金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.207, 15 Jan. 2022(上)
2021-12-10 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文13篇,涵盖了钛合金、中熵合金、高熵合金、高温合金等,国内科研单位包括上海交通大学、华南理工大学等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 207 目录
1. Grain boundary α-phase precipitation and coarsening: Comparing laser powder bed fusion with as-cast Ti-6Al-4V
晶界α相的析出和粗化:激光粉床熔化与铸态Ti-6Al-4V合金的比较
2. A new α + β Ti-alloy with refined microstructures and enhanced mechanical properties in the as-cast state
一种新型在铸态下具有精细的微观结构和优异的机械性能的α+β钛合金
3. Influence of precipitation on tension and compression twinning in Mg-6.5Zn alloy
析出物对Mg-6.5Zn合金拉压孪晶的影响
4. Deformation-induced grain boundary segregation mediated high-strain rate superplasticity in medium entropy alloy
中熵合金中变形诱导晶界偏析引发的高应变率超塑性
5. Advanced mechanical properties obtained via accurately tailoring stacking fault energy in Co-rich and Ni-depleted CoxCr33Ni67-x medium-entropy alloys
通过精确调整富钴贫镍CoxCr33Ni67-x中熵合金中的堆垛层错能获得优异的机械性能
6. Pre-straining alters hydrogen-assisted cracking site and local hydrogen diffusivity in a nitrogen-doped duplex steels
通过预应变改变掺氮双相钢中氢致开裂位置和局部氢扩散速率
7. Artificial neural network molecular mechanics of iron grain boundaries
铁晶界的人工神经网络分子动力学
8. Multiple deformation mechanisms induced by pre-twinning in CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy
CoCrFeNi高熵合金预孪晶引起的多重变形机制
9. The effect of deviations from precise [001] tensile direction on creep of Ni-base single crystal superalloys
与精确[001]拉伸方向的偏差对镍基单晶高温合金蠕变的影响
10. Atomic scale observation of FCC twin, FCC→9R and 9R→12R’ transformations in cold-rolled Hafnium
冷轧纯铪中FCC孪晶、FCC→9R和9R→12R'转变的原子尺度观察
11. Direct observation of grain boundary formation in bcc iron through TEM in situ compression test
通过TEM原位压缩试验直接观察bcc铁中晶界的形成
12. Effect of boron segregation on bainite nucleation during isothermal transformation
硼偏析对贝氏体在等温转变过程中形核的影响
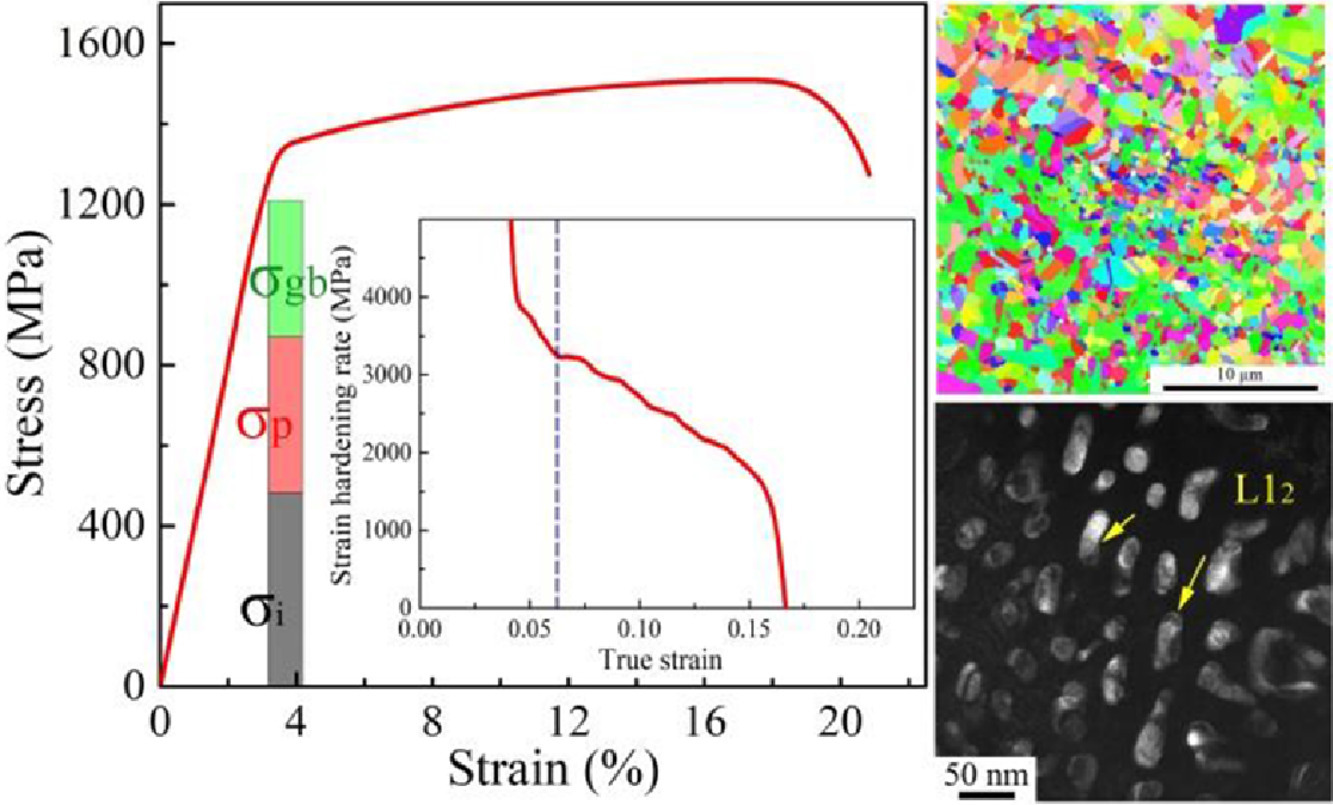
13. Superior strength-ductility synergy in a novel tailored nanoparticles- strengthened medium-entropy alloy
新型定制纳米粒子强化中熵合金优异的强度-塑性协同效果
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114261
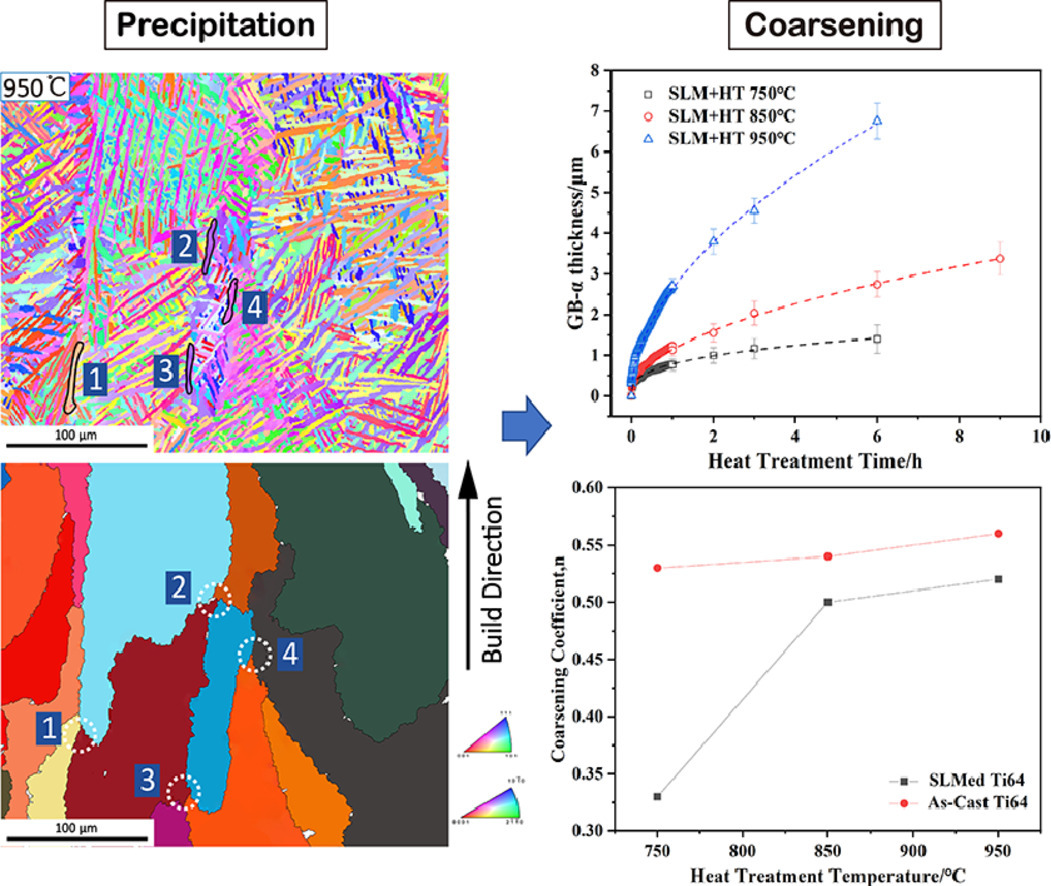
1. Grain boundary α-phase precipitation and coarsening: Comparing laser powder bed fusion with as-cast Ti-6Al-4V
晶界α相的析出和粗化:激光粉床熔化与铸态Ti-6Al-4V合金的比较
Jianwen Liu, Kai Zhang✉, Yi Yang, Hao Wang, Yuman Zhu, Aijun Huang
Kai Zhang: kai.zhang@monash.edu (上海科技大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114261
摘要
研究了激光粉床熔化(LPBF)成形的Ti-6Al-4V(Ti-64)中的晶界α相(GB-α)析出和粗化行为,并与铸态的Ti-64进行了比较。在退火过程中,LPBF成形的Ti-64中GB-α倾向于在β相晶界的三重边界(TJs)处析出。 GB-α的动力学分析表明,LPBF成形的在不同退火温度(750°C的体扩散和850°C与950°C的界面反应)下的粗化机制不同,而铸态的粗化机制是一致的(在三个温度下的皆是界面反应)。不一致的粗化机制归因于α片晶不同的形核机制所引起的GB-α曲率差异。这些发现有助于使GB-α形貌演变合理化,并有利于进一步控制LPBF成形的钛合金机械性能。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114260
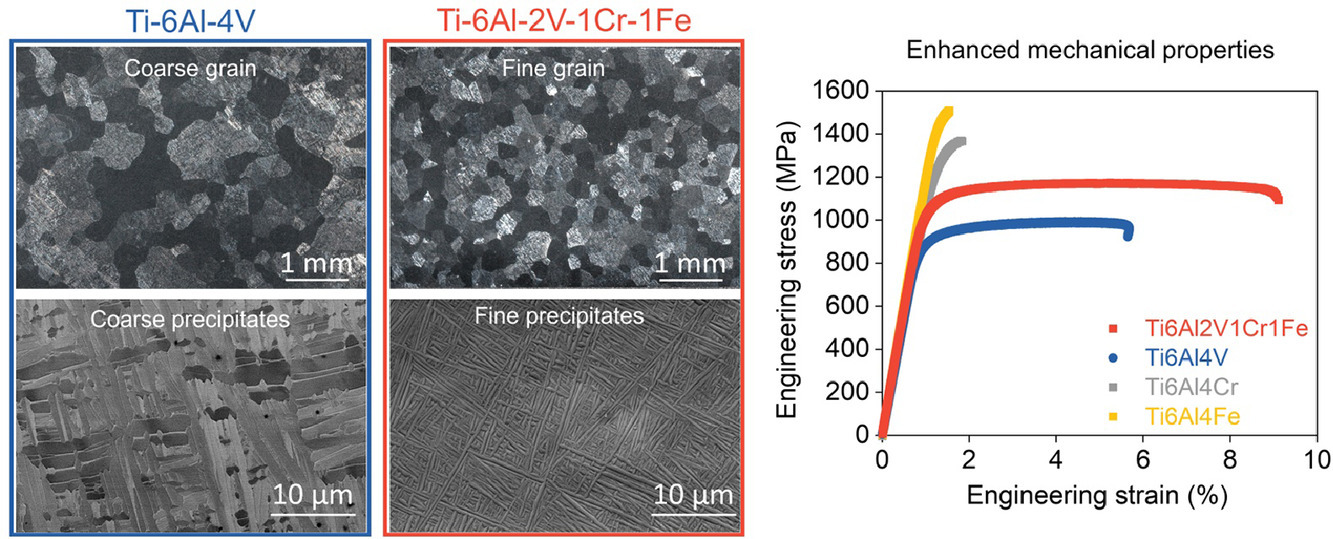
2. A new α + β Ti-alloy with refined microstructures and enhanced mechanical properties in the as-cast state
一种新型在铸态下具有精细的微观结构和优异的机械性能的α+β钛合金
Tianlong Zhang, Jiaming Zhu, Tao Yang, Junhua Luan, Haojie Kong, Weihong
Liu, Boxuan Cao, Shiwei Wu, Dong Wang, Yunzhi Wang, Chain-Tsuan Liu✉
Chain-Tsuan Liu: chainliu@cityu.edu.hk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114260
摘要
此项工作开发了一种新型(α + β)钛合金Ti-6Al-2V-1Cr-1Fe (wt%),该合金在铸态下具有细的晶粒尺寸与沉淀物及高的强度和优良的延展性。与铸态Ti-6Al-4V合金相比,新合金的晶粒尺寸和α板条厚度大幅细化了50~75%,屈服强度和延展性分别提高了19.7%和51.8%。晶粒尺寸细化是在 CALPHAD计算的帮助下,通过合金化调整合金的过冷能力来实现的。此外,Cr和Fe的合金化显着降低了α板条厚度。这种具有优异性能的低成本钛合金预计非常适用于铸态或打印态的各种结构应用件。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114253
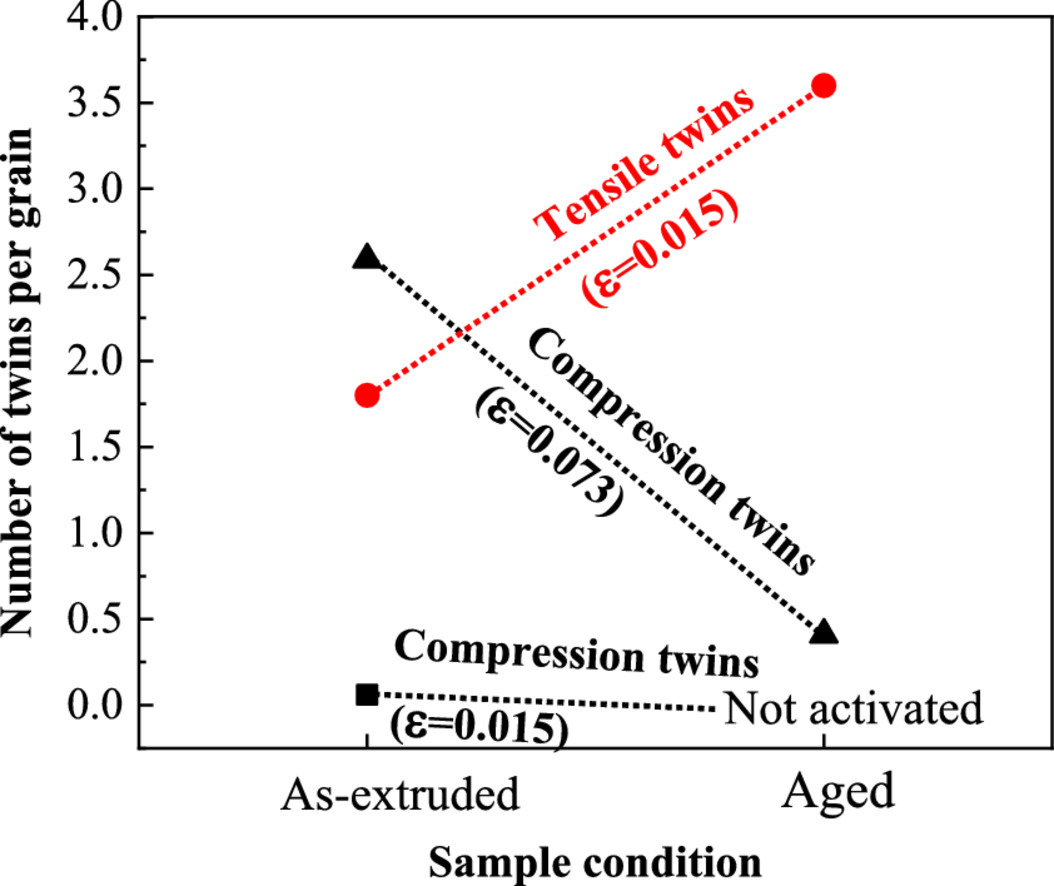
3. Influence of precipitation on tension and compression twinning in Mg-6.5Zn alloy
析出物对Mg-6.5Zn合金拉压孪晶的影响
Jun Wang✉, Mahmoud Reza Ghandehari Ferdowsi, Peter A. Lynch, Sitarama R. Kada, Matthew R. Barnett
J.P. Oliveira: jun.wang2@deakin.edu.au
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114253
摘要
根据不同的应力状态,镁合金可显示拉伸和/或压缩的孪晶。本文利用Mg-6.5Zn合金的双峰纹理,研究时效硬化如何影响两种不同类型的孪晶。我们发现,拉伸孪晶是由析出物刺激引发的(即在等效塑性应变下可以观察到更高的孪晶体积分数),而压缩孪晶是被析出物抑制的(即在等效塑性应变下观察到较低的孪晶体积分数)。压缩孪晶中较低的孪晶表面能和较大的孪晶位错Burgers矢量造成了这种差异。较大的Burgers矢量使压缩孪晶位错更能抵抗弯曲,表面能效应更为小。在其它条件一致的情况下,具有较低表面能的孪晶可以以较低的孪晶位错总含量传播。因此,需要更高的外加应力才能获得绕过沉淀物所需的Peach-Koehler力。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114239
4. Deformation-induced grain boundary segregation mediated high-strain rate superplasticity in medium entropy alloy
中熵合金中变形诱导晶界偏析引发的高应变率超塑性
Peyman Asghari-Red, Nhung Thi-Cam Nguyen, Alireza Zargaran, Praveen Sathiyamoorthi✉, Hyoung Seop Kim✉
Praveen Sathiyamoorthi: spravin88@postech.ac.kr
Hyoung Seop Kim: hskim@postech.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114239
摘要
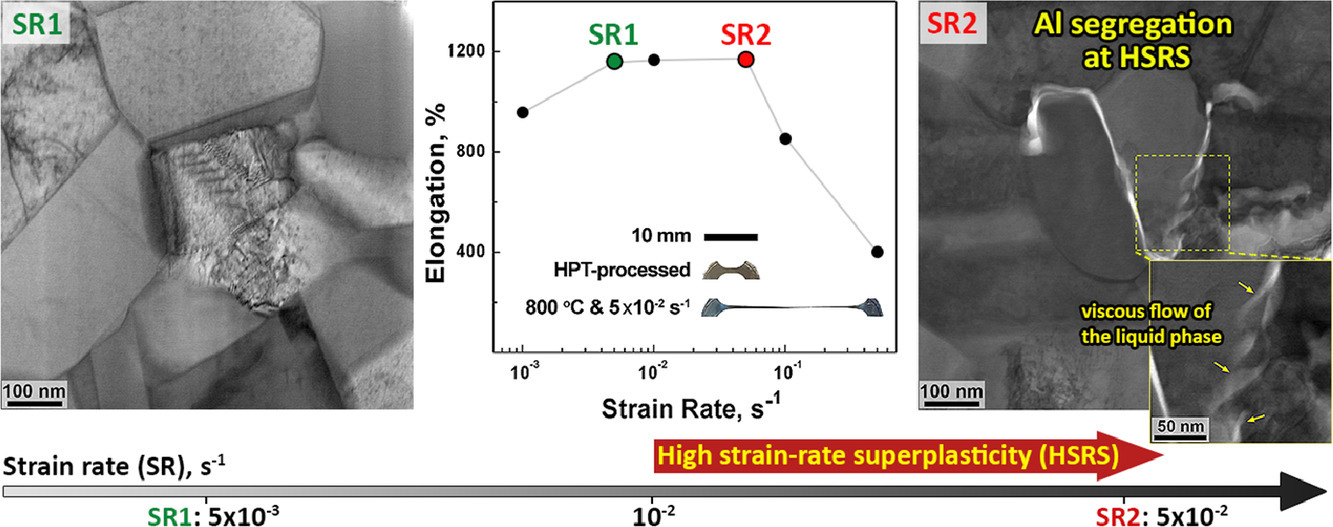
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114269
5. Advanced mechanical properties obtained via accurately tailoring stacking fault energy in Co-rich and Ni-depleted CoxCr33Ni67-x medium-entropy alloys
通过精确调整富钴贫镍CoxCr33Ni67-x中熵合金中的堆垛层错能获得优异的机械性能
Dong Huang, Yanxin Zhuang✉, Chunhui Wang
Yanxin Zhuang: yxzhuang@epm.neu.edu.cn(东北大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114269
摘要
本文设计了一种新型富钴贫镍的CoxCr33Ni67-x中熵合金。控制其中的C含量,使所研究的合金具有相同的短程有序(SRO),使Co、Ni含量的变化直接有效地体现在层错能的降低上。随着Co含量的增加N含量的减少,Co38Cr33Ni2合金的层错能降低到~12 mJ/m2,变形方式由孪生诱导塑性(TWIP)转变为相变诱导塑性(TRIP)。同时获得了839 MPa的拉伸强度和83%的均匀伸长率。
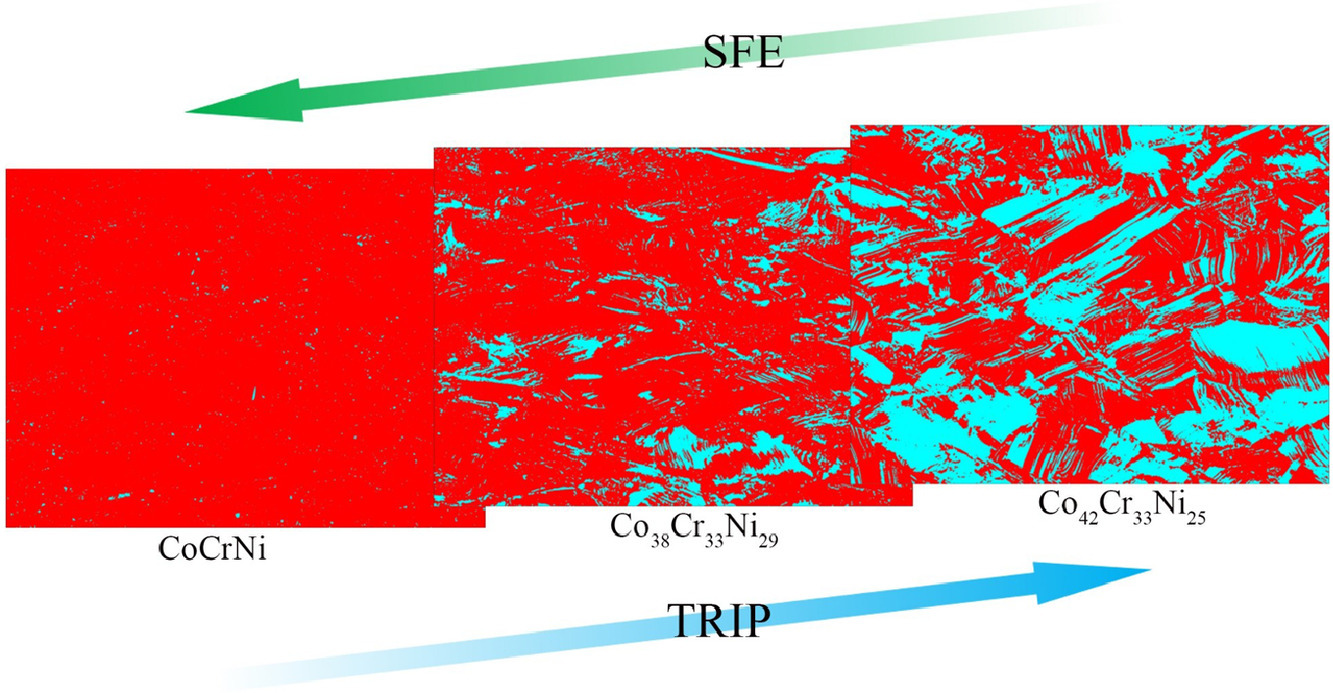
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114272
6. Pre-straining alters hydrogen-assisted cracking site and local hydrogen diffusivity in a nitrogen-doped duplex steels
通过预应变改变掺氮双相钢中氢致开裂位置和局部氢扩散速率
Milene Yumi Maeda✉, Motomichi Koyama✉, Hayato Nishimura, Osvaldo
Mitsuyuki Cintho, Eiji Akiyama
Milene Yumi Maeda: milenemaeda@gmail.com
Motomichi Koyama: koyama@imr.tohoku.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114272
摘要
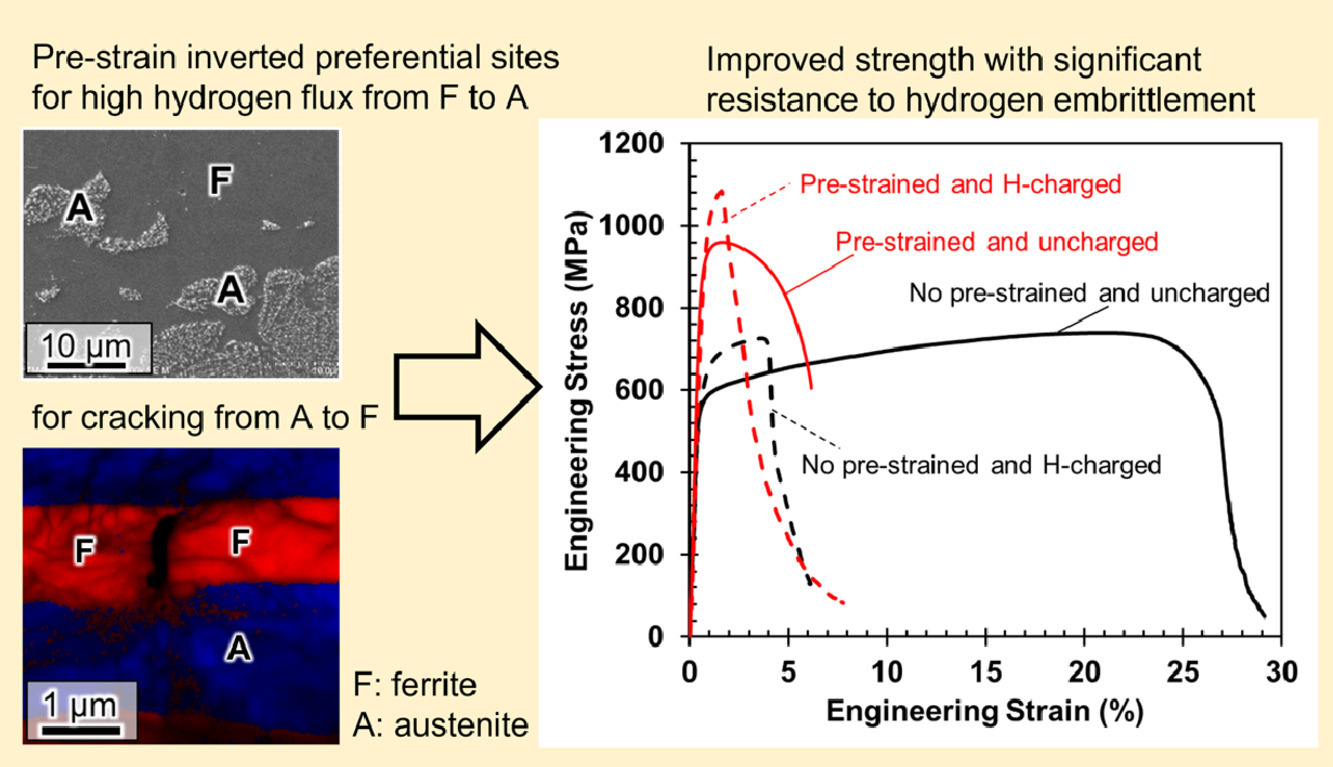
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114268
7. Artificial neural network molecular mechanics of iron grain boundaries
铁晶界的人工神经网络分子动力学
Yoshiori Shiihara✉, Ryosuke Kanazawa, Daisuke Matsunaka, Ivan Lobzenko,
Tomohito Tsuru, Masanori Kohyama, Hideki Mori
Yoshinori Shiihara: shiihara@toyota-ti.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114268
摘要

SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114266
8. Multiple deformation mechanisms induced by pre-twinning in CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy
CoCrFeNi高熵合金预孪晶引起的多重变形机制
Zhen Zhang, Zhihao Jiang, Yuehuang Xie, Sammy Lap Ip Chan, Jiamiao Liang✉,Jun Wang✉
Jiamiao Liang: jmliang@sjtu.edu.cn (上海交通大学)
Jun Wang: Junwang@sjtu.edu.cn(上海交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114266
摘要
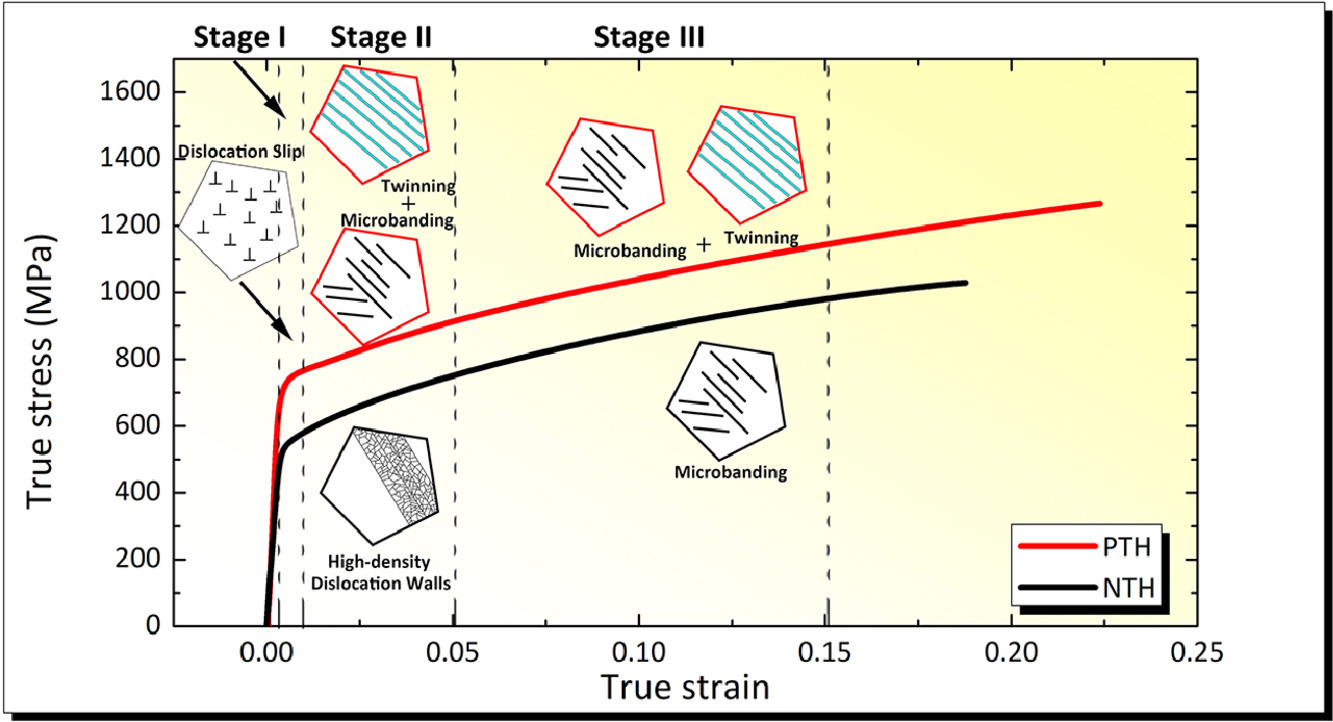
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114274
9. The effect of deviations from precise [001] tensile direction on creep of Ni-base single crystal superalloys
与精确[001]拉伸方向的偏差对镍基单晶高温合金蠕变的影响
L. Heep✉, D. Hurger, C. Bonnekoh, P. Wollgramm, A. Dlouhy, G. Eggeler
L. Heep: larissa.heep@rub.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114274
摘要
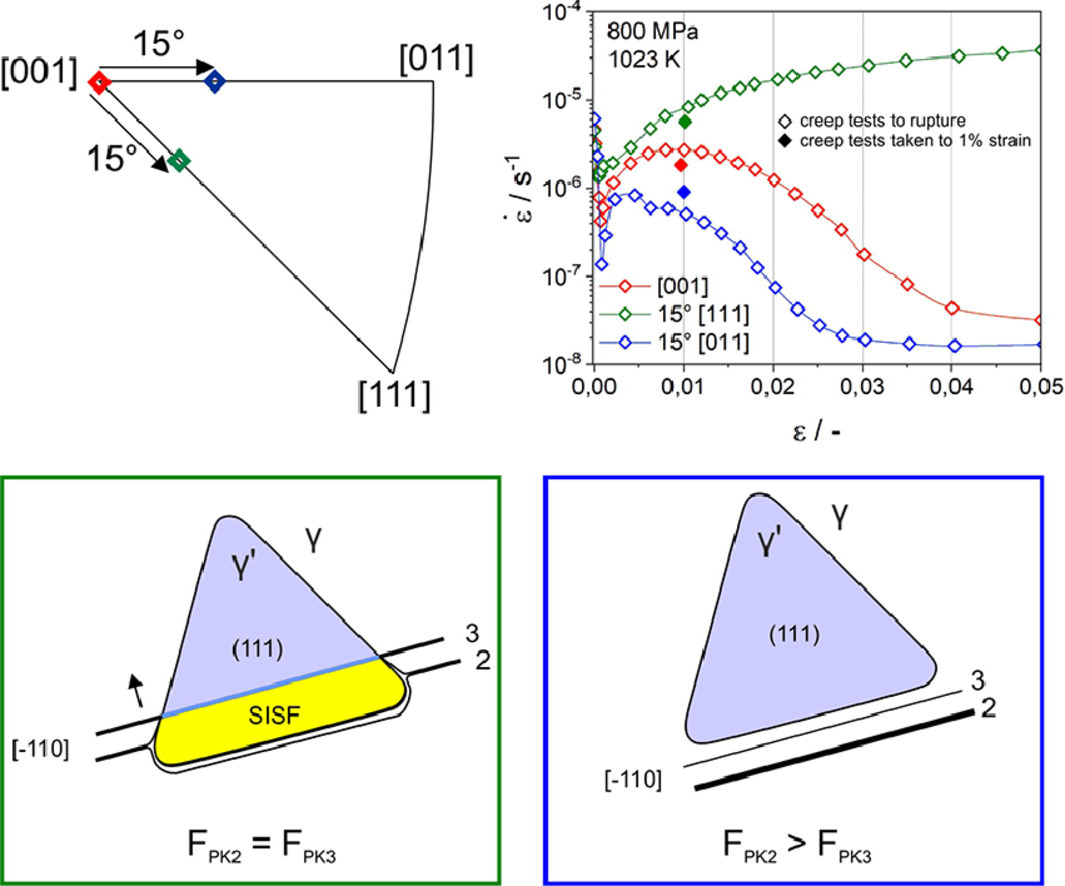
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114284
10. Atomic scale observation of FCC twin, FCC→9R and 9R→12R’ transformations in cold-rolled Hafnium
冷轧纯铪中FCC孪晶、FCC→9R和9R→12R'转变的原子尺度观察
Yingdong Zhang, Geping Li✉, Fusen Yuan, Fuzhou Han, Muhammad Ali,WenbinGuo, Jie Ren
Geping Li: gpli@imr.ac.cn (中国科学院金属研究所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114284
摘要
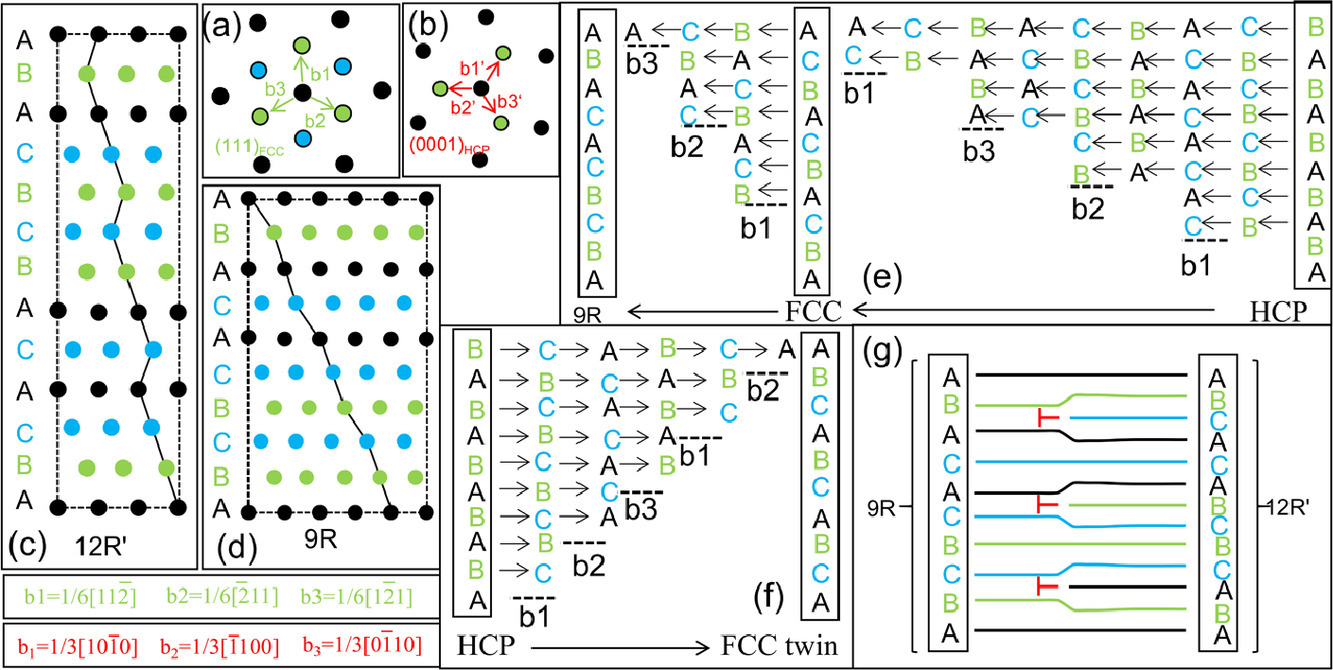
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114275
11. Direct observation of grain boundary formation in bcc iron through TEM in situ compression test
通过TEM原位压缩试验直接观察bcc铁中晶界的形成
Hongxing Li✉, Seiichiro Li, Nobuhiro Tsuji, Takahito Ohmura
Hongxing Li: li.hongxing.4x@kyoto-u.ac.jp
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114275
摘要
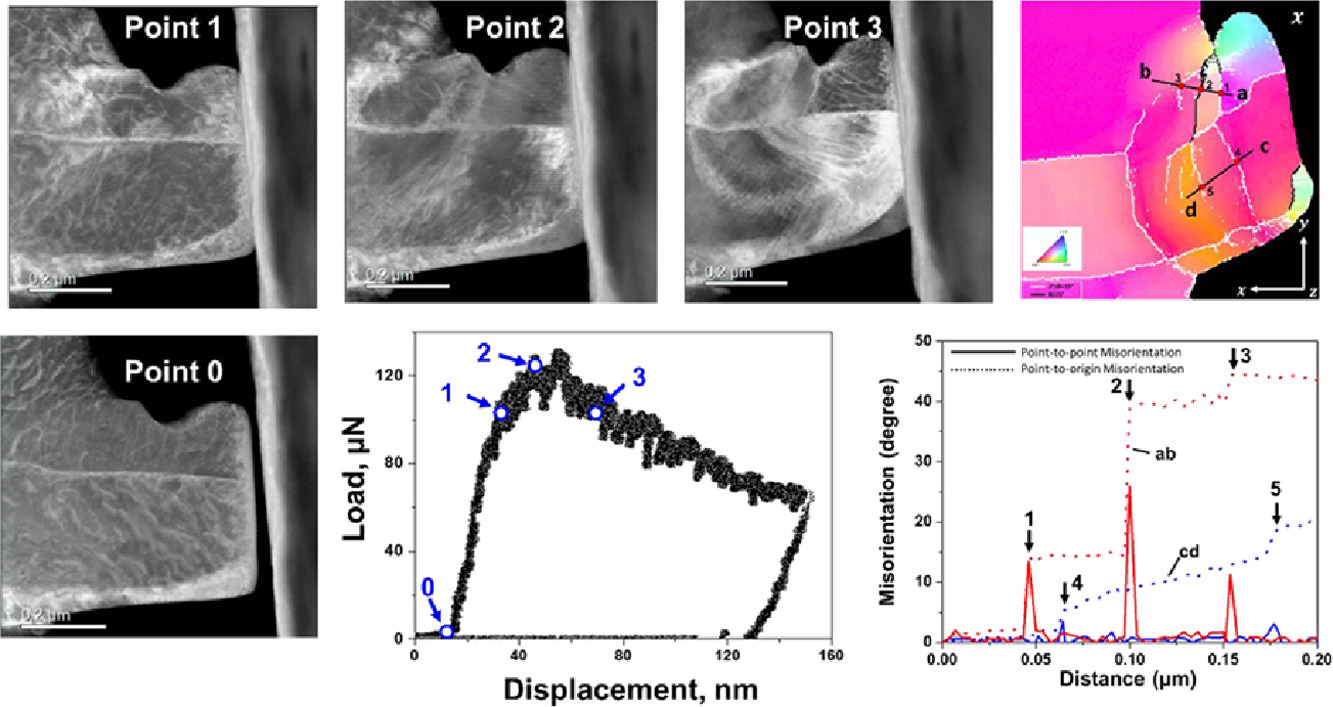
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114286
12. Effect of boron segregation on bainite nucleation during isothermal transformation
硼偏析对贝氏体在等温转变过程中形核的影响
P. Douhuet, G. Da Rosa, P. Maugis✉, J. Drillet, K. Hoummada✉
P. Maugis: philippe.maugis@univ-amu.fr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114286
摘要
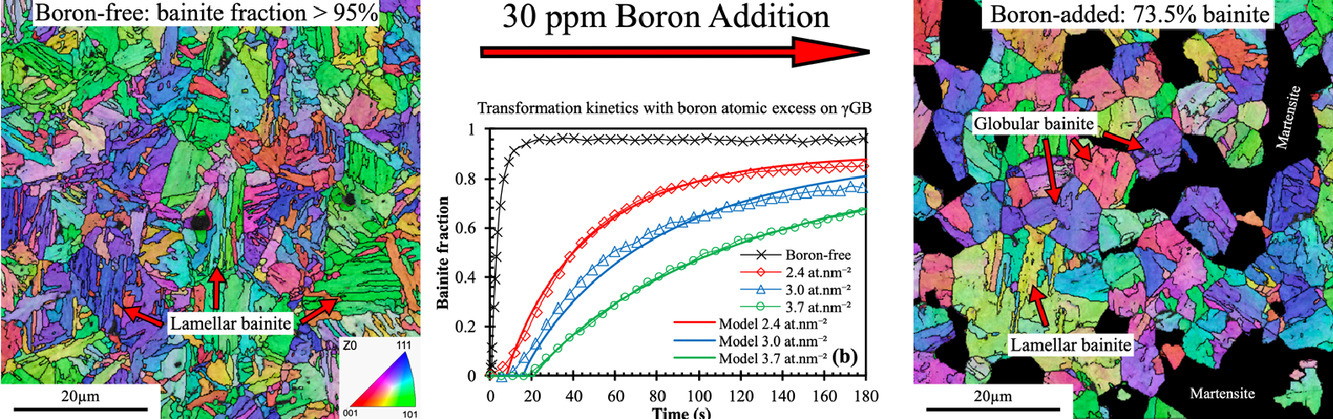
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114278
13. Superior strength-ductility synergy in a novel tailored nanoparticles- strengthened medium-entropy alloy
新型定制纳米粒子强化中熵合金优异的强度-塑性协同效果
Hanlin Peng, Lan Baker, Ling Hu✉, Liejun Li✉
Ling Hu: huling381@163.com (华南理工大学)
Liejun Li: liliejun@scut.edu.cn (华南理工大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114278
摘要