金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.218,1 Oct. 2021
2021-12-18 来源:GS-Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文17篇,涵盖了形状记忆合金、马氏体、高熵合金等,国内科研单位包括香港科技大学、中南大学、西安交通大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 218 目录
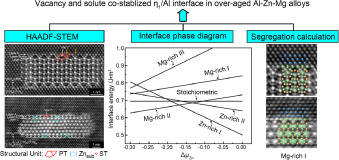
1. Vacancy and solute co-segregated η1 interface in over-aged Al-Zn-Mg alloys
过度时效Al-Zn-Mg合金中的空位和溶质共偏析η1界面
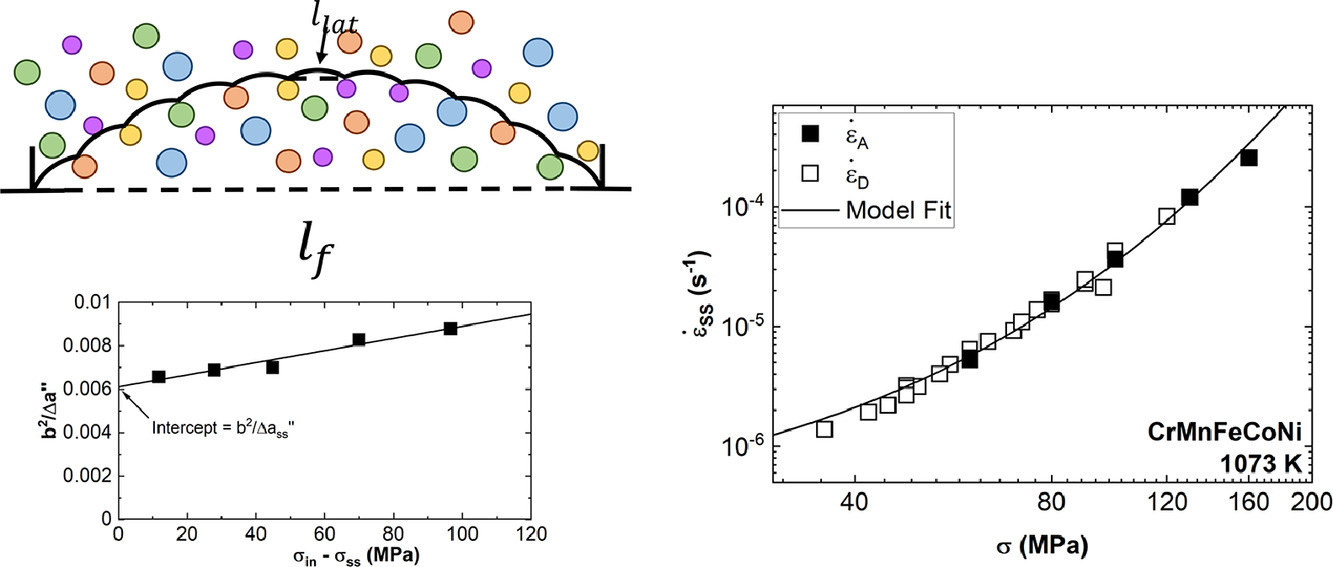
2. Elevated-temperature Deformation Mechanisms in a CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy
CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金的高温变形机制
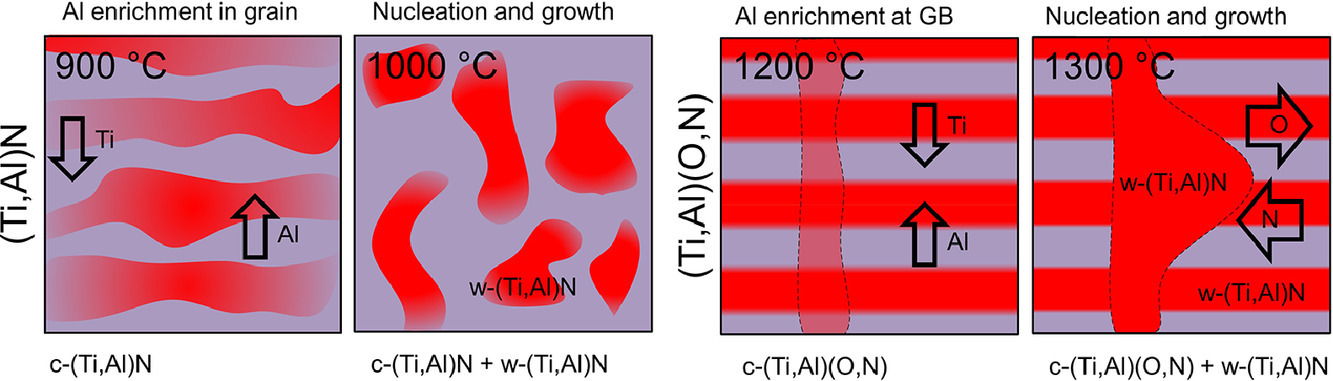
3. Enhanced thermal stability of (Ti,Al)N coatings by oxygen incorporation
通过氧掺入提高(Ti,Al)N涂层的热稳定性
4. NiTiHf shape memory alloys as phase change thermal storage materials
作为相变储热材料的NiTiHf形状记忆合金
5. J-integral analysis of the elastic strain fields of ferrite deformation twins using electron backscatter diffraction
利用电子背散射衍射分析铁氧体变形孪晶弹性应变场的j积分
6. Segregation competition and complexion coexistence within a polycrystalline grain boundary network
多晶晶界网络中存在的偏析竞争和络合共存
7. Evolution of martensitic microstructures in nanocrystalline NiTi wires deformed in tension
纳米晶NiTi钢丝拉伸变形中马氏体组织的演化
8. Microstructure tailoring of Al-containing compositionally complex alloys by controlling the sequence of precipitation and ordering
通过控制析出和排序的顺序对含铝成分复杂的合金进行组织调控
9. Tailoring thermal expansion of shape memory alloys through designed reorientation deformation
通过设计的再取向变形调整形状记忆合金的热膨胀
10. Learning from superelasticity data to search for Ti-Ni alloys with large elastocaloric effect
从超弹性数据中寻找具有大弹性热效应的Ti-Ni合金
11. Strain glass state in Ni-rich Ni-Ti-Zr shape memory alloys
富镍Ni-Ti-Zr形状记忆合金中的应变玻璃态
12. On the probabilistic assessment of variability in fatigue life in a near α titanium alloy Timetal 834: Crystallography of fatigue crack initiating facets
关于近α钛合金Timetal 834疲劳寿命变异的概率评估:疲劳裂纹起始面的晶体学
13. Multiple coupling modes to relax shear strain during grain boundary migration
晶界迁移过程中松弛剪切应变的多种耦合模式
14. Gibbs-Thomson effect as driving force for liquid film migration: Converting metallic into ceramic fibers through intrinsic oxidation
Gibbs-Thomson效应作为液膜迁移的驱动力:通过内在氧化将金属转化为陶瓷纤维
15. An electronic origin to the oscillatory segregation behavior in Ni-Cr and other BCC defects in FCC metals
FCC金属中Ni-Cr和其它BCC缺陷中振荡偏析行为的电子起源
16. First-principles disordered local-moment study on temperature dependence of spin polarization in Co2Fe(Ga0.5Ge0.5) Heusler alloy
Co2Fe(Ga0.5Ge0.5) Heusler合金自旋极化温度依赖的第一性原理无序局域矩研究
17. The grain boundary stiffness and its impact on equilibrium shapes and boundary migration: Analysis of the Σ5, 7, 9, and 11 boundaries in Ni
晶界刚度及其对平衡形状和晶界迁移的影响:Ni中Σ5、7、9和 11晶界的分析
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117082
1. Vacancy and solute co-segregated η1 interface in over-aged Al-Zn-Mg alloys
过度时效Al-Zn-Mg合金中的空位和溶质共偏析η1界面
Yizi Ou, Yong Jiang✉, Yiren Wang, Zhengqing Liu, Adrian Lervik, Randi Holmestad
Yong Jiang: yjiang@csu.edu.cn, 中南大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117082
摘要
本研究利用第一性原理和扫描透射电子显微镜(STEM)研究了过度时效的Al-Zn-Mg合金中的η1/Al界面。作为主要的η-MgZn2 沉淀类型之一,η1倾向于与Al 基体形成高度一致的界面,同时在其界面层上存在多种溶质偏析模式。界面相图显示出富镁界面和富锌界面,这取决于Zn的化学势范围。然而,进一步的偏析计算强烈地表明,STEM Z-对比成像的界面是一个空位和溶质共同稳定的富Mg结构,在相对较低的Zn化学势下是有利的。基于实验和计算结果,使用广义的结构模型阐明了η1/Al界面的深刻的热力学起源及其错综复杂的偏析行为得到了澄清。本研究还预测了在更高的Zn化学势下的η1/Al界面结构和偏析现象,以便今后进行实验验证。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117181
2. Elevated-temperature Deformation Mechanisms in a CrMnFeCoNi High-Entropy Alloy
CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金的高温变形机制
M.Zhang, E.P.Georgeb, J.C.Gibeling✉
J.C.Gibeling: jcgibeling@ucdavis.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117181
摘要
本研究在1073K下对CrMnFeCoNi 高熵合金进行了应力降低蠕变实验,以描述这种材料的稳态和瞬态蠕变特性。通过对恒定结构蠕变的测量,CrMnFeCoNi 变形的激活区被确定为∼100b2,并且随着施加应力的增加而减少,表明高温塑性变形存在着集中固溶和林位错控制。借助于最近的高熵合金固溶理论,使用Haasen 图对这两种机制进行了定量分离,结果显示CrMnFeCoNi的蠕变主要依赖于热激活,大部分的蠕变强度来自固溶硬化,尤其是在低外加应力下。本研究进行的总体分析显示,1073K下CrMnFeCoNi的稳态蠕变可以由现有的集中固溶硬化模型和林位错硬化模型充分描述。这一观察表明,有可能对这种合金从低温到高温的位错滑移动力学进行统一处理。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117204
3. Enhanced thermal stability of (Ti,Al)N coatings by oxygen incorporation
通过氧掺入提高了(Ti,Al)N涂层的热稳定性
Damian M. Holzapfel✉, Denis Music, Marcus Hans, Silas Wolff-Goodrich, David Holec, Dimitri Bogdanovski, Mirjam Arndt, Anders O.Eriksson, Kumar Yalamanchili, Daniel Primetzhofer, Christian H.Liebscher, Jochen M.Schneidera
Damian M. Holzapfel: holzapfel@mch.rwth-aachen.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117204
摘要
保护性涂层的热稳定性是先进的切削和成型应用以及能量转换的性能决定性特性之一。为了研究氧气的掺入对(Ti,Al)N 高温行为的影响,本研究使用反应电弧蒸发法合成了亚稳态的立方(Ti,Al)N 和(Ti,Al)(Ox N1-x)涂层。(Ti,Al)N 和(Ti,Al)(OxN1-x)涂层的X 射线衍射结果显示,与(Ti,Al)xN1-x相比,(Ti,Al)(OxN1-x)涂层在800°C左右开始了亚稳态分解,随后纤锌矿型固溶体的形成明显从1000°C 延迟到1300°C。结合空间分辨成分分析和量热数据计算出的空位形成能可以合理的解释这种热稳定性的增强。能量色散X射线光谱和原子探针断层扫描数据表明,与立方体(Ti,Al)(O,N)相比,在纤锌矿型固溶体中O的溶解度较低。因此,对于(Ti,Al)N 中富含AlN 的纤锌矿型的生长,只需要Ti 和Al 的迁移,而对于(Ti,Al)(O,N),除了移动的金属原子外,还需要非金属的迁移。在非金属子晶格上移动的先决条件是形成非金属空位,这需要比金属亚晶格更高的温度,因为与金属空位相比,非金属空位的形成能明显更大,这一概念与量热数据是一致的。此外量热数据也表明,在(Ti,Al)(O,N)中形成和生长纤锌矿型所需的综合能量比(Ti,Al)N 中大2 倍左右,导致本研究报告的热稳定性增加。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117175
4. NiTiHf shape memory alloys as phase change thermal storage materials
作为相变储热材料的NiTiHf形状记忆合金
N.Hite, D.J.Sharar, W.Trehern, T.Umale, K.C.Atli, A.A.Wilson, A.C.Leff, I.Karaman✉
I.Karaman: ikaraman@tamu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117175
摘要
最近的研究表明,镍钛形状记忆合金(SMAs)作为高品质(FOM)相变材料(PCMs)在热管理和存储方面的有效性,在此基础上,NiTiHf SMAs被探索作为具有高温性能的备选固-固相变材料。差示扫描量热法和阿基米德法被用来确定几种不同成分的NiTiHf SMAs 的相变温度、热滞后、相变焓和密度。在奥氏体阶段,Ni50.3Ti 29.7Hf 20(at. %)表现出32.5 J/g的高相变焓,31°C的相对低热滞后和11.19 Wm−1 K−1的热导率。总的来说,NiTiHf SMAs 表现出的FOM值比传统的PCMs高一个数量级,比二元NiTi SMAs中测得的FOM值高120%左右。在本研究中,相变温度、相变焓和热滞后有关的明确关系通过成分控制来调整NiTiHf SMAs的具体热能储存应用提供了可能。高FOM 值与超过500℃的相变温度相结合,使NiTiHf合金填补了高FOM PCMs 的FOM 与相变温度属性空间的空白区域。

ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117203
5. J-integral analysis of the elastic strain fields of ferrite deformation twins using electron backscatter diffraction
利用电子背散射衍射分析铁氧体变形孪晶弹性应变场的j积分
Abdalrhaman Koko✉, Elsiddig Elmukashfi, Kalin Dragnevski, Angus J.Wilkinson, Thomas James Marrow
AbdalrhamanKoko: abdo.koko@materials.ox.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117203
摘要
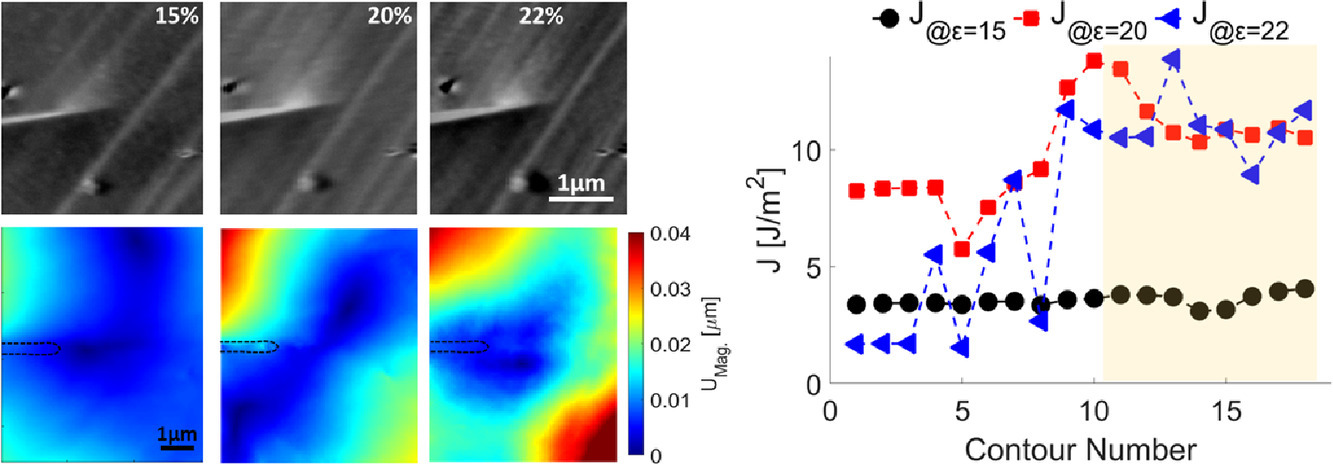
本研究利用高分辨率电子背散射衍射(HR-EBSD),对时效硬化双相不锈钢(Zeron 100:25%Cr,7%Ni)铁素体基体中的变形孪生体的应变场进行了原位和非原位(未加载)的研究。首次使用应变能量释放率(J-积分)对作用于双尖端的局部二维(2D)弹性应变场进行了参数化,然后分解为I型和II型应力强度因子(KI和KII)。根据HR-EBSD 互相关峰值高度和平均角度误差之间的关系,使用了一种改进的应变参考点选取方法。由KI描述的弹性场随着孪晶厚度增加而增大。由KII描述的平面内剪切力场在去除载荷后会变得松弛。而且讨论了目前二维分析的一些局限性,其目的是提供一种实验方法来量化描述孪晶增厚和传播的局部边界条件的场。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117213
6. Segregation competition and complexion coexistence within a polycrystalline grain boundary network
多晶晶界网络中存在的偏析竞争和络合共存
Pulkit Garg, Zhiliang Pan, Vladyslav Turlo, Timothy J.Rupert✉
Timothy J.Rupert: trupert@uci.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117213
摘要
界面偏析可以稳定晶粒结构,甚至导致晶界络合物的转变。然而,对多晶材料中这种现象的复杂性的理解是有限的,因为大多数研究集中在几何双晶上。在本研究中,使用混合Monte Carlo /分子动力学模拟研究了多晶Cu-Zr合金中的界面偏析和随后的络合物转变。在中等温度下,Zr掺杂对纯Cu多晶的晶粒尺寸和结构没有明显影响,其中晶界偏析是主要行为。边界网络内的偏析是不均匀的,一些边界的局部浓度比全局值大一个数量级,而其他边界几乎没有偏析,并且发现边界自由体积和能量等物理参数的变化与掺杂剂浓度相关。此外,在更高的温度下对另一个合金样品进行了研究,以探究界面结构中广泛的转变,其中相当一部分原本有序的边界过渡到非晶络合物,证明了多种络合物类型的共存,每一种都有自己的边界化学成分的分布。总的来说,本研究强调了界面偏析和络合结构在多晶体网络中可以是多样化的。本研究显示的研究结果补充了现有的对单个界面的计算和实验研究,有助于为揭开现实微结构中界面结构的复杂性铺平道路。

ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117166
7. Evolution of martensitic microstructures in nanocrystalline NiTi wires deformed in tension
纳米晶NiTi钢丝拉伸变形中马氏体组织的演化
Orsolya Molnárová, Ondřej Tyc, Luděk Heller, Hanuš Seiner, Petr Šittner✉
Petr Šittner: sittner@fzu.cz
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117166
摘要
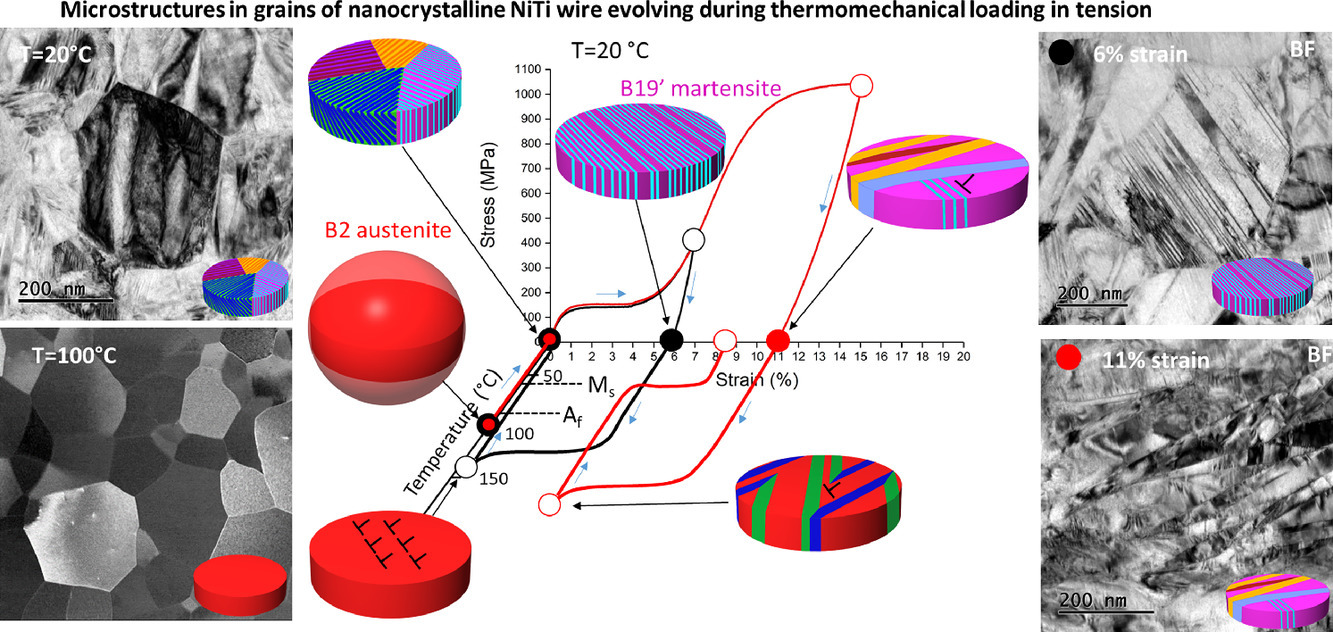
本研究介绍了一种可以重建纳米NiTi丝拉伸热机械加载过程中马氏体变化组织的实验方法。该方法是基于使用TEM中选择区域电子衍射以及暗场图像分析确定所有马氏体变体和界面的位置、尺寸和取向。
在室温(100°C)下,马氏体组织在NiTi 线材变形到重定向(转变)平台末端,应变达到7%,分别被发现包含单畴(001)复合孪晶马氏体填充变形线材的整个晶粒中。通过对在拉伸变形的<111>纤维织构的NiTi合金线中的应变调节进行理论处理,使这一观察结果合理化。并预测了变形率高达6.75%的NiTi合金线的晶粒中的这种单一的组织状态。在随后的卸载和超过Af 温度的无应力加热中,这种马氏体组织重新转化为母体奥氏体,产生NiTi丝典型的可恢复应变(6%),并伴随着非常小的未恢复应变(0.6% - 1.5%,取决于测试温度)。
当进一步的拉伸载荷达到15%的应变时,取向马氏体的塑性变形通过马氏体中协调的(100)和(20-1)变形孪晶在[100](001)位错滑移的协助下进行,从而在单个马氏体晶格中形成具有变形带的特征马氏体组织,且常常形成楔形。在随后的卸载和超过Af 温度的无应力加热中,这种马氏体组织转变为{114}孪生奥氏体组织,产生非常大的可恢复应变(10%)和大的未恢复应变(5%)。据称,位错滑移辅助马氏体中的(100)和(20-1)变形孪晶使NiTi具有优异的强度和变形能力,并通过引入{114}奥氏体孪晶来完成奥氏体组织的细化。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117217
8. Microstructure tailoring of Al-containing compositionally complex alloys by controlling the sequence of precipitation and ordering
通过控制析出和排序的顺序对含铝成分复杂的合金进行组织调控
Stephan Laube, Steven Schellert, Aditya Srinivasan Tirunilai, Daniel Schliephake, Bronislava Gorr, Hans-Jürgen Christ, Alexander Kauffmann✉, Martin Heilmaier
Alexander Kauffmann: alexander.kauffmann@kit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117217
摘要
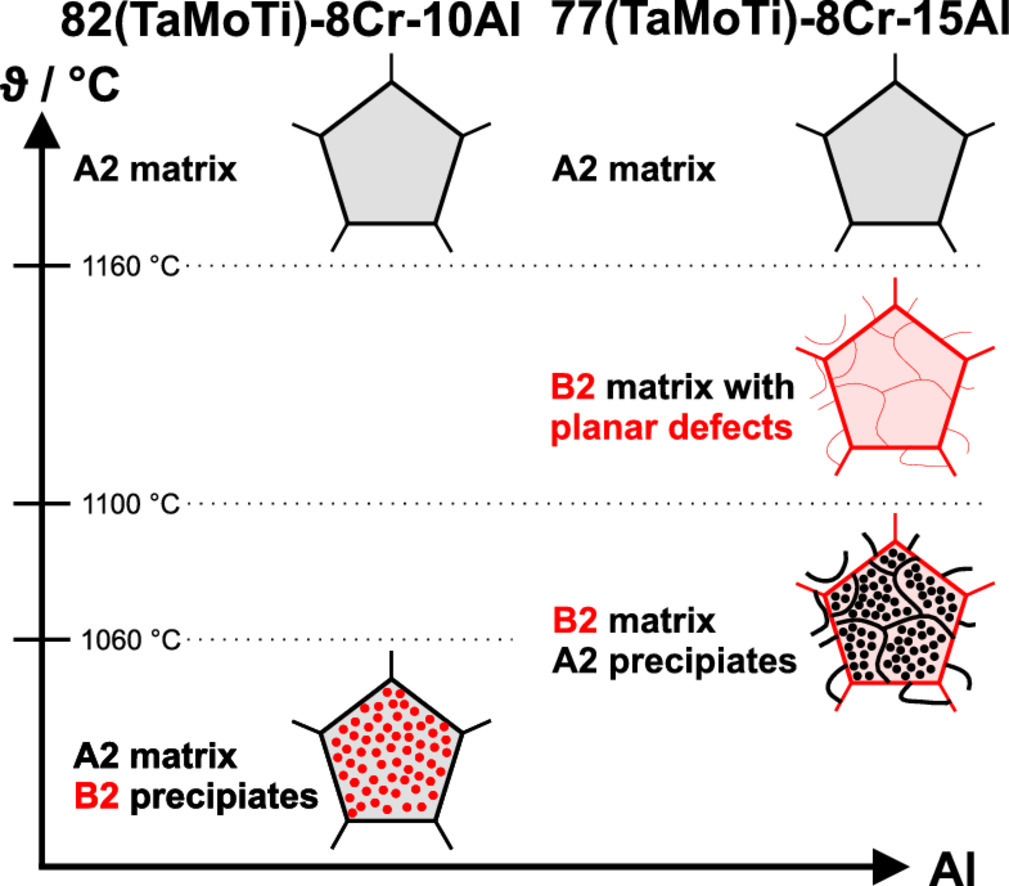
难熔金属基含铝成分的复杂合金(RCCA)是高温结构应用的有希望的候选材料。为了阐明复杂的相变,本研究进行了热力学计算以选择两种具有不同相变顺序的代表性合金。这些成分的样品是通过纯元素电弧熔化后进行均质化处理合成的,以实验验证室温组织并评估相变。均质化和淬火后的差示扫描量热法(DSC)、扫描(SEM)和透射电子显微镜(TEM)研究显示了多个不同的转变序列。(i) 82(TaMoTi)-8Cr-10Al(at.%)表现出与析出相的有序化同时存在的固态相分离。这导致了无序的基体和有序的析出相。热分析表明,当从高温A2 相冷却时,相分离和有序化分布在一个很大的温度范围内(约750-1250℃),在1055℃时出现峰值。(ii) 在77(TaMoTi)-8Cr-15Al合金中,1155℃的连续相变导致了具有平面断层的单相B2 基体。在稍低的温度下(约1096°C)发生相分离,导致B2基体在平面断层处和A2析出物处发生偏析。在两种所研究的成分中,A2相都富含Ta和Mo。相反,B2相富含Al和Ti,而Cr则均匀地分布在各相中。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117201
9. Tailoring thermal expansion of shape memory alloys through designed reorientation deformation
通过设计的再取向变形调整形状记忆合金的热膨胀
Qiao Li, Yusuke Onuki, Qingping Sun✉
Qingping Sun: meqpsun@ust.hk, 香港科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117201
摘要
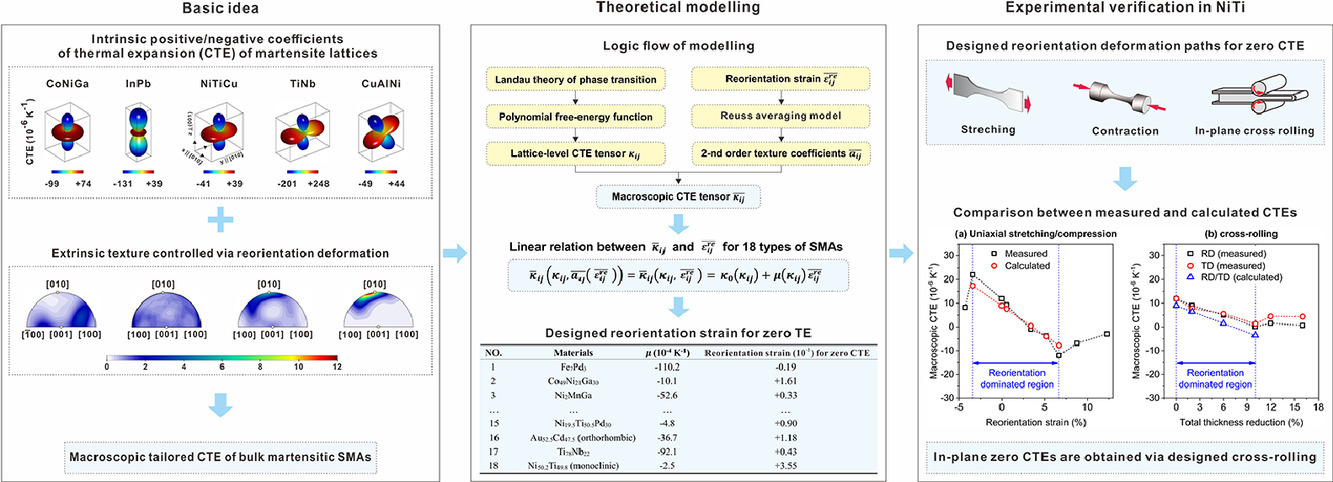
通过微观结构工程操纵宏观线性热膨胀(TE)是形状记忆合金(SMA)的一个新的研究课题。本研究采用建模和实验相结合的研究,以设计和调整基于再取向变形的多晶马氏体SMA的TE(CTE)系数。利用一阶相变的Landau 热力学理论,证明了大多数SMAs的马氏体晶格沿着相变伸长(收缩)的方向拥有内在负(正)TE。作为这种内在晶格级TE 和外在的再取向变形织构的共同作用,马氏体多晶体的整体线性CTE 随着再取向拉伸(收缩)量的增加而减少(增加)。设计的变形路径和应变幅度是为了在17种SMA中获得零线性TE,并得到了现有实验数据的验证。此外,通过在马氏体NiTi板上设计交叉轧制,获得了超低的面内CTE(+0.13×10−6 K−1∼+1.4×10 −6 K−1),这比SMA 的报告值要小,甚至比商用FeNi Invar合金(+2.0×10 −6 K−1)还要小。本研究为许多应用设计具有所需线性CTE 的SMA 提供了理论基础。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117200
10. Learning from superelasticity data to search for Ti-Ni alloys with large elastocaloric effect
从超弹性数据中寻找具有大弹性热效应的Ti-Ni合金
Lei Ding, Yumei Zhou✉, Yangyang Xu, Pengfei Dang, Xiangdong Ding, Jun Sun, Turab Lookman✉, Dezhen Xue✉
Yumei Zhou: zhouyumei@xjtu.edu.cn, 西安交通大学
Turab Lookman: turablookman@gmail.com
Dezhen Xue: xuedezhen@xjtu.edu.cn, 西安交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117200
摘要
在本研究中,形状记忆合金的可逆绝热温度变化(ΔTad)被证明与卸载期间反向马氏体相变所释放的机械功(ΔWu)成正比。由于在形状记忆合金中存在大量的超弹性应力-应变测量数据(ΔWu),所提出的关系使我们能够在没有热量测量的情况下预测ΔTad。从不同的Ti-Ni 合金的ΔWu 估算出的ΔTad 与直接测量值显示出良好的线性关系。此外,按照这样的设计标准,通过调整成分和热机械处理,实现了一组Ti-Ni 二元形状记忆合金的直接测量ΔTad 大于35K 的张力。较大的ΔTad 和ΔWu 可以归因于热机械处理后的晶粒细化和非均质内应力场,这增强了超弹性的临界应力和卸载时马氏体相变的可恢复性。

ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117232
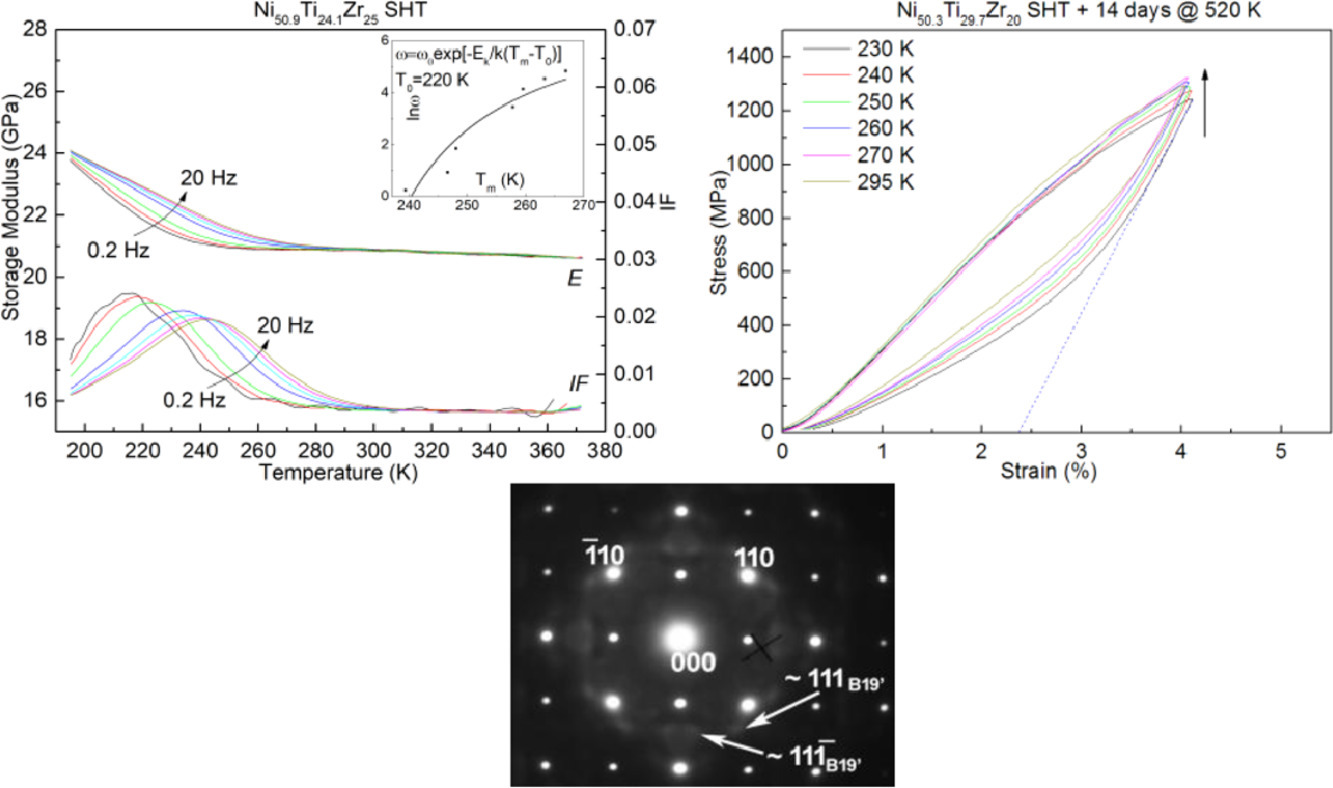
11. Strain glass state in Ni-rich Ni-Ti-Zr shape memory alloys
富镍Ni-Ti-Zr形状记忆合金中的应变玻璃态
S. Xu, J. Pons✉, R. Santamarta, I. Karaman, O. Benafan, R.D. Noebe
J. Pons: jaume.pons@uib.es
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117232
摘要
本研究报告了在富含镍的Ni-Ti-Zr 形状记忆合金中存在由H相沉淀的前体阶段诱导的应变玻璃状态,这是这种合金系统的典型情况。通过动态力学测试、电子衍射和透射电子显微镜(TEM)对应变玻璃进行了检测。弹性模量的测量也表明在这些合金中存在elinvar 效应。这种材料的应变玻璃状态在压缩时表现出超弹性效应,可恢复的应变水平超过4%,并且在230到300K的温度范围内,应力-应变曲线的温度依赖性很小。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117214
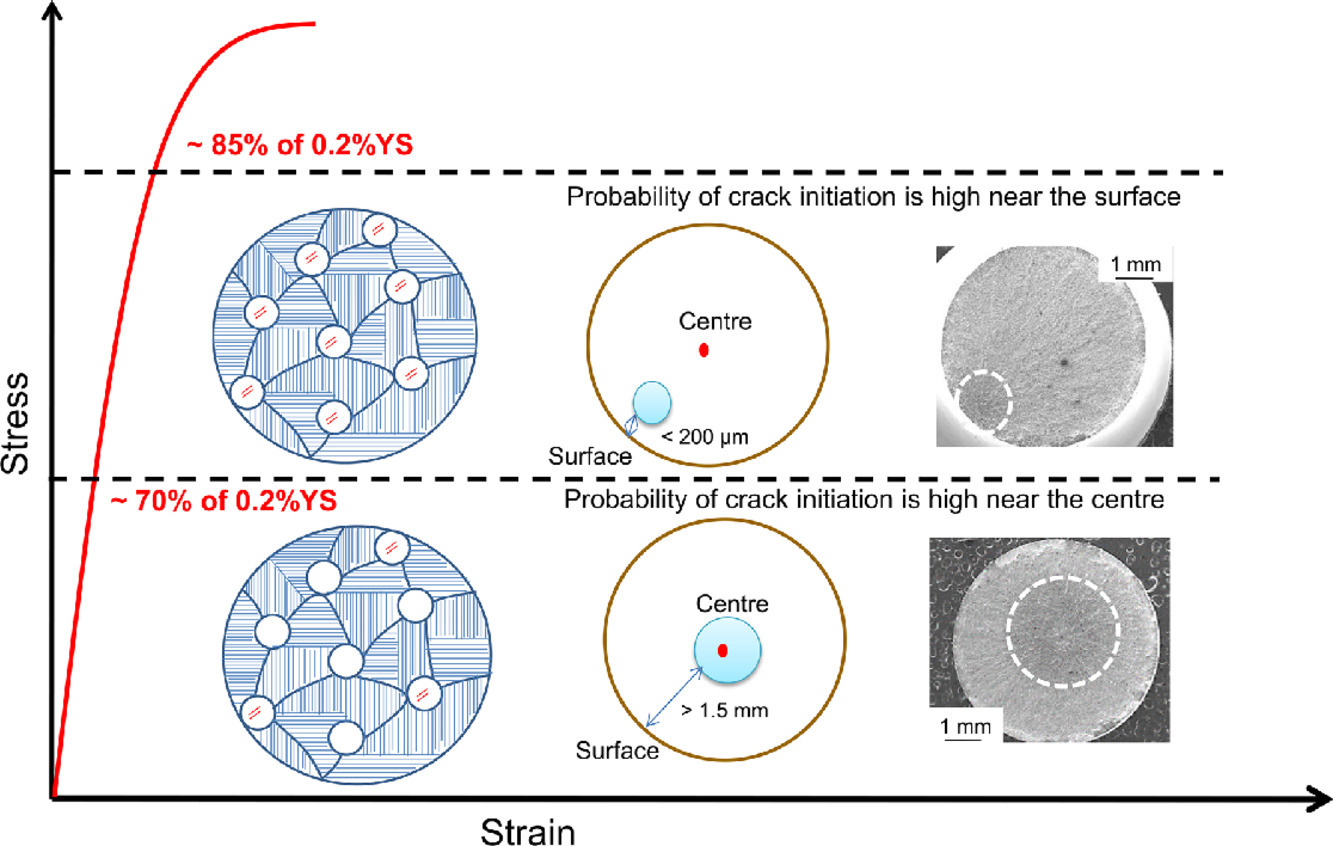
12. On the probabilistic assessment of variability in fatigue life in a near α titanium alloy Timetal 834: Crystallography of fatigue crack initiating facets
关于近α钛合金Timetal 834疲劳寿命变异的概率评估:疲劳裂纹起始面的晶体学
Kartik Prasad✉, Rajdeep Sarkar, Vajinder Singh, PGhosal, Amit Bhattacharjee, Hina Gokhale
Kartik Prasad: kartik@dmrl.drdo.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117214
摘要
在本研究中,研究了近α钛合金Timetal 834在五个最大循环应力水平(即826、778、680、583 和486 MPa)下的高循环疲劳行为的变化。结果发现,循环应力水平的降低导致疲劳寿命的变化增加。在所有的测试样品中,通过扫描电子显微镜对失效样品进行微观结构观察,发现疲劳断裂的部位为切面(s)。在大多数失效的样品中,这些切面的形态与相对较大的初级α晶粒(s)相似。对486兆帕的应力水平相对应的疲劳寿命的概率评估显示了累积分布函数中的三个斜率区域。这三个区域与切面的方向相吻合,即切面与加载轴的角度,这是用倾斜断裂法确定的。疲劳寿命<105次循环的样品显示出与加载轴的切面角≤30°,而在疲劳寿命>107次循环的长寿命样品中,切面角被发现接近45°。这反过来突出了剪切应力分量在提高Timetal 834 整体疲劳寿命中的主导地位。事实证明,基于机制的延长寿命方法可使得寿命延长四倍。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117222
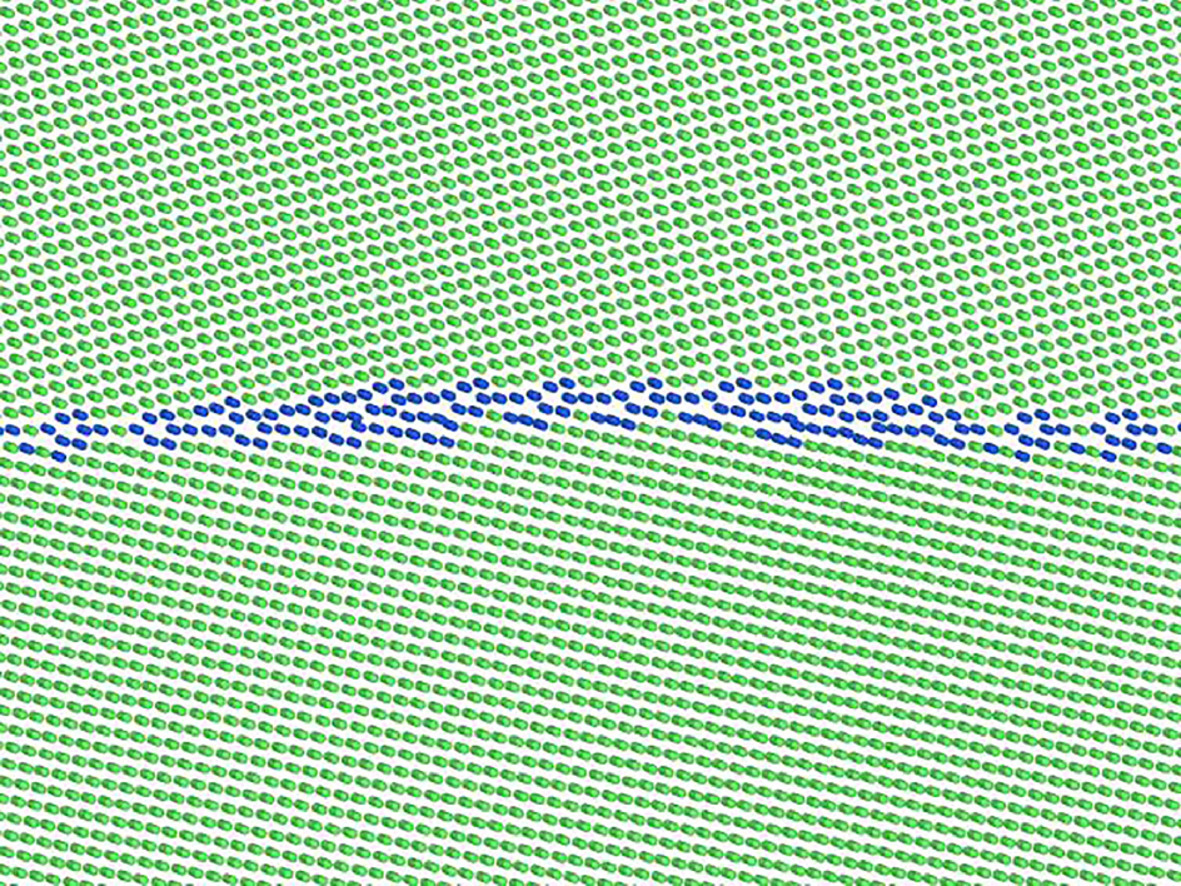
13. Multiple coupling modes to relax shear strain during grain boundary migration
晶界迁移过程中松弛剪切应变的多种耦合模式
N. Combe✉, F. Mompiou, M. Legros
N. Combe: combe@cemes.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117222
摘要
在没有位错活动的情况下,剪切耦合晶界(GB)迁移是一种有效的塑性机制,更适合在纳米晶金属。对于一个给定的GB,几种应力引起的迁移机制,被称为耦合模式,参与减少剪切产生的弹性能量。它们通过被称为断开的界面缺陷的形成和运动来运作,携带由其Burgers向量为特征的基本剪切应变。然而,到目前为止,耦合模式只在简单的剪切力下被研究,这种情况远没有在应力张量存在多个分量的多晶体中预期的那么复杂。本研究提出了一个更系统的模式,即复合剪切力被应用时的耦合模式。这促进了新的耦合模式的发现。本研究使用分子动力学模拟证明了这些多重耦合模式和它们的关联断开的操作。此外,研究还表明,即使在低温下,GB 迁移也可能通过两种模式的连续出现而发生:松弛的剪切力当时作为一个有效的参数出现,是由两个运行的基本机制的组合产生的。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117216
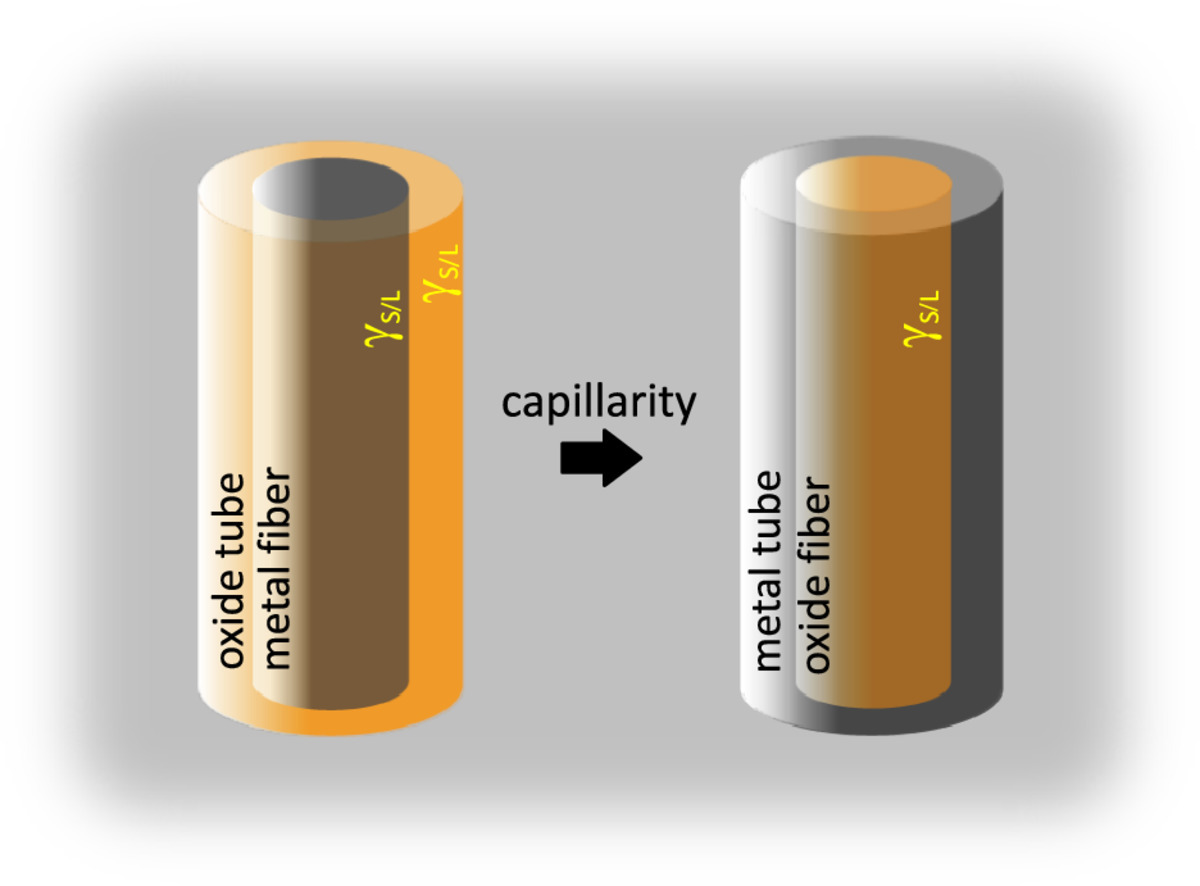
14. Gibbs-Thomson effect as driving force for liquid film migration: Converting metallic into ceramic fibers through intrinsic oxidation
Gibbs-Thomson效应作为液膜迁移的驱动力:通过内在氧化将金属转化为陶瓷纤维
M. Dias✉, M. Rosiński, P.C.R. Rodrigues, J.B. Correia, P.A. Carvalho✉
M. Dias: marta.dias@ctn.ist.utl.pt
P.A. Carvalho: patricia.carvalho@sintef.no
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117216
摘要
液膜迁移在材料工程中具有重要的实际意义。该现象已被证明取决于热梯度和相干应变,但似乎没有一个单一的驱动机制能够证明整个实验观察的合理性。另一方面,由于系统未知的三维几何形状,不可避免的毛细管效应常常被忽略。本研究通过一个圆柱形界面的微观结构设置,提出了主要由毛细作用支配的液膜迁移的证据,可以清楚地解释和建立模型。实验依靠的是分散在钨基体中的钽纤维强大的吸氧能力和脉冲等离子体压实提供的场增强扩散性。钽清除了存在于W粉中的残余氧,因此,氧化膜在纤维周围生长。这些在烧结过程中处于液态的氧化物管向纤维轴线迁移,最终成为被金属Ta 包围的氧化棒。这个过程是由Gibbs-Thomson 效应驱动的,它产生了整个液态膜所需的成分梯度。通过结合传入的O通量和毛细管驱动的迁移,对薄膜的演变进行了分析描述。并且研究了其他机制的可能贡献,并确定了Gibbs-Thomson效应与液膜迁移的一般现象的关联性。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117215
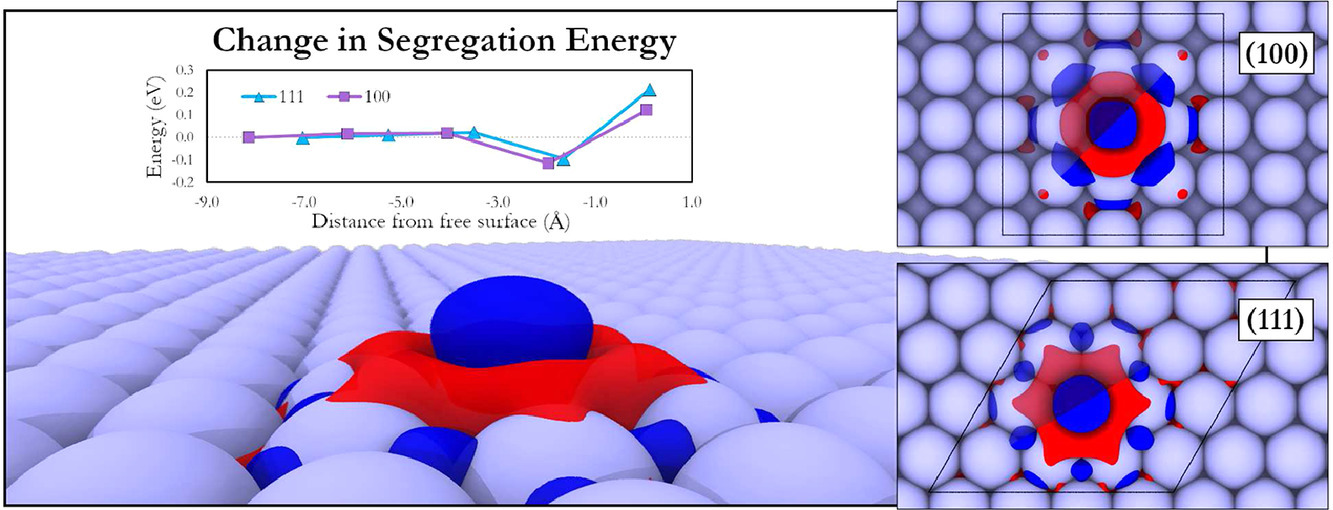
15. An electronic origin to the oscillatory segregation behavior in Ni-Cr and other BCC defects in FCC metals
FCC金属中Ni-Cr和其它BCC缺陷中振荡偏析行为的电子起源
Jacob Startt, Rémi Dingreville, Stephen Raiman, Chaitanya Deo✉
Chaitanya Deo: chaitanya.deo@me.gatech.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117215
摘要
Ni-Cr合金在低指数表面附近表现出振荡的偏析行为,其中首选的偏析物种从第一层的Ni变为第二层的Cr。在许多稀合金系統中,这种振荡模式是由于在偏析溶质或杂质原子周围的局部晶格中应力的弹性释放所造成的。这些应力大多被认为是由于溶质和宿主原子的原子大小不匹配造成的。然而,在Ni-Cr合金中,不存在明显的原子尺寸不匹配,这导致了关于这种合金中振荡行为的起源问题的质疑。本研究利用密度泛函理论对FCC Ni的(100)和(111)表面的单个Cr原子的偏析进行了建模,这种合金表现出这种振荡行为。并且使用Bader 电荷分析研究表明,负能量与Cr原子上的电荷量直接相关。当Ni原子从Cr原子上剥离价电荷时,Cr原子在尺寸上略有收缩。Cr的最大收缩和最高的正电荷发生在系统表现出振荡的负偏析能的表面的第二层中。然后研究发现这种行为在其他合金系统(Ag-Nb、Cu-Cr、Pt-Nb和Pt-V)中仍然存在,这些合金系统表现出与Ni-Cr类似的原子半径以及宿主和溶质之间的电负性差异。这些合金代表中主体金属表现出FCC基态结构,而溶质金属表现出BCC基态结构。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117218
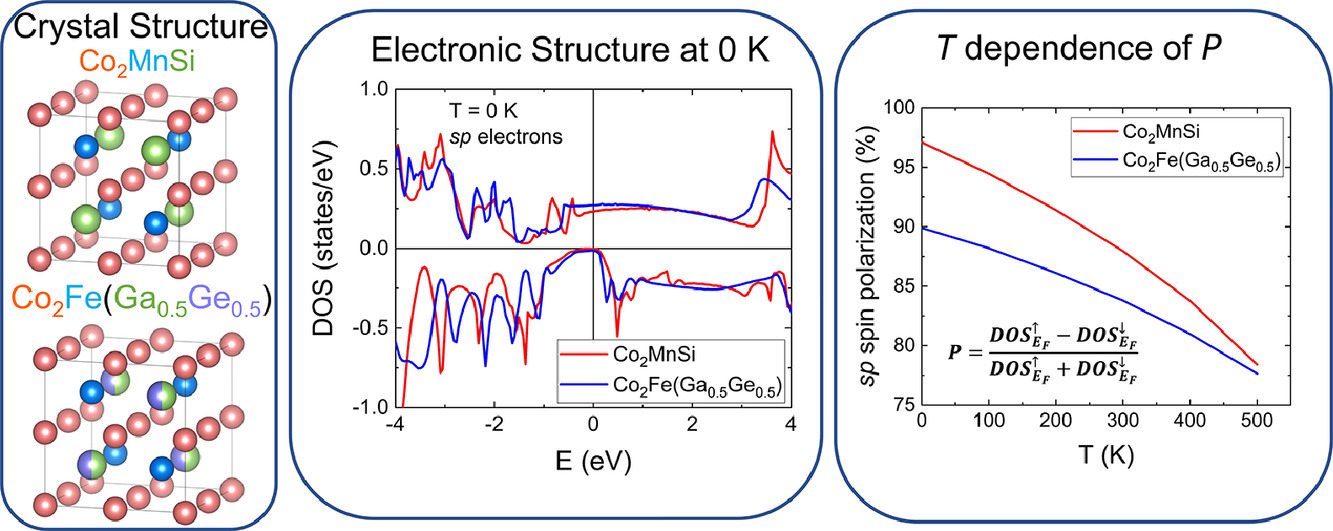
16. First-principles disordered local-moment study on temperature dependence of spin polarization in Co2Fe(Ga0.5Ge0.5) Heusler alloy
Co2Fe(Ga0.5Ge0.5) Heusler合金自旋极化温度依赖的第一性原理无序局域矩研究
Ivan Kurniawan, Kenji Nawa, Keisuke Masuda, Yoshio Miura✉, Kazuhiro Hono
Yoshio Miura: miura.yoshio@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117218
摘要
用半金属Co基Heusler合金(Co2YZ)制造的磁阻(MR)器件具有较大的MR比率,但会出现显著的温度退化。在有限的温度下,块状电极中的自旋极化减少是MR比率降低的一个可能原因。在这项研究中,使用密度函数理论和无序局部矩法研究了Co2Fe(Ga0.5Ge0.5)(CFGG)自旋极化的温度依赖性。研究发现,与众所周知的Co2MnSi (CMS)半金属相比,CFGG在有限温度下的自旋极化减少得更少,这是因为CFGG的居里温度比CMS高。另一方面,研究还发现通过电子和空穴掺杂在在刚性带模型中CFGG的半金属间隙中调节费米能级位置,可以改善自旋极化的温度依赖性。然而,与0K时的化学计量CFGG相比,电子和空穴掺杂对应的非化学计量的富Co和富Fe的CFGG显示出自旋极化的减少。因此,本研究提出通过改变Co2YZ的Y 和Z 位点组成来调节费米能级位置将是改善自旋极化的温度依赖性的必要条件。
ACTA
Vol. 218,1 Oct. 2021, 117220
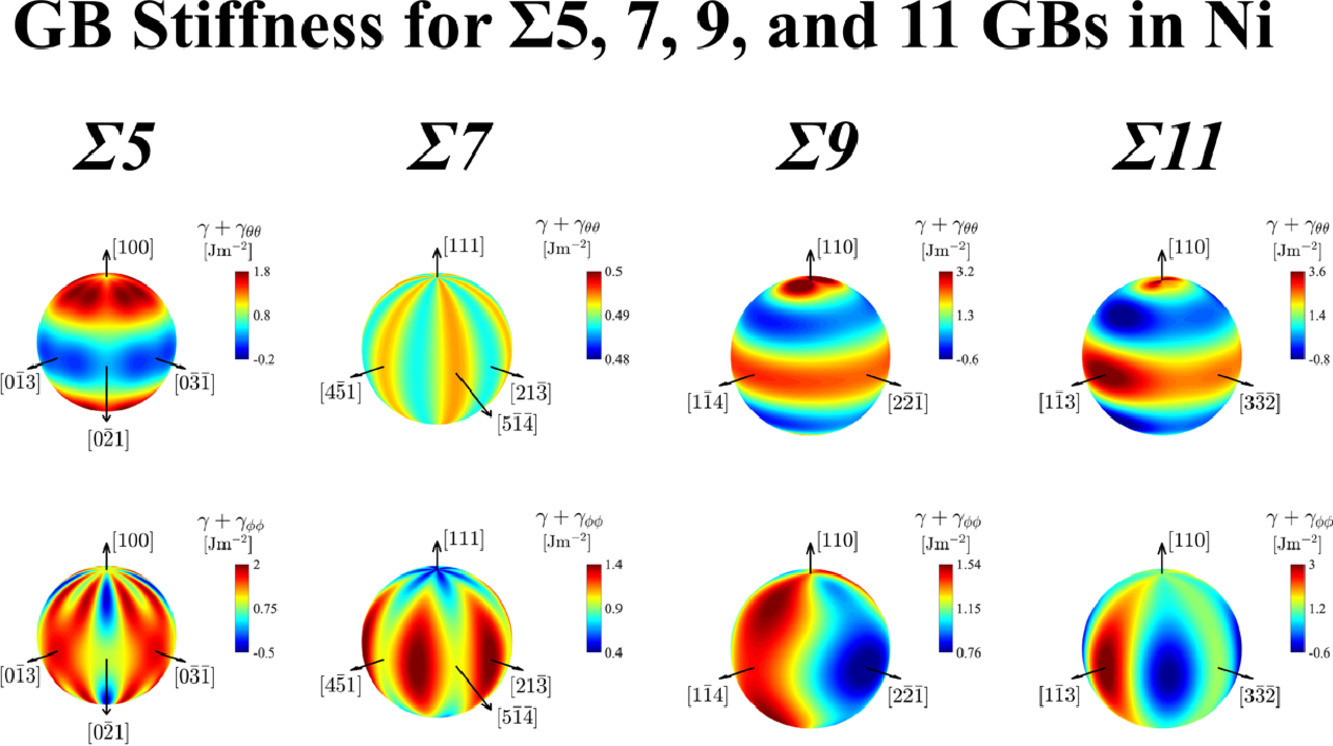
17. The grain boundary stiffness and its impact on equilibrium shapes and boundary migration: Analysis of the Σ5, 7, 9, and 11 boundaries in Ni
晶界刚度及其对平衡形状和晶界迁移的影响:Ni中Σ5、7、9和 11晶界的分析
Robert D. Moore, Timothy Beecroft, Gregory S.Rohrer, Christopher M.Barr, Eric R.Homer, Khalid Hattar, Brad L.Boyce, Fadi Abdeljawad✉
Fadi Abdeljawad: fabdelj@clemson.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117220
摘要
晶界(GBs)在材料加工过程中微观组织的形成及其随后在使用条件下的演变中起着关键作用。虽然GB取向偏差通常被用来描述边界的特性,但更完整的描述还应该考虑到GB平面法线,其中GB刚度是控制许多GB动态过程的相关特性。在本研究中,利用已发表的原子模拟数据构建了Ni中Σ5、7、9和11GBs的完整GB能量-平面法线图。函数拟合被用来获得GB刚度作为平面法向函数的完整映射,构建了平衡形状并确定GB迁移的驱动力。结果表明,GB 刚度的大小和各向异性可能比能量本身更大。此外,许多边界倾角被发现表现出负的刚度,表明有分面的倾向。GB 刚度分析结果显示与多晶Ni中的实验性GB平面法线分布有定性的一致性。从广义上讲,研究结果为解释在中尺度处理GB迁移和微观组织演变中GB属性的平面法相依赖提供了未来的途径。