金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.188,1 Nov. 2020(下)
2020-08-31 来源: Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文13篇,涵盖了9Cr钢、镁铝合金、中熵合金、高熵合金、锆合金、单晶钨等,国内科研单位包括浙江大学、北京交通大学、中科院、中南大学、上海交通大学、上海工程技术大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 188 目录
16. Nondestructive evaluation of macro segregation in creep strength enhanced 9Cr-1Mo-V-Nb steel
9Cr-1Mo-V-Nb蠕变强度强化钢宏观偏析的无损鉴定
17. Role of intersecting grain boundary on the deformation of twin-twin intersection
铁素体基氧化物弥散强化钢凝固过程中纳米氧化物的析出动力学
18. The engulfment of precipitate by extension twinning in Mg-Al alloy
Mg-Al合金中扩展孪生“吞噬”析出的现象研究
19. Oriented nucleation causing unusual texture transition during static recrystallization annealing in cold-rolled Mg-Zn-Gd alloys
冷轧Mg-Zn-Gd合金静态再结晶退火过程中定向形核引起异常的织构转变
20. Strengthening CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy by tuning lattice defects
通过调整晶格缺陷强化CoCrNi中熵合金
21. Assessing the influence of hydrogen on texture evolution in polycrystalline nickel deformed under uniaxial tension
评估多晶镍在单轴拉伸变形过程中氢对织构演化的影响
22. Phase decomposition in a nanocrystalline CrCoNi alloy
多晶CrCoNi合金的相分解行为
23. Impact of interstitial carbon on self-diffusion in CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys
间隙碳原子对CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金自扩散的影响
24. Reversion and re-aging of a peak aged Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy
峰时效状态的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金的逆转变和再时效行为
25. The gradual disappearance and re-appearance of yield drop by modulating the pre-strain history in a new zirconium alloy: Dislocation decomposition and recombination
新型锆合金中调节预应变历史引发屈服下降的逐渐消失与重现:位错分解与重组的影响
26. Up-hill diffusion of solute atoms towards slipped grain boundaries: A possible reason of decomposition due to severe plastic deformation
溶质原子向滑移晶界处的上坡扩散:强烈塑性变形引发分解的可能原因
27. Impact of krypton irradiation on a single crystal tungsten: Multi-modal X-ray imaging study
多模态X射线成像技术研究氪辐照对单晶钨的影响
28. Tuning magnetocaloric effect of Ho1-xGdxNi2 and HoNi2-yCoy alloys around hydrogen liquefaction temperature
在氢液化温度附近调节Ho1-xGdxNi2和HoNi2-yCoy合金的磁热效应
SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P179-182
16. Nondestructive evaluation of macro segregation in creep strength enhanced 9Cr-1Mo-V-Nb steel
9Cr-1Mo-V-Nb蠕变强度强化钢宏观偏析的无损鉴定
Kazuhiro Kimura✉, Kwangsik Kwak, Shoichi Nambu, Toshihiko Koseki
Kazuhiro Kimura: kimura.kazuhiro@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.039
摘要
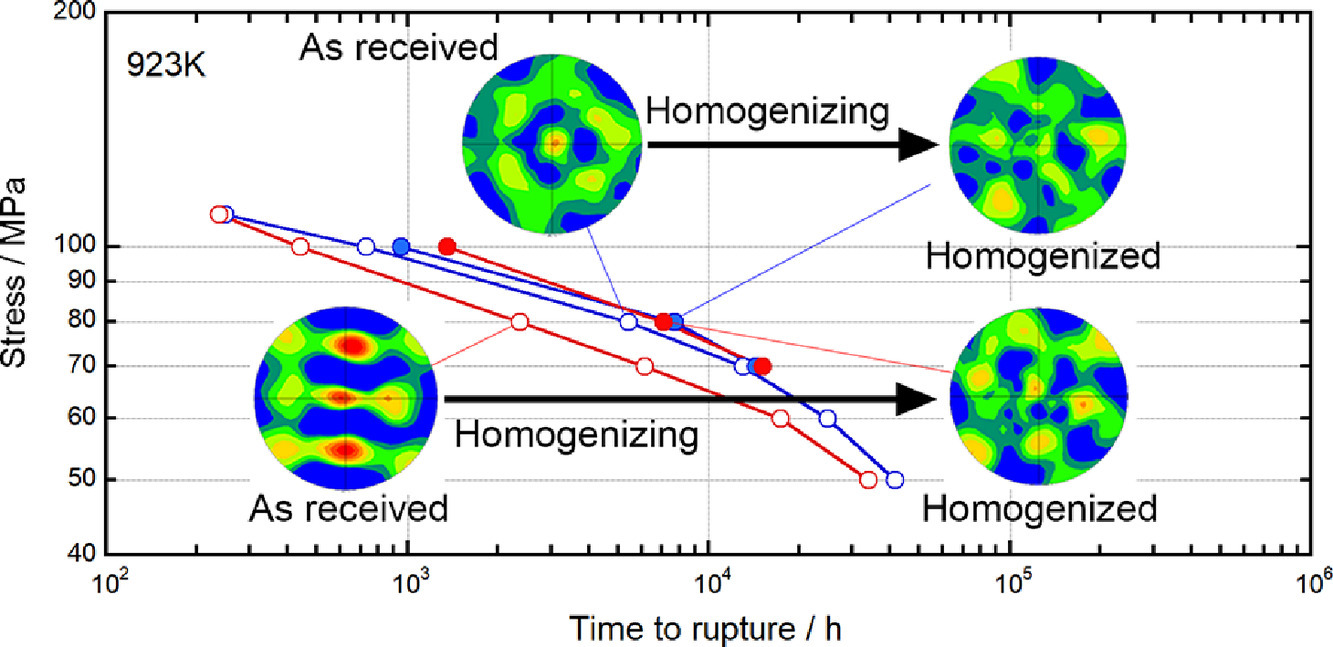
本工作研究了宏观偏聚和均匀化热处理对9Cr-1Mo-V-Nb钢(T91)抗蠕变强度的影响。结果表明织构,作为宏观偏聚的简单指标,可以用来评价钢的抗蠕变强度。
英文摘要
Effects of macro segregation and homogenizing heat treatment on creep strength of 9Cr-1Mo-V-Nb (Grade T91) steel have been investigated and it has been concluded that texture is useful feature to evaluate creep strength of the steel as a straightforward index of macro segregation.
SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P184-189
17. Role of intersecting grain boundary on the deformation of twin-twin intersection
交叉晶界对孪晶交叉变形的影响
Shuchun Zhao, Qi Zhu, Kexing Song, Haofei Zhou, Jiangwei Wang✉
Jiangwei Wang: jiangwei_wang@zju.edu.cn,浙江大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.034
摘要
高分辨透射电镜下的原位纳米力学测试结果表明,孪晶交叉区域的晶界(GBT)或者通过挪动(shuffling)过程进行迁移来促进位错传递,或者促使两个交叉孪晶间的位错交滑移。GBT处的应力状态、能垒和几何结构能够影响交叉区域的这两种位错活动。而且,新到来的孪晶内部的位错可以通过位错-GBT的反应穿过GBT。本工作的发现对于理解纳米孪晶材料的变形具有通用意义。
英文摘要
Using in situ nanomechanical testing under high-resolution transmission electron microscope, we reveal that the grain boundary at the twin-twin interaction region (referred to as GBT) can either migrate via a shuffling process to contribute to the dislocation transmission or facilitate the dislocation cross-slip between the two intersected twins. Stress condition, energy barrier and geometric structure of the GBT can influence these two modes of dislocation activities at the intersection region. Besides, the dislocations inside the incoming twin can traverse the GBT by dislocation-GBT reactions. These findings should have general implications to the understanding of the deformation of nanotwinned materials.

SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P195-199
18. The engulfment of precipitate by extension twinning in Mg-Al alloy
Mg-Al合金中扩展孪生“吞噬”析出的现象研究
Xiao-Zhi Tang, Ya-Fang Guo✉
Ya-Fang Guo: yfguo@bjtu.edu.cn,北京交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.020
摘要
为了理解Mg-Al合金中析出阻碍孪晶后引发塑性的强化机制,本文基于原子尺度的模拟实现了对于阻碍孪晶增厚引发的临界分切应力的测量,特别是在1.7×106 s-1的超低应变速率下。结果揭示了温度和应变速率对析出强化显著的耦合作用。当共格孪晶界的迁移为纯应力驱使而不存在热激活的情况下,由于背应力主导奥罗万应力(Orowan stress),这种强化效应就会消失。在有限的温度下,这种强化效应会变得很显著,且被高应变速率明显放大。
英文摘要
To understand the strengthening mechanism of precipitate against twin-mediated plasticity in magnesium–aluminum alloys, the measurements of the increase in the critical resolved shear stress due to impediment on twin thickening are accomplished based on atomistic simulation, specifically at a significantly low strain rate of 1.7 × 106 s-1. Results show conspicuous coupled effect of temperature and strain-rate on the precipitation strengthening. The strengthening effect vanishes if coherent twin boundary migration is purely stress-driven without thermal activations, due to the back-stress dominating over Orowan stress. At a finite temperature the strengthening effect becomes observable, and is distinctly amplified by high strain rates.

SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P200-205
19. Oriented nucleation causing unusual texture transition during static recrystallization annealing in cold-rolled Mg-Zn-Gd alloys
冷轧Mg-Zn-Gd合金静态再结晶退火过程中定向形核引起异常的织构转变
L.Y. Zhao, H. Yan✉, R.S. Chen✉, En-Hou Han
H. Yan: hyan@imr.ac.cn,中科院
R.S. Chen: rschen@imr.ac.cn,中科院
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.037
摘要
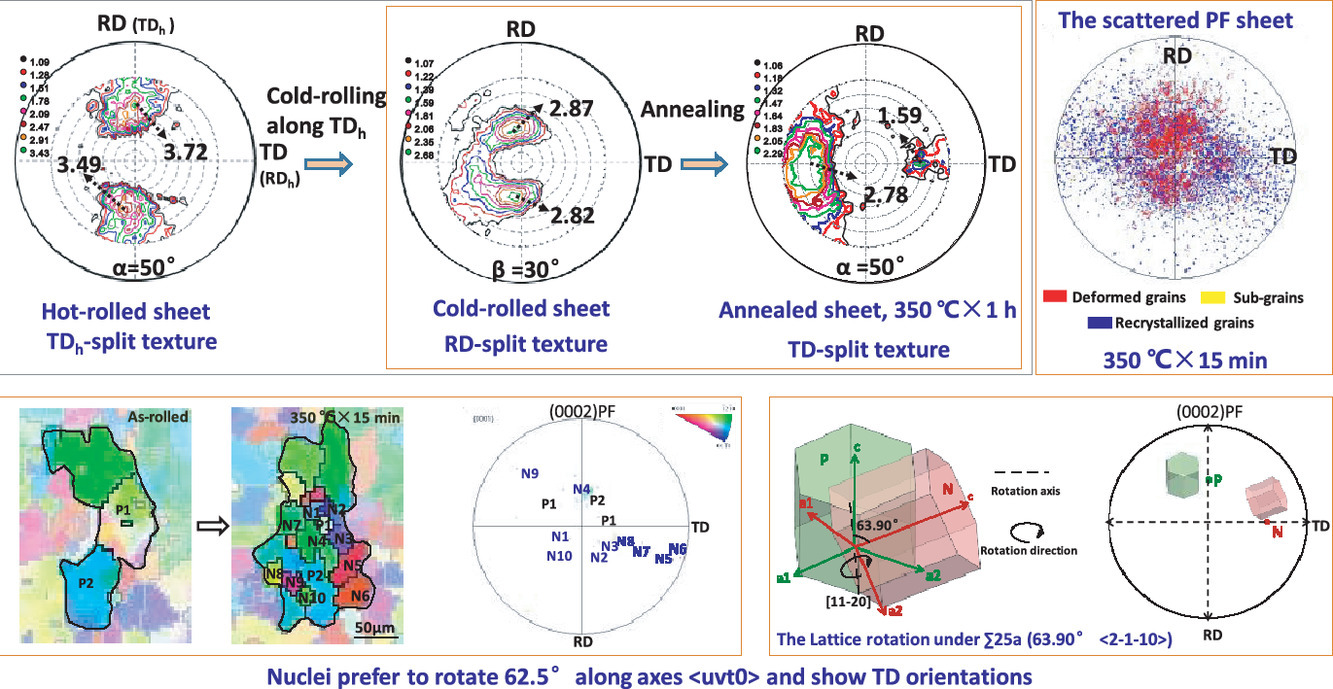
本工作通过准原位电子背散射衍射方法追踪了冷轧Mg-Zn-Gd合金退火过程中的静态再结晶、晶核取向和织构演化。我们观察到了从“轧制方向-分裂(rolling direction (RD)-split)”到“横向-分裂(transverse direction (TD)-split)”的异常织构转变和定向形核。从“RD”取向的原晶界处形核的晶核表现出“TD”取向,且和原晶粒呈现出大约62.5° <uvt0>的择优取向关系,这或许和基面<a>位错和低界面能有关。
英文摘要
The static recrystallization, nuclei orientations, and texture evolution of cold-rolled Mg-Zn-Gd alloys during annealing were tracked by quasi-in-situ electron backscatter diffraction method. An unusual texture transition from “rolling direction (RD)-split” to “transverse direction (TD)-split” occurred and oriented nucleation was observed. Nuclei originating from boundaries of the parent grain with “RD” orientation mainly exhibited “TD” orientations, and showed preferential misorientation relationship around 62.5° <uvt0> (including basal axes <11–20>, <10-10>, <41-50> and <52-70>) with respect to the parent grain, which may be related to basal <a> dislocations and low boundary energy.
SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P216-221
20. Strengthening CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy by tuning lattice defects
通过调整晶格缺陷强化CoCrNi中熵合金
Hua Huang, Jianying Wang, Hailin Yang✉, Shouxun Ji, Hailiang Yu, Zhilin Liu✉
Hailin Yang: y-hailin@csu.edu.cn,中南大学
Zhilin Liu: zhilin.liu@csu.edu.cn,中南大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.027
摘要
由于强度低,CrCoNi中熵合金尽管具有优异的低温性能,却并没有在室温条件下得到充分利用。本工作通过精细地调整多种晶格缺陷,在单相CrCoNi中熵合金中实现了优异的室温强度(1.6 GPa, 407.6 Hv)。电子显微技术表征表明此高强CrCoNi合金中存在粗晶(~30 μm)和超细晶(~1 μm)的有利异质结构,同时还存在高密度的位错胞、细小层错、超细纳米孪晶(厚度~9 nm)以及Lomer–Cottrell位错锁。
英文摘要
The CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy is not fully utilized at room temperature circumstance due to its low strength, despite excellent cryogenic mechanical properties. Here we report that, a superior room temperature strength (1.6 GPa and 407.6 Hv) has been obtained in the single phase CoCrNi medium-entropy alloy, by carefully tuning the formation of multiple lattice defects. Electron microscopy characterizations show that such high-strength CoCrNi alloy contains favorable heterostructures of coarsening grains (~30 μm) and ultrafine grains (~1 μm), together with the high density of dislocation cells, small stacking faults, ultrafine nanotwins (~9 nm in thickness) and Lomer–Cottrell locks.

SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P238-243
21. Assessing the influence of hydrogen on texture evolution in polycrystalline nickel deformed under uniaxial tension
评估多晶镍在单轴拉伸变形过程中氢对织构演化的影响
Zachary D. Harris✉, Michael A. Ritzo, Justine M. Schulte, Sean R. Agnew, James T. Burns
Zachary D. Harris: zdh8kt@virginia.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.035
摘要
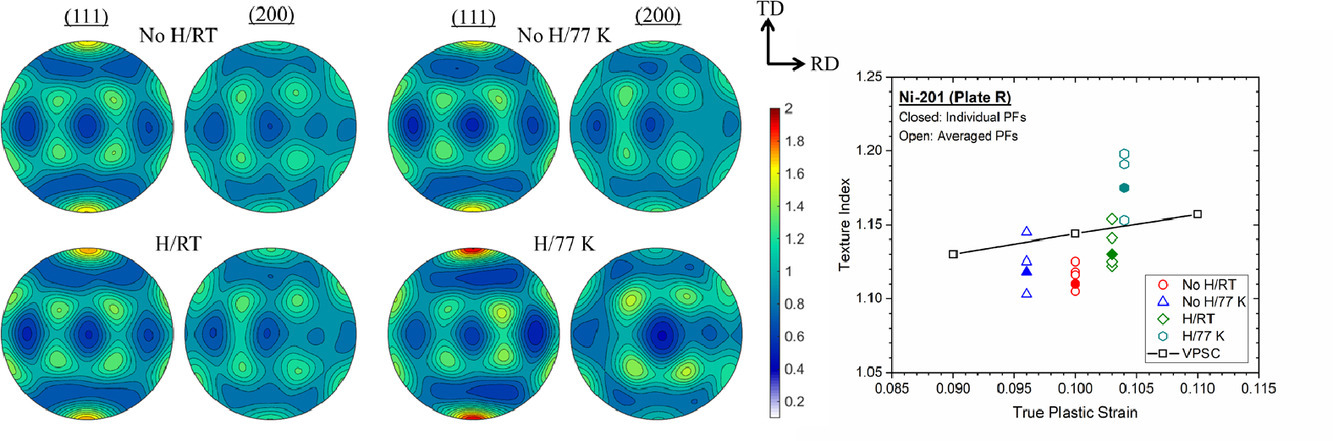
在室温和77K下将充氢和不充氢的多晶镍进行单轴拉伸变形至~0.1真实塑性应变,结果表明氢对织构演化没有显著影响。我们用电子背散射衍射分析了20,000+晶粒,完成了对不同状态样品以及收到的参考样品的织构评估。织构演变的相似性可归因于低应变变形下织构演变对潜在的氢诱导变形机制调整的不敏感性,晶体塑性模拟也证实了此结论。
英文摘要
Uniaxial tensile experiments on hydrogen-charged and non-charged polycrystalline nickel deformed to a true plastic strain of ~0.1 at room temperature and 77 K reveal that hydrogen has no measurable effect on texture evolution. Texture measurements were completed on samples of each condition, as well as an as-received reference specimen, using electron backscatter diffraction data collected from >20,000 individual grains. Crystal plasticity simulations support the conclusion that the similarity is attributable to the insensitivity of small-strain deformation texture evolution to potential hydrogen-induced modifications in deformation mechanisms.
SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P259-263
22. Phase decomposition in a nanocrystalline CrCoNi alloy
多晶CrCoNi合金的相分解行为
Y.J. Li✉, A. Kostka, A. Savan, A. Ludwig✉
Y.J. Li: yujiao.li@rub.de
A. Ludwig: alfred.ludwig@rub.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.054
摘要
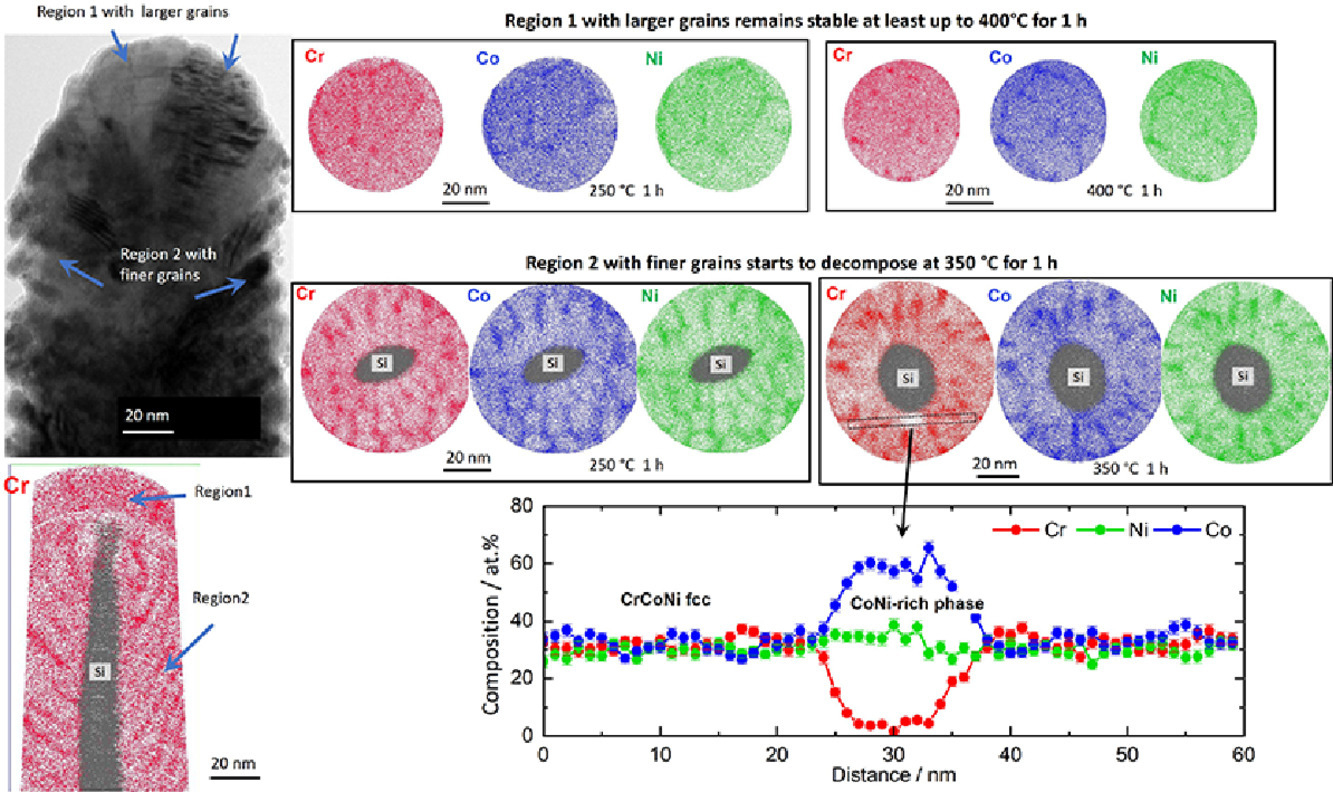
本工作利用原子探针层析成像和透射电子显微技术的组合处理平台(可进行合成、处理和直接原子尺度的表征),研究了纳米晶CrCoNi合金的相稳定性。在用一样品中观察到,相比于大的晶粒尺寸区域(20nm),富CoNi相在小晶粒尺寸区域(10nm)的相分解动力学更快。化学分析表明Co和Cr的扩散在相分解中发挥着重要作用。CrMnFeCoNi和CrCoNi合金相稳定性的比较研究表明元素偏聚或许通过提供额外的化学驱动力促进了相分解。
英文摘要
Phase stability of a nanocrystalline CrCoNi alloy is investigated using the combinatorial processing platform approach, which enables synthesis, processing and direct atomic-scale characterizations of alloys by atom probe tomography and transmission electron microscopy. Phase decomposition with formation of CoNi-rich phase occurs faster in the smaller (10 nm) grain-sized region than the larger one (20 nm), both being present in the same sample. Chemical analyses indicate that diffusion of Co and Cr plays an important role in phase decomposition. Comparison of phase stability between CrMnFeCoNi and CrCoNi implies that elemental segregation may promote phase decomposition by providing an additional chemical driving force for it.
SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P264-268
23. Impact of interstitial carbon on self-diffusion in CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloys
间隙碳原子对CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金自扩散的影响
O.A. Lukianova✉, Z. Rao, V. Kulitckii, Z. Li, G. Wilde, S.V. Divinski✉
O.A. Lukianova: sokos100@mail.ru
S.V. Divinski: divin@uni-muenster.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.044
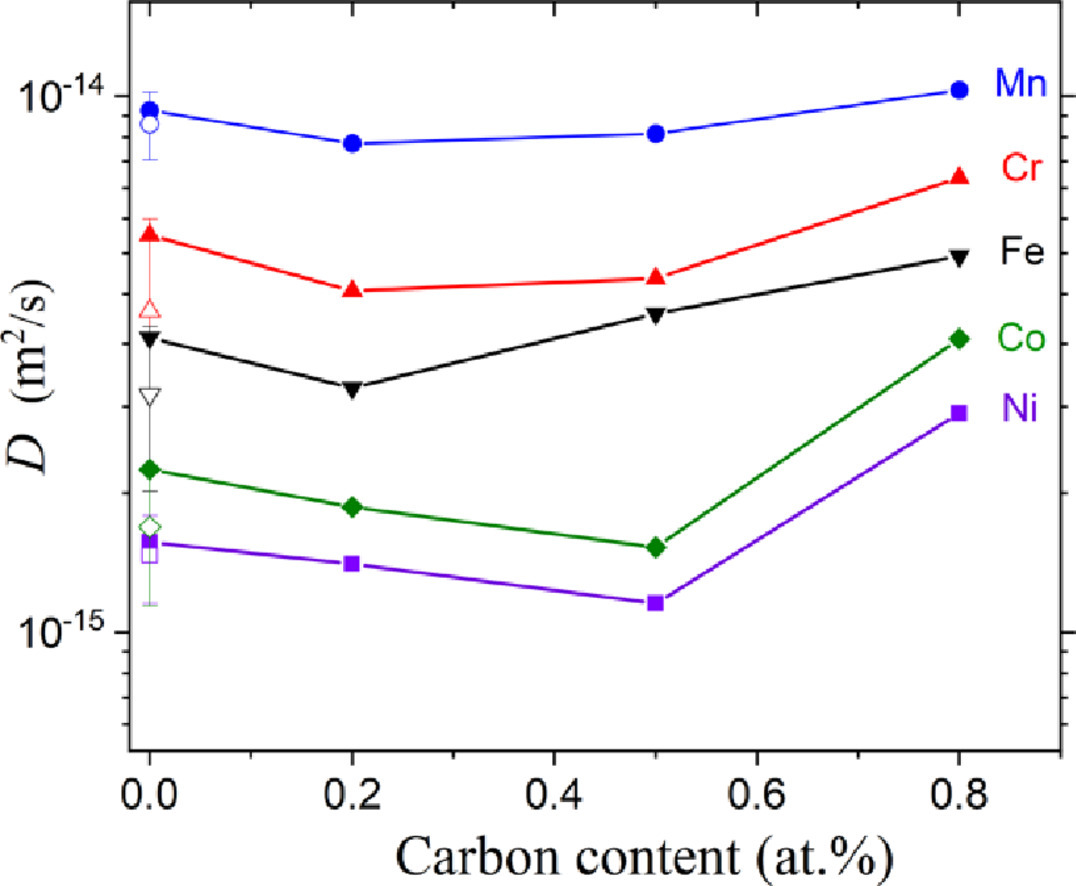
摘要
本工作用放射性指示剂测量了1373K下含有0.2, 0.5, 0.8原子百分比的CoCrFeNiMn基高熵合金中基体元素的扩散行为。结果表明扩散系数和碳含量成非单调的关系。根据间隙溶解碳原子对合金中空位浓度和迁移能垒的影响,我们讨论了低碳合金中的扩散迟滞现象。在高碳合金中,碳化物的形成改变了观察到的趋势,主要原因可能是总空位浓度的增加。
英文摘要
Tracer diffusion of the matrix elements in CoCrFeNiMn-based high-entropy alloys with 0.2, 0.5 and 0.8 at.% carbon is measured at 1373 K. The diffusion coefficients are found to depend non-monotonously on the carbon content. The diffusion retardation in low-C alloys is discussed in terms of the impact of interstitially-dissolved carbon on the vacancy concentration and the migration barriers in the alloy. In high-C alloys, formation of carbides alternates the observed trends, most probably by increasing the total vacancy concentration.
SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P269-273
24. Reversion and re-aging of a peak aged Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy
峰时效状态的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金的逆转变和再时效行为
Huan Zhao✉, Baptiste Gault, Dirk Ponge, Dierk Raabe
Huan Zhao: h.zhao@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.049
摘要
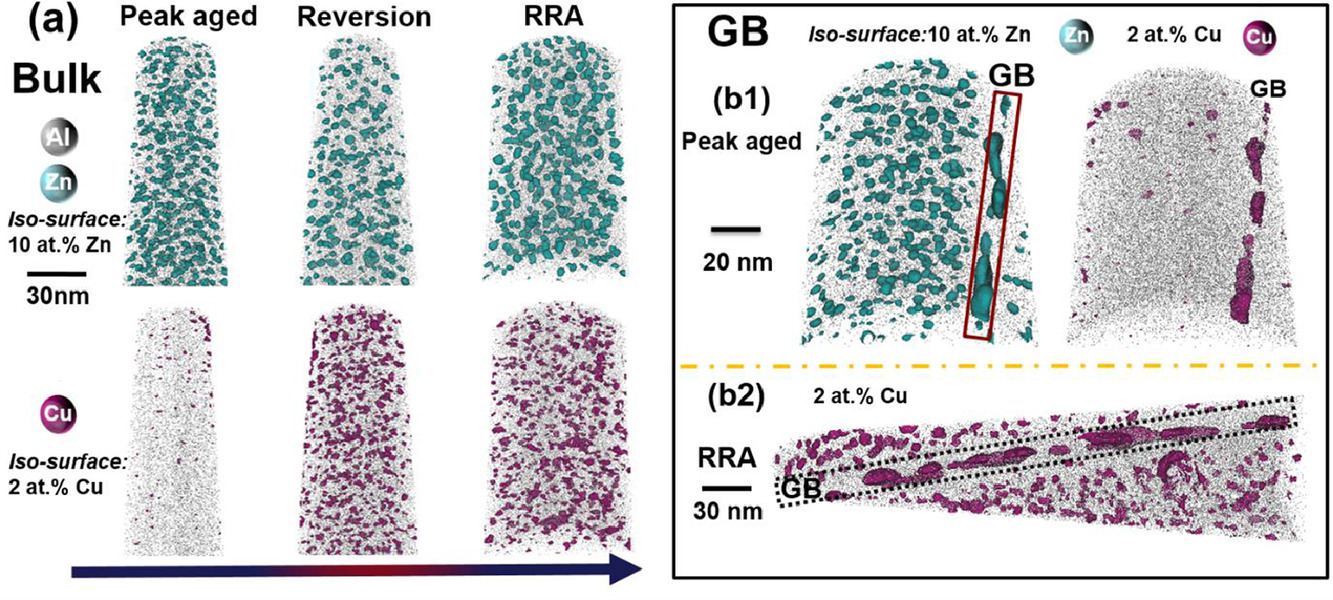
高强Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金对应力腐蚀开裂(SCC)具有很高的敏感性,从而极大地限制了其服役寿命。逆转变和再时效(RRA)回火在不牺牲强度的情况下,提供了更高的抗应力腐蚀性能,然而性能提高的微观组织原因仍难以解释。在Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金中,我们观察到在峰时效和RRA回火样品中晶粒内部存在相似的细小析出的弥散分布。然而,在RRA过程中,晶粒内部的析出会富Cu,降低基体中的Cu含量以及块体和晶界间Cu析出成分的相对差异。本工作丰富了目前Al-Zn-Mg-Cu合金中Cu对于抗应力腐蚀性能关键作用的认识。
英文摘要
High-strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys are highly susceptible to stress corrosion cracking (SCC) which severely limits their lifetime. Reversion and re-aging (RRA) temper provides a higher SCC resistance at no loss in strength, yet the microstructural origins of these enhanced properties remain elusive. In an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy, we show that the fine precipitate dispersion in the grain interiors is similar in the peak aged and RRA tempers. However, upon RRA, precipitates inside the grains are enriched in Cu, lowering the Cu matrix content, and reducing the relative difference in the Cu precipitate composition between bulk and grain boundaries. This study enriches the current understanding on the critical role of Cu related to SCC resistance in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys.
SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P280-284
25. The gradual disappearance and re-appearance of yield drop by modulating the pre-strain history in a new zirconium alloy: Dislocation decomposition and recombination
新型锆合金中调节预应变历史引发屈服下降的逐渐消失与重现:位错分解与重组的影响
Huigang Shi, Jiuxiao Li✉, Jianwei Mao, Weijie Lu✉
Weijie Lu: luweijie@sjtu.edu.cn,上海交通大学
Jiuxiao Li: lijiuxiao@126.com,上海工程技术大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.051
摘要
我们报道了新型锆合金中的一个有趣的现象:通过对预应变历史的调节,屈服下降(yield drop)逐渐消失,随后又重新出现。初始的屈服下降是晶体中可动位错缺少引起的,预应变(<1%)引入的大量可动位错导致了屈服下降的消失。屈服下降的再现是由于不全位错的重组。由预应变(>9%)引入的不全位错会重组到相同的棱镜面上,重新获得移动性,造成了屈服下降的重现。
英文摘要
We report an interesting phenomenon in a new zirconium alloy where the yield drop gradually disappeared and re-appeared by modulating the pre-strain history. The initial yield drop is caused by the lack of mobile dislocations in crystal, and increased density of mobile dislocations introduced by pre-strain (< 1%) lead to the disappearance of yield drop. The latter one can be explained by the recombination of partial dislocations. That is, the climb-dissociated partials introduced by pre-strain deformation (> 9%) recombine onto the same prism plane to regain its moving ability, resulting in the re-appearance of yield drop.

SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P285-289
26. Up-hill diffusion of solute atoms towards slipped grain boundaries: A possible reason of decomposition due to severe plastic deformation
溶质原子向滑移晶界处的上坡扩散:强烈塑性变形引发分解的可能原因
Zsolt Kovács✉, Nguyen Q. Chinh
Zsolt Kovács: kovacszs@metal.elte.hu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.055
摘要
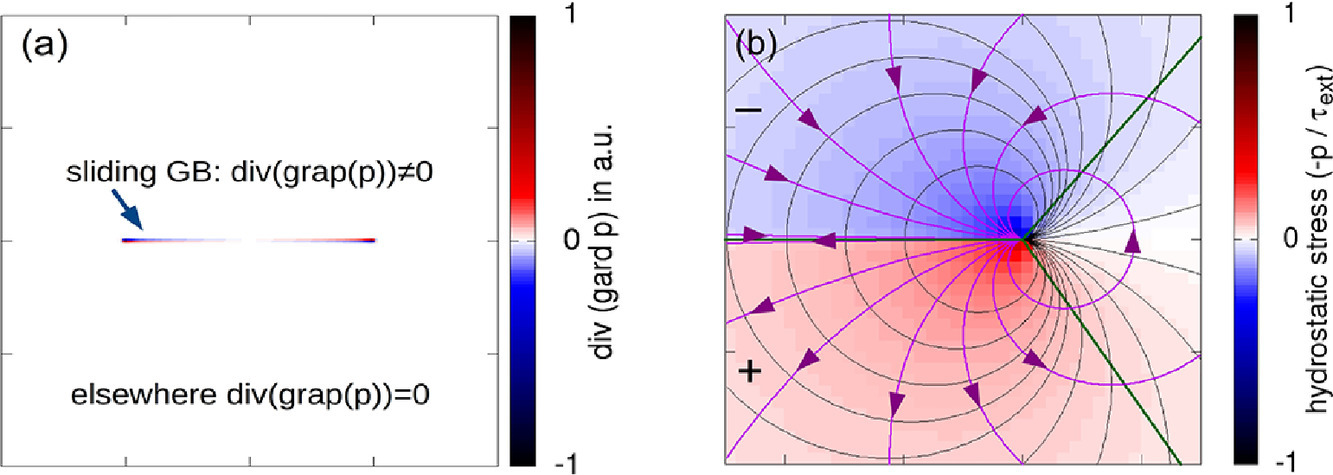
过饱和固溶体经历强烈塑性变形后经常表现出固溶体的分解,造成一种奇怪的晶界现象——沿晶界形成富溶质原子的纳米薄层。基于局部的晶界滑移,此现象可以用静水压力场的形成来解释。压力场会诱发溶质气团的上坡扩散,引起溶质原子聚集于存在应力的晶界处。
英文摘要
Supersaturated solid solutions subjected to severe plastic deformation often exhibit decomposition of the solid solution, leading to a peculiar grain boundary phenomenon, the formation of few nanometer thin layer enriched in solute atoms along grain boundaries. Based on localized grain boundary sliding, this phenomenon can be explained by the formation of hydrostatic stress field, which induces up-hill diffusion in the solute atmosphere, resulting in solute atom accumulation along the stressed grain boundaries.
SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P296-301
27. Impact of krypton irradiation on a single crystal tungsten: Multi-modal X-ray imaging study
多模态X射线成像技术研究氪辐照对单晶钨的影响
Simerjeet K. Gill✉, Mehmet Topsakal, Ericmoore Jossou, Xiaojing Huang✉, Khalid Hattar, Julia Mausz, Mohamed Elbakhshwan, Hanfei Yan, Yong S.Chu, Cheng Sun, Lingfeng He, Jian Gan, Lynne Ecker
Simerjeet K. Gill: gills@bnl.gov
Xiaojing Huang: xjhuang@bnl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.024
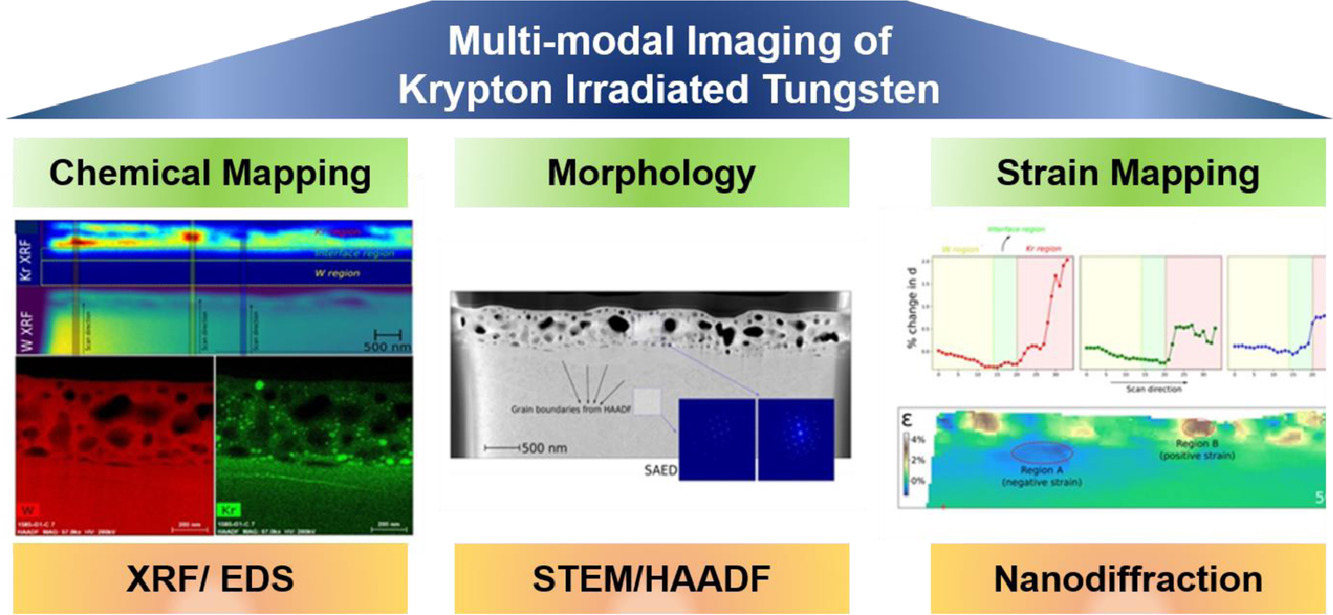
摘要
在核燃料基质或面对等离子体材料中,理解惰性气体的产生所导致的微观结构和应变演化对设计下一代核反应堆至关重要,因为它们会导致体积膨胀和灾难性失效。我们展示了一种多模态方法,将基于同步加速器的纳米级X射线成像技术与原子级电子显微技术相结合,用来描绘氪辐照引起的单晶钨的化学成分、形貌和晶格畸变。氪辐照后的单晶钨经历了表面变形,形成了包含氪的空洞。而且,在氪辐照的区域观察到了正应变场,导致了钨基体下的压缩状态。
英文摘要
Understanding microstructural and strain evolutions induced by noble gas production in the nuclear fuel matrix or plasma-facing materials is crucial for designing next generation nuclear reactors, as they are responsible for volumetric swelling and catastrophic failure. We describe a multimodal approach combining synchrotron-based nanoscale X-ray imaging techniques with atomic-scale electron microscopy techniques for mapping chemical composition, morphology and lattice distortion in a single crystal W induced by Kr irradiation. We report that Kr-irradiated single crystal W undergoes surface deformation, forming Kr containing cavities. Furthermore, positive strain fields are observed in Kr-irradiated regions, which lead to compression of underlying W matrix.
SCRIPTA Vol. 188, 1 Nov. 2020, P302-306
28. Tuning magnetocaloric effect of Ho1-xGdxNi2 and HoNi2-yCoy alloys around hydrogen liquefaction temperature
在氢液化温度附近调节Ho1-xGdxNi2和HoNi2-yCoy合金的磁热效应
Jiawei Lai, Xin Tang, Hossein Sepehri-Amin✉, Kazuhiro Hono
Hossein Sepehri-Amin: h.sepehriamin@nims.go.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.07.046
摘要
本工作表明,在Ho1-xGdxNi2-yCoy合金中,用Gd代替Ho和用Co代替Ni可以调节HoNi2化合物在氢液化温度附近的巨磁热效应。虽然Ho1-xGdxNi2-yCoy的居里温度由于立方结构的晶格膨胀可以从15K调节到32K,但在氢液化温度附近仍保留22.0 J/kgK的巨大熵变。在20-32K宽温度范围内观察到的类桌子状(table-like)熵变,使得它们成为极有潜力的磁热材料,用于利用爱立信循环(Ericsson cycle)的低温磁制冷。
英文摘要
We show the giant magnetocaloric effect of HoNi2 compound can be tuned around hydrogen liquefaction temperature by substituting Ho with Gd and Ni with Co in Ho1-xGdxNi2-yCoy. While the Curie temperature of Ho1-xGdxNi2-yCoy can be tuned from 15 to 32 K originating from the lattice expansion of the cubic structure, giant entropy change of 22.0 J/kgK is retained near the hydrogen liquefaction temperature. A table-like entropy change observed in a broad temperature range of 20 to 32 K makes them promising as magnetocaloric materials for cryogenic magnetic refrigeration utilizing an Ericsson cycle.

微信公众号:Goal Science
投稿邮箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
