金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.206, 1 Jan. 2022
2021-12-10 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文14篇,涵盖了中熵合金、高熵合金、不锈钢、中锰钢、镁合金等,国内科研单位包括中国科学院金属研究所、东北大学、北京科技大学、西安交通大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 206 目录
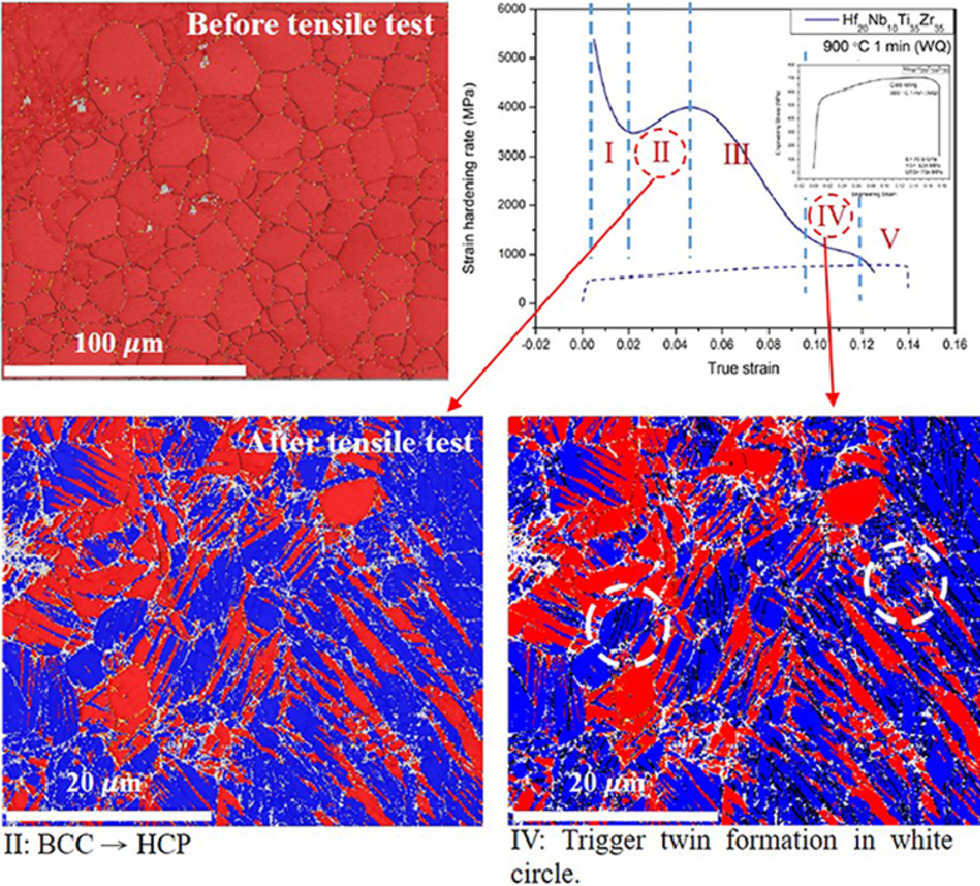
1. Strengthening mechanisms and microstructural evolution of ductile refractory medium-entropy alloy Hf20Nb10Ti35Zr35
韧性难熔中熵合金Hf20Nb10Ti35Zr35的强化机制及微观组织演化
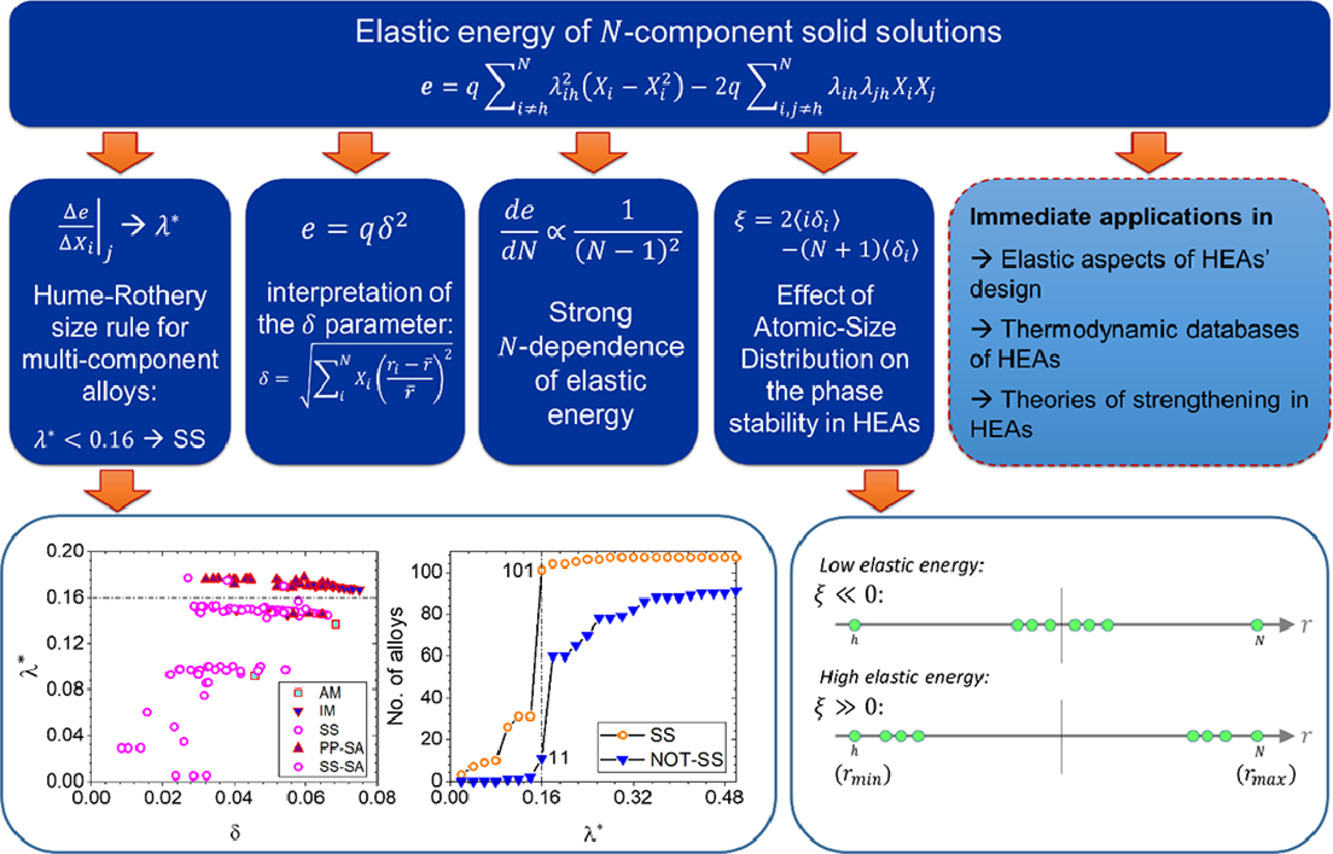
2. Elastic energy of multi-component solid solutions and strain origins of phase stability in high-entropy alloys
高熵合金中多组分固溶体的弹性能和相稳定性的应变源
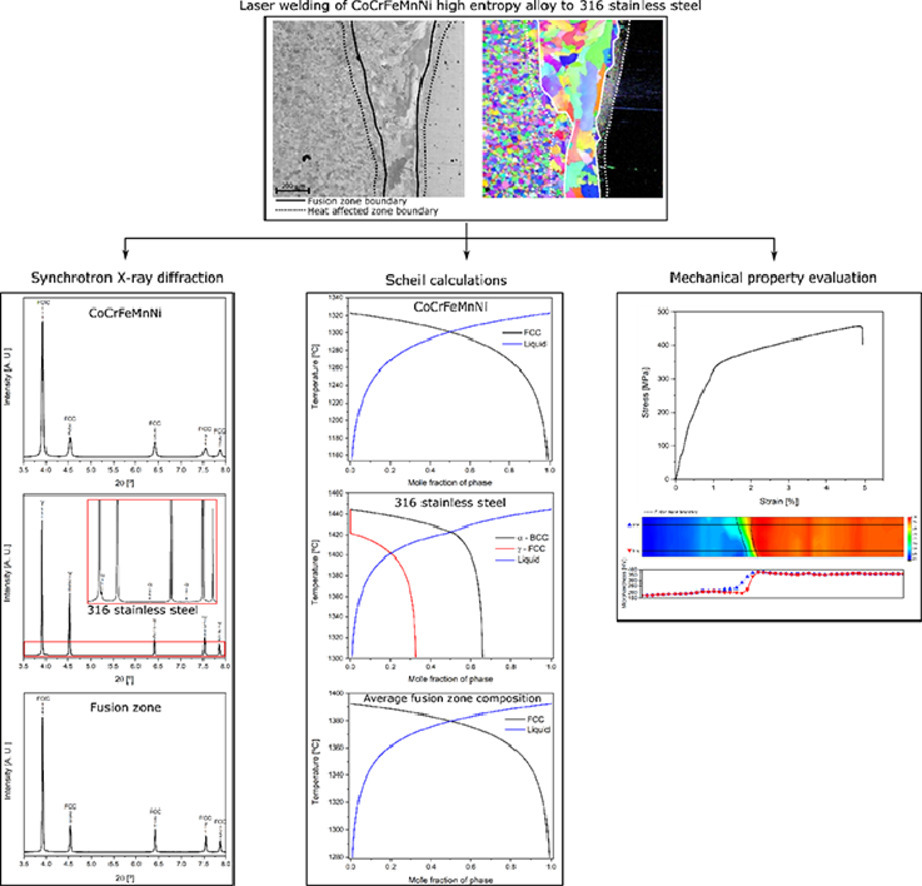
3. Dissimilar laser welding of a CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy to 316 stainless steel
CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金与316不锈钢的异种激光焊接
4. Effects of inclusion types on the high-cycle fatigue properties of high-strength steel
夹杂物类型对高强钢高周疲劳性能的影响
5. In suit observation of faceted growth and morphological instability of a complex-regular eutectic in Zn−Mg−Al system
Zn−Mg−Al体系中复杂规则共晶的晶面生长和不稳定形态的原位观察
6. Mechanisms of austenite growth during intercritical annealing in medium manganese steels
中锰钢临界退火过程中奥氏体的生长机制
7. Designing TiVNbTaSi refractory high-entropy alloys with ambient tensile ductility
室温下具有拉伸塑性的TiVNbTaSi难熔高熵合金
8. The cross-transition of deformation twinning in magnesium
镁中变形孪晶的交叉转变
9. In-situ observation of the phase evolution during an electromagnetic-assisted sintering experiment of an intermetallic γ-TiAl based alloy
金属间化合物γ-TiAl基合金电磁辅助烧结实验中相演变的原位观察
10. Dislocation facilitated formation and evolution of basal-prismatic/prismatic-basal interfaces in a Mg alloy
位错促进了镁合金中基底-棱柱/棱柱-基底界面的形成和演化
11. Unprecedented age-hardening and its structural requirement in a severely deformed Al-Cu-Mg alloy
严重变形的Al-Cu-Mg合金中前所未有的时效硬化及其结构要求
12. A new dynamic recrystallization mechanism in adiabatic shear band of an α/β dual phase titanium alloy: Composition redistribution
α/β双相钛合金绝热剪切带动态再结晶的新机制:成分再分布
13. A modified pearlite microstructure to overcome the strength-plasticity trade-off of heavily drawn pearlitic wire
一种改进的珠光体显微组织以克服重拉珠光体丝的强度-塑性制约
14. Single crystalline-like crystallographic texture formation of pure tungsten through laser powder bed fusion
通过激光粉床熔化制备纯钨的单晶状晶体织构
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114225
1. Strengthening mechanisms and microstructural evolution of ductile refractory medium-entropy alloy Hf20Nb10Ti35Zr35
韧性难熔中熵合金Hf20Nb10Ti35Zr35的强化机制及微观组织演化
I-An Su, Ko-Kai Tseng, Jien-Wei Yeh✉, Badr EI-Sayed, Chia-Heng Liu, Shing-Hoa Wang✉
Jien-Wei Yeh: jwyeh@mx.nthu.edu.tw
Shing-Hoa Wang: shwang@email.ntou.edu.tw
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114225
摘要
一种亚稳态β型中熵难熔合金Hf20Nb10Ti35Zr35在固溶处理状态下为具有延展性的BCC结构。时效处理后的合金可达到高的强度和延展性的结合。其强化机制包括相变诱导塑性、孪晶诱导塑性和沉淀强化。这些多重强化机制可以作为合金设计和提高合金力学性能的基础。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114226
2. Elastic energy of multi-component solid solutions and strain origins of phase stability in high-entropy alloys
高熵合金中多组分固溶体的弹性能和相稳定性的应变源
Reza Darvishi Kamachali✉, Lei Wang
Reza Darvishi Kamachali: reza.kamachali@bam.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114226
摘要
多组分固溶体的混合弹性能是通过拓展Eshelby的球孔模型推导出来的。通过探究化学成分和晶格错配度对弹性能影响,我们推导出晶格应变系数λ*。通过研究几种高熵合金和高温合金,我们提出大多数多元固溶体是稳定对当λ* < 0.16时,这概括了二元合金的Hume-Rothery原子尺寸规则。我们还揭示了多分散指数δ,常用于描述多组分合金中的应变,它可直接表示弹性能(e),其中e = qδ2, q是弹性常数。此外,量化了组成元素的(i)数量和(ii)原子尺寸分布对高熵合金相稳定性的影响。目前的推导和讨论为更全面地考虑高熵合金的弹性效应拓展了道路,为对其热力学性质的定量评估和研究相关的强化机制提供了直接支持。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114219
3. Dissimilar laser welding of a CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy to 316 stainless steel
CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金与316不锈钢的异种激光焊接
J.P. Oliveira✉, Jiajia Shen, Z. Zeng, Jeong Min Park, Yeon Taek Choi, N. Schell, E. Maawad, N. Zhou, Hyoung Seop Kim
J.P. Oliveira: jp.oliveira@fct.unl.pt
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114219
摘要
在这项工作中,将轧制的CoCrFeMnNi高熵合金激光焊接到316不锈钢上,并获得了无缺陷的接头。通过耦合显微电镜、高能同步加速X射线衍射、机械性能评估和热力学计算,对焊接接头的微观组织演变进行了评价和解释。熔合区显微组织由单一的FCC相组成,在该位置观察到硬度的增加,这是由于形成了新的固溶体(由两种基础材料的混合引起)。此外,在不锈钢熔化时在熔合区中渗入碳也有助于达到的强化效果。焊接接头具有良好的力学性能,在熔合区发生断裂是由于有大尺寸晶粒在该位置形成。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114232
4. Effects of inclusion types on the high-cycle fatigue properties of high-strength steel
夹杂物类型对高强钢高周疲劳性能的影响
P. Wang, B. Wang, Y, Liu, P. Zhang✉, Y.K. Luan, D.Z. Li, Z.F. Zhang✉
P. Zhang: pengzhang@imr.ac.cn (中国科学院金属研究所)
Z.F. Zhang: zhfzhang@imr.ac.cn (中国科学院金属研究所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114232
摘要
本文研究了不同类型夹杂物对高强钢的高周疲劳断裂行为的影响,研究发现,高碳铬轴承钢的疲劳裂纹主要起源于基体与氧化物夹杂的界面,而内部的氮化物夹杂则是疲劳破坏的起源。即使考虑应力幅值和夹杂物尺寸,由不同类型夹杂物引起的两种疲劳开裂模式通常也会导致疲劳寿命有很大差异。因此,本文首次建立夹杂物类型因子来统一夹杂物类型对疲劳性能的影响,修正后的应力强度因子可以很好地预测疲劳寿命。这些结果区分了夹杂物类型在疲劳性能方面的差异以及在高强度钢冶金中微量元素的控制作用。
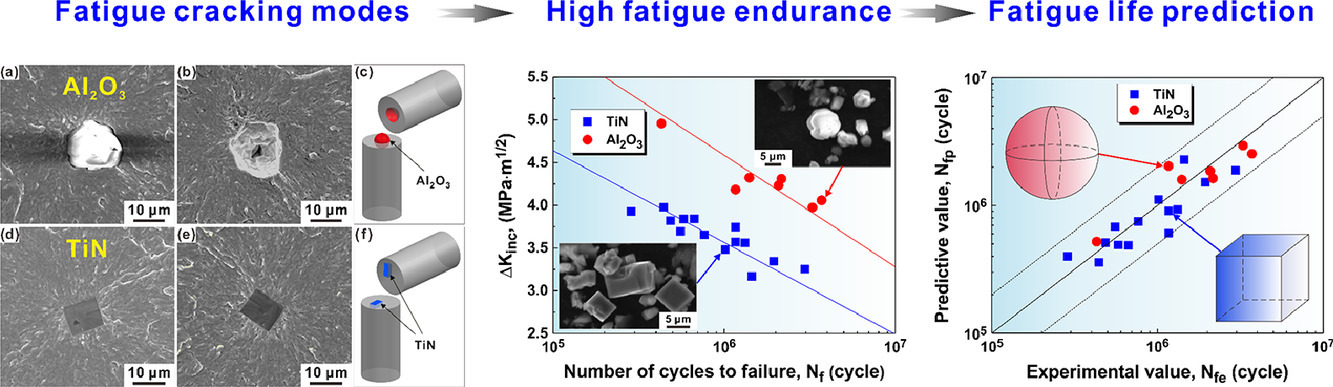
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114224
5. In suit observation of faceted growth and morphological instability of a complex-regular eutectic in Zn−Mg−Al system
Zn−Mg−Al体系中复杂规则共晶的晶面生长和不稳定形态的原位观察
Yeqing Wang, Jianrong Gao✉, Wenhao Sun, Ashwin J. Shahani✉
Jianrong Gao: jgao@mail.neu.edu.cn (东北大学)
Ashwin J. Shahani: shahani@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114224
摘要
使用同步加速器X射线研究了Zn-3Mg-4Al (wt.%)合金凝固过程中三相共晶的生长动力学。通过原位观察发现,三相共晶在初级Mg2Zn11上成核后,以大晶面形态生长,该晶面是由于Mg2Zn11的优先生长。基于密度泛函理论的计算,证实该先导相是具有高度各向异性的平衡形状。还观察到共晶-液体界面在凝固过程中不稳定,在过冷液体中会产生宏观台阶。由于Mg2Zn11晶体的各向异性,界面不稳定性的开始可能具有取向依赖性。
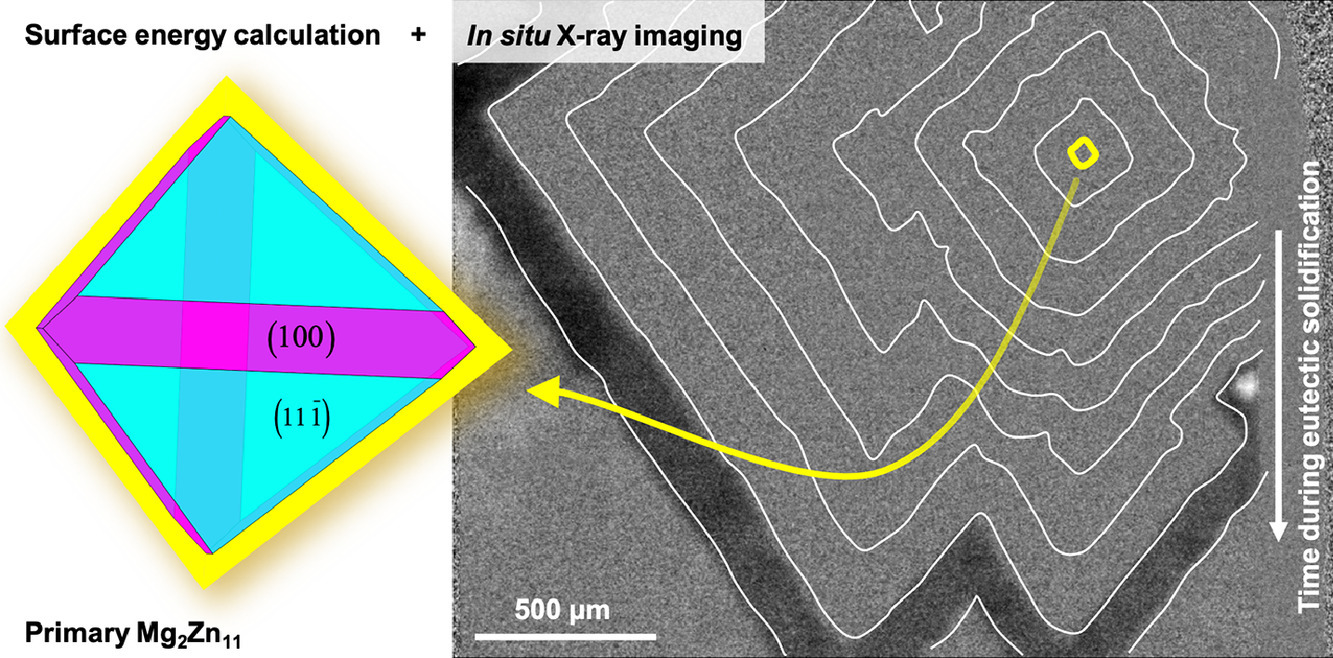
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114228
6. Mechanisms of austenite growth during intercritical annealing in medium manganese steels
中锰钢临界退火过程中奥氏体的生长机制
Rama Srinivas Varanasi✉, Marta Lipinska-Chwatek, Joachim Mayer, Baptiste Gault, Dirk Ponge
Rama Srinivas Varanasi: srinivas@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114228
摘要
第三代先进高强中锰钢(3-12 wt.%)通常由超细晶双相(奥氏体-铁素体)微观结构组成,该组织通过在马氏体的临界温度(≤0.5Tmelt)退火获得,该温度下Mn的体扩散极其缓慢。然而,锰的配分对于在退火期间从马氏体基体中生长出奥氏体十分重要,因此,晶界(GB)和位错提供的“短路”扩散对奥氏体生长至关重要。然而,这种影响在文献中并没有得到很好的解释。在目前的工作中,我们研究了成分为Fe-10Mn-0.05C-1.5Al (wt.%)的冷轧钢在临界退火过程中奥氏体的生长机制。我们提供了锰通过GB扩散、GB迁移和位错扩散迁移到奥氏体的证据。此外,还报告了GB错误取向对奥氏体生长的影响。
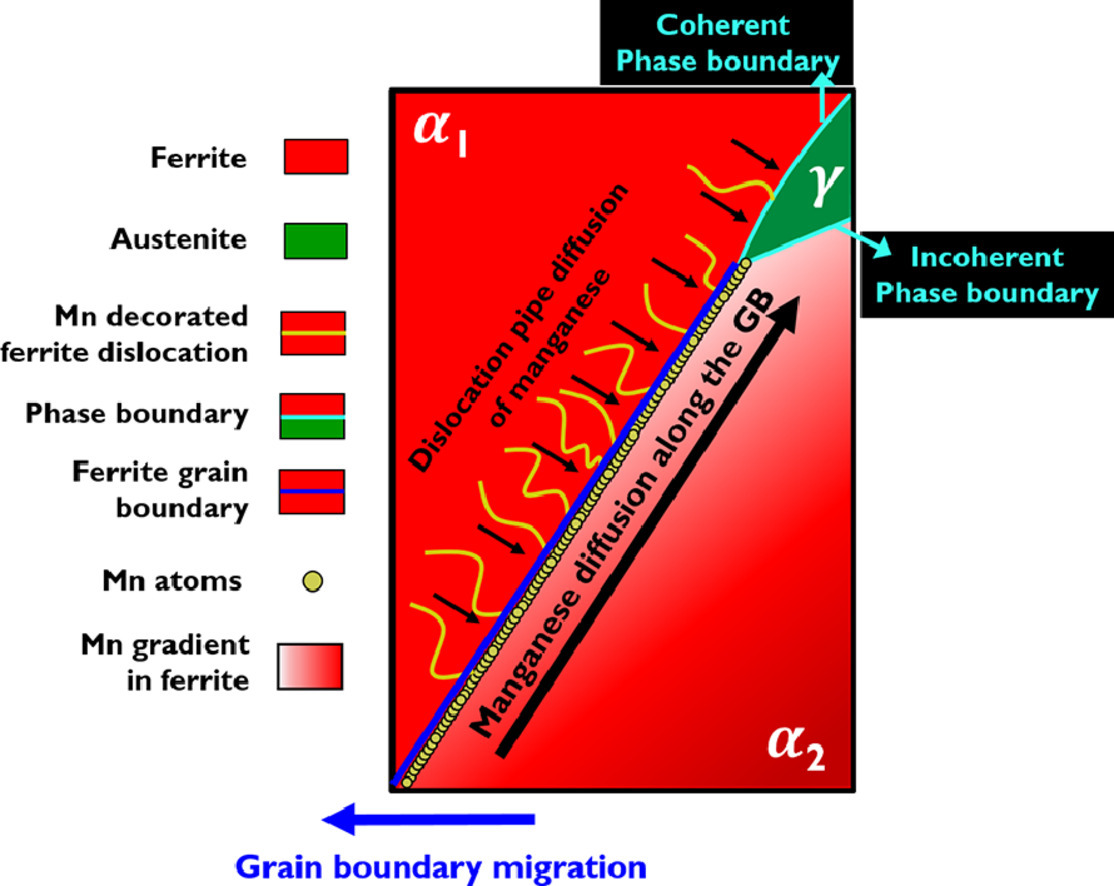
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114230
7. Designing TiVNbTaSi refractory high-entropy alloys with ambient tensile ductility
室温下具有拉伸塑性的TiVNbTaSi难熔高熵合金
Z.Q. Xu, Z.L. Ma✉, Y.Tan, X.W. Cheng✉
Z.L. Ma: 无邮箱信息 (北京科技大学)
X.W. Cheng: 无邮箱信息 (北京科技大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114230
摘要
在难熔高熵合金(RHEAs)中添加抗氧化元素(如Al、Cr、Si)可提高其高温抗氧化性,但通常会降低室温塑性,这对RHEAs的进一步应用提出了极大的挑战。为了解决这个问题,这项研究中首先确定了具有拉伸塑性的 TiVNbTa合金成分组成,添加Si将其合金化,然后通过简单的热轧工艺使最初脆性的TiVNbTaSi0.1韧性化。热加工有效地细化了TiVNbTaSi0.1的微观结构并析出了高密度的纳米硅化物,这有助于达到前所未有的机械性能,即约1250MPa的屈服强度和约8%的拉伸塑性。与已报道的塑性 RHEA相比,TiVNbTaSi0.1显示出优异的抗氧化性,并且TiVNbTa和 TiVNbTaSi0.1在大于500℃的温度下均表现出更高的相稳定性。TiVNbTaSi0.1的这些卓越性能凸显了其在高温应用中的巨大潜力。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114231
8. The cross-transition of deformation twinning in magnesium
镁中变形孪晶的交叉转变
Nan Yang, Bo-Yu Liu✉, Fei Liu, Zhi-Wei Shan✉
Bo-Yu Liu: boyuliu@xjtu.edu.cn (西安交通大学)
Zhi-Wei Shan: zwshan@mail.xjtu.edu.cn (西安交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114231
摘要
变形孪晶通过孪晶位错在特定的孪晶平面上并沿着特定的孪晶方向滑动,因此,孪晶变体应该保留其身份并且无法转化为其他变体。然而,这项研究证明,对于镁中的{1012}变形孪晶,一个孪晶变体可以通过参与棱柱-基底界面迁移而转变为其共轭变体以响应外加载荷。我们将这种转变称为变形孪生的交叉转变,这有望拓宽对孪生机制的理解。
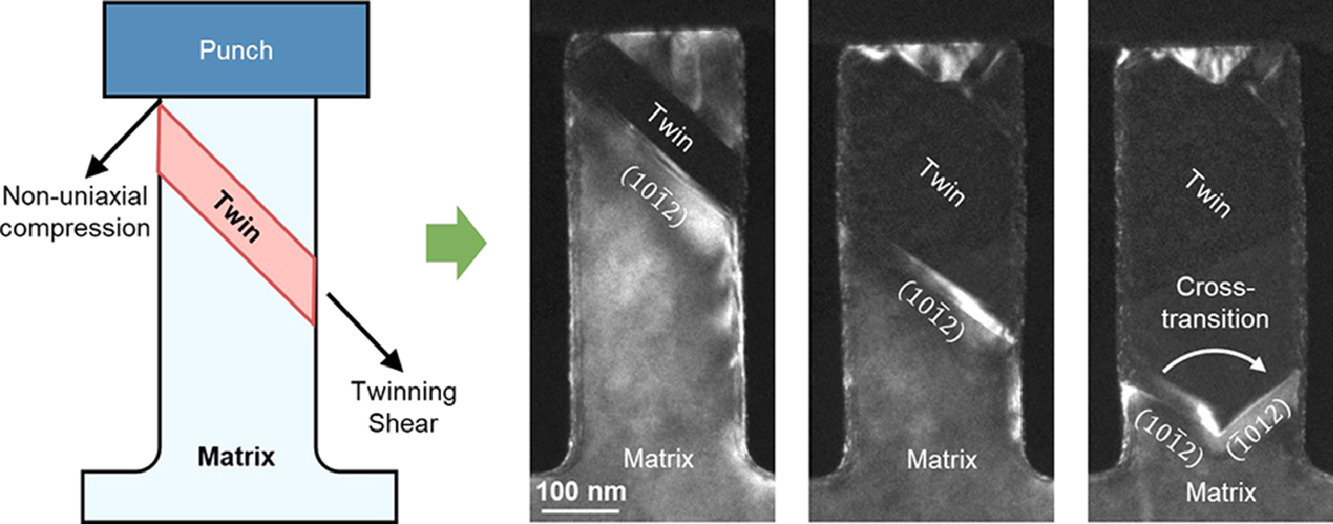
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114233
9. In-situ observation of the phase evolution during an electromagnetic-assisted sintering experiment of an intermetallic γ-TiAl based alloy
金属间化合物γ-TiAl基合金电磁辅助烧结实验中相演变的原位观察
Michael Musi✉, Benjamin Galy, Jean-Philippe Monchoux, Alain Couret, Helmut Clemens, Svea Mayer
Michael Musi: michael.musi@unileoben.ac.at
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114233
摘要
电磁辅助烧结为金属间γ-TiAl基粉末的高效致密化提供了可能。由于致密材料的微观结构及其机械性能可以通过施加温度分布来控制,因此相转变的动力学特别令人感兴趣。本研究描述了在使用感应加热的电磁辅助烧结过程中,通过高能X射线原位观察相演变的衍射装置。从Ti-46.3Al-2.2W-0.2B(at.%)粉末开始,该实验首次提供了对该粉末固结过程中非平衡和平衡相变的时间分辨的见解。在相同温度下致密的放电等离子烧结材料与电磁辅助烧结试样的具有一致的微观结构,这再次验证了两种技术的可转移性,并允许将确定的相变数据分配给放电等离子体烧结技术。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114237
10. Dislocation facilitated formation and evolution of basal-prismatic/prismatic-basal interfaces in a Mg alloy
位错促进了镁合金中基底-棱柱/棱柱-基底界面的形成和演化
Huhu Su, Xinzhe Zhou, Shijian Zheng✉, Hengqiang Ye, Zhiqing Yang✉
Shijian Zheng: sjzheng@hebut.edu.cn (河北工业大学)
Zhiqing Yang: yangzq@imr.ac.cn (中国科学院金属研究所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114237
摘要
根据原子级分辨率的实验观察和界面缺陷理论,研究并模拟了镁合金中基底-棱柱/棱柱-基底(BP/PB)界面的形成和演化。发现BP/PB界面可以由60°基底的1/3<1120>位错(即<a60>)、<c+a60>和来自于{1120}取向孪晶附近的非对称倾斜晶界的{1120}不连续孪晶发射形成。BP/PB界面向{1120}孪晶边界转变可通过<a60>和<c+a60>位错的发射而来,导致了{1120}孪晶的形核。 此外,每一侧的BP/PB界面都可以发出{1120} TDs以促进BP/PB界面的迁移。该实验结果可能有助于深入了解六方密排材料中BP/PB界面的形成和演化的位错辅助机制。
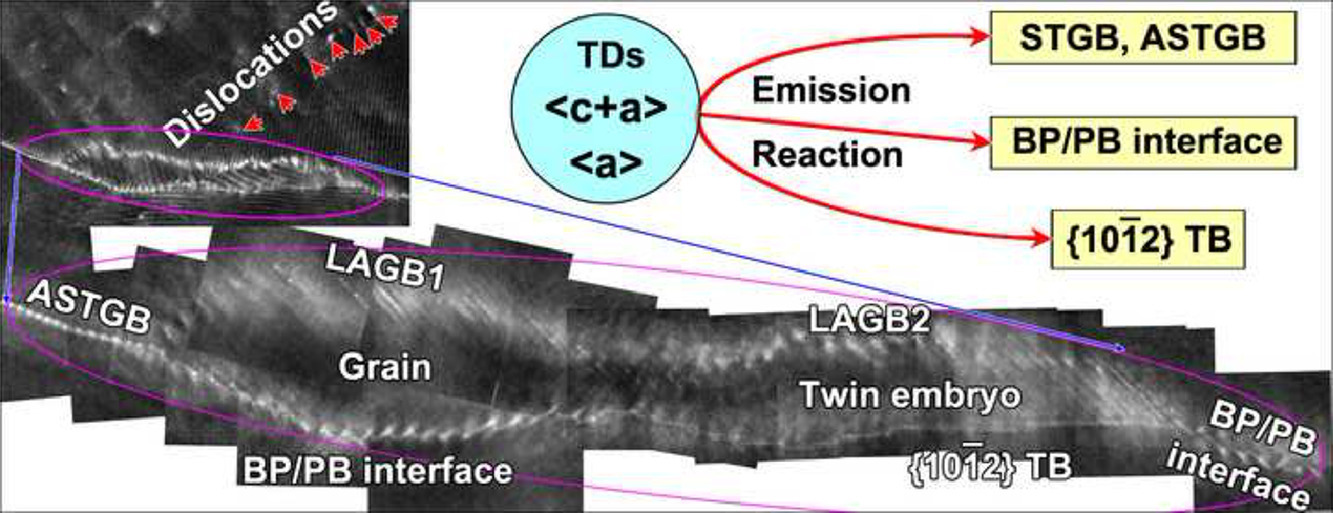
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114240
11. Unprecedented age-hardening and its structural requirement in a severely deformed Al-Cu-Mg alloy
严重变形的Al-Cu-Mg合金中前所未有的时效硬化及其结构要求
Ran Yang, Zongqiang Feng✉, Tian Huang, Guilin Wu, Andrew Godfrey, Xiaoxu Huang✉
Zongqiang Feng: zqfeng@cqu.edu.cn (重庆大学)
Xiaoxu Huang: xiaoxuhuang@cqu.edu.cn (重庆大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114240
摘要
通过在液氮温度下进行表面滑动摩擦处理,在Al-Cu-Mg合金(Al 2024) 表面形成了纳米梯度结构。时效处理后,表层实现了前所未有的时效硬化,显微硬度值大于320 HV,是传统沉淀硬化(150 HV)可达到的两倍以上,远高于先前报道的最大值(280 HV)。透射电镜和原子探针扫描分析表明,表层变形纳米晶结构的形成导致了时效过程中Cu和Mg向窄间距晶界的偏析增强,相应地抑制了沉淀的产生。增强的晶界偏析而不是沉淀被认为是造成大量时效硬化的原因,尽管由晶界偏析引起的潜在硬化机制需要进一步研究。
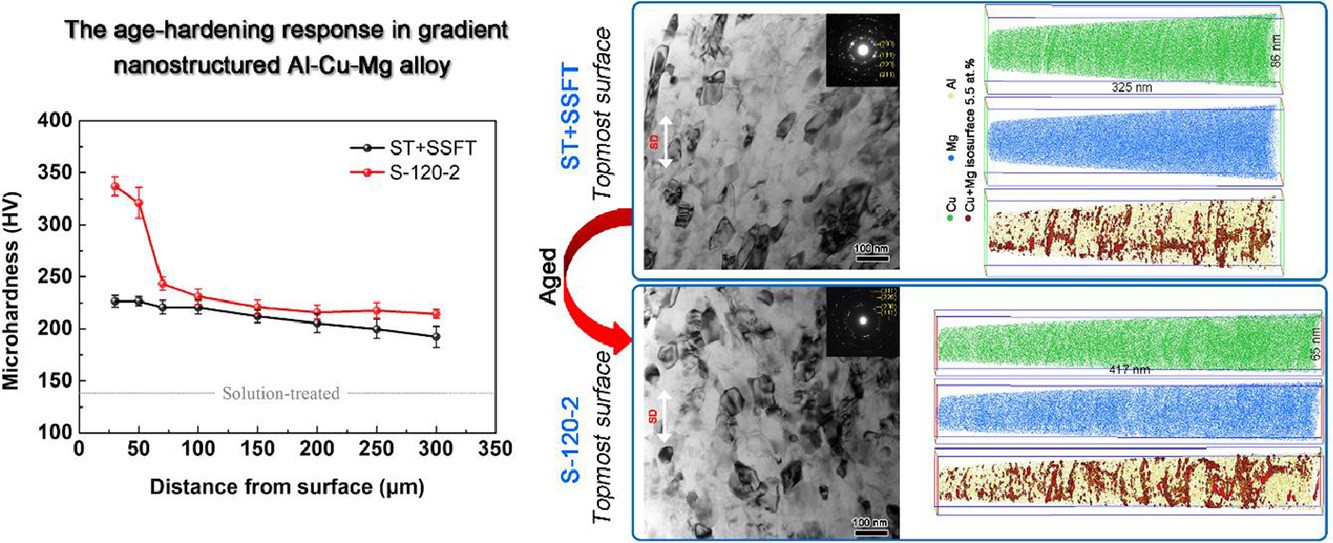
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114229
12. A new dynamic recrystallization mechanism in adiabatic shear band of an α/β dual phase titanium alloy: Composition redistribution
α/β双相钛合金绝热剪切带动态再结晶的新机制:成分再分布
Xinjie Zhu, Qunbo Fan✉, Duoduo Wang, Haichao Gong, Yu Gao, Feng Qian, Shenbao Jin, Gang Sha
Qunbo Fan: fanqunbo@bit.edu.cn (北京科技大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114229
摘要
本文利用原子探针技术研究了α/β双相Ti-5.5Mo-7.2Al-4.5Zr-2.6Sn-2.1Cr钛合金的绝热剪切带(ASBs)的成分分布特征及其对动态再结晶(DRX)的影响。结果表明,在ASB过渡区,在α/β界面观察到清晰的晶界(GB)。然而,在ASB中心区域,α/β界面形成了“模糊GB”,在“模糊GB”中积累了大量位错。此外,在部分β相区,β相稳定元素(Mo/Cr)变得相当稀疏,形成更细的α晶粒;而在某些α相区,β相稳定元素富集,形成了更细的β晶粒,从而将原始晶粒与DRX细晶分离开来。α/β晶粒和α/β界面独特的成分分布特征被定义为成分再分布,这是局部塑性变形和绝热温升共同作用的结果。
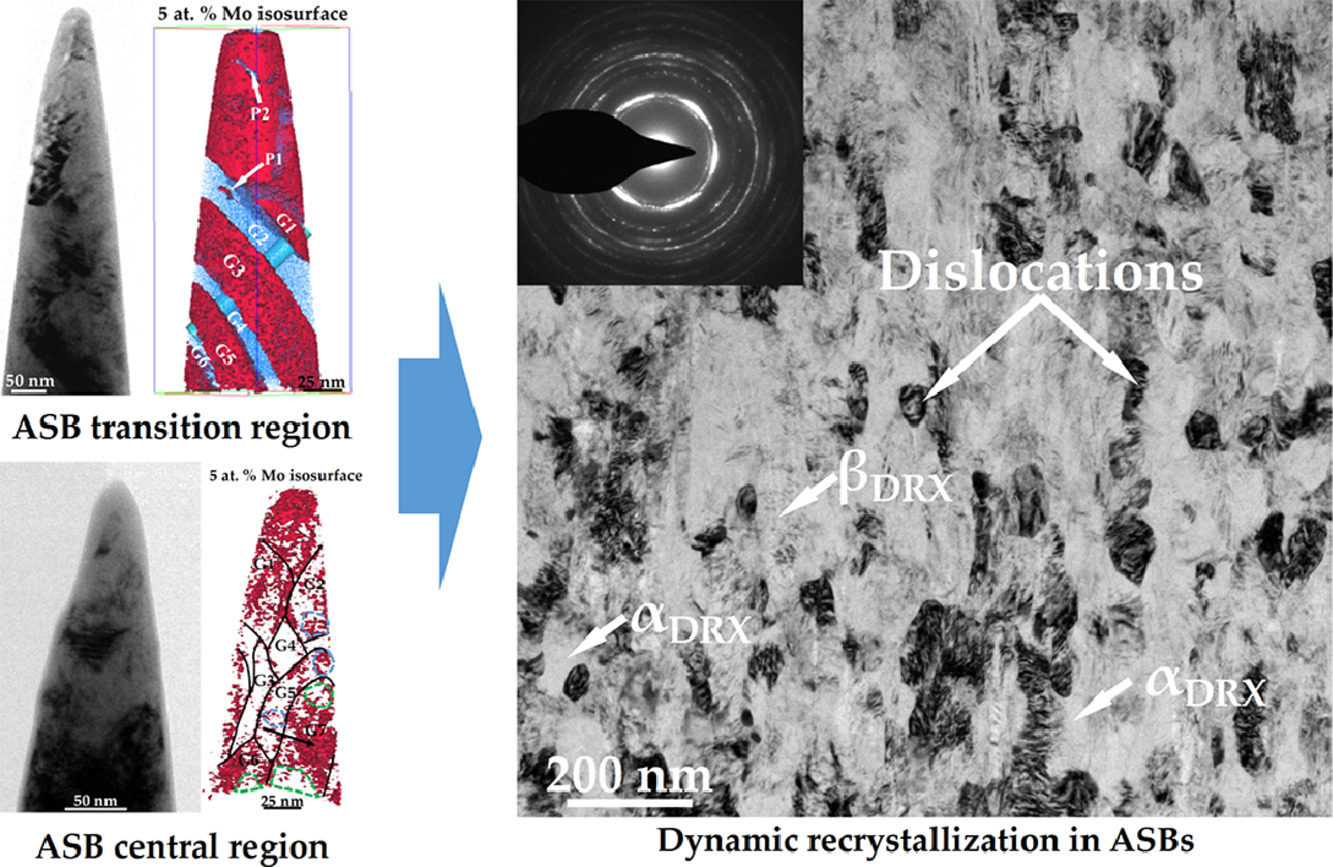
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114236
13. A modified pearlite microstructure to overcome the strength-plasticity trade-off of heavily drawn pearlitic wire
一种改进的珠光体显微组织以克服重拉珠光体丝的强度-塑性制约
Lichu Zhou, Feng Fang✉, Masayshi Kumagai, Ed Pickering, Xiaodan Zhang
Feng Fang: fangfeng@seu.edu.cn (东南大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114236
摘要
拉拔珠光体钢丝可以达到超高强度早已被证实,然而,这通常会损害拉伸和扭转延展性。在这项工作中,我们采用了一种改进的微观结构,通过一个涉及简单的多次拉伸和退火步骤的过程来克服这些问题。在这种显微组织中,传统的珠光体渗碳体板条被渗碳体纳米颗粒所取代,这些颗粒由富含置换元素的晶界桥接。在经过这种改进的加工路线后,发现0.92%C钢丝表现出2300 MPa的抗拉强度、6.4%的均匀延伸率和0.73的均匀扭转应变。在相同应变下,新工艺加工的线材的极限强度高于传统工艺制备的线材,但拉伸和扭转延展性要好得多——实际上它们与无应变珠光体钢棒的延展性相匹配。
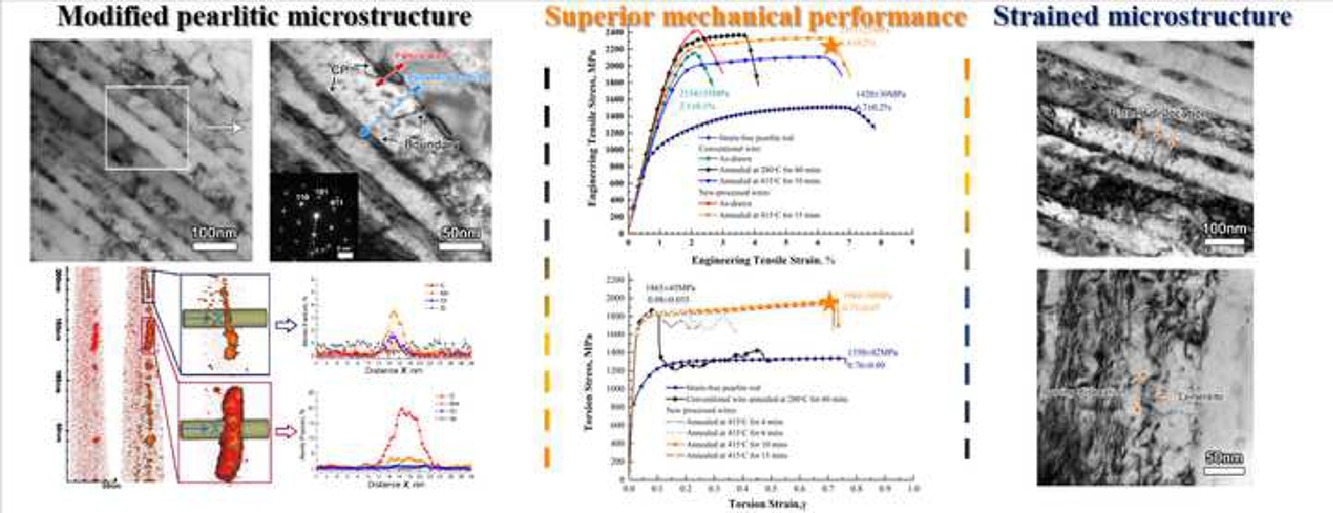
SCRIPTA
Vol. 206, 1 Jan. 2022, 114252
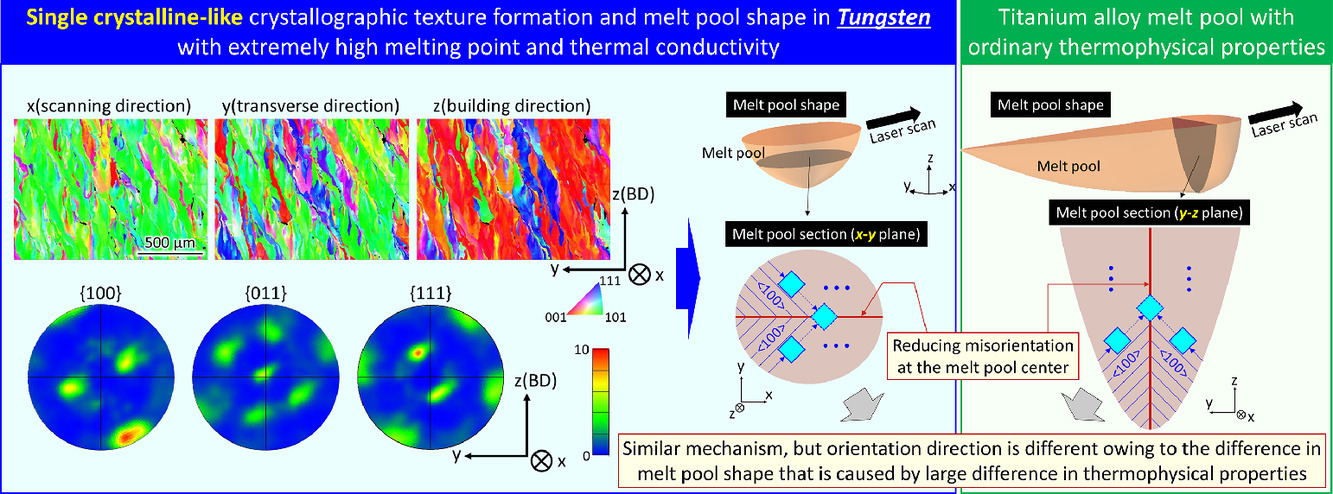
14. Single crystalline-like crystallographic texture formation of pure tungsten through laser powder bed fusion
通过激光粉床熔化制备纯钨的单晶状晶体织构
Tsubasa Todo, Takuya Ishimoto, Ozkan Gokcekaya, Jongyeong Oh, Takayoshi Nakano✉
Takayoshi Nakano: nakano@mat.eng.osaka-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114252
摘要
通过激光粉床熔化(LPBF)技术首次成功地制备出独特的钨晶体结构。由于钨极高的熔点和高的导热性,LPBF技术难以制造高密度钨产品。通过调整激光工艺参数,我们成功地制造出致密度高达99.1%的纯钨零件,这是迄今为止报道的最高值。更重要的是,该制品中出现一种类似单晶的显着晶体结构,<011>优先沿激光扫描方向取向。形成这种结构是为了减少熔池中心的晶粒取向错误,熔池左右两半部的凝固前沿在此处相遇。这种结构的形成机制与具有普通热性质的常规合金相似,然而,决定晶体取向的晶体生长方向性因熔池形态而异。