金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.205, 1 Dec. 2021(下)
2021-12-03 来源:Goal Science
本期包含金属材料领域论文9篇,涵盖了高温合金、高熵合金等,国内科研单位包括中国科学院金属研究所、东莞理工大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 205 目录
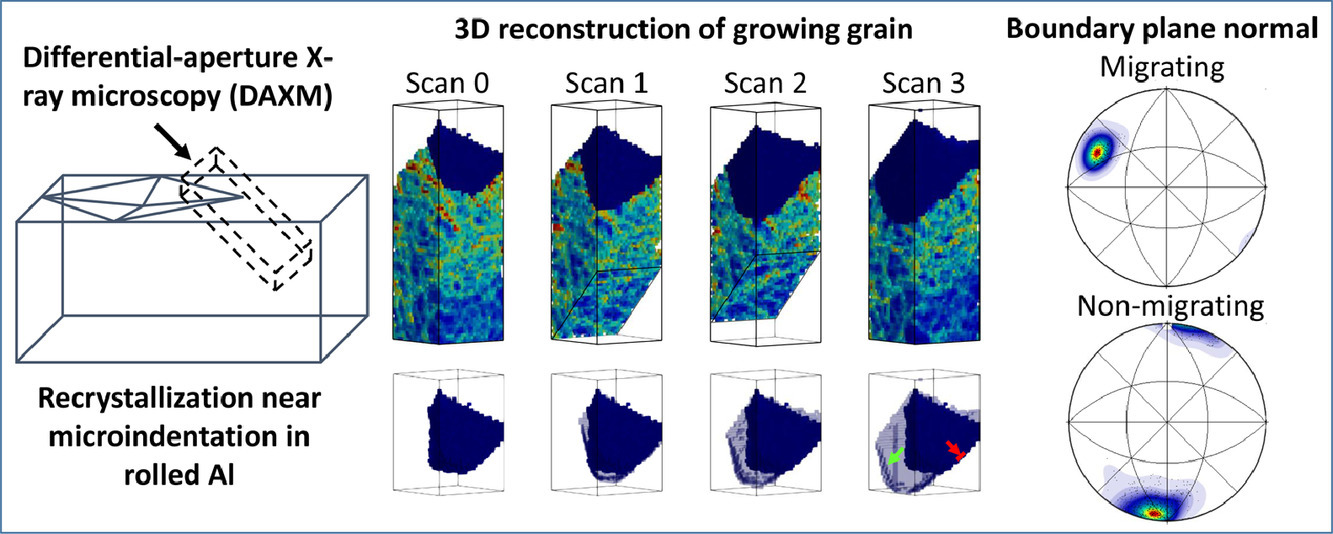
1. Recrystallization boundary migration in the 3D heterogeneous microstructure near a hardness indent
硬度压痕附近3D异质组织中的再结晶边界迁移
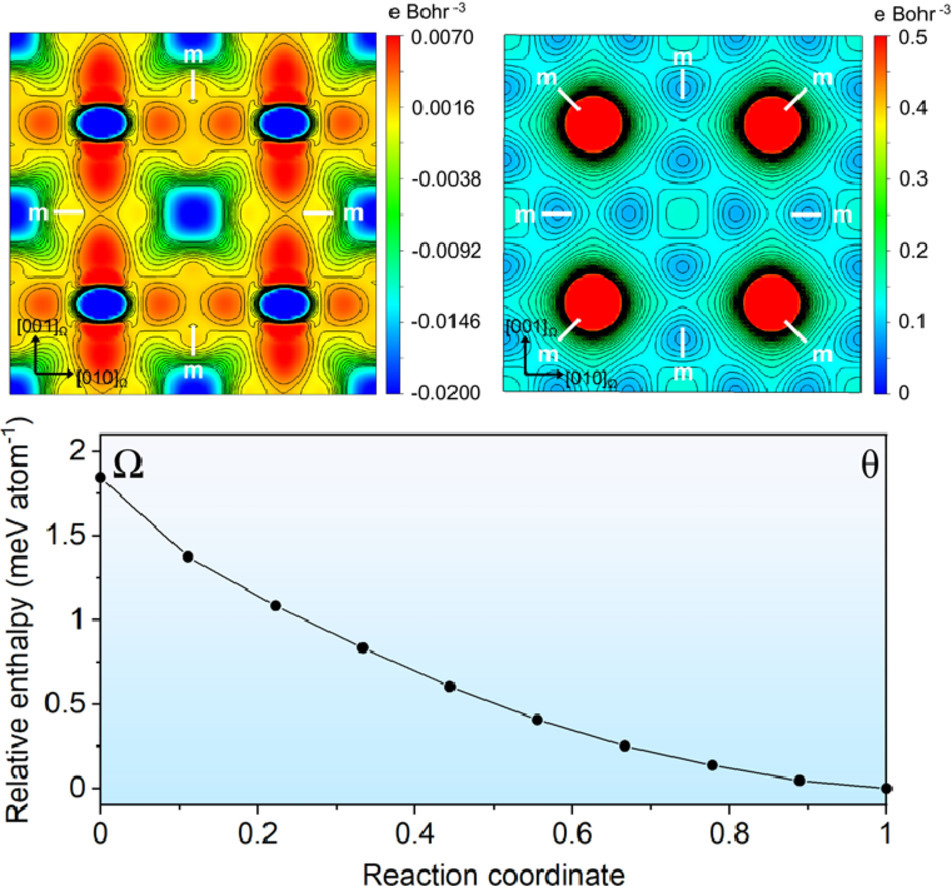
2. Revisit of the structure of Ω precipitate in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys
重新审视Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金中Ω析出物的结构
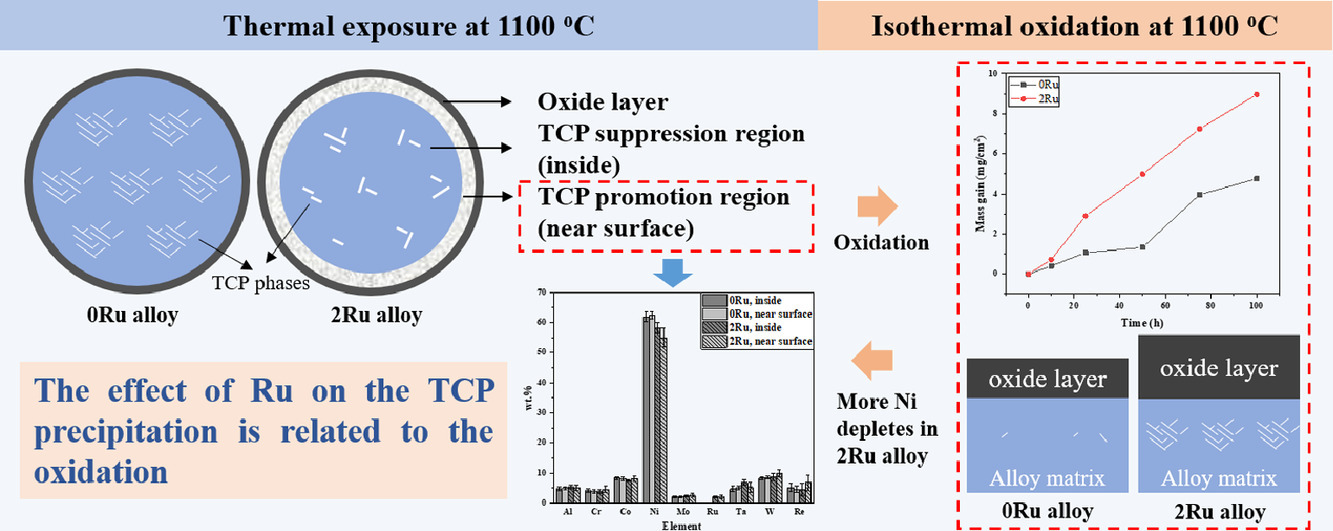
3. Dual effects of Ru on the microstructural stability of a single crystal superalloy
Ru对单晶高温合金显微组织稳定性的双重影响
4. Oxygen-induced refinement of α precipitates in an aged metastable β Ti-15-333 alloy
时效亚稳态β Ti-15-333合金中α析出物的氧诱导细化
5. In-situ TEM observation of shear induced microstructure evolution in Cu-Nb alloy
Cu-Nb合金剪切诱导显微组织演变的原位TEM观察
6. Deciphering the role of multiple generations of annealing twins on texture evolution in cold-rolled high entropy alloys during annealing
解读多代退火孪晶对冷轧高熵合金退火过程中织构演变的作用
7. Nano-precipitation leading to linear zero thermal expansion over a wide temperature range in Ti22Nb
纳米沉淀导致Ti22Nb在很宽的温度范围内零线性热膨胀
8. Effect of Zr addition on metastable Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation of Cu-Fe alloys
Zr添加对Cu-Fe合金亚稳态液-液相分离的影响
9. Development of a high-strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-based alloy via multi-strengthening mechanisms
通过多重强化机制开发高强度Al-Zn-Mg-Cu基合金
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114187
1. Recrystallization boundary migration in the 3D heterogeneous microstructure near a hardness indent
硬度压痕附近3D异质组织中的再结晶边界迁移
Chuanshi Hong✉, Yubin Zhang, Adam Lindkvist, Wenjun Liu, Jon Tischler, Ruqing Xu, Dorte Juul Jensen✉
Chuanshi Hong: cshong@imr.ac.cn
Dorte Juul Jensen: doje@mek.dtu.dk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114187
摘要
采用3D中跟踪轻轧纯Al的硬度压痕附近的异质组织中再结晶过程中的边界迁移。使用同步加速器白光束差分孔径X射线显微镜检查多步异位退火后的微观结构,并辅以扫描电子显微镜观测。从驱动力和边界特征方面观察和分析了非均质再结晶边界迁移。结果揭示了迁移和静止边界非常相似的局部存储能量和边界取向差,而晶界法线有显着差异。讨论了晶界迁移率和变形组织形态对晶界迁移的影响。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114204
2. Revisit of the structure of Ω precipitate in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag alloys
重新审视Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金中Ω析出物的结构
S.L. Yang, N. Wilson, J.F. Nie✉
J.F. Nie: jianfeng.nie@monash.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114204
摘要
通过第一性原理密度泛函理论(DFT)计算重新检查Al-Cu-Mg-Ag合金中Ω析出物的结构表明,广泛接受的“亚稳”Ω相的正交结构实际上是四方晶系,与二元Al-Cu合金中的平衡θ相相同。 当四方θ(即 Ω)作为薄板嵌入α-Al基体中时,周围α-Al基体施加的弹性变形可以将四方结构的原始4倍对称降低到正交结构的2倍对称。DFT计算结果还表明,θ/α-Al 界面处存在的Mg和Ag可以显着促进θ的形成。Ω结构的澄清以及Mg和Ag在θ形成中的作用提供了,对如何促进显微结构中关键强化成分的固有强平衡相沉淀的见解。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114209
3. Dual effects of Ru on the microstructural stability of a single crystal superalloy
Ru对单晶高温合金显微组织稳定性的双重影响
Jingxia Sun, Jinlai Liu✉, Jinguo Li✉, Chao Chen, Xinguang Wang, Yizhou Zhou, Xiaofeng Sun
Jinlai Liu: jlliu@imr.ac.cn(中国科学院金属研究所)
Jinguo Li: jgli@imr.ac.cn (中国科学院金属研究所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114209
摘要
通常,Ru可以抑制大多数单晶高温合金中TCP相的析出。然而,在本研究中,我们发现该抑制作用与相对于样品表面的位置有关:Ru抑制样品内部TCP相的沉淀,但在近表面区域却促进它。TCP相的促进被证明与氧化有关。微观结构分析表明,Ru通过扰乱氧化结构的阻挡性能而降低了抗氧化性。由于不良的抗氧化性,更多的Ni原子被消耗,导致了向样品内部的浓度梯度,这改变了TCP的析出驱动力。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114206
4. Oxygen-induced refinement of α precipitates in an aged metastable β Ti-15-333 alloy
时效亚稳态β Ti-15-333合金中α析出物的氧诱导细化
Kathleen Chou, Owen Neill, Emmanuelle A. Marquis✉
Emmanuelle A. Marquis: emarq@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114206
摘要
通过细化晶内α析出物来提高时效亚稳态β钛合金的强度,先前已经使用结构和成分不均匀性的异质成核来证明。这里我们发现,在β Ti-15-333合金的时效过程中,升高的氧含量(高达1.7 at.%)也可以诱导α相细化,为获得精细的α板条提供了额外的途径。 此外,氧诱导的细化与ω辅助的α成核相结合,导致α尺寸显着减小,约为50 nm。与不含氧的试样相比,在微柱压缩过程中,用更高的氧浓度获得的更细的α沉淀物导致压缩屈服强度的增加。这些发现强调了使用高氧含量来提升β Ti合金中α组织的细化和沉淀强化。
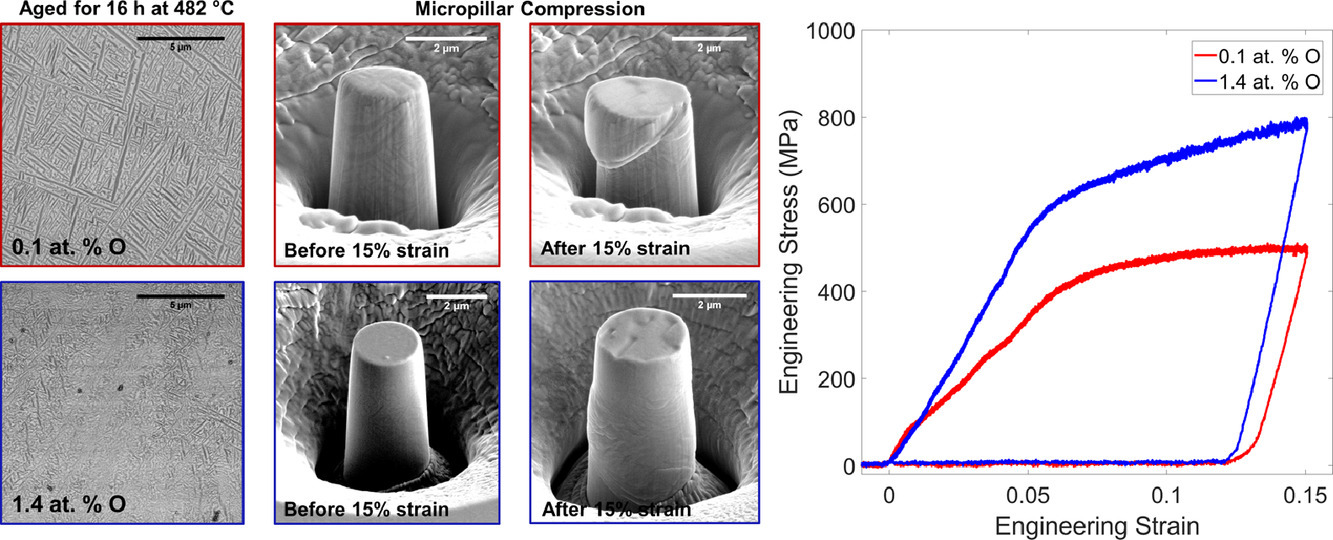
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114214
5. In-situ TEM observation of shear induced microstructure evolution in Cu-Nb alloy
Cu-Nb合金剪切诱导显微组织演变的原位TEM观察
Shuang Li, Matthew Olszta, Lei Li, Bharat Gwalani, Ayoub Soulami, Cynthia A. Powell, Suveen Mathaudhu, Arun Devaraj, Chongmin Wang✉
Chongmin Wang: chongmin.wang@pnnl.gov
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114214
摘要
多相合金中的相界控制着塑性变形过程中不同相间的缺陷相互作用和化学混合。近年来,多相合金中缺陷与相界的动态相互作用,尤其是非互溶合金,引起了越来越多的研究兴趣。在这里,我们描述了一种进行原位TEM剪切变形以直接观察Cu-Nb 合金界面微观结构演变的新方法。独特的双剪切试样几何结构通过聚焦离子束技术进行微加工,以在TEM内推动加载时施加剪切变形。从实时观察中,我们发现具有锯齿形形态的相界有效地阻止了在Cu晶粒中成核的堆垛层错滑入Nb晶粒。同时,Cu相通过滑移或孪生机制承受最大的塑性变形。这项工作有助于理解剪切变形过程中多相合金中的剪切变形和相界行为。
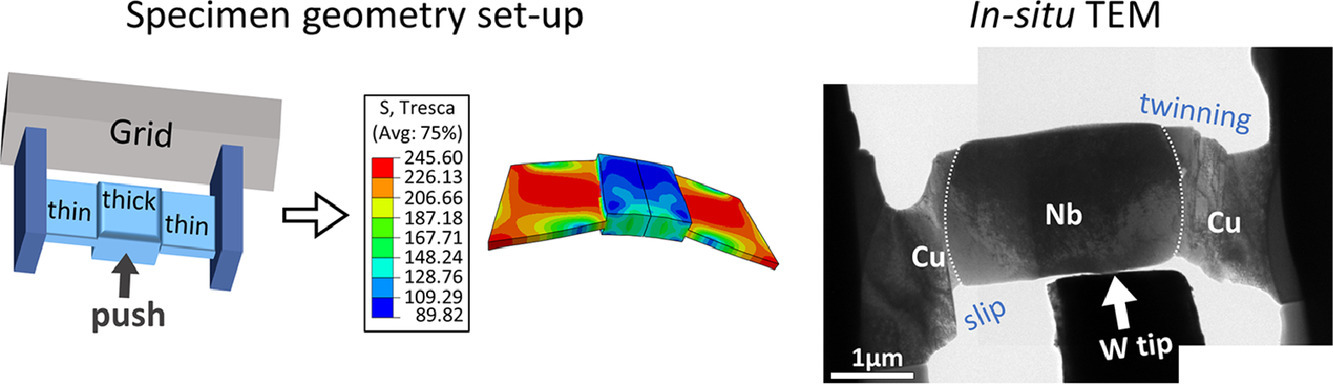
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114221
6. Deciphering the role of multiple generations of annealing twins on texture evolution in cold-rolled high entropy alloys during annealing
解读多代退火孪晶对冷轧高熵合金退火过程中织构演变的作用
Lalit Kaushik, Jaiveer Singh, Joo-Hee Kang, Yoon Seok Ko, Dong-Ik Kim, Jin-Yoo Suh, Shi-Hoon Choi✉
Shi-Hoon Choi: shihoon@scnu.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114221
摘要
低层错能(SFE)材料中多代退火孪晶(MGAT)的出现导致显著的织构弱化,并伴随一些新的显著的织构成分的演变。然而,MGAT和织构演化之间的确切关联是一个长期存在的谜。在目前的研究中,MGAT的存在通过透射菊池衍射(TKD)和高分辨率电子背散射衍射(EBSD)在部分(700 °C/5 min)和完全(700 °C/1 h)再结晶的等原子CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金中都得到证实。此外,研究了潜在成核位点(Brasss、Gross和S方向)附近的孪生簇,以深入了解MGAT对织构发展的贡献。新发现的取向(φ1 = 90°,Φ=30°,φ2 = 45°)表明其根源为Brass取向的第二代孪晶,而立方取向则是从S取向的第一代和第五代孪晶演化而来。
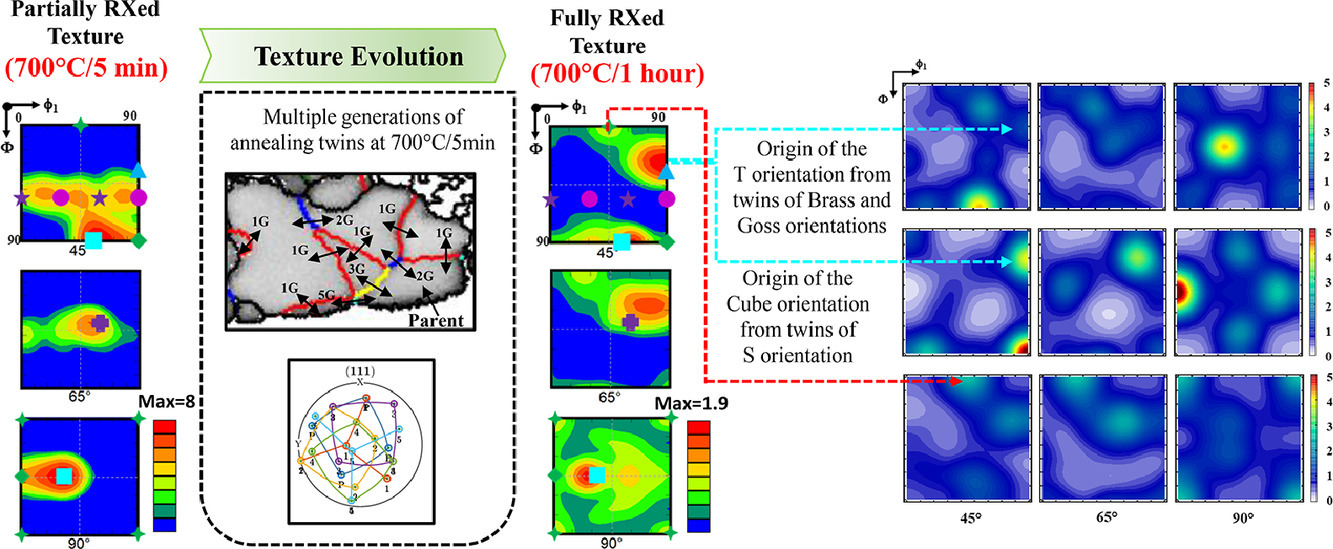
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114222
7. Nano-precipitation leading to linear zero thermal expansion over a wide temperature range in Ti22Nb
纳米沉淀导致Ti22Nb在很宽的温度范围内零线性热膨胀
Haoliang Wang, Daniel Kuok Zheng Lai, Juping Xu, Wen Yin, Chenghao Song, Yuliang Zhao, Yang Yang, Matthias Bonisch✉, Zhenzhong Sun✉
Matthias Bonisch: matthias.bonisch@kuleuven.be
Zhenzhong Sun: sunzz@dgut.edu.cn (东莞理工大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114222
摘要
某些冷加工马氏体钛合金沿特定样品方向表现出可调节的线性热膨胀。这些有趣的特性与斜方晶αʺ马氏体的各向异性热膨胀有关。然而,以这种方式获得的定制膨胀仅限于单相马氏体温度场,低于马氏体向奥氏体的逆转变温度。在这里,我们证明了通过扩散形成的正交αʺiso也可以调节热膨胀在典型Ti22Nb合金中。更重要的是,相对于冷加工马氏体合金,发生定制线性热膨胀的温度范围大大拓宽。我们阐明了热循环过程中纳米尺寸αʺiso的形成路径,并解决了与母相的晶体学位向关系。这些发现为设计具有大工作温度范围的低/负热膨胀钛合金提供了新途径。
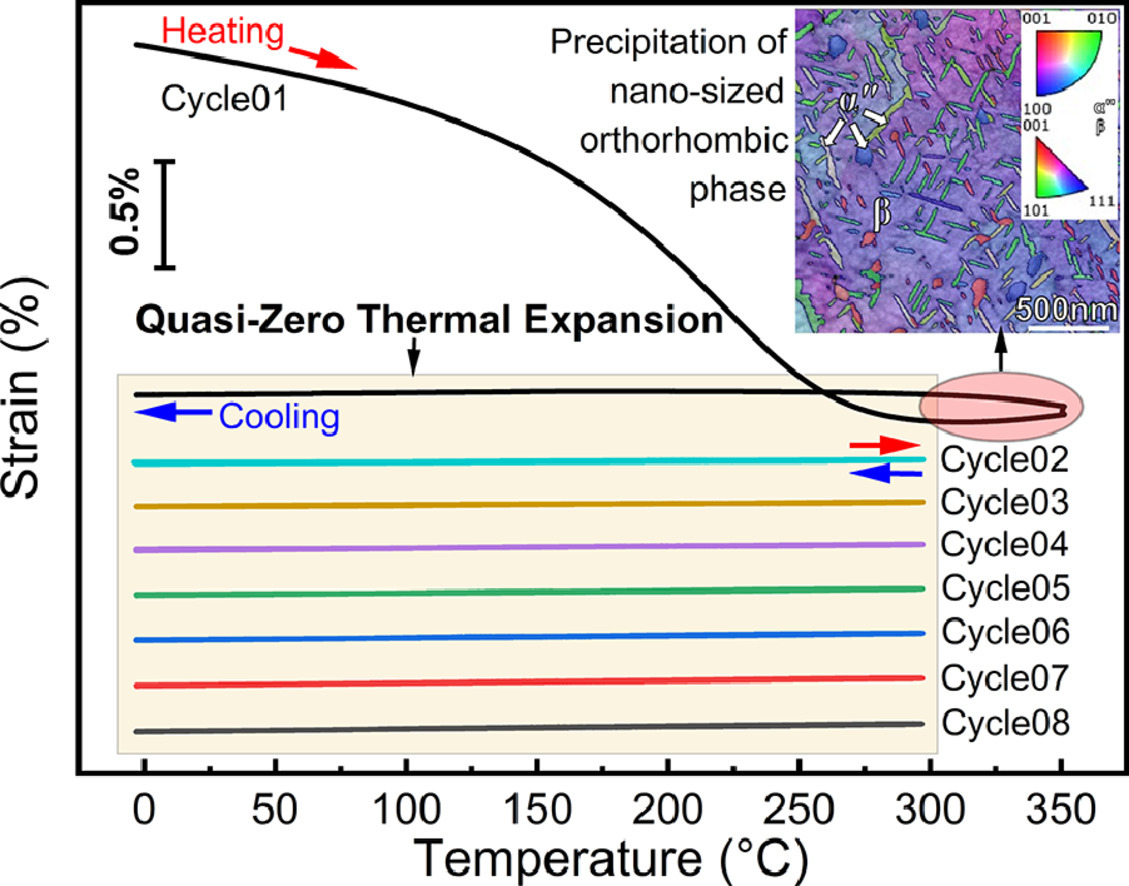
SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114218
8. Effect of Zr addition on metastable Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation of Cu-Fe alloys
Zr添加对Cu-Fe合金亚稳态液-液相分离的影响
Ho-Joon Moon, Tae-min Yeo, Seung Hoon Lee, Jung-Wook Cho✉
Jung-Wook Cho: jungwook@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114218
摘要
在由60 wt.%或 80 wt.% Cu组成的Cu-Fe合金中研究了液-液相分离(LLPS)行为,其中添加了0或1 wt.%的Zr。两种无Zr合金在γ-Fe成核之前的亚稳态旋节线温度下都清楚地显示出LLPS,而添加Zr的合金在没有LLPS的情况下显示出γ-Fe相演变。Zr通过降低混合焓和加速异相成核来非常有效地激活γ-Fe成核。热仪器分析和经典成核理论相结合可有效评估低于Cu-Fe合金液相线温度的LLPS行为。此外,可以通过添加Zr来控制Cu-Fe合金的凝固机制。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 205, 1 Dec. 2021, 114216
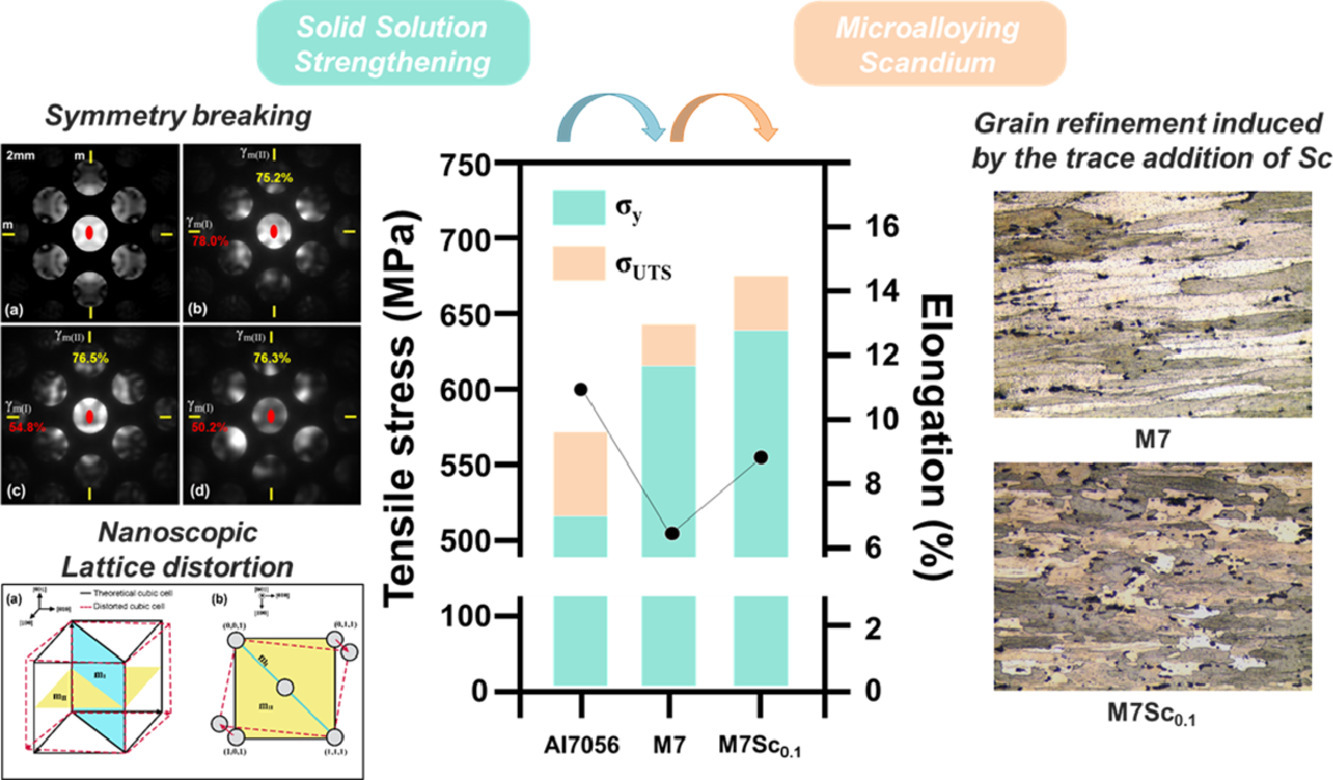
9. Development of a high-strength Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-based alloy via multi-strengthening mechanisms
通过多重强化机制开发高强度Al-Zn-Mg-Cu基合金
Sung-Jae Won, Hyeongsub So, Leeseung Kang, Soong Ju Oh, Kyou-Hyun Kim✉
Kyou-Hyun Kim: khkim1308@kitech.re.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114216
摘要
我们通过添加微量Sc和优化Mg/Cu含量,开发了高强度的Al-Zn-Mg-Cu基合金(7xxx系列),其力学性能为σUTS=672 MPa(σy=644 MPa)和ε=8.6%。基于定量的对称测试,机械强度的提高源于随着Mg/Cu量的增加,过量的Mg和Cu溶质引起了纳米结构畸变。此外,Sc微合金化诱导晶粒细化,从而提高机械性能。