金属顶刊双语导读丨Acta Mater. Vol.215,15 Aug. 2021(上)
2021-12-10 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文15篇,涵盖了高温合金、低碳钢、高熵合金等,国内科研单位包括北京工业大学、清华大学、北京科技大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 215 目录
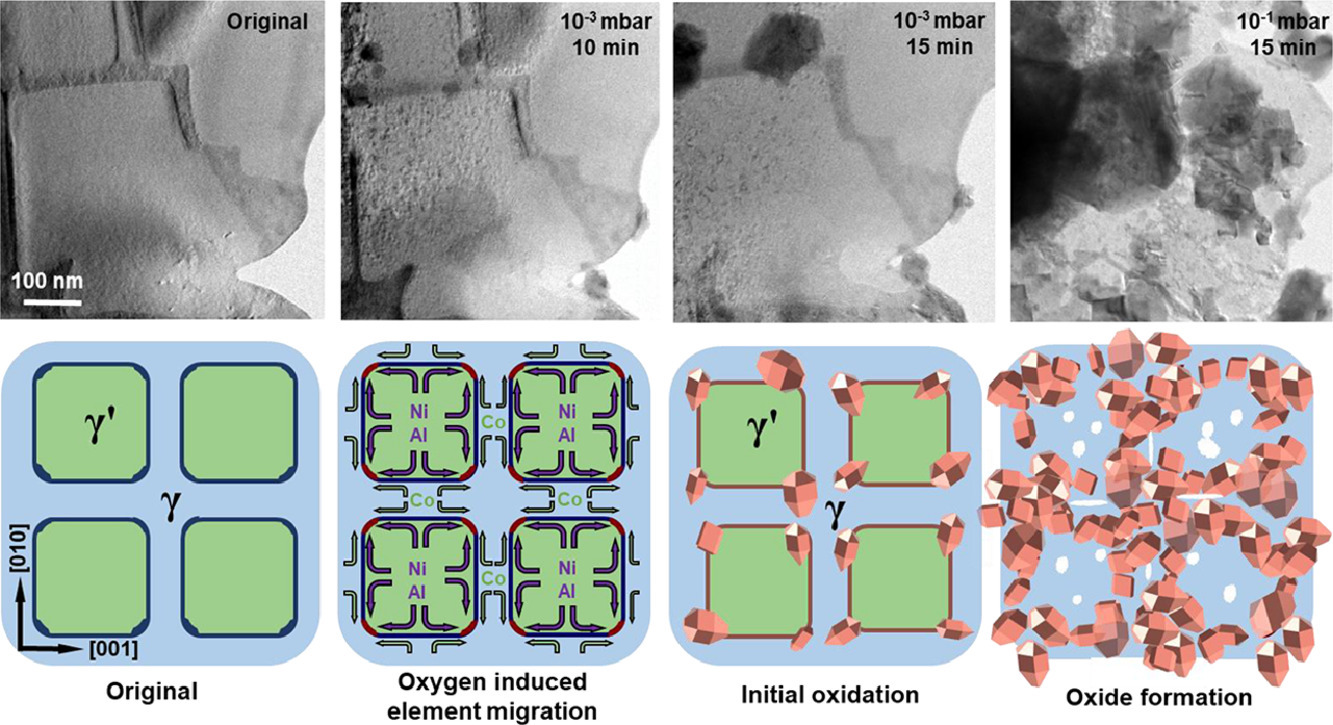
1. Initial oxidation of Ni-based superalloy and its dynamic microscopic mechanisms: The interface junction initiated outwards oxidation
镍基高温合金的初始氧化及其动态微观机制:界面连接处引发的向外氧化
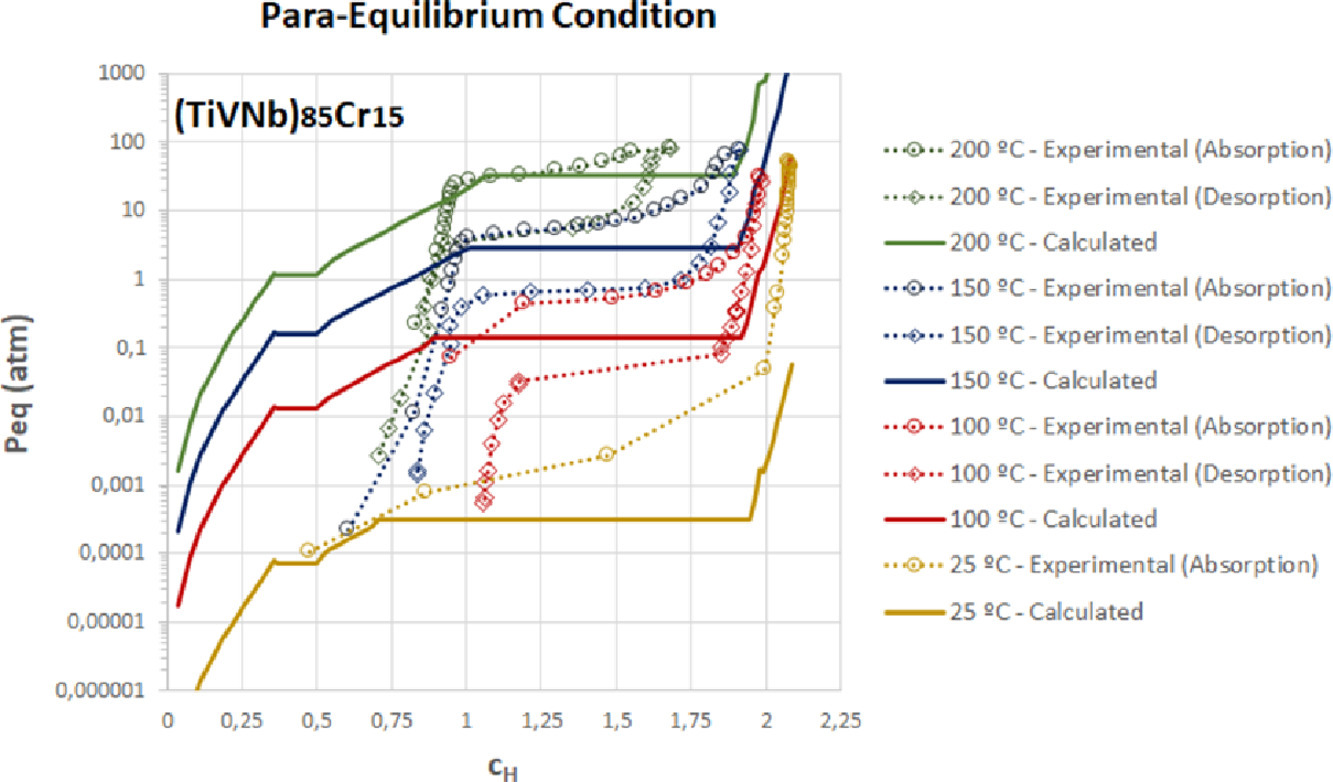
2. Thermodynamic modelling of hydrogen-multicomponent alloy systems: Calculating pressure-composition-temperature diagrams
氢基多组份合金体系的热力学模型:计算压力-成分-温度图
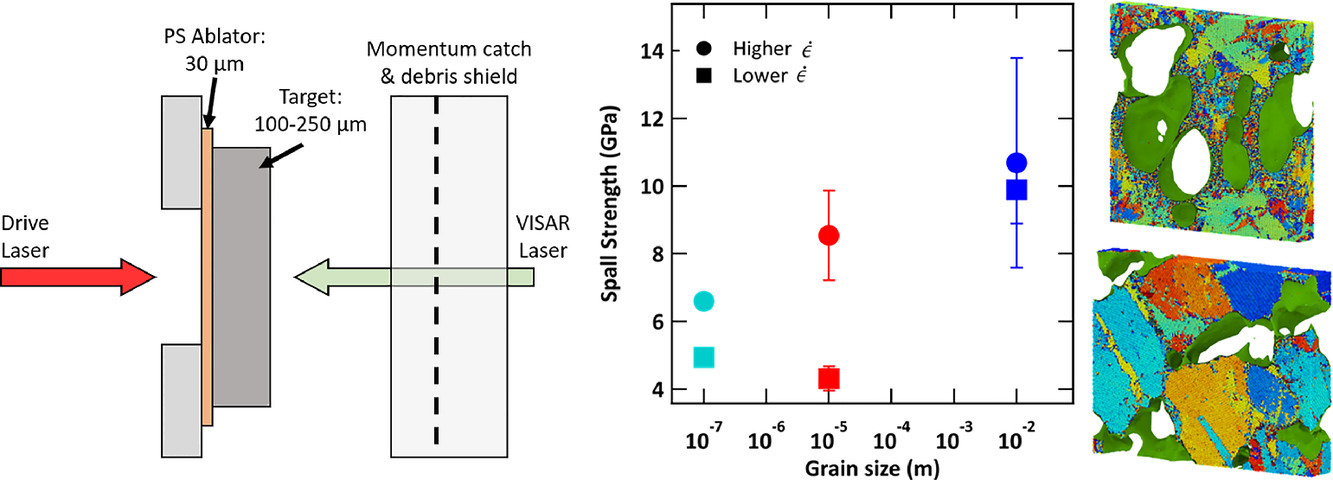
3. Towards the ultimate strength of iron: spalling through laser shock
实现铁的极限强度:通过激光冲击实现剥落
4. Correlation between grain size and carbon content in white etching areas in bearings
轴承中白色蚀刻区的晶粒尺寸和碳含量之间的相关性
5. A simple yet general model of binary diffusion coefficients emerged from a comprehensive assessment of 18 binary systems
通过对18个二元体系的综合评估,得到了一个简单而普遍的二元扩散系数模型
6. Unraveling the effects of Nb interface segregation on ferrite transformation kinetics in low carbon steels
揭示 Nb 界面偏析对低碳钢中铁素体转变动力学的影响
7. Interplay between cracking and delamination in incrementally deposited plasma sprayed coatings
增量沉积等离子喷涂涂层开裂与分层的相互作用
8. Evaluation of the influence of B and Nb microalloying on the microstructure and strength of 18% Ni maraging steels (C350) using hardness, spherical indentation and tensile tests
采用硬度、球形压痕和拉伸试验评估B和Nb微合金化对18%Ni 马氏体时效钢(C350)的组织和强度的影响
9. Deformation mechanisms of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy under low-cycle-fatigue loading
CoCrFeMnNi 高熵合金在低周疲劳载荷下的变形机制
10. Twinning pathways in Fe and Fe–Cr alloys from first-principles theory
基于第一性原理的Fe和Fe -Cr合金中的孪晶途径
11. Inference and uncertainty propagation of GB structure-property models: H diffusivity in [100] tilt GBs in Ni
GB 结构-性能模型的推理和不确定性传播:镍中[100]倾斜GBs的H扩散率
12. Ultra-fine-grained and gradient FeCrAl alloys with outstanding work hardening capability
具有优异加工硬化能力的超细晶粒和梯度FeCrAl合金
13. Enhancement of vacancy diffusion by C and N interstitials in the equiatomic FeMnNiCoCr high entropy alloy
等原子FeMnNiCoCr高熵合金中C和N间质对空位扩散的增强作用
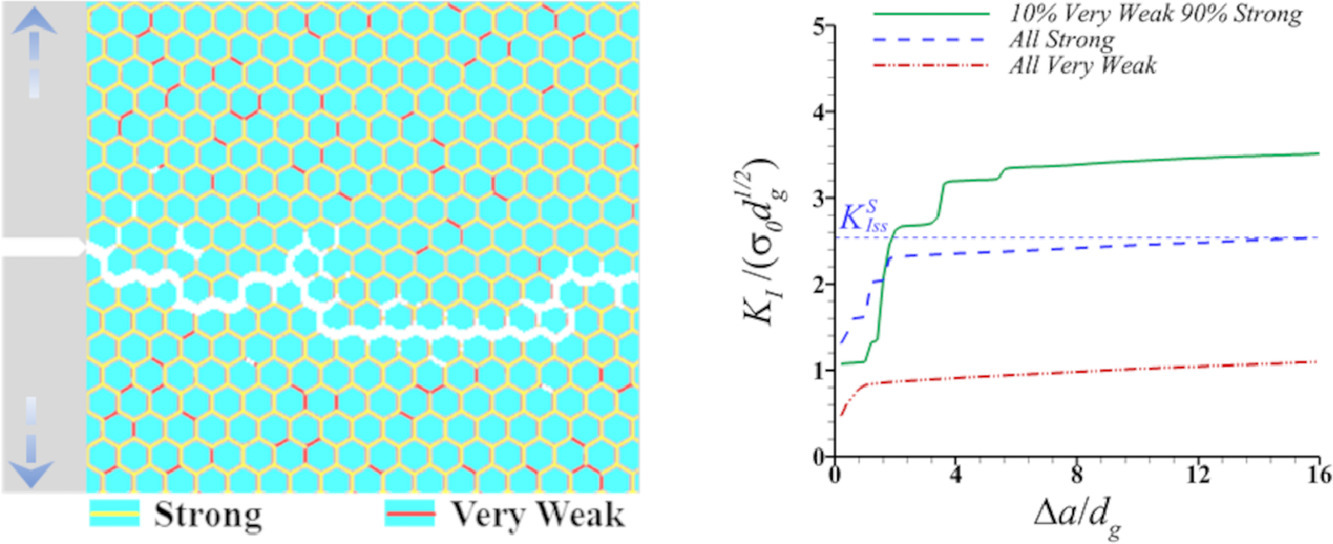
14. Toughening of interface networks through the introduction of weak links
通过引入薄弱环节强化界面网络
15. Segregation-assisted phase transformation and anti-phase boundary formation during creep of a γ′-strengthened Co-based superalloy at high temperatures
γ′ 强化 Co 基超合金在高温下蠕变过程中的偏析辅助相变和反相边界形成
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 116991
1. Initial oxidation of Ni-based superalloy and its dynamic microscopic mechanisms: The interface junction initiated outwards oxidation
镍基高温合金的初始氧化及其动态微观机制:界面连接处引发的向外氧化
Yadi Zhai, Yanhui Chen, Yunsong Zhao, Haibo Long, Xueqiao Li, Qingsong Deng, Hui Lu, Xiaomeng Yang, Guo Yang, Wei Li, Luyan Yang, Shengcheng Mao, Ze Zhang, Ang Li✉, Xiaodong Han✉.
Ang Li: ang.li@bjut.edu.cn,北京工业大学
Xiaodong Han: xdhan@bjut.edu.cn,北京工业大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116991
摘要
少量的初始氧化可以诱发快速腐蚀并导致灾难性的失效,因此了解高温初始氧化机制及其动态过程通常是很重要的。我们通过用Cs校正的环境透射电子显微镜对从室温至900℃的纳米和原子尺度的动态过程进行原位观察和研究,揭示了第三代镍基高温合金的初始氧化机制。在低温下,初始氧化从γ/γ′界面开始。缺氧的高温氧化过程更倾向于在γ/γ′界面的交叉结处产生氧化位点。氧化物纳米粒子的生长速率取决于氧化温度,在低于600℃时生长速度较低,高于 700℃时则快速生长。并且进一步观察到了从γ′和γ相到γ/γ′界面的质量转移,特别是在这些界面的连接处,会导致氧化物的积累。这项研究提供了对包括 Al 和 Cr 元素在内的界面相、界面连接引发的向外氧化的直接观察。这些结果阐明了含有相间界面的第二相的材料和缺氧条件下的材料以及有保护涂层的材料的初始氧化机制。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117070
2. Thermodynamic modelling of hydrogen-multicomponent alloy systems: Calculating pressure-composition-temperature diagrams
氢基多组份合金体系的热力学模型:计算压力-成分-温度图
Guilherme Zepona✉, Bruno Hessel Silva, Claudia Zlotea, Walter José Botta,Yannick Champion
Guilherme Zepona: zepon@ufscar.br
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117070
摘要
合金作为储氢介质的适用性主要取决于其压力-组成-温度(PCT)图。由于 PCT 图与成分有关,因此可以探索高熵合金、复杂的浓缩合金或多组分合金的广阔成分领域,以便为每种应用设计出具有良好性能的合金。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个热力学模型来计算体心(BCC)多成分合金的PCT 图。各相的熵是用具有位点阻塞效应的间隙固溶体的理想构型熵来描述的。作为第一个近似值,假定一个相的氢偏摩尔焓是常数,所以氢混合焓与氢浓度呈线性变化。此外,用一个简单的理想混合定律,近似地计算了具有相同结构的多组分合金相的氢偏焓。利用实验数据和DFT计算对测试合金的八种元素(Ti、V、Cr、Ni、Zr、Nb、Hf 和 Ta)的焓项进行参数化。四个不同体系的六种BCC多成分合金的实验PCTs与计算结果进行了比较,结果非常一致。本文提出的模型和参数可以作为不同的储氢应用开发强大的合金设计工具的基础。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117072
3. Towards the ultimate strength of iron: spalling through laser shock
实现铁的极限强度:通过激光冲击实现剥落
Gaia Righi, Carlos J. Ruestes, Camelia V. Stan, Suzanne J. Ali, Robert E. Rudd, Megumi Kawasaki , Hye-Sook Park, Marc A. Meyers✉
Marc A.Meyersa: mameyers@ucsd.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117072
摘要
材料的极限强度是在应变速率接近德拜频率时达到,即在原子尺度的变形时间接近于原子从平衡状态移动到其极端分离位置的时间(对于铁来说,约 5.5 × 1013 s−1)。本文对单晶、多晶和纳米晶铁进行了高功率脉冲激光实验,产生了应变速率接近德拜频率的拉伸脉冲, 106 s−1 – 107 s−1 ,时间长度为纳秒。我们发现铁的强度在 5 到 10GPa 之间变化,比静态抗拉强度高了10倍。此外,超细粒度的铁样品的抗拉强度(4~6GPa)比单晶铁(10Gpa)的低。 而且MD模拟结果显示,这是由于在纳米和多晶条件下在晶界处的空隙的起始位置不同而引起。在单晶铁中观察到稀疏的逃逸空隙(直径为5 μm)和表面熔化的现象,这可能是由于在发生足够的变形时应变引起的熔化。用分子动力学方法模拟了分离导致剥落的过程,并确定了在实验恢复的试样中观察到的机制:在单晶中,空隙在孪晶的交汇处成核,而在纳米晶试样中晶界是空隙成核的主要来源。对空穴表面剪切环发射所产生的位错进行了解析计算,发现几何上必要的位错密度与分子动力学计算的预测一致。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117048
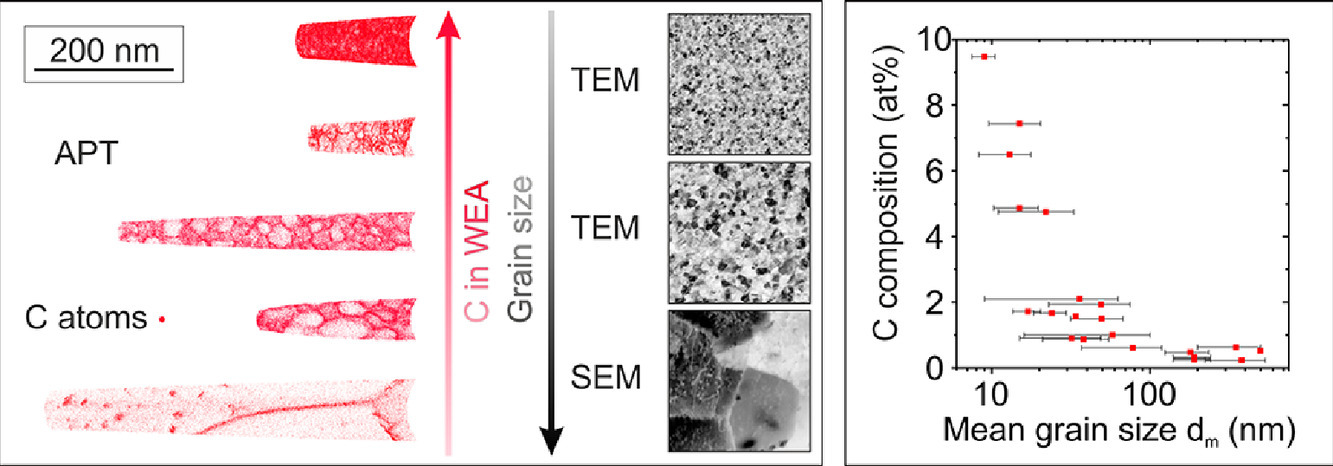
4. Correlation between grain size and carbon content in white etching areas in bearings
轴承中白色蚀刻区的晶粒尺寸和碳含量之间的相关性
D. Mayweg, L. Morsdorf, Y. Li, M. Herbig✉
M. Herbig: d.mayweg@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117048
摘要
轴承在滚动接触疲劳期间过早失效往往与白色蚀刻裂纹(WECs)的形成有关。 WECs 的裂纹表面摩擦将原来的贝氏体/马氏体组织转变为纳米晶铁素体组成的白色蚀刻区(WEAs),其晶粒尺寸和碳含量在WEA内有所不同。本文中,我们通过原子探针断层扫描和扫描电子显微镜研究显示,在100Cr6 轴承中形成的 WEAs 的晶粒大小和碳含量之间存在反比例关系,这些轴承在使用中因 WECs 失效。我们通过碳偏析降低晶界能来解释这一现象。根据碳含量的不同,这降低了再结晶和晶粒粗化的驱动力,从而稳定了纳米晶组织。对于替代元素铬却没有观察到这种影响。最小的晶粒尺寸(<10 nm)直接出现在分解渗碳体析出相的旁边,它们作为碳源,导致铁素体中的碳含量高达9.5 %。相应地,碳含量最低的WEA 段表现出最大的晶粒尺寸。在WEAs 的子区域中增加碳含量不仅导致晶粒尺寸变小,还会导致晶界和晶粒内部的平均碳含量升高。我们的结果表明,模型实验中显示的通过碳晶界偏析实现铁素体组织稳定的机制也适用于100Cr6工艺合金实际轴承应用中发生的与 WEC 失效有关的组织改变。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117077
5. A simple yet general model of binary diffusion coefficients emerged from a comprehensive assessment of 18 binary systems
通过对18个二元体系的综合评估,得到了一个简单而普遍的二元扩散系数模型
Wei Zhong, Qiaofu Zhang, Jicheng Zhao✉
Jicheng Zhao: jczhao@umd.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117077
摘要
这项研究是迄今为止最全面的测试,旨在为二元固溶体扩散行为的可靠数学描述确定最佳的拟合参数数量。我们对 18 个不同的二元体系进行了系统的测试,得出了一个非常简单的模型,只有一个拟合参数/常数,可以从实验扩散数据中评估。模型中的其余的量是纯元素的自扩散和杂质(稀释)扩散系数,以及可以从相关二元体系的 CALPHAD 热力学评估中计算出的热力学系数。单参数 Z-Z-Z 模型已被证明是非常可靠和稳健的,因为本研究中测试的18个二元体系包括非常不对称的体系,如Co-Pd和Fe-Pd以及Nb-Ti,其实验扩散系数数据覆盖了9个数量级,温度范围跨越 1200℃(从800℃ 到2000℃)。 Z-Z-Z 模型允许在根据相互扩散或所有实验扩散数据中评估出唯一常数后,可靠地计算出任何温度下任何成分的示踪剂和本征扩散系数。将这中简单而稳定的模型从二元系统扩展到三元和高阶系统时将大大减少拟合参数,并提高未来用于模拟材料动力学过程的多组分扩散(原子迁移率)数据库的可靠性。

ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117081
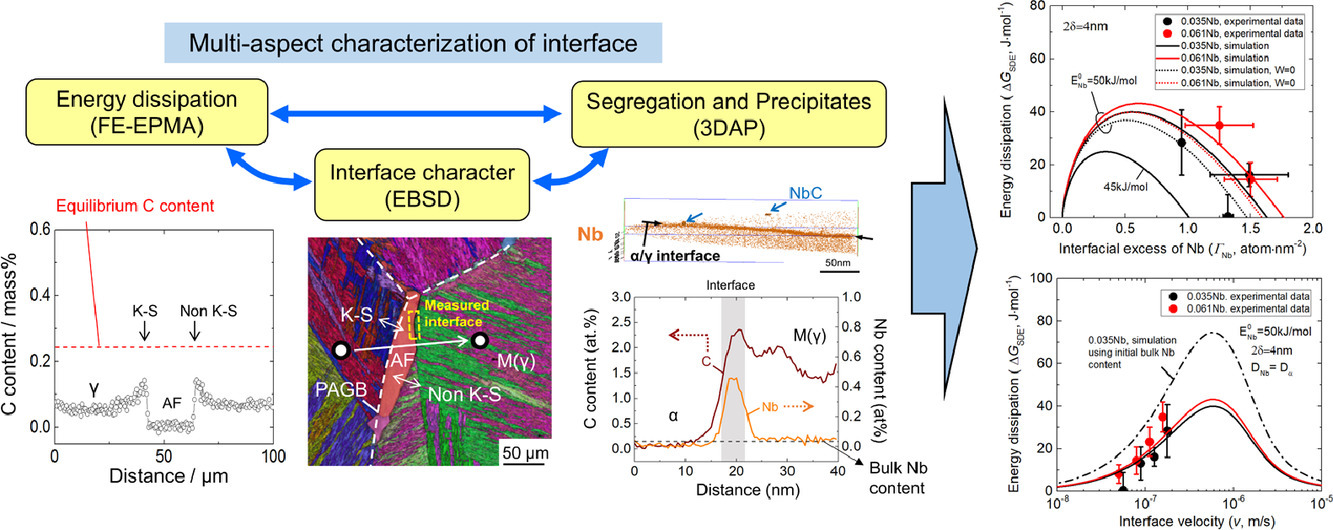
6. Unraveling the effects of Nb interface segregation on ferrite transformation kinetics in low carbon steels
揭示 Nb 界面偏析对低碳钢中铁素体转变动力学的影响
Haokai Dong✉, Yongjie Zhang✉, Goro Miyamoto, Masahiro Inomoto, Hao Chen, Zhigang Yang, Tadashi Furuhara
Haokai Dong: dong-hk16@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn, 清华大学
Yongjie Zhang: yongjie@imr.tohoku.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117081
摘要
添加少量的Nb可以显著地阻碍铁素体的生长。其原因被归结为Nb在迁移的铁素体/奥氏体界面上的偏析产生的溶质拖曳效应(SDE)。然而,由于表征技术的限制,元素偏析、SDE 和界面速度之间的关系还没有得到定量阐明。同时,Nb 原子和C原子之间的强亲和力会在界面上导致碳化物析出,即相间析出,这可能会影响Nb的偏析行为,使问题变得更加复杂。因此,在本研究中,定量研究了 Fe-0.08C-(0.035, 0.061)Nb模型合金中Nb偏析量、能量耗散、NbC析出物和界面速率的界面信息。结果表明,在迁移的铁素体/奥氏体界面上的能量耗散随保温时间的延长或转化温度的升高而降低。 Nb原子更倾向于在非K-S界面偏析,而不是在近K-S界面。而且非K-S界面上的Nb偏析量随着时间的延长而增加,而提高块状Nb含量或降低相变温度并不会导致偏析的明显增加。Nb 偏析、能量耗散和界面速率之间的关系可以通过优化参数(即偏析能量、界面厚度和跨界面扩散率)的SDE模型得到很好的再现。NbC相间析出的发生通过消耗铁素体中的Nb溶质来削弱SDE,从而间接地影响了相变动力学。相比之下,它们的钉扎效应起到的作用很小。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117074
7. Interplay between cracking and delamination in incrementally deposited plasma sprayed coatings
增量沉积等离子喷涂涂层开裂与分层的相互作用
Shalaka V. Shinde✉, Sanjay Sampath
Shalaka V.Shinde: Shalaka.shinde@stonybrook.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117074
摘要
几十年来,受限薄膜和涂层在制造和使用过程中的开裂和分层一直是科学研究的重要的课题。过去大量的工作集中在开发基于预测稳态能量释放率的分析模型,以确定薄膜中裂纹和 或分层的发生。这些模型已经被整合成“设计图”。然而,这种设计图的可用实验验证的范围是有限的。此外,这些分析性的设计图缺乏对分层薄膜加工过程中细微差别的描述,如渐进式增量沉积。
在这项研究中,基于上述模型定义了渐进沉积的等离子喷涂涂层中裂纹和分层之间的相互作用。在调整模型和主要假设后,进行了一套精心设计的实验,以探测不同陶瓷和工艺条件的反应, 从而可以对裂纹或分层进行观察。这些实验阐明了决定这种应力松弛事件发生的潜在条件。实验数据与适用于单一的、孤立的、快速凝固的液滴(飞溅)和增量沉积的厚等离子喷涂涂层的分析设计图相一致,从而为先进涂层的稳健设计和加工提供了一个框架。

ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117071
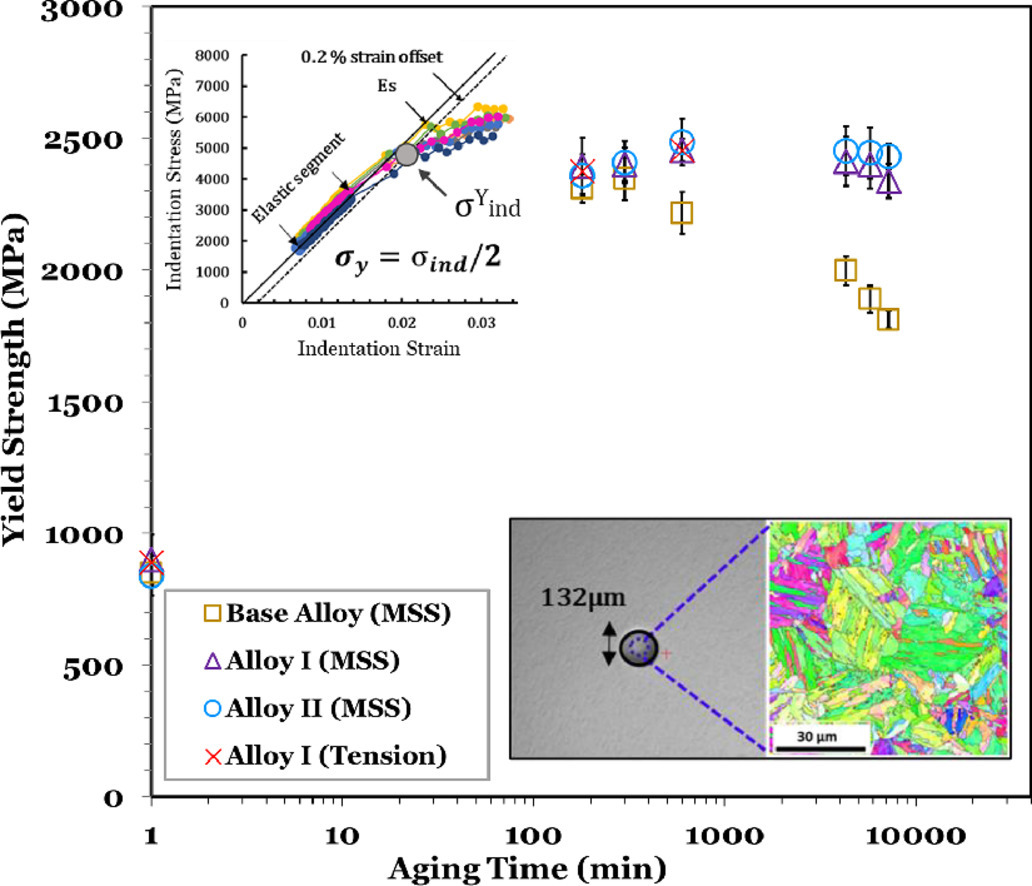
8. Evaluation of the influence of B and Nb microalloying on the microstructure and strength of 18% Ni maraging steels (C350) using hardness, spherical indentation and tensile tests
采用硬度、球形压痕和拉伸试验评估B和Nb微合金化对18%Ni 马氏体时效钢(C350)的组织和强度的影响
SepidehParvinian, Daniel E.Sievers, Hamid Garmestani, Surya R.Kalidindi✉
Surya R.Kalidindi: surya.kalidindi@me.gatech.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117071
摘要
含有极少量B和Nb的微合金钢可以提高其机械性能。在本工作中,我们设计并进行了实验分析,以评估用少量B和Nb对18% 镍马氏体时效钢进行微合金化的优点。实验包括合成具有所需成分的小体积材料(标记为基础合金、合金I和合金II),进行时效热处理,并使用维氏硬度、球形压痕应力-应变关系和标准化拉伸试验的组合进行机械性能评估。使用SEM/EDS、EBSD和X射线衍射(XRD)研究了这些合金的组织。这项研究的结果表明,在时效过程中的,添加B和Nb的微合金钢在较长的暴露时间延缓了析出物的粗化,并保持了其峰值时效强度。此外,将硬度和球形压痕应力-应变关系的估计值与标准化的拉伸试验相比较,表明球形压痕关系提供了高度可靠的拉伸屈服强度估计值,而且成本和工作量都大大降低。这项研究证实了利用球形压痕应力-应变关系来快速探索材料组成和工艺空间的可行性。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117089
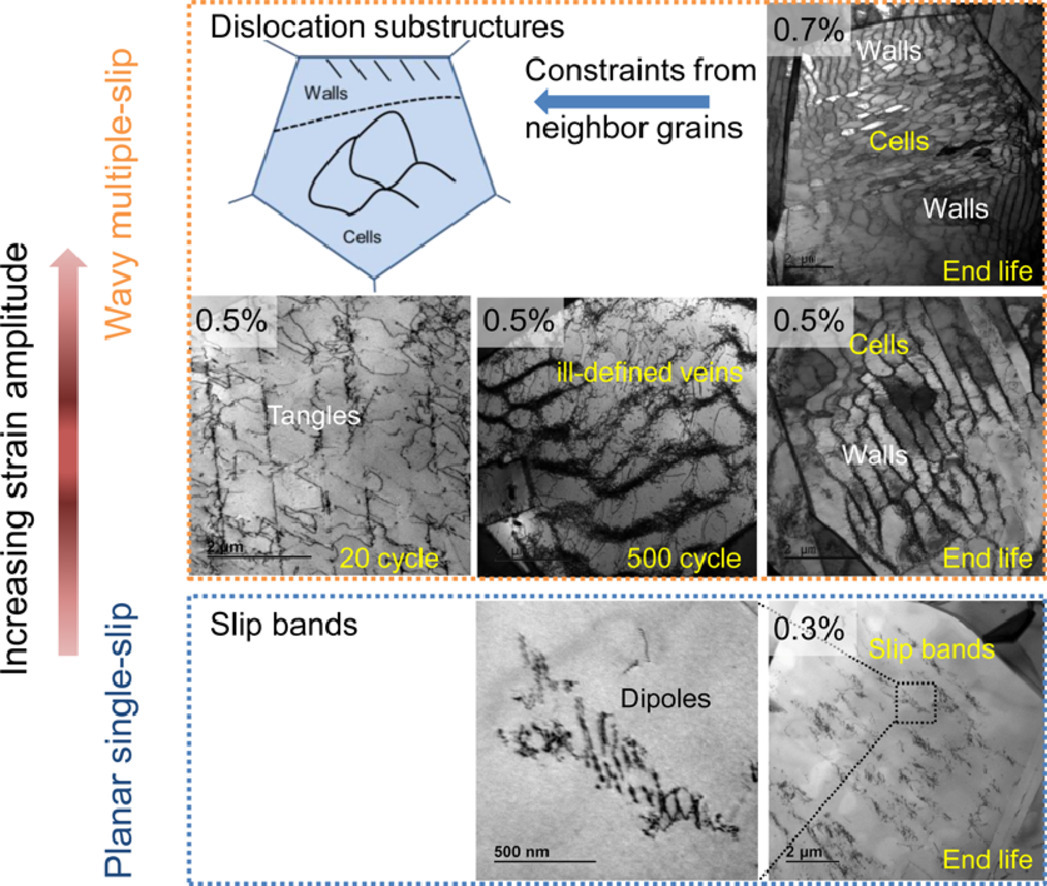
9. Deformation mechanisms of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy under low-cycle-fatigue loading
CoCrFeMnNi 高熵合金在低周疲劳载荷下的变形机制
Kaiju Lu✉, Ankur Chauhan✉, Aditya Srinivasan Tirunilai, Jens Freudenberger, Alexander Kauffmann, Martin Heilmaier, JarirAktaa
Kaiju Lu: kaiju.lu@kit.edu
Ankur Chauhan: ankurskchauhan@gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117089
摘要
等轴面心立方(FCC)CoCrFeMnNi 高熵合金(HEAs)在低周疲劳(LCF)期间的塑性变形是通过位错亚结构的形成来积累的,从而导致裂纹的产生。虽然这些亚结构以前也有报道,但很少有人阐明其形成机制以及应变幅度、循环次数和晶粒取向的影响。在这项研究中,对室温下两种不同晶粒尺寸的CoCrFeMnNi的循环变形行为和组织演变进行了研究。通过透射电子显微镜进行的组织研究表明,虽然低应变振幅(0.3%)下的位错结构主要由平面滑移带组成,但在较高的应变振幅(0.5% 和 0.7%)下,包括脉络、壁、迷宫和细胞在内的波浪形亚结构占主导地位。随着周期数的增加,滑移模式也从最初的平面滑移变为波浪形滑移。在静脉、壁、迷宫和细胞中的位错被发现具有不同的Burgers矢量,这表明除了波浪形滑动外,多重滑移也有助于它们的形成。此外,晶粒中不同的位错亚结构更多的是由来自相邻晶粒的约束决定的,而不是由其取向决定的。此外,单个晶粒中各种位错结构的形成也与相邻晶粒的约束效应有关。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117094
10. Twinning pathways in Fe and Fe–Cr alloys from first-principles theory
基于第一性原理的Fe和Fe -Cr合金中的孪晶途径
Wang Ci, Stephan Schönecker✉, Li Wei, Yang Yaochun, Hu Qing-Miao✉, Levente Vitos
Stephan Schönecker: stesch@kth.se
Hu Qing-Miao: qmhu@imr.ac.cn 中科院沈阳金属所
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117094
摘要
利用密度函数理论,我们确定了Cr摩尔分数 ≤0.5的铁磁(FM)体心立方Fe和Fe-Cr合金中 {11-2}〈-111〉孪晶体系的广义堆垛层错能(GSFE)。我们采用了反射和等腰孪晶途径,并通过将 FM 的结果与磁无序的顺磁性(PM)状态的结果进行对比,揭示了磁性排序对 GSFE 的影响。结果表明,在这种二元结构中,等腰孪晶边界构型在能量上是优先的。长程磁序的损失降低了GSFE的振幅,但无论铬含量如何,都会增加了孪晶界迁移(TBM)的能量。在 FM 和 PM 状态下,孪晶界形成(TBF)能量和 TMB 能量显示出对Cr含量的非线性相关性,并且Cr对这些特性的影响取决于磁状态。我们讨论了在均匀的 Fe-50 wt.% Cr合金中实验观察到的稳定的孪晶界结构和变形孪晶的结果,其温度略高于磁有序温度。
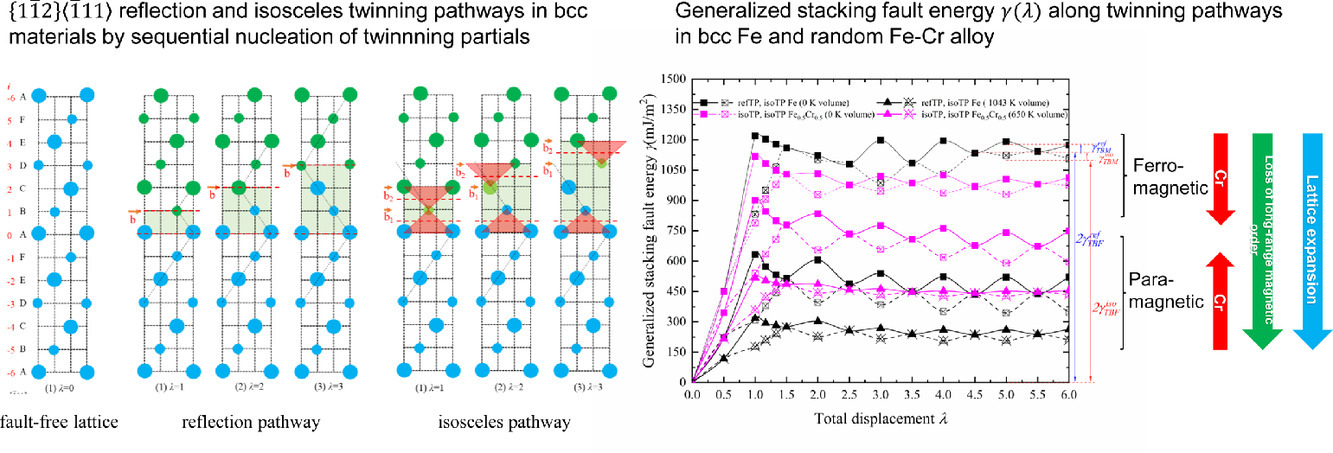
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 116967
11. Inference and uncertainty propagation of GB structure-property models: H diffusivity in [100] tilt GBs in Ni
GB 结构-性能模型的推理和不确定性传播:镍中[100]倾斜GBs的H扩散率
Oliver K.Johnson, Eric R.Homer, David T.Fullwood, David E.Page, Kathryn F.Varela, Sterling G.Baird✉
Sterling G.Baird: ojohnson@byu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.116967
摘要
在这项工作中,我们提出了一种非参数贝叶斯方法,用于开发具有内置不确定性量化(UQ)的晶界(GB)结构-性能模型。我们利用这种方法,根据分子动力学(MD)数据推断出镍中[100]倾斜的GBs在700K时的H扩散率的结构-性能模型。一旦开发出 GB 的结构-性能模型,它就可以用作多晶有效性质、组织演变等中尺度模拟的输入。本文提出的贝叶斯方法的一个重要优势是它有利于将不确定性从基础结构-性能模型传播到中尺度建模的输出预测。利用这种能力,我们对多晶体的有效扩散率进行了中尺度模拟,以研究结构-性能模型的不确定性和GB网络结构之间的相互作用。我们观察到GB网络中晶体学相关性和空间相关性之间的基本相互作用,导致某些类型的组织(那些具有大量J2和J3型三重结的结构)在其有效特性上表现出本质上更大的不确定性。此外,数据和代码在补充材料中提供。
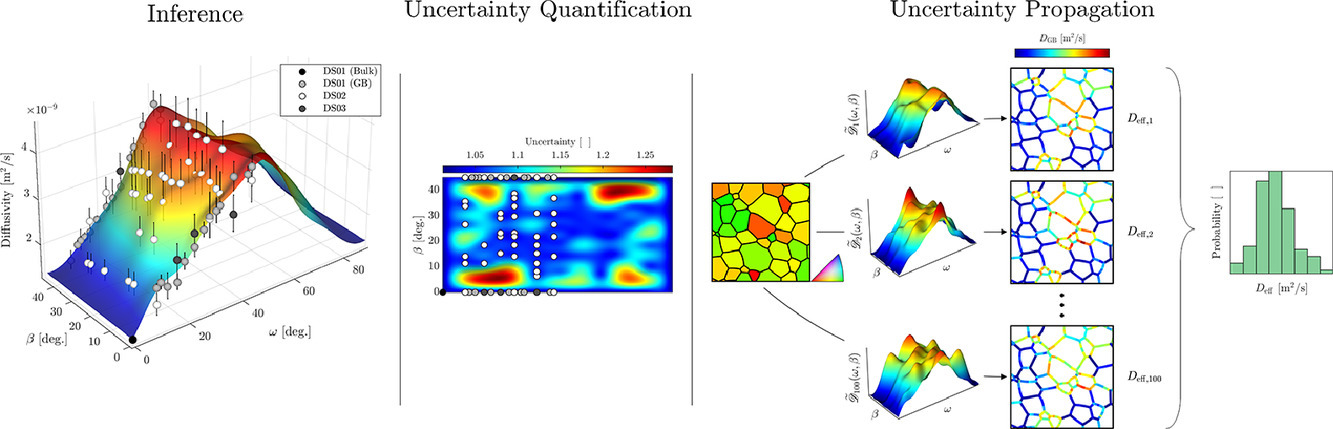
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117049
12. Ultra-fine-grained and gradient FeCrAl alloys with outstanding work hardening capability
具有优异加工硬化能力的超细晶粒和梯度FeCrAl合金
Tianyi Sun, Zhongxia Shang, JaehunCho, Jie Ding, Tongjun Niu, Yifan Zhang, Bo Yang, Dongyue Xie, Jian Wang, Haiyan Wang, Xinghang Zhang✉
Xinghang Zhang: xzhang98@purdue.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117049
摘要
FeCrAl合金是下一代核反应堆有前途的耐事故燃料包壳材料。晶粒细化可使得FeCrAl合金的力学性能得到改善。然而, Al的加入保留了铁素体相,但使得常规的形变热处理难以细化晶粒。在这项研究中,对模型FeCrAl合金C35M进行表面机械磨削处理。显微观察显示表面形成了纳米层和超细晶亚层的梯度组织。原位微柱压缩试验显示,梯度FeCrAl合金具有较高的流动应力,超过1.4GPa,并具有良好的加工硬化能力。采用改进的 Kocks-Mecking 模型来解释与晶粒大小有关的加工硬化行为。这项研究为设计具有高强度和良好加工硬化能力的梯度铁素体钢提供了理论依据,可用于各种工业应用。
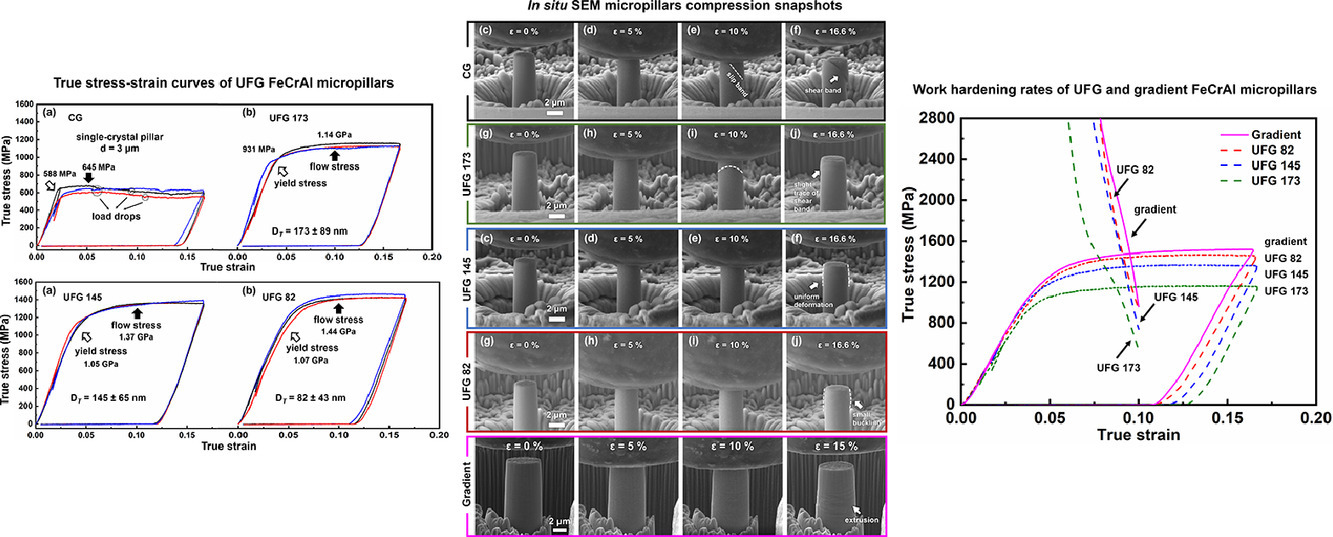
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117093
13. Enhancement of vacancy diffusion by C and N interstitials in the equiatomic FeMnNiCoCr high entropy alloy
等原子FeMnNiCoCr高熵合金中C和N间质对空位扩散的增强作用
Eryang Lu✉, Junlei Zhao, Ilja Makkonen, Kenichiro Mizohata, Zhiming Li, Mengyuan Hua, Flyura Djurabekova, Filip Tuomisto
Eryang Lu: eryang.lu@helsinki.fi
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117093
摘要
我们提出了在等原子单相高熵合金(FeMnNiCoCr)中由C和N间隙引起的原子扩散特性均匀化的证据。这一现象表现由粒子辐射引起的单空位缺陷的直接试验确定的迁移势垒分布的意外间质诱导的减少和变窄。我们通过正电子湮灭光谱观察到的现象被最先进的理论计算所解释,该计算预测C/N间质在富含Mn和Cr的区域优先定位,导致随机合金中单空位尺寸分布变窄和减少。这一现象可能对辐射下的机械行为产生重大影响,因为元素运动的局部变化对高熵合金中的溶质强化有深刻的影响。
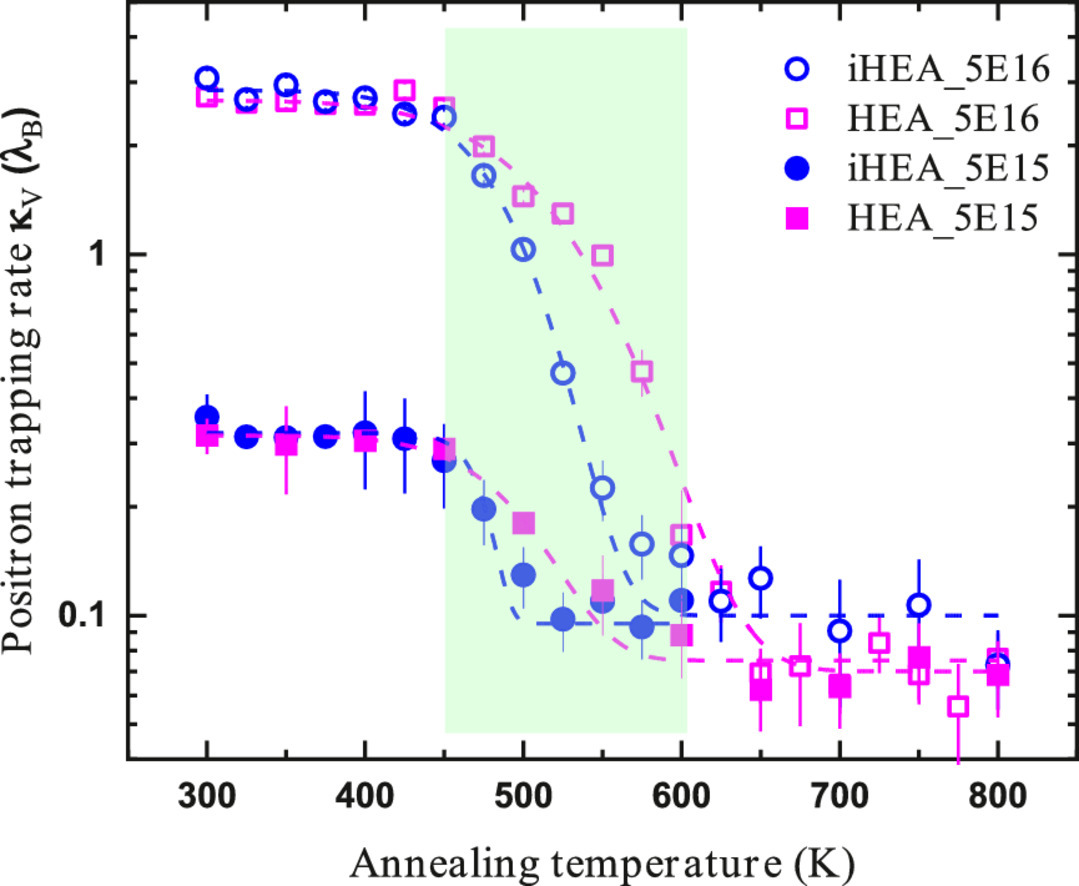
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117090
14. Toughening of interface networks through the introduction of weak links
通过引入薄弱环节强化界面网络
Edwin Chiu, Michael J.Demkowicz, Ankit Srivastava✉
Ankit Srivastava: ankit.sri@tamu.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117090
摘要
多晶材料对晶间断裂的抵抗力取决于相邻晶粒之间界面的韧性。通过对模型二维微观结构的有限元模拟,我们证明了仅包含高韧性界面的多晶体的稳态抗裂性是次优的:通过在界面网络的随机位置引入少数弱界面,可以提高其抗裂性。此外,这些界面越弱,其增韧效果就越大。这些弱界面通过裂纹的偏转和分支、二次裂纹的成核以及完整界面内的非弹性耗散来增强材料。我们的研究结果表明,以抗断裂为导向的材料开发不应旨在消除所有的弱界面,而应明智地纳入低比例的弱界面。
ACTA
Vol. 215,15 Aug. 2021, 117099
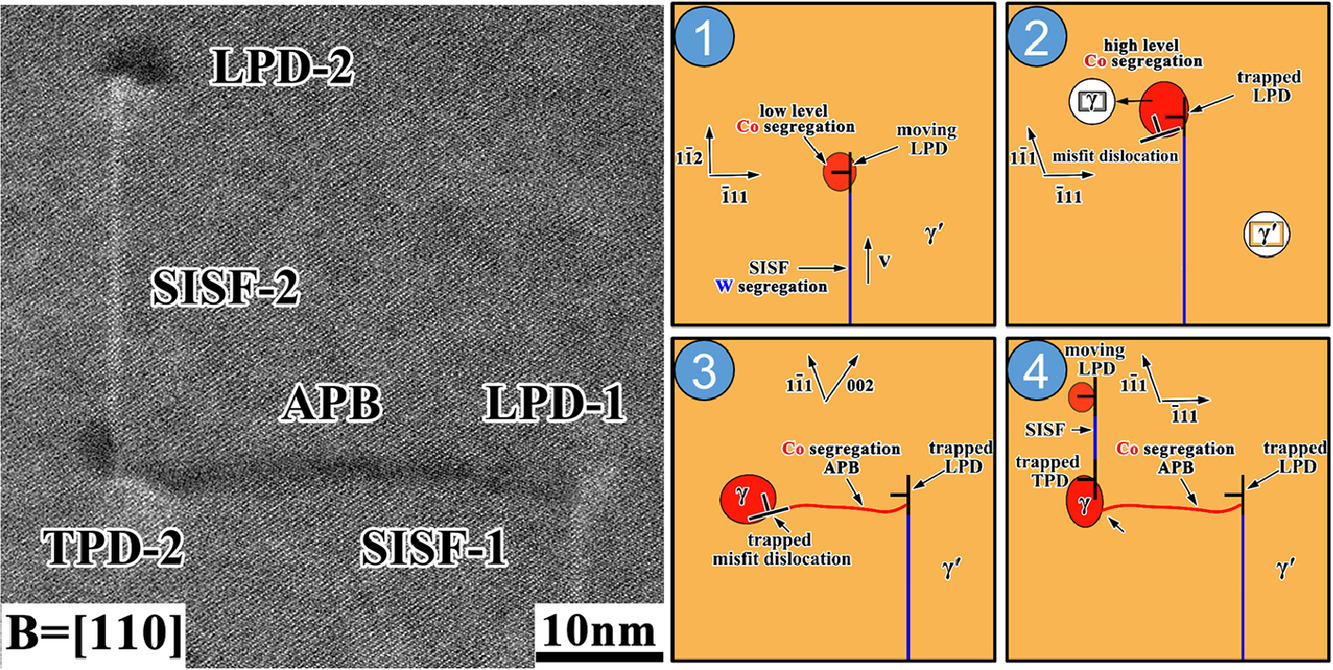
15. Segregation-assisted phase transformation and anti-phase boundary formation during creep of a γ′-strengthened Co-based superalloy at high temperatures
γ′ 强化 Co 基超合金在高温下蠕变过程中的偏析辅助相变和反相边界形成
Song Lu, Stoichko Antonov, Fei Xue, Longfei Li✉, Qiang Feng✉
Longfei Li: lilf@skl.ustb.edu.cn, 北京科技大学
Qiang Feng: qfeng@skl.ustb.edu.cn, 北京科技大学
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2021.117099
摘要
在这项研究中,分析了γ′ 强化 Co 基超合金在982 °C/248 Mpa-1% 和 1000 °C/137 Mpa-1% 下蠕变的蠕变缺陷和偏析辅助的局部相变过程。在无镍的Co基合金中发现了一种非共面变形构型,即重复的超晶格本征堆垛断层和反相边界(...SISF APB...),并发现其受到局部元素偏析的帮助,在较高的应力条件下更有利。此外,观察到在(-111)平面上具有a/6<1-12> 型位移的SISF和在 (-111) 平面上具有a/2<110> 型位移形核的 APB 有相连。据估计,在 LPD 附近的γ前偏析辅助的局部 γ′→γ 相变过程的演变顺序为: γ′→ 亚稳态 γ→γ+γ′1 。亚稳态的γ的形成产生了一个新的具有错位的应变/应力γ/γ′ 界面,该界面导致了位错的成核和蠕变应力,从而在γ′相中产生APBs。 γ 和 γ′1 的分离似乎是通过 γ 和 γ′ 在近(-111)平面和向SISF一侧的定向重分布而引起的。结果表明沿着平面断层的W偏析辅助的γ′→χ 相变是通过形成单层 a/6<112> 型位移的 SISF 来降低变形阻力,而 LPD 处的 Co 偏析辅助的 γ′→γ 相变被认为是通过在局部 γ/γ′ 界面捕获移动位错来提高变形阻力。