金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.209, 1 Mar. 2022
2021-12-18 来源:GS-Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文19篇,涵盖了铝合金、形状记忆合金、中熵合金、高温合金等,国内科研单位包括上海交通大学、西安交通大学、东北大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 209 目录
1. Nanomechanical and microstructural characterization on the synergetic strengthening in selectively laser melted austenitic stainless steel
选择性激光熔化的协同强化奥氏体不锈钢的纳米力学和微观结构表征
2. Chemical short-range order strengthening mechanism in CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy under nanoindentation
纳米压痕下CoCrNi中熵合金的化学短程有序强化机制
3. The role of texture on superelasticity and elastocaloric effect in severely rolled Ti-44Ni-5Cu-1Al (at%) shape memory alloy
织构对重轧Ti-44Ni-5Cu-1Al (at%)形状记忆合金超弹性和弹热效应的影响
4. Cross-kink unpinning controls the medium- to high-temperature strength of body-centered cubic NbTiZr medium-entropy alloy
交叉扭结脱钉控制体心立方NbTiZr中熵合金的中高温强度
5. Abnormal grain growth in ultrafine grained Ni under high-cycle loading
高周载荷下超细晶镍晶粒的异常长大
6. Simultaneously increasing the strength and decreasing the modulus in TiNi alloys via plastic deformation
通过塑性变形提高TiNi合金强度的同时降低模量
7. Shock-induced amorphization in medium entropy alloy CoCrNi
中熵合金CoCrNi的冲击诱导非晶化
8. Room Temperature Deformation-induced Solute Segregation and its Impact on Twin Boundary Mobility in a Mg-Y Alloy
室温变形引起的溶质偏析及其对Mg-Y合金双晶界迁移率的影响
9. Avoiding abnormal grain growth when annealing selective laser melted pure titanium by promoting nucleation
通过促进形核避免选择性激光熔化纯钛退火时的异常晶粒生长
10. Influence of microtwins on Portevin-Le Châtelier effect of a Ni-Co based disk superalloy
微孪晶对Ni-Co基圆盘高温合金Portevin-Le Châtelier效应的影响
11. Surface boundary-dendrite interactions in thin metallic Al-alloy samples
薄金属铝合金样品中的表面边界-枝晶相互作用
12. Anisotropic grain boundary area and energy distributions in tungsten
氦分配到纳米晶Cu-Ta合金中的核壳Ta纳米团簇
13. Molecular dynamics simulation of vacancy and void effects on strain-induced martensitic transformations in Fe-50 at.% Ni model concentrated solid solution alloy
Fe-50 at.% Ni模型浓固溶体合金中空位和空隙对应变诱发马氏体转变的影响的分子动力学模拟
14. Superior hardness–corrosion-resistance combination in a Co-, Cu-modified Ni–Cr–Mo alloy via multiple nanoscale segregation mechanisms
通过多种纳米级偏析机制在Co-、Cu-改性的Ni-Cr-Mo合金中实现优异的硬度-耐腐蚀性能组合
15. Divorced eutectoid transformation in high-Al added steels due to heterogenous nucleation of κ-carbide
κ型碳化物异质成核导致高Al钢中的异质共析转变
16. Stability of single-atomic-layer-height disconnections on (1012) twin boundary in Mg
镁(1012)孪晶边界上单原子层高度不连续的稳定性
17. Developing a low-alloyed fine-grained Mg alloy with high strength-ductility based on dislocation evolution and grain boundary segregation
基于位错演化和晶界偏析的高强延性低合金细晶镁合金的研制
18. Exploiting tube high-pressure shearing to prepare a microstructure in Pb-Sn alloys for unprecedented superplasticity
利用管高压剪切在Pb-Sn合金中制备微观结构以获得超塑性
19. Interface structure of (130) twin in the U-14.0 at.% Nb alloy: an experimental and theoretical study
U-14.0 at.% Nb合金中(130)孪晶的界面结构:实验和理论研究性
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114359
1. Nanomechanical and microstructural characterization on the synergetic strengthening in selectively laser melted austenitic stainless steel
选择性激光熔化的协同强化奥氏体不锈钢的纳米力学和微观结构表征
Dong-Hyun Lee✉, Zhe Gao, Jeong-Min Park, Yakai Zhao, Jin-Yoo Suh✉, Eric A. Jagle, Koichi Tsuchiya, Ypadrasta Ramamurty, Jae-il Jang✉
Dong-Hyun Lee: dhlee@cnu.ac.kr
Jin-Yoo Suh: jinyoo@kist.re.kr
Jae-il Jang: jijang@hanyang.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114359
摘要
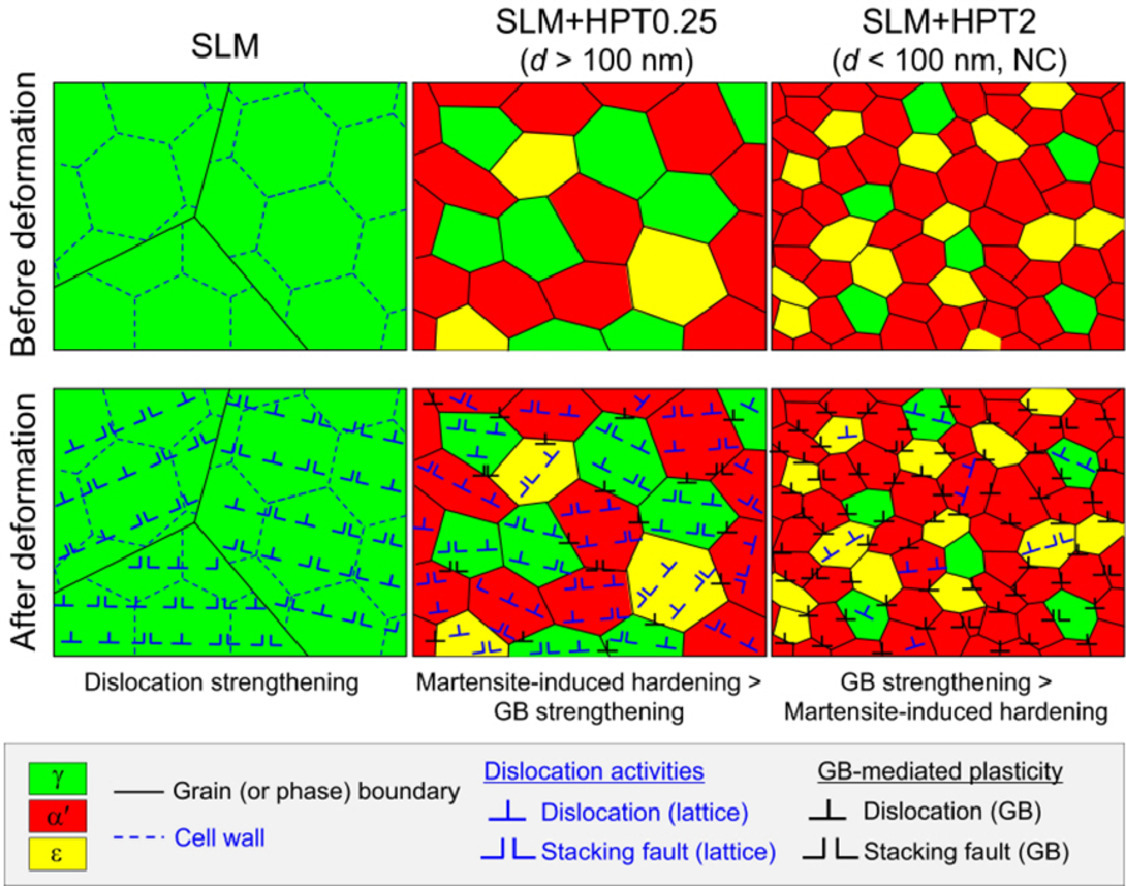
通过详细的纳米力学和微观结构表征,研究了由于高压扭转(HPT)而发生显著强化的选择性激光熔化304L不锈钢。在打印态合金中,位错硬化是主要的强化机制。然而,在热等静压(HPT)之后,晶粒细化和马氏体相变的协同主导了合金的强度。在纳米晶状态下,晶界介导的塑性占主导地位,阻碍了马氏体诱导的硬化。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114364
2. Chemical short-range order strengthening mechanism in CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy under nanoindentation
纳米压痕下CoCrNi中熵合金的化学短程有序强化机制
Xiaofeng Yang, Yongzhi Xi, Chenyun He, Hao Chen, Xiancheng Zhang✉, ShanTung Tu
Hao Chen: haochen@ecust.edu.cn(华东理工大学)
Xiancheng Zhang: xczhang@ecust.edu.cn(华东理工大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114364
摘要
使用纳米压痕的分子动力学(MD)模拟研究了CoCrNi中熵合金(MEA)中化学短程有序(SRO)结构的强化效果,建立了SRO参数与力学性能之间的定量关系。结果表明,CoCrNi MEA的强度和硬度随着化学SRO参数的增加而增加,并在SRO结构稳定的情况下达到稳定值。与随机固溶(RSS)状态模型相比,中间SRO模型的平均硬度增加了8.1%,稳定SRO模型的平均硬度增加了13.7%。SRO模型的位错形核力比RSS模型大55%。此外,在纳米压痕过程中观察到由局部Ni SRO结构引起的位错钉扎以及促进的独特位错相互作用。最后,结果还表明,随着温度的升高,硬度的增强变得更加显著(11.4% at 70K,17.24% at 300K和23.8% at 800K)。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114334
3. The role of texture on superelasticity and elastocaloric effect in severely rolled Ti-44Ni-5Cu-1Al (at%) shape memory alloy
织构对重轧Ti-44Ni-5Cu-1Al (at%)形状记忆合金超弹性和弹热效应的影响
Ruihang Hou, Fei Xiao✉, Zhu Li, Xuejun Jin✉
Fei Xiao: xfei@sjtu.edu.cn (上海交通大学)
J. Haley: jin@sjtu.edu.cn (上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114334
摘要
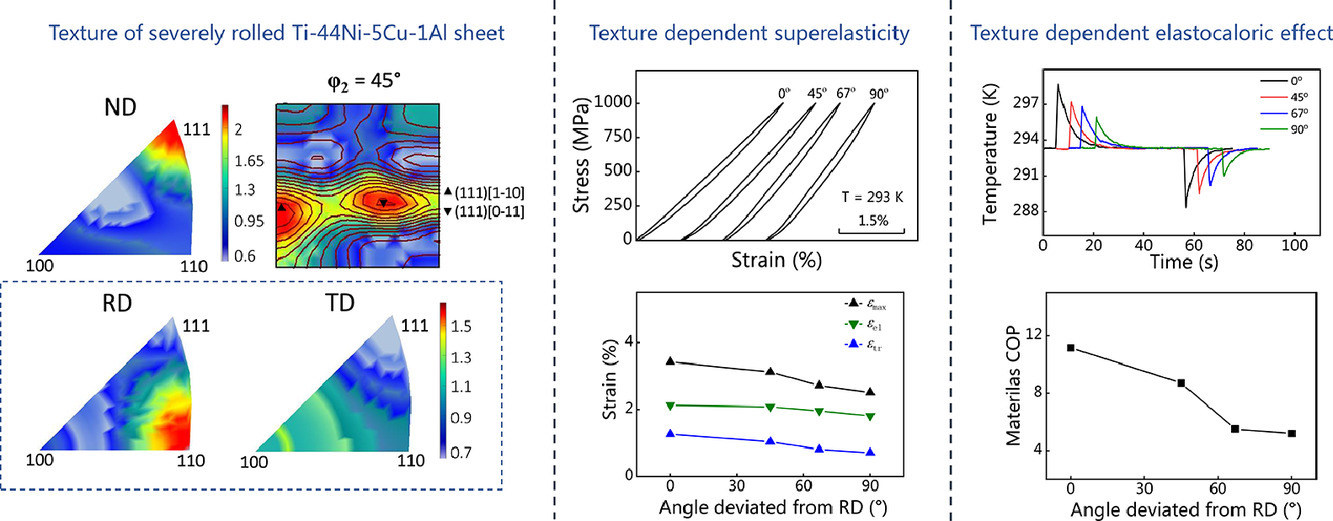
研究了晶体织构对纳米晶粒Ti-44Ni-5Cu-1Al轧制板超弹性和回弹热效应的影响。拉伸方向与轧制方向不同取向角的应力-应变曲线表明,板材的拉伸应变沿<110>的轧制方向(RD)最大,平行于<100>的横向(TD)最小。 通过分析每个应变分量的演变,进一步研究了这种织构依赖性。随着取向角的增加,晶间约束效应在TD上达到最大值。因此,转变应变和绝热温度变化具有类似的单调递减趋势。板材的材料性能系数在RD上达到11.2,该值使得严格轧制的Ti-44Ni-5Cu-1Al板有可能成为室温下固态制冷应用的潜在候选者。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114367
4. Cross-kink unpinning controls the medium- to high-temperature strength of body-centered cubic NbTiZr medium-entropy alloy
交叉扭结脱钉控制体心立方NbTiZr中熵合金的中高温强度
Rajeshwar R. Eleti✉, Nikita Stepanov, Nikita Yurchenko, Sergey Zherebtsov, Francesco Maresca
Rajeshwar R. Eleti: rajeshwar.eleti@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114367
摘要
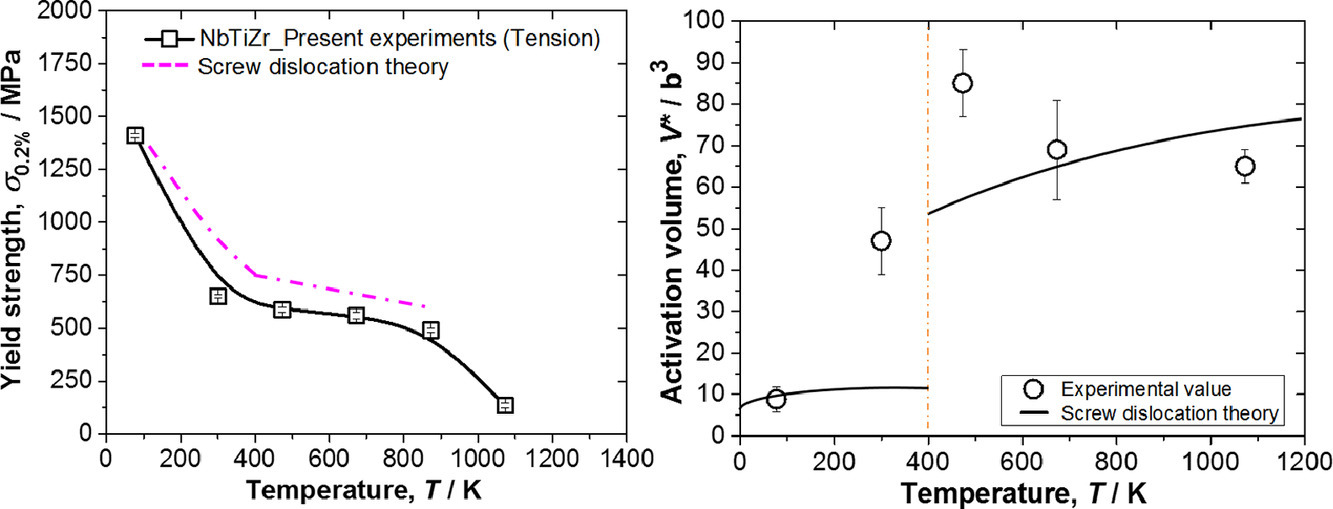
通过不同温度下的拉伸试验研究了NbTiZr体心立方(BCC)中熵合金(MEA)的变形机制。屈服强度(YS)在77 K至300 K之间表现出强烈的温度依赖性,而对300 K至873 K之间的温度不敏感,随后在1073 K处显着下降。TEM研究表明合金变形受螺旋-错位滑移所控制。除了1073 K外,在所有温度下都常观察到具有交叉扭结/弯折的螺旋位错。在473 K变形的微观结构显示出位错环/碎片,表明在中高温下交叉扭结强化占主导地位,导致屈服强度对温度不敏感。NbTiZr的行为与交叉扭结强化机制一致,激活体积的观察值和预测值之间的比较也证实了这一点。1073 K的TEM研究与交叉扭结/边缘偶极子的湮灭一致,这可以解释在该温度以上观察到的强度下降。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114372
5. Abnormal grain growth in ultrafine grained Ni under high-cycle loading
高周载荷下超细晶镍晶粒的异常长大
Alejandro Barrios, Yin Zhang, Xavier Maeder, Gustavo Castelluccio✉, Olivier Pierron✉, Ting Zhu✉
Gustavo Castelluccio: castellg@cranfield.ac.uk
Olivier Pierron: olivier.pierron@me.gatech.edu
Ting Zhu: ting.zhu@me.gatech.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114372
摘要
多晶材料中会发生晶粒异常长大,只有一小部分晶粒急剧生长以消耗其他晶粒。 在这里,我们研究了在环境温度下很少被研究的高周载荷下超细晶粒金属中的晶粒异常生长。在大量低应变幅度(< 0.3%)的循环加载下(最多109次),在平均初始晶粒尺寸小于640 nm的电镀镍微束中观察到晶粒的异常生长。这种异常生长主要发生在沿<100>取向拉伸/压缩载荷方向的晶粒族中。微观力学分析表明,晶粒的弹性各向异性决定了晶粒异常生长的热力学驱动力,因此<100>取向晶粒族的最低应变能密度主导着晶粒生长。这项工作揭示了一种独特的晶粒异常生长类型,可用于定制材料中的微观晶粒结构。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114374
6. Simultaneously increasing the strength and decreasing the modulus in TiNi alloys via plastic deformation
通过塑性变形提高TiNi合金强度的同时降低模量
Zhizhi Xu, Yanshuang Hao, Yuanchao Ji✉, Andong Xiao, Yu Qian, Wenjia Wang, Xiaobing Ren
Yuanchao Ji: jyc.xjtu@xjtu.edu.cn (西安交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114374
摘要
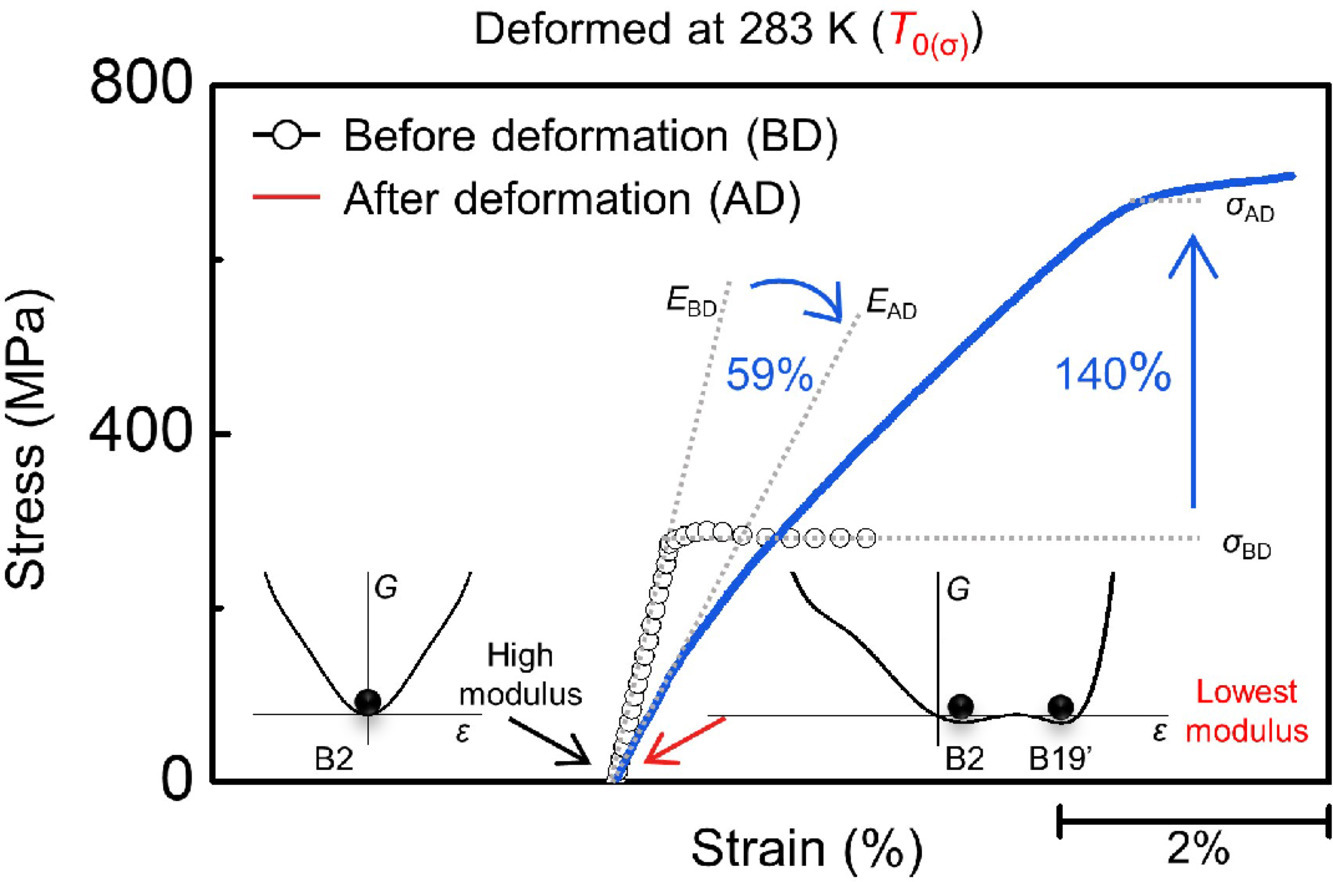
同时增加强度和降低模量是具有挑战性的,因为它们通常是相互排斥的。 这项工作报告了一种简单的方法,通过对Ti49.2Ni50.8形状记忆合金在T0(σ) ∼283 K(T0(σ)表示变形后奥氏体和马氏体之间的平衡温度)进行塑性变形,使其屈服应力提高140%,杨氏模量降低59%。通过整合实验和朗道理论,我们发现除了由于应变硬化引起的强度增加外,模量降低还源于从奥氏体状态到特殊双相状态的变化。奥氏体和应力诱发马氏体具有相同的自由能,因此在T0(σ)处表现出最低的模量。在另一种铁弹性Ti49Ni51合金中也发现了类似的结果,这意味着使用T0(σ)塑性变形策略可以进一步优化其他铁弹性材料的性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114379
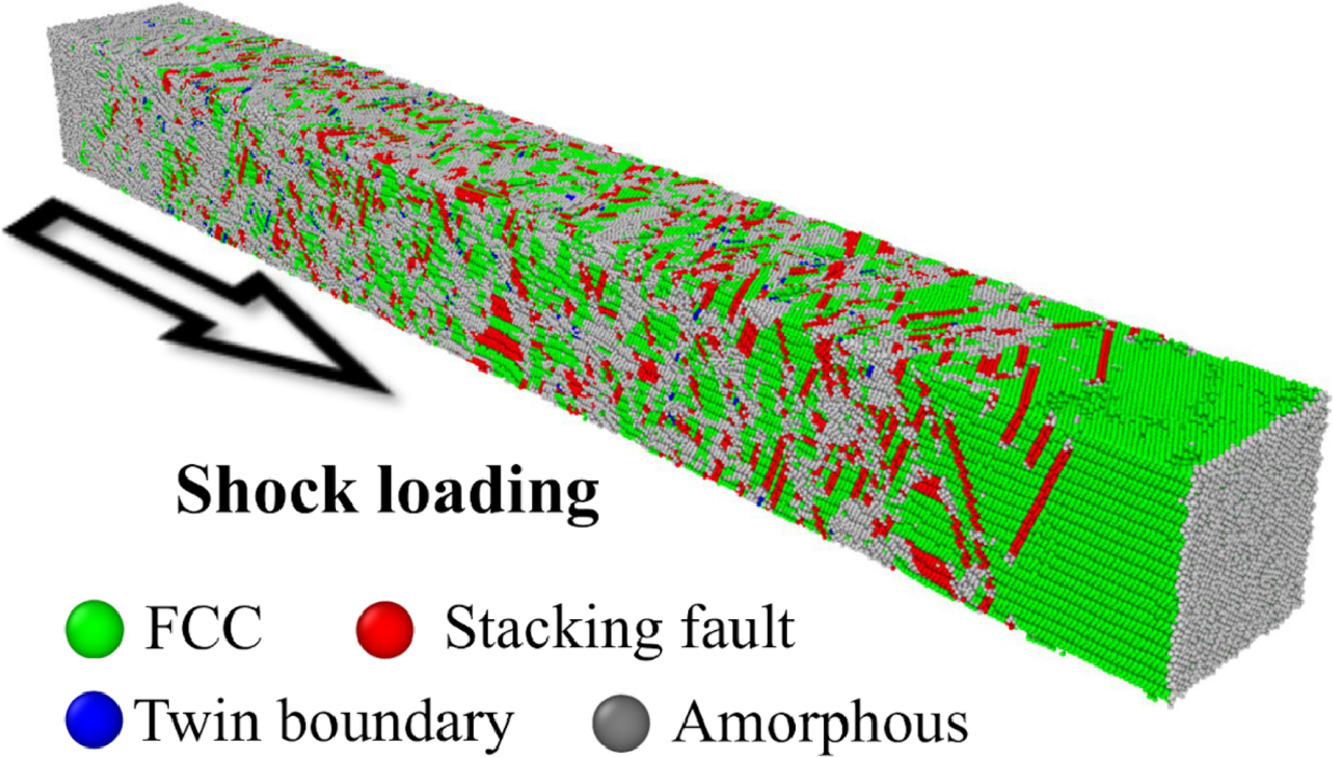
7. Shock-induced amorphization in medium entropy alloy CoCrNi
中熵合金CoCrNi的冲击诱导非晶化
Wu-Rong Jian✉, Zhucheng Xie, Shouzhi Xu, Xiaohu Yao✉, Irene J. Beyelein
Raymundo Arroyave: wurong@ucsb.edu
Xiaohu Yao: yaoxh@scut.edu.cn
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114379
摘要
通过分子动力学模拟研究CoCrNi、中等熵合金(MEA)及其无晶格畸变的平均场变体中冲击引起的非晶化。研究表明存在一个临界速度,高于该速度会发生非晶化。在800 m/s的低冲击速度下,位错滑移和孪晶占主导地位,不会发生非晶化,但随着冲击速度的增加,变形机制从滑移和孪晶转变为固态非晶化。在超高冲击速度下,随着冲击波的前兆发生广泛的非晶化,消除了剥落强度的各向异性。与平均场模型相比,MEA中的晶格畸变导致更多的非晶化和较低的剥落强度,因为空隙优先在非晶区成核和生长。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114375
8. Room Temperature Deformation-induced Solute Segregation and its Impact on Twin Boundary Mobility in a Mg-Y Alloy
室温变形引起的溶质偏析及其对Mg-Y合金双晶界迁移率的影响
Xin Wang✉, Yang Hu, Kehang Yu, Subhash Mahajan, Irene J. Beterlein, Enrique J. Lavernia, Timothy J. Rupert, Julie M. Schoenung
Xin Wang: xinw15@uci.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114375
摘要
合金的机械行为受溶质原子偏析的影响,这会影响变形机制,例如滑移和孪生。这项研究报告了Mg-Y合金室温变形诱导溶质偏析的原子级研究。在位错核心处观察到高浓度的Y。此外,我们发现{1012}孪晶以相干孪晶边界和基底棱柱面为界,它们分别包含周期性偏析的富Y柱和纳米级富Y簇。观察到的偏析排列从能量方面归因于这样一个事实,即它最大限度地减少了整体晶格畸变,并且在动力学上受到溶质原子和晶体缺陷之间的动态相互作用以及塑性变形过程中滑移孪生相互作用的辅助。此外,隔离的Y原子会产生钉扎效应并导致孪晶边界迁移率的各向异性。这一发现为控制镁合金的机械响应提供了一种潜在的新合金设计途径。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114377
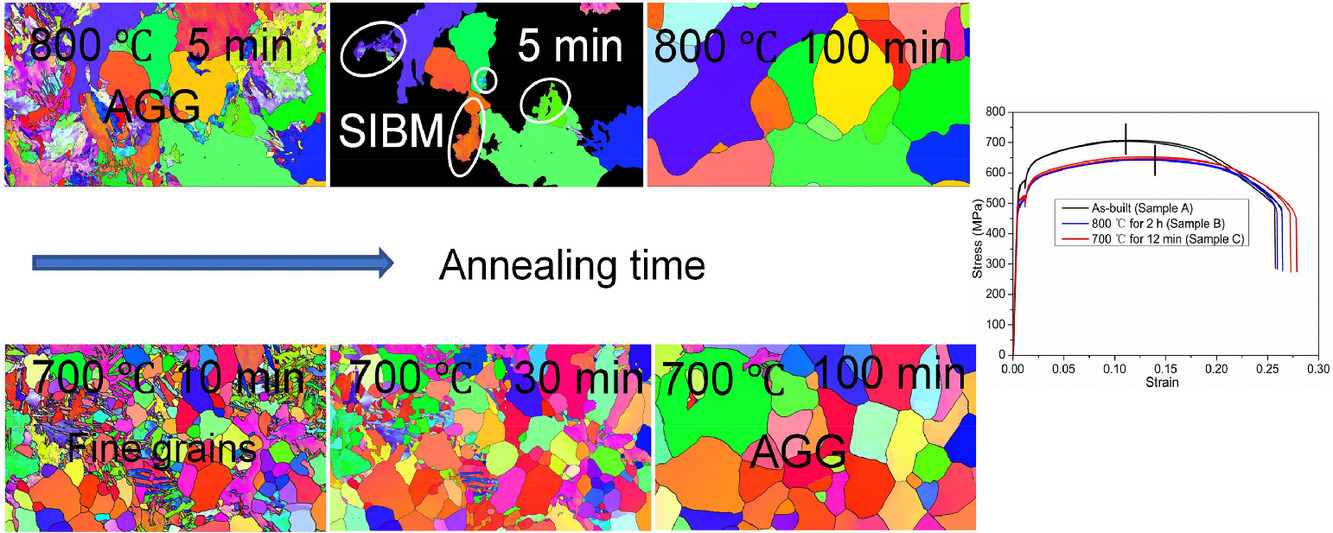
9. Avoiding abnormal grain growth when annealing selective laser melted pure titanium by promoting nucleation
通过促进形核避免选择性激光熔化纯钛退火时的异常晶粒生长
Kewei Chen, De Jun Huang, Hua Li✉, Ning Jia, Warren Chong
Hua Li: lihua@ntu.edu.sg
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114377
摘要
在这项研究中,选择性激光熔化(SLM)商业纯钛(CP-Ti)的再结晶过程,被在800℃和700℃下的进行了准原位电子背散射衍射(EBSD)观测。异常晶粒生长(AGG)最初出现在800℃退火开始时,主要由应变诱导边界迁移(SIBM)引起。然而,在700℃退火开始时,由于更多的再结晶形核形成了许多小的等轴晶粒,随后由于二次再结晶而形成AGG。 基于这些发现,适当控制700℃的退火时间可以减轻AGG以获得具有弱织构的细等轴晶粒,从而提高SLM CP-Ti的拉伸性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114385
10. Influence of microtwins on Portevin-Le Châtelier effect of a Ni-Co based disk superalloy
微孪晶对Ni-Co基圆盘高温合金Portevin-Le Châtelier效应的影响
Xingwei Huang, Xinzhe Zhou, Weizhen Wang, Chuangyong Cui, Hengqiang Ye, Zhiqing Yang✉
Zhiqing Yang: yangzq@imr.ac.cn (中国科学院金属研究所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114385
摘要
通过拉伸试验和透射电子显微镜研究了微孪晶(MT)对Ni-Co基高温合金的Portevin-Le Châtelier (PLC)效应的影响。两组样品在725℃下预应变以产生MT。MTs的存在提高了合金的屈服强度,但它将PLC效应从B型变为C型,并在400℃拉伸变形期间将锯齿幅度增加了约6倍。微观结构表征表明,位错-MT相互作用导致γ基体和γ'沉淀物中的MT断裂,为位错滑动创造了软通道。基于沿着这些软通道的突然塑性流动以及随后由于位错倍增引起的应变硬化,高锯齿幅度被合理化。这些结果表明,与传统上接受的位错-溶质相互作用相比,MTs对PLC效应的影响要显著得多。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114386
11. Surface boundary-dendrite interactions in thin metallic Al-alloy samples
薄金属铝合金样品中的表面边界-枝晶相互作用
Maike Becker✉, Matthias Kolbe, Sonja Steinbach, Florian Kargl
Maike Becker: maike.becker@dlr.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114386
摘要
使用原位X射线、X射线断层扫描分析和电子背散射衍射研究了薄Al-15 wt.%Cu(200 µm)和Al-29 wt.%Ge (500 µm)合金中枝晶的晶体取向和生长方向。Al-Cu合金在微重力条件下凝固,而Al-Ge样品在地面上水平加工。研究发现:(i)枝晶在微重力下在表面两侧成核,但由于浮力在法向重力下在顶面附近积累;(ii)枝晶沿优选的面内结晶方向生长,即对于Al-15 wt.%Cu 是<100> ,对于Al-29 wt.%Ge是<100>、<110>和<210>,表明这种Al-Ge组合物的固液界面各向异性在这些<xy0>方向上是相似的;(iii) Al-Cu中略微倾斜的枝晶臂在接触后沿样品边界生长,而Al-Ge中倾斜枝晶臂的尖端从未接触边界,而是从次级分支产生新的初级尖端。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114384
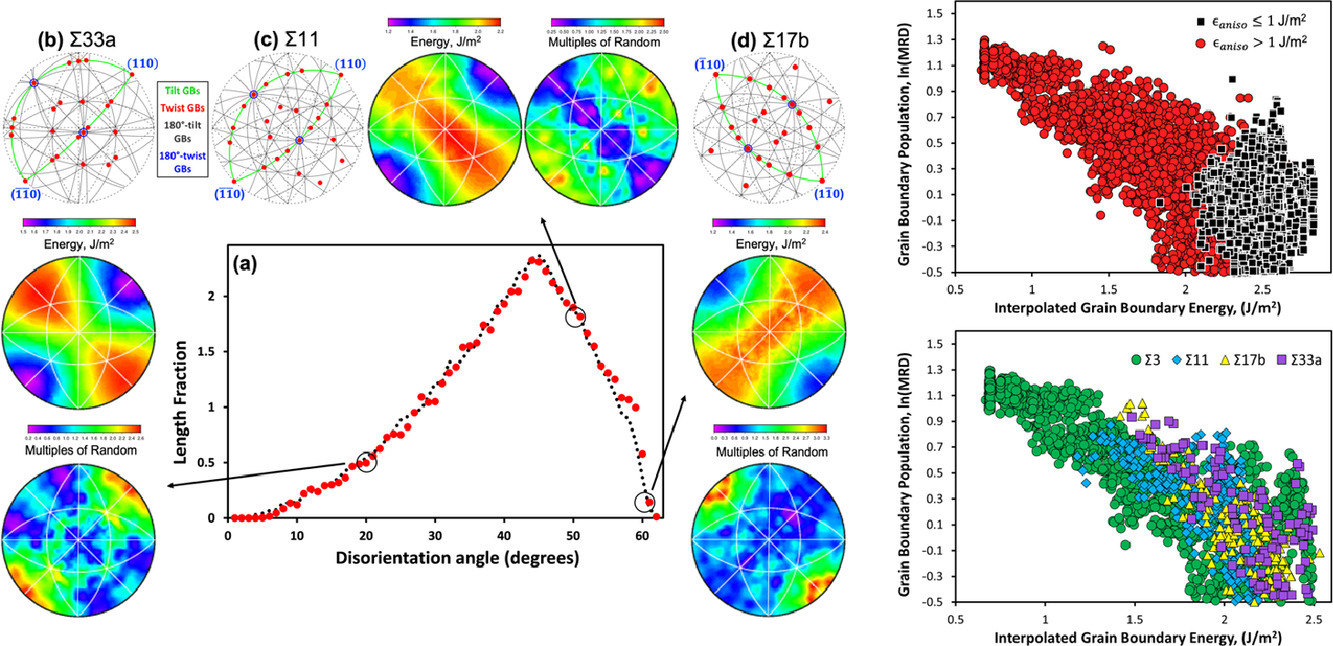
12. Anisotropic grain boundary area and energy distributions in tungsten
氦分配到纳米晶Cu-Ta合金中的核壳Ta纳米团簇
Ooraphan Chirayutthanasak, Rajchawit Sarochawikastie, Apiwat Wisitsorasak, Nopporn Rujisamphan, Timofey Frolov, Tomas Oppelstrup, Somsak Dangtip, Gregory S. Rohrer, Sutatch Ratanaphan✉
Sutatch Ratanphan: sutatch.ratanaphan@mail.kmutt.ac.th
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114384
摘要
描述钨的微观结构演化需要对各向异性晶界能量进行定量描述。我们提出了钨的晶界能量函数,它指定了任意边界的能量,给定了它的五个宏观晶体参数。测量的晶界面积与函数在Σ11、Σ17b和Σ33a取向差处给出的晶界能量的比较(通过测量或原子计算难以确定)揭示了与其他研究中观察到的相似的逆相关性。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114394
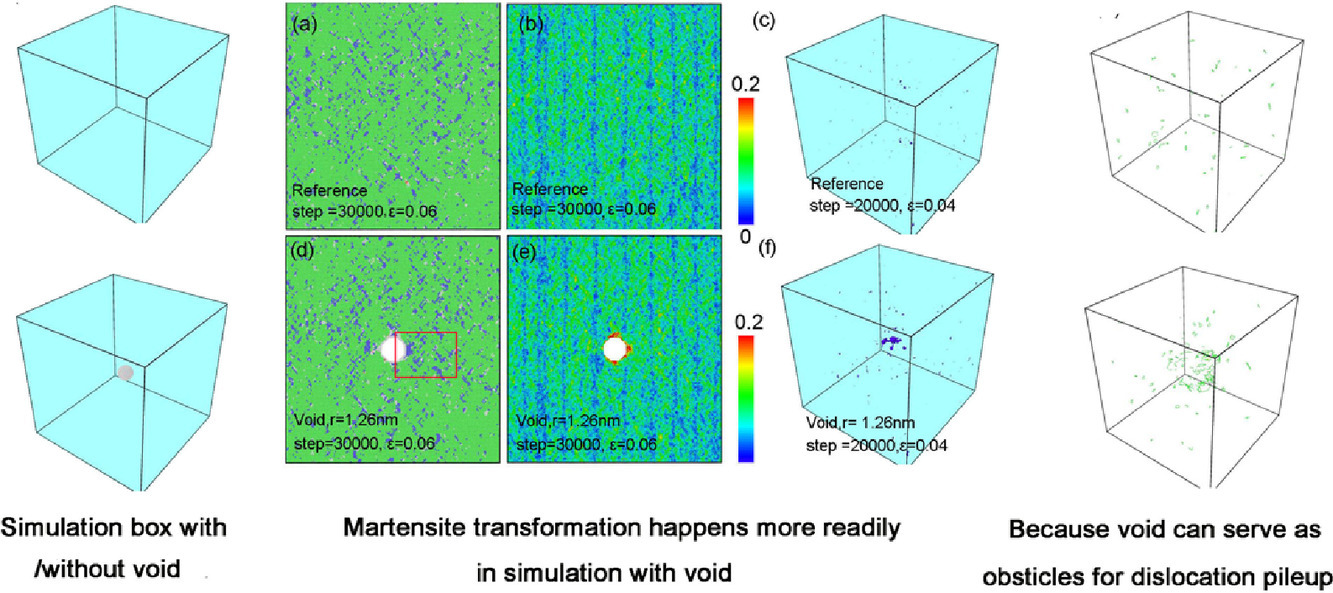
13. Molecular dynamics simulation of vacancy and void effects on strain-induced martensitic transformations in Fe-50 at.% Ni model concentrated solid solution alloy
Fe-50 at.% Ni模型浓固溶体合金中空位和空隙对应变诱发马氏体转变的影响的分子动力学模拟
Chao Yang✉, Yash Pachaury, Anter EI-Azab, Janelle Wharry
Chao Yang: yang1913@purdue.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114394
摘要
应变引起的马氏体转变可以提高一些面心立方(FCC)金属和合金的强度和延展性。辐照引起的缺陷,如空位、位错环和空隙,在比原始材料更广泛的机械载荷条件下激活马氏体转变。然而,辐照使马氏体转变的机制仍不清楚。在这项工作中,我们使用分子动力学模拟来研究空位和空隙对模型浓缩固溶体合金Fe-50 at.% Ni中应变诱发马氏体转变的影响。已经发现,单个空位对转变没有可解决的影响,因为它们以相对微不足道的幅度减少堆垛层错能量,并且仅当空位位于堆垛层错平面时才这样做。然而,由于位错堆积,空隙通过空隙周围的剪切应变积累激活马氏体转变。空隙越大,这种效果越明显。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114389
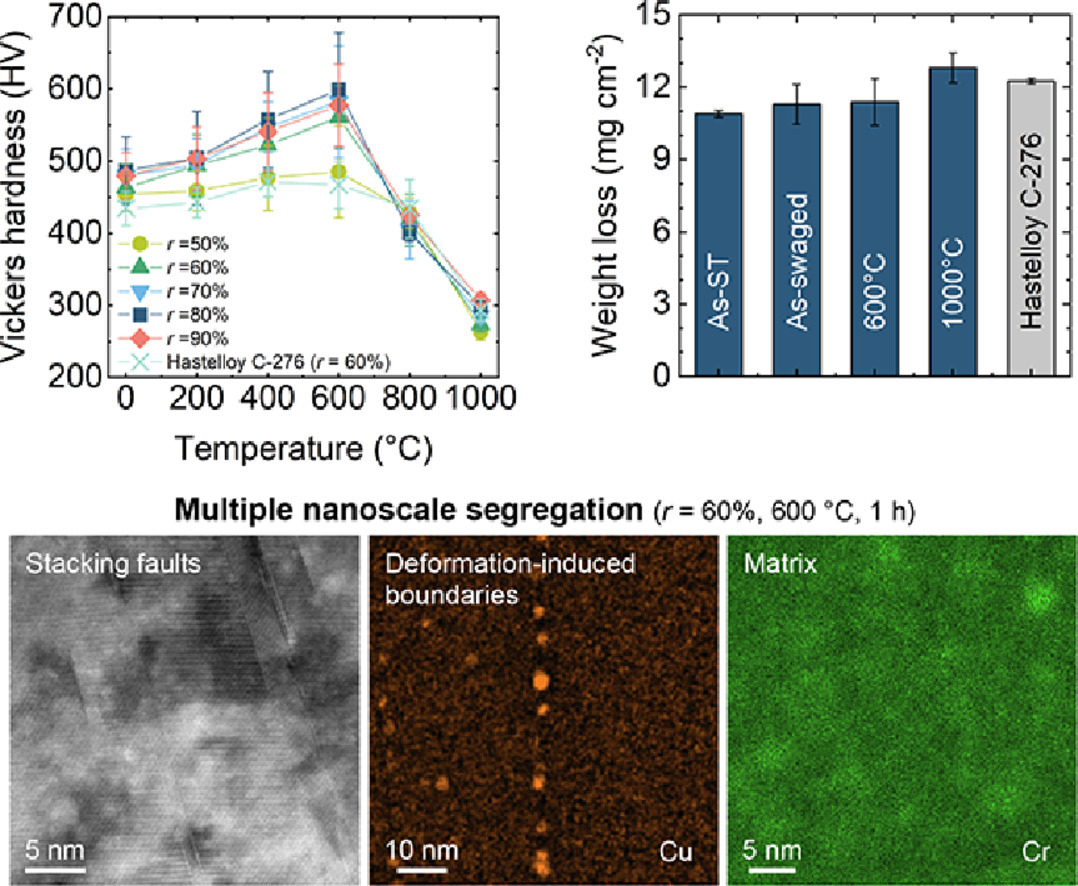
14. Superior hardness–corrosion-resistance combination in a Co-, Cu-modified Ni–Cr–Mo alloy via multiple nanoscale segregation mechanisms
通过多种纳米级偏析机制在Co-、Cu-改性的Ni-Cr-Mo合金中实现优异的硬度-耐腐蚀性能组合
Haruka Shima, Manami Mori✉, Kenta Yamanaka✉, Kazuo Yoshida, Toshihiro Yamazaki, Akihiko Chiba
Manami Mori: m-mori@sendai-nct.ac.jp
Kenta Yamanaka: k_yamanaka@imr.tohoku.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114389
摘要
Ni-Cr-Mo耐腐蚀合金的硬化促进了其工业应用的扩展,然而,它仍然具有挑战性。在此,我们报告了在适当的冷锻/时效条件下Co-、Cu-改性的Ni-Cr-Mo合金的显着硬化。时效硬化发生在相对较短的时间内(约0.5小时),并在冷锻后变得清晰,面积减少≥60%,在500-600℃时表现出峰值硬度。时效后获得了常规Ni-Cr-Mo合金无法达到的优异硬度(HV599)。扫描透射电子显微镜显示多种纳米级偏析机制,包括堆垛层错处的Suzuki偏析和严重冷锻面心立方矩阵内的富铬纳米域,都是导致硬化的原因。此外,Cu与Cr和Mo一起沿变形诱导边界的偏析导致纳米级Cu沉淀在整个基体中的精细分布,从而进一步硬化。通过这种策略实现了硬度和腐蚀性能的卓越组合。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114395
15. Divorced eutectoid transformation in high-Al added steels due to heterogenous nucleation of κ-carbide
κ型碳化物异质成核导致高Al钢中的异质共析转变
J.C. Pang, W.F. Yang, G.D. Wang, S.J. Zheng, R.D.K. Misra, H.L. Yi✉
H.L. Yi: hlyi@ral.neu.edu.cn (东北大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114395
摘要
低密度1.25C-5Al-1.5Cr钢在异质共析转变(DET)中同时包含渗碳体和κ-碳化物,成功地从416 ± 3 HV20软化到285 ± 1 HV20。计算出两种碳化物之间的平面失配率为5.26%,这表明分散在钢中的未溶解渗碳体颗粒在DET过程中为κ-碳化物提供了异质成核位点。κ-碳化物和渗碳体之间的取向关系(OR)为(100)κ//(110)θ和[011]κ//[111]θ。该研究还表明,只有渗碳体在临界间奥氏体化过程中保留下来,并且在冷却过程中作为κ-碳化物的有效成核剂。最后,球状κ-碳化物与渗碳体连接并分散在铁素体基体中,并在DET反应后存在。首次定义了κ-碳化物和渗碳体之间的取向关系(OR)。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114407
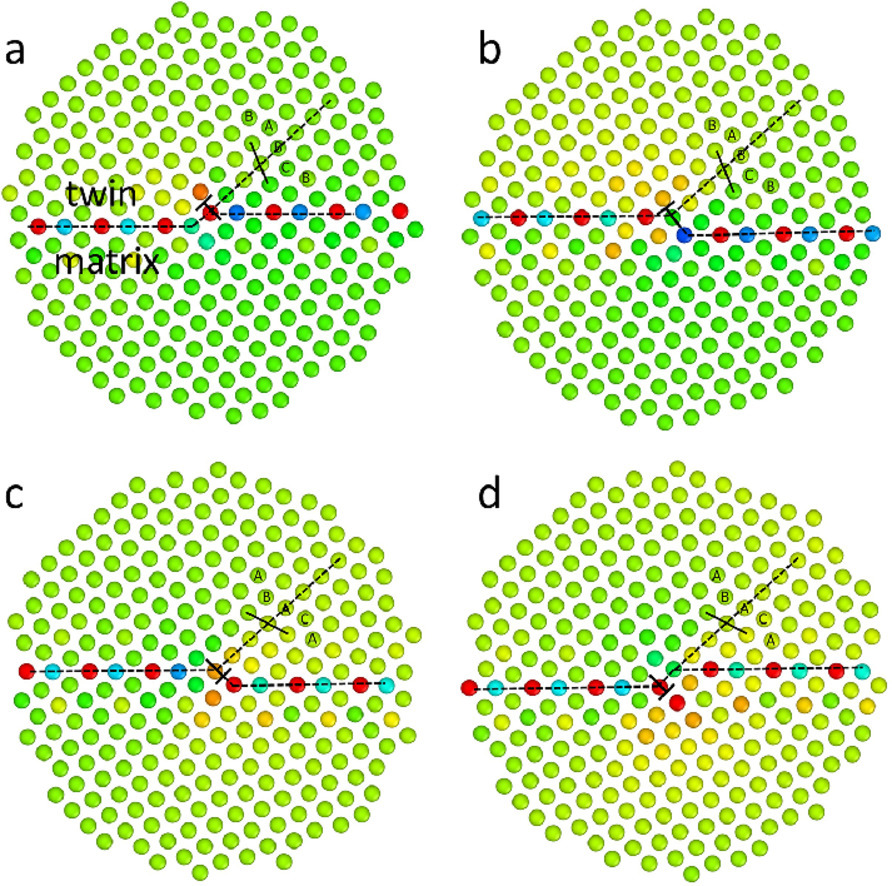
16. Stability of single-atomic-layer-height disconnections on (1012) twin boundary in Mg
镁(1012)孪晶边界上单原子层高度不连续的稳定性
Y. Yue, Y. Zhang, J.F. Nie✉
J.F. Nie: jianfeng.nie@monash.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114407
摘要
使用分子动力学模拟研究了镁(1012)孪晶边界上单原子层高度不连续的四种不同配置。发现当它们中的每一个都与相关的I1堆垛层错连接时,堆叠顺序更改为 BABCB,棱柱形基底(PB)单原子层高度不连续开比基底棱柱形(BP)更稳定。相比之下,当它们中的每一个都与ABACA堆叠序列变化相关的I1断层连接时,BP单原子层高度不连续比PB更稳定。一个稳定的BP(或PB)单原子层高度不连续性,当其阶梯方向随着相连I1断层的横断面的变化而变化时,可以转变为稳定的PB(或BP)单原子层高断路。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114414
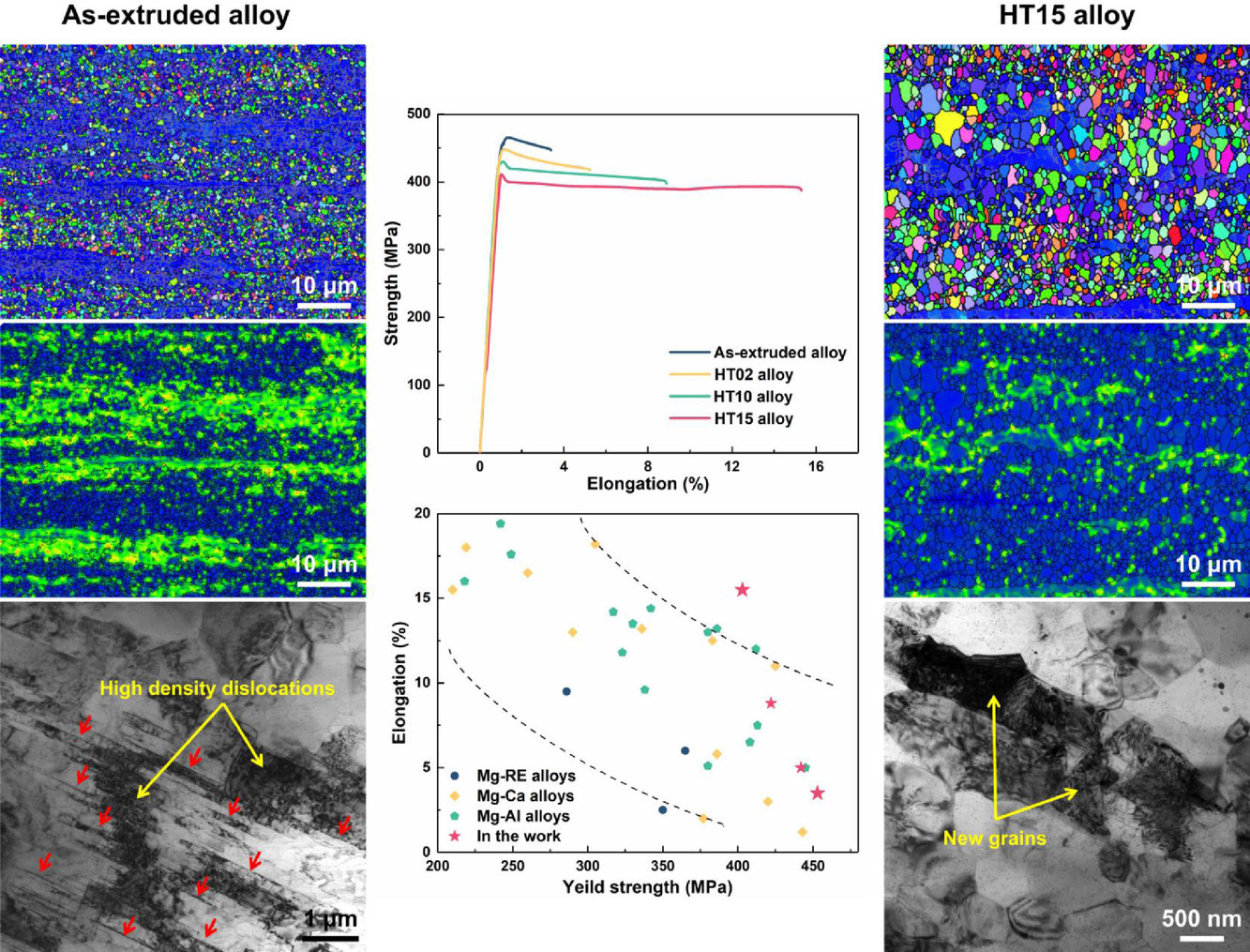
17. Developing a low-alloyed fine-grained Mg alloy with high strength-ductility based on dislocation evolution and grain boundary segregation
基于位错演化和晶界偏析的高强延性低合金细晶镁合金的研制
Zhi Zhang, Jinghuai Zhang✉, Jinshu Xie, Shujuan Liu, Yuying He, Kai Guan, Ruizhi Wu
Jinghuai Zhang: zhangjinghuai@hrbeu.edu.cn(哈尔滨工程大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114414
摘要
采用低温低速挤压法制备了一种新型低合金Mg-2Sm-0.8Mn-0.6Ca- 0.5Zn (wt.%)合金。挤压态合金具有超高屈服强度(YS,453 MPa),但延伸率较差(3.2%),这主要是由于形成了含有高密度残余位错和Mn纳米颗粒的细晶结构。更重要的是,经过随后的简单退火,该合金表现出高强度和高延展性的优异结合,YS为403 MPa,延伸率为15.5%。Sm/Zn/Ca的晶界(GB)共偏析有效抑制晶粒生长对于退火合金保持高强度至关重要。适当降低位错密度,尤其是不可移动的长S-<c+a>位错向新GB的演变,是退火合金延展性显着提高的关键因素。因此,我们提出了一种主要基于位错演化和GB偏析的高强高延性低合金镁合金的开发新策略。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114390
18. Exploiting tube high-pressure shearing to prepare a microstructure in Pb-Sn alloys for unprecedented superplasticity
利用管高压剪切在Pb-Sn合金中制备微观结构以获得超塑性
Kui Lin, Zheng Li, Ying Liu, En Ma✉, Jing Tao Wang✉, Terence G. Langdon
En Ma: maen@xjtu.edu.cn(西安交通大学)
Jing Tao Wang: jtwang@njust.edu.cn (南京理工大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114390
摘要
超塑性Pb-Sn合金是通过管高压剪切(t-HPS)从固溶体块开始一步生产的。Pb-40 wt% Sn合金在室温1.0 × 10−3 s−1的应变率下显示出高达1870%的超塑性伸长率,将该条件下的最大伸长率的最佳应变率提高了一个数量级,超过传统的铸造铅锡合金。这种前所未有的室温超塑性归因于具有微米数量级均匀尺寸的等轴晶粒,特别是由于几乎相等比例的Pb和Sn的良好混合域。这种微观结构无法通过传统的热机械加工在铸造共晶或亚共晶合金中获得,而是在室温t-HPS生成的成分型直接结果。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 209, 1 Mar. 2022, 114417
19. Interface structure of (130) twin in the U-14.0 at.% Nb alloy: an experimental and theoretical study
U-14.0 at.% Nb合金中(130)孪晶的界面结构:实验和理论研究性
Xin Wang, Wenyuan Wang✉, Chao Lu, Yawen Zhao, Ruizhi Qiu, Tao Shi, Ping Zhou, He Huang, Tao Fa✉
Wenyuan Wang: wywang@alum.imr.ac.cn (中国工程物理研究院)
Tao Fa: fatao@caep.cn(中国工程物理研究院)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114417
摘要
这项工作使用球差校正TEM结合第一性原理计算对U-14.0 at.% Nb合金中的(130)孪晶系统进行了实验和理论研究,首次明确给出了(130)孪晶的原子结构及其孪晶晶界能。我们证明了伪正交晶系中广泛使用的(130)孪晶系实际上是单斜晶系中的(101)孪晶系。通过第一性原理计算,我们还发现,由于Nb原子处的耗尽电荷区和Nb原子周围的富电荷区,Nb的局部原子结构显著影响了孪晶界能量。这些结果可能有助于我们更好地理解低对称性U金属和U-Nb合金的变形机制。


