金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.199,15 Oct. 2020(上)
2020-10-14 来源: Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文17篇,涵盖了316L不锈钢、3D打印、高熵合金、钛合金、纳米合金、高温合金、双相不锈钢等,国内科研单位包括浙江大学、台湾国立清华大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 199 目录
ACTA Vol. 199,15 Oct. 2020, P19-33
1. Origin of dislocation structures in an additively manufactured austenitic stainless steel 316L
增材制造316L不锈钢中位错结构的起源
K.M. Bertsch✉, G. Meric de Bellefon, B. Kuehl, D.J. Thoma
K.M. Bertsch:bertsch5@llnl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.063
摘要
本实验首次通过几何约束方法对增材制造不锈钢中的热应力进行了控制,从而系统研究了位错组织的起源。我们制备了杆、壁和矩形棱柱等多种不同维度的316L不锈钢零件,评估了热膨胀/收缩对缺陷组织形成的影响,在此基础上阐明增材制造过程中位错微观组织的起源。我们对使用直接能量沉积(DED)和选区激光熔化(SLM)两种方法制备的多维度组件中的位错密度、组织、偏析、析出相和错配进行了比较分析。发现在DED方法制备的部件中,位错密度与局部错配和偏析无关,但在一维部件中ρ⊥约为1012m−2,而在三维部件中则上升到了约1014m−2。在DED和SLM制备的三维部件中的高位错密度与组织中形成了约300-450nm的位错胞有关。在某些情况下,位错胞与枝晶偏析重叠。这些结果表明,枝晶偏析、析出相和局部错配对加工过程中的位错结构有一定影响,但并不是导致有序的胞状结构的直接原因。位错结构是增材制造过程中的热变形导致的,主要受到熔池周围的约束条件和热循环控制。
英文摘要
In this experiment, the origin of dislocation structures in AM stainless steels was systematically investigated by controlling the effect of thermal stress through geometric constraints for the first time. Stainless steel 316L parts were produced in the form of “1D” rods, “2D” walls, and "3D" rectangular prisms to evaluate the effect of constraints to thermal expansion/shrinkage on the development of defect microstructures and to elucidate the origin of additively manufactured (AM) dislocation microstructures. Dislocation density, organization, chemical micro-segregation, precipitate structures, and misorientations were analyzed as a function of increasing constraints around solidifying material in 1D, 2D, and 3D components built using both directed energy deposition (DED) and powder-bed selective laser melting (SLM). In DED parts, the dislocation density was not dependent on local misorientations or micro-segregation patterns, but evolved from approximately ρ⊥=1012m−2 in 1D parts to ρ⊥=1014m−2 in 3D parts, indicating that it is primarily thermal distortions that produce AM dislocation structures. In DED 3D parts and SLM parts, dislocation densities were highest (ρ⊥≈1014m-2) and corresponded to the formation of dislocation cells approximately 300-450 nm in diameter. Dislocation cells overlapped with dendrite micro-segregation in some but not all cases. The results illustrate that dendritic micro-segregation, precipitates, or local misorientations influence how the dislocations organize during processing, but are not responsible for producing the organized cell structures. This work shows that AM dislocation structures originate due to thermal distortions during printing, which are primarily dictated by constraints surrounding the melt pool and thermal cycling.

ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P42-52
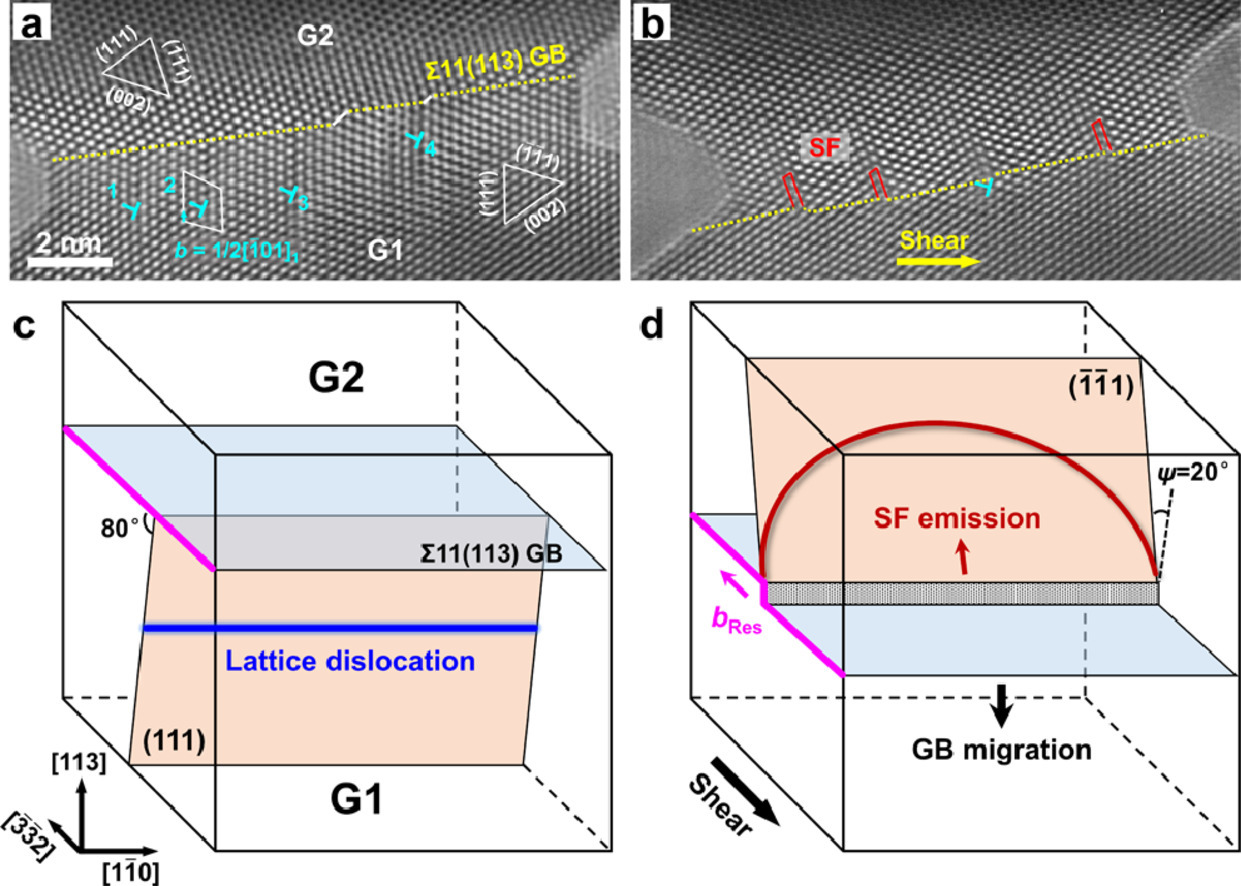
2. In situ atomistic observation of grain boundary migration subjected to defect interaction
缺陷相互作用下晶界迁移的原位原子观察
Q. Zhu, S.C. Zhao, C. Deng✉, X.H. An, K.X. Song, S.X. Mao✉, J.W. Wang✉
C. Deng:Chuang.Deng@umanitoba.ca,浙江大学
S.X. Mao:sxm2@pitt.edu
J.W. Wang:jiangwei_wang@zju.edu.cn
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.021
摘要
晶粒长大和再结晶都可以被视作是晶界迁移的结果。晶界迁移的过程中常常会遇到晶格缺陷,而这两者相互作用的原子层面动态机制仍不清晰。因此在本文中,我们通过结合原位纳米机械测试和分子动力学模拟系统地研究了Au移动中的Σ11(113)对称倾侧晶界和不同晶格缺陷(包括全位错、层错和纳米孪晶)之间的相互作用机制。实验表明,在局部原子位移控制晶界-缺陷相互作用的条件下,Σ11 (113)GB表现出一种保守的缺陷容纳机制和与之耦合的晶界-孪晶演化。此外,切变耦合的晶界迁移不受缺陷的影响,因为晶界上含有可滑动断点。这些发现为晶界在不同晶格缺陷影响下的原子尺度迁移机制提供了全面的实验理解,极大推动了晶界主导塑性理论的发展。
英文摘要
Grain boundary (GB) migration associated with grain growth and recrystallization encounters lattice defects frequently, while the atomistic mechanisms of GB-defect interactions during these dynamic processes remain largely unclear. Here, we systematically investigate the atomistic mechanism of the interactions between migrating Σ11(113) symmetrical tilt GBs and different lattice defects, including full dislocation, stacking fault and nanotwin in Au, via the integrated in situ nanomechanical testing and molecular dynamics simulations. Experimental evidence demonstrated a conservative defect accommodation mechanism of Σ11(113) GB and a coupled GB-twin evolution, where localized atom displacement dominated the GB-defect interactions. Moreover, the shear-coupled GB migration was unperturbed by the interaction, due to the glissile residual disconnections left on the GB. These findings provide a comprehensive experimental understanding on the atomistic mechanism of GB migration under the influence of different lattice defects, which significantly advances the theoretical development of GB-dominated plasticity under more realistic circumstances.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P53-62
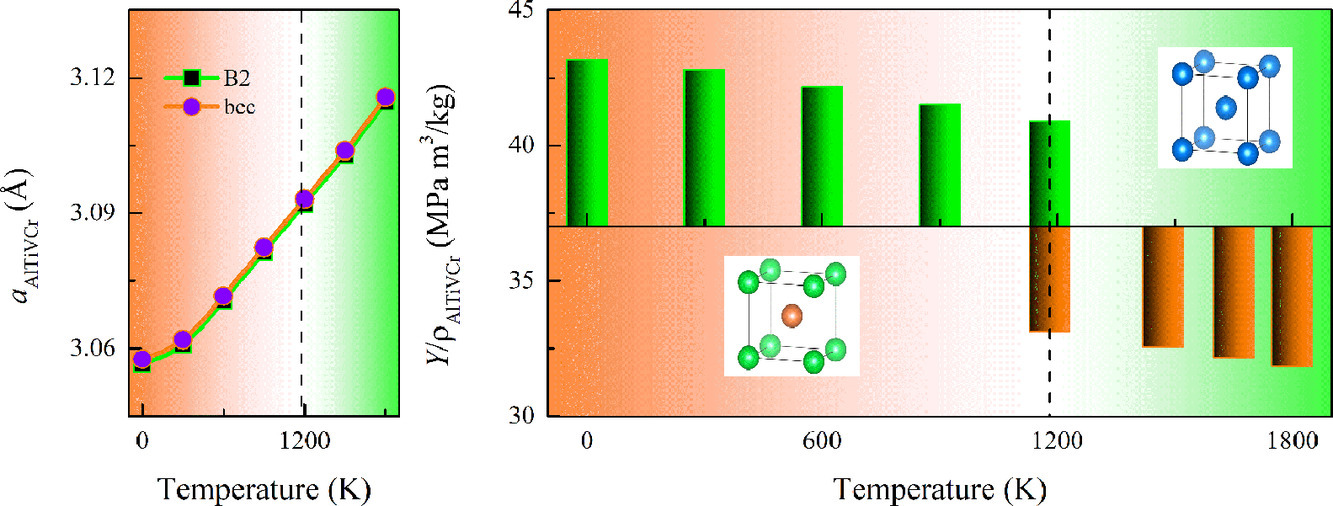
3. Chemical ordering controlled thermo-elasticity of AlTiVCr1-xNbx high-entropy alloys
AlTiVCr1-xNbx 高熵合金中由化学有序控制的热弹性研究
Shuo Huang✉, Wei Li, Olle Eriksson, Levente Vitos✉
S. Huang:shuoh@kth.se
L. Vitos:levente@kth.se
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.005
摘要
多组元体系中各组成相的稳定性极大地影响材料在高温下的机械性能。在本研究中,我们重点研究了BCC结构的AlTiVCr1-xNbx (0 ≤ x ≤ 1)合金中的化学有序。对于合金元素分布的第一性原理计算表明体系中存在B2型部分有序结构。我们作出了无序和部分有序相的弹性参数随成分和温度的变化图。我们发现体系对于有序无序转变十分敏感,尤其是富Cr体系。对于体系有序程度的合理调控可以改善材料的机械性能,同时保持材料的密度不变。我们进一步对可能具有高比强度、低热膨胀和高弹性软化抗性的合金体系进行了预测,这些材料的热机械性能有望和高温合金以及其他高温结构材料进行竞争。
英文摘要
The stability of constituent phases in multi-component system always plays a prominent role in tailoring their mechanical performance at elevated temperatures. In this work, we highlight a chemical ordering feature in the AlTiVCr1-xNbx (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) alloys with body-centered cubic crystal structure. The quantum-mechanical first-principle investigations of these alloys on the elemental distribution identify a family of B2 type of partially ordered configurations. We map out the elastic parameters in detail as a function of composition and temperature for disordered and partially ordered phases. A great sensitivity to the order-disorder transformation is revealed, especially for the Cr-rich system. Our results demonstrate that a proper control of the ordering level in these alloys can facilitate the optimal tuning of their mechanical performance while keeping the density almost unchanged. The study presented here further predicts that these alloys possess high specific stiffness, low thermal expansion, and large elastic softening resistance. It is demonstrated that the considered alloys have thermal and mechanical properties that compete with superalloys and other high temperature structural materials.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P63-72
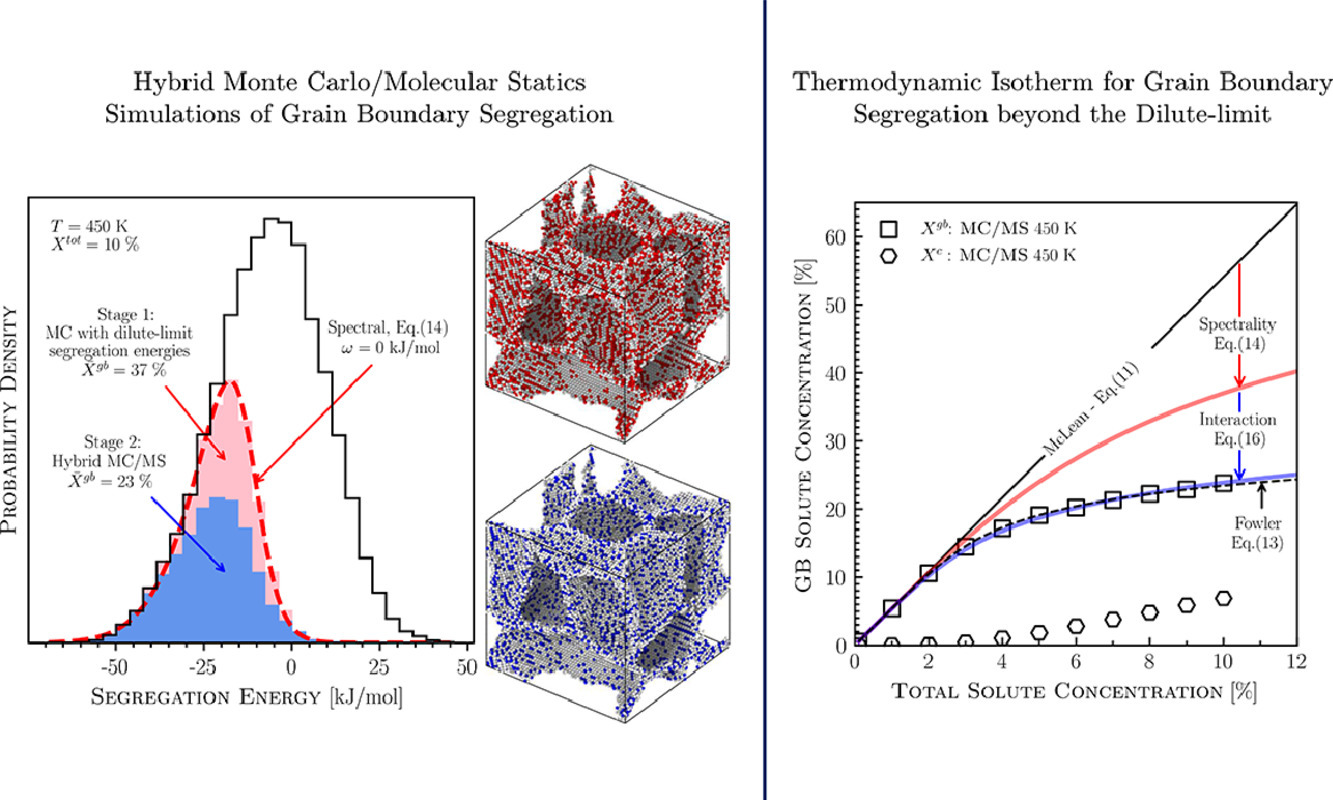
4. Grain boundary segregation beyond the dilute limit: Separating the two contributions of site spectrality and solute interactions
区分溶质位置和溶质相互作用对稀溶液极限以上晶界偏聚的贡献
Malik Wagih, Christopher A. Schuh✉
C.A. Schuh:schuh@mit.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.022
摘要
晶界处的元素偏聚对材料性能有显著影响,对它的调控已经逐渐变成一种常见的材料设计理念。在超过过稀溶液浓度极限情况下,学界普遍认为晶界偏聚和材料的成分密切相关。通过对Al中Mg偏聚的蒙特卡洛/分子静态混合模拟,我们把这种成分对偏聚的影响分成了两个方面:(1)界面处的局部原子环境 (2)溶质元素之间的相互作用。通常,文献中只讨论了影响因素(2),在此我们指出,两种因素对于定量理解二元合金中的晶界元素偏聚是同等重要的。最后,我们做出了关于晶界位置和溶质元素相互作用的热力学偏聚等浓度图。McLean或Fowler-Guwggenheim等经典图谱通常只能在较为有限的温度和成分范围内对晶界偏聚进行描述,而我们作的这一图谱在整个成分-温度空间内都十分准确。
英文摘要
Solute segregation at grain boundaries (GBs) is known to have a profound impact on material properties, and as such is becoming routinely used as an element in alloy design. Beyond the dilute limit, the extent of solute GB segregation is known to be concentration dependent. Using hybrid Monte Carlo/Molecular Statics simulations of Mg segregation in Al, we decouple the two contributions to this composition dependence: (i) spectrality of atomic environments at the boundary and (ii) solute-solute interactions. Although only contribution (ii) is typically considered in the literature, we argue that both contributions are equally important to understand concentration dependence and correctly quantify GB solute segregation in a binary alloy. Finally, a thermodynamic segregation isotherm is outlined that accounts for both the spectrality of grain boundary sites and solute-solute interactions. Unlike classical isotherms like those of McLean or Fowler-Guggenheim, which can be successfully fitted to GB segregation data only over a limited range of composition and temperature, our proposed model is shown to be accurate across the composition-temperature space.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P73-84
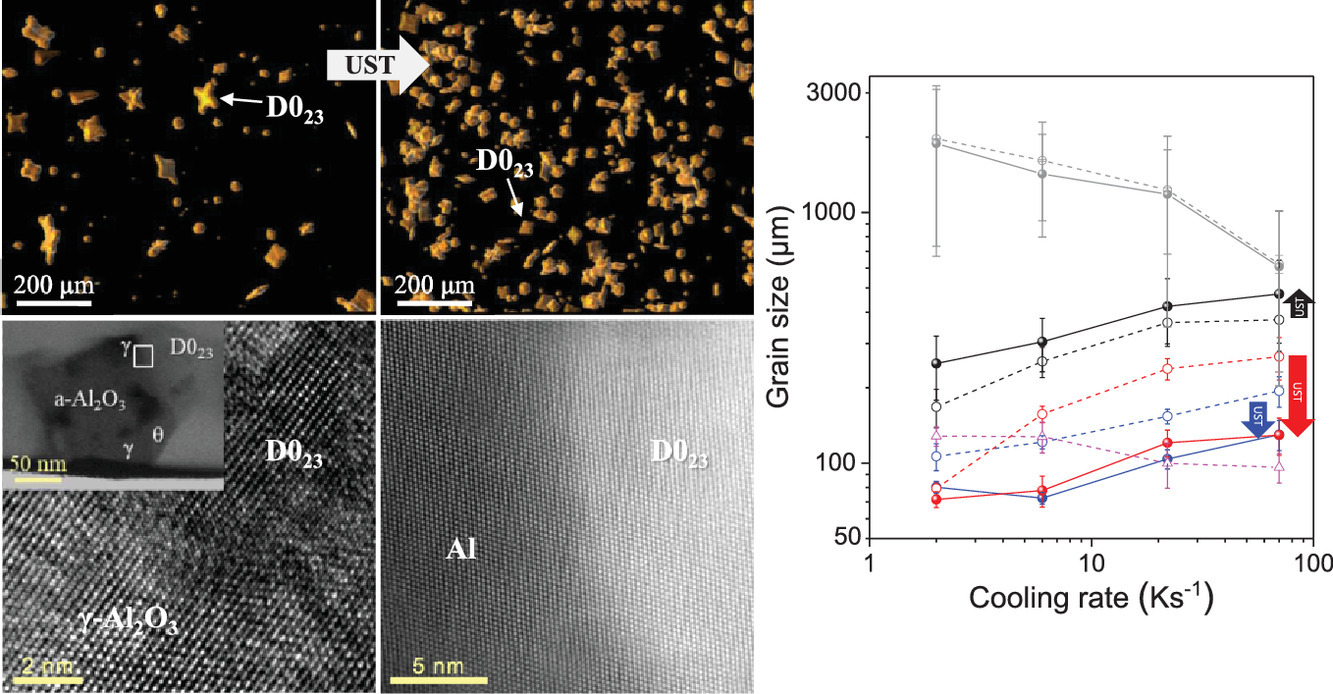
5. Mechanism of ultrasound-induced microstructure modification in Al–Zr alloys
利用超声熔炼对Al-Zr合金进行组织调控的机理研究
Jae-Gil Jung✉, Young-Hee Cho, Sung-Dae Kim, Soo-Bae Kim, Sang-Hwa Lee, Kyung Song, Kwangjun Euh, Jung-Moo Lee
J.-G. Jung:jgjung@kims.re.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.025
摘要
我们通过对纯Al和几种Al-Zr合金(Al–0.3Zr–0.1Ti, Al–0.5Zr, Al–0.5Zr–0.5Mg–0.9Si)在不同冷却速率(0.2–70 K s−1)下进行凝固,研究了超声熔炼(UST)对金属间化合物粒子和α-Al的影响。研究发现,超声熔炼会促进α-Al的形核,从而降低D023结构Al3Zr和 Al3(Zr,Ti) 粒子的尺寸,提高其体积分数和密度。高分辨率TEM表征表明,空位的浸润效应和弥散分布的γ-Al2O3变质剂有助于细化初生金属间化合物颗粒。随着冷却速率的增加,初生金属间化合物粒子形成减少,导致Al-Zr合金的晶粒尺寸增大。在无钛Al-Zr合金中,超声熔炼细化了Al3Zr的尺寸,提高了Al3Zr的数密度,导致晶粒细化;而对于含钛Al-Zr合金,超声诱导晶粒细化只能在非常低的的冷却速率下实现0.2 K s−1,这可能是由于超声熔炼抑制了Ti的生长所产生副作用。快速凝固使组织中生成了大量L12-Al3Zr纳米沉淀(~ 5nm),这一显著的时效硬化不受超声熔炼的影响。因此,本研究表明,在高冷却速率下,UST可以降低时效硬化Al-Zr合金的晶粒粗化。
英文摘要
This work probes the effect of ultrasonic melt treatment (UST) on primary intermetallic particles and α-Al using pure Al and Al–Zr alloys (Al–0.3Zr–0.1Ti, Al–0.5Zr, Al–0.5Zr–0.5Mg–0.9Si) solidified at various cooling rates of 0.2–70 K s−1. The application of UST is shown to decrease the size and increase the number density and volume fraction of D023-structured primary Al3Zr and Al3(Zr,Ti) particles with a high nucleation potency for α-Al formation. High-resolution transmission electron microscopy analysis reveals that the cavitation-induced wetting and dispersion of γ-Al2O3 inoculant particles contribute to the refinement of primary intermetallic particles. The grain size of Al–Zr alloys increases with increasing cooling rate because of the concomitantly reduced formation of primary intermetallic inoculant particles. The UST-induced refinement of primary Al3Zr particles and the increased number density lead to grain refinement in Ti-free Al–Zr alloys. For the Ti-containing Al–Zr alloy, UST-induced grain refinement is achieved only at a very low cooling rate of 0.2 K s−1, possibly because of the side effects of UST on the growth-restricting influence of Ti. The fast cooling–induced solidification enables significant age-hardening by L12-Al3Zr nanoprecipitation (~5 nm) and is not affected by UST. Thus, this study shows that UST can be used to reduce the degree of grain coarsening of age-hardenable Al–Zr alloys at high cooling rates.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P107-115
6. Thermodynamic route for self-forming 1.5 nm V-Nb-Mo-Ta-W high-entropy alloy barrier layer: Roles of enthalpy and mixing entropy
V-Nb-Mo-Ta-W高熵合金中自发形成1.5nm阻隔层的热力过程中焓和混合熵的作用
Yu-Ting Hsiao, Chi-Huan Tung, Su-Jien Lin, Jien-Wei Yeh, Shou-Yi Chang✉
S.-Y. Chang:changsy@mx.nthu.edu.tw,台湾国立清华大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.029
摘要
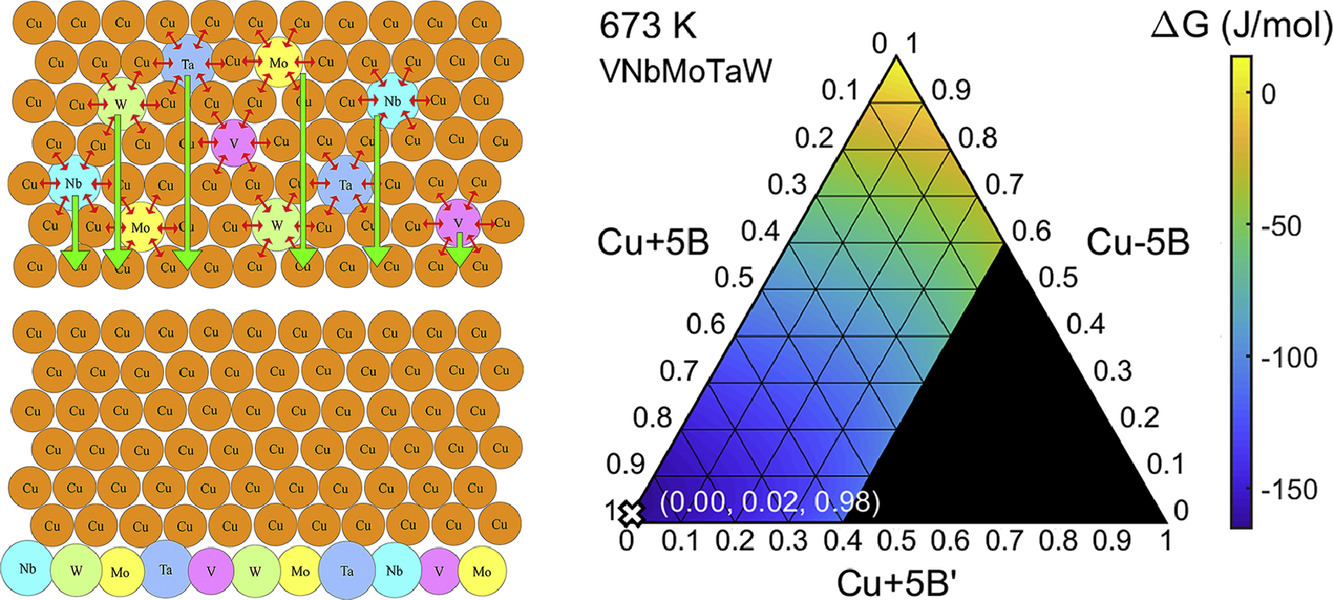
本研究报道了一种自发形成的V-Nb-Mo-Ta-W超薄高熵合金层的热力学路径,这种合金层有望成为一种具有广阔实用前景的扩散壁垒。研究发现,在掺杂了1到5种金属元素(V, Nb, Mo, Ta, W)共计1.2at.% 的铜合金薄膜中,这些元素会自发偏聚。在焓和混合熵的吉布斯自由能竞争下,5种合金元素在Cu/Si界面处形成了固溶合金层,而3种元素在晶界形成了金属间化合物团簇。决定这些合金元素最终状态的因素包括Cu的焓,合金元素和的焓,以及合金元素的混合焓。这种1.5 nm厚的自发形成五元合金层在700°C显著阻碍了Cu和Si的相互扩散,且性能优于其他已实用化的阻隔材料。
英文摘要
This study reports a thermodynamic route for self-forming an ultrathin V-Nb-Mo-Ta-W high-entropy alloy layer for potential use as a promising diffusion barrier. In Cu alloy films minor-doped with 1.2 at.% of one-to-five metallic elements (V, Nb, Mo, Ta and W), the alloying elements spontaneously segregated. Under the competition of enthalpy and mixing entropy that determines the delta Gibbs free energy, one and, in particular, five alloying element(s) formed an alloy solution layer at the Cu/Si interface, whereas three alloying elements differently formed intermetallic compound clusters at the grain boundaries of Cu. Dominant factors for the final states of the alloying elements include the large positive enthalpy between Cu and the alloying elements, the negative enthalpy among the alloying elements, and the low-to-high mixing entropy among the alloying elements. The self-forming quinary alloy layer of only 1.5 nm thick provided excellent resistance to the interdiffusion of Cu and Si up to 700°C, better than practical and other newly developed barrier materials.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P116-128
7. A mean-field model of static recrystallization considering orientation spreads and their time-evolution
考虑取向传播及其时间演化的静态再结晶平均场模型
A. Després✉, M. Greenwood, C.W. Sinclair
A. Després:arthur.despres@alumni.ubc.ca
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.013
摘要
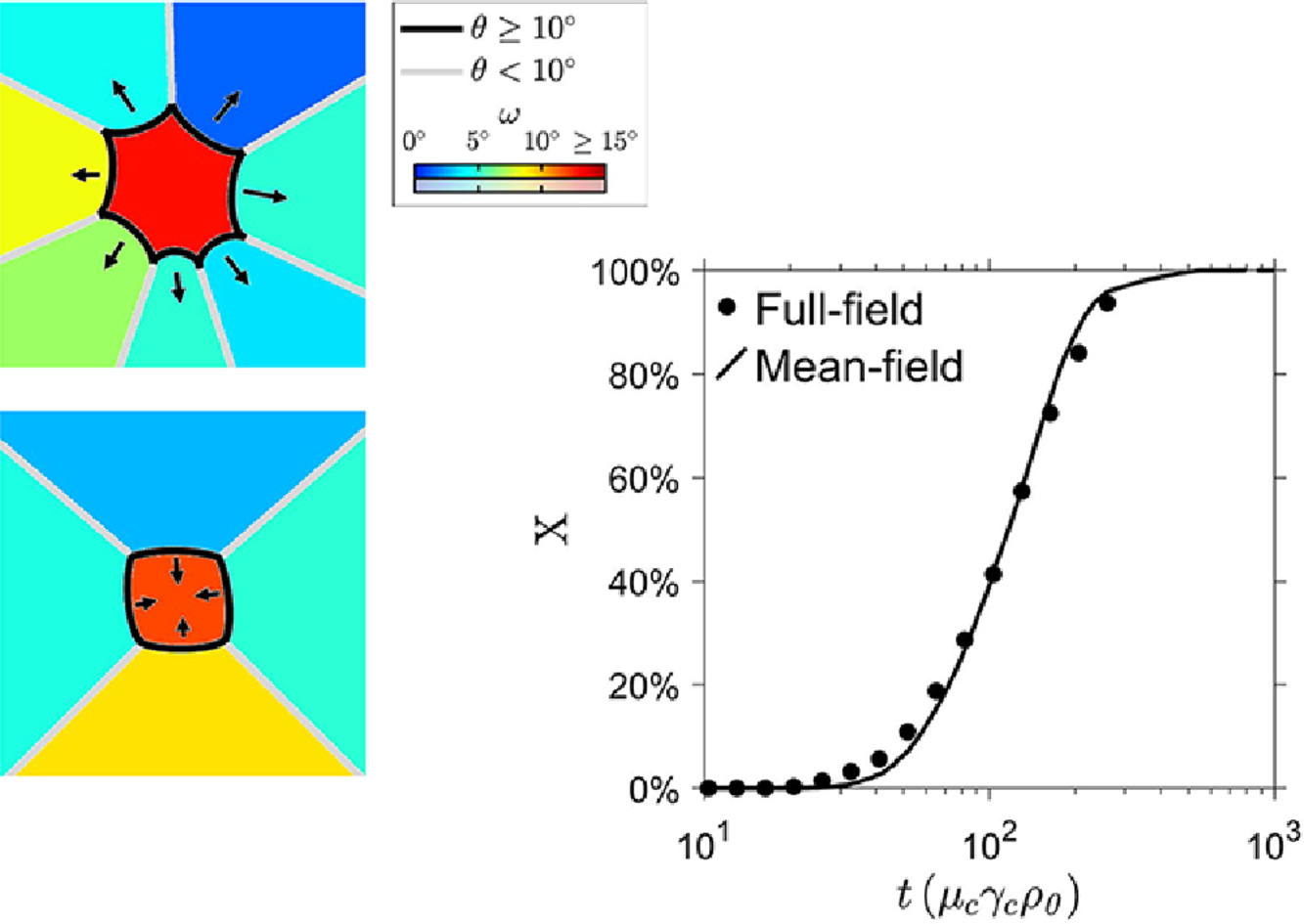
在本研究中,我们构建了一种平均场模型用于模拟晶体材料在静态再结晶过程中的组织演化。模型考虑了一群单一晶粒/亚晶在均匀材料中的长大。计算晶粒长大速率所需的单个晶粒和材料整体的晶界性质均是基于材料的晶体学取向分布进行静态估计得到。再结晶是不同晶粒相互竞争长大的结果。我们首先对采用的算法进行了阐述,随后我们将平均场模型与二维顶点全场模型进行了比较,发现平均场模型能够更准确地预测晶界性质随时间的变化以及晶粒取向等再结晶动力参数。这一研究结果使我们能够进一步探究晶粒取向对晶界性质、再结晶形成和再结晶动力学的影响。这一模型还能够将实验实测参数作为输入,研究形变和再结晶之间的关系。
英文摘要
In this paper, we develop a mean-field model for simulating the microstructure evolution of crystalline materials during static recrystallization. The model considers a population of individual cells (i.e. grains and subgrains) growing in a homogeneous medium representing the average microstructure properties. The average boundary properties of the individual cells and of the medium, required to compute growth rates, are estimated statistically as a function of the microstructure topology and of the distribution of crystallographic orientations. Recrystallized grains arise from the competitive growth between cells. After a presentation of the algorithm, the model is compared to full-field simulations of recrystallization performed with a 2D Vertex model. It is shown that the mean-field model predicts accurately the evolution of boundary properties with time, as well as several recrystallization parameters including kinetics and grain orientations. The results allow one to investigate the role of orientation spreads on the determination of boundary properties, the formation of recrystallized grains and recrystallization kinetics. The model can be used with experimentally obtained inputs to investigate the relationship between deformation and recrystallization microstructures.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P129-140
8. The influence of microstructural condition on the phase transformations in Ti-24Nb (at.%)
组织状态对Ti-24Nb (at.%)合金相变的影响
E.M. Hildyard, L.D. Connor, L.R. Owen, D. Rugg, N. Martin, H.J. Stone, N.G. Jones✉
N.G. Jones:ngj22@cam.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.004
摘要
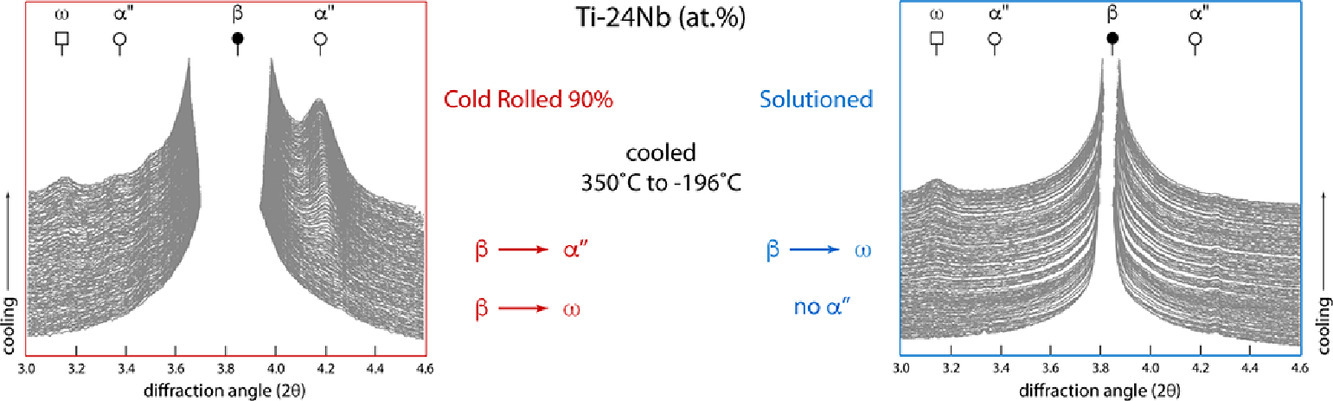
Ti-Nb合金在较广的温度范围内具备超弹性和形状记忆效应,这使得它们很有工业应用潜力。然而,不同文献对于给定成分合金相变行为的报导具有显著区别,且目前为止其原因尚无法解释,这极大地限制了Ti-Nb合金的应用。为了研究这些差异的原因,我们选取了两种具有不同微观组织的Ti-24Nb合金,其中一种为冷轧态(CR),另一种为固溶态(ST),通过在三步热循环处理结合同步辐射对其相变行为进行了研究。当材料从350˚C冷却到-196˚C时,CR合金发生了β-αʺ和β-ω两种相变,而ST合金只发生了β-ω相变。这一结果表明Ti-Nb合金的相变行为,尤其是对β-αʺ相变,显著受到材料预处理的影响,且关于αʺ和ω相的互斥理论需要优化改进。我们发现材料的部分特征与单一热驱动的马氏体形成机制不符,并对涵盖了其他因素的机制描述进行了讨论。
英文摘要
Ti-Nb based alloys exhibit superelastic and shape memory properties over a wide range of temperatures, making them attractive for industrial applications. However, within the literature there are significant variations in the reported transformation behaviour for a given composition that remain unexplained. These variations are problematic to engineering design and limit the industrial uptake of these alloys. To investigate the source of these discrepancies, the transformation behaviour of Ti-24Nb (at.%) in two significantly different microstructural conditions, following cold rolling (CR) and following a subsequent solution heat treatment (ST), has been studied using in situ synchrotron diffraction data whilst undergoing a three step thermal cycle. When cooling from 350 to -196˚C, the CR condition material underwent both the β to αʺ and β to ω transformations, whilst only the β to ω transformation was observed in the ST condition material. These results show that the transformation behaviour of Ti-Nb alloys, in particular the β to αʺ transformation, is significantly influenced by prior processing and that theories of mutual exclusivity between αʺ and ω phase formation need revisiting. In addition, several features within the datasets were inconsistent with a solely thermally driven martensite formation mechanism and an alternative description that includes other factors is discussed.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P141-154
9. An experimental and modeling investigation of tensile creep resistance of a stable nanocrystalline alloy
一种稳定纳米合金的抗拉伸蠕变实验和模拟研究
C. Kale, S. Srinivasan, B.C. Hornbuckle, R.K. Koju, K. Darling, Y. Mishin✉, K.N. Solanki ✉
Y. Mishin:ymishin@gmu.edu
K.N. Solanki:kiran.solanki@asu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.020
摘要
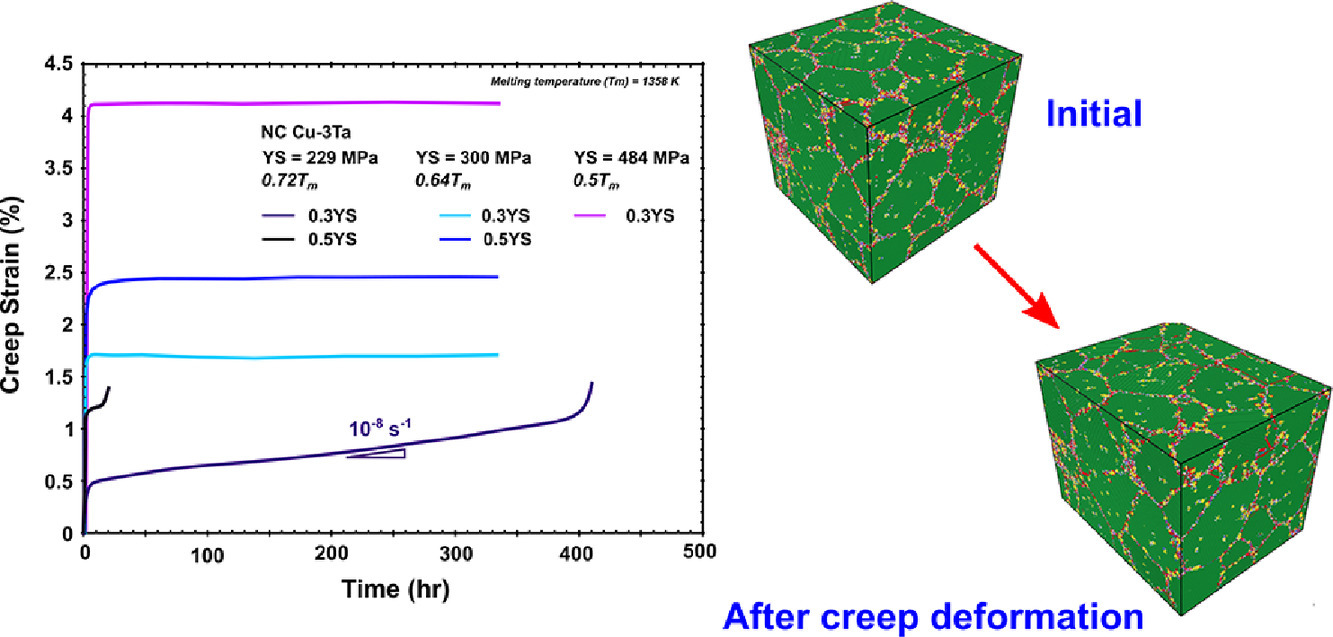
纳米晶材料与粗晶材料相比,在室温下往往具有更高的强度,更好的韧性和更好的耐磨性。但是,由于纳米晶的吉布斯自由能较高,因此在高温下很不稳定。实验上,常在相对较低的温度就已经观测到纳米晶的显著长大,这在很大程度上限制了纳米晶材料的实际应用。在本文中,我们提出了一种新的设计思路,大幅提高了纳米Cu-Ta合金在高温(0.64熔点)下的拉伸蠕变性能。这一设计思路通过固溶使得材料在晶界处和晶粒内部产生溶质元素的纳米团簇分布。我们发现加入Ta元素形成纳米团簇能够阻碍高温下的晶界迁移和位错运动。这使得材料表现出反常的拉伸蠕变行为,例如,不会出现在绝大多数材料中都有的稳态蠕变。这种设计策略能够帮助我们较为容易地大规模生产抗蠕变纳米晶部件,并可以应用于其他多组分系统中,如镍基合金。
英文摘要
Nanocrystalline (NC) materials possess excellent room temperature properties, such as high strength, wear resistance, and toughness as compared to their coarse-grained counterparts. However, due to the excess free energy, NC microstructures are unstable at higher temperatures. Significant grain growth is observed already at moderately low temperatures, limiting the broader applicability of NC materials. Here, we present a design approach that leads to a significant improvement in the high temperature tensile creep resistance (up to 0.64 of the melting temperature) of a NC Cu-Ta alloy. The design approach involves alloying of pure elements to create a distribution of nanometer sized solute clusters within the grains and along the grain boundaries. We demonstrate that the addition of Ta nanoclusters inhibits the migration of grain boundaries at high temperatures and reduces the dislocation motion. This leads to a highly unusual tensile creep behavior, including the absence of any appreciable steady-state creep deformation normally observed in almost all materials. This design strategy can be readily scaled-up for bulk manufacturing of creep-resistant NC parts and transferred to other multicomponent systems such as Ni-based alloys.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P169-180
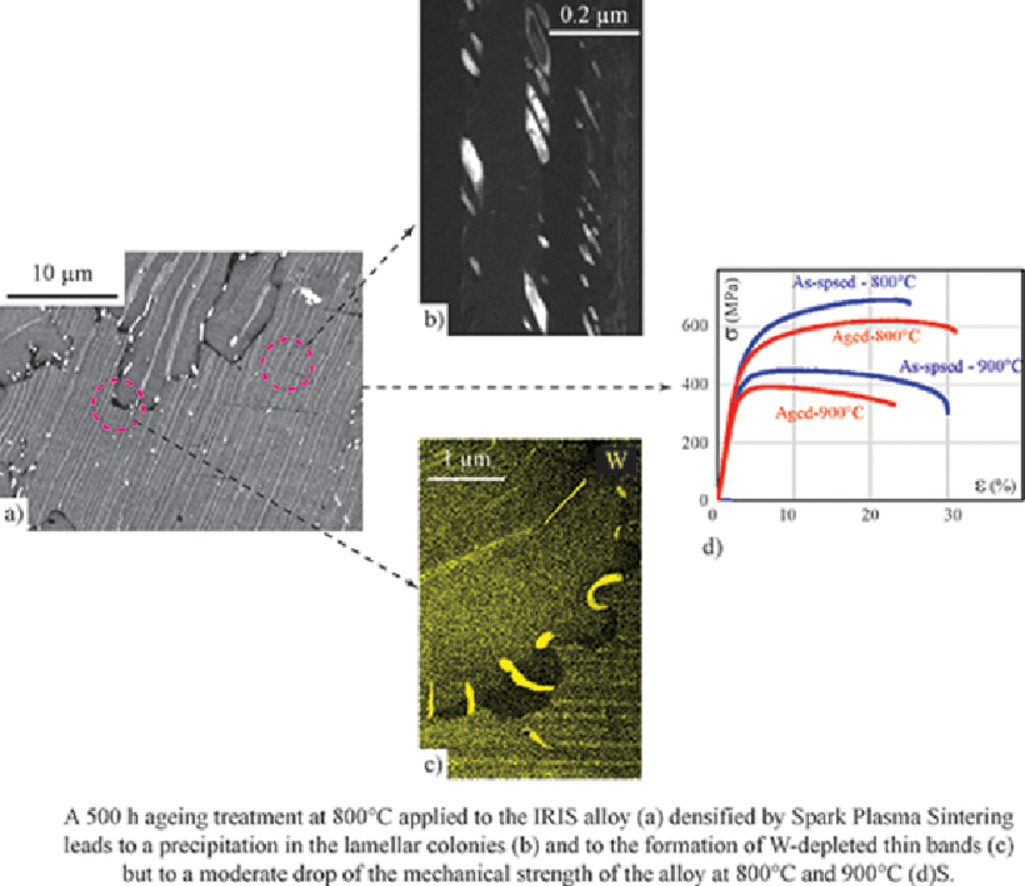
10. Effect of ageing on the properties of the W-containing IRIS-TiAl alloy
时效处理对含钨IRIS-TiAl合金性能的影响
Alain Couret✉, David Reyes, Marc Thomas, Nicolas Ratel-Ramond, Christophe Deshayes, Jean-Philippe Monchoux
A. Couret:alain.couret@cemes.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.07.061
摘要
我们研究了800 °C回火对IRIS合金(Ti49.9Al48W2B0.1)性能的影响。经等离子烧结致密化后的合金初始组织主要为γ晶粒围绕的层状组织。我们对时效处理后合金的强度和蠕变性能进行了相应力学实验测量;并用扫描、透射电子显微镜和X射线衍射对材料的组织变化进行了表征。结果表明,组织演变主要表现为层片状区域的收缩和β0相的析出,同时伴随钨的偏析和α2层宽度的减小。由于钨的低扩散率,使得这些组织变化相对有限。与之形成对比的是,在室温和高温下时效,可以对材料的机械性能产生不可忽视的影响。我们从微观组织的演变和不同温度下的变形机理等方面对实验结果进行了解释和讨论。
英文摘要
The effects of ageing at 800 °C on the properties of the IRIS alloy (Ti49.9Al48W2B0.1) are studied. The initial microstructure of this alloy densified by Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is mainly composed of lamellar colonies which are surrounded by γ grains. The evolutions of the alloy strength and creep resistance resulting from this ageing treatment are measured by the related mechanical tests. The microstructural changes are investigated by scanning and transmission electron microscopies and by X-ray diffraction.The main structural evolutions consist in a shrinkage of the lamellar areas and in a precipitation of β0 phase, which is accompanied by a moderate segregation of tungsten and a decrease of the α2 lamellar width. However, these evolutions are relatively limited and the microstructural stability is found to result mainly from the low diffusivity of tungsten. Conversely, a moderate effect of this ageing treatment on mechanical properties, at room and high temperatures, is measured. Such experimental results are interpreted and discussed in terms of the microstructural evolutions and of the deformation mechanisms which are activated at different temperatures under various solicitations.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P181-192
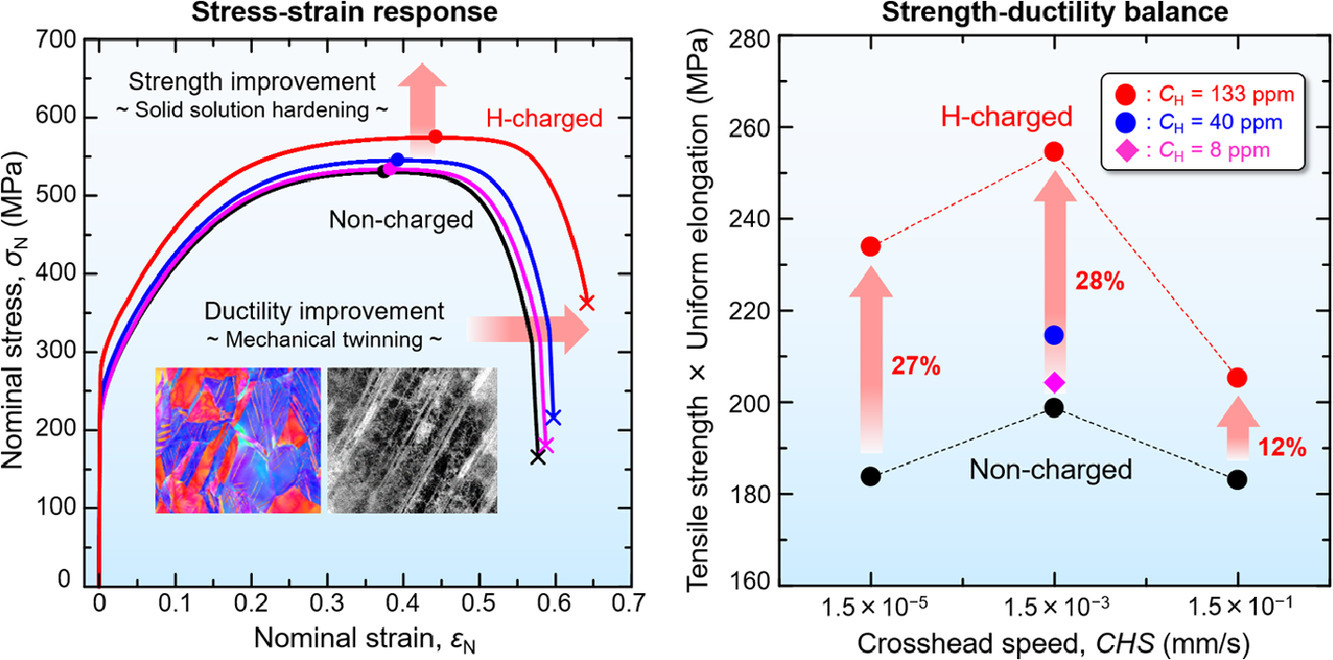
11. Hydrogen, as an alloying element, enables a greater strength-ductility balance in an Fe-Cr-Ni-based, stable austenitic stainless steel
氢作为一种合金元素使铁铬镍基奥氏体不锈钢具有更好的强度-延展性平衡
Yuhei Ogawa✉, Hyuga Hosoi, Kaneaki Tsuzaki, Timothée Redarce, Osamu Takakuwa, Hisao Matsunaga
Y. Ogawa:ogawa.yuhei.778@m.kyushu-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.024
摘要
我们发现,在商业化Fe-24Cr-19Ni合金中预充~7000 at.ppm的H溶质可以在不同变形速率拉伸试验中对材料的强度和延展性产生独特影响。其中,氢对材料强度的影响表现为屈服强度、流动应力和拉伸强度的提高;而对延展性的影响表现为均匀延伸率和断裂应变的增加,并且这两者的提高随着氢浓度的增加而更加显著。我们把拉伸强度与均匀伸长率之间的乘积作为强韧性的综合指标,在特定的中间应变速率下,给出了充氢对材料性能的最大优化。我们认为,屈服/流动应力的增加是由于固溶强化,而延展性的增强主要是因为机械孪晶。应力松弛实验间接揭示了动态氢-位错的相互作用对材料性能的关键影响,支持了我们的结论。
英文摘要
After pre-charging at the gaseous phase with a concentration of ~7,000 at. ppm, solute hydrogen was discovered to have an abnormal effect on both the strength and ductility enhancement of a commercially-available, Fe-24Cr-19Ni-based, stable austenitic stainless steel that had been subjected to tensile testing at various strain-rates. Specifically, the impact of hydrogen on material strength was accompanied by amplified yield and flow stresses, as well as tensile strength, while the improvement in ductility featured extended uniform elongation and strain-to-fracture, both of which became more pronounced as hydrogen concentration intensified. The product between tensile strength and uniform elongation served as indicators of the strength-ductility balance, at which hydrogen maximally optimized the indicator at the particular intermediate strain-rate. The yield/flow stress augmentations were interpreted in terms of solid-solution strengthening, whereas the enhanced ductility was primarily ascribed to the facilitation of mechanical twinning, whereby dynamic hydrogen-dislocation interaction exerted a critical influence as was indirectly revealed by supplemental stress-relaxation experiments.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P193-208
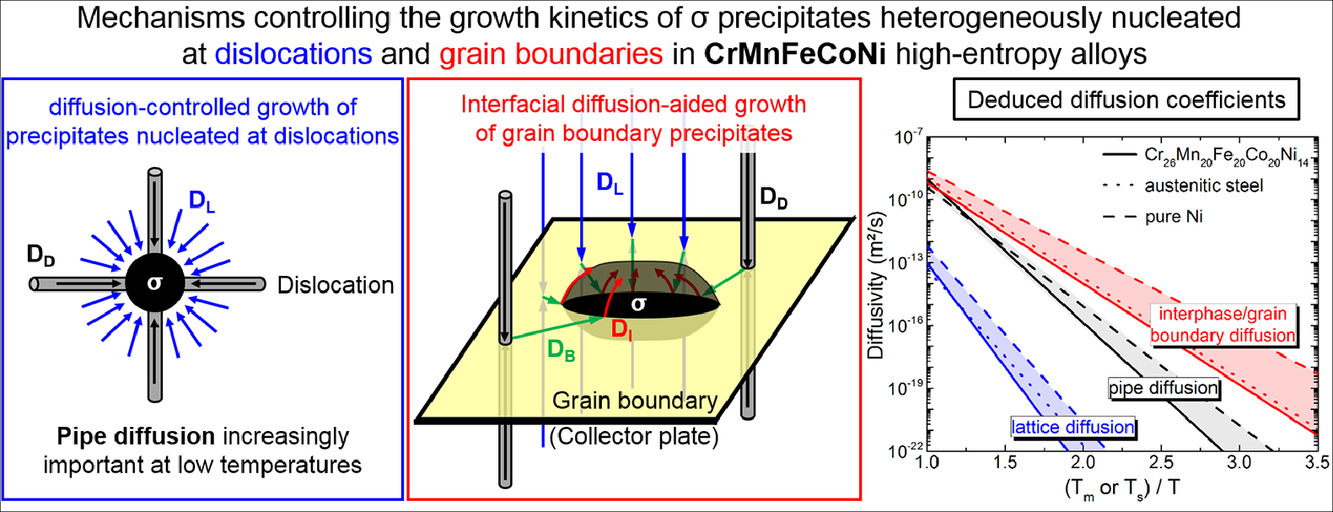
12. Growth kinetics of σ-phase precipitates and underlying diffusion processes in CrMnFeCoNi high-entropy alloys
CrMnFeCoNi高熵合金中σ相析出物的长大动力学及扩散过程
Guillaume Laplanche✉
Guillaume Laplanche:guillaume.laplanche@rub.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.023
摘要
我们研究了高熵合金中控制σ析出长大的关键机制和元素扩散过程。我们采用FCC单相Cr26Mn20Fe20Co20Ni14 合金作为研究对象,通过在600 °C-1000 °C进行0.1 h到1000 h的等温热处理使材料中析出σ相。我们对晶界处析出的σ相和晶粒内析出的σ相分别研究,发现晶粒内的σ析出是由于Cr向Mn、Fe、Co的扩散和Ni向Mn、Fe、Co的远离导致的,而晶界σ析出的长大速率则与界面扩散控制的盘状析出长大机制预测吻合。通过实验获得的动力学数据,我们推导得到了晶格扩散系数和缺陷扩散系数。在800 °C以上,析出长大主要受Cr在FCC基体中的扩散控制,扩散系数DL = 9.8×10-4exp[(-300 kJ/mol)/(RT)] m2/s。较低温度下,析出动力学因位错处的快速扩散而增加,扩散系数DD = 5.0×10-3exp[(-205 kJ/mol)/(RT)] m2/s。沿σ/FCC界面的Cr扩散速率可以通过晶界析出的粗化动力学推导并用阿伦尼乌斯公式表示,DI = 0.5×10-4exp[(-145 kJ/mol)/(RT)] m2/s。这一数值与合金中的晶界扩散系数大体相当。
英文摘要
Key mechanisms and elementary diffusion processes that control the growth kinetics of σ precipitates in high-entropy alloys were investigated in the present study. For this purpose, an off-equiatomic Cr26Mn20Fe20Co20Ni14 alloy with an initially single-phase FCC structure was subjected to isothermal heat treatments, which are known to promote the formation of σ phase, i.e., aging between 600 °C and 1000 °C for times ranging from 0.1 h to 1000 h. The growth kinetics of σ precipitates at grain boundaries of the FCC matrix and those located within the interior of the grains were analyzed separately. The latter precipitates are found to grow through direct substitutional diffusion of Cr-solutes towards and Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni away from them and the growth rate of the allotriomorphs can be rationalized by the collector plate mechanism of interfacial diffusion-aided growth. From the growth-kinetics data obtained in the present study, lattice interdiffusion coefficients as well as diffusivities along crystalline defects were obtained. Above 800 °C, the growth kinetics are dominated by lattice interdiffusion of Cr in the FCC matrix described by DL = 9.8×10-4exp[(-300 kJ/mol)/(RT)] m2/s. At lower temperatures, the growth kinetics are enhanced by fast interdiffusion along dislocation pipes, which temperature dependence is given by DD = 5.0×10-3exp[(-205 kJ/mol)/(RT)] m2/s. The Cr-diffusivity along σ/FCC interphase boundaries deduced from the thickening kinetics of grain boundary precipitates can be represented by the Arrhenius relationship DI = 0.5×10-4exp[(-145 kJ/mol)/(RT)] m2/s, which is similar to that found for grain boundary interdiffusion in metals and alloys.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P209-224
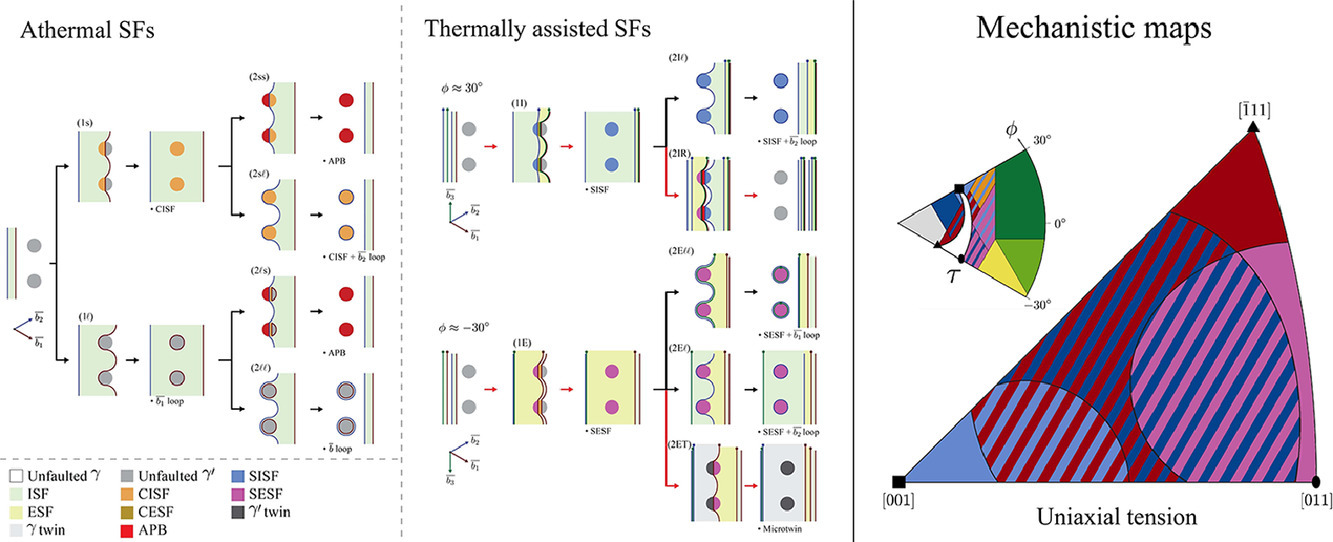
13. Stress orientation dependence for the propagation of stacking faults and superlattice stacking faults in nickel-based superalloys
镍基高温合金中应力取向对层错和超晶格层错扩展的影响
F.D. León-Cázares✉, F. Monni, C.M.F. Rae
F.D. León-Cázares:fdl22@cam.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.032
摘要
超晶格层错的扩展是在影响镍基高温合金中温蠕变性能的主要因素。根据位错的分布以及位错与析出的相互作用,这些平面缺陷可能在各种位置出现。尽管文献中已经对这些层错进行了大量表征,但是尚未有系统理论用于解释这些层错的配置情况。我们通过拉伸蠕变实验结合TEM、SEM和EBSD对多晶中的层错类型进行了定量研究。我们观测到了一种由析出层错和基体层错共同组成的新型缺陷结构,并提出了其形成机制。结合文献中的一些单晶数据,我们把实验结果纳入了已有的稳定预测框架中,以衡量取向对这些层错的影响。我们首先建立了一系列不同位错构型在立方和球形析出条件下发生层错扩展的一维力学平衡分析模型,随后将该模型应用到了6种超晶格和孪晶结构。模型提供了用于解释了应力、取向和微观结构的全新物理图像,这些预测结果与实验能够很好地定性吻合。
英文摘要
Superlattice stacking fault propagation dominates the creep deformation behaviour of nickel-based superalloys at intermediate temperatures. These planar defects may appear under many different configurations depending on the dislocation arrangements and their interactions with the precipitates. Whilst these have been spotted and described before, no systematic way to explain their configurations has been provided. The current study quantifies the types of faults in multiple grains within a tensile crept polycrystalline alloy via a combination of scanning transmission electron microscopy and electron backscatter diffraction. A new defect consisting of a superlattice intrinsic stacking fault in the precipitates and an extrinsic stacking fault in the matrix is observed and a mechanism for its formation is proposed. In combination with data from the literature on single crystals, the results are incorporated into a robust framework to discern the orientation dependencies of these faults. A comprehensive analytical model based on a series of one-dimensional force balances on different dislocation configurations is developed first for the case of athermal stacking fault propagation for the cases of cuboidal and spherical precipitates. The model is then extended to include six configurations of superlattice faults and microtwinning. This results in novel mechanistic maps that account for stress, orientation and microstructure, with excellent qualitative agreement with experiments.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P225-239
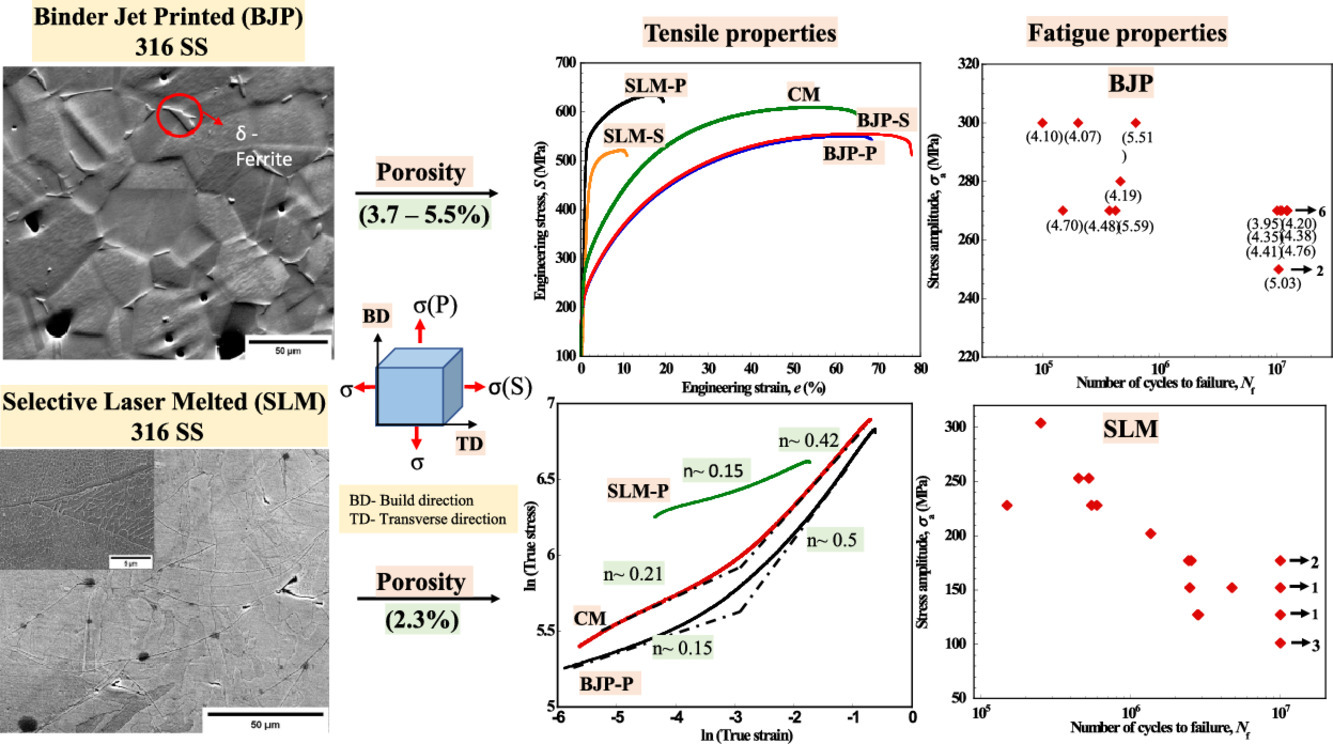
14. Fatigue strength of additively manufactured 316L austenitic stainless steel
增材制造316L奥氏体不锈钢的疲劳强度
Punit Kumar, R. Jayaraj, J. Suryawanshi, U.R. Satwik, J. McKinnell, U. Ramamurty✉
U. Ramamurty:uram@ntu.edu.sg
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.033
摘要
我们研究了使用粘结喷印方式(BJP)和选区激光熔化(SLM)两种方式制备的316L不锈钢的组织和性能,并将其与传统方式(CM)制备的材料进行了比较,其中着重比较了它们的无缺口疲劳性能。结果表明,尽管BJP材料中含有大量孔洞,但是其加工硬化行为、韧性和疲劳性能都与CM材料十分接近。相比之下,SLM材料则强度更高(尤其是屈服强度),并且尽管孔洞比BJP样品小得多,但韧性却明显更差。我们基于这两种材料不同的加工环境导致的组织差异对这些实验结果进行了合理解释。在准静态和循环载荷作用下,BJP合金塑性变形早期阶段普遍存在的平面滑移机制以及其他微观结构因素导致了在孔洞形核的小裂纹的中止,因此孔隙率对BJP合金的延展性和疲劳强度均无不利影响。而在SLM合金中,一方面胞状组织可以显著提高屈服强度;另一方面胞状组织太细,而柱状晶晶粒较大且取向差较小,因此无法引起裂纹转向或中止。以上的实验结果对具有良好机械性能的增材制造合金设计具有重要的指导意义。
英文摘要
The microstructures and mechanical properties of the 316L austenitic stainless steel fabricated using binder jet printing (BJP) and selective laser melting (SLM) were investigated and compared with those of the conventionally manufactured (CM) alloy, with particular emphasis on the unnotched fatigue resistance. Results show that the work hardening behavior, ductility, and fatigue strength (σf) of the BJP specimens, which contain significant amounts of pores, are surprisingly comparable to those of the CM alloy. In contrast, the SLM specimens are considerably stronger, especially in terms of the yield strength, less ductile, and far inferior in terms of σf although the porosity in them is relatively smaller as compared to the BJP specimens. These results are rationalized by recourse to the distinct microstructures in the two additively manufactured alloys, which stem from the different processing conditions experienced by them. The planar slip regime that prevails in the early stages of plastic deformation of the BJP alloys and a combination of other microstructural factors lead to the arrest of small cracks that nucleate at the corners of the pores, both under quasi-static and cyclic loads; as a result, neither ductility nor fatigue strength are adversely affected by the porosity in the BJP alloys. In the SLM alloy, the cellular structure, which enhances the yield strength considerably, is too fine whereas the columnar grains are minimally misoriented and coarse enough to induce any crack deflection or arrest. Implications of these results in terms of possible directions for designing AM alloys with high mechanical performance are discussed.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P240-252
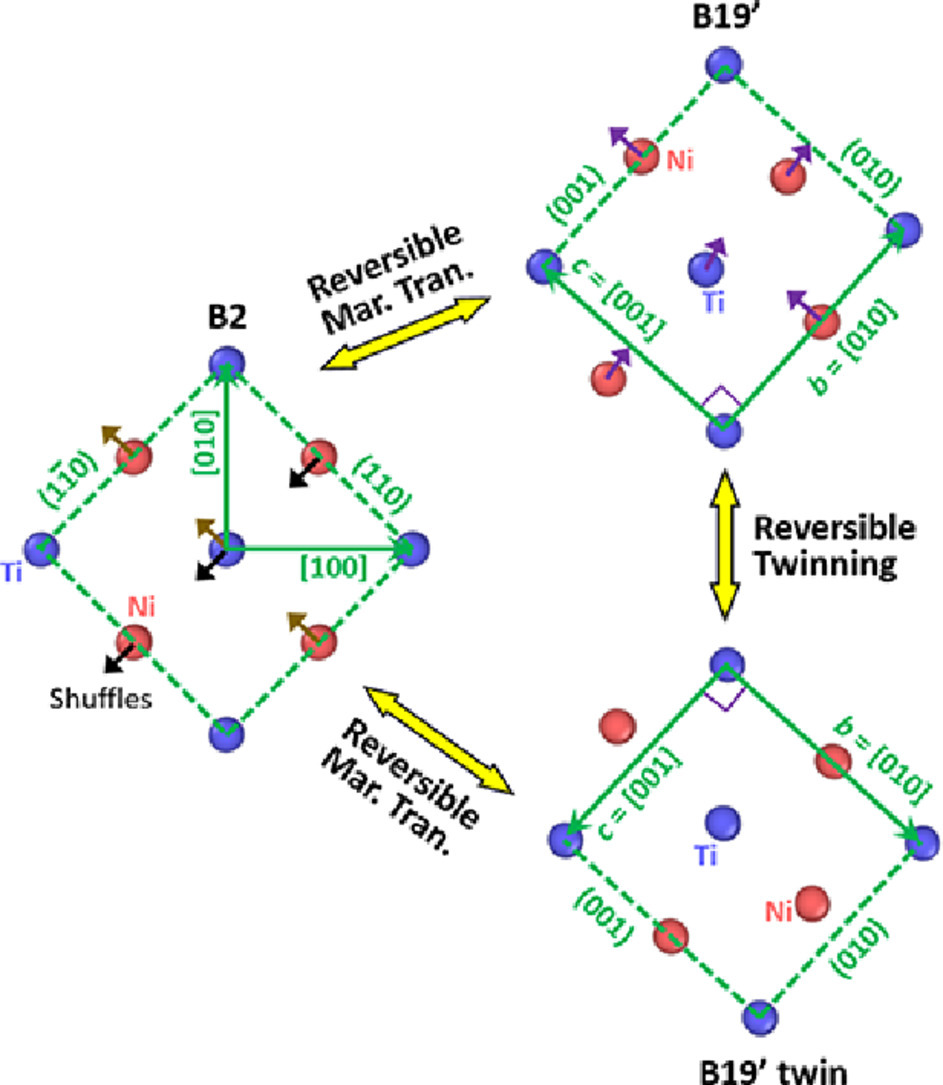
15. Structural origin of reversible martensitic transformation and reversible twinning in NiTi shape memory alloy
镍钛形状记忆合金可逆马氏体相变和可逆孪晶在组织层面的起因
Bin Li✉, Yidi Shen, Qi An
B. Li:binl@unr.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.039
摘要
在过去的几十年中,关于NiTi形状记忆合金中BCC奥氏体(B2)到单斜马氏体(B19′)相变和马氏体孪晶的机制取得了长足的进展。但目前为止,原子层面关于晶格关联的研究却鲜有报导,这使得我们难以全面而完整地理解马氏体相变和孪晶的机理。因此,我们对B2 → B19′相变和该过程中发生的孪晶进行了原子尺度模拟,并且着重关注了相变和孪晶中的晶格关联。模拟结果表明,当马氏体在奥氏体中形核时,马氏体会自发地与奥氏体形成孪晶关系。即,我们成功模拟了这种自适应过程。随后组织发生合并,一些马氏体晶粒长大,而邻近晶粒消失,这一过程中界面是弹性的,其迁移可逆。最终,孪晶马氏体形成。在B2→B19′转变过程中,B19′单斜结构可被视为一种形变了的密排六方(HCP)结构。在这一视角下,NiTi合金中的马氏体相变本质上类似于BCC↔HCP相变,只是其中发生了可逆的原子震荡;同样地,孪晶过程本质上也类似于HCP金属中的{101-2}孪晶。另一个重要发现是,B19′马氏体表现出一种非常特殊的双晶结构:单斜晶胞中较弱的Ti-Ti键合使得晶胞容易发生二次取向。因此,两个不同取向的晶胞可以共存在同一马氏体晶粒中而使马氏体失去了长周期结构,这为体系在适应应变时提供了额外的自由度。这些结果很好地解释了B19 '马氏体对拉伸的极强适应性及其变形可逆的原因。
英文摘要
Much progress has been made over the past few decades in resolving the mechanism for the transformation from ordered body-centered-cubic (B2) austenite to monoclinic martensite (B19′) in NiTi shape memory alloy, as well as the twinning mechanisms in martensite. However, so far no lattice correspondence analyses on the atomic scale have been conducted, as a result, these mechanisms have not been completely understood in terms of the pathways for reversible phase transition and reversible twinning in martensite. In this work, atomistic simulations were performed to investigate how B2 austenite transforms to B19′ martensite and how twins are formed during phase transformation. In particular, lattice correspondence in the structural evolutions was carefully analyzed to reveal the martensitic transformation mechanism and twinning mechanism with much better clarity. The simulation results show that, when martensite grains were nucleated in austenite, they already formed a twin relationship as a natural result of the crystal structure. Thus, self-accommodation is achieved naturally. Coalescence occurred subsequently and some martensite grains grew at the expense of their neighbors, indicating that the interfaces are elastically mobile and their migration is reversible. Eventually twinned martensite variants were created. It is shown that, in the B2 → B19′ transformation, the B19′ monoclinic structure can be treated as a distorted hexagonal close-packed (HCP) structure. With this treatment, it is demonstrated that the martensitic transformation is essentially similar to BCC ↔ HCP transformation which only involves atomic shuffles and is reversible, and twinning in martensite is essentially similar to {101-2} twinning in HCP metals which only involves atomic shuffles and is reversible as well. Another significant discovery is that the B19′ martensite exhibits a very special dual-lattice structure: the relatively weak Ti-Ti bonding of the monoclinic unit cell permits easy reorientation of lattice units. As a result, two differently oriented lattice units co-exist in the same martensite grain which loses long range periodicity, providing an extra degree of freedom for accommodating external and internal strains. These results explain well why B19′ martensite is extremely adaptive to straining and why deformation is reversible.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P253-263
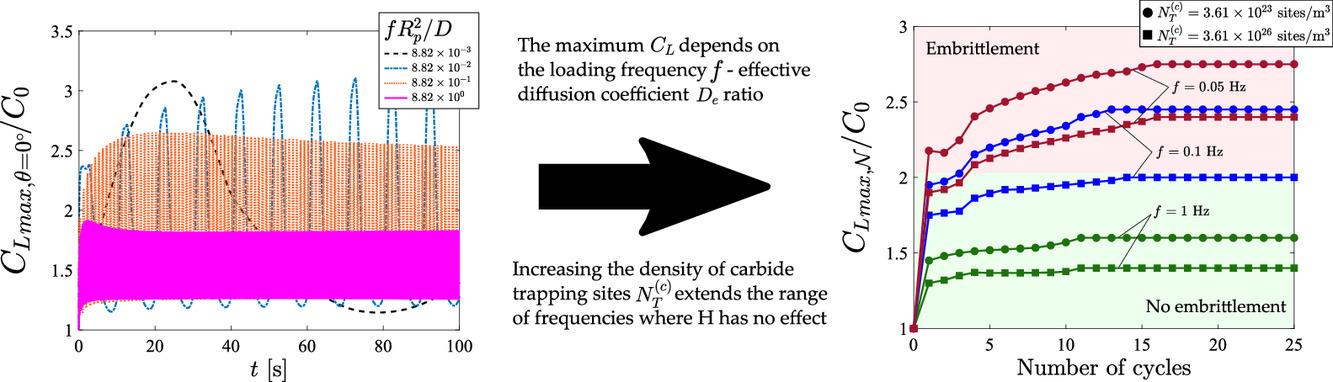
16. Analysis of the influence of microstructural traps on hydrogen assisted fatigue
组织中的氢陷阱对氢致疲劳断裂的影响分析
Rebeca Fernández-Sousa, Covadonga Betegón, Emilio Martínez-Pañeda✉
E. Martínez-Pañeda:e.martinez-paneda@imperial.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.030
摘要
我们研究了循环载荷下组织中的氢陷阱对氢扩散和氢脆的影响。我们建立了一个能涵盖多种氢陷阱的有限元模型,并用它解释了裂纹尖端形貌和氢浓度随载荷频率、结合能和陷阱密度的变化关系。结果表明,晶格中的最大氢浓度对载荷频率和有效扩散系数的比值十分敏感。在预充氢的样品(封闭系统)和暴露在氢源下的样品(开放系统)中都观测到了这一结果。我们设计了实验确定了惰性环境下的氢致脆化临界浓度。随后,我们定量研究和讨论了高陷阱密度材料对循环载荷过程中对氢脆的缓和作用。结果表明,与静态条件下不同,增加陷阱密度是一种可行且可同时应用于封闭和开放系统的抗氢致疲劳合金设计策略。
英文摘要
We investigate the influence of microstructural traps on hydrogen diffusion and embrittlement in the presence of cyclic loads. A mechanistic, multi-trap model for hydrogen transport is developed, implemented into a finite element framework, and used to capture the variation of crack tip lattice and trapped hydrogen concentrations as a function of the loading frequency, the trap binding energies and the trap densities. We show that the maximum value attained by the lattice hydrogen concentration during the cyclic analysis exhibits a notable sensitivity to the ratio between the loading frequency and the effective diffusion coefficient. This is observed for both hydrogen pre-charged samples (closed-systems) and samples exposed to a permanent source of hydrogen (open-systems). Experiments are used to determine the critical concentration for embrittlement, by mapping the range of frequencies where the output is the same as testing in inert environments. We then quantitatively investigate and discuss the implications of developing materials with higher trap densities in mitigating embrittlement in the presence of cyclic loads. It is shown that, unlike the static case, increasing the density of “beneficial traps” is a viable strategy in designing alloys resistant to hydrogen assisted fatigue for both closed- and open-systems.
ACTA Vol. 199, 15 Oct. 2020, P278-287
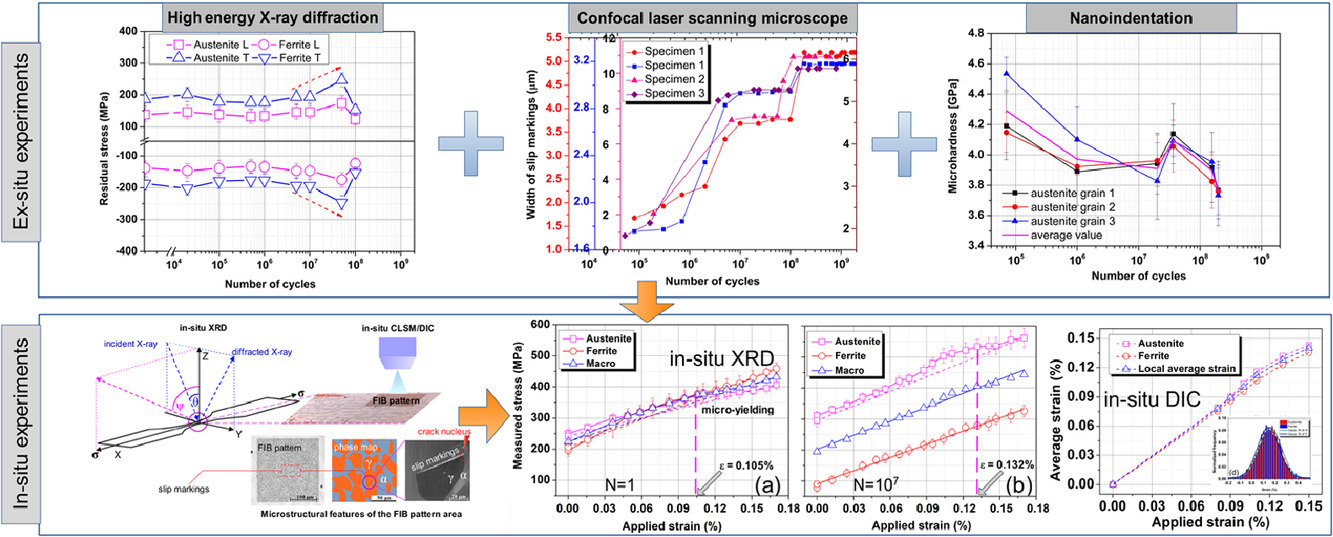
17. Microcrack initiation mechanism of a duplex stainless steel under very high cycle fatigue loading condition: The significance of load partitioning and micro residual stresses
载荷配分和微残余应力对双相不锈钢高周疲劳载荷下微裂纹萌生过程的影响
Hongwang Fu✉, Benjamin Dönges, Ulrich Krupp, Ullrich Pietsch, Claus-Peter Fritzen, Xinbing Yun, Hans-Jürgen Christ✉
H. Fu:hongwangfu@djtu.edu.cn
H.-J. Christ:Hans-Juergen.Christ@unisiegen.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.042
摘要
金属材料在超高周疲劳(VHCF)下的响应长期以来一直是疲劳理论中一个富有挑战性的问题。我们采用了几种敏感性较高的技术手段,如高能X射线衍射(HEXRD)、激光共聚焦扫描显微镜(CLSM)、纳米压痕、透射电子显微镜(TEM)等,对双相不锈钢(DSS)在超高周疲劳下的响应进行了研究。随后我们在观测到的变化阶段对样品进行了原位XRD和 DIC实验,以研究微裂纹的萌生机制。实验结果表明,材料中的奥氏体相在VHCF过程中表现出了反复的软化-硬化-软化行为。原位实验表明,在这一阶段,两相之间存在应力配分和应力转移,这说明循环过程会显著影响外加载荷在材料中的分布。DIC结果表明,卸载后的残余应变在相界处表现出强烈的变化,说明微残余应力发生了明显增长。在此基础上,我们提出了一种VHCF加载下DSS的统一裂纹萌生机制。
英文摘要
Investigation on the cyclic response of metallic materials in very high cycle fatigue (VHCF) is a challenging problem, which hinders the development of fatigue theories. To overcome this difficulty, we initially applied several sensible techniques, e.g., High-energy X-ray diffraction (HEXRD), confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM), nanoindentation and transmission electron microscope (TEM) to investigate the cyclic response of a duplex stainless steel (DSS) in the VHCF regime. In-situ XRD and in-situ digital image correlation (DIC) experiments were subsequently performed at observed changing stages, intending to explore the underlying mechanism of microcrack initiation. The first-hand results obtained revealed that the austenite phase exhibits cyclic softening-hardening-softening behavior during the VHCF process. The in-situ investigations performed at the cyclic softening and hardening stages showed a load partitioning and a load transfer between the two phases, implying the cyclic response can significantly affect the distribution of the applied load. Residual strain obtained by DIC technique after unloading exhibited strong variations at phase boundaries, suggesting micro residual stresses have developed pronouncedly. Based on all the experimental findings, a unified crack initiation mechanism for the investigated DSS during VHCF loading was proposed.
微信公众号:Goal Science
投稿邮箱:wechat@gs-metals.com
投稿微信:GSmaterial
