金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.203, 1 Oct. 2021(上)
2021-08-08 来源:Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文10篇,涵盖了马氏体、中熵合金等,国内科研单位包括西安交通大学、燕山大学、上海交通大学、浙江大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 203 目录
1. A high-strength heat-resistant Al−5.7Ni eutectic alloy with spherical Al3Ni nano-particles by selective laser melting
激光选区熔化制备含球形Al3Ni纳米颗粒的高强度耐热Al-5.7Ni共晶合金
2. Ferroelectric-relaxor boundary in La-modified Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3 crossover showing enhanced dielectric and piezoelectric properties
La改性的 Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3中的铁电-弛豫边界显示增强的介电和压电性能
3. Revealing atomic-scale vacancy-solute interaction in nickel
揭示镍中原子级空位-溶质的相互作用
4. Effect of geometric lath orientation on fatigue crack propagation via out-of-plane dislocation glide in martensitic steel
几何板条取向对马氏体钢中平面外位错滑移所引起的疲劳裂纹扩展的影响
5. HfB2 ceramic polycrystals: A low-temperature metal-like ceramic at high temperatures?
HfB2多晶陶瓷:高温下的低温金属状陶瓷?
6. Anisotropic nitriding behavior upon formation of expanded hcp in Co-Cr alloys
在Co-Cr合金中形成膨胀hcp时的各向异性渗氮行为
7. Stress-dependent incipient plasticity of a face-centered-cubic-based Al0.3CoCrFeNi multi-principal element alloy with nano-scaled phase separation
具有纳米级相分离的面心立方基Al0.3CoCrFeNi多主元素合金的应力相关初始塑性
8. Enhanced defect annihilation capability of the graphene/copper interface: An in situ study
石墨烯/铜界面增强的缺陷消除能力:原位研究
9. Fluence-dependent microstructure and nanomechanical property in Co-Ni-V medium entropy alloy thin films
Co-Ni-V中熵合金薄膜中的通量相关微观组织和纳米力学性能
10. In-situ TEM investigation of unfaulting behavior of Frank loops in FCC Pd during H2+ & He+ dual-beam irradiation
H2+和He+双光束辐照时Frank环在FCC Pd中的无故障行为的原位TEM研究
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114034
1. A high-strength heat-resistant Al−5.7Ni eutectic alloy with spherical Al3Ni nano-particles by selective laser melting
激光选区熔化制备含球形Al3Ni纳米颗粒的高强度耐热Al-5.7Ni共晶合金
Junwang Deng, Chao Chen✉, Xiaochun Liu✉, Yunping Li, Kechao Zhou, Shengmin Guo
Chao Chen: pkhqchenchao@126.com, 中南大学
Xiaochun Liu: xcliu@csust.edu.cn, 长沙理工大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114034
摘要
传统的高强度锻造铝合金对增材制造 (AM) 过程中产生的裂纹敏感,而共晶铝合金能够很好地进行打印。 为了探索AM制备的高强度耐热铝合金,在本文中,我们提出通过使用Al-5.7Ni合金来延迟凝固范围,从而减轻裂纹形成趋势。该合金AM部分的特征是均匀分布的球形 Al3Ni 纳米颗粒,平均尺寸约为33 nm。它们与基体呈现出新的共格晶体学关系:<110>Al//<113>Al3Ni和{111}Al//{211}Al3Ni。这种无裂纹合金具有优异的机械性能,室温拉伸强度为 410 MPa,300°C拉伸强度为 140 MPa,这主要归功于弥散强化的Al3Ni纳米颗粒具有优异热稳定性。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114042
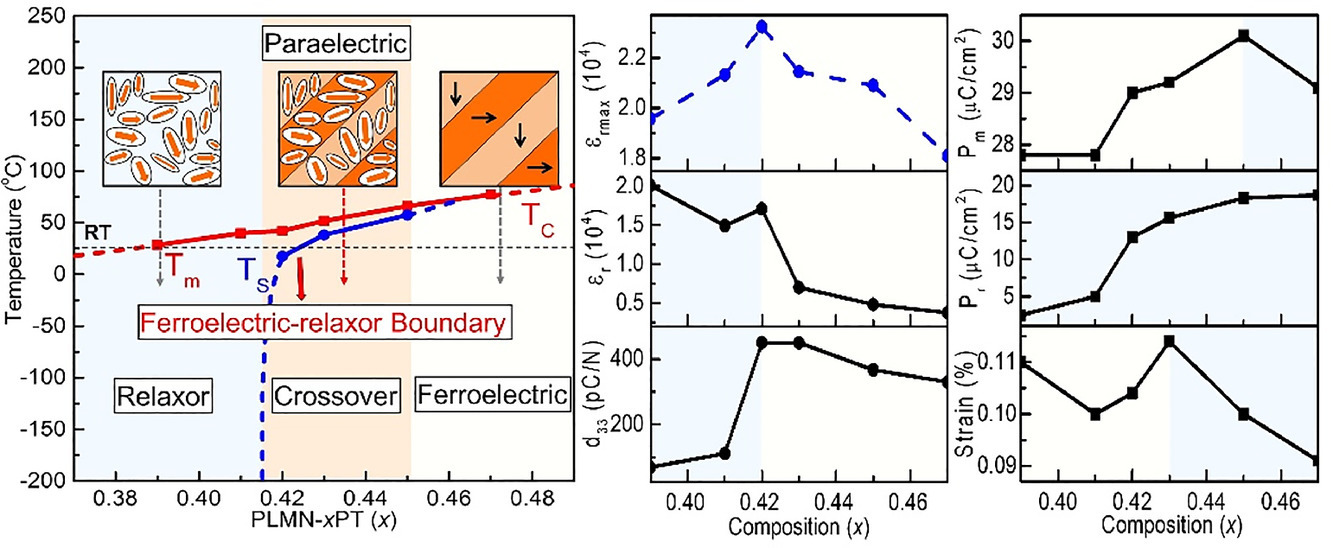
2. Ferroelectric-relaxor boundary in La-modified Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3 crossover showing enhanced dielectric and piezoelectric properties
La改性的 Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3中的铁电-弛豫边界显示增强的介电和压电性能
Yang Yang✉, Andong Xiao, Jiantuo Zhao✉, Xiaobing Ren
Yang Yang: yangyangz@xjtu.edu.cn, 西安交通大学
Jiantuo Zhao: jtzhao@xjtu.edu.cn, 西安交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114042
摘要
系统研究了La改性的Pb(Mg1/3Nb2/3)O3-xPbTiO3交叉陶瓷的介电和压电性能。在渗透区域,有一个铁电-弛豫边界将铁电态和弛豫态分开,这是由随着温度降低从弛豫到铁电态的自发跃迁决定的。在铁电-弛豫边界处,与相邻铁电体相比,最大介电常数从18,200增加到23,500,压电系数 (d33) 从300 pC/N 增加到450 pC/N,同时电应变从0.09%提高到0.12%。这些增强可能源于自发转变的存在以及宏观域和极性纳米域配置的共存引起的极化旋转的低能垒。这项工作表明交叉区域的铁电-弛豫边界可能成为提高铁电材料介电和压电性能的有效途径。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114036
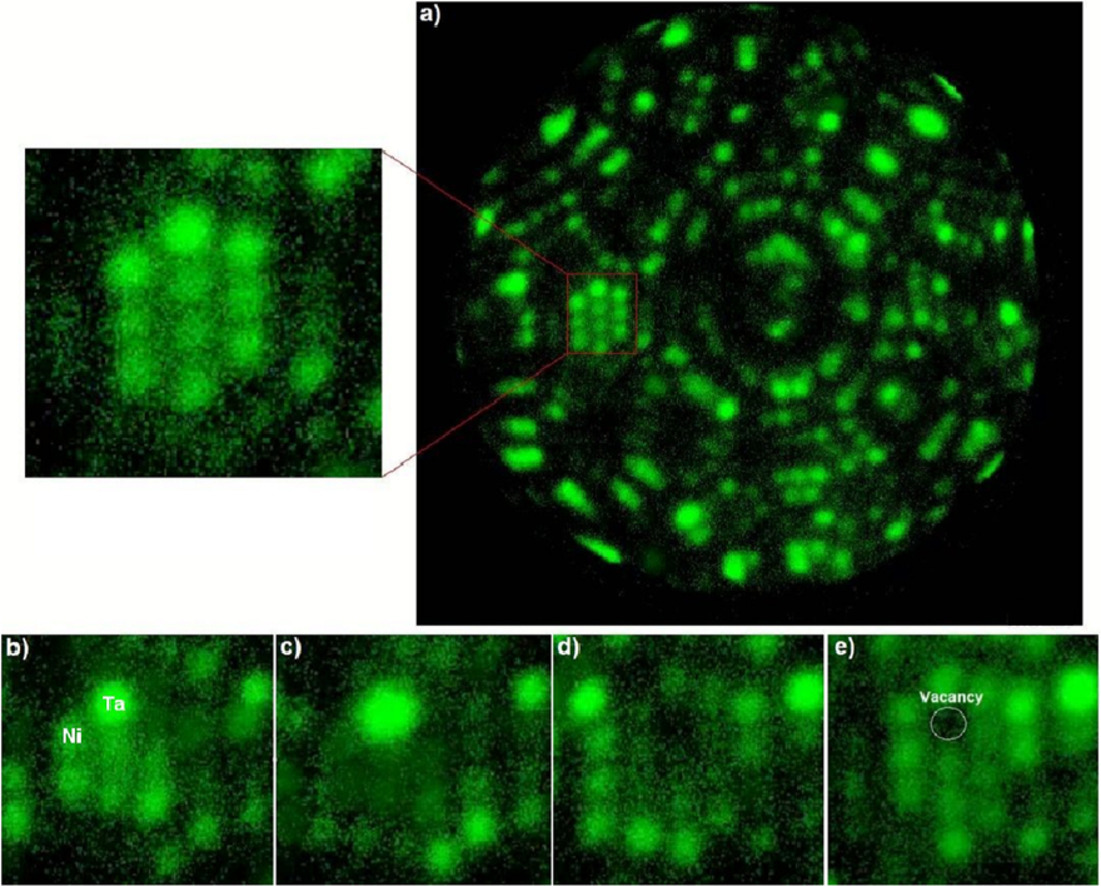
3. Revealing atomic-scale vacancy-solute interaction in nickel
揭示镍中原子级空位-溶质的相互作用
Felipe F. Morgado✉, Shyam Katnagallu, Christoph Freysoldt, Benjamin Klaes, François Vurpillot, Jörg Neugebauer, Dierk Raabe, Steffen Neumeier, Baptiste Gault✉, Leigh T. Stephenson✉
Felipe F. Morgado: f.ferraz@mpie.de
Baptiste Gault: b.gault@mpie.de
Leigh T. Stephenson: l.stephenson@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114036
摘要
人们普遍认为,不同类型的晶体缺陷,例如空位或位错,会极大地影响材料的物理和机械性能。然而,对固体中的单个空位进行成像并揭示它们的原子邻域仍然是显微镜和微观分析的前沿之一。在这里,我们研究了蠕变变形的二元Ni-2 at.% Ta合金。原子探针断层扫描显示 Ta的随机分布。场离子显微镜,在密度泛函理论和飞行时间质谱法的对比解释下,证明了Ta与空位的正相关,支持了先前由原子模拟预测的正溶质空位相互作用。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114045
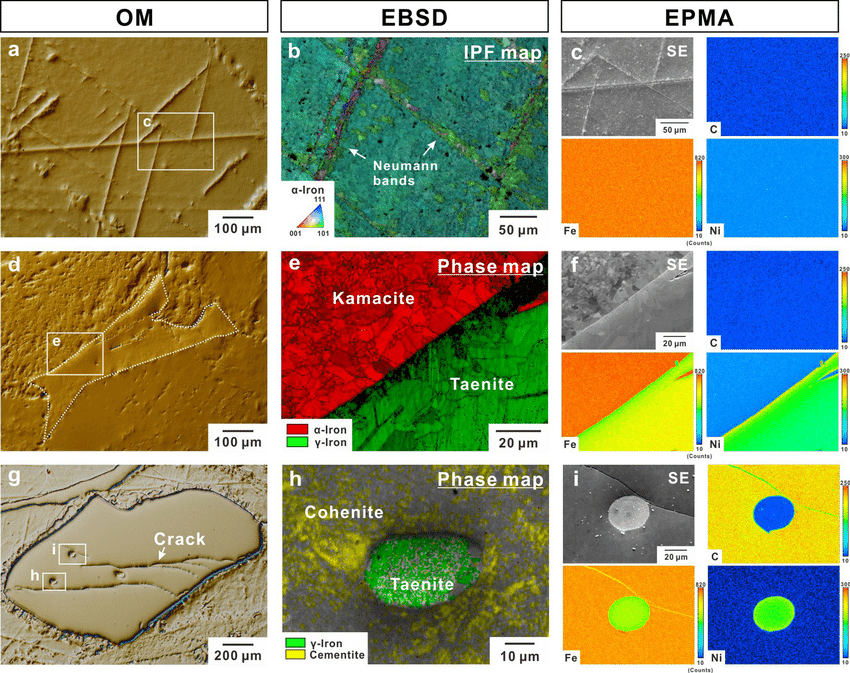
4. Effect of geometric lath orientation on fatigue crack propagation via out-of-plane dislocation glide in martensitic steel
几何板条取向对马氏体钢中平面外位错滑移所引起的疲劳裂纹扩展的影响
Shohei Ueki, Yoji Mine✉, Xinyu Lu, Yu Lung Chiu, Paul Bowen, Kazuki Takashima
Yoji Mine: mine@msre.kumamoto-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114045
摘要
使用三维电子背散射衍射 (3D-EBSD) 技术检测中碳钢马氏体板条疲劳裂纹尖端前的应变累积。本研究的目的是解释由于平面外滑移激活而导致的裂纹扩展机制,其Burgers矢量没有裂纹扩展方向的分量,对疲劳裂纹扩展具有很高的抵抗力。3D-EBSD分析显示晶体中几乎没有取向差,同时粗板条中的疲劳裂纹扩展有利于在其纵向方向上的位错滑动。这表明这些板条有助于应变调节。相反,应变优先累积在不利于纵向滑动的粗板条中,促进裂纹扩展。这表明马氏体板条的几何各向异性和分布支配着马氏体碳钢的疲劳裂纹扩展阻力。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114037
5. HfB2 ceramic polycrystals: A low-temperature metal-like ceramic at high temperatures?
HfB2多晶陶瓷:高温下的低温金属状陶瓷?
Eugenio Zapata-Solvas, Bibi Malmal Moshtaghioun, Diego Gomez-Garcia✉, Arturo Dominguez-Rodriguez, William E. Lee
Diego Gomez-Garcia: dgomez@us.es
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114037
摘要
二硼化铪(HfB2)是一种耐高温(在3000°C以上熔化)陶瓷,在高温下具有许多潜在的应用。 为了使其能够在特定温度下长时间使用,必须了解其高温可塑性。本文研究了在900°C和 2000°C 之间的温度下,在空气和还原性气氛中的机械响应,解释了低温下紧凑包装金属塑性的经典模型框架中的数据。特别是,评估了弗里德尔定律和位错模式的相似性原则。这表明HfB2是具有“金属”机械性能的陶瓷材料的一个独特例子。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114041
6. Anisotropic nitriding behavior upon formation of expanded hcp in Co-Cr alloys
在Co-Cr合金中形成膨胀hcp时的各向异性渗氮行为
Maryam Akhlaghi✉, Stenfan Martin, Johannes Dallman, Rainer Hock, Carolin Korner, Andreas Leineweber
Maryam Akhlaghi: maryam.akhlaghi@fau.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114041
摘要
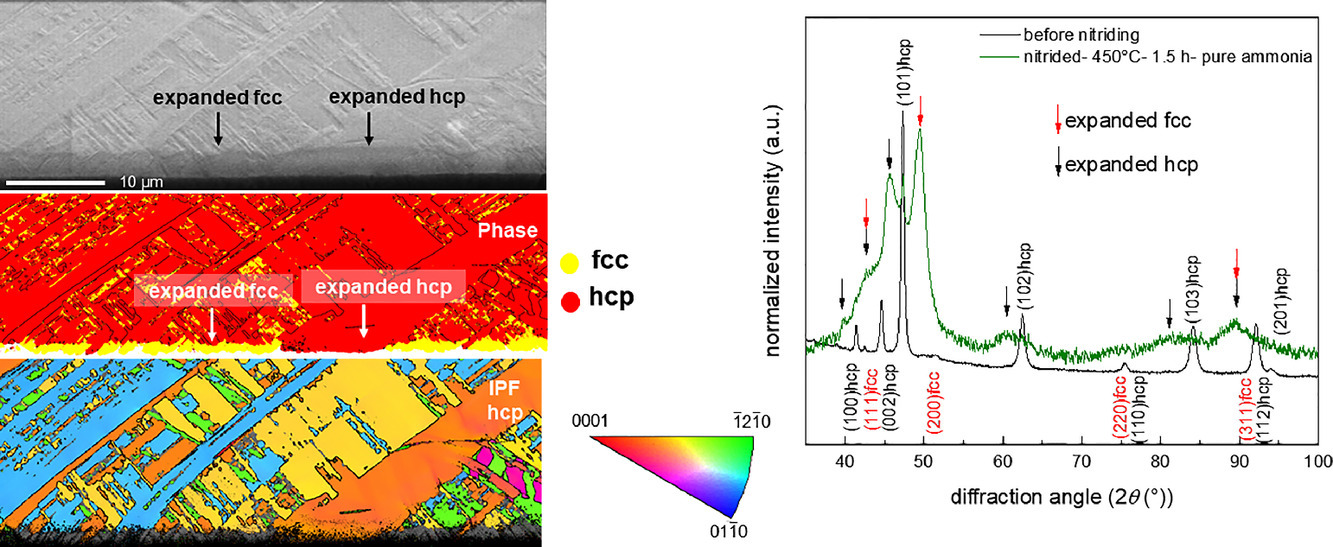
本文研究了具有初始hcp晶体结构的Co-Cr合金在气态氮化后从六方密堆积(hcp)到面心立方 (fcc)晶体结构的转变。在400°C低温渗氮的早期阶段,X射线衍射图中hcp基板反射的低角度侧的新反射可归因于hcp相的形成及表面的晶格膨胀。长时间的氮化处理和在较高温度下的氮化会导致这种膨胀的hcp转变为膨胀的fcc。上述所观察到的各项异性转变发生在不同取向的hcp 晶粒上。相对于渗氮方向,基面滑移模式的最高施密德因子在hcp方向上的转变较慢。这是从渗氮早期发展的宏观应力及其对hcp变体塑性各向异性变形的影响的角度进行讨论的。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114053
7. Stress-dependent incipient plasticity of a face-centered-cubic-based Al0.3CoCrFeNi multi-principal element alloy with nano-scaled phase separation
具有纳米级相分离的面心立方基Al0.3CoCrFeNi多主元素合金的应力相关初始塑性
L.J. Zhang, P.F. Yu, C.Z. Zhang, J.T. Fan, G. Li✉
G. Li: gongli@ysu.edu.cn, 燕山大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114053
摘要
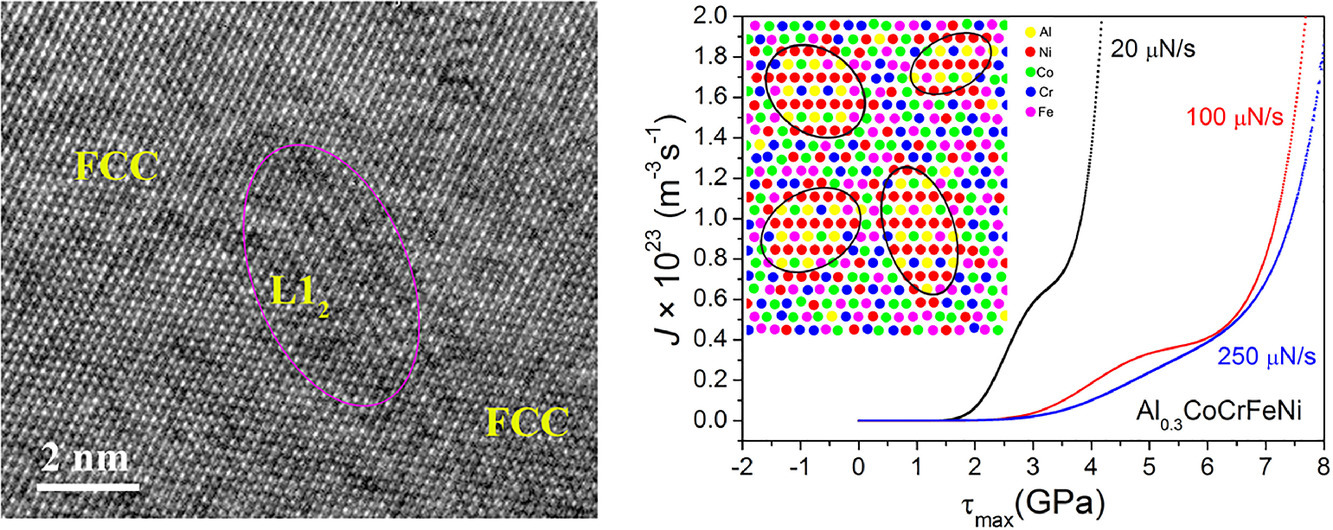
通过测量具有纳米级相分离的面心立方Al0.3CoCrFeNi多主元素合金中的第一次弹出行为来探测应力相关的初始塑性。大量压痕测量表明,最大剪切应力的双峰分布的操作与不同的位错成核位点有关。这种双峰分布现象可用于表征合金的结构异质性。计算活化体积和位错成核率以进一步研究不同的位错成核机制。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114001
8. Enhanced defect annihilation capability of the graphene/copper interface: An in situ study
石墨烯/铜界面增强的缺陷消除能力:原位研究
K.M. Yang, P.Z. Tang, Q. Zhang, H.Y. Ma, E.Q. Liu, M. Li, X. Zhang, Jin Li✉ ,Y. Liu, T.X. Fan✉
Jin Li: lijin2019@hit.edu.cn, 哈尔滨工业大学(深圳校区)
T.X. Fan: txfan@sjtu.edu.cn, 上海交通大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114001
摘要
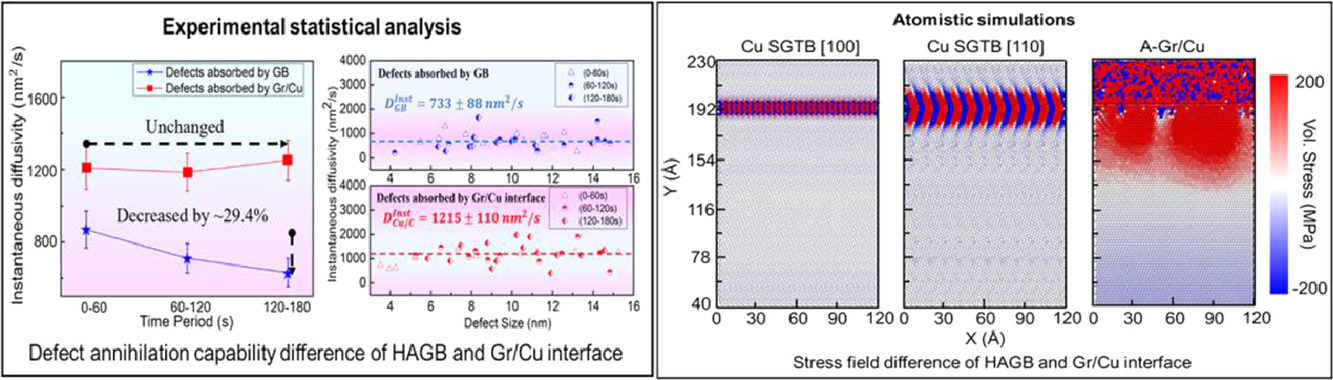
众所周知,高能重离子辐射通常会引起缺陷并最终导致材料降解。界面,例如大角度晶界(HAGB),通常用作缺陷吸收处以减轻辐射损伤。然而,HAGB在辐射过程中通常是不稳定的。 在这里,我们通过在透射电子显微镜下使用原位Kr++离子辐照来研究石墨烯(Gr)/Cu复合材料的界面辐照响应。结果表明,与Cu中的HAGB相比,Gr/Cu界面表现出更高的缺陷湮灭能力。此外,原子模拟表明Gr/Cu界面的应力场范围略高和较大,这有助于增强缺陷吸收能力。目前的发现对于理解和设计具有优异辐照耐受性的新型碳/金属复合材料至关重要。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114050
9. Fluence-dependent microstructure and nanomechanical property in Co-Ni-V medium entropy alloy thin films
Co-Ni-V中熵合金薄膜中的通量相关微观组织和纳米力学性能
Min Hu, Qingping Cao✉, Xiaodong Wang, Dongxian Zhang, Jian-Zhong Jiang✉
Qingping Cao: caoqp@zju.edu.cn, 浙江大学
Jian-Zhong Jiang: jiangjz@zju.edu.cn, 浙江大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114050
摘要
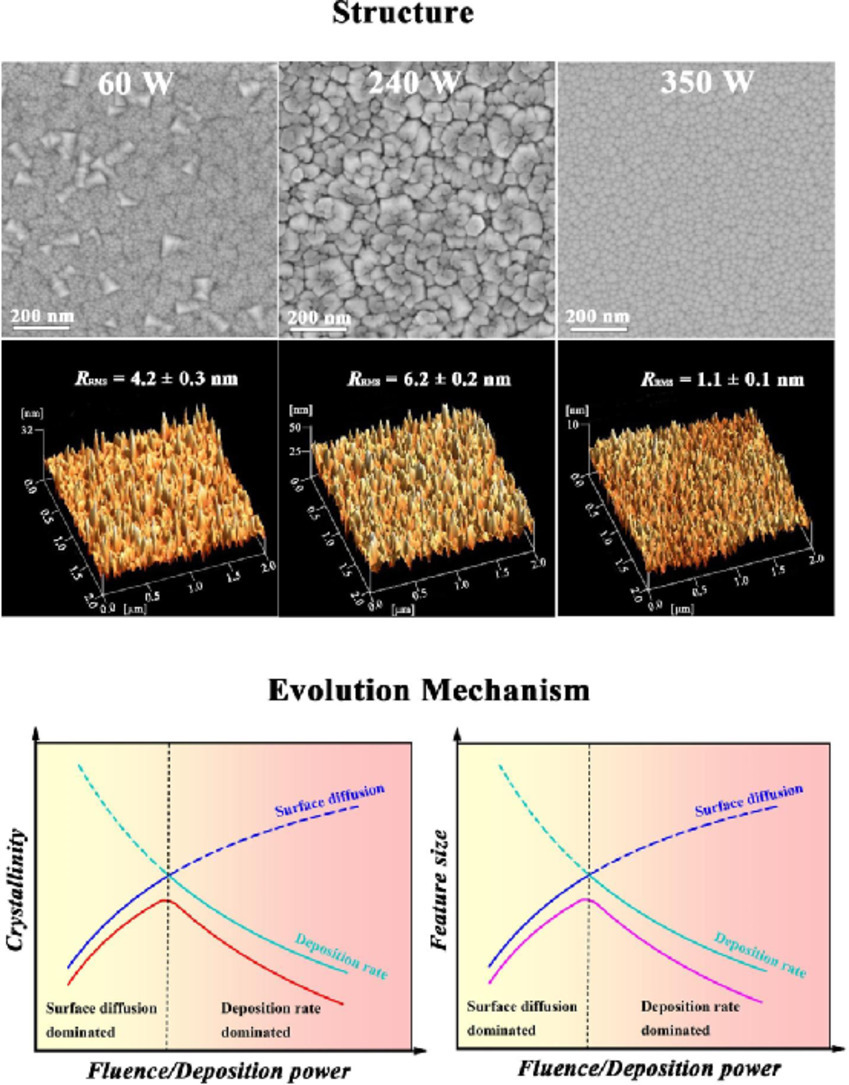
通过调节沉积功率,合成了一系列以纳米柱状方式生长的具有不同微观组织和形貌的 Co-Ni-V中熵合金薄膜。随着通量的增加,结晶度和纳米柱的尺寸都经历了先增加然后减少的过程,这受吸附原子表面扩散与沉积速率竞争的控制。同时,能流的连续强化归因于低注量下的结合改善和边界的减少以及高注量范围内的非晶化强化作用。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 203, 1 Oct. 2021, 114047
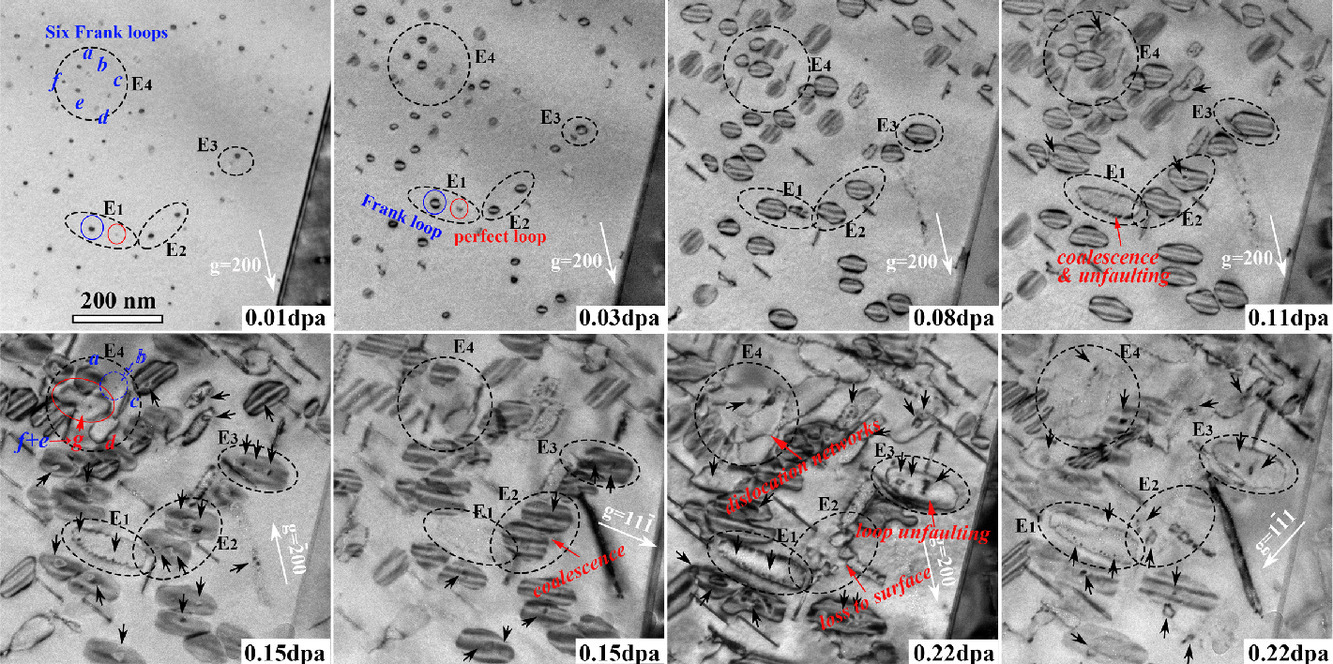
10. In-situ TEM investigation of unfaulting behavior of Frank loops in FCC Pd during H2+ & He+ dual-beam irradiation
H2+和He+双光束辐照时Frank环在FCC Pd中的无故障行为的原位TEM研究
Yipeng Li, Guang Ran✉, Qing Han, Yong Xin, Xinyi Liu, Xiaoqiu Ye
Guang Ran: gran@xmu.edu.cn, 厦门大学,福建核工程研究中心
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114047
摘要
在塑性变形、淬火或粒子照射下,有缺陷的弗兰克位错环 (FDL) 可以转变为无故障的完美位错环 (PDL)。在这里,我们报告了通过透射电子显微镜中的原位离子辐照对钯 (Pd) 中 FDL的无缺陷过程的直接观察。 结果表明,FDL的无缺陷过程是三个过程的组合,涉及相邻FDL之间的相互作用、FDL和PDL之间的相互作用以及FDL内Shockley部分位错的形核和生长。同时,气泡倾向于在位错环内成核,PDLs比 FDLs捕获更多的He/H2,这首次证实了辐照诱导的环在Pd的老化中起着重要作用,并且无缺陷加强了这一过程。