金属顶刊双语导读丨Scripta Mater. Vol.207, 15 Jan. 2022(下)
2021-12-11 来源:GS_Metals

本期包含金属材料领域论文13篇,涵盖了增材制造、镁合金、高温合金、马氏体等,国内科研单位包括西安交通大学、天津大学、中国科学院金属研究所等(通讯作者单位)。
Vol. 207 目录
1. Alloy design strategy for microstructural-tailored scandium-modified aluminium alloys for additive manufacturing
用于增材制造的微结构定制钪改性铝合金的合金设计策略
2. Influence of grain size and grain boundary misorientation on the fatigue crack initiation mechanisms of textured AZ31 Mg alloy
晶粒尺寸和晶界取向差对织构AZ31镁合金疲劳裂纹萌生机制的影响
3. Influence of the microstructural homogeneity on the high-temperature oxidation behavior of a single crystalline Ni-base superalloy
显微组织均匀性对镍基单晶高温合金高温氧化行为的影响
4. Enhancing reversible entropy change of all-d-metal Ni37.5Co12.5Mn35Ti15 alloy by multiple external fields
多外场增强全d金属Ni37.5Co12.5Mn35Ti15合金可逆熵变
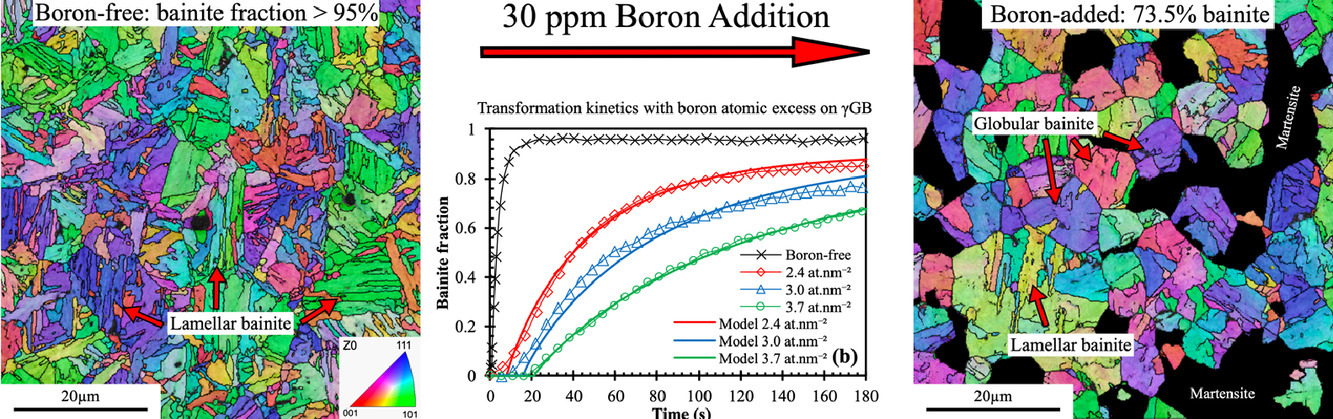
5. Effect of microstructure heterogeneity on the mechanical properties of friction stir welded reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steel
显微组织异质性对搅拌摩擦焊还原活化铁素体/马氏体钢力学性能的影响
6. Hydrogen-assisted failure in Inconel 718 fabricated by laser powder bed fusion: The role of solidification substructure in the embrittlement
激光粉床熔化制造的Inconel 718氢辅助失效:凝固亚结构在脆化中的作用
7. Synthesis of high-entropy alloy thin films via grain boundary diffusion–assisted solid-state alloying
通过晶界扩散辅助固态合金化合成高熵合金薄膜
8. Deformation twinning-induced dynamic recrystallization during laser powder bed fusion
激光粉床熔融过程中变形孪晶诱导的动态再结晶
9. Mechanical response of the constrained nanostructured layer in heterogeneous laminate
异质层压板中受限纳米结构层的机械响应
10. Prediction of growth velocity of undercooled multicomponent metallic alloys using a machine learning approach
使用机器学习方法预测过冷多组分金属合金的生长速度
11. Martensitic transformation within nanotwins enhances fatigue damage resistance of a nanotwinned austenitic stainless steel
纳米孪晶内的马氏体相变增强了纳米孪晶奥氏体不锈钢的抗疲劳损伤能力
12. In situ transmission electron microscopy investigation of nucleation of GP zones under natural aging in Al-Zn-Mg alloy
Al-Zn-Mg合金自然时效下GP区形核的原位透射电镜研究
13. Grain boundary segregation and its implications regarding the formation of the grain boundary α phase in the metastable β-Titanium Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–3Cr alloy
亚稳态β-钛Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr合金中晶界偏析及其对晶界α相形成的影响
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114277
1. Alloy design strategy for microstructural-tailored scandium-modified aluminium alloys for additive manufacturing
用于增材制造的微结构定制钪改性铝合金的合金设计策略
D. Schimback✉, P. Mair, M. Bartl, F. Palm, G. Leichtfried, S. Mayer, P.J. Uggowitzer, S. Pogatscher
D. Schimback: david-erich.schimbaeck@airbus.com
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114277
摘要
为了充分发挥增材制造技术的潜力,有必要通过智能合金设计策略使材料适应工艺。为此,为了推导和研究各种材料概念,研究了Sc改性铝合金在激光粉末床熔合生产过程中的微观结构演变。添加Mg作为主要元素(Al-4.4Mg-0.8Sc-0.3Zr-0.5Mn)会产生双峰微观结构。相比之下,如果添加Cr作为主要元素(Al-2.6Cr-0.7Sc-0.3Zr),则外延晶粒生长会跨越多个焊道,从而产生明显的织构;添加Ti作为主要元素(Al-1Ti-1Sc-0.4Zr)会产生均匀的超细晶粒组织。这些微观结构之间的差异源于晶粒生长限制因素和溶质与初级沉淀结构的相互作用。因此,对关键冶金因素的精确控制产生了可以根据某些要求量身定制的新型材料。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114304
2. Influence of grain size and grain boundary misorientation on the fatigue crack initiation mechanisms of textured AZ31 Mg alloy
晶粒尺寸和晶界取向差对织构AZ31镁合金疲劳裂纹萌生机制的影响
Abbas Jamali, Anxin Ma, Javier LLorca✉
Javier LLorca: javier.llorca@upm.es
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114304
摘要
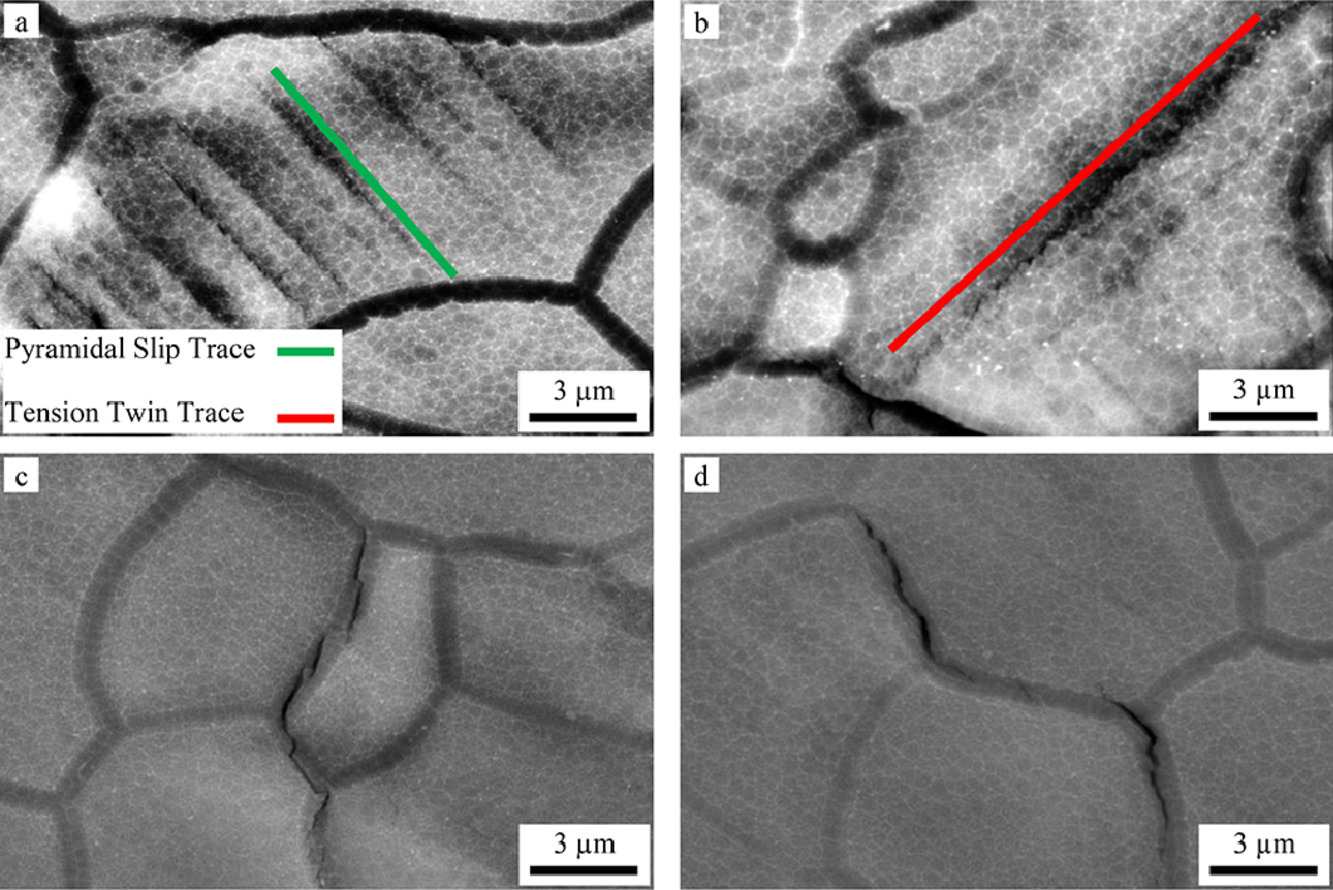
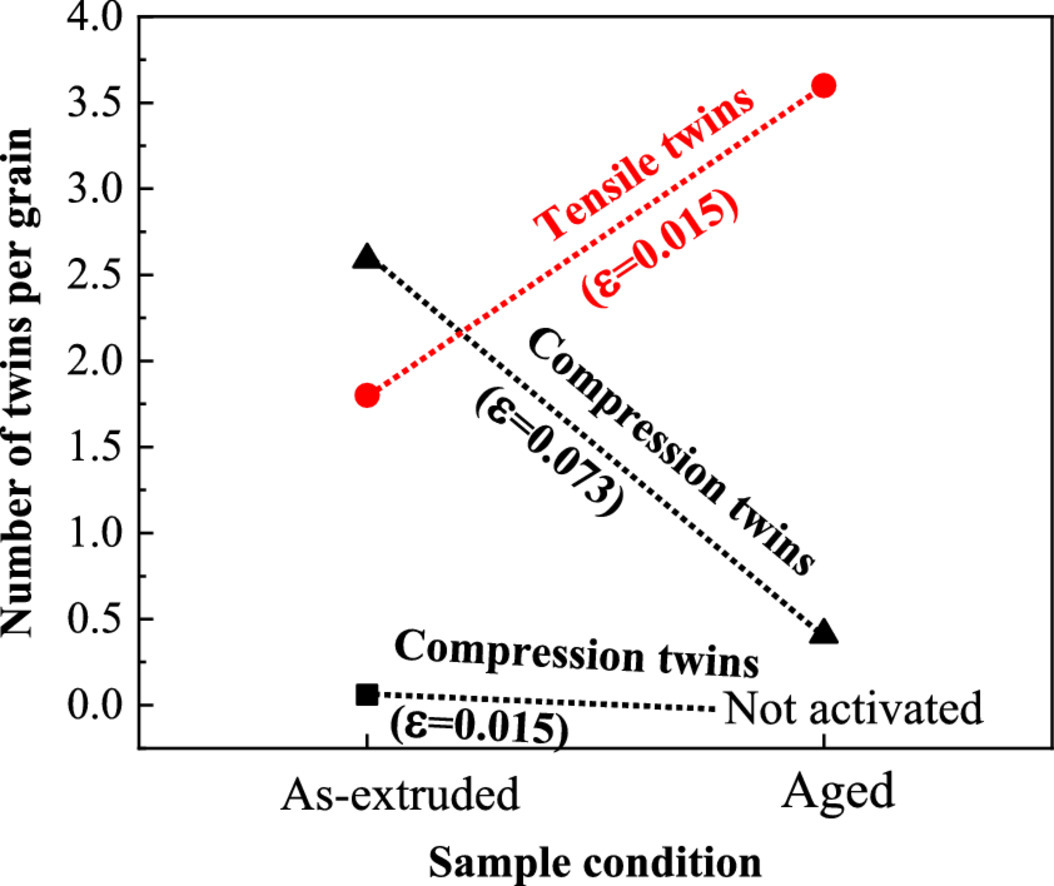
对织构AZ31B-O镁合金沿轧制方向进行完全反向、应变控制的循环变形,并在50次循环后(约占疲劳寿命的33%)分析变形和裂纹萌生机制。在2100个晶粒中的538个中发现了对应于金字塔滑移或拉伸孪晶的不同变形带。滑移轨迹分析表明,72.3%是锥体滑移带,18.4%是孪晶边界。仅在9.1%的具有变形带的晶粒中发现了金字塔滑移和孪晶。50次循环后裂纹普遍存在。在约15%的小晶粒(< 20 µm)中发现了晶界裂纹,它们主要与大角度晶界(>40º)相关。还发现裂纹是由平行于大晶粒(>45 µm)的金字塔滑移带或孪晶界的穿晶裂纹引起的。大多数(>60%)大晶粒在50次循环后出现穿晶裂纹。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114224
3. Influence of the microstructural homogeneity on the high-temperature oxidation behavior of a single crystalline Ni-base superalloy
显微组织均匀性对镍基单晶高温合金高温氧化行为的影响
J. Pistor✉, S.P. Hagen✉, S. Virtanen✉, C. Korner✉
J. Pistor: julian.pistor@fau.de
S.P. Hagen: sebastian.p.hagen@fau.de
S. Virtanen: virtanen@ww.uni-erlangen.de
C. Korner: carolin.koerner@fau.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114224
摘要
通过选择电子束熔化(SEBM)进行的增材制造最近被证明是一种用于生产CMSX-4单晶(SX)镍基高温合金的有趣技术。本研究的目的是比较SX SEBM样品与由Bridgman熔模铸造获得的传统试样的高温抗氧化性。因此,TGA重量分析在850和1050 °C下在空气中进行100小时。由于在氧化之前进行固溶退火,在SEBM试样中,凝固引起的元素偏析可以完全均匀化,而对于传统试样仍然很明显。由于残留元素偏析,在氧化过程中出现了不均匀的氧化皮,在枝晶区域表现出高于平均水平的氧化皮厚度。因此,在存在偏析的情况下,TGA显示出更高的质量增加。总之,对于均质SEBM样品观察到更好的高温抗氧化性。
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114303
4. Enhancing reversible entropy change of all-d-metal Ni37.5Co12.5Mn35Ti15 alloy by multiple external fields
多外场增强全d金属Ni37.5Co12.5Mn35Ti15合金可逆熵变
Yao Liu✉, Andong Xiao, Tianzi Yang, Zhitong Xu, Xianglong Zhou, Tianyu Ma✉
Yao Liu: liuyao12@xjtu.edu.cn (西安交通大学)
Tianyu Ma: matianyu@xjtu.edu.cn (西安交通大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114303
摘要
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114306
5. Effect of microstructure heterogeneity on the mechanical properties of friction stir welded reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steel
显微组织异质性对搅拌摩擦焊还原活化铁素体/马氏体钢力学性能的影响
Shengli Li, Napat Vajragupta, Abhishek Biswas, Wenshen Tang, Hao Wang, Aleksander kostka, Xinqi Yang✉, Alexander Hartmaier
Xinqi Yang: xqyang@tju.edu.cn (天津大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114306
摘要
本文研究了搅拌摩擦焊还原活化铁素体/马氏体钢不同区域的显微硬度分布,并通过电子背散射分析将其与各个区域的分级马氏体显微组织相关联。结果表明,搅拌摩擦焊过程中不同亚区的原始奥氏体晶粒尺寸、包块尺寸和宽度的变化受峰值温度和有效应变速率的影响。显微硬度的分布与在不同区域观察到的几何必要位错密度直接相关。

SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114308
6. Hydrogen-assisted failure in Inconel 718 fabricated by laser powder bed fusion: The role of solidification substructure in the embrittlement
激光粉床熔化制造的Inconel 718氢辅助失效:凝固亚结构在脆化中的作用
Dong-Hyun Lee✉, Yakai Zhao, Soo Yeol Lee, Dirk Ponge, Eric A. Jagle
Dong-Hyun Lee: dhlee@cnu.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114308
摘要
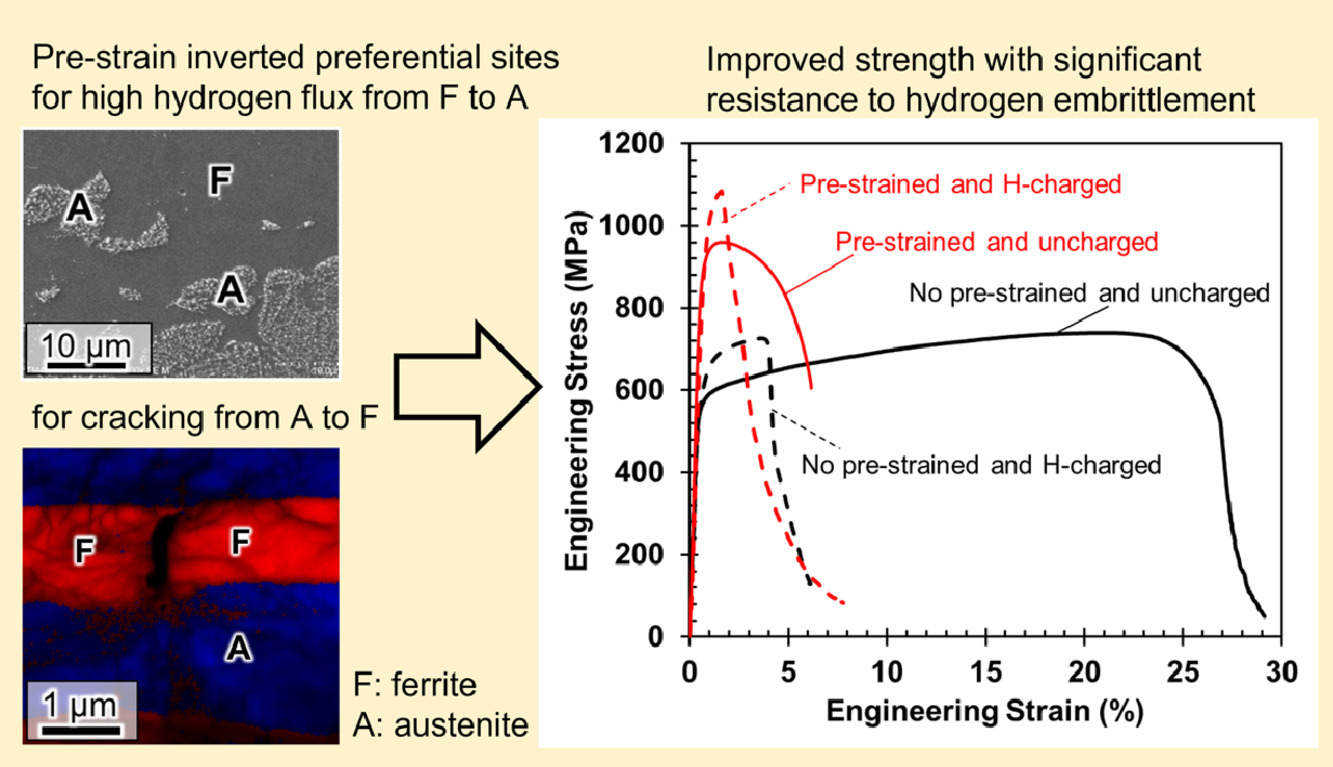
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114302
7. Synthesis of high-entropy alloy thin films via grain boundary diffusion–assisted solid-state alloying
通过晶界扩散辅助固态合金化合成高熵合金薄膜
Seungjin Nam, Sang Jun Kim, Moon J. Kim, Manuel Quevedo-Lopez, Jun Yeon
Hwang, Eun Soo Park✉, Hyunjoo Choi✉
Eun Soo Park: espark@snu.ac.kr
Hyunjoo Choi: hyunjoo@kookmin.ac.kr
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114302
摘要

SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114307
8. Deformation twinning-induced dynamic recrystallization during laser powder bed fusion
激光粉床熔融过程中变形孪晶诱导的动态再结晶
Hossein Eskandari Sabzi, Xiao-Hui Li, Chi Zhang, Hanwei Fu, David San-Martin, Pedro E.J. Rivera-Diaz-del-Castillo✉
Pedro E.J. Rivera-Diaz-del-Castillo: p.rivera1@lancaster.ac.uk
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114307
摘要

SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114310
9. Mechanical response of the constrained nanostructured layer in heterogeneous laminate
异质层压板中受限纳米结构层的机械响应
Hanfei Wang, Yueguang Wei✉, Zhifu Zhao, ZHongya Lin, Fengjiao Guo, Qian Cheng, Chongxiang Huang✉, Yuntian Zhu
Yueguang Wei: weiyg@pku.edu.cn (北京大学)
Chongxiang Huang: chxhuang@scu.edu.cn (四川大学)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114310
摘要
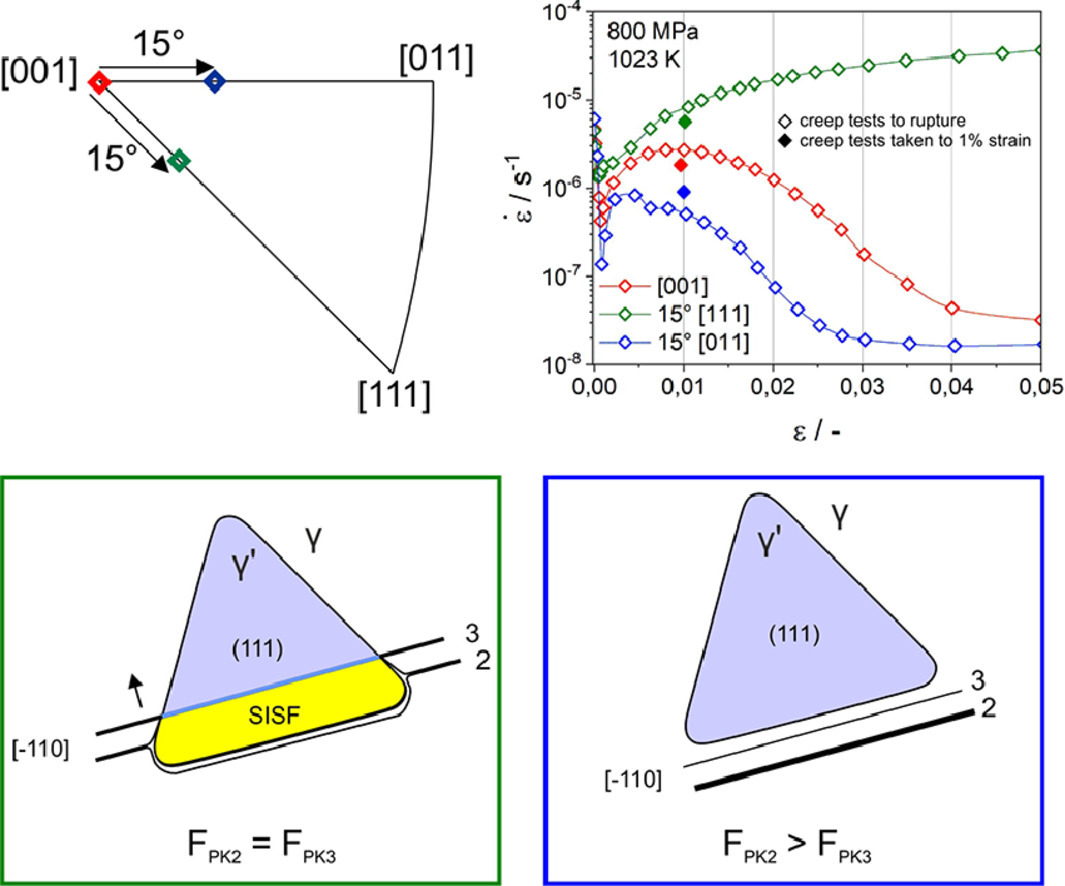
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114309
10. Prediction of growth velocity of undercooled multicomponent metallic alloys using a machine learning approach
使用机器学习方法预测过冷多组分金属合金的生长速度
Vanga Sreekar, Rahul M.R.✉, Gandham Phanikumar
Rahul M.R.: rahulmr@iitism.ac.in
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114309
摘要
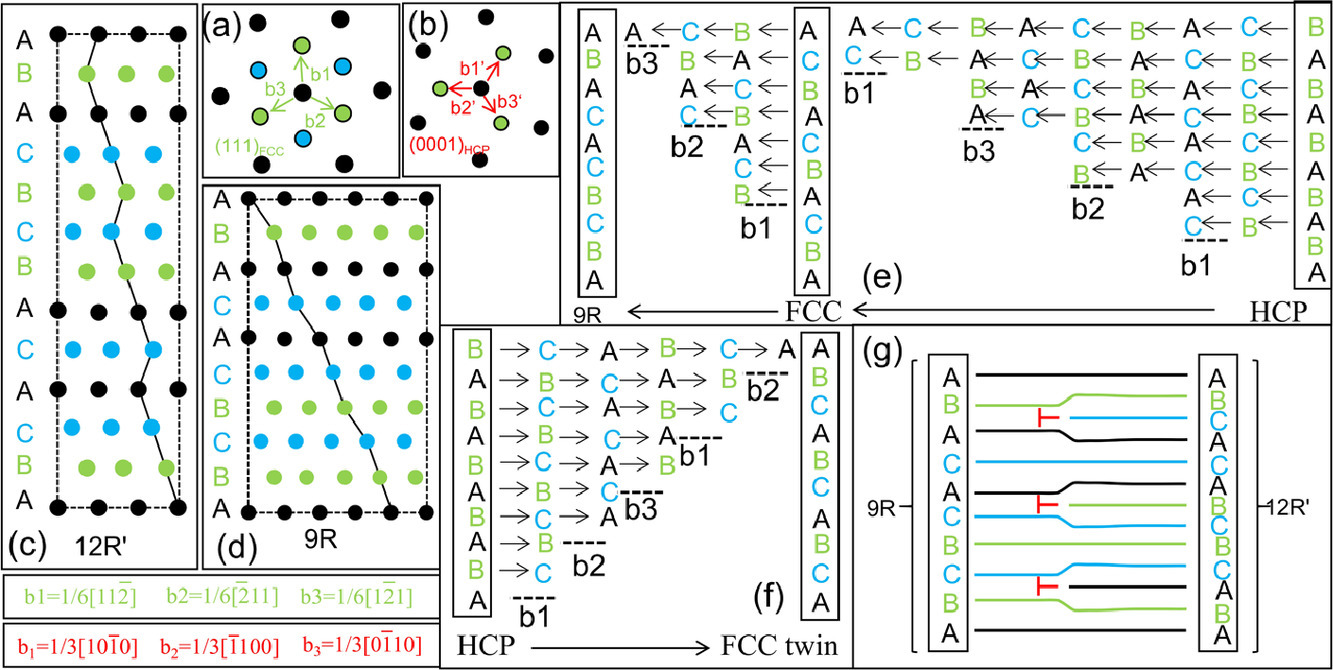
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114313
11. Martensitic transformation within nanotwins enhances fatigue damage resistance of a nanotwinned austenitic stainless steel
纳米孪晶内的马氏体相变增强了纳米孪晶奥氏体不锈钢的抗疲劳损伤能力
Q. Li, D.Y. Liu, F.K. Yan, N.R. Tao✉
N.R. Tao: nrtao@imr.ac.cn (中国科学院金属研究所)
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114313
摘要
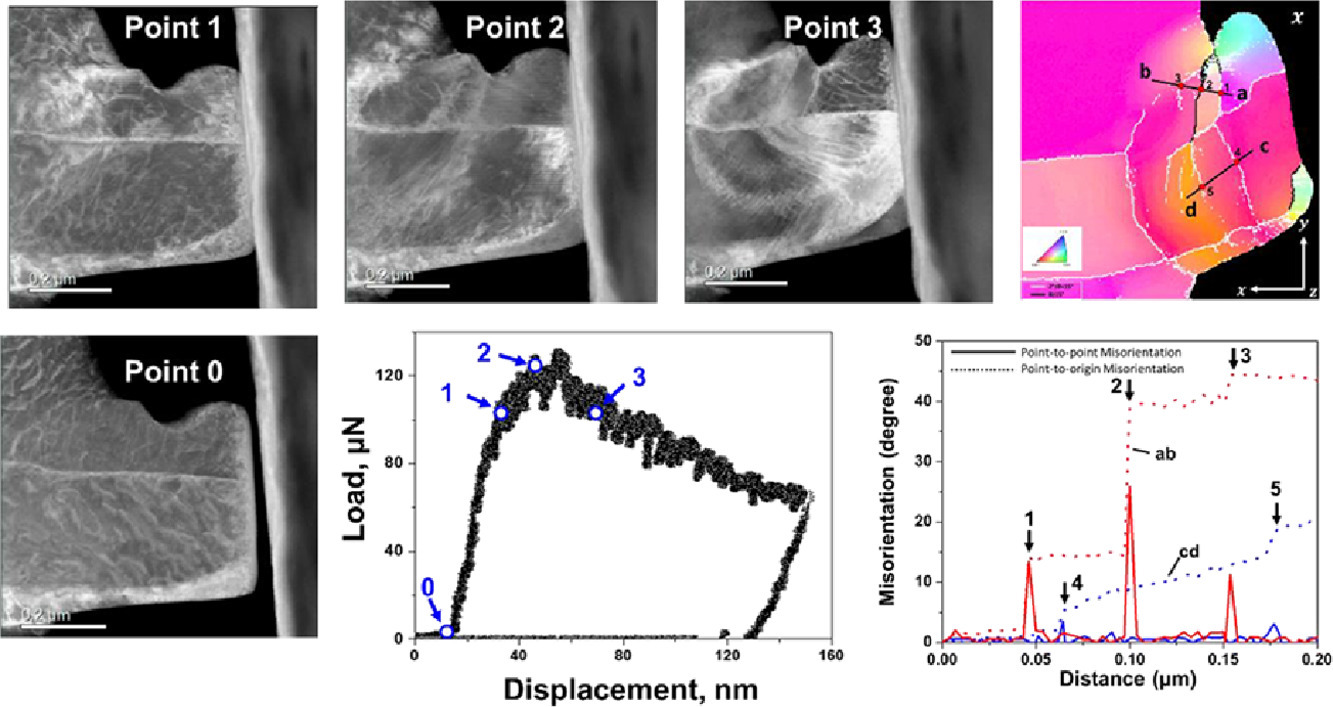
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114319
12. In situ transmission electron microscopy investigation of nucleation of GP zones under natural aging in Al-Zn-Mg alloy
Al-Zn-Mg合金自然时效下GP区形核的原位透射电镜研究
Arya Chatterjee✉, Liang Qi, Amit Misra
Arya Chatterjee: archatte@umich.edu
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114319
摘要
SCRIPTA
Vol. 207, 15 Jan. 2022, 114320
13. Grain boundary segregation and its implications regarding the formation of the grain boundary α phase in the metastable β-Titanium Ti–5Al–5Mo–5V–3Cr alloy
亚稳态β-钛Ti-5Al-5Mo-5V-3Cr合金中晶界偏析及其对晶界α相形成的影响
T.S. Prithiv, Zachary Kloenne, Dian Li, Rongpei Shi, Yufeng Zheng, Hamish L. Fraser, Baptiste Gault, Stoichko Antonov✉
Stoichko Antonov: s.antonov@mpie.de
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scriptamat.2021.114320
摘要