquezRossy: marquezae@ornl.gov
Yousub Lee: leey@ornl.gov
Sebastien N.Dryepondt: dryepondtsn@ornl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117133
摘要
增材制造技术已经成为潜在的颠覆性工艺,其可能的影响范围包括供应链物流、原型设计和新型材料合成。许多工作说明了熔融的工艺可以控制微观组织的能力,最近有一些研究人员甚至生产了单晶。然而,关于能够打印单晶的工艺窗口,仍有许多问题有待解决。此外,据观察,这些增材制造的单晶表现出平行于扫描方向的首选<011>二级取向。在本文中,我们研究了通过电子束熔化实现单晶打印的制造条件。利用空间填充实验设计来有效探索制造空间。使用市售的粉末和定制的熔体合金,成功地获得了单晶。通过这些探索性实验获得的微观组织表现出连续的柱状结构,范围从弱织构的多晶、近单晶到完全单晶材料。此外还进行了复杂的几何实验来研究晶粒选择机制。我们发现,晶粒选择机制与体积尺度的几何形状无关,并且因此必须由局部传热和凝固动力学驱动。此外,晶粒选择被证明是由相互竞争的驱动力所驱动的;一个是倾向于外延生长,另一个是由强加的加工条件所驱动的。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117121
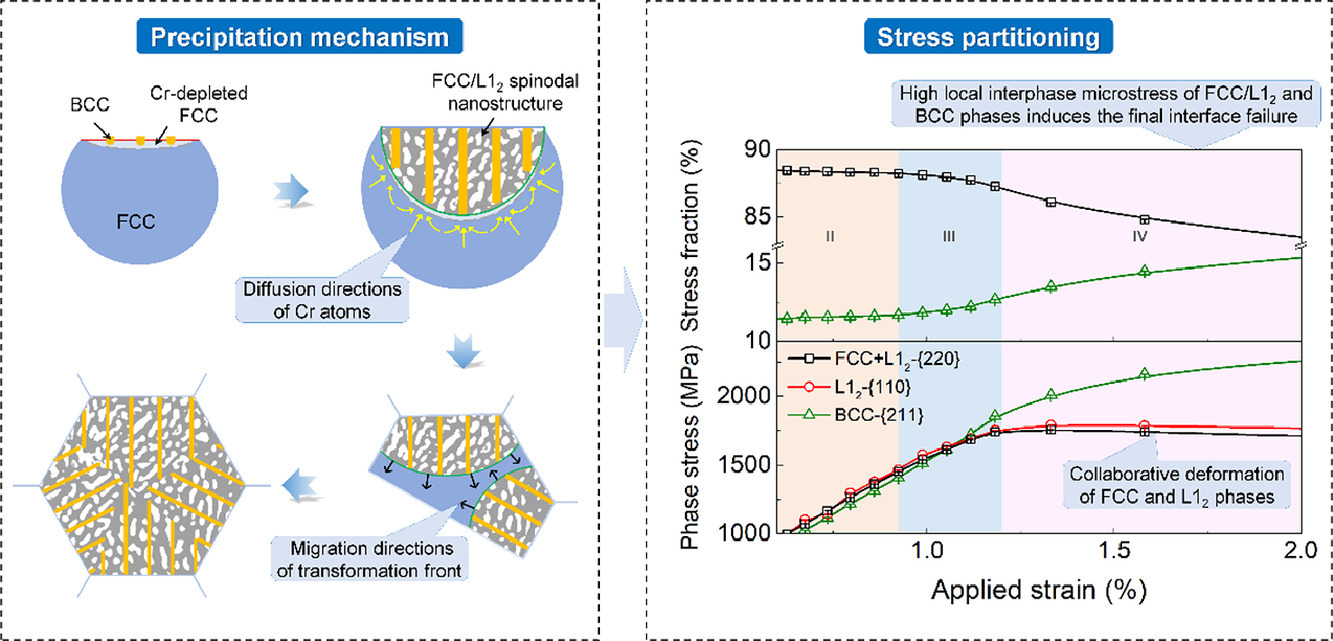
13. Precipitation and micromechanical behavior of the coherent ordered nanoprecipitation strengthened Al-Cr-Fe-Ni-V high entropy alloy
共格有序纳米析出相强化Al-Cr-Fe-Ni-V高熵合金的析出和微观力学行为
Linjing Wang, Liang Wang✉, Shangcheng Zhou, Qian Xiao, Yao Xiao, Xutao Wang, Tangqing Cao, Yang Ren, Yao-Jian Liang, Lu Wang, Yunfei Xue✉
Liang Wang: 7520190080@bit.edu.cn, 北京理工大学
Yunfei Xue: xueyunfei@bit.edu.cn, 北京理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117121
摘要
共格有序的纳米沉淀(CON)硬化是一种打破强度-韧性权衡的有效策略。揭示析出机制及其对力学性能的影响对于进一步优化CON强化合金具有重要意义。在本文中,我们研究了新开发的CON强化的Al0.5Cr0.9FeNi2.5V0.2高熵合金(HEA)中共格的 FCC/L12旋节线纳米结构和纳米层状BCC 相的析出和力学行为。我们发现由预变形引起的高密度缺陷促进了 Cr的偏析,导致了成分的重新分布。基体的热力学状态转变为旋节线状态,L12相的有序能增加,促进了共格的FCC/L12旋节线纳米结构的形成。同时,Cr的偏析促进了富含Cr的纳米薄片状BCC相的析出。在拉伸变形过程中,FCC相首先屈服,然后依次是 L12和 BCC 相。L12和BCC强化相促成了超高的宏观屈服强度。由于低失配互联的旋节线纳米结构, FCC和L12相之间的相应力差异不大,这可以避免应力集中并保持延展性。刚性BCC相的纳米片状特征延迟了裂纹的萌生和扩展。本研究不仅揭示了预变形对CONs形成和细化的重要影响,而且还揭示了CONs的变形机制,这为CON强化合金的显微组织优化和力学性能改进提供了新的思路。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117144
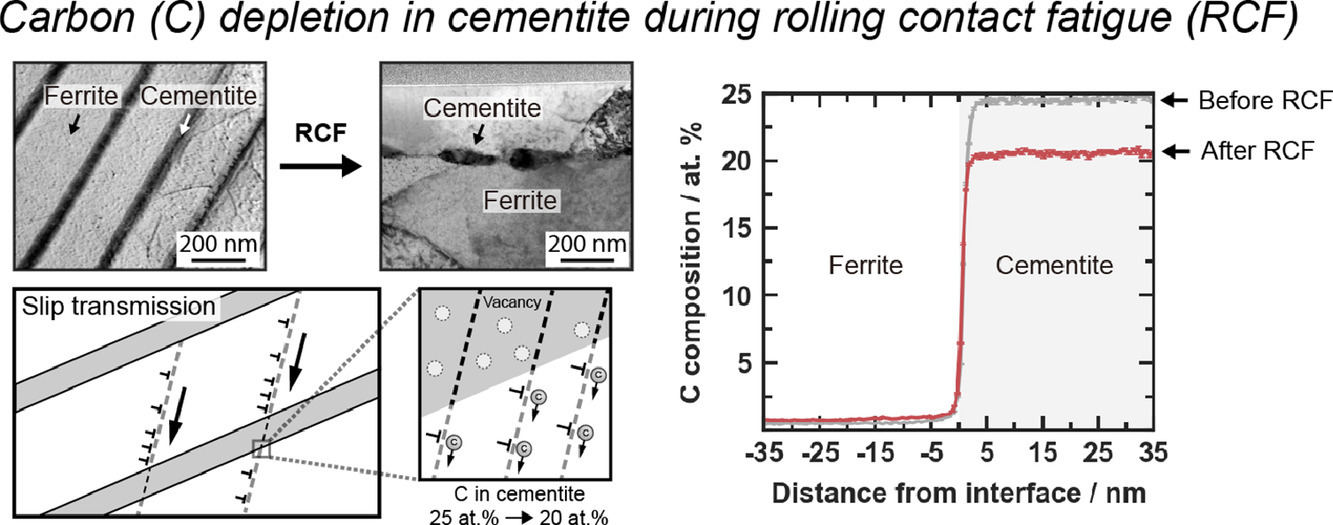
14. Under-stoichiometric cementite in decomposing binary Fe-C pearlite exposed to rolling contact fatigue
在滚动接触疲劳下分解二元Fe-C珠光体的低化学计量渗碳体
P.-Y. Tung✉, X. Zhou, D. Mayweg, L. Morsdorf, M. Herbig
P.-Y. Tung: p.tung@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117144
摘要
在本文中,研究了具有珠光体显微组织的二元Fe-0.74C(wt.%)钢在滚动接触疲劳过程中变形驱动的渗碳体分解的基本原理。为了揭示所涉及的纳米级机制,我们应用透射电子显微镜和原子探针断层扫描,以及在同一探针体积上结合两种技术进行相关的结构和化学分析。在Hertzian接触应力约1250MPa的情况下,经过约32,500次单个球体接触后,渗碳体片层的碳(C)含量持续下降至约 20%,与变形前25%的原始化学成分相比,减少了20%。通过原子探针尖上的电子衍射,我们表明这种低于化学计量的渗碳体仍然保持其晶体结构。通过在滚动接触疲劳后在150℃和250℃进行30分钟的退火实验,解决了滚动接触疲劳过程中温度升高对渗碳体分解的潜在影响。我们的结果表明,渗碳体片层的滑移传递主要是对观察到的渗碳体中的碳耗尽的主要原因。我们使用滑移轨迹分析法定量地讨论了从铁素体到渗碳体的滑移传输,并将滑移活动量与观察到的C消耗相关联。通过这种方式,我们解释了通过滑移传递和位错的溶质拖曳共同形成的低于化学计量的渗碳体,其中C通过渗碳体片层的位错滑行而从渗碳体中运出。只有在这之后,以相溶解方式进行的渗碳体分解才被认为是通过位错-侧滑机制发生的。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117150
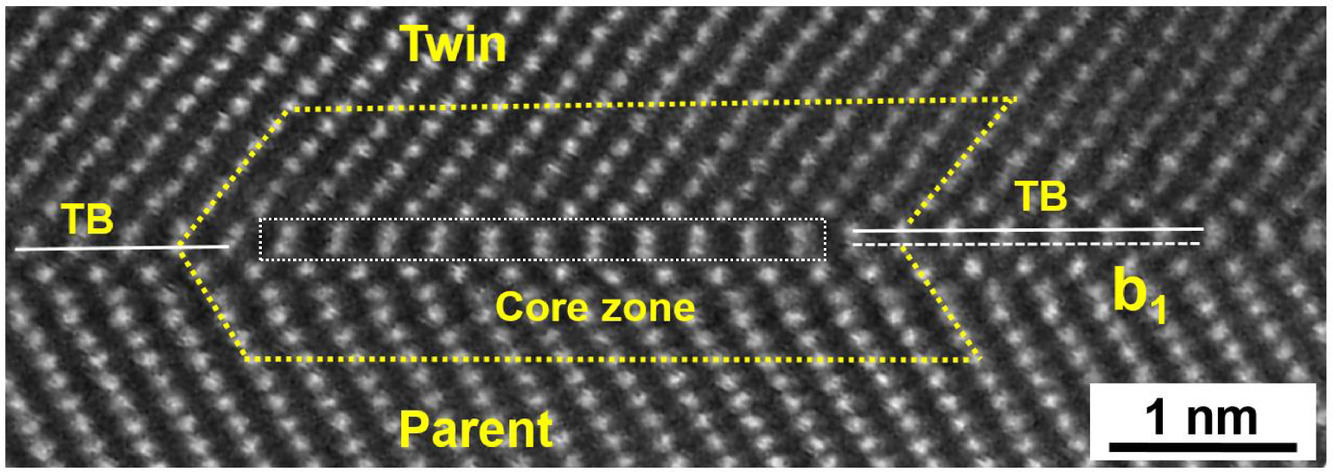
15. A half-shear-half-shuffle mechanism and the single-layer twinning dislocation for {11-22}<11-2-3> mode in hexagonal close-packed titanium
六方紧密堆积钛中{11-22} <11-2-3>模式下的半剪切-半侧滑机制和单层孪晶位错
Jingwei Li, Manling Sui✉, Bin Li✉
Manling Sui: mlsui@bjut.edu.cn, 北京工业大学
Bin Li: binl@unr.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117150
摘要
在六方紧密堆积(HCP)金属的孪晶模式中,{11-22} <11-2-3>模式的机制尤其令人困惑和争议。在文献报道中,有三种可能的第二不变平面,即{11-22} <11-2-3>孪晶模式的K2平面:已被广泛接受并对应于三层带状孪晶位错的{11-2-4};被认为是不利的{11-22};和只在原子模拟中观察到并且对应于单层孪生位错(0002)。{11-2-4}是由经典的孪晶理论预测的,实验测量的钛和锆的孪晶剪切s的大小与预测很一致。然而,{11-2-4}从未在模拟中得到验证,表明(0002)应该是K2平面。由于缺乏对孪晶位错结构的实验观察,这一矛盾一直没有得到解决。在这项工作中,通过扫描透射电子显微镜(STEM)观察并结合原子模拟,在原子尺度上解析变形纯钛的孪晶边界结构。原子分辨率STEM明确显示,孪晶位错只涉及单个孪晶面,K2面为(0002),这与原子模拟结果一致。STEM结果还揭示了半剪切-半侧滑的过程,其表现为由单层孪晶位错的滑动产生的独特孪晶界结构。为了解释这些结果,对所有三个K2平面的晶格对应关系进行了非常详细的研究。特别是,在经典理论的框架内分析了晶格转换中所需要的剪切和侧滑。这些分析很好地解释了为什么(0002)是比{11-2-4}和 {11-2-2}更有利的K2平面,并妥善地解决了经典孪晶理论的预测与模拟结果之间的不一致。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117158
16. Non-thermal melting of tungsten under intense electronic excitations
钨在强电子激发下的非热熔化
X.B. Ye, Z.H. He, Fei Gao, B.C. Pan✉
B.C. Pan: bcpan@ustc.edu.cn, 中国科学技术大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117158
摘要
由超快激光和材料中的快速离子引起的非热效应非常有趣,具有科学意义和技术重要性。然而,非热效应对超快过程的潜在物理学原理仍不清楚,所提出的机制也有争议。基于紧束缚理论下的微扰近似,对钨的非热效应进行了广泛的研究。研究证明由强烈的电子激发的非热效导致了钨晶体熔点的急剧下降,以及钨板内部的非热熔化。本文分析表明,非热力是导致本体系统熔点下降的主要原因。值得注意的是,非热效应与W薄膜的表面效应相结合,增强了表面附近原子运动方向的有序性,防止了表面区域的熔化,但导致了薄膜内部区域的非热熔化。本文的工作还展示了非热熔化和原子间力之间的统一关系。这种关系在被超快激光或快速离子照射的金属和半导体中是普遍存在的,并且在很早以前就已经被很好地确立了。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117134
17. The role of nitrogen in the oxidation behaviour of a Ti6242S alloy: a nanoscale investigation by atom probe tomography
氮在Ti6242S合金氧化行为中的作用:通过原子探针断层扫描进行的纳米级研究
C. Dupressoire, M. Descoins, A.Vande Put, E. Epifano, D. Mangelinck, P. Emile, D. Monceaua✉
D. Monceaua: daniel.monceau@toulouse-inp.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117134
摘要
当钛基合金在空气中高温条件下使用时,在其表面会形成氧化层,但也会在其金属基体中溶解大量的氧,这是导致脆化的原因。此外,氮是次要的氧化剂,它也会溶解在合金中并使之脆化。本文利用Ti-6Al-2Sn-4Zr-2Mo-0.1Si钛基合金在650℃合成空气(N2-20%O2)和Ar-20%O2混合物中进行了1000 小时的氧化实验,结果表明氮气可以减少氧化皮的生长和氧的溶解。此外原子探针断层扫描被用来研究合金/氧化物界面。结果显示,氮效应是由于氮氧化物和氮化物(Ti2N)界面层的形成,同时也是由于富氮的α-钛基固溶体的形成,这些固溶体都是氧气的扩散屏障,因为它们的氧溶解度很低。本文还比较了实验结果和热力学计算。
ACTA
Vol. 216,1 Sep. 2021, 117113
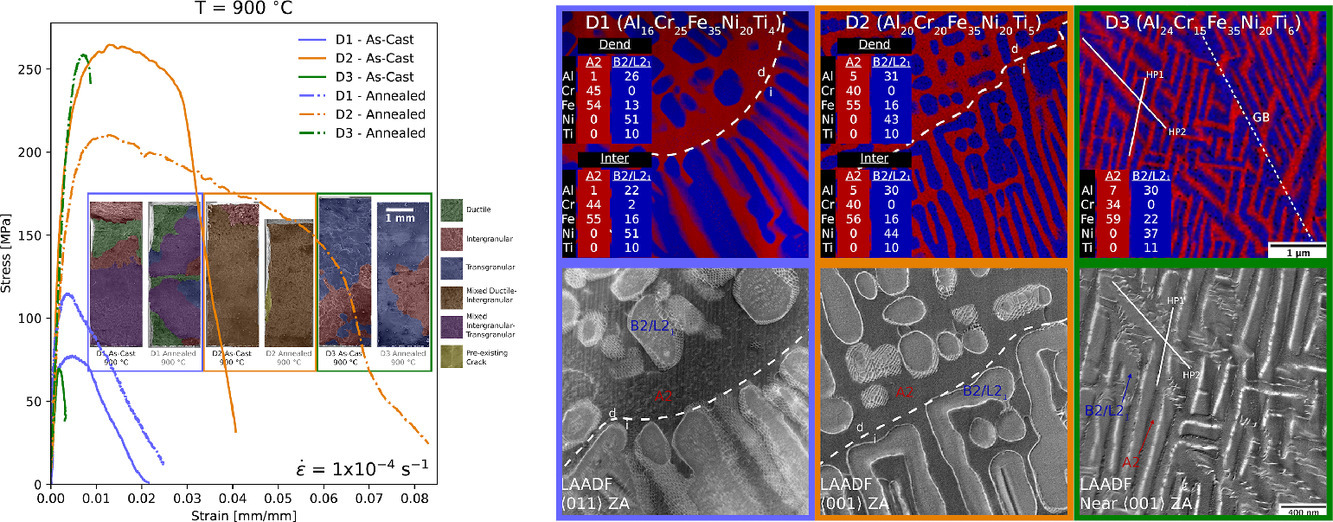
18. Towards superior high temperature properties in low density ferritic AlCrFeNiTi compositionally complex alloys
在低密度铁素体 AlCrFeNiTi 成分复杂合金中实现优异的高温性能
Silas Wolff-Goodrich, Sebastian Haas, Uwe Glatzel, Christian H. Liebscher
Silas Wolff-Goodrich: s.wolffgoodrich@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117113
摘要
三种表现出随成分变化的平滑微观组织梯度的新型沉淀强化bcc合金已经通过感应铸造的方式以块状形式制造。所有这三种合金无论是在铸态还是在900℃长期退火后都是由无序的A2-(Fe, Cr)和L21有序的 (Ni,Fe)2AlTi 型相的混合物组成。无序相与有序相的比例、初生枝晶分数和整体显微组织的粗糙度都随着Cr被Al和Ti取代而降低。通过对扫描透射电子显微镜期间获得的能量色散光谱数据进行的域平均主成分分析,量化了相组成的差异。整体拉伸试验显示,这些合金在900 ℃下的保留接近250MPa的强度,其中含有纳米级的迷宫式有序和无序相的排列。一种合金含有具有延展性的枝晶区域和高抗蠕变的枝晶间区域的双相微结构,显示出高温延展性和强度之间的良好平衡。对于这种合金,在700、750和800℃温度下进行了广泛载荷条件下的拉伸蠕变试验,发现其蠕变率的上限超过了类似的铁素体高温合金,并可与一些传统的高温结构合金(包括Inconel 617和718)相媲美,但密度和原材料成本要低得多。