金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.195, 1 Apr. 2021
2021-02-24 来源:Goal Science

Vol. 195 目录
1. Phase stability of the amorphous phase and non-equilibrium phase in a β Ti-Zr-based shape memory alloy
β Ti-Zr基形状记忆合金非晶相和非平衡相的相稳定性
2. Local atomic structures of Gd and Zn atoms in extruded Mg-Gd-Zn alloys
挤压Mg-Gd-Zn合金中Gd和Zn原子的局部原子结构
3. Architectured multi-metal CoCrFeMnNi-Inconel 718 lamellar composite by high-pressure torsion
高压扭转构造多金属CoCrFeMnNi-Inconel 718层状复合材料
4. Formation of {11-22} contraction twins in titanium through reversible martensitic phase transformation
通过可逆马氏体相变在钛中形成{11-22}收缩孪晶
5. Mitigating the Hall-Petch breakdown in nanotwinned Cu by amorphous intergranular films
通过将V添加剂与原位TiC颗粒相结合强化FeCrNiCu高熵合金
6. Hierarchical refinement of nickel-microalloyed titanium during additive manufacturing
镍微合金化钛在增材制造中的分层细化
7. Improving the hydrogen cycling properties by Mg addition in Ti-V-Zr-Nb refractory high entropy alloy
添加Mg改善Ti-V-Zr-Nb耐火高熵合金的氢循环性能
8. The effect of low temperature heat treatment on stress corrosion crack initiation in machined 316L stainless steel in high-temperature hydrogenated water
低温热处理对加工316L不锈钢在高温氢化水中应力腐蚀裂纹萌生的影响
9. Nanoprecipitates induced dislocation pinning and multiplication strategy for designing high strength, plasticity and conductivity Cu alloys
利用纳米析出诱导位错钉扎和增殖策略设计高强度、高塑性和高导电性铜合
10. Evaluating the Taylor hardening model in polycrystalline Ti using high energy X-ray diffraction microscopy
使用高能X射线衍射显微镜评估多晶Ti中的泰勒硬化模型
SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113721
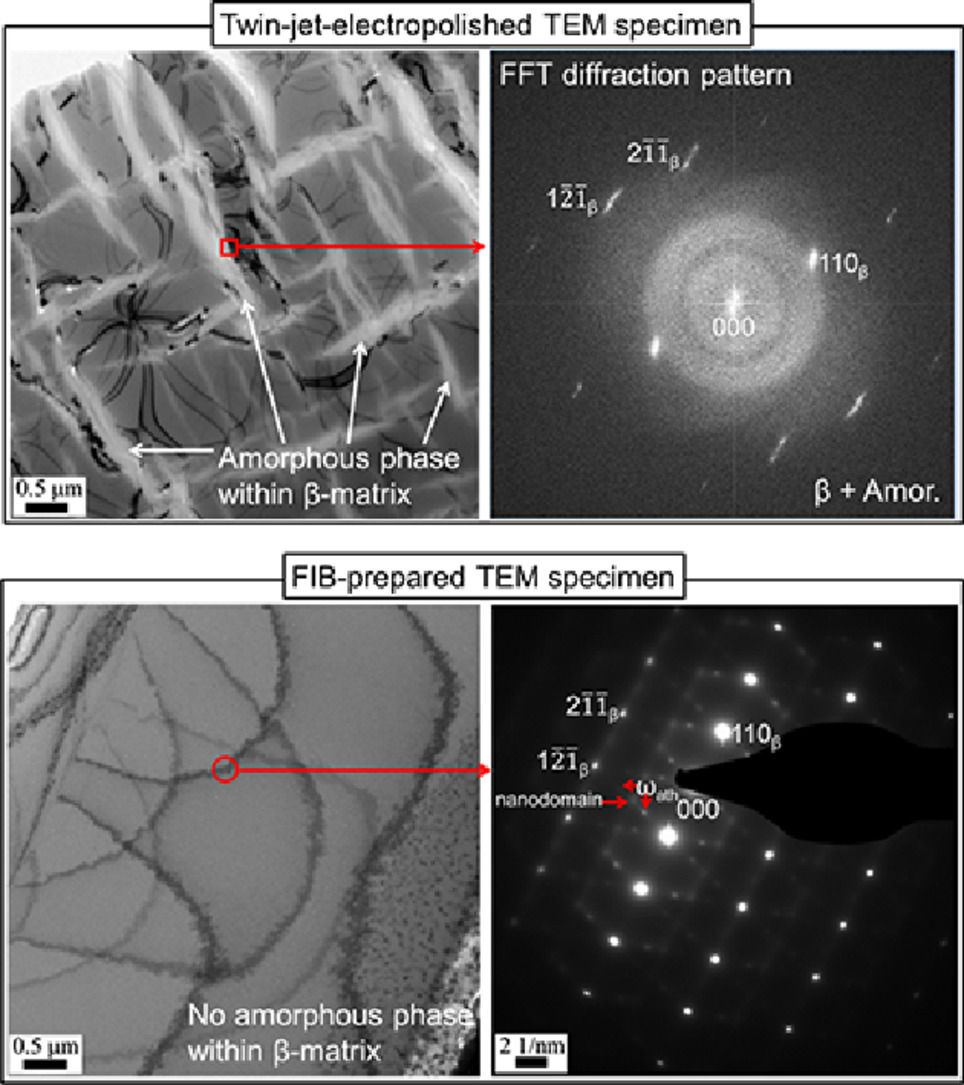
1. Phase stability of the amorphous phase and non-equilibrium phase in a β Ti-Zr-based shape memory alloy
β Ti-Zr基形状记忆合金非晶相和非平衡相的相稳定性
Shuanglei Li, Mi-Seon Choi, Tae-Hyun Nam✉
Tae-Hyun Nam: tahynam@gnu.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113721
摘要
本文研究了Ti-Zr-Nb-Sn形状记忆合金(SMA)中亚稳β相的非晶化以及非晶相和非平衡相的相稳定性。通过透射电子显微镜观察到双喷电解薄箔样品中均匀嵌入β基体的透镜状非晶相。同时,在β基体中观察到了非平衡非热ω相和纳米畴相的同时存在。这些非平衡相可以很好地与非晶相的形成进行竞争,抑制非晶相的产生,导致通过X射线衍射(XRD)和电子背散射衍射(EBSD)以及透射电镜(TEM) 技术在块状样品观察不到非晶相。我们认为双喷电解TEM样品中观察到的非晶相是由于在双喷电解抛光过程中引入了与氢有关的假象。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113720
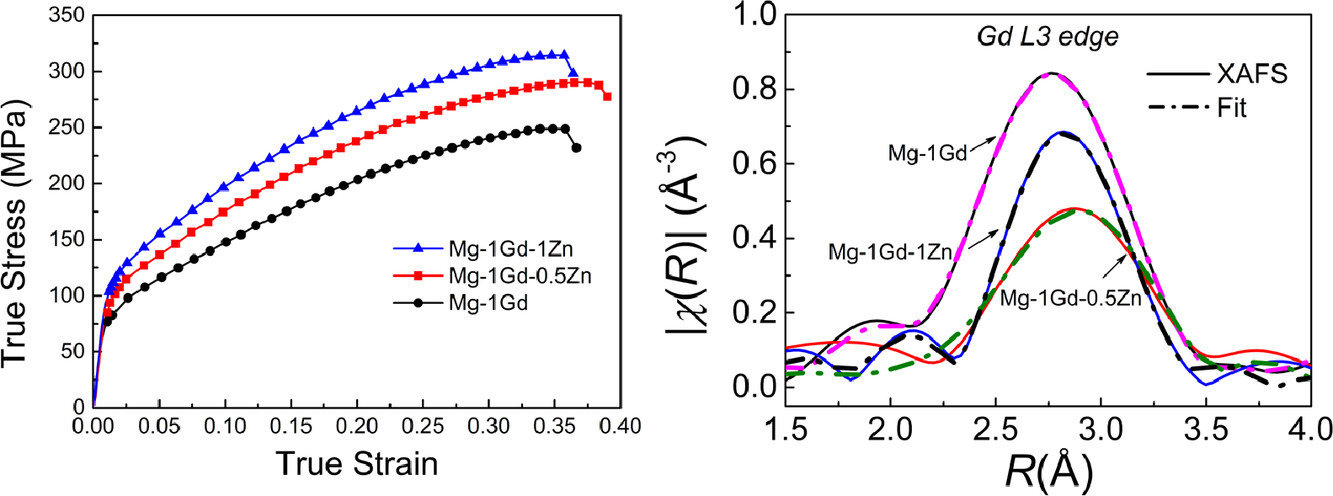
2. Local atomic structures of Gd and Zn atoms in extruded Mg-Gd-Zn alloys
挤压Mg-Gd-Zn合金中Gd和Zn原子的局部原子结构
J.J. Zong, J. Zhao, X.D. Wang✉, P.F. An, J. Zhang, T.D. Hu, Q.P. Cao, D.X. Zhang, B. Jiang✉, J.Z. Jiang✉
X.D. Wang: wangxd@zju.edu.cn 浙江大学
B. Jiang: jiangbinrong@cqu.edu.cn 重庆大学
J.Z. Jiang: jiangjz@zju.edu.cn 浙江大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113720
摘要
少量添加Gd和Zn可以显著改善挤压Mg-1 wt.%Gd-xZn (x = 0, 0.5, 1 wt.%) 合金的力学性能。然而,目前仍然不清楚它们是如何改变合金结构的。我们利用X射线吸收谱精细结构发现Zn原子倾向于与Gd结合,0.5 wt.% Zn的加入大大降低了Gd原子的配位数(CN),形成了强化的双固溶体强化。然而,1 wt.% Zn不仅增加了Zn和Gd的CNs,而且促进了Mg3Zn3Gd2相的形成。与晶粒细化的强化效果相比,固溶强化并不是主导因素。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113722
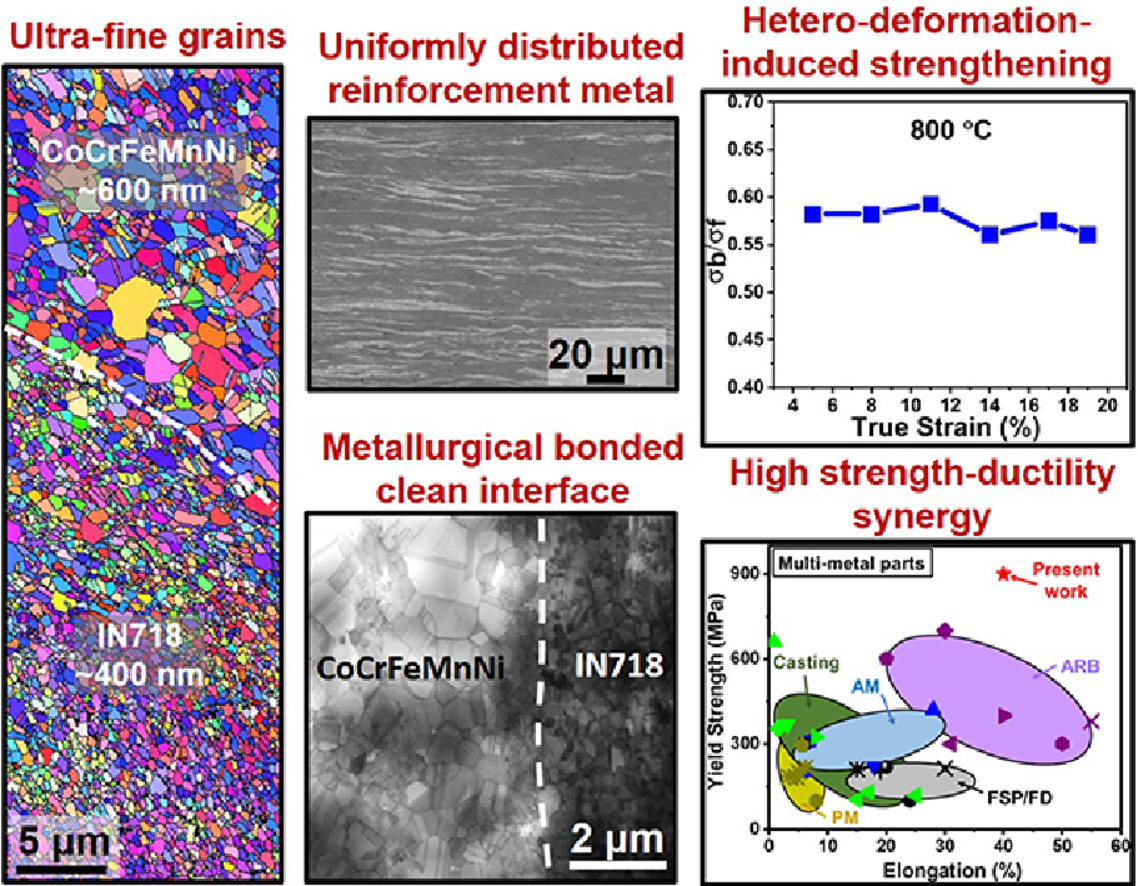
3. Architectured multi-metal CoCrFeMnNi-Inconel 718 lamellar composite by high-pressure torsion
高压扭转构造多金属CoCrFeMnNi-Inconel 718层状复合材料
G.M. Karthik, Peyman Asghari-Rad, Praveen Sathiyamoorthi, Alireza Zargaran, Eun Seong Kim, Taek Soo Kim, Hyoung Seop Kim✉
Hyoung Seop Kim: hskim@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113722
摘要
近年来,研究人员对多金属复合材料进行了广泛的探索,以填补其强度-延伸率窗口的空白区域。然而,由于大多数加工制备技术都涉及熔化/凝固和高温,因此制备这些复合材料具有挑战性,而且仅限于几种材料体系。本研究提出了一种基于粉末冶金的高压扭转方法,来制备多金属复合材料。高压扭转后实现了以高熵合金(CoCrFeMnFe)为基体和均匀分布的镍基高温合金(Inconel 718)为增强材料的层状纳米晶复合材料。本方法在基体和增强体中都产生了具有超细晶粒尺寸的优良冶金结合界面。该复合材料的屈服强度为900 MPa,延伸率为40%,克服了多金属复合材料长期以来的挑战。本研究提出了一种通用的多金属复合材料的制备方法,可以拓宽复合材料的制备界限,实现强度和延展性的协同提升。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113694
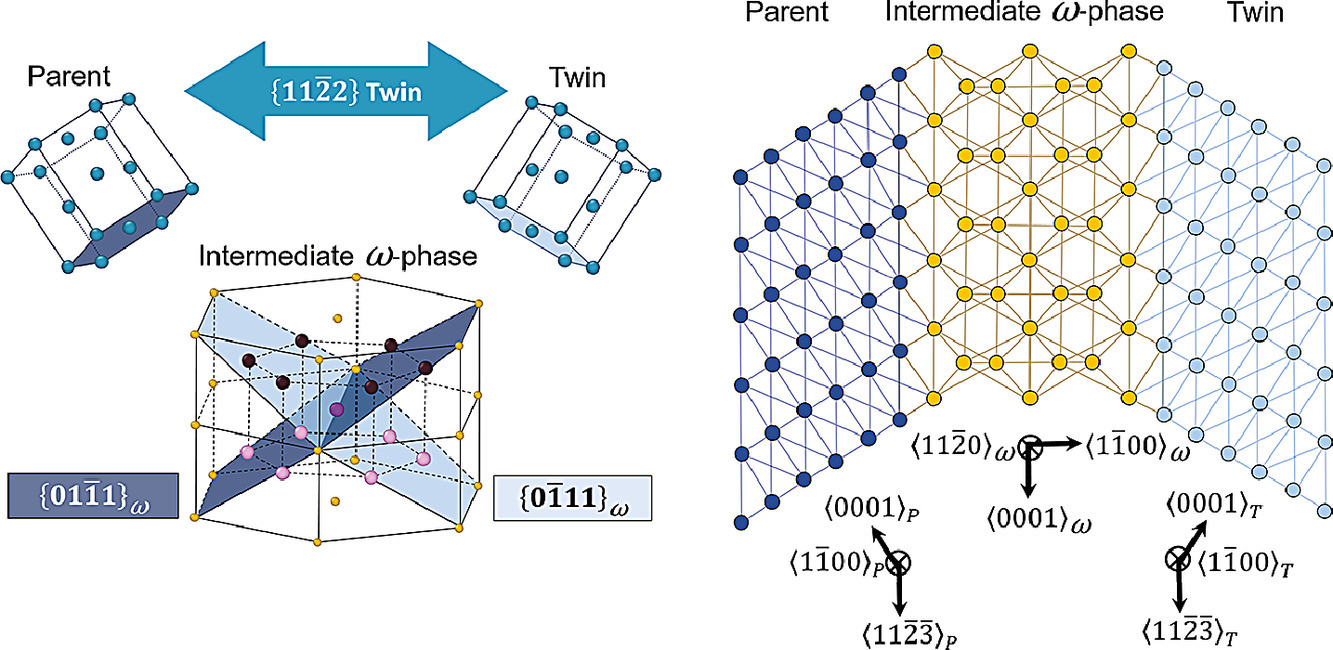
4. Formation of {11-22} contraction twins in titanium through reversible martensitic phase transformation
通过可逆马氏体相变在钛中形成{11-22}收缩孪晶
Amir Hassan Zahiri, Jamie Ombogo, Lei Cao✉
Lei Cao: leicao@unr.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2020.113694
摘要
我们报道了通过可逆的α→ω→α马氏体相变,在α-钛中发现了一种非常规的{11-22}孪晶机制。具体来说,母相α-相首先转变为一个中间ω-相,然后迅速转变为孪生α-相,从而形成{11-22}收缩孪晶。此外,我们还证明了可逆α→ω→α相变遵循着α-母相、ω-中间相和α-孪生相之间的严格取向关系。最后,我们证明了在shuffle、shear和conjugate孪晶平面上,我们的机制与经典孪晶理论是一致的。本研究揭示了中间ω-相在孪生过程中的重要作用,为现有的{11-22}孪生机制提供了重要的细节信息。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113724
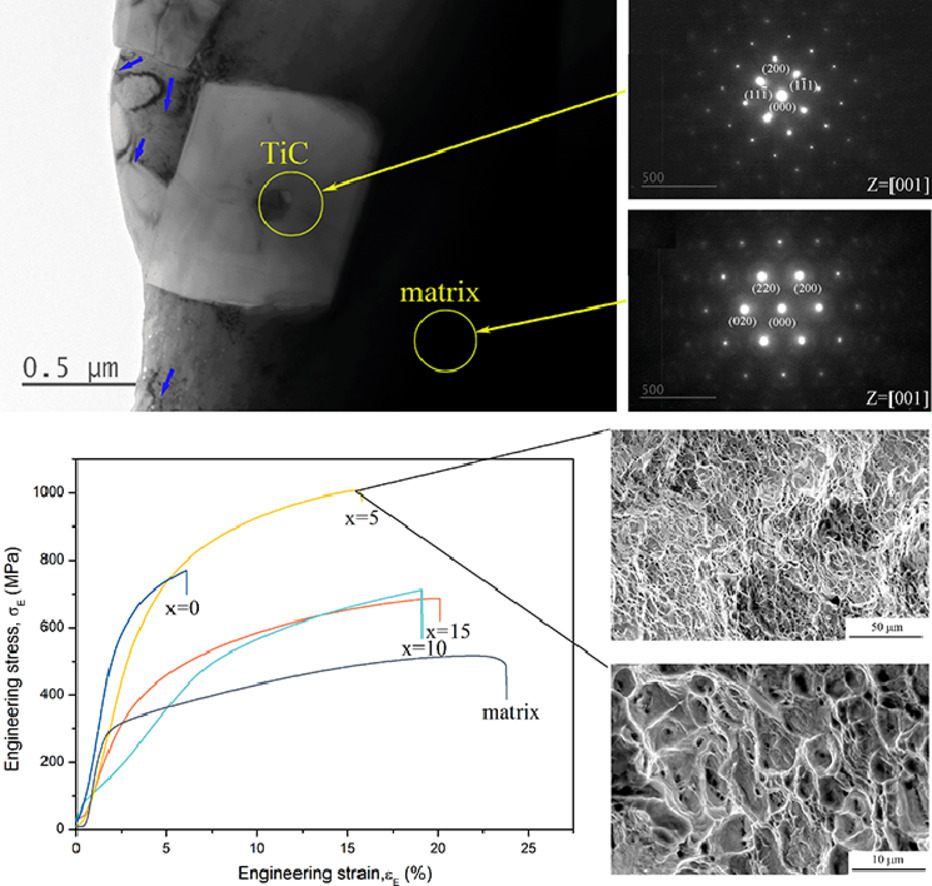
5. Strengthening FeCrNiCu high entropy alloys via combining V additions with in-situ TiC particles
通过将V添加剂与原位TiC颗粒相结合强化FeCrNiCu高熵合金
Hao Wu, Sirui Huang, Heguo Zhu✉, Zonghan Xie
Heguo Zhu: zhg1200@njust.edu.cn
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113724
摘要
我们研究了V的添加和原位TiC颗粒的形成对FeCrNiCu高熵合金组织和力学性能的影响。研究发现,V的加入使FeCrNiCu基体的结构由FCC(即面心立方)转变为FCC+BCC(即面心立方+体心立方)。铸态10 vol.%TiC/FeCrNiCuV0.1高熵合金基复合材料具有优良的力学性能,屈服强度和抗拉强度分别为653.5 MPa和1006.5 MPa。我们评价了V添加和原位TiC颗粒在FeCrNiCu中产生的额外强化,发现理论预测与实验结果吻合较好。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113727
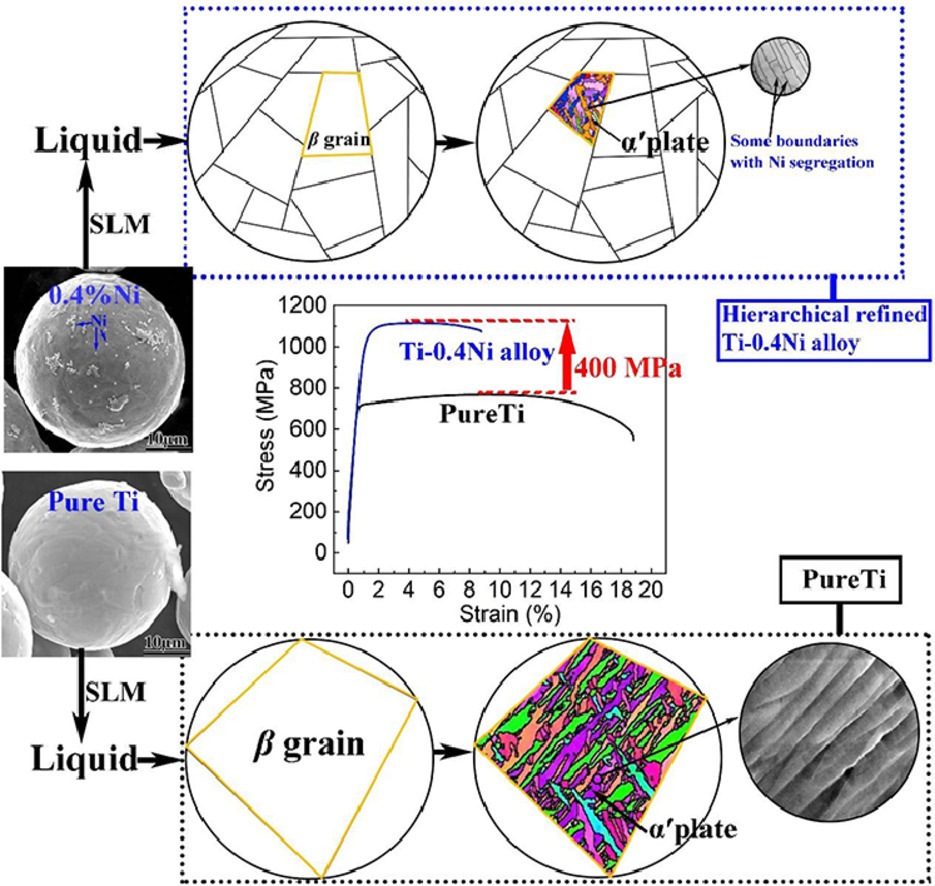
6. Hierarchical refinement of nickel-microalloyed titanium during additive manufacturing
镍微合金化钛在增材制造中的分层细化
Zhihui Xiong, Xiaotong Pang, Shilong Liu✉, Zhuguo Li✉, R.D.K. Misra
Shilong Liu: sliu6@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学
Zhuguo Li: lizg@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113727
摘要
本文阐述了镍(Ni)对选择性激光熔化钛合金晶粒细化和强化的显著微合金化作用。在选择性激光熔化Ti-0.4Ni合金中,添加0.4 wt.%的Ni可避免脆性共析Ti2Ni相的形成,获得由纳米α′条组成的超细韧性组织。Ni的固溶强化和晶粒细化作用使Ti-0.4Ni合金的强度由纯Ti的~745 MPa显著提高到~1120 MPa,延伸率达到8.8%。本文强调了对钛合金进行Ni微合金化处理,可以提高增材制造钛合金的性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113742
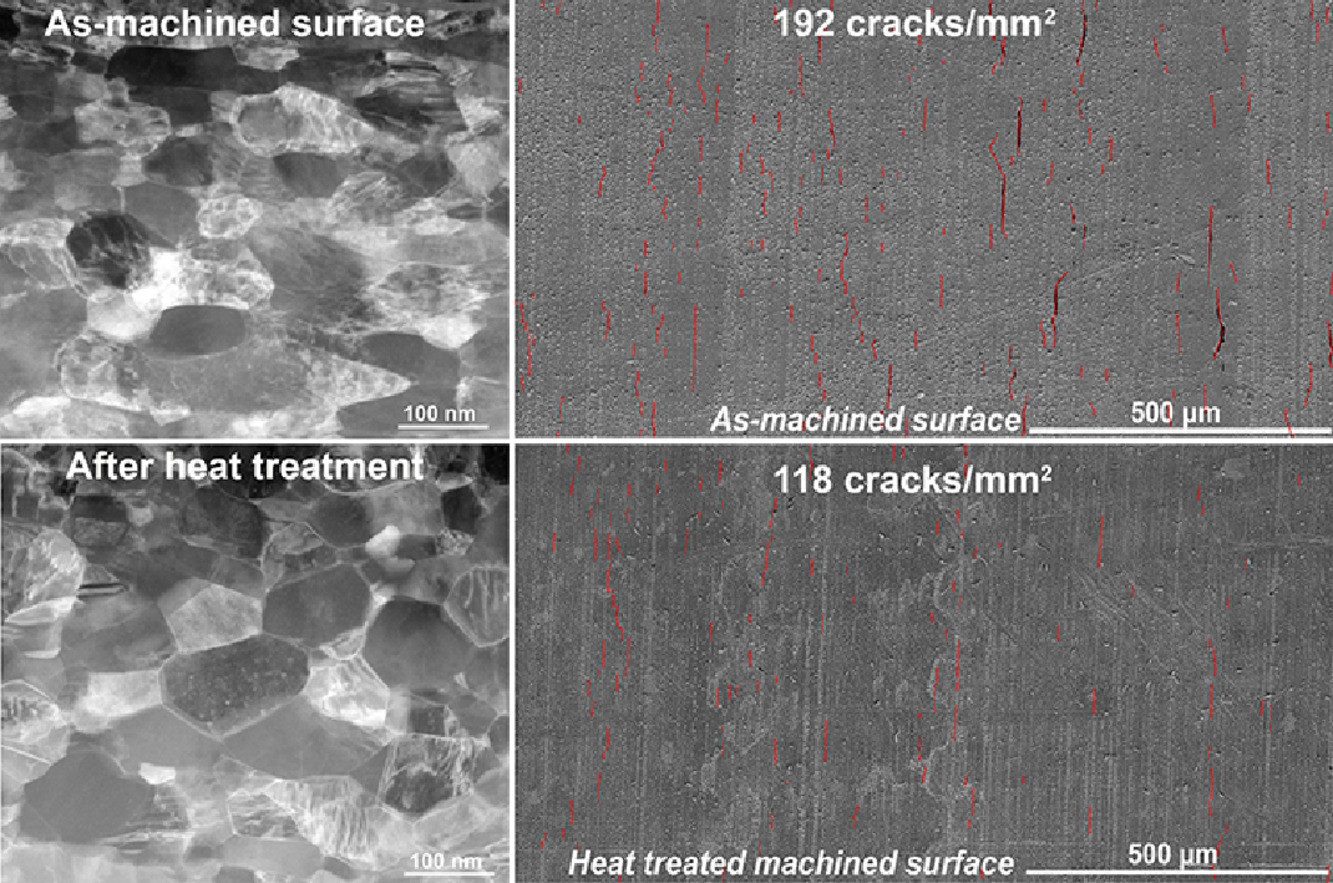
7. The effect of low temperature heat treatment on stress corrosion crack initiation in machined 316L stainless steel in high-temperature hydrogenated water
低温热处理对加工316L不锈钢在高温氢化水中应力腐蚀裂纹萌生的影响
Litao Chang✉, Kudzanai Mukahiwa, Jonathan Duff, M. Grace Burke, Fabio Scenini
Litao Chang: changlitao@sinap.ac.cn
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113742
摘要
在高温氢化水中进行慢应变速率拉伸(SSRT)测试之前,将冷轧316L不锈钢进行650℃/10小时的热处理,发现316L不锈钢的应力腐蚀开裂(SCC)起始敏感性显著降低。热处理试样加工表面的单位面积裂纹比加工状态减少了~50%,比抛光后减少了>70%。我们将此结果归结于加工表面外变形层超细晶粒的再结晶行为,这会导致拉伸残余应力和纳米压痕硬度的降低。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113740
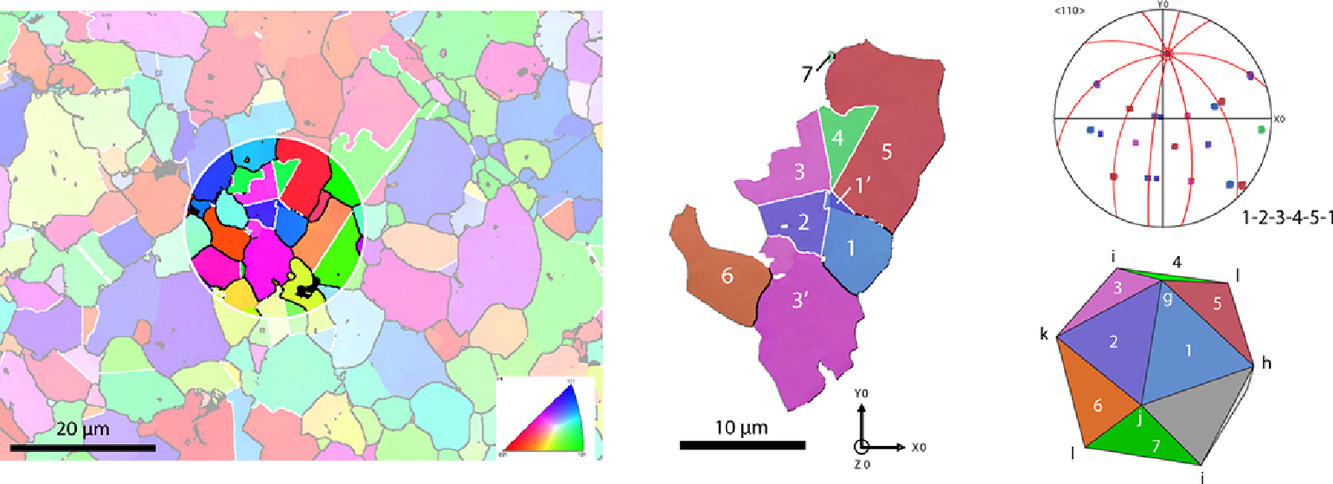
8. New insights into the origin of fine equiaxed microstructures in additively manufactured Inconel 718
增材制造Inconel 718中细小等轴微观组织起源的新见解
I. Cazic, J. Zollinger✉, S. Mathieu, M. El Kandaoui, P. Plapper, B. Appolaire
J. Zollinger: julien.zollinger@univ-lorraine.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113740
摘要
在增材制造Inconel 718合金中,经常会观察到细等轴晶粒区域。本文基于EBSD中晶粒对晶粒的取向分析表明,这些区域中许多相邻晶粒的组合都显示出多孪晶的取向关系;它们具有共同的⟨110⟩方向,并表现出5倍对称性。本文用实验证明,在Inconel 718合金中观察到的晶粒细化是由于二十面体短程有序(ISRO)介导的形核机制所致。这是ISRO介导的fcc镍形核的首次报道,它拓宽了镍基高温合金增材制造中微观组织控制的的见解。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113741
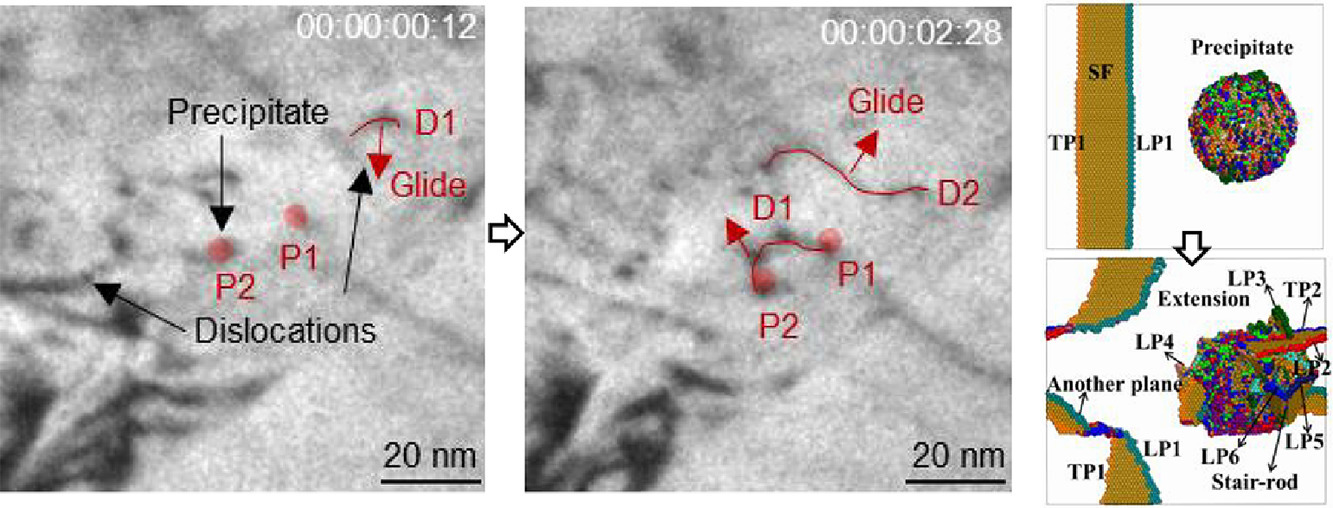
9. Nanoprecipitates induced dislocation pinning and multiplication strategy for designing high strength, plasticity and conductivity Cu alloys
利用纳米析出诱导位错钉扎和增殖策略设计高强度、高塑性和高导电性铜合金
Huiya Yang, Keqiang Li, Yeqiang Bu, Jinming Wu, Youtong Fang, Liang Meng, Jiabin Liu✉, Hongtao Wang✉
Jiabin Liu: liujiabin@zju.edu.cn 浙江大学
Hongtao Wang: htw@zju.edu.cn 浙江大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113741
摘要
本文提出了一种用于设计高强度、高塑性和高导电性铜合金的纳米析出诱导位错钉扎和增殖的策略。也就是说,纳米析出可以作为位错的障碍和来源。此外,析出净化了铜基体,保证了导电性能。为了验证这一策略,我们通过固溶处理、轧制和时效处理,在Cu-Fe-Ti合金中引入了致密位错和纳米析出。原位透射电镜应变和分子动力学模拟结果表明,纳米析出不仅阻碍了位错的滑移,还促进了位错的增殖,造成合金的抗拉强度为590 MPa,均匀伸长率为6%。Cu基体经析出纯化后的电导率为69% IACS。因此,该策略为开发高强度、高塑性、高导电性合金开辟了一条新的途径。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 195, 1 Apr. 2021, 113743
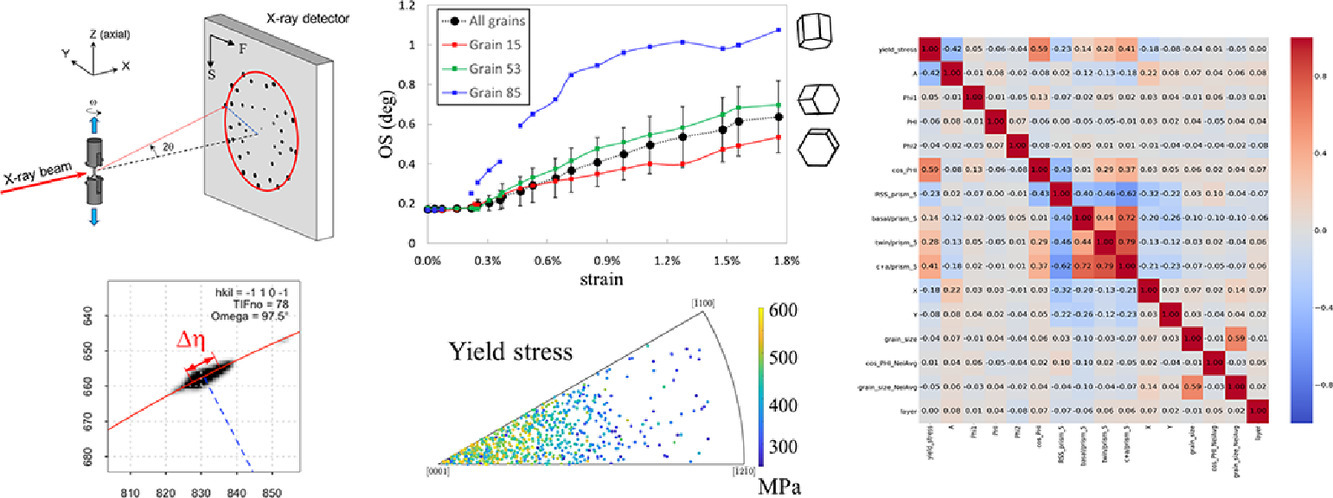
10. Evaluating the Taylor hardening model in polycrystalline Ti using high energy X-ray diffraction microscopy
使用高能X射线衍射显微镜评估多晶Ti中的泰勒硬化模型
Leyun Wang✉, Ziliang Lu, Hancheng Li, Zhijie Zheng, Gaoming Zhu, Jun-Sang Park, Xiaoqin Zeng, Thomas R. Bieler
Leyun Wang: leyunwang@sjtu.edu.cn 上海交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.113743
摘要
利用高能X射线衍射显微镜(HEDM)对多晶Ti样品中的近1000个晶粒进行了标定,并对其在拉伸试验中的变形进行了表征。对于每个晶粒,其相关衍射峰的位置被用来分析其演变的晶体取向和应力张量。我们测量了不同加载步骤下每个峰值的方位角宽度,以便测量初始屈服行为以及提供每个晶粒中位错密度演化的估量。我们利用上述数据对Taylor硬化模型进行了逐晶粒评价,表明该模型可以反映大部分晶粒的硬化情况。我们统计分析了所有晶粒的屈服应力和应变硬化系数与晶粒取向、晶粒尺寸、滑移系统和周围环境的关系,以考察屈服应力和硬化之间的联系。